0000771856falseFY2024http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#ServiceMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#ServiceMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#ServiceMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#ServiceMemberP3Yhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationiso4217:USDxbrli:sharesiso4217:USDxbrli:sharescsbr:subsidiarycsbr:segmentcsbr:institutionxbrli:pure00007718562023-05-012024-04-3000007718562023-10-3100007718562024-07-1800007718562024-02-012024-04-3000007718562024-04-3000007718562023-04-3000007718562022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-04-300000771856us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-04-300000771856us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-04-300000771856us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-04-3000007718562022-04-300000771856us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-04-300000771856csbr:OperatingSubsidiariesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:OperatingSubsidiariesMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsNonrecurringMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsNonrecurringMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2023-04-300000771856srt:MinimumMember2024-04-300000771856srt:MaximumMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-04-300000771856csbr:FewContractsMember2024-05-01srt:MinimumMember2024-04-300000771856srt:MaximumMembercsbr:FewContractsMember2024-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:OtherMachineryAndEquipmentMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:OtherMachineryAndEquipmentMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:AssetUnderConstructionMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:AssetUnderConstructionMember2023-04-300000771856us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2024-04-300000771856us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-04-300000771856csbr:FinanceLeasedAssetsMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:FinanceLeasedAssetsMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:EquipmentMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:EquipmentMember2024-04-300000771856csbr:A2022FinanceLeaseMember2021-05-012022-04-300000771856csbr:A2022FinanceLeaseMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:A2022FinanceLeaseMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:A2023FinanceLeaseMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:A2023FinanceLeaseMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:PharmacologyServicesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:PharmacologyServicesMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:PersonalizedOncologyServicesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:PersonalizedOncologyServicesMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:OneCustomerMemberus-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:OneCustomerMemberus-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:OneCustomerMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:OneCustomerMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856srt:MinimumMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856srt:MaximumMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:TranslationalOncologySolutionsCostOfSalesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:TranslationalOncologySolutionsCostOfSalesMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:EquityIncentivePlan2021Member2022-04-300000771856csbr:EquityIncentivePlan2021Member2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:EquityIncentivePlan2021Member2024-04-300000771856srt:MaximumMembercsbr:EquityIncentivePlan2010Member2011-02-182011-02-180000771856csbr:EquityIncentivePlan2010Member2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:EquityIncentivePlan2010Member2021-03-010000771856csbr:IndependentDirectorsMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2013-12-122013-12-120000771856srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2013-12-122013-12-120000771856csbr:ChairpersonOfACommitteeMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2013-12-122013-12-120000771856csbr:IndependentDirectorsMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2020-05-012021-04-300000771856csbr:OptionsAndCashMembercsbr:IndependentDirectorsMembersrt:MaximumMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2020-05-012021-04-300000771856srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2020-05-012021-04-300000771856csbr:ChairpersonOfACommitteeMembersrt:MinimumMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2020-05-012021-04-300000771856csbr:ChairpersonOfACommitteeMembersrt:MaximumMembercsbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2020-05-012021-04-300000771856csbr:DirectorCompensationPlanMember2013-12-122013-12-120000771856csbr:DirectorsAndEmployeesMember2023-04-300000771856csbr:NonEmployeesMember2023-04-300000771856csbr:DirectorsAndEmployeesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:NonEmployeesMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:DirectorsAndEmployeesMember2024-04-300000771856csbr:NonEmployeesMember2024-04-300000771856csbr:DirectorsAndEmployeesMember2022-04-300000771856csbr:NonEmployeesMember2022-04-3000007718562021-05-012022-04-300000771856csbr:DirectorsAndEmployeesMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:NonEmployeesMember2022-05-012023-04-3000007718562023-03-2900007718562013-04-300000771856us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMembercsbr:BoardMemberOneMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMembercsbr:BoardMemberOneMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:CorporateHeadquartersMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:CorporateHeadquartersMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:RockvilleMDMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:RockvilleMDMember2022-05-012023-04-300000771856csbr:MilanItalyMember2023-05-012024-04-300000771856csbr:MilanItalyMember2022-05-012023-04-30
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| | | | | | | | |
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2024 |
or
| | | | | | | | |
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the transition period from to |
Commission file number 001-11504
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | |
| Delaware | 52-1401755 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer |
| incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) |
| |
One University Plaza, Suite 307 | 07601 |
Hackensack, New Jersey | (Zip Code) |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
(201) 808-8400
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of Each Class | | Trading Symbol(s) | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | | CSBR | | The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | | ¨ | | Accelerated filer | | ¨ |
| | | |
| Non-accelerated filer | | x
| | Smaller reporting company | | x |
| | | | Emerging growth company | | ¨ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on the attestation to its management’s effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262 (b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ¨
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of
the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements.
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of
incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No þ
The approximate aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant as of October 31, 2023 was $22.0 million based on the closing price of the Registrant’s common stock as quoted on the Nasdaq Capital Market as of that date.
The number of shares of common stock of the Registrant outstanding as of July 18, 2024 was 13,593,766.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
INDEX TO FORM 10-K
FOR THE YEAR ENDED APRIL 30, 2024
| | | | | | | | |
|
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 1C. | | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| | |
|
| Item 5. | | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| Item 9C. | | |
| | |
|
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| | |
|
| Item 15. | | |
| Item 16. | | |
| Signatures | | |
As used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K (this "Annual Report"), “Champions Oncology, Inc.,” “Champions,” the “Company,” “we,” “ours,” and “us” refer to Champions Oncology, Inc. and its subsidiaries, except where the context otherwise requires or as otherwise indicated.
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, (the "Exchange Act") that inherently involve risk and uncertainties. Forward-looking statements may be identified by the words “project,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “expect,” “estimate,” “intend,” “should,” “would,” “could,” “will,” “may,” “likely” or similar expressions. Forward-looking statements in this Annual Report include statements about our business strategies and products development activities, including the anticipated benefits and risks associated with those strategies as well as statements about the sufficiency of our capital resources. One should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. We cannot guarantee that we will achieve the plans, intentions or expectations expressed or implied in our forward-looking statement. There are a number of important factors that could cause actual results, levels of activity, performance or events to differ materially from those expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements we make. These important factors are described under “Risk Factors” set forth below. In addition, any forward-looking statements we make in this Annual Report speak only as of the date of this document, and we do not intend to update any such forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances that occur after that date, except as required by law. As a result of these and other factors, our stock price may fluctuate dramatically.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Overview
We are a technology-enabled research organization engaged in creating technology solutions to be utilized in drug discovery and development. Our research center operates in both regulatory and non-regulatory environments and consists of a comprehensive set of computational and experimental research platforms. Our pharmacology, biomarker, and data platforms are designed to facilitate drug discovery and development at lower costs and increased speeds.
At the core of our research platforms is our unique, proprietary bank of Patient Derived Xenograft (PDX) models. This preeminent bank of PDX models is deployed into advanced in vivo and ex vivo pharmacology platforms, providing an enhanced level of insight into therapeutic programs. We currently have approximately 1,500 PDX Models in our TumorBank that we believe reflect the characteristics of patients who enroll in clinical trials (late stage, pretreated and metastatic). This characteristic of our TumorBank is an important differentiator to other established PDX banks. We implant and expand these tumors in mice, which allows for future studies and additional characterization of the tumor. Additional analytical and pharmacology experimental platforms are also available to augment the information gained from studies performed.
The PDX bank is highly characterized at the molecular, phenotypic and pharmacological levels, which provides a differentiated layer of data for our large oncology dataset (the "Datacenter"). The Datacenter combines our proprietary dataset with other large publicly available datasets. This dataset currently includes approximately 3,500 molecular datasets (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, phosphor-proteomics), approximately 3,000 clinical drug responses, approximately 3,500 in vivo drug responses, and the accompanying clinical information on the patients from which they were derived (pre and post tumor sample acquisition of drug treatments and responses, age, gender, ethnicity, tumor stage, tumor grade, location of tumor biopsy, histology, etc.) derived from our TumorBank. One unique feature of this proprietary dataset is the fact that it is derived from a living TumorBank. This allows us to continue characterizing the TumorBank over time and increase the depth of characterization of the accumulated data. The combination of the breadth and depth of the TumorBank, and associated characterization, drives the value of our Datacenter. The Datacenter also includes approximately 20,000 publicly available datasets including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and functional genomics, and patient outcome. This Datacenter facilitates our computational approach to drug discovery and provides the foundation to our Software as a Service ("SaaS") offerings. Collectively, our computational and experimental research platforms enable a more rapid and precise approach to drug discovery and development.
Through our technology platforms, we have designed an ecosystem of business lines consisting of:
•The sale of research services utilizing our innovative research platforms to biopharmaceutical companies
•The sale of oncology research SaaS tools to cancer research scientists
•The discovery and development of novel oncology therapeutics
Translational Oncology Solutions (TOS) Business
Research Services
Our research services utilize our research center to assist pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with their drug development process. We perform studies which we believe may predict the efficacy of experimental oncology drugs or approved drugs as stand-alone therapies or in combination with other drugs and can simulate the results of human clinical trials. These studies include in vivo studies that rely on implanting multiple tumors from our TumorBank in mice and testing the therapy of interest on these tumors. Studies may also include bioinformatics analysis that reveal the differences in the genetic signatures of the tumors that responded to a therapy as compared to the tumors that did not respond. Our studies can be used to determine which types of cancer, if any, may be inhibited by a drug. The studies can also be used to identify specific sub-populations, often characterized by particular genetic mutations that are differentially sensitive or resistant to a drug or drug combination. Additionally, we provide computational or experimental support to identify novel therapeutic targets, select appropriate patient populations for clinical evaluation, identify potential therapeutic combination strategies, and develop biomarker hypothesis of sensitivity or resistance. These studies include the use of our in vivo, ex vivo, analytical and computational platforms.
Increasing the breadth of the TumorBank is an important strategic effort of the Company. We invest significant research and development resources to increase the number of PDX Models in our TumorBank and add unique and different sub-types of cancer that are not historically addressed. This effort also allows us to build highly valuable PDX models derived from patients with resistance to specific therapies or important molecular annotations. We also invest significant resources to increase the depth of characterization of the TumorBank. For each model, this characterization includes phenotypic analysis, molecular analyses, and pharmacologic analysis. This depth of characterization, in an individual tumor basis, is unique and not widely available.
We have performed studies for approximately 500 different pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies over the past ten years, have a high rate of repeat business, and contract with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies across North America, Europe and Asia. Studies are performed in a preclinical non-regulatory environment, as well as a Good Clinical Regulatory Practice (GCLP) regulatory environment for clinical evaluation. Typical studies are in the $125,000 price range, with an increasing number of studies in the $250,000 to $500,000 range. Studies performed in a regulatory environment can be much larger than those performed within a non-regulatory environment. Revenue from this business has grown at an average annual growth rate of 13% since 2019 and represents the primary source of our current revenue stream.
Software As A Service (SaaS) Business
Our SaaS business, launched during the fiscal year ended April 30, 2021, is centered around our proprietary software platform and data tool, Lumin Bioinformatics ("Lumin"), which contains comprehensive information derived from our research services and clinical studies and is sold to customers on an annual subscription basis. The software was developed by a team that consisted of bioinformatics scientists and mathematicians as well as software engineers. Lumin leverages Champions’ large Datacenter coupled with analytics and artificial intelligence to provide a robust tool for computational cancer research. It is the combination of the Datacenter and the analytics that create the foundation for Lumin. Insights developed using Lumin can provide the basis for biomarker hypotheses, reveal potential mechanisms of therapeutic resistance, and guide the direction of additional preclinical evaluations. During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2023, we recorded an impairment charge for the capitalized software development costs of Lumin related to return on investment guidelines. However, we continue to maintain the Lumin platform and sell subscriptions as part of our product offerings as the Lumin data is an integral part of the Company’s long term strategy and value proposition.
Drug Discovery and Development Business
Our nascent drug discovery and development business leverages the computational and experimental capabilities within our platforms. Our discovery strategy utilizes our Datacenter, coupled with artificial intelligence and other advanced computational analytics, to identify novel therapeutic targets. We then employ the use of our proprietary experimental platforms to rapidly validate these targets for further drug development efforts. Our efforts center around three areas of focus:
1.Targeted therapy with drug conjugates
2.Immune oncology
3.Cell therapy
Our drug discovery and development business is dependent on a dedicated research and development team, made up of computational and experimental scientists. Importantly, the scientific teams within our Drug Discovery and Development teams are appropriately segregated from our other businesses.
We have a rich pipeline of targets at various stages of discovery and validation, with a select group that has progressed to therapeutic development. Our commercial strategy for the validated targets and therapeutics established from this business is wide-ranging and still being developed. It will depend on many factors, and will be specific for each target or therapeutic area identified.
We regularly evaluate strategic options to create additional value from our drug discovery business, which may include, but are not limited to, potential spin-out transactions or capital raises.
Our sales and marketing efforts are dependent on a dedicated sales force of approximately 27 professionals that sell our services directly to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Our research services team is focused on identifying and selling studies to new customers as well as increasing our revenue from our existing customer base. We spend significant resources in informing our customers and reaching out to new contacts within companies that we currently serve. These efforts are aimed at moving our customers along the adoption curve for our research platforms, thereby increasing the number of studies and the average study size. Our success in these efforts is demonstrated by the growing number of customers who have increased their annual spend on our services over the years.
For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2024, revenues from our products and services totaled approximately $50.1 million, a decrease of approximately 7% from the previous year.
Our Current Strategy
Our strategy is to use our various platform technologies to drive multiple synergistic revenue streams. We continue to build upon this with investments in research and development. Our enterprise strategy consists of the following:
•Establish a global leadership position in oncology research
•A focus on bringing better drugs to patients faster
•Leading innovation in oncology research and development platforms
•Cultivating a solid reputation for the quality of data acquisition and interpretation
•Collaborations across the global biopharma landscape
•Profitable growth across all business lines
Our Growth and Expansion Strategy
Our strategy is to continue to use our various platform technologies to drive multiple synergistic revenue streams.
Our strategy for growth has multiple components:
•Growing our TumorBank: We grow our TumorBank in two ways. First, we leverage a medical affairs team that works with a well-established clinical network to facilitate access to patients diagnosed with prioritized tumor subtypes. Second, we maintain the ability to utilize our legacy Personalized Oncology Services business to establish novel PDX models from patients who use this service. The PDX models are then deeply characterized at the phenotypic, molecular, and pharmacologic levels. This data characterization is then added to our Datacenter.
•Adding new experimental technologies: The fields of oncology research and drug development are evolving rapidly. To keep up with new approaches, we continuously add new technologies to platform. We are currently investing in developing additional proprietary pharmacology platforms aimed at enhancing the scientific output and driving innovation in the oncology research sector. We are also investing in the development of sophisticated analytical platforms which allow scientists to derive deeper insights when using our pharmacology platforms. Once these experimental technologies are established they are made available to our research and development and target discovery teams.
•Computational power: We have developed sophisticated and innovative computational approaches. We have also invested in the development of novel artificial intelligence, data structures, and analytics. Our goal is to leverage our
unique Datacenter to establish elegant ways to better understand the molecular dynamics of cancer, and the development of novel therapeutics.
Competition
Champions currently competes in three different markets:
Research Services: Pharmaceutical companies rely on outsourcing preclinical studies to Clinical Research Organizations. Competition in this industry is intense and based significantly on scientific, technological, and market forces, which include the effectiveness of the technology and products and the ability to commercialize technological developments. The Company faces significant competition from other healthcare companies in the United States and abroad. The majority of these competitors are, and will be, substantially larger than the Company, and have substantially greater resources and operating histories. There can be no assurance that developments by other companies will not render our products or technologies obsolete or non-competitive or that we will be able to keep pace with the technological or product developments of our competitors. These companies, as well as academic institutions, governmental agencies, and private research organizations also compete with us in recruiting and retaining highly qualified scientific, technical and professional personnel and consultants.
SaaS: There are two important components of Lumin: the Datacenter and the Analytics. While we feel our Datacenter is unique, there are a large number of publicly available datasets that can be accessed free of charge for computational research. This publicly available data repertoire is constantly growing as academic labs publish results. We continue to find ways to differentiate our dataset, however there can be no assurance that developments by other companies or academic institutions in data curation will not render our Datacenter obsolete or non-competitive. The second component of Lumin is the data analytics. While there are a minimal number of software solutions that offer the degree of analytics available within Lumin, the know-how and workflows of these analytics are well established in bioinformatics labs across academia and the biopharmaceutical industry. As a result, the barrier to entry for developing a SaaS tool leveraging these analytics is relatively low.
Drug Discovery and Development: Our Drug Discovery and Development business places us in a good position of also competing against the same customers of our Research Services and/or SaaS businesses: the global biopharmaceutical industry. The global oncology drug market is estimated to be as high as $223 billion in 2023. Competition in this industry is strong and based significantly on scientific and technological forces, which rely solely on the effectiveness of therapeutics designed to treat cancer. The Company faces significant competition from other biopharmaceutical companies in the United States and abroad. The competitors have a wide range of strategic and operational approaches. Our business strategy is to work with differentiated therapeutic targets and research areas. However, given the intense degree of privacy from our competitors, we cannot guarantee that others within the industry are not also working on these targets. Further, some competitors will operate with no laboratory or experimental operations, while others will have varying degrees of laboratory space and experimental capabilities. There can be no assurance that developments by other companies will not render experimental platforms obsolete or non-competitive or that we will be able to keep pace with the technological or product developments of our competitors. These companies, as well as academic institutions, governmental agencies, and private research organizations also compete with us in recruiting and retaining highly qualified scientific, technical and professional personnel and consultants.
Research and Development
For the fiscal years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, we spent approximately $9.5 million and $11.5 million, respectively, to further develop our platforms. We continue to expand our TumorBank via the inclusion of tumor tissue and implanted models through research collaborations and relationships with hospitals and academic institutions. Our research and development efforts were focused on increasing our understanding of our TumorGraft models, their clinical predictability, improving growth and tumor take rates, and other biological and molecular characteristics of the models. We are investing in developing additional proprietary pharmacology platforms aimed at enhancing the scientific output and driving innovation in the oncology research sector.
We are also investing in the acquisition of sophisticated analytical platforms which allow scientists to derive deeper insights when using our pharmacology platforms.
Government Regulation
The research, development, and marketing of our products, the performance of our legacy Personalized Oncology Solutions ("POS") testing services, and the operation of our facilities are generally subject to federal, state, local, or foreign legislation,
including licensure of our laboratory located in Rockville, Maryland by the State of Maryland and compliance with federal, state, local or foreign legislation applicable to the use of live animals in scientific testing, research and education.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the "FDA") has claimed regulatory authority over laboratory developed tests such as our legacy POS products, but has generally not exercised it. The FDA has announced regulatory and guidance initiatives that could increase federal regulation of our business. We are subject to federal and international regulations with regard to shipment of hazardous materials, including those issued by the Department of Transportation and the International Air Transit Authority. These regulations require interstate, intrastate, and foreign shipments to comply with applicable labeling, documentation, and training requirements.
Human Capital Resources
As of July 15, 2024, we had 210 full-time employees, including 96 with doctoral or other advanced degrees. Of our workforce, 160 employees are engaged in research and development and laboratory operations, 30 employees are engaged in sales and marketing, and 20 employees are engaged in finance and administration.
We believe that our future success will depend, in part, on our ability to continue to attract, hire, and retain qualified personnel. We continue to seek additions to our science and technical staff, although the competition for such personnel in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries is intense. Attracting, developing, and retaining skilled and experienced employees in our industry is crucial to our ability to compete effectively. Our ability to recruit and retain such employees depends on a number of factors, including our corporate culture and work environment, our corporate philosophy, internal talent development and career opportunities, and compensation and benefits.
None of our employees are represented by a labor union or covered by collective bargaining agreements. We have never experienced a work stoppage and believe our relationship with our employees is good.
Company History
We were incorporated as a merger and acquisition company under the laws of the State of Delaware on June 4, 1985, under the name “International Group, Inc.” In September 1985, the Company completed a public offering and shortly thereafter acquired the worldwide rights to the Champions sports theme restaurant concept and changed its name to “Champions Sports, Inc.” In 1997, the Company sold its Champions service mark and concept to Marriott International, Inc. and until 2005, was a consultant to Marriott International, Inc. and operated one Champions Sports Bar Restaurant. In January 2007, the Company changed its business direction to focus on biotechnology and subsequently changed its name to Champions Biotechnology, Inc. On May 18, 2007, the Company acquired Biomerk, Inc., at which time we began focusing on our current line of business. In April 2011, the Company changed its name to Champions Oncology, Inc. to reflect the Company's new strategic focus on developing advanced technologies to personalize the development and use of oncology drugs.
Available Information
Our internet website address is www.championsoncology.com. Information on our website is not part of this Annual Report. Through our website, we make available, free of charge, access to all reports filed with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, (the "SEC"), including our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, our Current Reports on Form 8-K, our Proxy Statements on Schedules 14A and amendments to those reports, as filed with or furnished to the SEC pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Copies of any materials we file with, or furnish to, the SEC can also be obtained free of charge through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
You should carefully consider the risks described below together with all of the other information included in this Annual Report. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks not presently known, or those we currently consider insignificant, may also impair our business operations in the future.
We historically incurred losses from operating activities, may require significant capital and may never achieve sustained profitability. These conditions raise a substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2024, the Company had a net loss of approximately $7.3 million and used cash flows in operations of approximately $6.1 million. These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from these uncertainties.
In its report dated July 19, 2024, EisnerAmper LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern as we have suffered recurring losses from operations and have insufficient liquidity to fund our future operations. If we are unable to improve our liquidity position, we may not be able to continue as a going concern. The accompanying consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result if we are unable to continue as a going concern and, therefore, be required to realize our assets and discharge our liabilities other than in the normal course of business which could cause investors to suffer the loss of all or a substantial portion of their investment. As of April 30, 2024, we had cash on hand of $2.6 million. Based on our available cash at April 30, 2024, in order to continue to fund our operations we may need to raise additional equity or debt capital in the near term and cannot provide any assurance that we will be successful in doing so. If we are unable to obtain additional financing in the near future, we may be required to pursue a reorganization proceeding, including under applicable bankruptcy or insolvency laws. Holders of our common shares will likely not receive any value or payments in a restructuring or similar scenario. In the event we pursue bankruptcy protection, we will be subject to the risks and uncertainties associated with such proceedings. There can be no guarantees that if we seek bankruptcy protection, we will emerge from bankruptcy protection as a going concern or that holders of our common shares will receive any recovery from any bankruptcy proceedings.
The amount of our income or losses and liquidity requirements may vary significantly from year-to-year and quarter-to-quarter and will depend on, among other factors:
•the cost of continuing to build out our TumorGraft bank;
•the cost and rate of progress toward growing our technology platforms;
•the cost and rate of progress toward building our business units;
•the cost of increasing our research and development;
•the cost of renting our laboratory and animal testing facilities and payment for associated services;
•the timing and cost of obtaining and maintaining any necessary regulatory approvals;
•the cost of expanding and building out our infrastructure; and
•the cost incurred in hiring and maintaining qualified personnel.
Currently, we derive revenue primarily from research services, while pursuing efforts to further develop our drug discovery business units.
To become sustainably profitable, we will need to generate revenues to offset our operating costs, including our research and development and general and administrative expenses. We may not achieve or sustain our revenue or profit objectives. If we incur losses in the future and/or we are unable to obtain sufficient capital either from operations or externals sources, ultimately, we may have to cease operations.
In order to grow revenues, we must invest capital to implement our sales and marketing efforts and to successfully develop our technology platforms. Our sales and marketing efforts may never generate significant increases in revenues or achieve profitability and it is possible that we will be required to raise additional capital to continue our operations. If we must devote a substantial amount of time to raising capital, it will delay our ability to achieve our business goals within the time frames that we now expect, which could increase the amount of capital we need. In addition, the amount of time expended by our management on fundraising distracts them from concentrating on our business affairs. If we require additional capital and are not successful in raising the needed capital, we may have to cease operations.
We may incur greater costs than anticipated, which could result in sustained losses.
We use reasonable efforts to assess and predict the expenses necessary to pursue our business strategies. However, implementing our business strategies may require more employees, capital equipment, supplies or other expenditure items than management has predicted. Similarly, the cost of compensating additional management, employees and consultants or other operating costs may be more than we estimate, which could result in ongoing and sustained losses.
We may not be able to implement our business strategies, which could impair our ability to continue operations.
Implementation of our business strategies will depend in large part on our ability to (i) attract and maintain a significant number of customers; (ii) effectively provide acceptable services to our customers; (iii) develop and license new products and technologies; (iv) maintain appropriate internal procedures, policies, and systems; (v) hire, train, and retain skilled employees and management; (vi) continue to operate despite increasing competition in our industry; and (vii) establish, develop and
maintain our name recognition. Our inability to obtain or maintain any or all these factors could impair our ability to implement our business strategies successfully, which could have material adverse effects on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our laboratories are subject to regulation and licensure requirements, and the healthcare industry is highly regulated; we may face substantial penalties, and our business activities may be impacted, if we fail to comply.
Our research services are performed in laboratories that are subject to state regulation and licensure requirements. Such regulation and requirements are subject to change, and may result in additional costs or delays in providing our products to our customers. In addition, the healthcare industry in general is highly regulated in the United States at both the federal and state levels. We seek to conduct our business in compliance with all applicable laws, but many of the laws and regulations potentially applicable to us are vague or unclear. These laws and regulations may be interpreted or applied by an authority in a way that could require us to make changes in our business. We may not be able to obtain all regulatory approvals needed to operate our business or sell our products. If we fail to do so, we could be subject to civil and criminal penalties or fines or lose the authorizations necessary to operate our business, as well as incur additional liabilities from third parties. If any of these events happened, they could hurt our business and financial results.
If our laboratory facilities are damaged or destroyed, or we have a dispute with one of our landlords, our business would be negatively affected.
We currently utilize several office suites where our laboratories are located within one facility in Rockville, Maryland. If this facility was to be significantly damaged or destroyed, we could suffer a loss of our ongoing and future drug studies, as well as our TumorBank. In addition, we lease the laboratories from a third party. If we had a dispute with our landlord or otherwise could not utilize our space, it would take time to find and move to a new facility, which could negatively affect our results of operations.
Any health crisis impacting our colony of laboratory mice could have a negative impact on our business.
Our research services operations depend on having a colony of live mice available. If this population experienced a health crisis, such as a virus or other pathogen, such crisis would affect the success of our existing and future business, as we would have to rebuild the population and repeat current studies.
We have limited experience marketing and selling our products and may need to rely on third parties to successfully market and sell our products and generate revenues.
Currently, we rely on the internet, word of mouth, and a small sales force to market our services. We have to compete with other pharmaceutical, biotechnology and life science technology and service companies to recruit, hire, train, and retain marketing and sales personnel. However, there can be no assurance that we will be able to develop in-house sales, and as a result, we may not be able to generate product revenue.
We will continue to be dependent upon key employees.
Our success, currently, is dependent upon the efforts of several full-time key employees, the loss of the services of one or more of which would have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition. We intend to continue to develop our management team and attract and retain qualified personnel in all functional areas to expand and grow our business. This may be difficult in the healthcare industry where competition for skilled personnel is intense.
Because our industry is very competitive and many of our competitors have substantially greater capital resources and more experience in research and development, we may not succeed in selling or increasing sales of our products and technologies.
We are engaged in a rapidly changing and highly competitive field. Potential competitors in the United States and abroad are numerous and include providers of clinical research services, most of which have substantially greater capital resources and more experience in research and development capabilities. Furthermore, new companies will likely enter our market from the United States and abroad, as scientific developments surrounding other pre-clinical and clinical services grow in the multibillion dollar oncology marketplace. Our competitors may succeed in selling their products to our pharmaceutical and biotech customers more effectively than we sell our products. In addition, academic institutions, hospitals, governmental agencies, and other public and private research organizations also may conduct similar research, seek patent protection, and may develop and commercially introduce competing products or technologies on their own or through joint ventures. If one or
more of our competitors succeeds in developing similar technologies and products that are more effective or successful than any of those that we currently sell or will develop, our results of operations will be significantly adversely affected.
If we are unable to protect our intellectual property, we may not be able to compete as effectively.
It is important in the healthcare industry to obtain patent and trade secret protection for new technologies, products, and processes. Our success will depend, in part, upon our ability to obtain, enjoy, and enforce protection for any products we have, develop or acquire under United States and foreign patent laws and other intellectual property laws, preserve the confidentiality of our trade secrets, and operate without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. Where appropriate, we will seek patent protection for certain aspects of our technology. However, while our TumorGraft Technology Platform is proprietary and requires significant know-how to both initiate and operate, it is not patented. It is, therefore, possible for competitors to develop other implantation procedures, or to discover the same procedures utilized by us, that could compete with us in our market.
It also is unclear whether efforts to secure our trade secrets will provide useful protection. While we will use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our employees or consultants may unintentionally or willfully disclose our proprietary information to competitors resulting in a loss of protection. Enforcing a claim that someone else illegally obtained and is using our trade secrets, like patent litigation, is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets. Finally, our competitors may independently develop equivalent knowledge, methods and know-how.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
We rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, to maintain our competitive position. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. We also seek to enter into confidentiality and invention assignment agreements with our employees and consultants. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Our trade secrets may also be obtained by third parties by other means, such as breaches of our physical or computer security systems. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they communicate it, from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our competitive position would be harmed.
Claims by others that our products infringe their patents or other intellectual property rights could adversely affect our financial condition.
The healthcare industry has been characterized by frequent litigation regarding patent and other intellectual property rights. Patent applications are maintained in secrecy in the United States and also are maintained in secrecy outside the United States until the application is published. Accordingly, we can conduct only limited searches to determine whether our technology infringes the patents or patent applications of others. Any claims of patent infringement asserted by third parties would be time-consuming and could likely:
•result in costly litigation;
•divert the time and attention of our technical personnel and management;
•require us to develop non-infringing technology; or
•require us to enter into royalty or licensing agreements.
Research service studies are subject to cancellation based on changes in customer’s development plans.
Our revenue is primarily derived from studies performed for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to assist in the development of oncology drugs. There are many factors that could result in the change of our customers development plans for specific drugs, including without limitation to their research and development budgets and drug development strategies. These changes could lead to the cancellation or modification of on-going or planned studies. This would have a negative impact on the Company’s revenue growth and profit margin.
We face competition in the life science market for computational software and for bioinformatics products.
The market for our computational software platform for the life science market is competitive. We currently face competition from other scientific software providers, larger technology and solutions companies, in-house development by our customers and academic and government institutions, and the open-source community. Some of our competitors and potential competitors have longer operating histories in certain segments of our industry than we do and could have greater financial, technical, marketing, research and development, and other resources. We could also face competition from open-source software initiatives, in which developers provide software and intellectual property free over the Internet. In addition, some of our customers spend significant internal resources in order to develop their own software. There can be no assurance that our current or potential competitors will not develop products, services, or technologies that are comparable to, superior to, or render obsolete, the products, services, and technologies we offer. There can be no assurance that our competitors will not adapt more quickly than we do to technological advances and customer demands, thereby increasing such competitors' market share relative to ours. Any material decrease in demand for our technologies or services may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Drug development programs, particularly those in early stages of development, may never be commercialized.
Our future success depends, in part, on our ability to select successful product candidates, complete preclinical development of these product candidates and advance them to and through clinical trials. Early-stage product candidates in particular require significant investment in development, preclinical studies and clinical trials, regulatory clearances and substantial additional investment before they can be commercialized, if at all.
Our research and development programs may not lead to commercially viable products for several reasons, and are subject to the risks and uncertainties associated with drug development. For example, we may fail to identify promising product candidates, our product candidates may fail to be safe and effective in preclinical tests or clinical trials, or we may have inadequate financial or other resources to pursue discovery and development efforts for new product candidates. From time to time, we may establish and announce certain development goals for our product candidates and programs. However, given the complex nature of the drug discovery and development process, it is difficult to predict accurately if and when we will achieve these goals. If we are unsuccessful in advancing our research and development programs into clinical testing or in obtaining regulatory approval, our long-term business prospects will be harmed.
Impairment of goodwill or other long-term assets may adversely impact future results of operations.
We have intangible assets and goodwill on our balance sheet. If the future growth and operating results of our business are not as strong as anticipated and/or our market capitalization declines, this could impact the assumptions used in calculating the fair value of goodwill or recoverability of any future capitalized software development costs. To the extent any future impairment occurs, the carrying value of our assets will be written down to an implied fair value and an impairment charge will be made to our income from continuing operations. Such an impairment charge could materially and adversely affect our operating results.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carry-forwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited.
Under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change” (generally defined as a greater than 50% change (by value) in its equity ownership over a three-year period), the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change net operating loss carry-forwards and other pre-change tax attributes (such as research tax credits) to offset its post-change income may be limited. We believe that our 2016 public offering, taken together with our private placements and other transactions that have occurred since then, may have triggered an “ownership change” limitation. We may also experience ownership changes in the future as a result of subsequent shifts in our stock ownership. As a result, if we earn net taxable income, our ability to use our pre-change net operating loss carry-forwards to offset U.S. federal taxable income may be subject to limitations, which potentially could result in increased future tax liability to us.
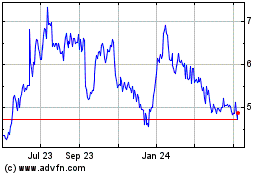
We have a limited market for our common stock, which makes our securities very speculative.
Trading activity in our common stock is and has been limited. As a result, an investor may find it difficult to dispose of, or to obtain accurate quotations of the price of our common stock. There can be no assurance that a more active market for our common stock will develop, or if one should develop, there is no assurance that it will be sustained. This could severely limit the liquidity of our common stock, and would likely have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common stock and on our ability to raise additional capital. Furthermore, like many stocks quoted on the Nasdaq Capital Market, trading in our common stock is thin and characterized by wide fluctuations in trading prices, due to many factors that may have little to do
with our operations or business prospects. This volatility could depress the market price of our common stock for reasons unrelated to operating performance.
Investment in our common stock may be diluted if we issue additional shares in the future.
We may issue additional shares of common stock, which will reduce shareholders’ percentage ownership and may dilute per share value. Our certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 200,000,000 shares of common stock. As of July 18, 2024, we had 13,714,099 shares of common stock issued and 13,593,766 outstanding. The future issuance of all or part of the remaining authorized common stock would result in substantial dilution in the percentage of the common stock held by existing shareholders. The issuance of common stock for future services, acquisitions, or other corporate actions may have the effect of diluting the value of the shares held by existing shareholders, and might have an adverse effect on any market for our common stock.
To the extent that we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities or convertible debt securities in the future, our stockholders may experience significant dilution. Sale of additional equity and/or convertible debt securities at prices below certain levels will trigger anti-dilution provisions with respect to certain securities we have previously sold. If additional funds are raised through a credit facility or the issuance of debt securities or preferred stock, lenders under the credit facility or holders of these debt securities or preferred stock would likely have rights that are senior to the rights of holders of our common stock, and any credit facility or additional securities could contain covenants that would restrict our operation.
Potential future sales or issuances of our common stock to raise capital, or the perception that such sales could occur, could cause dilution to our current stockholders and the price of our common stock to fall.
We have historically supported our operations through the issuance of equity and may continue to do so in the future. Although we may not be successful in obtaining financing through equity sales on terms that are favorable to us, if at all, any such sales that do occur could result in substantial dilution to the interests of existing holders of our common stock.
Additionally, the sale of a substantial number of shares of our common stock or other equity securities to any new investors, or the anticipation of such sales, could cause the trading price of our common stock to fall.
Our stock price is volatile and therefore investors may not be able to sell their common stock at or above the price they paid for it.
The stock market in general and the market for biotechnology companies in particular have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. As a result of this volatility, investors may not be able to sell their common stock at or above the price they paid for it. The market price for our common stock may be influenced by many factors, including:
•regulatory developments in the United States and foreign countries;
•variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us;
•changes in the healthcare payment system overseas to the degree we receive revenue from such healthcare systems overseas;
•announcements by us of significant acquisition, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments;
•sales of significant shares of stock by large investors;
•intellectual property, product liability, or other litigation against us; and
•the other key facts described in this “Risk Factors” section.
Certain provisions of our charter and bylaws and of our contractual agreements contain provisions that could delay and discourage takeover attempts and any attempts to replace our current management by stockholders.
Certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, and our contractual agreements could make it difficult for or prevent a third party from acquiring control of us or changing our board of directors (the "Board" or Board of Directors") and management. These provisions include:
•requirements that our stockholders comply with advance notice procedures in order to nominate candidates for election to our Board of Directors or to place stockholders’ proposals on the agenda for consideration at meetings of stockholders; and
•in connection with private placements of our stock in 2011, 2013 and 2015, we covenanted that we would not merge or consolidate with another company unless either the transaction and the trading volume of our stock met certain thresholds
and qualifications or we obtained the consent of certain of the investors who purchased our stock in those private placements.
Certain provisions of Delaware law make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us and make a takeover more difficult to complete, even if such a transaction were in the stockholders’ interest.
The Delaware General Corporation Law contains provisions that may have the effect of making it more difficult or delaying attempts by others to obtain control of us, even when these attempts may be in the best interests of our stockholders. We also are subject to the anti-takeover provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibit us from engaging in a “business combination” with an “interested stockholder” unless the business combination is approved in a prescribed manner and prohibit the voting of shares held by persons acquiring certain numbers of shares without obtaining requisite approval. The statutes have the effect of making it more difficult to effect a change in control of a Delaware company.
Our management and four significant stockholders collectively own a substantial majority of our common stock.
Collectively, our officers, our directors and three significant stockholders own or exercise voting and investment control of approximately 71% of our outstanding common stock as of July 18, 2024. As a result, investors may be prevented from affecting matters involving our company, including:
•the composition of our Board of Directors and, through it, any determination with respect to our business direction and policies, including the appointment and removal of officers;
•any determinations with respect to mergers or other business combinations;
•our acquisition or disposition of assets; and
•our corporate financing activities.
Furthermore, this concentration of voting power could have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing a change of control or other business combination that might otherwise be beneficial to our stockholders. This significant concentration of share ownership may also adversely affect the trading price for our common stock because investors may perceive disadvantages in owning stock in a company that is controlled by a small number of stockholders.
We have not paid any cash dividends in the past and have no plans to issue cash dividends in the future, which could cause the value of our common stock to have a lower value than other similar companies which do pay cash dividends.
We have not paid any cash dividends on our common stock to date and do not anticipate any cash dividends being paid to holders of our common stock in the foreseeable future. While our dividend policy will be based on the operating results and capital needs of the business, it is anticipated that any earnings will be retained to finance our future expansion. As we have no plans to issue cash dividends in the future, our common stock could be less desirable to other investors and as a result, the value of our common stock may decline, or fail to reach the valuations of other similarly situated companies who have historically paid cash dividends in the past.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our common stock adversely, the price of our common stock and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock may be influenced by the research and reports that securities or industry analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any of the analysts who may cover us change their recommendation regarding our common stock adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, the price of our common stock would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us was to cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause the price of our common stock or trading volume to decline.
Our business operations could be disrupted if our information technology systems fail to perform adequately.
We rely on information technology networks and systems, including the Internet, to process, transmit, and store information, to manage and support a variety of business processes and activities, and to comply with regulatory, legal, and tax requirements. Our information technology systems, some of which are dependent on services provided by third parties, may be vulnerable to damage, interruption, or shutdown due to any number of causes outside of our control such as catastrophic events, natural disasters, fires, power outages, systems failures, telecommunications failures, employee error or malfeasance, security breaches, computer viruses or other malicious codes, ransomware, unauthorized access attempts, denial of service attacks,
phishing, hacking, and other cyberattacks. While we have experienced threats to our data and systems, to date, we are not aware that we have experienced a material breach. Cyberattacks are occurring more frequently, are constantly evolving in nature and are becoming more sophisticated. Additionally, continued geopolitical turmoil, including the Russia-Ukraine military conflict, has heightened the risk of cyberattacks. While we attempt to continuously monitor and mitigate against cyber risks, we may incur significant costs in protecting against or remediating cyberattacks or other cyber incidents.
Sophisticated cybersecurity threats pose a potential risk to the security and viability of our information technology systems, as well as the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data stored on those systems, including cloud-based platforms. In addition, new technology that could result in greater operational efficiency may further expose our computer systems to the risk of cyber-attacks. If we do not allocate and effectively manage the resources necessary to build and sustain the proper technology infrastructure and associated automated and manual control processes, we could be subject to billing and collection errors, business disruptions, or damage resulting from security breaches. If any of our significant information technology systems suffer severe damage, disruption, or shutdown, and our business continuity plans do not effectively resolve the issues in a timely manner, our product sales, financial condition, and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected, and we could experience delays in reporting our financial results. In addition, there is a risk of business interruption, violation of data privacy laws and regulations, litigation, and reputational damage from leakage of confidential information. Any interruption of our information technology systems could have operational, reputational, legal, and financial impacts that may have a material adverse effect on our business.
A pandemic, epidemic, or outbreak of an infectious disease in the United States or elsewhere may adversely affect our business and we are unable to predict the potential impact.
We are subject to risks related to public health crises such as the global pandemic associated with COVID-19. The global spread of COVID-19 resulted in the World Health Organization declaring the outbreak a “pandemic,” or a worldwide spread of a new disease, in early 2020. This virus eventually spread world wide to most countries, and to all 50 states within the United States. In response, most countries around the world imposed quarantines and restrictions on travel and mass gatherings in an effort to contain the spread of the virus. Employers worldwide were also required to increase, as much as possible, the capacity and arrangement for employees to work remotely. The restrictions and travel bans have been eased or lifted completely as global society as a whole returned to pre-pandemic business and personal practices. Although, to date, these restrictions have not materially impacted our operations, the effect on our business, from the spread of COVID-19 or any new and similar viral crisis and the actions implemented by the governments of the United States and elsewhere across the globe implemeted to deal with such, may, once again, worsen over time and we are unable to predict the potential impact on our business.
Any outbreak of contagious diseases, or other adverse public health developments, could have a material and adverse effect on our business operations. These could include disruptions or restrictions on our ability to travel, pursue partnerships and other business transactions, receive shipments of biologic materials, as well as be impacted by the temporary closure of the facilities of suppliers. The spread of an infectious disease, like COVID-19, may also result in the inability of our suppliers to deliver supplies to us on a timely basis. In addition, health professionals may reduce staffing and reduce or postpone meetings with clients in response to the spread of an infectious disease. Though we have not yet experienced such events, if they would occur, they could result in a period of business disruption, and in reduced operations, any of which could materially affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. However, as of the date of this Annual Report, we have not experienced a material adverse effect on our business nor the need for reduction in our work force; and, currently, we do not expect any material impact on our long-term activity. The extent to which any spread of disease, like that of the COVID-19 pandemic, impacts our business will depend on future developments which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including, but not limited to, information which may emerge concerning the spreading and severity of the any infectious diseases, the actions to contain these, or treat their impact.
Deterioration in general economic conditions in the United States and globally, including the effect of prolonged periods of inflation on our customers and suppliers, could harm our business and results of operations.
Our business and results of operations could be adversely affected by changes in national or global economic conditions. These conditions include but are not limited to inflation, rising interest rates, availability of capital markets, energy availability and costs (including fuel surcharges), the negative impacts caused by pandemics and public health crises (such as the COVID-19 pandemic), negative impacts resulting from the military conflicts between Russia and the Ukraine and/or in the Middle East, and the effects of governmental initiatives to manage economic conditions. Impacts of such conditions could be passed on to our business in the form of a reduced customer base and/or potential for new bookings due to possible reductions in pharmaceutical and biotech industry-wide spend on research and development and/or economic pressure on our suppliers to pass on increased costs.
Our Chief Executive Officer resides in Israel and we have several customers with their operations located in Israel, and, therefore, our leadership continuity and results may be adversely affected by political, economic, and military instability in Israel.
One of our wholly owned subsidiaries is based in Israel. While we do not have a physical facility located in Israel, our Chief Executive Officer resides there and we have several customers whose operations are based there. Accordingly, political, economic, and military conditions in Israel may directly affect our business. Since the establishment of the modern State of Israel in 1948, a number of armed conflicts have taken place between Israel and its neighboring countries. Any hostilities involving Israel or the interruption or curtailment of trade between Israel and its trading partners could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and leadership continuity.
Any armed conflicts, war, terrorist activities, or political instability in the region and the consequences thereof, such as our customers' ability to conduct operations and pay their suppliers of goods and services (such as our company), could adversely affect business conditions and could harm our results of operations.
It is currently not possible to predict the duration or severity of the ongoing war or its effects on our business, operations, and financial conditions. The ongoing war is rapidly evolving and developing, and could disrupt our customers' business and operations. While we have not experienced any disruptions that have materially impacted our business or results of operations, there can be no assurances that further unforeseen events will not have a material adverse effect on us or our operations in the future.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Risk Management and Strategy
We believe we maintain an information technology and security program appropriate for a company of our size, taking into account our operations and risks. We recognize the critical importance of maintaining the trust and confidence of our investors, employees, customers and vendors. Our cybersecurity policies and processes are integrated into the Company's enterprise risk management program. We have implemented processes designed to assess, identify, and manage risks from potential unauthorized occurrences on or through our information technology systems that may result in adverse effects on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of these systems and the data residing therein. These processes include mechanisms, controls, and certain technologies designed to prevent or mitigate system intrusion or data loss, theft, misuse, or other security incidents or vulnerabilities and maintain a stable and secure information technology environment. For example, we conduct ongoing monitoring of critical systems for any compromised or potentially compromised accounts. We conduct regular trainings on cyber and information security, along with phishing simulations, among other topics. In addition, we consult with an outside information technology consultant on a regular basis to assist with assessing, identifying, and managing cybersecurity risks, including to anticipate future threats and trends, and their impact on the Company’s risk environment.
Governance
Our Board of Directors oversees our risk management process. The Audit Committee, by way of Board delegation, retains oversight of the Company’s cybersecurity risks. The senior leadership team, including our Chief Financial Officer and Chief Executive Officer, provides periodic reports to our Board, as applicable. Our Vice President of Technology is responsible for leading the assessment and management of cybersecurity threats and periodically updating the Audit Committee as needed.
To date, we have not identified risks from known cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any prior cybersecurity incidents, that have materially affected us, including our operations, business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition.
Item 2. Properties
The Company currently leases its office and laboratory facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. Rent expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term from the lease commencement date through the
scheduled expiration date. Rent expenses totaled $1.8 million and $1.9 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The Company considers its facilities adequate for its current operational needs.
The Company leases the following facilities:
•One University Plaza, Suite 307, Hackensack, New Jersey 07601, which, since November 2011, serves as the Company’s corporate headquarters. The lease expires in November 2026. The Company recognized $77,000 and $83,000 of rental costs relative to this lease for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
•1330 Piccard Drive, Suite 025, Rockville, MD 20850, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its primary service offerings. The lease expires February 28, 2029. The Company recognized $1.7 million of rental costs relative to this lease for each of fiscal 2024 and 2023.
•VIA LEONE XIII, 14, Milan, Italy, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its flow cytometry service offerings. The Company consolidated its lab and office space leases at this location into one lease during fiscal 2023. The lease expires October 31, 2028. The Company recognized $50,000 and $98,000 of rental costs in Italy for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
To the knowledge of our management team, there is no litigation currently pending or contemplated against us, any of our officers or directors in their capacity as such, or against any of our property.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Principal Market or Markets
Our shares of common stock are currently quoted on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “CSBR.” Our common stock commenced trading on the Nasdaq Capital Market on August 21, 2015. Prior to such date, our shares of common stock were traded over-the-counter and quoted on the OTCQB Marketplace.
The table below sets forth the high and low bid prices of our common stock, as reported on Nasdaq for the periods shown:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | High | | Low |
| Fiscal Year Ended April 30, 2024: | | | |
| First quarter | $ | 7.32 | | | $ | 4.17 | |
| Second quarter | 7.01 | | | 5.10 | |
| Third quarter | 7.13 | | | 4.51 | |
| Fourth quarter | 6.26 | | | 4.74 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | High | | Low |
| Fiscal Year Ended April 30, 2023: | | | |
| First quarter | $ | 9.53 | | | $ | 6.81 | |
| Second quarter | 9.88 | | | 6.90 | |
| Third quarter | 7.24 | | | 3.75 | |
| Fourth quarter | 5.54 | | | 3.95 | |
Approximate Number of Holders of Common Stock
As of July 18, 2024 there were approximately 1,900 record holders of the Company’s common stock.
Dividends
Holders of our common stock are entitled to receive such dividends as may be declared by our Board of Directors. No dividends have been declared or paid with respect to our common stock and no dividends are anticipated to be paid in the foreseeable future. Any future decisions as to the payment of dividends will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors, subject to applicable law.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Plan category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options,
warrants and rights | Weighted-average
exercise price of outstanding options,
warrants and rights | Number of securities remaining available
for future issuance under equity
compensation plans (excluding securities
reflected in column (a)) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 1,484,895 | 4.65 | 1,252,998 |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — |
| Total | 1,484,895 | 4.65 | 1,252,998 |
Recent Sales by the Company of Unregistered Securities
None.
Repurchases of Securities
On March 29, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program authorizing the Company to purchase up to an aggregate of $5.0 million of the Company’s common stock. The share repurchase program is designed in accordance with Rule 10b-18 of the Exchange Act. The shares may be purchased from time to time in the open market, as permitted under applicable rules and regulations, at prevailing market prices. The timing and amount of repurchases will depend on market conditions, share price, applicable legal requirements and other factors. The program does not obligate the Company to acquire a minimum number of shares. As of April 30, 2024, the Company had purchased approximately 120,300 shares of its common stock, at an average price of $5.73 per share, totaling approximately $708,000 and leaving an available balance of approximately $4.3 million authorized by the Board for use in the program as of that date.
Use of Proceeds
None.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
You should read the following discussion and analysis together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report. This discussion contains forward-looking statements that are based on our current expectations, estimates, and projections about our business and operations. Our actual results may differ materially from those currently anticipated and expressed in such forward-looking statements as a result of a number of factors, including those we discuss under Item 1A – “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report.
Overview and Recent Developments
We are a technology-enabled research organization engaged in creating transformative technology solutions to be utilized in drug discovery and development. Our research center consists of a comprehensive set of computational and experimental research platforms. Our pharmacology, biomarker, and data platforms are designed to facilitate drug discovery and development at lower costs and increased speeds. We perform studies which we believe may predict the efficacy of experimental oncology drugs or approved drugs as stand-alone therapies or in combination with other drugs and can stimulate the results of human clinical trials. These studies include in vivo studies that rely on implanting multiple tumors from our TumorBank in mice and testing the therapy of interest on these tumors. Studies may also include bioinformatics analysis that reveal the differences in the genetic signatures of the tumors that responded to a therapy as compared to the tumors that did not respond. Additionally, we provide computational or experimental support to identify novel therapeutic targets, select appropriate patient populations for clinical evaluation, identify potential therapeutic combination strategies, and develop biomarker hypothesis of sensitivity or resistance. These studies include the use of our in vivo, ex vivo, analytical and computational platforms.
We are engaged in the development and sale of advanced technology solutions and products to personalize the development and use of oncology drugs through our Translational Oncology Solutions ("TOS"). This technology ranges from computational-based discovery platforms, unique oncology software solutions, and innovative and proprietary experimental tools such as in vivo, ex vivo and biomarker platforms. Utilizing our TumorGraft Technology Platform (the "Platform"), a comprehensive bank of unique, well characterized models, we provide select services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies seeking personalized approaches to drug development. By performing studies to predict the efficacy of oncology drugs, our Platform facilitates drug discovery with lower costs and increased speed of drug development as well as increased adoption of existing drugs.
We also sell Lumin Bioinformatics ("Lumin"), an oncology data-driven software program which contains comprehensive information derived from our research services and clinical studies. Lumin leverages Champions’ large Datacenter coupled with analytics and artificial intelligence to provide a robust tool for computational cancer research. It is the combination of the Datacenter and the analytics that create a foundation for Lumin. Insights developed using Lumin can provide the basis for biomarker hypotheses, reveal potential mechanisms of therapeutic resistance, and guide the direction of additional preclinical evaluations. During fiscal 2023, we recorded an asset impairment related to Lumin software development costs of $807,000. There were no impairment charges recorded for fiscal 2024.
Our drug discovery and development business leverages the computational and experimental capabilities within our platforms. Our discovery strategy utilizes our rich and unique Datacenter, coupled with artificial intelligence and other advanced computational analytics, to identify novel therapeutic targets. We then employ the use of our proprietary experimental platforms to rapidly validate these targets for further drug development efforts.
We have a pipeline of targets at various stages of discovery and validation, with a select group that has progressed to early stage therapeutic development. Our commercial strategy for the validated targets and therapeutics established from this business is wide-ranging and still being developed. It will depend on many factors, and will be specific for each target or therapeutic area identified. Any expenses associated with this part of our business are research and development and are expensed as incurred.
We regularly evaluate strategic options to create additional value from our drug discovery business, which may include, but are not limited to, potential spin-out transactions or capital raises.
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes our operating results for the periods presented below (dollars in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Years Ended April 30, |
| 2024 | | % of
Revenue | | 2023 | | % of
Revenue | | % Change |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Oncology services revenue | $ | 50,155 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 53,870 | | | 100.0 | % | | (6.9) | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Costs and operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of oncology services | 29,401 | | | 58.6 | | | 29,532 | | | 54.8 | | | (0.4) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | 9,544 | | | 19.0 | | | 11,545 | | | 21.4 | | | (17.3) | |
| Sales and marketing | 7,064 | | | 14.1 | | | 7,002 | | | 13.0 | | | 0.9 | |
| General and administrative | 11,067 | | | 22.1 | | | 10,240 | | | 19.0 | | | 8.1 | |
| Loss on disposal of equipment | 435 | | | 0.9 | | | — | | | — | | | 100.0 | |
| Asset Impairment | — | | | — | | | 807 | | | 1.5 | | | (100.0) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total costs and operating expenses | 57,511 | | | 114.7 | | | 59,126 | | | 109.7 | | | (2.7) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | (7,356) | | | (14.7) | | | (5,256) | | | (9.8) | | | 40.0 | |
Oncology Services Revenue
Oncology services revenue, which is primarily derived from research services, was $50.2 million and $53.9 million, for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, a decrease of $3.7 million, or 6.9%. The decrease in revenue was primarily due to a combination of factors including an increase in study cancellations during fiscal year 2023 and a slowdown of bookings expansion. These two factors reduced our net bookings and available convertible revenue in the current year.
Cost of Oncology Services
Cost of oncology services were $29.4 million and $29.5 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, a slight decrease of $0.1 million or 0.4%. Gross margin was 41% for the twelve months ended April 30, 2024 compared to 45% for the twelve months ended April 30, 2023. The decrease in gross margin was the result of relatively unchanged variable costs on a revenue decline. Variable costs were a higher percentage of revenue due to increases in mice and supply expenses. These increases were caused by operational inefficiencies creating the need for additional mice and lab supplies.
Research and Development
Research and development expense was $9.5 million and $11.5 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, a decrease of $2.0 million or (17.3)%. The decrease was primarily due to cost cutting measures along with a reduction in research and development work required as our newer platforms mature. These factors led to a decline in compensation and lab supply expenses. The decrease was also due to a reduction in spend for our drug discovery and development programs.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense was $7.1 million and $7.0 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, remaining relatively flat with a slight increase of $0.1 million or 0.9%. The increase was mainly due to increased conference attendance.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expense was $11.1 million and $10.2 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, an increase of $0.8 million, or 8.1%. General and administrative expense was primarily comprised of compensation, insurance, professional fees, IT, and depreciation and amortization expenses. The general and administrative expense increase was primarily due to compensation and recruiting expenses due to the addition to the executive team. Additionally, non-cash stock compensation and allowances for estimated credit losses and bad debt reserves increased. These increases were partially offset by a decrease in IT and professional fees.
Asset Impairment
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, we assessed the recoverability of the Lumin capitalized software development costs by comparing the forecasted future revenues from Lumin sales, based on management’s best estimates and using appropriate assumptions and projections, to the carrying amount of the capitalized asset. Several factors were considered in this analysis, including, the decrease in Lumin revenue growth from the prior year, the deceleration of new Lumin bookings in the current year, and the strategic consideration for additional capital investment into the platform, sales team, and marketing campaigns to bolster awareness and growth. As the carrying value was determined not to be recoverable from future revenues, an impairment loss was recognized for the year ending April 30, 2023 equal to the amount by which the carrying amount exceeded the future revenues, or, its net book value at that date of $807,000. There were no impairment charges for the year ending April 30, 2024.
Loss on Disposal of Equipment
Loss on disposal of equipment was $435,000 and zero for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. For the year ended April 30, 2024, the loss resulted from the disposal of equipment which could no longer be utilized and had a net book value, or carrying value on the balance sheet, as of the disposal date.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income, net, was $48,000 for the year ended April 30, 2024. Other expense, net, was $11,000 for the year ended April 30, 2023. For the year ended April 30, 2024, other income resulted primarily from interest income of $92,000 partially offset by foreign currency transaction net losses of approximately $16,000 and interest expense of $28,000. For the year ended April 30, 2023, other expense, net resulted primarily from foreign currency transaction net losses.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Under ASC Subtopic 205-40, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern (“ASC 205-40”), the Company has the responsibility to evaluate whether conditions and/or events raise substantial doubt about its ability to meet its future financial obligations as they become due within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued. The following conditions raised substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern: a history of net losses, working capital deficits, accumulated deficit and declining cash position. Going concern matters are more fully discussed in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. No adjustments have been made to the financials statements as a result this uncertainty.
Our liquidity needs have typically arisen from the funding of our research and development programs and the launch of new products, working capital requirements, and other strategic initiatives. Most recently, we have met these cash requirements through cash on hand, working capital management, and sales of products and services. In the past, we have also received proceeds from certain private placements and public offerings of our securities. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company had a net loss of approximately $7.3 million and a net loss of approximately $5.3 million, respectively. While we believe we have strategies to increase our revenues and reduce our costs which can be implemented without disrupting the business or completely restructuring the Company, there can be no assurances. In order to continue to fund our operations we may need to raise additional equity or debt capital in the near term and cannot provide any assurance that we will be successful in doing so, and if we can, on whether the terms will be acceptable to us. If we are unable to obtain additional financing in the near future, we may be required to pursue a reorganization proceeding, including under applicable bankruptcy or insolvency laws.
Cash Flows
The following discussion relates to the major components of our cash flows:
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $6.1 million for the year ended April 30, 2024. Net cash provided by operating activities was $4.0 million for the year ended April 30, 2023. The decrease in cash from operations was primarily due to the net loss realized in fiscal 2024.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $836,000 and $2.9 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The cash used was for the investment in lab and computer equipment.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities was $527,000 for the year ended April 30, 2024. Net cash provided by financing activities was $11,000 for the year ended April 30, 2023. Cash flows used in financing activities was for the repurchase of common stock per our stock buyback program and financing lease payments and was offset by stock options exercise proceeds.
Critical Accounting Policies
The following discussion of critical accounting policies identifies the accounting policies that require application of management’s most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. It is not intended to be a comprehensive list of all of our significant accounting policies, which are more fully described in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements included in this document. In many cases, the accounting treatment of a particular transaction is specifically dictated by generally accepted accounting principles, with no need for management’s judgment in their application. There are also areas in which the selection of an available alternative policy would not produce a materially different result.
General
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States ("GAAP"). The preparation of the consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Significant estimates of the Company include, among other things, accounts receivable realization, revenue recognition, valuation allowance for deferred tax assets, recoverability of capitalized software development costs, and stock-based compensation and warrant assumptions. We base our estimates on historical experience, our observance of trends in particular areas and information or valuations and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances and which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that may not be readily apparent from other sources. Actual amounts could differ significantly from amounts previously estimated.
Revenue Recognition
The Company accounts for revenue under the Financial Accounting Standards Board's ("FASB") Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. In accordance with ("ASC 606"), revenue is now recognized when, or as, a customer obtains control of promised services. The amount of revenue recognized reflects the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled to receive in exchange for these services.
A performance obligation is a promise (or a combination of promises) in a contract to transfer distinct goods or services to a customer and is the unit of accounting under ASC 606 for the purposes of revenue recognition. A contract's transaction price is allocated to each separate performance obligation based upon the standalone selling price and is recognized as revenue, when, or as, the performance obligation is satisfied. The majority of the Company's contracts have a single performance obligation because the promise to transfer individual services is not separately identifiable from other promises in the contracts, and therefore, is not distinct.
The majority of the Company's revenue arrangements are service contracts that are completed within a year or less. There are a few contracts that range in duration between 1 and 3 years. Substantially all of the Company's performance obligations, and associated revenue, are transferred to the customer over time. Most of the Company's contracts can be terminated by the customer without cause. In the event of termination, the Company's contracts provide that the customer pay the Company for services rendered through the termination date. The Company generally receives compensation based on a predetermined invoicing schedule relating to specific milestones for that contract. In addition, in certain instances a customer contract may include forms of variable consideration such as performance incentives or other provisions that can increase or decrease the transaction price. This variable consideration is generally awarded upon achievement of certain performance metrics. For the purposes of revenue recognition, variable consideration is assessed on a contract-by-contract basis and the amount to be recorded is estimated based on the assessment of the Company's anticipated performance and consideration of all information that is reasonably available. Variable consideration is recognized as revenue if and when it is deemed probable that a significant
reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is resolved in the future.
Amendments to contracts are common. The Company evaluates each amendment which meets the criteria of a contract modification under ASC 606. Each modification is further evaluated to determine whether the contract modification should be accounted for as a separate contract or as a continuation of the original agreement.
The Company accounts for amendments as a separate contract when they meet the criteria under ASC 606-10-25-12.
Stock-Based Payments
We typically recognize expense for stock-based payments based on the fair value of awards on the date of grant. We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate fair value. The option pricing model requires us to estimate certain key assumptions such as expected life, volatility, risk free interest rates, and dividend yield to determine the fair value of stock-based awards. These assumptions are based on historical information and management judgment. We expense stock-based payments over the period that the awards are expected to vest. In the event of forfeitures, compensation expense is adjusted. We report cash flows resulting from tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized from those options (excess tax benefits) as financing cash flows when the cash tax benefit is received.
Recoverability of Capitalized Software Development Costs
The Company accounts for the cost of computer software obtained or developed for internal use as well as the software development and implementation costs associated with a hosting arrangement ("internal-use software") that is a service contract
in accordance and with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other. We capitalize certain costs in the development of our internal-use software when the preliminary project stage is completed and the software has reached the point of technological feasibility. Capitalization of these costs ceases once the project is substantially complete and the software is ready for its intended purpose and available for sale. Capitalized costs are recorded as an asset and then amortized using the straight-line method over an estimated useful economic life of three years.
Capitalized software development costs are stated at gross cost less accumulated amortization. Recoverability of these capitalized costs is determined at each balance sheet date by comparing the forecasted future revenues from the related product, based on management’s best estimates using appropriate assumptions and projections at the time, to the carrying amount of the capitalized software development costs. If the carrying value is determined not to be recoverable from future revenues, an impairment loss is recognized equal to the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the future revenues. During fiscal 2023, we recorded an asset impairment charge related to software development costs of $807,000. There were no impairment charges related to software development costs recorded during fiscal 2024.
Accounting for Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method to account for income taxes. Significant management judgment is required in determining the provision for income taxes, deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance recorded against net deferred tax assets. In preparing the consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. This process involves estimating the actual current tax liability together with assessing temporary differences resulting from differing treatment of items, such as deferred revenue, depreciation on property, plant and equipment, goodwill and losses for tax and accounting purposes. These differences result in deferred tax assets, which include tax loss carry-forwards, and liabilities, which are included within the consolidated balance sheet. We then assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income, and to the extent that recovery is not likely or there is insufficient operating history, a valuation allowance is established. To the extent a valuation allowance is established or increased in a period, we include an expense within the tax provision of the consolidated statements of operations. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, we have established a full valuation allowance for all deferred tax assets.
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, we recognized a liability for uncertain tax positions on the balance sheet relative to foreign operations in the amount of $181,000. We do not anticipate any significant unrecognized tax benefits will be recorded during the next 12 months. Any interest or penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits is recognized in income tax expense. The Company has not accrued any additional penalties or interest during the year ended April 30, 2024 as we believe the liability for uncertain tax positions accurately reflects penalties and/or interest as of this date.
Accounting Pronouncements Adopted
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses". This update requires immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses. Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The Company adopted this ASU on May 1, 2023 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Off-Balance Sheet Financing
We have no off-balance sheet debt or similar obligations. We have no transactions or obligations with related parties that are not disclosed, consolidated into or reflected in our reported results of operations or financial position. We do not guarantee any third-party debt.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Not applicable.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The consolidated financial statements required pursuant to this Item are included in Item 15 of this Annual Report and are presented beginning on page F-1.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Management's Report on Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, under the supervision and with the participation of our Principal Executive Officer (our Chief Executive Officer) and Principal Financial Officer (our Chief Financial Officer), has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of April 30, 2024, the end of our fiscal year covered by this Annual Report. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or person performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management recognizes that any disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives, and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of April 30, 2024, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of April 30, 2024, our disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. This rule defines internal control over financial reporting as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, Company management to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. Management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting using the components established in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
A system of internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A material weakness is any deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
Based upon this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of April 30, 2024, the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report.
Changes in Internal Controls
There were no changes in the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting during the quarter ended April 30, 2024, that materially affected, or were reasonably likely to materially affect the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not Applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item will be contained in our 2024 Proxy Statement and such information is incorporated herein by this reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item will be contained in our 2024 Proxy Statement and such information is incorporated herein by this reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item will be contained in our 2024 Proxy Statement and such information is incorporated herein by this reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item will be contained in our 2024 Proxy Statement and such information is incorporated herein by this reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by this Item will be contained in our 2024 Proxy Statement and such information is incorporated herein by this reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a)1. Financial Statements
| | | | | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-2 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-3 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations | F-4 |
| Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders' (Deficiency) Equity | F-5 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-6 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-7 |
(a)2. Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable.
(a)3. Exhibits required to be filed by Item 601 of Regulation S-K.
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit No. | | |
| | |
| 3.1 | | |
| | |
| 3.1.1 | | |
| | |
| 3.2 | |
|
| | |
| 4.1 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.1 | | Employment Agreement, dated November 5, 2013, between the Company and Ronnie Morris, M.D. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 12, 2013) *** |
| | |
| 10.2 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.3 | | |
| | |
| 10.4 | | |
| | |
| 10.5 | | |
| | |
| 10.6 | | |
| | |
| 10.7 | | |
| | |
| 10.8 | | |
| | |
| 10.9 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.10 | | |
| | |
| 10.11 | | |
| | |
| 10.12 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.13 | | |
| | |
| 10.14 | | |
| | |
| 10.15 | | |
| | |
| 10.16 | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.17 | | Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to (i) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 24, 2011, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto, (ii) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 28, 2013, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto, and (iii) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 11, 2015, between the Company. And each investor identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.18 | | |
| | |
| 10.19 | | |
| | |
| 10.20 | | |
| | |
| 10.21 | | |
| | |
| 14 | | |
| | |
| 21 | | |
| | |
| 23.1 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 31.1 | | |
| | |
| 31.2 | | |
| | |
| 32.1 | | |
| | |
| 101.INS* | | XBRL Instance Document. |
| 101.SCH* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| 101.CAL* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.DEF* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| 101.LAB* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| 101.PRE* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
___________________________
* Filed herewith
** Furnished hereto.
*** Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
Not Required.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | |
| CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC. |
| |
| July 19, 2024 | /s/ RONNIE MORRIS |
| Ronnie Morris |
| Chief Executive Officer |
| (principal executive officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ RONNIE MORRIS | | Chief Executive Officer and Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| Ronnie Morris | | (principal executive officer) | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ DAVID MILLER | | Chief Financial Officer | | July 19, 2024 |
| David Miller | | (principal financial and accounting officer) | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ JOEL ACKERMAN | | Director, | | July 19, 2024 |
| Joel Ackerman | | Chairman of the Board of Directors | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ DAVID SIDRANSKY | | Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| David Sidransky | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ ROBERT BRAININ | | Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| Robert Brainin | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ SCOTT R. TOBIN | | Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| Scott R. Tobin | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ DANIEL MENDELSON | | Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| Daniel Mendelson | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ PHILIP BREITFELD | | Director | | July 19, 2024 |
| Philip Breitfeld | | | | |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Champions Oncology, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Champions Oncology, Inc. and Subsidiaries (the “Company") as of April 30, 2024 and 2023, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ (deficiency) equity, and cash flows for each of the years then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of the Company as of April 30, 2024 and 2023, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company has experienced net losses and negative cash flows from operations that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 2. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Revenue Recognition
As described further in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, revenues are primarily derived from contracts with customers to provide pharmacology services with payments based on fixed fee arrangements. The Company recognizes revenue over time using a progress-based input method that depicts the transfer of control over the life of the performance obligation. Revenue is recognized for the single performance obligation over time due to the Company's right to payment for work
performed to date and the performance does not create an asset with an alternative use. Customer payments may be made in advance or on a schedule in the statement of work (“SOW”) unrelated to when revenue is recognized resulting in deferred revenue. The determination of the progress as the overall performance obligation is being completed is based on the worked performed in accordance with the SOW and requires management estimates. Pharmacology services revenues for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were approximately $47.0 million and $50.7 million, respectively. Pharmacology deferred revenue as of April 30, 2024 and 2023 was approximately $12.0 million and $12.7 million, respectively.
We identified the accounting for revenue and the related deferred revenue recognized over time as a critical audit matter due to the complexity and subjectivity of management’s estimate of the progress towards completion of its projects. This in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgement and subjectivity and significant audit effort was required in performing procedures to evaluate management’s determination of the project completion progress, related costs incurred and deferred revenue.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the financial statements. We obtained an understanding and evaluated the design of controls relating to the Company's revenue recognition and deferred revenue. Our audit procedures related to the recognition of revenue over time and deferred revenue included the following procedures, among others, (i) testing the Company’s estimates of project progress by evaluating the appropriate SOW and customer correspondence documentation, (ii) testing the significant assumptions used to develop the estimates of project progress pursuant to the SOW and (iii) testing completeness and accuracy of the underlying data.
/s/ EisnerAmper LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2015.
EISNERAMPER LLP
West Palm Beach, Florida
July 19, 2024
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF APRIL 30
(In Thousands except for shares)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash | $ | 2,618 | | | $ | 10,118 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 9,526 | | | 8,011 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,495 | | | 1,328 | |
| | | |
| Total current assets | 13,639 | | | 19,457 | |
| | | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | 6,252 | | | 7,318 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 5,721 | | | 7,186 | |
| Other long term assets | 185 | | | 15 | |
| Goodwill | 335 | | | 335 | |
| | | |
| Total assets | $ | 26,132 | | | $ | 34,311 | |
| | | |
LIABILITIES
AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 5,800 | | | $ | 5,334 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 2,160 | | | 2,270 | |
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 1,337 | | | 1,208 | |
| Other current liabilities | 150 | | | 145 | |
| Deferred revenue | 12,094 | | | 12,776 | |
| | | |
| Total current liabilities | 21,541 | | | 21,733 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Non-current portion operating lease liabilities | 6,093 | | | 7,391 | |
| | | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 401 | | | 551 | |
| | | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 28,035 | | | $ | 29,675 | |
| | | |
| Stockholders' (deficiency) equity: | | | |
Common stock, $.001 par value; 200,000,000 shares authorized; 13,714,099 and 13,558,650 shares issued; and 13,593,766 and 13,544,228 shares outstanding at April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively | 14 | | | 14 | |
| Treasury Stock, at cost | (708) | | | (74) | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 83,384 | | | 82,013 | |
| Accumulated deficit | (84,593) | | | (77,317) | |
| | | |
| Total stockholders' (deficiency) equity | (1,903) | | | 4,636 | |
| | | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' (deficiency) equity | $ | 26,132 | | | 34,311 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Dollars in Thousands Except Share and Per Share Amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | | |
| | | |
| Oncology services revenue | $ | 50,155 | | | $ | 53,870 | |
| | | |
| Costs and operating expenses: | | | |
| Cost of oncology services | 29,401 | | | 29,532 | |
| | | |
| Research and development | 9,544 | | | 11,545 | |
| Sales and marketing | 7,064 | | | 7,002 | |
| General and administrative | 11,067 | | | 10,240 | |
| Loss on disposal of equipment | 435 | | | — | |
| Asset impairment | — | | | 807 | |
| | | |
| Total costs and operating expenses | 57,511 | | | 59,126 | |
| | | |
| Loss from operations | (7,356) | | | (5,256) | |
| | | |
| Other income (expense): | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Other income (expense), net | 48 | | | (11) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Loss before income tax expense | (7,308) | | | (5,267) | |
| (Benefit) provision for income tax | (32) | | | 68 | |
| | | |
| Net loss | $ | (7,276) | | | $ | (5,335) | |
| | | |
| Net loss per common share outstanding | | | |
| basic and diluted | $ | (0.54) | | | $ | (0.39) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding | | | |
| basic and diluted | 13,547,604 | | | 13,541,559 | |
| | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ (DEFICIENCY) EQUITY
(In Thousands except for shares)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total
Stockholders'
(Deficiency) Equity |
| | Common Stock | | Treasury Stock | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | Accumulated
Deficit | | | |
| | Shares | | Amount | | Shares | | Amount | | | | |
| Balance, April 30, 2022 | 13,522,441 | | | $ | 14 | | | — | | | — | | | $ | 81,064 | | | $ | (71,982) | | | | | $ | 9,096 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 864 | | | — | | | | | 864 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options | 36,209 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 85 | | | — | | | | | 85 | |
| Repurchase of common stock | — | | | — | | | 14,422 | | | (74) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (74) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (5,335) | | | | | (5,335) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, April 30, 2023 | 13,558,650 | | | $ | 14 | | | 14,422 | | | $ | (74) | | | $ | 82,013 | | | $ | (77,317) | | | | | $ | 4,636 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,118 | | | — | | | | | 1,118 | |
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options | 155,449 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 253 | | | — | | | | | 253 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Repurchase of common stock | — | | | — | | | 105,911 | | | (634) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (634) | |
| Net loss | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (7,276) | | | | | (7,276) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, April 30, 2024 | 13,714,099 | | | $ | 14 | | | 120,333 | | | $ | (708) | | | $ | 83,384 | | | $ | (84,593) | | | | | $ | (1,903) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in Thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended April 30, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Operating activities: | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (7,276) | | | $ | (5,335) | |
| | | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash (used in) provided by operating activities: | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 1,118 | | | 864 | |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | 1,867 | | | 2,246 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net loss on disposal of equipment | 435 | | | — | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 1,066 | | | 952 | |
| | | |
| Asset impairment | — | | | 807 | |
| | | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses | 476 | | | 195 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (1,991) | | | 1,308 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (167) | | | (184) | |
| | | |
| Other long term assets | (169) | | | — | |
| Accounts payable | 465 | | | 2,465 | |
| Accrued liabilities | (109) | | | (145) | |
| Operating lease liabilities | (1,169) | | | (907) | |
| | | |
| Deferred revenue | (683) | | | 1,706 | |
| | | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | (6,137) | | | 3,972 | |
| | | |
| Investing activities: | | | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | (836) | | | (2,872) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (836) | | | (2,872) | |
| | | |
| Financing activities: | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Proceeds from exercise of options | 253 | | | 85 | |
| Repurchases of common stock | (634) | | | (74) | |
| | | |
| Finance lease payments | (146) | | | — | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (527) | | | 11 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| (Decrease) increase in cash | (7,500) | | | 1,111 | |
| Cash, beginning of year | 10,118 | | | 9,007 | |
| | | |
| Cash, end of year | $ | 2,618 | | | $ | 10,118 | |
| | | |
| Non-cash financing and investing activities: | | | |
| Purchased equipment under finance lease | — | | | 368 | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities | $ | — | | | $ | 231 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Organization and Basis of Presentation
Background
Champions Oncology, Inc. (the “Company”), is engaged in drug discovery and development through data-driven research strategies and innovative pharmacology, biomarker and data platforms. The Company’s TumorGraft Technology Platform is an approach to personalizing cancer care based upon the implantation of human tumors in immune-deficient mice. The Company provides a technology platform to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies using proprietary TumorGraft studies, which the Company believes may be predictive of how drugs may perform in clinical settings. Utilizing the TumorGraft Technology Platform (the "Platform"), a comprehensive Bank of unique, well characterized "Patient Derived XenoGrafts" (PDX) models, the Company offers multiple services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies seeking personalized approaches to drug development. By performing studies to predict the efficacy of oncology drugs, our Platform is designed to facilitate drug discovery with lower costs and increased speed of drug development as well as increased adoption of existing drugs.
The Company has four operating subsidiaries: Champions Oncology (Israel), Limited, Champions Biotechnology U.K., Limited, Champions Oncology S.R.L., and Corellia AI, Inc. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, there were no revenues earned by these subsidiaries.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). The Company operates in one reportable business segment.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Foreign Currency
The Company’s foreign subsidiaries functional currency is the U.S. dollar. Transaction gains and losses are recognized in earnings. The Company is subject to foreign exchange rate fluctuations in connection with the Company’s international operations.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates include, among other things, accounts receivable realization, revenue recognition, valuation allowance for deferred tax assets, recoverability of capitalized software development costs, and stock-based compensation and warrant assumptions. We base our estimates on historical experience, our observance of trends in particular areas and information or valuations and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances and which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that may not be readily apparent from other sources. Actual amounts could differ significantly from amounts previously estimated.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers only those investments which are highly liquid, readily convertible to cash, and with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company had cash balances of $2.6 million and $10.1 million, respectively, and no cash equivalents. The Company maintains its cash balances in three major financial institutions. The Company regularly monitors the financial stability of these financial institutions and believes that it is not exposed to any significant credit risk in its cash. If any liquidity and/or financial stability concerns arise with respect to
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
banks and financial institutions, either nationally or in specific regions, the Company's ability to access cash or enter into new financing arrangements may be threatened, which could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition and results of operations.
Liquidity and Going Concern
In accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Subtopic 205-40, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern (“ASC 205-40”), the Company has the responsibility to evaluate whether conditions and/or events raise substantial doubt about its ability to meet its obligations as they become due within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued. As required under ASC 205-40, management’s evaluation should initially not take into consideration the potential mitigating effects of management’s plans that have not been fully implemented as of the date the financial statements are issued. The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern.
In performing this evaluation, we concluded that under the standards of ASC 205-40 the following conditions raised substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern:
•a history of net losses, including a net loss of $7.3 million for the year ending April 30 2024;
•cash used in operations of $6.1 million for the year ended April 30, 2024;
•working capital deficit of $7.9 million as of April 30, 2024; and
•an accumulated deficit of $84.6 million.
The Company's liquidity needs have typically arisen from the funding of our research and development programs and the launch of new products, working capital requirements, and other strategic initiatives. Most recently, the Company has met these cash requirements through cash on hand, working capital management, and sales of products and services. In the past, the Company has also received proceeds from certain private placements and public offerings of our securities. While the Company believes it has strategies to increase revenues and reduce costs which can be implemented without disrupting the business or completely restructuring the Company, there can be no assurances. Should the Company be required to raise additional capital or seek to obtain financing, there can be no assurance that management would be successful in raising such capital or obtaining such financing on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from these uncertainties.
Fair Value
The carrying value of cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, and other current assets, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities approximate their fair value based on the liquidity or the short-term maturities of these instruments. The fair value hierarchy promulgated by GAAP consists of three levels:
•Level one — Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
•Level two — Inputs other than level one inputs that are either directly or indirectly observable; and
•Level three — Unobservable inputs developed using estimates and assumptions, which are developed by the reporting entity and reflect those assumptions that a market participant would use.
Determining which category an asset or liability falls within the hierarchy requires significant judgment. The Company evaluates its hierarchy disclosures each quarter. The Company has no assets or liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring and/or non-recurring basis during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is recorded at cost and primarily consists of laboratory equipment, furniture and fixtures, computer hardware and software, and internally developed software. Assets in progress include equipment or software not yet placed in service. Depreciation and amortization is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the various assets ranging from three to seven years. Refer to Footnote 4, "Property and Equipment" for a detailed discussion.
Leases
The Company accounts for its leases under Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") ASC Topic 842, Leases ("ASC 842"). Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases and are
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both a right-of-use ("ROU") asset and lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right-of-use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right-of-use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term.
Amortization expense for the ROU asset associated with its finance leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease and interest expense associated with its finance lease is recognized on the balance of the lease liability using the effective interest method based on the estimated incremental borrowing rate.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Impairment losses are to be recognized when the carrying amount of a long-lived asset is not recoverable or exceeds its fair value. The Company evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that a carrying value may not be recoverable. The Company uses estimates of future cash flows over the remaining useful life of a long- lived asset or asset group to determine the recoverability of the asset. These estimates only include the net cash flows directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the asset or asset group. For the year ending April 30, 2023, the Company recognized an impairment loss of $807,000 for its Lumin Bioinformatics platform ("Lumin") resulting from a recoverability analysis performed at that date. The net book value of Lumin at April 30, 2023 was zero. The Company did not recognized any impairment losses for the Company’s long-lived assets for the year ending April 30, 2024. Refer to Note 4, "Property and Equipment".
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired in a business combination. The Company evaluates the carrying value of goodwill annually in connection with the annual budgeting and forecast process and also between annual evaluations if events occur or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of the reporting unit to which goodwill was allocated to below its carrying amount. Such circumstances could include, but are not limited to: (1) a significant adverse change in legal factors, market conditions, or in business climate, (2) unanticipated competition, or (3) an adverse action or assessment by a regulator. When evaluating goodwill for impairment, we may first perform an assessment qualitatively whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s carrying amount exceeds its fair value, referred to as a “step zero” approach. Subsequently (if necessary after step zero), an entity should perform its goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value. Under FASB's Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2014-02, Topic 350, "Intangibles—Goodwill and Other" goodwill impairment is measured as the excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit over its fair value.
The Company assesses goodwill impairment by reporting unit. Translational Oncology Solutions ("TOS") is the only reporting unit with remaining goodwill. Judgments regarding the existence of impairment indicators are based on legal factors, market conditions and operational performance of the businesses. Future events, including but not limited to continued declines in economic activity, loss of contracts or a significant number of customers, or a rapid increase in costs or capital expenditures, could cause us to conclude that impairment indicators exist and that goodwill is impaired. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company's annual assessment did not result in any impairment indicators.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue represents payments received in advance of products to be delivered or services to be performed. When products are delivered and/or services are performed, deferred revenue is recognized as earned. Revenue related to deferred revenue is expected to be recognized within one year.
Other Non-Current Liabilities
Other non-current liabilities represent amounts for uncertain tax positions relating to one of our foreign entities and a financing lease of laboratory equipment in exchange for a lab supplies purchasing commitment.
Cost of Oncology Services
Cost of oncology services relates primarily to our TOS business unit. TOS costs consist of direct costs related to laboratory supplies, mice purchases, and maintenance costs for studies completed internally as well as charges from Contract Research
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Organizations for studies handled externally. Indirect costs include salaries and other payroll related costs of compensation for personnel directly engaged in providing TOS products and services. All costs of performing studies in-house are expensed as incurred. All costs of performing studies from external sources, are expensed when incurred.
Research and Development
Research and development costs represent both costs incurred internally for research and development activities, including personnel costs, mice purchases, and maintenance, as well as costs incurred externally to facilitate research activities, such as tumor tissue procurement and characterization expenses. All research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expenses represent costs incurred to promote the Company’s products offered, including salaries, benefits and related costs of our sales and marketing personnel, and represent costs of advertising and other selling and marketing expenses. All sales and marketing costs, including advertising costs, are expensed as incurred.
Earnings Per Share
Basic net income or loss per share is computed by dividing the net income or loss for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed by dividing the net income for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock plus dilutive potential common stock considered outstanding during the period. Such dilutive shares consist of incremental shares that would be issued upon exercise of the Company’s common stock purchase warrants and stock options. Dilutive earnings per share is not presented when it would be antidilutive to do so.
Stock-based Payments
The Company typically recognizes expense for stock-based payments based on the fair value of awards on the date of grant. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate fair value. The Black-Scholes option valuation model was developed for use in estimating the fair value of short-traded options that have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. The option pricing model requires the Company to estimate certain key assumptions such as expected life, volatility, risk free interest rates and dividend yield to determine the fair value of stock-based awards. These assumptions are based on historical information and management judgment. The risk-free interest rate used is based on the United States treasury security rate with a term consistent with the expected term of the award at the time of the grant. Since the Company has limited option exercise history, it has generally elected to estimate the expected life of an award based upon the Securities and Exchange Commission-approved “simplified method” noted under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 with the continued use of this method extended under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110. Estimated volatility is based upon the historical volatility of the Company's common stock. The Company does not anticipate paying a dividend, and therefore, no expected dividend yield was used.
The Company expenses stock-based payments over the period that the awards are expected to vest. In the event of forfeitures, compensation expense is adjusted. The Company expenses modification charges in the period of modification and, if required, over the remaining period the awards are expected to vest. The Company will report cash flows resulting from tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized from those options (excess tax benefits) as financing cash flows, if they should arise.
Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes have been provided to show the effect of temporary differences between the recognition of expenses for financial and income tax reporting purposes and between the tax basis of assets and liabilities, and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company assesses the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered through tax planning strategies or from future taxable income, and to the extent that recovery is not likely or there is insufficient operating history, a valuation allowance is established. The Company adjusts the valuation allowance in the period management determines it is more likely than not that net deferred tax assets will or will not be realized. Changes in valuation allowances from period to period are included in the tax provision in the period of change. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company provided a valuation allowance for all net deferred tax assets, as recovery is not more likely than not based on an insufficient history of earnings.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company reflects tax benefits only if it is more likely than not that we will be able to sustain the tax position, based on its technical merits. If a tax benefit meets this criterion, it is measured and recognized based on the largest amount of benefit that is cumulatively greater than 50% likely to be realized. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company has recorded $181,000 of liabilities related to uncertain tax positions relative to one of its foreign operations.
The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and/or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense. The Company accrued $0 for any additional interest and or penalties on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, as the Company believes its recorded liability for uncertain tax positions covers any potential interest and/or penalties. The Company does not anticipate any significant unrecognized tax benefits to be recorded during the next 12 months. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company recognized a benefit for income taxes of $32,000 and a provision for income taxes of $68,000, respectively. These amounts are mainly attributable to taxable income earned in Israel and Italy relating to transfer pricing, U.S. state net operating loss limitations and, in fiscal 2024, net of a return to provision adjustment in Israel of $95,000.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with ASC 606, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers". The objective of the standard is to establish a single comprehensive revenue recognition model that is designed to create greater comparability of financial statements across industries and jurisdictions. Under this standard, companies recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in amounts that reflect the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
All revenue is generated from contracts with customers. The Company recognizes revenue when control of these services is transferred to the customer in an amount, referred to as the transaction price, that reflects the consideration to which the Company is expected to be entitled in exchange for those services. The Company determines revenue recognition utilizing the following five steps: (1) identification of the contract with a customer, (2) identification of the performance obligations in the contract (promised goods or services that are distinct), (3) determination of the transaction price, (4) allocation of the transaction price to the performance obligations, and (5) recognition of revenue when, or as, the Company transfers control of the product or service for each performance obligation. The Company records revenues net of any tax assessments by governmental authorities, such as value added taxes, that are imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue generating transactions.
The majority of the Company's revenue arrangements are service contracts that are completed within a year or less. There are a few contracts that range in duration between 1 and 3 years. Substantially all of the Company's performance obligations, and associated revenue, are transferred to the customer over time. Most of the Company's contracts can be terminated by the customer without cause. In the event of termination, the Company's contracts provide that the customer pay the Company for services rendered through the termination date. The Company generally receives compensation based on a predetermined invoicing schedule relating to specific milestones for that contract.
Amendments to contracts are common. The Company evaluates each amendment which meets the criteria of a contract modification under ASC 606. Each modification is further evaluated to determine whether the contract modification should be accounted for as a separate contract or as a continuation of the original agreement.
The Company accounts for amendments as a separate contract as they meet the criteria under ASC 606-10-25-12.
Pharmacology Study and Other Services
The Company generally enters into contracts with customers to provide oncology services with payments based on fixed-fee arrangements. At contract inception, the Company assesses the services promised in the contracts with customers to identify the performance obligations in the arrangement. The Company's fixed-fee arrangements for oncology services are considered a single performance obligation because the Company provides a highly-integrated service.
The Company recognizes revenue over time using a progress-based input method since there is no single output measure that would fairly depict the transfer of control over the life of the performance obligation. Revenue is recognized for the single performance obligation over time due to the Company's right to payment for work performed to date and the performance does not create an asset with an alternative use. The Company recognizes revenue as portions of the overall performance obligation are completed as this best depicts the progress of the performance obligation.
Incremental Costs of Obtaining a Contract (Sales Commissions)
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Under ASC 606, the costs of obtaining a contract can be expensed immediately, rather than capitalized and amortized, if the amortization period is one year or shorter. Sales commissions for the Company represent contract costs with a term of one year or less. Therefore, under ASC 606, the Company elected the practical expedient to expense these costs as incurred.
Variable Consideration
In some cases, contracts provide for variable consideration that is contingent upon the occurrence of uncertain future events, such as the success of the initial performance obligation. Variable consideration is estimated at the expected value or at the most likely amount depending on the type of consideration. Estimated amounts are included in the transaction price to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is resolved. The estimate of variable consideration and determination of whether to include estimated amounts in the transaction price are based largely on an assessment of its anticipated performance and all information (historical, current and forecasted) that is reasonably available to the Company.
Trade Receivables, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue
In general, billings and payments are established by contractual provisions including predetermined payment schedules, which may or may not correspond to the timing of the transfer of control of the Company's services under the contract. In general, the Company's intention in its invoicing (payment terms) is to maintain cash neutrality over the life of the contract. Upfront payments, when they occur, are intended to cover certain expenses the Company incurs at the beginning of the contract. Neither the Company nor its customers view such upfront payments and contracted payment schedules as a means of financing. Unbilled services primarily arise when the revenue recognized exceeds the amount billed to the customer. Such situations occur due to divergences between revenue recognition and the invoicing milestones which are based on predetermined payment terms.
Deferred revenue consists of unearned payments received in excess of revenue recognized. As the contracted services are subsequently performed and the associated revenue recognized, the deferred revenue balance is reduced by the amount of the revenue recognized during the period. Deferred revenue is classified as a current liability on the consolidated balance sheet as the Company expects to recognize the associated revenue in less than one year.
Accounting Pronouncements Adopted
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses". This update required immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses ("CECL"). Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The Company adopted this ASU on May 1, 2023 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Note 3. Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue
Accounts receivable and unbilled services were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 | | April 30, 2022 |
| | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | $ | 4,886 | | | $ | 3,843 | | | $ | 6,037 | |
| Unbilled services | 5,941 | | | 4,993 | | | 4,106 | |
| Total accounts receivable and unbilled services | 10,827 | | | 8,836 | | | 10,143 | |
| Less: allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses | (1,301) | | | (825) | | | (630) | |
| Total accounts receivable, net | $ | 9,526 | | | $ | 8,011 | | | $ | 9,513 | |
Deferred revenue was as follows (in thousands):
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 |
| | | | |
| Deferred revenue | $ | 12,094 | | | $ | 12,776 | |
Deferred revenue is shown as a current liability on the Company's balance sheet.
Note 4. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Furniture and fixtures | $ | 246 | | | $ | 246 | |
| Computer equipment and software | 2,152 | | | 2,102 | |
| Laboratory equipment | 11,506 | | | 10,390 | |
| Capitalized software development costs | 1,888 | | | 1,888 | |
| Assets in progress | 3 | | | 1,079 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 317 | | | 111 | |
| | | |
| Total property and equipment | 16,112 | | | 15,816 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (10,391) | | | (8,630) | |
| | | |
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 5,721 | | | $ | 7,186 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense was $1.9 million and $2.2 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Depreciation and amortization expense, excluding expense recorded under finance leases, was $1.7 million and $2.1 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, property, plant and equipment included gross assets held under finance leases of $1.0 million, respectively. Related depreciation expense for these assets was $146,000 and $135,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
During the year ended April 30, 2024, the Company disposed of lab equipment with a cost of $542,000 and accumulated depreciation of $107,000 as of the disposal date, resulting in a loss on disposal of equipment recorded of $435,000. There were no disposals and therefore no gain or loss recorded during the year ended April 30, 2023.
Capitalized software development costs under a hosting arrangement
The Company accounts for the cost of computer software obtained or developed for internal use as well as the software development and implementation costs associated with a hosting arrangement ("internal-use software") that is a service contract in accordance and with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other ("ASC-350"). We capitalize certain costs in the development of our internal-use software when the preliminary project stage is completed and it is probable that the project itself will be completed and the software will perform as intended. These capitalized costs include personnel and related expenses for employees and costs of third-party consultants who are directly associated with and who devote time to these internal-use software projects. Capitalization of these costs ceases once the project is substantially complete and the software is ready for its intended purpose. Costs incurred for significant upgrades, increased functionality, and enhancements to the Company's internal-use software solutions are also capitalized. Costs incurred for training, maintenance, and minor modifications are expensed as incurred. Capitalized software development costs are amortized using the straight-line method over an estimated useful economic life of three years.
The Company capitalized development and implementation costs in accordance with accounting guidance for its bioinformatics platform, Lumin. Lumin is the Company's oncology data-driven software program and data tool which operates as Software as a Service (SaaS). These capitalized costs represent salaries, including direct payroll-related costs, certain software development consultant expenses and molecular sequencing programming costs incurred in the engineering and
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
coding of the software development. Total capitalized gross asset costs for the Lumin platform that was launched and placed into service were $1.9 million. During the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2023, an impairment loss for Lumin was recognized equal to the amount by which the carrying amount exceeded the future net revenues, or, its net book value at April 30, 2023 of $807,000. Amortization expense related to this asset was $0 and $630,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Finance Lease
During fiscal 2022, the Company recognized a finance lease for laboratory equipment. This equipment was obtained as the result of a laboratory supplies purchase commitment with costs of approximately $370,000 at inception through December 2025. Cash payments for this lease are in the form of consideration for purchasing lab supplies under a purchase commitment agreement. The present value of the minimum future obligations of $370,000 was calculated based on an interest rate of 3.25%. Depreciation and amortization expense related to this finance lease was $75,000 and $72,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Interest on the related finance lease liability was approximately $6,000 and $8,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
During fiscal 2023, the Company recognized a finance lease for laboratory equipment. This equipment was obtained as the result of a laboratory supplies purchase commitment with costs of approximately $368,000 at inception through December 2025. Cash payments for this lease are in the form of consideration for purchasing lab supplies under a purchase commitment agreement. The present value of the minimum future obligations of $368,000 was calculated based on an interest rate of 3.5%. Depreciation and amortization expense related to this finance lease was $71,000 and $63,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Interest on the related finance lease liability was approximately $9,000 and $11,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| 2025 | $ | 160 | |
| 2026 | 140 | |
| 2027 | 80 | |
| 2028 | 7 | |
| Thereafter | — | |
| Total undiscounted liabilities | 387 | |
| Less: Imputed interest | (16) | |
| Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 371 | |
| | |
| | |
Note 5. Revenue from Contracts with Customers
Oncology Services Revenue
The following table represents disaggregated revenue for the twelve months ended April 30, 2024 and 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended April 30, | |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | |
| Pharmacology services | $ | 47,035 | | | $ | 50,708 | | |
| Other TOS revenue | 3,102 | | | 3,046 | | |
| Personalized oncology services | 18 | | | 116 | | |
| Total oncology services revenue | $ | 50,155 | | | $ | 53,870 | | |
Other TOS revenue represents additional services provided to the Company's pharmaceutical and biotechnology customers, specifically flow cytometry services and SaaS provided via our Lumin Bioinformatics software.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Contract Balances
Contract assets include unbilled amounts typically resulting from revenue recognized in excess of the amounts billed to the customer for which the right to payment is subject to factors other than the passage of time. These amounts may not exceed their net realizable value. Contract assets are classified as current. Contract liabilities consist of customer payments received in advance of performance and billings in excess of revenue recognized, net of revenue recognized from the balance at the beginning of the period. Contract assets and liabilities are presented on the balance sheet on a net contract-by-contract basis at the end of each reporting period. Refer to Note 3 for related balances.
Note 6. Significant Customers
For the year ended April 30, 2024, one of our customers accounted for more than 10% of our total revenue, at 10%. For the year ended April 30, 2023, one of our customers accounted for more than 10% of our total revenue, at 14%. This was the same customer for both years.
As of April 30, 2024, one customer accounted for 12% of our total accounts receivable balance. As of April 30, 2023, the same customer accounted for 14% of our total accounts receivable balance.
Note 7. Commitments and Contingencies
Legal Matters
The Company is not currently party to any legal matters to its knowledge. The Company is not aware of any other matters that would have a material impact on the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
Registration Payment Arrangements
The Company has entered into an Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement in connection with the March 2015 Private Placement. This Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement contains provisions that may call for the Company to pay penalties in certain circumstances. This registration payment arrangement primarily relates to the Company’s ability to file a registration statement within a particular time period, have a registration statement declared effective within a particular time period and to maintain the effectiveness of the registration statement for a particular time period. The Company has not accrued any liquidated damages associated with the Amended and Restated Registration Right Agreement as the Company has filed the required registration statement and anticipates continued compliance with the agreement.
Royalties
The Company contracts with third-party vendors to license tumor samples for development into PDX models and use in our TOS business. These types of arrangements have an upfront fee ranging from approximately nil to $30,000 per tumor sample depending on the successful growth of the tumor model and ability to develop them into a sellable product. The upfront costs are expensed as incurred. In addition, under certain agreements, for a limited period of time, the Company is subject to royalty payments if the licensed tumor models are used for sale in our TOS business, ranging from 2% to 20% of the contract price after recouping certain initiation costs. Some of these arrangements also set forth an annual minimum royalty due regardless of tumor models used for sale. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, we have recognized approximately $362,000 and $212,000 in expense related to these royalty arrangements, respectively.
Note 8. Stock-based Payments
Stock-based compensation in the amount of $1.1 million and $864,000 was recognized for years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Stock-based compensation costs were recorded as follows (in thousands):
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| General and administrative | $ | 706 | | | $ | 505 | |
| Sales and marketing | 168 | | | 192 | |
| Research and development | 21 | | | 19 | |
| TOS cost of sales | 223 | | | 148 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 1,118 | | | $ | 864 | |
The Company has in place a 2021 Equity Incentive Plan and 2010 Equity Incentive Plan ("the Plans"). In general, these plans provide for stock-based compensation to the Company’s employees, directors and non-employees. The plans also provide for limits on the aggregate number of shares that may be granted, the term of grants and the strike price of option awards.
2021 Equity Incentive Plan
As part of the 2021 Annual Shareholders Meeting, shareholders approved the adoption of the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan (“2021 Equity Plan”). The purpose of the 2021 Equity Plan is to grant (i) Non-statutory Stock Options; (ii) Incentive Stock Options; (iii) Restricted Stock Awards; and/or (iv) Stock Appreciation Rights (collectively, stock-based compensation) to its employees, directors and non-employees. Total stock awards under the 2021 Equity Plan shall not exceed 2 million shares of common stock. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights expire no later than ten years from the date of grant and the awards vest as determined by the Board of Directors (the "Board") or Chief Executive Officer. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights have a strike price not less than 100% of the fair market value of the common stock subject to the option or right at the date of grant. As of April 30, 2024, approximately 1.3 million shares were left to issue under this plan.
2010 Equity Incentive Plan
On February 18, 2011, shareholders owning a majority of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company executed a written consent approving the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (“2010 Equity Plan”). The purpose of the 2010 Equity Plan is to grant (i) Non-statutory Stock Options; (ii) Restricted Stock Awards; and (iii) Stock Appreciation Rights (collectively, stock-based compensation) to its employees, directors and non-employees. Total stock awards under the 2010 Equity Plan shall not exceed 30,000,000 shares of common stock. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights expire no later than ten years from the date of grant and the awards vest as determined by the Board. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights have a strike price not less than 100% of the fair market value of the common stock subject to the option or right at the date of grant. After February 2021, no more shares were available to be issued from this plan.
Director Compensation Plan
On December 12, 2013, the Compensation Committee of the Board (the "Committee") adopted changes to the Director Compensation Plan of 2010 (the “Director Plan”) effective December 1, 2013. Under the Director Plan, independent directors of the Company were entitled to an annual award of a five-year option to purchase 8,333 shares of the Company’s common stock, and the Chairman of the Board of the Company was entitled to an annual award of a five-year option to purchase 16,667 shares of the Company’s common stock. Independent directors who serve as chairperson of a committee were also to receive an annual grant of a five-year option to purchase 1,667 shares of the Company’s common stock. During fiscal year 2021, the Committee adopted the Director Compensation Plan of 2021 (the "2021 Plan"). Under the 2021 Plan, independent directors are entitled to an annual base compensation of $100,000 which can be received in either ten-year company options or a combination of company options and cash, not to exceed $35,000. The Chairman of the Board’s annual compensation was set at an equivalent of $150,000. Compensation for independent directors who serve as chairperson of a committee was set at an equivalent of between $110,000 to $120,000. All options issued under the 2021 Plan vest quarterly at a rate of 25%. Option grants will typically be issued after the annual shareholder meeting which will generally be held in October of each year. New directors will receive compensation upon joining the Board equal to a pro-rata equivalent for the remainder of the year. Options issued under the 2021 Plan are issued pursuant to the 2021 Equity Plan.
Stock Option Grants
Black-Scholes weighted average assumptions used to calculate the fair value of options granted during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows:
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Expected term in years | 6 | | 6 |
| Risk-free interest rates | 4.0% - 4.5% | | 2.9% - 3.9% |
| Volatility | 63% - 64% | | 61% - 63% |
| Dividend yield | 0% | | 0% |
The weighted average fair value of stock options granted during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, was $3.75 and $4.31, respectively. The Company’s stock options activity and related information as of and for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
| Outstanding, May 1, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | $ | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | |
| Granted | 444,730 | | | — | | | 444,730 | | | 6.08 | | | 9.5 | | $ | — | |
| Exercised | (155,449) | | | — | | | (155,449) | | | 2.31 | | | | | |
| Canceled | (50,535) | | | — | | | (50,535) | | | 4.82 | | | | | |
| Forfeited | (40,750) | | | — | | | (40,750) | | | 6.21 | | | | | |
| Expired | (54,166) | | | — | | | (54,166) | | | 12.78 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding, April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable as of April 30, 2024 | 1,481,145 | | | 3,750 | | | 1,484,895 | | | 4.65 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
| Outstanding, May 1, 2022 | 1,617,324 | | | 40,915 | | | 1,658,239 | | | 4.51 | | 4.9 | | $ | 6,131,000 | |
| Granted | 186,720 | | | — | | | 186,720 | | | 7.22 | | | 9.4 | | — | |
| Exercised | (36,209) | | | — | | | (36,209) | | | 3.21 | | | | | |
| Canceled | (13,874) | | | — | | | (13,874) | | | 3.93 | | | | | |
| Forfeited | (14,625) | | | — | | | (14,625) | | | 7.94 | | | | | |
| Expired | — | | | (4,584) | | | (4,584) | | | 5.40 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding, April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable as of April 30, 2023 | 1,436,932 | | | 1,875 | | | 1,438,807 | | | 4.35 | | | 3.8 | | $ | 2,681,000 | |
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Share Repurchase Program
On March 29, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program authorizing the Company to purchase up to an aggregate of $5.0 million of the Company’s common stock. The share repurchase program is designed in accordance with Rule 10b-18 of the Exchange Act. The shares may be purchased from time to time in the open market, as permitted under applicable rules and regulations, at prevailing market prices. The timing and amount of repurchases will depend on market conditions, share price, applicable legal requirements and other factors. The program does not obligate the Company to acquire a minimum number of shares. As of April 30, 2024, the Company had purchased approximately 120,300 shares of its common stock, at an average price of $5.73 per share, totaling approximately $708,000 and leaving an available balance of approximately $4.3 million authorized by the Board for use in the program as of that date.
Note 9. Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes
The components of the (benefit) provision for income taxes are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, 2024 |
| | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total |
| Current | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, 2023 |
| | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total |
| Current | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | |
A reconciliation between the Company’s effective tax rate and the United States statutory tax rate for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Federal income tax at statutory rate | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % |
| US vs. foreign tax rate difference | (0.1) | | | (0.2) | |
| State income tax, net of federal benefit | (2.3) | | | 2.2 | |
| Permanent differences | 0.4 | | | (0.5) | |
| Increase in uncertain tax position | — | | | — | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Change in valuation allowance | (18.5) | | | (23.8) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Income tax expense | 0.5 | % | | (1.3) | % |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities as of April 30, 2024 and 2023 consist of the following (in thousands):
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Accrued liabilities | $ | 1,269 | | | $ | 273 | |
| Operating leases | 279 | | | 403 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | (318) | | | (297) | |
| | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 3,792 | | | 4,024 | |
| Capitalized research and development costs | 4,046 | | | 2,597 | |
| | | |
| Net operating loss carry-forward | 9,038 | | | 9,756 | |
| | | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 18,106 | | | 16,756 | |
| Less: Valuation allowance | (18,106) | | | (16,756) | |
| | | |
| Net deferred tax asset | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Management has evaluated the available evidence about future tax planning strategies, taxable income, and other possible sources of realization of deferred tax assets and has established a full valuation allowance against its net deferred tax assets as of April 30, 2024 and 2023. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company recorded a valuation allowance of $18.1 million and $16.8 million, respectively. The net changes in the valuation allowance of $1.4 million and $1.3 million during the fiscal years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, were mainly due to increases in the deferred tax asset related to capitalized research expenses and other timing differences. Management continues to assess the realizability of the deferred tax assets at each interim and annual balance sheet date based upon actual and forecasted operating results.
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company’s estimated U.S. net operating loss carry-forwards were approximately $38.6 million and $41.3 million, respectively. Net operating losses generated prior to May 1, 2018 have a 20-year carryforward and will begin expiring in 2025 for federal and 2031 for state purposes. Losses generated in the fiscal years since the year ended April 30, 2019 may be carried forward indefinitely. A valuation allowance has been recorded against all of these loss carryforwards.
Under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, certain substantial changes in the Company’s ownership may result in a limitation on the amount of net operating losses that may be utilized in future years. During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2013, approximately $12.0 million of the Company’s net operating losses became subject to limitation under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 in connection with an ownership change on January 28, 2013. As a result of the ownership change, the Company’s annual limitation on its use of net operating loss carry-forwards is approximately $432,000.
The Company files income tax returns in various jurisdictions with varying statutes of limitations. As of April 30, 2024, the earliest tax year still subject to examination for state purposes is fiscal 2020. The Company’s tax years for periods ending April 30, 2002 and forward are subject to examination by the United States and certain states due to the carry-forward of unutilized net operating losses.
The following table indicates the changes to the Company’s uncertain tax positions for the period and years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 in thousands:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | |
| Addition based on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | |
| Payment made on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | |
| Addition based on tax positions related to current year | — | | | — | |
| | | |
| Balance, end of year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | |
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the above amounts of $181,000 for each fiscal year were included in other long-term liabilities.
Note 10. Earnings Per Share
A reconciliation of net income and number of shares used in computing basic and diluted earnings per share was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share computation (dollars in thousands): | | | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (7,276) | | | $ | (5,335) | |
| Weighted Average common shares - basic and diluted | 13,547,604 | | | 13,541,559 | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.54) | | | $ | (0.39) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
The following table reflects the total potential stock-based instruments outstanding at April 30, 2024 and 2023 that could have an effect on the future computation of dilution per common share. These figures were not included in the above calculation as, to do so, would be antidilutive:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended April 30 |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Stock options | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Total common stock equivalents | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | |
Note 11. Related Party Transactions
Related party transactions include transactions between the Company and its shareholders, management, or affiliates. The following transactions were in the normal course of operations and were measured at the exchange amount, which is the amount of consideration established and agreed to by the parties.
Consulting Services
For both years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company paid a member of its Board of Directors $36,000 for consulting services unrelated to his duties as a board member. All of the amounts paid to these related parties have been recognized in expense in the period the services were performed within general and administrative expenses.
Note 12. Leases
The Company accounts for its leases under ASC 842. Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases, and are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both an operating lease ROU asset and operating lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right of use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right of use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term. Variable lease expenses, if any, are recorded when incurred. The Company has elected to apply the short-term lease exemption practical expedient for each class of underlying assets and excludes short-term leases having initial terms of 12 months or less. The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term for these short-term leases. The Company has determined that no material embedded leases exist. Under ASC 842, the Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of remaining lease payments over the lease term. For this purpose, the Company considers only payments that are fixed and determinable at the time of commencement. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments.
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Operating Leases
The Company currently leases certain office equipment and its office and laboratory facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. Rent expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term from the lease commencement date through the scheduled expiration date. Rent expenses totaled $1.8 million and $1.9 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
The Company leases the following facilities:
•One University Plaza, Suite 307, Hackensack, New Jersey 07601, which, since November 2011, serves as the Company’s corporate headquarters. The lease expires in November 2026. The Company recognized $77,000 and $83,000 of rent expense relative to this lease for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
•1330 Piccard Drive Suite 025, Rockville, MD 20850, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its primary service offerings. The Company executed the original lease in January 2017. The lease was amended to expand the premises and extend the expiration date in March 2020 and again in December 2020. The operating commencement date was August 11, 2017. This lease expires in February 2029. The Company recognized $1.7 million of rent expense for both fiscal 2024 and 2023.
•VIA LEONE XIII, 14, Milan, Italy, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its flow cytometry service offerings. The Company executed separate leases for its laboratory space and office space during fiscal 2022. During fiscal 2023, the Company executed a new lease to consolidate its office and laboratory space at a new nearby location in Italy. The lease expires October 31, 2028 and it replaces the previous two leases, which were terminated during fiscal 2023. The Company recognized $50,000 and $98,000 of rent expense associated with the leases in Italy for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
ROU assets and lease liabilities related to our current operating leases are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2023 |
Operating lease right-of-use assets, net
| 6,252 | | 7,318 | |
Current portion of operating lease liabilities
| 1,337 | | 1,208 | |
| Non-current portion of operating lease liabilities | 6,093 | | 7,391 | |
As of April 30, 2024, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 4.7 years and 5.88%, respectively. As of April 30, 2023, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 5.7 years and 5.82%, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments for operating leases due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| 2025 | $ | 2,902 | |
| 2026 | 2,950 | |
| 2027 | 2,916 | |
| 2028 | 2,867 | |
| 2029 | 2,392 | |
| Thereafter | — | |
| Total undiscounted liabilities | 14,027 | |
| Less: Imputed interest | (6,597) | |
| Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 7,430 | |
The composition of total lease cost for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows (in thousands):
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended April 30 | |
| 2024 | | 2023 | |
| Operating lease costs | $ | 1,680 | | | $ | 1,566 | | |
| | | | |
| Financing lease costs: | | | | |
| Amortization of leased assets | 146 | | | 135 | | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | 15 | | | 19 | | |
| | | | |
| Total lease costs | $ | 1,841 | | | $ | 1,720 | | |
| | | | |
Refer to Note 4, Property and Equipment, for more information on financing leases.
Exhibit Index
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit No. | | |
| | |
| 3.1 | | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Company’s Information Statement on Schedule 14C filed March 7, 2011) |
| | |
| 3.1.1 | | Certificate of Amendment to Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3(i) to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 28, 2015) |
| | |
| 3.2 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 9, 2017)
|
| | |
| 4.1 | | Description of Registered Securities (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed July 28, 2020) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.1 | | Employment Agreement, dated November 5, 2013, between the Company and Ronnie Morris, M.D. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 12, 2013) |
| | |
| 10.2 | | Amendment to Employment Agreement, dated March 16, 2015, between the Company and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 20, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.3 | | Offer Letter dated June 3, 2013 between the Company and David Miller (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 3, 2013) |
| | |
| 10.4 | | 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Company’s Definitive Information Statement on Schedule 14C filed March 7, 2011) |
| | |
| 10.5 | | Form of Note Purchase Agreement, dated December 1, 2014, between the Company and each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 5, 2014) |
| | |
| 10.6 | | Form of Convertible Promissory Note, dated December 1, 2014, issued to each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris in connection with the Note Purchase Agreement, dated December 1, 2014 between the Company and each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 5, 2014) |
| | |
| 10.7 | | Amendment No. 1 to Convertible Promissory Note, dated December 1, 2014 issued to Joel Ackerman in connection with the Note Purchase Agreement, dated December 1, 2014, between the Company and each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 2, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.8 | | Amendment No. 1 to Convertible Promissory Note, dated December 1, 2014 issued to Ronnie Morris in connection with the Note Purchase Agreement, dated December 1, 2014, between the Company and each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 2, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.9 | | Amended and Restated 2011 Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 24, 2011, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.10 | | Form of warrant issued to each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 24, 2011, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 30, 2013) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.11 | | Amendment No. 1 to warrants, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 24, 2011, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.12 | | Amended and Restated 2013 Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 28, 2013, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.13 | | Form of warrant issued to each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 28, 2013, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 30, 2013) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 10.14 | | Amendment No. 1 to warrants, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 28, 2013, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.15 | | Put Right Agreement, dated January 29, 2014, between the Company and each of Joel Ackerman and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 6, 2014) |
| | |
| 10.16 | | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 11, 2015, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 12, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.17 | | Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated March 13, 2015, between the Company and each person or entities that are signatories to (i) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 24, 2011, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto, (ii) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 28, 2013, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto, and (iii) the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 11, 2015, between the Company. And each investor identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.18 | | Form of Investor Warrant issued to each person or entities that are signatories to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 11, 2015, between the Company and each investor identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 17, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.19 | | Option Exchange Agreement, dated March 16, 2015, between the Company and Joel Ackerman (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 20, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.20 | | Option Exchange Agreement, dated March 16, 2015, between the Company and Ronnie Morris (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 20, 2015) |
| | |
| 10.21 | | Option Exchange Agreement, dated March 16, 2015, between the Company and David Miller (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 20, 2015) |
| | |
| 14 | | Code of Ethics (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14 of the April 30, 2008 Form 10-KSB) |
| | |
| 21 | | |
| | |
| 23.1 | | |
| | |
| | |
| 31.1 | | |
| | |
| 31.2 | | |
| | |
| 32.1 | | |
| | |
| 97 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| 101.INS* | | XBRL Instance Document. |
| 101.SCH* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| 101.CAL* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.DEF* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| 101.LAB* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| 101.PRE* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
101.LAB* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
101.PRE* | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
__________________________
* Filed herewith
** Furnished hereto.
*** Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
Exhibit 4.1
RIDER X
DESCRIPTION OF THE REGISTRANT'S SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12 OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934, AS AMENDED
As of the April 30, 2024, Champions Oncology, Inc. has authorized capital stock consisting of 200,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share. The following description summarizes the material terms of common stock.
Holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote per share. Our certificate of incorporation, as amended, does not provide for cumulative voting. Holders of our common stock are entitled to receive ratably such dividends, if any, as may be declared by our board of directors out of legally available funds. Upon liquidation, dissolution or winding-up, the holders of our common stock are entitled to share ratably in all of our assets which are legally available for distribution, after payment of our provision for all liabilities.
Exhibit 21
SUBSIDIARIES OF CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
Name Incorporated in
Champions Oncology UK Limited United Kingdom
Champions Oncology, Israel, Limited Israel
Champions Oncology, SRL Italy
Corellia AI Inc United States
Exhibit 23.1
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
We consent to the incorporation by reference in the Registration Statement of Champions Oncology, Inc. on Form S-8 (No. 333-182747) of our report dated July 19, 2024 , on our audits of the consolidated financial statements as of April 30, 2024 and 2023 and for each of the years then ended, which report is included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to be filed on or about July 19, 2024. Our report includes an explanatory paragraph about the existence of substantial doubt concerning the Company's ability to continue as a going concern.
/s/ EisnerAmper LLP
EISNERAMPER LLP
West Palm Beach, Florida
July 19, 2024
EXHIBIT 31.1
CERTIFICATION OF PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER
I, Ronnie Morris, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Champions Oncology, Inc., a Delaware corporation;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15(d)-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in the Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiary, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
5. The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
| | | | | |
| | /s/ Ronnie Morris |
| | Ronnie Morris |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
| | (Principal Executive Officer) |
Date: 7/19/24
EXHIBIT 31.2
CERTIFICATION OF PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER
I, David Miller, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Champions Oncology, Inc., a Delaware corporation;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15(d)-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in the Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiary, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
5. The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
| | | | | |
| | /s/ David Miller |
| | David Miller |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
| | (Principal Financial Officer) |
Date: 7/19/24
EXHIBIT 32.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350, AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE U.S. SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Champions Oncology, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the year ended April 30, 2023, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), each of the undersigned, in the capacities and on the dates indicated below, hereby certifies pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the U.S. Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of our knowledge:
(i) the Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(ii) the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| | | | | |
| | /s/ Ronnie Morris |
| | Ronnie Morris |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
| | (Principal Executive Officer) |
| | |
| | /s/ David Miller |
| | David Miller |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
| | (Principal Financial Officer) |
Date: 7/19/24
EXHIBIT 97
Clawback Policy
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION CLAWBACK POLICY
Adopted as of December 1, 2023
The Board of Directors (the “Board”) of Champions Oncology, Inc. (the “Company”) has adopted the following executive compensation clawback policy (this “Policy”). This Policy shall supplement any other clawback or compensation recovery policy or policies adopted by the Company or included in any agreement between the Company, or any subsidiary of the Company, and a person covered by this Policy. If any such other policy or agreement provides that a greater amount of compensation shall be subject to clawback, such other policy or agreement shall apply to the amount in excess of the amount subject to clawback under this Policy.
This Policy shall be interpreted to comply with Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Rule 10D-1 and Listing Rule 5608 (the “Listing Rule”) of The Nasdaq Stock Market, LLC (“Nasdaq”), as may be amended or supplemented and interpreted from time to time by Nasdaq. To the extent this Policy is in any manner deemed inconsistent with the Listing Rule, this Policy shall be treated as having been amended to be compliant with the Listing Rule.
1. Definitions. Unless the context otherwise requires, the following definitions apply for
purposes of this Policy:
(a) Executive Officer. An executive officer is the Company’s chief executive officer, president, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer (or if there is no such accounting officer, the controller), any vice-president of the Company in charge of a principal business unit, division, or function (such as sales, administration, or finance), any other officer who performs a policy-making function, or any other person who performs similar policy making functions for the Company. Executive officers of the Company’s subsidiaries are deemed executive officers of the Company if they perform such policy making functions for the Company. Policy-making function is not intended to include policy-making functions that are not significant. Identification of an executive officer for purposes of the Listing Rule would include at a minimum executive officers identified in the Listing Rule.
(b) Financial Reporting Measures. Financial reporting measures are measures that are determined and presented in accordance with the accounting principles used in preparing the Company’s financial statements, and any measures that are derived wholly or in part from such measures. Stock price and total shareholder return are also financial reporting measures. A financial reporting measure need not be presented within the
financial statements or included in a filing with the SEC and may be such financial measures as may be determined by the Board or the Compensation Committee thereof (the “Compensation Committee”).
(c) Incentive-Based Compensation. Incentive-based compensation is any
compensation that is granted, earned or vested based wholly or in part upon the attainment of a financial reporting measure.
(d) Received. Incentive-based compensation is deemed “received” in the Company’s fiscal period during which the financial reporting measure specified in the incentive-based compensation award is attained, even if the payment or grant of the incentive-based compensation occurs after the end of that period.
2. Application of this Policy. The recovery of Incentive-Based Compensation from an Executive Officer as provided for in this Policy shall apply only in the event that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement due to the material noncompliance of the Company with any financial reporting requirement under the United States securities laws, including any required accounting restatement to correct an error in previously issued financial statements that is material to the previously issued financial statements, or that would result in a material misstatement if the error were corrected in the current period or left uncorrected in the current period.1
3. Recovery Period.
(a) The Incentive-Based Compensation subject to recovery is the Incentive-Based Compensation Received during the three (3) completed fiscal years immediately receding the date that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement as described in Section 2 above, provided that the person served as an Executive Officer at any time during the performance period applicable to the Incentive-Based Compensation in question. The date that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement shall be determined pursuant to the Listing Rule.
(b) Notwithstanding the foregoing, this Policy shall only apply if the Incentive-Based Compensation is Received (i) while the Company has a class of securities listed on Nasdaq and (ii) on or after October 2, 2023.
(c) The provisions of the Listing Rule shall apply with respect to Incentive-Based Compensation received during a transition period arising due to a change in the Company’s fiscal year.
4. Erroneously Awarded Compensation. The amount of Incentive-Based Compensation subject to recovery from the applicable Executive Officers under this Policy (“Erroneously Awarded Compensation”) shall be equal to the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation Received that exceeds the amount of Incentive Based-Compensation that otherwise would have been Received had it been determined based on the restated amounts and
1 NOTE: questions as to “materiality” will be made by the Compensation Committee in coordination with the Audit Committee, and companies should review the charters for those committees and consider updates authorizing them to oversee and make determinations under the Company’s Clawback policy.
shall be computed without regard to any taxes paid. For Incentive-Based Compensation based on stock price or total shareholder return, where the amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation is not subject to mathematical recalculation directly from the information in an accounting restatement: (a) the amount shall be based on a reasonable estimate by the Company’s Chief Financial Officer (or principal accounting officer, if the office of Chief Financial Officer is not then filled) of the effect of the accounting restatement on the stock price or total shareholder return upon which the Incentive-Based Compensation was received, which estimate shall be subject to the review and approval of the Compensation Committee; and (b) the Company must maintain reasonable documentation of the determination of that reasonable estimate and provide such documentation to Nasdaq if requested. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if the proposed Incentive-Based Compensation recovery would affect compensation paid to the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, the determination shall be made by the Compensation Committee.
5. Timing of Recovery. The Company shall recover any Erroneously Awarded Compensation reasonably promptly, except to the extent that the conditions of paragraphs (a), (b), or (c) below apply. The Compensation Committee shall determine the repayment schedule for each amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation in a manner that complies with this “reasonably promptly” requirement. Such determination shall be consistent with any applicable legal guidance by the SEC, Nasdaq, judicial opinion, or otherwise. The determination of “reasonably promptly” may vary from case to case and the Compensation Committee is authorized to adopt additional rules or policies to further describe what repayment schedules satisfy this requirement.
(a) Erroneously Awarded Compensation need not be recovered if the direct expense paid to a third party to assist in enforcing (or making determinations in connection with the enforcement of) this Policy would exceed the amount to be recovered and the Compensation Committee has made a determination that recovery would be impracticable. Before concluding that it would be impracticable to recover any amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation based on expense of enforcement, the Company shall (i) make a reasonable attempt to recover such Erroneously Awarded Compensation, (ii) document such reasonable attempt or attempts to recover, and (iii) provide appropriate documentation to the Compensation Committee or Nasdaq, if requested.
(b) Erroneously Awarded Compensation need not be recovered if recovery would
violate home country law where that law was adopted prior to November 28, 2022. Before concluding that it would be impracticable to recover any amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation based on a violation of home country law, the Company shall obtain an opinion of home country counsel, in form and substance that would be reasonably acceptable to Nasdaq, that recovery would result in such a violation and shall provide such opinion to Nasdaq, if requested.
(c) Erroneously Awarded Compensation need not be recovered if recovery would likely cause an otherwise tax-qualified retirement plan, under which benefits are broadly available to employees of the Company, to fail to meet the requirements of 26 U.S.C.
401(a)(13) or 26 U.S.C. 411(a) and the regulations thereunder (as such provision may be amended, modified or supplemented).
6. Compensation Committee Decisions. Decisions of the Compensation Committee with respect to this Policy shall be final, conclusive and binding on all Executive Officers subject to this Policy.
7. No Indemnification. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in any other policy of the Company or any agreement between the Company and an Executive Officer, no Executive Officer shall be indemnified by the Company against the loss arising from the recovery of any Erroneously Awarded Compensation.
8. Agreement to Policy by Executive Officers2. The Company shall take reasonable steps to inform Executive Officers of this Policy and obtain their express agreement to this Policy, which steps may constitute the inclusion of this Policy as an attachment to any award that is accepted by an Executive Officer. This Policy shall be deemed to apply to each employment or grant agreement between the Company or any of its subsidiaries and any Executive Officer subject to this Policy.
2 Companies should be advised to have the executive officers acknowledge this in writing (similar to the Insider Trading Policy acknowledgement). Also consider if amendments should be made to employment agreements, grant award forms, etc.
Cover - USD ($)
$ in Millions |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Jul. 18, 2024 |
Oct. 31, 2023 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Apr. 30, 2024
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--04-30
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
001-11504
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
CHAMPIONS ONCOLOGY, INC.
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
DE
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
52-1401755
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
One University Plaza
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line Two |
Suite 307
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
07601
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
Hackensack
|
|
|
| Entity Address, State or Province |
NJ
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
201
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
808-8400
|
|
|
| Title of 12(b) Security |
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share
|
|
|
| Trading Symbol |
CSBR
|
|
|
| Security Exchange Name |
NASDAQ
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Non-accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
true
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| ICFR Auditor Attestation Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 22.0
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding (in shares) |
|
13,593,766
|
|
| Documents Incorporated by Reference |
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0000771856
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2024
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDocuments incorporated by reference. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-23
| Name: |
dei_DocumentsIncorporatedByReferenceTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 2 such as Street or Suite number
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the state or province.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressStateOrProvince |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:stateOrProvinceItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(b) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b
| Name: |
dei_Security12bTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the Exchange on which a security is registered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection d1-1
| Name: |
dei_SecurityExchangeName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarExchangeCodeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTrading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.
| Name: |
dei_TradingSymbol |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:tradingSymbolItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Current assets: |
|
|
| Cash |
$ 2,618
|
$ 10,118
|
| Accounts receivable, net |
9,526
|
8,011
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,495
|
1,328
|
| Total current assets |
13,639
|
19,457
|
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net |
6,252
|
7,318
|
| Property and equipment, net |
5,721
|
7,186
|
| Other long term assets |
185
|
15
|
| Goodwill |
335
|
335
|
| Total assets |
26,132
|
34,311
|
| Current liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts payable |
5,800
|
5,334
|
| Accrued liabilities |
2,160
|
2,270
|
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities |
1,337
|
1,208
|
| Other current liabilities |
150
|
145
|
| Deferred revenue |
12,094
|
12,776
|
| Total current liabilities |
21,541
|
21,733
|
| Non-current portion operating lease liabilities |
6,093
|
7,391
|
| Other non-current liabilities |
401
|
551
|
| Total liabilities |
28,035
|
29,675
|
| Stockholders' (deficiency) equity: |
|
|
| Common stock, $.001 par value; 200,000,000 shares authorized; 13,714,099 and 13,558,650 shares issued; and 13,593,766 and 13,544,228 shares outstanding at April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively |
14
|
14
|
| Treasury Stock, at cost |
(708)
|
(74)
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
83,384
|
82,013
|
| Accumulated deficit |
(84,593)
|
(77,317)
|
| Total stockholders' (deficiency) equity |
(1,903)
|
4,636
|
| Total liabilities and stockholders' (deficiency) equity |
$ 26,132
|
$ 34,311
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue received from shareholders in common stock-related transactions that are in excess of par value or stated value and amounts received from other stock-related transactions. Includes only common stock transactions (excludes preferred stock transactions). May be called contributed capital, capital in excess of par, capital surplus, or paid-in capital. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapitalCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477796/946-210-45-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 210
-Topic 946
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477796/946-210-45-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_Cash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated impairment loss, of asset representing future economic benefit arising from other asset acquired in business combination or from joint venture formation or both, that is not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Goodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liability recognized for present obligation requiring transfer or otherwise providing economic benefit to others. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
| Name: |
us-gaap_Liabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncurrent assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits in future periods, and amount of other assets that are expected to be realized or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseAndOtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated depreciation and amortization, of property, plant, and equipment and finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount allocated to previously issued common shares repurchased by the issuing entity and held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481520/505-30-50-4
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockCommonValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (Parenthetical) - $ / shares
|
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Statement of Financial Position [Abstract] |
|
|
| Common stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
200,000,000
|
200,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued (in shares) |
13,714,099
|
13,593,766
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
13,558,650
|
13,544,228
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfFinancialPositionAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Income Statement [Abstract] |
|
|
| Revenue, Product and Service [Extensible Enumeration] |
Service [Member]
|
Service [Member]
|
| Oncology services revenue |
$ 50,155,000
|
$ 53,870,000
|
| Costs and operating expenses: |
|
|
| Cost, Product and Service [Extensible Enumeration] |
Service [Member]
|
Service [Member]
|
| Cost of oncology services |
$ 29,401,000
|
$ 29,532,000
|
| Research and development |
9,544,000
|
11,545,000
|
| Sales and marketing |
7,064,000
|
7,002,000
|
| General and administrative |
11,067,000
|
10,240,000
|
| Loss on disposal of equipment |
435,000
|
0
|
| Asset impairment |
0
|
807,000
|
| Total costs and operating expenses |
57,511,000
|
59,126,000
|
| Loss from operations |
(7,356,000)
|
(5,256,000)
|
| Other income (expense): |
|
|
| Other income (expense), net |
48,000
|
(11,000)
|
| Loss before income tax expense |
(7,308,000)
|
(5,267,000)
|
| (Benefit) provision for income tax |
(32,000)
|
68,000
|
| Net loss |
$ (7,276,000)
|
$ (5,335,000)
|
| Net loss per common share outstanding |
|
|
| Net loss per common share outstanding, basic (in usd per share) |
$ (0.54)
|
$ (0.39)
|
| Net loss per common share outstanding, diluted (in usd per share) |
$ (0.54)
|
$ (0.39)
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic (in shares) |
13,547,604
|
13,541,559
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, diluted (in shares) |
13,547,604
|
13,541,559
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs related to goods produced and sold and services rendered by an entity during the reporting period. This excludes costs incurred during the reporting period related to financial services rendered and other revenue generating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(2)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfGoodsAndServicesSold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total of expenses of managing and administering the affairs of an entity, including affiliates of the reporting entity, which are not directly or indirectly associated with the manufacture, sale or creation of a product or product line. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long lived assets held for use (including those held for disposal by means other than sale). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsHeldForUse |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpenseAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Excludes Selling, General and Administrative Expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingCostsAndExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpensesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for research and development. Includes, but is not limited to, cost for computer software product to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed and writeoff of research and development assets acquired in transaction other than business combination or joint venture formation or both. Excludes write-down of intangible asset acquired in business combination or from joint venture formation or both, used in research and development activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482916/730-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 730
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479532/912-730-25-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total amount of expenses directly related to the marketing or selling of products or services.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingAndMarketingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates type of cost from product sold and service rendered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_TypeOfCostGoodOrServiceExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates type of revenue from product and service. Includes, but is not limited to, revenue from contract with customer and other sources.
| Name: |
us-gaap_TypeOfRevenueExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ (DEFICIENCY) EQUITY - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Total |
Common Stock |
Treasury Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
| Beginning balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2022 |
|
13,522,441
|
|
|
|
| Beginning balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2022 |
|
|
0
|
|
|
| Beginning balance at Apr. 30, 2022 |
$ 9,096
|
$ 14
|
$ 0
|
$ 81,064
|
$ (71,982)
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
864
|
|
|
864
|
|
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options (in shares) |
|
36,209
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options |
85
|
$ 0
|
|
85
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock (in shares) |
|
0
|
14,422
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
(74)
|
|
$ (74)
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (5,335)
|
|
|
|
(5,335)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2023 |
13,544,228
|
13,558,650
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2023 |
|
|
14,422
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Apr. 30, 2023 |
$ 4,636
|
$ 14
|
$ (74)
|
82,013
|
(77,317)
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
1,118
|
|
|
1,118
|
|
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options (in shares) |
|
155,449
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock on exercise of stock options |
253
|
$ 0
|
|
253
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock (in shares) |
|
0
|
105,911
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
(634)
|
|
$ (634)
|
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (7,276)
|
|
|
|
(7,276)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2024 |
13,558,650
|
13,714,099
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Apr. 30, 2024 |
|
|
120,333
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Apr. 30, 2024 |
$ (1,903)
|
$ 14
|
$ (708)
|
$ 83,384
|
$ (84,593)
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase to additional paid-in capital (APIC) for recognition of cost for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-13
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidInCapitalSharebasedCompensationRequisiteServicePeriodRecognitionValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInStockholdersEquityRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of stock issued attributable to transactions classified as other.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of shares of stock issued attributable to transactions classified as other.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares that have been repurchased during the period and have not been retired and are not held in treasury. Some state laws may govern the circumstances under which an entity may acquire its own stock and prescribe the accounting treatment therefore. This element is used when state law does not recognize treasury stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478448/946-505-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchasedDuringPeriodShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the value of stock that has been repurchased during the period and has not been retired and is not held in treasury. Some state laws may mandate the circumstances under which an entity may acquire its own stock and prescribe the accounting treatment therefore. This element is used when state law does not recognize treasury stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478009/946-205-45-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478448/946-505-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchasedDuringPeriodValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of previously issued common shares repurchased by the issuing entity and held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockCommonShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Operating activities: |
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (7,276,000)
|
$ (5,335,000)
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash (used in) provided by operating activities: |
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
1,118,000
|
864,000
|
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
1,867,000
|
2,246,000
|
| Net loss on disposal of equipment |
435,000
|
0
|
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
1,066,000
|
952,000
|
| Asset impairment |
0
|
807,000
|
| Allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses |
476,000
|
195,000
|
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts receivable |
(1,991,000)
|
1,308,000
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
(167,000)
|
(184,000)
|
| Other long term assets |
(169,000)
|
0
|
| Accounts payable |
465,000
|
2,465,000
|
| Accrued liabilities |
(109,000)
|
(145,000)
|
| Operating lease liabilities |
(1,169,000)
|
(907,000)
|
| Deferred revenue |
(683,000)
|
1,706,000
|
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
(6,137,000)
|
3,972,000
|
| Investing activities: |
|
|
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(836,000)
|
(2,872,000)
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(836,000)
|
(2,872,000)
|
| Financing activities: |
|
|
| Proceeds from exercise of options |
253,000
|
85,000
|
| Repurchases of common stock |
(634,000)
|
(74,000)
|
| Finance lease payments |
(146,000)
|
0
|
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(527,000)
|
11,000
|
| (Decrease) increase in cash |
(7,500,000)
|
1,111,000
|
| Cash, beginning of year |
10,118,000
|
9,007,000
|
| Cash, end of year |
2,618,000
|
10,118,000
|
| Non-cash financing and investing activities: |
|
|
| Purchased equipment under finance lease |
0
|
368,000
|
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities |
$ 0
|
$ 231,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncrease (Decrease) In Operating Lease, Right Of Use Assets
| Name: |
csbr_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseRightOfUseAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in lease obligation from new lease. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalLeaseObligationsIncurred |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477401/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe current period expense charged against earnings on long-lived, physical assets not used in production, and which are not intended for resale, to allocate or recognize the cost of such assets over their useful lives; or to record the reduction in book value of an intangible asset over the benefit period of such asset; or to reflect consumption during the period of an asset that is not used in production. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow for principal payment on finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeasePrincipalPayments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long lived assets held for use (including those held for disposal by means other than sale). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsHeldForUse |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate amount of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in amount due within one year (or one business cycle) from customers for the credit sale of goods and services. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate amount of expenses incurred but not yet paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478345/912-310-45-11
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInContractWithCustomerLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLiabilitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in noncurrent assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherNoncurrentAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in prepaid expenses, and assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInPrepaidDeferredExpenseAndOtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoncashInvestingAndFinancingItemsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow to reacquire common stock during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRepurchaseOfCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of long-lived, physical assets that are used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale; includes cash outflows to pay for construction of self-constructed assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquirePropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow from exercise of option under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (reversal of expense) for expected credit loss on accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479319/326-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProvisionForDoubtfulAccounts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in right-of-use asset obtained in exchange for operating lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RightOfUseAssetObtainedInExchangeForOperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Organization and Basis of Presentation
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
| Organization and Basis of Presentation |
Organization and Basis of Presentation Background Champions Oncology, Inc. (the “Company”), is engaged in drug discovery and development through data-driven research strategies and innovative pharmacology, biomarker and data platforms. The Company’s TumorGraft Technology Platform is an approach to personalizing cancer care based upon the implantation of human tumors in immune-deficient mice. The Company provides a technology platform to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies using proprietary TumorGraft studies, which the Company believes may be predictive of how drugs may perform in clinical settings. Utilizing the TumorGraft Technology Platform (the "Platform"), a comprehensive Bank of unique, well characterized "Patient Derived XenoGrafts" (PDX) models, the Company offers multiple services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies seeking personalized approaches to drug development. By performing studies to predict the efficacy of oncology drugs, our Platform is designed to facilitate drug discovery with lower costs and increased speed of drug development as well as increased adoption of existing drugs. The Company has four operating subsidiaries: Champions Oncology (Israel), Limited, Champions Biotechnology U.K., Limited, Champions Oncology S.R.L., and Corellia AI, Inc. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, there were no revenues earned by these subsidiaries.
Basis of Presentation The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). The Company operates in one reportable business segment.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for organization, consolidation and basis of presentation of financial statements disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480424/946-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480424/946-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/810/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/205/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies Principles of Consolidation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Foreign Currency
The Company’s foreign subsidiaries functional currency is the U.S. dollar. Transaction gains and losses are recognized in earnings. The Company is subject to foreign exchange rate fluctuations in connection with the Company’s international operations. Use of Estimates The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates include, among other things, accounts receivable realization, revenue recognition, valuation allowance for deferred tax assets, recoverability of capitalized software development costs, and stock-based compensation and warrant assumptions. We base our estimates on historical experience, our observance of trends in particular areas and information or valuations and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances and which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that may not be readily apparent from other sources. Actual amounts could differ significantly from amounts previously estimated.
Cash and Cash Equivalents The Company considers only those investments which are highly liquid, readily convertible to cash, and with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company had cash balances of $2.6 million and $10.1 million, respectively, and no cash equivalents. The Company maintains its cash balances in three major financial institutions. The Company regularly monitors the financial stability of these financial institutions and believes that it is not exposed to any significant credit risk in its cash. If any liquidity and/or financial stability concerns arise with respect to banks and financial institutions, either nationally or in specific regions, the Company's ability to access cash or enter into new financing arrangements may be threatened, which could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition and results of operations.
Liquidity and Going Concern
In accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Subtopic 205-40, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern (“ASC 205-40”), the Company has the responsibility to evaluate whether conditions and/or events raise substantial doubt about its ability to meet its obligations as they become due within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued. As required under ASC 205-40, management’s evaluation should initially not take into consideration the potential mitigating effects of management’s plans that have not been fully implemented as of the date the financial statements are issued. The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern.
In performing this evaluation, we concluded that under the standards of ASC 205-40 the following conditions raised substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern:
•a history of net losses, including a net loss of $7.3 million for the year ending April 30 2024; •cash used in operations of $6.1 million for the year ended April 30, 2024; •working capital deficit of $7.9 million as of April 30, 2024; and •an accumulated deficit of $84.6 million.
The Company's liquidity needs have typically arisen from the funding of our research and development programs and the launch of new products, working capital requirements, and other strategic initiatives. Most recently, the Company has met these cash requirements through cash on hand, working capital management, and sales of products and services. In the past, the Company has also received proceeds from certain private placements and public offerings of our securities. While the Company believes it has strategies to increase revenues and reduce costs which can be implemented without disrupting the business or completely restructuring the Company, there can be no assurances. Should the Company be required to raise additional capital or seek to obtain financing, there can be no assurance that management would be successful in raising such capital or obtaining such financing on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
The accompanying financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from these uncertainties.
Fair Value The carrying value of cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, and other current assets, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities approximate their fair value based on the liquidity or the short-term maturities of these instruments. The fair value hierarchy promulgated by GAAP consists of three levels: •Level one — Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; •Level two — Inputs other than level one inputs that are either directly or indirectly observable; and •Level three — Unobservable inputs developed using estimates and assumptions, which are developed by the reporting entity and reflect those assumptions that a market participant would use.
Determining which category an asset or liability falls within the hierarchy requires significant judgment. The Company evaluates its hierarchy disclosures each quarter. The Company has no assets or liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring and/or non-recurring basis during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023.
Property and Equipment Property and equipment is recorded at cost and primarily consists of laboratory equipment, furniture and fixtures, computer hardware and software, and internally developed software. Assets in progress include equipment or software not yet placed in service. Depreciation and amortization is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the various assets ranging from three to seven years. Refer to Footnote 4, "Property and Equipment" for a detailed discussion.
Leases
The Company accounts for its leases under Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") ASC Topic 842, Leases ("ASC 842"). Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases and are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both a right-of-use ("ROU") asset and lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right-of-use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right-of-use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term.
Amortization expense for the ROU asset associated with its finance leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease and interest expense associated with its finance lease is recognized on the balance of the lease liability using the effective interest method based on the estimated incremental borrowing rate.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Impairment losses are to be recognized when the carrying amount of a long-lived asset is not recoverable or exceeds its fair value. The Company evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that a carrying value may not be recoverable. The Company uses estimates of future cash flows over the remaining useful life of a long- lived asset or asset group to determine the recoverability of the asset. These estimates only include the net cash flows directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the asset or asset group. For the year ending April 30, 2023, the Company recognized an impairment loss of $807,000 for its Lumin Bioinformatics platform ("Lumin") resulting from a recoverability analysis performed at that date. The net book value of Lumin at April 30, 2023 was zero. The Company did not recognized any impairment losses for the Company’s long-lived assets for the year ending April 30, 2024. Refer to Note 4, "Property and Equipment".
Goodwill Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired in a business combination. The Company evaluates the carrying value of goodwill annually in connection with the annual budgeting and forecast process and also between annual evaluations if events occur or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of the reporting unit to which goodwill was allocated to below its carrying amount. Such circumstances could include, but are not limited to: (1) a significant adverse change in legal factors, market conditions, or in business climate, (2) unanticipated competition, or (3) an adverse action or assessment by a regulator. When evaluating goodwill for impairment, we may first perform an assessment qualitatively whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s carrying amount exceeds its fair value, referred to as a “step zero” approach. Subsequently (if necessary after step zero), an entity should perform its goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value. Under FASB's Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2014-02, Topic 350, "Intangibles—Goodwill and Other" goodwill impairment is measured as the excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit over its fair value.
The Company assesses goodwill impairment by reporting unit. Translational Oncology Solutions ("TOS") is the only reporting unit with remaining goodwill. Judgments regarding the existence of impairment indicators are based on legal factors, market conditions and operational performance of the businesses. Future events, including but not limited to continued declines in economic activity, loss of contracts or a significant number of customers, or a rapid increase in costs or capital expenditures, could cause us to conclude that impairment indicators exist and that goodwill is impaired. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company's annual assessment did not result in any impairment indicators. Deferred Revenue Deferred revenue represents payments received in advance of products to be delivered or services to be performed. When products are delivered and/or services are performed, deferred revenue is recognized as earned. Revenue related to deferred revenue is expected to be recognized within one year.
Other Non-Current Liabilities
Other non-current liabilities represent amounts for uncertain tax positions relating to one of our foreign entities and a financing lease of laboratory equipment in exchange for a lab supplies purchasing commitment. Cost of Oncology Services Cost of oncology services relates primarily to our TOS business unit. TOS costs consist of direct costs related to laboratory supplies, mice purchases, and maintenance costs for studies completed internally as well as charges from Contract Research Organizations for studies handled externally. Indirect costs include salaries and other payroll related costs of compensation for personnel directly engaged in providing TOS products and services. All costs of performing studies in-house are expensed as incurred. All costs of performing studies from external sources, are expensed when incurred. Research and Development Research and development costs represent both costs incurred internally for research and development activities, including personnel costs, mice purchases, and maintenance, as well as costs incurred externally to facilitate research activities, such as tumor tissue procurement and characterization expenses. All research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Sales and Marketing Sales and marketing expenses represent costs incurred to promote the Company’s products offered, including salaries, benefits and related costs of our sales and marketing personnel, and represent costs of advertising and other selling and marketing expenses. All sales and marketing costs, including advertising costs, are expensed as incurred. Earnings Per Share Basic net income or loss per share is computed by dividing the net income or loss for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed by dividing the net income for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock plus dilutive potential common stock considered outstanding during the period. Such dilutive shares consist of incremental shares that would be issued upon exercise of the Company’s common stock purchase warrants and stock options. Dilutive earnings per share is not presented when it would be antidilutive to do so. Stock-based Payments The Company typically recognizes expense for stock-based payments based on the fair value of awards on the date of grant. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate fair value. The Black-Scholes option valuation model was developed for use in estimating the fair value of short-traded options that have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. The option pricing model requires the Company to estimate certain key assumptions such as expected life, volatility, risk free interest rates and dividend yield to determine the fair value of stock-based awards. These assumptions are based on historical information and management judgment. The risk-free interest rate used is based on the United States treasury security rate with a term consistent with the expected term of the award at the time of the grant. Since the Company has limited option exercise history, it has generally elected to estimate the expected life of an award based upon the Securities and Exchange Commission-approved “simplified method” noted under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 with the continued use of this method extended under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110. Estimated volatility is based upon the historical volatility of the Company's common stock. The Company does not anticipate paying a dividend, and therefore, no expected dividend yield was used. The Company expenses stock-based payments over the period that the awards are expected to vest. In the event of forfeitures, compensation expense is adjusted. The Company expenses modification charges in the period of modification and, if required, over the remaining period the awards are expected to vest. The Company will report cash flows resulting from tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized from those options (excess tax benefits) as financing cash flows, if they should arise. Income Taxes Deferred income taxes have been provided to show the effect of temporary differences between the recognition of expenses for financial and income tax reporting purposes and between the tax basis of assets and liabilities, and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company assesses the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered through tax planning strategies or from future taxable income, and to the extent that recovery is not likely or there is insufficient operating history, a valuation allowance is established. The Company adjusts the valuation allowance in the period management determines it is more likely than not that net deferred tax assets will or will not be realized. Changes in valuation allowances from period to period are included in the tax provision in the period of change. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company provided a valuation allowance for all net deferred tax assets, as recovery is not more likely than not based on an insufficient history of earnings. The Company reflects tax benefits only if it is more likely than not that we will be able to sustain the tax position, based on its technical merits. If a tax benefit meets this criterion, it is measured and recognized based on the largest amount of benefit that is cumulatively greater than 50% likely to be realized. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company has recorded $181,000 of liabilities related to uncertain tax positions relative to one of its foreign operations.
The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and/or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense. The Company accrued $0 for any additional interest and or penalties on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, as the Company believes its recorded liability for uncertain tax positions covers any potential interest and/or penalties. The Company does not anticipate any significant unrecognized tax benefits to be recorded during the next 12 months. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company recognized a benefit for income taxes of $32,000 and a provision for income taxes of $68,000, respectively. These amounts are mainly attributable to taxable income earned in Israel and Italy relating to transfer pricing, U.S. state net operating loss limitations and, in fiscal 2024, net of a return to provision adjustment in Israel of $95,000.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with ASC 606, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers". The objective of the standard is to establish a single comprehensive revenue recognition model that is designed to create greater comparability of financial statements across industries and jurisdictions. Under this standard, companies recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in amounts that reflect the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
All revenue is generated from contracts with customers. The Company recognizes revenue when control of these services is transferred to the customer in an amount, referred to as the transaction price, that reflects the consideration to which the Company is expected to be entitled in exchange for those services. The Company determines revenue recognition utilizing the following five steps: (1) identification of the contract with a customer, (2) identification of the performance obligations in the contract (promised goods or services that are distinct), (3) determination of the transaction price, (4) allocation of the transaction price to the performance obligations, and (5) recognition of revenue when, or as, the Company transfers control of the product or service for each performance obligation. The Company records revenues net of any tax assessments by governmental authorities, such as value added taxes, that are imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue generating transactions.
The majority of the Company's revenue arrangements are service contracts that are completed within a year or less. There are a few contracts that range in duration between 1 and 3 years. Substantially all of the Company's performance obligations, and associated revenue, are transferred to the customer over time. Most of the Company's contracts can be terminated by the customer without cause. In the event of termination, the Company's contracts provide that the customer pay the Company for services rendered through the termination date. The Company generally receives compensation based on a predetermined invoicing schedule relating to specific milestones for that contract.
Amendments to contracts are common. The Company evaluates each amendment which meets the criteria of a contract modification under ASC 606. Each modification is further evaluated to determine whether the contract modification should be accounted for as a separate contract or as a continuation of the original agreement.
The Company accounts for amendments as a separate contract as they meet the criteria under ASC 606-10-25-12.
Pharmacology Study and Other Services
The Company generally enters into contracts with customers to provide oncology services with payments based on fixed-fee arrangements. At contract inception, the Company assesses the services promised in the contracts with customers to identify the performance obligations in the arrangement. The Company's fixed-fee arrangements for oncology services are considered a single performance obligation because the Company provides a highly-integrated service.
The Company recognizes revenue over time using a progress-based input method since there is no single output measure that would fairly depict the transfer of control over the life of the performance obligation. Revenue is recognized for the single performance obligation over time due to the Company's right to payment for work performed to date and the performance does not create an asset with an alternative use. The Company recognizes revenue as portions of the overall performance obligation are completed as this best depicts the progress of the performance obligation.
Incremental Costs of Obtaining a Contract (Sales Commissions) Under ASC 606, the costs of obtaining a contract can be expensed immediately, rather than capitalized and amortized, if the amortization period is one year or shorter. Sales commissions for the Company represent contract costs with a term of one year or less. Therefore, under ASC 606, the Company elected the practical expedient to expense these costs as incurred.
Variable Consideration
In some cases, contracts provide for variable consideration that is contingent upon the occurrence of uncertain future events, such as the success of the initial performance obligation. Variable consideration is estimated at the expected value or at the most likely amount depending on the type of consideration. Estimated amounts are included in the transaction price to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is resolved. The estimate of variable consideration and determination of whether to include estimated amounts in the transaction price are based largely on an assessment of its anticipated performance and all information (historical, current and forecasted) that is reasonably available to the Company.
Trade Receivables, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue
In general, billings and payments are established by contractual provisions including predetermined payment schedules, which may or may not correspond to the timing of the transfer of control of the Company's services under the contract. In general, the Company's intention in its invoicing (payment terms) is to maintain cash neutrality over the life of the contract. Upfront payments, when they occur, are intended to cover certain expenses the Company incurs at the beginning of the contract. Neither the Company nor its customers view such upfront payments and contracted payment schedules as a means of financing. Unbilled services primarily arise when the revenue recognized exceeds the amount billed to the customer. Such situations occur due to divergences between revenue recognition and the invoicing milestones which are based on predetermined payment terms.
Deferred revenue consists of unearned payments received in excess of revenue recognized. As the contracted services are subsequently performed and the associated revenue recognized, the deferred revenue balance is reduced by the amount of the revenue recognized during the period. Deferred revenue is classified as a current liability on the consolidated balance sheet as the Company expects to recognize the associated revenue in less than one year.
Accounting Pronouncements Adopted In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses". This update required immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses ("CECL"). Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The Company adopted this ASU on May 1, 2023 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Receivables [Abstract] |
|
| Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue |
Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue Accounts receivable and unbilled services were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 | | April 30, 2022 | | | | | | | | Accounts receivable | $ | 4,886 | | | $ | 3,843 | | | $ | 6,037 | | | Unbilled services | 5,941 | | | 4,993 | | | 4,106 | | | Total accounts receivable and unbilled services | 10,827 | | | 8,836 | | | 10,143 | | | Less: allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses | (1,301) | | | (825) | | | (630) | | | Total accounts receivable, net | $ | 9,526 | | | $ | 8,011 | | | $ | 9,513 | |
Deferred revenue was as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 | | | | | | | Deferred revenue | $ | 12,094 | | | $ | 12,776 | |
Deferred revenue is shown as a current liability on the Company's balance sheet.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for claims held for amounts due to entity, excluding financing receivables. Examples include, but are not limited to, trade accounts receivables, notes receivables, loans receivables. Includes disclosure for allowance for credit losses. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/310-10/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LoansNotesTradeAndOtherReceivablesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Property and Equipment
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| Property and Equipment |
Property and Equipment Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Furniture and fixtures | $ | 246 | | | $ | 246 | | | Computer equipment and software | 2,152 | | | 2,102 | | | Laboratory equipment | 11,506 | | | 10,390 | | | Capitalized software development costs | 1,888 | | | 1,888 | | | Assets in progress | 3 | | | 1,079 | | | Leasehold improvements | 317 | | | 111 | | | | | | | Total property and equipment | 16,112 | | | 15,816 | | | Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (10,391) | | | (8,630) | | | | | | | Property and equipment, net | $ | 5,721 | | | $ | 7,186 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense was $1.9 million and $2.2 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Depreciation and amortization expense, excluding expense recorded under finance leases, was $1.7 million and $2.1 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, property, plant and equipment included gross assets held under finance leases of $1.0 million, respectively. Related depreciation expense for these assets was $146,000 and $135,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
During the year ended April 30, 2024, the Company disposed of lab equipment with a cost of $542,000 and accumulated depreciation of $107,000 as of the disposal date, resulting in a loss on disposal of equipment recorded of $435,000. There were no disposals and therefore no gain or loss recorded during the year ended April 30, 2023.
Capitalized software development costs under a hosting arrangement
The Company accounts for the cost of computer software obtained or developed for internal use as well as the software development and implementation costs associated with a hosting arrangement ("internal-use software") that is a service contract in accordance and with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other ("ASC-350"). We capitalize certain costs in the development of our internal-use software when the preliminary project stage is completed and it is probable that the project itself will be completed and the software will perform as intended. These capitalized costs include personnel and related expenses for employees and costs of third-party consultants who are directly associated with and who devote time to these internal-use software projects. Capitalization of these costs ceases once the project is substantially complete and the software is ready for its intended purpose. Costs incurred for significant upgrades, increased functionality, and enhancements to the Company's internal-use software solutions are also capitalized. Costs incurred for training, maintenance, and minor modifications are expensed as incurred. Capitalized software development costs are amortized using the straight-line method over an estimated useful economic life of three years. The Company capitalized development and implementation costs in accordance with accounting guidance for its bioinformatics platform, Lumin. Lumin is the Company's oncology data-driven software program and data tool which operates as Software as a Service (SaaS). These capitalized costs represent salaries, including direct payroll-related costs, certain software development consultant expenses and molecular sequencing programming costs incurred in the engineering and coding of the software development. Total capitalized gross asset costs for the Lumin platform that was launched and placed into service were $1.9 million. During the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2023, an impairment loss for Lumin was recognized equal to the amount by which the carrying amount exceeded the future net revenues, or, its net book value at April 30, 2023 of $807,000. Amortization expense related to this asset was $0 and $630,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Finance Lease
During fiscal 2022, the Company recognized a finance lease for laboratory equipment. This equipment was obtained as the result of a laboratory supplies purchase commitment with costs of approximately $370,000 at inception through December 2025. Cash payments for this lease are in the form of consideration for purchasing lab supplies under a purchase commitment agreement. The present value of the minimum future obligations of $370,000 was calculated based on an interest rate of 3.25%. Depreciation and amortization expense related to this finance lease was $75,000 and $72,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Interest on the related finance lease liability was approximately $6,000 and $8,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
During fiscal 2023, the Company recognized a finance lease for laboratory equipment. This equipment was obtained as the result of a laboratory supplies purchase commitment with costs of approximately $368,000 at inception through December 2025. Cash payments for this lease are in the form of consideration for purchasing lab supplies under a purchase commitment agreement. The present value of the minimum future obligations of $368,000 was calculated based on an interest rate of 3.5%. Depreciation and amortization expense related to this finance lease was $71,000 and $63,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Interest on the related finance lease liability was approximately $9,000 and $11,000 for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 160 | | | 2026 | 140 | | | 2027 | 80 | | | 2028 | 7 | | | Thereafter | — | | | Total undiscounted liabilities | 387 | | | Less: Imputed interest | (16) | | | Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 371 | | | | | | | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/360/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-6
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Revenue from Contracts with Customers
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| Revenue from Contracts with Customers |
Revenue from Contracts with Customers Oncology Services Revenue
The following table represents disaggregated revenue for the twelve months ended April 30, 2024 and 2023: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | Pharmacology services | $ | 47,035 | | | $ | 50,708 | | | | Other TOS revenue | 3,102 | | | 3,046 | | | | Personalized oncology services | 18 | | | 116 | | | | Total oncology services revenue | $ | 50,155 | | | $ | 53,870 | | |
Other TOS revenue represents additional services provided to the Company's pharmaceutical and biotechnology customers, specifically flow cytometry services and SaaS provided via our Lumin Bioinformatics software. Contract Balances Contract assets include unbilled amounts typically resulting from revenue recognized in excess of the amounts billed to the customer for which the right to payment is subject to factors other than the passage of time. These amounts may not exceed their net realizable value. Contract assets are classified as current. Contract liabilities consist of customer payments received in advance of performance and billings in excess of revenue recognized, net of revenue recognized from the balance at the beginning of the period. Contract assets and liabilities are presented on the balance sheet on a net contract-by-contract basis at the end of each reporting period. Refer to Note 3 for related balances.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure of revenue from contract with customer to transfer good or service and to transfer nonfinancial asset. Includes, but is not limited to, disaggregation of revenue, credit loss recognized from contract with customer, judgment and change in judgment related to contract with customer, and asset recognized from cost incurred to obtain or fulfill contract with customer. Excludes insurance and lease contracts. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-15
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Significant Customers
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Risks and Uncertainties [Abstract] |
|
| Significant Customers |
Significant Customers For the year ended April 30, 2024, one of our customers accounted for more than 10% of our total revenue, at 10%. For the year ended April 30, 2023, one of our customers accounted for more than 10% of our total revenue, at 14%. This was the same customer for both years. As of April 30, 2024, one customer accounted for 12% of our total accounts receivable balance. As of April 30, 2023, the same customer accounted for 14% of our total accounts receivable balance.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for any concentrations existing at the date of the financial statements that make an entity vulnerable to a reasonably possible, near-term, severe impact. This disclosure informs financial statement users about the general nature of the risk associated with the concentration, and may indicate the percentage of concentration risk as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 275
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/275/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RisksAndUncertaintiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Commitments and Contingencies
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Commitments and Contingencies |
Commitments and Contingencies Legal Matters The Company is not currently party to any legal matters to its knowledge. The Company is not aware of any other matters that would have a material impact on the Company’s financial position or results of operations. Registration Payment Arrangements The Company has entered into an Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement in connection with the March 2015 Private Placement. This Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement contains provisions that may call for the Company to pay penalties in certain circumstances. This registration payment arrangement primarily relates to the Company’s ability to file a registration statement within a particular time period, have a registration statement declared effective within a particular time period and to maintain the effectiveness of the registration statement for a particular time period. The Company has not accrued any liquidated damages associated with the Amended and Restated Registration Right Agreement as the Company has filed the required registration statement and anticipates continued compliance with the agreement.
Royalties The Company contracts with third-party vendors to license tumor samples for development into PDX models and use in our TOS business. These types of arrangements have an upfront fee ranging from approximately nil to $30,000 per tumor sample depending on the successful growth of the tumor model and ability to develop them into a sellable product. The upfront costs are expensed as incurred. In addition, under certain agreements, for a limited period of time, the Company is subject to royalty payments if the licensed tumor models are used for sale in our TOS business, ranging from 2% to 20% of the contract price after recouping certain initiation costs. Some of these arrangements also set forth an annual minimum royalty due regardless of tumor models used for sale. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, we have recognized approximately $362,000 and $212,000 in expense related to these royalty arrangements, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 405
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/405-30/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/450/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478522/954-440-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Stock-based Payments
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Stock-based Payments |
Stock-based Payments Stock-based compensation in the amount of $1.1 million and $864,000 was recognized for years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Stock-based compensation costs were recorded as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | General and administrative | $ | 706 | | | $ | 505 | | | Sales and marketing | 168 | | | 192 | | | Research and development | 21 | | | 19 | | | TOS cost of sales | 223 | | | 148 | | | | | | | | | | | Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 1,118 | | | $ | 864 | |
The Company has in place a 2021 Equity Incentive Plan and 2010 Equity Incentive Plan ("the Plans"). In general, these plans provide for stock-based compensation to the Company’s employees, directors and non-employees. The plans also provide for limits on the aggregate number of shares that may be granted, the term of grants and the strike price of option awards.
2021 Equity Incentive Plan As part of the 2021 Annual Shareholders Meeting, shareholders approved the adoption of the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan (“2021 Equity Plan”). The purpose of the 2021 Equity Plan is to grant (i) Non-statutory Stock Options; (ii) Incentive Stock Options; (iii) Restricted Stock Awards; and/or (iv) Stock Appreciation Rights (collectively, stock-based compensation) to its employees, directors and non-employees. Total stock awards under the 2021 Equity Plan shall not exceed 2 million shares of common stock. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights expire no later than ten years from the date of grant and the awards vest as determined by the Board of Directors (the "Board") or Chief Executive Officer. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights have a strike price not less than 100% of the fair market value of the common stock subject to the option or right at the date of grant. As of April 30, 2024, approximately 1.3 million shares were left to issue under this plan.
2010 Equity Incentive Plan On February 18, 2011, shareholders owning a majority of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company executed a written consent approving the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (“2010 Equity Plan”). The purpose of the 2010 Equity Plan is to grant (i) Non-statutory Stock Options; (ii) Restricted Stock Awards; and (iii) Stock Appreciation Rights (collectively, stock-based compensation) to its employees, directors and non-employees. Total stock awards under the 2010 Equity Plan shall not exceed 30,000,000 shares of common stock. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights expire no later than ten years from the date of grant and the awards vest as determined by the Board. Options and Stock Appreciation Rights have a strike price not less than 100% of the fair market value of the common stock subject to the option or right at the date of grant. After February 2021, no more shares were available to be issued from this plan. Director Compensation Plan On December 12, 2013, the Compensation Committee of the Board (the "Committee") adopted changes to the Director Compensation Plan of 2010 (the “Director Plan”) effective December 1, 2013. Under the Director Plan, independent directors of the Company were entitled to an annual award of a five-year option to purchase 8,333 shares of the Company’s common stock, and the Chairman of the Board of the Company was entitled to an annual award of a five-year option to purchase 16,667 shares of the Company’s common stock. Independent directors who serve as chairperson of a committee were also to receive an annual grant of a five-year option to purchase 1,667 shares of the Company’s common stock. During fiscal year 2021, the Committee adopted the Director Compensation Plan of 2021 (the "2021 Plan"). Under the 2021 Plan, independent directors are entitled to an annual base compensation of $100,000 which can be received in either ten-year company options or a combination of company options and cash, not to exceed $35,000. The Chairman of the Board’s annual compensation was set at an equivalent of $150,000. Compensation for independent directors who serve as chairperson of a committee was set at an equivalent of between $110,000 to $120,000. All options issued under the 2021 Plan vest quarterly at a rate of 25%. Option grants will typically be issued after the annual shareholder meeting which will generally be held in October of each year. New directors will receive compensation upon joining the Board equal to a pro-rata equivalent for the remainder of the year. Options issued under the 2021 Plan are issued pursuant to the 2021 Equity Plan. Stock Option Grants Black-Scholes weighted average assumptions used to calculate the fair value of options granted during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Expected term in years | 6 | | 6 | | Risk-free interest rates | 4.0% - 4.5% | | 2.9% - 3.9% | | Volatility | 63% - 64% | | 61% - 63% | | Dividend yield | 0% | | 0% |
The weighted average fair value of stock options granted during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, was $3.75 and $4.31, respectively. The Company’s stock options activity and related information as of and for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | | Outstanding, May 1, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | $ | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | Granted | 444,730 | | | — | | | 444,730 | | | 6.08 | | | 9.5 | | $ | — | | | Exercised | (155,449) | | | — | | | (155,449) | | | 2.31 | | | | | | | Canceled | (50,535) | | | — | | | (50,535) | | | 4.82 | | | | | | | Forfeited | (40,750) | | | — | | | (40,750) | | | 6.21 | | | | | | | Expired | (54,166) | | | — | | | (54,166) | | | 12.78 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Outstanding, April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable as of April 30, 2024 | 1,481,145 | | | 3,750 | | | 1,484,895 | | | 4.65 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | | Outstanding, May 1, 2022 | 1,617,324 | | | 40,915 | | | 1,658,239 | | | 4.51 | | 4.9 | | $ | 6,131,000 | | | Granted | 186,720 | | | — | | | 186,720 | | | 7.22 | | | 9.4 | | — | | | Exercised | (36,209) | | | — | | | (36,209) | | | 3.21 | | | | | | | Canceled | (13,874) | | | — | | | (13,874) | | | 3.93 | | | | | | | Forfeited | (14,625) | | | — | | | (14,625) | | | 7.94 | | | | | | | Expired | — | | | (4,584) | | | (4,584) | | | 5.40 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Outstanding, April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable as of April 30, 2023 | 1,436,932 | | | 1,875 | | | 1,438,807 | | | 4.35 | | | 3.8 | | $ | 2,681,000 | |
Share Repurchase Program
On March 29, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program authorizing the Company to purchase up to an aggregate of $5.0 million of the Company’s common stock. The share repurchase program is designed in accordance with Rule 10b-18 of the Exchange Act. The shares may be purchased from time to time in the open market, as permitted under applicable rules and regulations, at prevailing market prices. The timing and amount of repurchases will depend on market conditions, share price, applicable legal requirements and other factors. The program does not obligate the Company to acquire a minimum number of shares. As of April 30, 2024, the Company had purchased approximately 120,300 shares of its common stock, at an average price of $5.73 per share, totaling approximately $708,000 and leaving an available balance of approximately $4.3 million authorized by the Board for use in the program as of that date.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/718/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfCompensationRelatedCostsShareBasedPaymentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes |
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes The components of the (benefit) provision for income taxes are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, 2024 | | | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total | | Current | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, 2023 | | | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total | | Current | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | |
A reconciliation between the Company’s effective tax rate and the United States statutory tax rate for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Federal income tax at statutory rate | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % | | US vs. foreign tax rate difference | (0.1) | | | (0.2) | | | State income tax, net of federal benefit | (2.3) | | | 2.2 | | | Permanent differences | 0.4 | | | (0.5) | | | Increase in uncertain tax position | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | Change in valuation allowance | (18.5) | | | (23.8) | | | | | | | | | | | Income tax expense | 0.5 | % | | (1.3) | % |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities as of April 30, 2024 and 2023 consist of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | As of April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Accrued liabilities | $ | 1,269 | | | $ | 273 | | | Operating leases | 279 | | | 403 | | | Depreciation and amortization | (318) | | | (297) | | | | | | | Stock-based compensation expense | 3,792 | | | 4,024 | | | Capitalized research and development costs | 4,046 | | | 2,597 | | | | | | | Net operating loss carry-forward | 9,038 | | | 9,756 | | | | | | | Total deferred tax assets | 18,106 | | | 16,756 | | | Less: Valuation allowance | (18,106) | | | (16,756) | | | | | | | Net deferred tax asset | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Management has evaluated the available evidence about future tax planning strategies, taxable income, and other possible sources of realization of deferred tax assets and has established a full valuation allowance against its net deferred tax assets as of April 30, 2024 and 2023. For the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company recorded a valuation allowance of $18.1 million and $16.8 million, respectively. The net changes in the valuation allowance of $1.4 million and $1.3 million during the fiscal years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively, were mainly due to increases in the deferred tax asset related to capitalized research expenses and other timing differences. Management continues to assess the realizability of the deferred tax assets at each interim and annual balance sheet date based upon actual and forecasted operating results.
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company’s estimated U.S. net operating loss carry-forwards were approximately $38.6 million and $41.3 million, respectively. Net operating losses generated prior to May 1, 2018 have a 20-year carryforward and will begin expiring in 2025 for federal and 2031 for state purposes. Losses generated in the fiscal years since the year ended April 30, 2019 may be carried forward indefinitely. A valuation allowance has been recorded against all of these loss carryforwards. Under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, certain substantial changes in the Company’s ownership may result in a limitation on the amount of net operating losses that may be utilized in future years. During the fiscal year ended April 30, 2013, approximately $12.0 million of the Company’s net operating losses became subject to limitation under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 in connection with an ownership change on January 28, 2013. As a result of the ownership change, the Company’s annual limitation on its use of net operating loss carry-forwards is approximately $432,000.
The Company files income tax returns in various jurisdictions with varying statutes of limitations. As of April 30, 2024, the earliest tax year still subject to examination for state purposes is fiscal 2020. The Company’s tax years for periods ending April 30, 2002 and forward are subject to examination by the United States and certain states due to the carry-forward of unutilized net operating losses.
The following table indicates the changes to the Company’s uncertain tax positions for the period and years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 in thousands: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | | | Addition based on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | | | Payment made on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | | | Addition based on tax positions related to current year | — | | | — | | | | | | | Balance, end of year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | |
As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the above amounts of $181,000 for each fiscal year were included in other long-term liabilities.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income tax. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 231
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-231
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477891/740-270-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/740/tableOfContent
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Earnings Per Share
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Earnings Per Share [Abstract] |
|
| Earnings Per Share |
Earnings Per Share A reconciliation of net income and number of shares used in computing basic and diluted earnings per share was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Basic and diluted net loss per share computation (dollars in thousands): | | | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (7,276) | | | $ | (5,335) | | | Weighted Average common shares - basic and diluted | 13,547,604 | | | 13,541,559 | | | Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.54) | | | $ | (0.39) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The following table reflects the total potential stock-based instruments outstanding at April 30, 2024 and 2023 that could have an effect on the future computation of dilution per common share. These figures were not included in the above calculation as, to do so, would be antidilutive: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Stock options | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | | | | | | | | | | | Total common stock equivalents | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for earnings per share. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/260/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Related Party Transactions
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Related Party Transactions [Abstract] |
|
| Related Party Transactions |
Related Party Transactions Related party transactions include transactions between the Company and its shareholders, management, or affiliates. The following transactions were in the normal course of operations and were measured at the exchange amount, which is the amount of consideration established and agreed to by the parties. Consulting Services For both years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company paid a member of its Board of Directors $36,000 for consulting services unrelated to his duties as a board member. All of the amounts paid to these related parties have been recognized in expense in the period the services were performed within general and administrative expenses.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for related party transactions. Examples of related party transactions include transactions between (a) a parent company and its subsidiary; (b) subsidiaries of a common parent; (c) and entity and its principal owners; and (d) affiliates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477968/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477968/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(g)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(e))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/850/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-6
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RelatedPartyTransactionsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Leases
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Leases |
Leases The Company accounts for its leases under ASC 842. Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases, and are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both an operating lease ROU asset and operating lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right of use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right of use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term. Variable lease expenses, if any, are recorded when incurred. The Company has elected to apply the short-term lease exemption practical expedient for each class of underlying assets and excludes short-term leases having initial terms of 12 months or less. The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term for these short-term leases. The Company has determined that no material embedded leases exist. Under ASC 842, the Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of remaining lease payments over the lease term. For this purpose, the Company considers only payments that are fixed and determinable at the time of commencement. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Operating Leases
The Company currently leases certain office equipment and its office and laboratory facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. Rent expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term from the lease commencement date through the scheduled expiration date. Rent expenses totaled $1.8 million and $1.9 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
The Company leases the following facilities: •One University Plaza, Suite 307, Hackensack, New Jersey 07601, which, since November 2011, serves as the Company’s corporate headquarters. The lease expires in November 2026. The Company recognized $77,000 and $83,000 of rent expense relative to this lease for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively. •1330 Piccard Drive Suite 025, Rockville, MD 20850, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its primary service offerings. The Company executed the original lease in January 2017. The lease was amended to expand the premises and extend the expiration date in March 2020 and again in December 2020. The operating commencement date was August 11, 2017. This lease expires in February 2029. The Company recognized $1.7 million of rent expense for both fiscal 2024 and 2023. •VIA LEONE XIII, 14, Milan, Italy, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its flow cytometry service offerings. The Company executed separate leases for its laboratory space and office space during fiscal 2022. During fiscal 2023, the Company executed a new lease to consolidate its office and laboratory space at a new nearby location in Italy. The lease expires October 31, 2028 and it replaces the previous two leases, which were terminated during fiscal 2023. The Company recognized $50,000 and $98,000 of rent expense associated with the leases in Italy for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
ROU assets and lease liabilities related to our current operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2023 | Operating lease right-of-use assets, net
| 6,252 | | 7,318 | | Current portion of operating lease liabilities
| 1,337 | | 1,208 | | | Non-current portion of operating lease liabilities | 6,093 | | 7,391 | |
As of April 30, 2024, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 4.7 years and 5.88%, respectively. As of April 30, 2023, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 5.7 years and 5.82%, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments for operating leases due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 2,902 | | | 2026 | 2,950 | | | 2027 | 2,916 | | | 2028 | 2,867 | | | 2029 | 2,392 | | | Thereafter | — | | | Total undiscounted liabilities | 14,027 | | | Less: Imputed interest | (6,597) | | | Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 7,430 | |
The composition of total lease cost for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | Operating lease costs | $ | 1,680 | | | $ | 1,566 | | | | | | | | | Financing lease costs: | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | 146 | | | 135 | | | | Interest on lease liabilities | 15 | | | 19 | | | | | | | | | Total lease costs | $ | 1,841 | | | $ | 1,720 | | | | | | | |
Refer to Note 4, Property and Equipment, for more information on financing leases.
|
| Leases |
Leases The Company accounts for its leases under ASC 842. Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases, and are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both an operating lease ROU asset and operating lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right of use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right of use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term. Variable lease expenses, if any, are recorded when incurred. The Company has elected to apply the short-term lease exemption practical expedient for each class of underlying assets and excludes short-term leases having initial terms of 12 months or less. The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term for these short-term leases. The Company has determined that no material embedded leases exist. Under ASC 842, the Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of remaining lease payments over the lease term. For this purpose, the Company considers only payments that are fixed and determinable at the time of commencement. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Operating Leases
The Company currently leases certain office equipment and its office and laboratory facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. Rent expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term from the lease commencement date through the scheduled expiration date. Rent expenses totaled $1.8 million and $1.9 million for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
The Company leases the following facilities: •One University Plaza, Suite 307, Hackensack, New Jersey 07601, which, since November 2011, serves as the Company’s corporate headquarters. The lease expires in November 2026. The Company recognized $77,000 and $83,000 of rent expense relative to this lease for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively. •1330 Piccard Drive Suite 025, Rockville, MD 20850, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its primary service offerings. The Company executed the original lease in January 2017. The lease was amended to expand the premises and extend the expiration date in March 2020 and again in December 2020. The operating commencement date was August 11, 2017. This lease expires in February 2029. The Company recognized $1.7 million of rent expense for both fiscal 2024 and 2023. •VIA LEONE XIII, 14, Milan, Italy, which consists of laboratory and office space where the Company conducts operations related to its flow cytometry service offerings. The Company executed separate leases for its laboratory space and office space during fiscal 2022. During fiscal 2023, the Company executed a new lease to consolidate its office and laboratory space at a new nearby location in Italy. The lease expires October 31, 2028 and it replaces the previous two leases, which were terminated during fiscal 2023. The Company recognized $50,000 and $98,000 of rent expense associated with the leases in Italy for fiscal 2024 and 2023, respectively.
ROU assets and lease liabilities related to our current operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2023 | Operating lease right-of-use assets, net
| 6,252 | | 7,318 | | Current portion of operating lease liabilities
| 1,337 | | 1,208 | | | Non-current portion of operating lease liabilities | 6,093 | | 7,391 | |
As of April 30, 2024, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 4.7 years and 5.88%, respectively. As of April 30, 2023, the weighted average remaining operating lease term and the weighted average discount rate were 5.7 years and 5.82%, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments for operating leases due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 2,902 | | | 2026 | 2,950 | | | 2027 | 2,916 | | | 2028 | 2,867 | | | 2029 | 2,392 | | | Thereafter | — | | | Total undiscounted liabilities | 14,027 | | | Less: Imputed interest | (6,597) | | | Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 7,430 | |
The composition of total lease cost for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | Operating lease costs | $ | 1,680 | | | $ | 1,566 | | | | | | | | | Financing lease costs: | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | 146 | | | 135 | | | | Interest on lease liabilities | 15 | | | 19 | | | | | | | | | Total lease costs | $ | 1,841 | | | $ | 1,720 | | | | | | | |
Refer to Note 4, Property and Equipment, for more information on financing leases.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for finance leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of lessee's finance lease and maturity analysis of finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeFinanceLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for operating leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of operating lease and maturity analysis of operating lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection v
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_PvpTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph A
| Name: |
ecd_TradingArrByIndTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Basis of Presentation |
Basis of Presentation The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). The Company operates in one reportable business segment.
|
| Principles of Consolidation |
Principles of Consolidation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
|
| Foreign Currency |
Foreign Currency The Company’s foreign subsidiaries functional currency is the U.S. dollar. Transaction gains and losses are recognized in earnings. The Company is subject to foreign exchange rate fluctuations in connection with the Company’s international operations.
|
| Use of Estimates |
Use of Estimates The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates include, among other things, accounts receivable realization, revenue recognition, valuation allowance for deferred tax assets, recoverability of capitalized software development costs, and stock-based compensation and warrant assumptions. We base our estimates on historical experience, our observance of trends in particular areas and information or valuations and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances and which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that may not be readily apparent from other sources. Actual amounts could differ significantly from amounts previously estimated.
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and Cash Equivalents The Company considers only those investments which are highly liquid, readily convertible to cash, and with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
|
| Fair Value |
Fair Value The carrying value of cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, and other current assets, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities approximate their fair value based on the liquidity or the short-term maturities of these instruments. The fair value hierarchy promulgated by GAAP consists of three levels: •Level one — Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; •Level two — Inputs other than level one inputs that are either directly or indirectly observable; and •Level three — Unobservable inputs developed using estimates and assumptions, which are developed by the reporting entity and reflect those assumptions that a market participant would use. Determining which category an asset or liability falls within the hierarchy requires significant judgment. The Company evaluates its hierarchy disclosures each quarter.
|
| Property and Equipment |
Property and Equipment Property and equipment is recorded at cost and primarily consists of laboratory equipment, furniture and fixtures, computer hardware and software, and internally developed software. Assets in progress include equipment or software not yet placed in service. Depreciation and amortization is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the various assets ranging from three to seven years.
|
| Leases |
Leases
The Company accounts for its leases under Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") ASC Topic 842, Leases ("ASC 842"). Under this guidance, arrangements meeting the definition of a lease are classified as operating or financing leases and are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet as both a right-of-use ("ROU") asset and lease liability, calculated by discounting fixed lease payments over the lease term at the rate implicit in the lease or the Company’s incremental borrowing rate. As the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses an incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. Lease liabilities are increased by interest and reduced by payments each period, and the right-of-use asset is amortized over the lease term. For operating leases, interest on the lease liability and the amortization of the right-of-use asset result in straight-line rent expense over the lease term.
Amortization expense for the ROU asset associated with its finance leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease and interest expense associated with its finance lease is recognized on the balance of the lease liability using the effective interest method based on the estimated incremental borrowing rate.
|
| Impairment of Long-Lived Assets |
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Impairment losses are to be recognized when the carrying amount of a long-lived asset is not recoverable or exceeds its fair value. The Company evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that a carrying value may not be recoverable. The Company uses estimates of future cash flows over the remaining useful life of a long- lived asset or asset group to determine the recoverability of the asset. These estimates only include the net cash flows directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the asset or asset group.
|
| Goodwill |
Goodwill Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired in a business combination. The Company evaluates the carrying value of goodwill annually in connection with the annual budgeting and forecast process and also between annual evaluations if events occur or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of the reporting unit to which goodwill was allocated to below its carrying amount. Such circumstances could include, but are not limited to: (1) a significant adverse change in legal factors, market conditions, or in business climate, (2) unanticipated competition, or (3) an adverse action or assessment by a regulator. When evaluating goodwill for impairment, we may first perform an assessment qualitatively whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s carrying amount exceeds its fair value, referred to as a “step zero” approach. Subsequently (if necessary after step zero), an entity should perform its goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value. Under FASB's Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2014-02, Topic 350, "Intangibles—Goodwill and Other" goodwill impairment is measured as the excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit over its fair value. The Company assesses goodwill impairment by reporting unit. Translational Oncology Solutions ("TOS") is the only reporting unit with remaining goodwill. Judgments regarding the existence of impairment indicators are based on legal factors, market conditions and operational performance of the businesses. Future events, including but not limited to continued declines in economic activity, loss of contracts or a significant number of customers, or a rapid increase in costs or capital expenditures, could cause us to conclude that impairment indicators exist and that goodwill is impaired.
|
| Deferred Revenue and Revenue Recognition |
Deferred Revenue Deferred revenue represents payments received in advance of products to be delivered or services to be performed. When products are delivered and/or services are performed, deferred revenue is recognized as earned. Revenue related to deferred revenue is expected to be recognized within one year. Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with ASC 606, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers". The objective of the standard is to establish a single comprehensive revenue recognition model that is designed to create greater comparability of financial statements across industries and jurisdictions. Under this standard, companies recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in amounts that reflect the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
All revenue is generated from contracts with customers. The Company recognizes revenue when control of these services is transferred to the customer in an amount, referred to as the transaction price, that reflects the consideration to which the Company is expected to be entitled in exchange for those services. The Company determines revenue recognition utilizing the following five steps: (1) identification of the contract with a customer, (2) identification of the performance obligations in the contract (promised goods or services that are distinct), (3) determination of the transaction price, (4) allocation of the transaction price to the performance obligations, and (5) recognition of revenue when, or as, the Company transfers control of the product or service for each performance obligation. The Company records revenues net of any tax assessments by governmental authorities, such as value added taxes, that are imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue generating transactions.
The majority of the Company's revenue arrangements are service contracts that are completed within a year or less. There are a few contracts that range in duration between 1 and 3 years. Substantially all of the Company's performance obligations, and associated revenue, are transferred to the customer over time. Most of the Company's contracts can be terminated by the customer without cause. In the event of termination, the Company's contracts provide that the customer pay the Company for services rendered through the termination date. The Company generally receives compensation based on a predetermined invoicing schedule relating to specific milestones for that contract.
Amendments to contracts are common. The Company evaluates each amendment which meets the criteria of a contract modification under ASC 606. Each modification is further evaluated to determine whether the contract modification should be accounted for as a separate contract or as a continuation of the original agreement.
The Company accounts for amendments as a separate contract as they meet the criteria under ASC 606-10-25-12.
Pharmacology Study and Other Services
The Company generally enters into contracts with customers to provide oncology services with payments based on fixed-fee arrangements. At contract inception, the Company assesses the services promised in the contracts with customers to identify the performance obligations in the arrangement. The Company's fixed-fee arrangements for oncology services are considered a single performance obligation because the Company provides a highly-integrated service.
The Company recognizes revenue over time using a progress-based input method since there is no single output measure that would fairly depict the transfer of control over the life of the performance obligation. Revenue is recognized for the single performance obligation over time due to the Company's right to payment for work performed to date and the performance does not create an asset with an alternative use. The Company recognizes revenue as portions of the overall performance obligation are completed as this best depicts the progress of the performance obligation.
Incremental Costs of Obtaining a Contract (Sales Commissions) Under ASC 606, the costs of obtaining a contract can be expensed immediately, rather than capitalized and amortized, if the amortization period is one year or shorter. Sales commissions for the Company represent contract costs with a term of one year or less. Therefore, under ASC 606, the Company elected the practical expedient to expense these costs as incurred.
Variable Consideration
In some cases, contracts provide for variable consideration that is contingent upon the occurrence of uncertain future events, such as the success of the initial performance obligation. Variable consideration is estimated at the expected value or at the most likely amount depending on the type of consideration. Estimated amounts are included in the transaction price to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is resolved. The estimate of variable consideration and determination of whether to include estimated amounts in the transaction price are based largely on an assessment of its anticipated performance and all information (historical, current and forecasted) that is reasonably available to the Company.
Trade Receivables, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue
In general, billings and payments are established by contractual provisions including predetermined payment schedules, which may or may not correspond to the timing of the transfer of control of the Company's services under the contract. In general, the Company's intention in its invoicing (payment terms) is to maintain cash neutrality over the life of the contract. Upfront payments, when they occur, are intended to cover certain expenses the Company incurs at the beginning of the contract. Neither the Company nor its customers view such upfront payments and contracted payment schedules as a means of financing. Unbilled services primarily arise when the revenue recognized exceeds the amount billed to the customer. Such situations occur due to divergences between revenue recognition and the invoicing milestones which are based on predetermined payment terms.
Deferred revenue consists of unearned payments received in excess of revenue recognized. As the contracted services are subsequently performed and the associated revenue recognized, the deferred revenue balance is reduced by the amount of the revenue recognized during the period. Deferred revenue is classified as a current liability on the consolidated balance sheet as the Company expects to recognize the associated revenue in less than one year.
|
| Other Non-Current Liabilities |
Other Non-Current Liabilities
Other non-current liabilities represent amounts for uncertain tax positions relating to one of our foreign entities and a financing lease of laboratory equipment in exchange for a lab supplies purchasing commitment.
|
| Cost of Oncology Services |
Cost of Oncology Services Cost of oncology services relates primarily to our TOS business unit. TOS costs consist of direct costs related to laboratory supplies, mice purchases, and maintenance costs for studies completed internally as well as charges from Contract Research Organizations for studies handled externally. Indirect costs include salaries and other payroll related costs of compensation for personnel directly engaged in providing TOS products and services. All costs of performing studies in-house are expensed as incurred. All costs of performing studies from external sources, are expensed when incurred.
|
| Research and Development |
Research and Development Research and development costs represent both costs incurred internally for research and development activities, including personnel costs, mice purchases, and maintenance, as well as costs incurred externally to facilitate research activities, such as tumor tissue procurement and characterization expenses. All research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
|
| Sales and Marketing |
Sales and Marketing Sales and marketing expenses represent costs incurred to promote the Company’s products offered, including salaries, benefits and related costs of our sales and marketing personnel, and represent costs of advertising and other selling and marketing expenses. All sales and marketing costs, including advertising costs, are expensed as incurred.
|
| Earnings Per Share |
Earnings Per Share Basic net income or loss per share is computed by dividing the net income or loss for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed by dividing the net income for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock plus dilutive potential common stock considered outstanding during the period. Such dilutive shares consist of incremental shares that would be issued upon exercise of the Company’s common stock purchase warrants and stock options. Dilutive earnings per share is not presented when it would be antidilutive to do so.
|
| Stock-based Payments |
Stock-based Payments The Company typically recognizes expense for stock-based payments based on the fair value of awards on the date of grant. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate fair value. The Black-Scholes option valuation model was developed for use in estimating the fair value of short-traded options that have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. The option pricing model requires the Company to estimate certain key assumptions such as expected life, volatility, risk free interest rates and dividend yield to determine the fair value of stock-based awards. These assumptions are based on historical information and management judgment. The risk-free interest rate used is based on the United States treasury security rate with a term consistent with the expected term of the award at the time of the grant. Since the Company has limited option exercise history, it has generally elected to estimate the expected life of an award based upon the Securities and Exchange Commission-approved “simplified method” noted under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 with the continued use of this method extended under the provisions of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110. Estimated volatility is based upon the historical volatility of the Company's common stock. The Company does not anticipate paying a dividend, and therefore, no expected dividend yield was used. The Company expenses stock-based payments over the period that the awards are expected to vest. In the event of forfeitures, compensation expense is adjusted. The Company expenses modification charges in the period of modification and, if required, over the remaining period the awards are expected to vest. The Company will report cash flows resulting from tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized from those options (excess tax benefits) as financing cash flows, if they should arise.
|
| Income Taxes |
Income Taxes Deferred income taxes have been provided to show the effect of temporary differences between the recognition of expenses for financial and income tax reporting purposes and between the tax basis of assets and liabilities, and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company assesses the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered through tax planning strategies or from future taxable income, and to the extent that recovery is not likely or there is insufficient operating history, a valuation allowance is established. The Company adjusts the valuation allowance in the period management determines it is more likely than not that net deferred tax assets will or will not be realized. Changes in valuation allowances from period to period are included in the tax provision in the period of change. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company provided a valuation allowance for all net deferred tax assets, as recovery is not more likely than not based on an insufficient history of earnings. The Company reflects tax benefits only if it is more likely than not that we will be able to sustain the tax position, based on its technical merits. If a tax benefit meets this criterion, it is measured and recognized based on the largest amount of benefit that is cumulatively greater than 50% likely to be realized. As of April 30, 2024 and 2023, the Company has recorded $181,000 of liabilities related to uncertain tax positions relative to one of its foreign operations. The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and/or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense.
|
| Accounting Pronouncements Adopted |
Accounting Pronouncements Adopted In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses". This update required immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses ("CECL"). Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The Company adopted this ASU on May 1, 2023 and the adoption did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
|
| X |
- DefinitionOther Non-current Liabilities [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
csbr_OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSales And Marketing Expense, Policy
| Name: |
csbr_SalesAndMarketingExpensePolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for basis of accounting, or basis of presentation, used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS).
| Name: |
us-gaap_BasisOfAccountingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEntity's cash and cash equivalents accounting policy with respect to restricted balances. Restrictions may include legally restricted deposits held as compensating balances against short-term borrowing arrangements, contracts entered into with others, or company statements of intention with regard to particular deposits; however, time deposits and short-term certificates of deposit are not generally included in legally restricted deposits. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478546/942-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy regarding (1) the principles it follows in consolidating or combining the separate financial statements, including the principles followed in determining the inclusion or exclusion of subsidiaries or other entities in the consolidated or combined financial statements and (2) its treatment of interests (for example, common stock, a partnership interest or other means of exerting influence) in other entities, for example consolidation or use of the equity or cost methods of accounting. The accounting policy may also address the accounting treatment for intercompany accounts and transactions, noncontrolling interest, and the income statement treatment in consolidation for issuances of stock by a subsidiary. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConsolidationPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cost of product sold and service rendered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 705
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/705/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfSalesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for fair value measurements of financial and non-financial assets, liabilities and instruments classified in shareholders' equity. Disclosures include, but are not limited to, how an entity that manages a group of financial assets and liabilities on the basis of its net exposure measures the fair value of those assets and liabilities.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for (1) transactions denominated in a currency other than the reporting enterprise's functional currency, (2) translating foreign currency financial statements that are incorporated into the financial statements of the reporting enterprise by consolidation, combination, or the equity method of accounting, and (3) remeasurement of the financial statements of a foreign reporting enterprise in a hyperinflationary economy. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/830/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ForeignCurrencyTransactionsAndTranslationsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for goodwill and intangible assets. This accounting policy also may address how an entity assesses and measures impairment of goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/350-30/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/350-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for leasing arrangement entered into by lessee. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeasesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477798/958-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for costs it has incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483044/730-10-05-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpensePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue from contract with customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for award under share-based payment arrangement. Includes, but is not limited to, methodology and assumption used in measuring cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.C.Q3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.1.Q5)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.3.Q2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.2.Q6)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/718/tableOfContent
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationOptionAndIncentivePlansPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for the use of estimates in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_UseOfEstimates |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Receivables [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services, and Advanced Billings |
Accounts receivable and unbilled services were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 | | April 30, 2022 | | | | | | | | Accounts receivable | $ | 4,886 | | | $ | 3,843 | | | $ | 6,037 | | | Unbilled services | 5,941 | | | 4,993 | | | 4,106 | | | Total accounts receivable and unbilled services | 10,827 | | | 8,836 | | | 10,143 | | | Less: allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses | (1,301) | | | (825) | | | (630) | | | Total accounts receivable, net | $ | 9,526 | | | $ | 8,011 | | | $ | 9,513 | |
|
| Summary of Advanced Billings |
Deferred revenue was as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | | April 30, 2023 | | | | | | | Deferred revenue | $ | 12,094 | | | $ | 12,776 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of receivable, contract asset, and contract liability from contract with customer. Includes, but is not limited to, change in contract asset and contract liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerAssetAndLiabilityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the various types of trade accounts and notes receivable and for each the gross carrying value, allowance, and net carrying value as of the balance sheet date. Presentation is categorized by current, noncurrent and unclassified receivables. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAccountsNotesLoansAndFinancingReceivableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Property and Equipment (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Furniture and fixtures | $ | 246 | | | $ | 246 | | | Computer equipment and software | 2,152 | | | 2,102 | | | Laboratory equipment | 11,506 | | | 10,390 | | | Capitalized software development costs | 1,888 | | | 1,888 | | | Assets in progress | 3 | | | 1,079 | | | Leasehold improvements | 317 | | | 111 | | | | | | | Total property and equipment | 16,112 | | | 15,816 | | | Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (10,391) | | | (8,630) | | | | | | | Property and equipment, net | $ | 5,721 | | | $ | 7,186 | |
|
| Summary of Finance Lease Liability to be Paid |
Future minimum lease payments due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 160 | | | 2026 | 140 | | | 2027 | 80 | | | 2028 | 7 | | | Thereafter | — | | | Total undiscounted liabilities | 387 | | | Less: Imputed interest | (16) | | | Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 371 | | | | | | | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of finance lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to finance lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Disaggregation of Revenue |
The following table represents disaggregated revenue for the twelve months ended April 30, 2024 and 2023: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | Pharmacology services | $ | 47,035 | | | $ | 50,708 | | | | Other TOS revenue | 3,102 | | | 3,046 | | | | Personalized oncology services | 18 | | | 116 | | | | Total oncology services revenue | $ | 50,155 | | | $ | 53,870 | | |
Other TOS revenue represents additional services provided to the Company's pharmaceutical and biotechnology customers, specifically flow cytometry services and SaaS provided via our Lumin Bioinformatics software.
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of disaggregation of revenue into categories depicting how nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Stock-based Payments (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of allocation of share based compensation expense |
Stock-based compensation costs were recorded as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | General and administrative | $ | 706 | | | $ | 505 | | | Sales and marketing | 168 | | | 192 | | | Research and development | 21 | | | 19 | | | TOS cost of sales | 223 | | | 148 | | | | | | | | | | | Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 1,118 | | | $ | 864 | |
|
| Summary of valuation assumptions for stock options |
Black-Scholes weighted average assumptions used to calculate the fair value of options granted during the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Expected term in years | 6 | | 6 | | Risk-free interest rates | 4.0% - 4.5% | | 2.9% - 3.9% | | Volatility | 63% - 64% | | 61% - 63% | | Dividend yield | 0% | | 0% |
|
| Summary of stock option activity |
The Company’s stock options activity and related information as of and for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | | Outstanding, May 1, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | $ | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | Granted | 444,730 | | | — | | | 444,730 | | | 6.08 | | | 9.5 | | $ | — | | | Exercised | (155,449) | | | — | | | (155,449) | | | 2.31 | | | | | | | Canceled | (50,535) | | | — | | | (50,535) | | | 4.82 | | | | | | | Forfeited | (40,750) | | | — | | | (40,750) | | | 6.21 | | | | | | | Expired | (54,166) | | | — | | | (54,166) | | | 12.78 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Outstanding, April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2024 | 1,883,166 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,919,497 | | | 5.04 | | | 5.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable as of April 30, 2024 | 1,481,145 | | | 3,750 | | | 1,484,895 | | | 4.65 | | | 4.2 | | $ | 2,172,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Directors
and
Employees | | Non-
Employees | | Total | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | | Outstanding, May 1, 2022 | 1,617,324 | | | 40,915 | | | 1,658,239 | | | 4.51 | | 4.9 | | $ | 6,131,000 | | | Granted | 186,720 | | | — | | | 186,720 | | | 7.22 | | | 9.4 | | — | | | Exercised | (36,209) | | | — | | | (36,209) | | | 3.21 | | | | | | | Canceled | (13,874) | | | — | | | (13,874) | | | 3.93 | | | | | | | Forfeited | (14,625) | | | — | | | (14,625) | | | 7.94 | | | | | | | Expired | — | | | (4,584) | | | (4,584) | | | 5.40 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Outstanding, April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Vested and expected to vest as of April 30, 2023 | 1,739,336 | | | 36,331 | | | 1,775,667 | | | 4.80 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 2,683,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable as of April 30, 2023 | 1,436,932 | | | 1,875 | | | 1,438,807 | | | 4.35 | | | 3.8 | | $ | 2,681,000 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of allocation of amount expensed and capitalized for award under share-based payment arrangement to statement of income or comprehensive income and statement of financial position. Includes, but is not limited to, corresponding line item in financial statement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure for stock option plans. Includes, but is not limited to, outstanding awards at beginning and end of year, grants, exercises, forfeitures, and weighted-average grant date fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationStockOptionsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the significant assumptions used during the year to estimate the fair value of stock options, including, but not limited to: (a) expected term of share options and similar instruments, (b) expected volatility of the entity's shares, (c) expected dividends, (d) risk-free rate(s), and (e) discount for post-vesting restrictions. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedPaymentAwardStockOptionsValuationAssumptionsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Components of Income Tax Expense |
The components of the (benefit) provision for income taxes are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, 2024 | | | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total | | Current | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (32) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, 2023 | | | Federal | | State | | Foreign | | Total | | Current | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | $ | — | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 68 | |
|
| Summary of Effective Income Tax Rate Reconciliation |
A reconciliation between the Company’s effective tax rate and the United States statutory tax rate for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Federal income tax at statutory rate | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % | | US vs. foreign tax rate difference | (0.1) | | | (0.2) | | | State income tax, net of federal benefit | (2.3) | | | 2.2 | | | Permanent differences | 0.4 | | | (0.5) | | | Increase in uncertain tax position | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | Change in valuation allowance | (18.5) | | | (23.8) | | | | | | | | | | | Income tax expense | 0.5 | % | | (1.3) | % |
|
| Summary of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities |
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities as of April 30, 2024 and 2023 consist of the following (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | As of April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Accrued liabilities | $ | 1,269 | | | $ | 273 | | | Operating leases | 279 | | | 403 | | | Depreciation and amortization | (318) | | | (297) | | | | | | | Stock-based compensation expense | 3,792 | | | 4,024 | | | Capitalized research and development costs | 4,046 | | | 2,597 | | | | | | | Net operating loss carry-forward | 9,038 | | | 9,756 | | | | | | | Total deferred tax assets | 18,106 | | | 16,756 | | | Less: Valuation allowance | (18,106) | | | (16,756) | | | | | | | Net deferred tax asset | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
|
| Summary of Unrecognized Tax Benefits Roll Forward |
The following table indicates the changes to the Company’s uncertain tax positions for the period and years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 in thousands: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | | | Addition based on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | | | Payment made on tax positions related to prior years | — | | | — | | | Addition based on tax positions related to current year | — | | | — | | | | | | | Balance, end of year | $ | 181 | | | $ | 181 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the reconciliation using percentage or dollar amounts of the reported amount of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for the year to the amount of income tax expense that would result from applying domestic federal statutory tax rates to pretax income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 231
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-231
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEffectiveIncomeTaxRateReconciliationTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the change in unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsRollForwardTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Earnings Per Share (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Earnings Per Share [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Earnings Per Share, Basic and Diluted |
A reconciliation of net income and number of shares used in computing basic and diluted earnings per share was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Basic and diluted net loss per share computation (dollars in thousands): | | | | | Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (7,276) | | | $ | (5,335) | | | Weighted Average common shares - basic and diluted | 13,547,604 | | | 13,541,559 | | | Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.54) | | | $ | (0.39) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| Summary of Antidilutive Securities Excluded from Computation of Earnings Per Share |
The following table reflects the total potential stock-based instruments outstanding at April 30, 2024 and 2023 that could have an effect on the future computation of dilution per common share. These figures were not included in the above calculation as, to do so, would be antidilutive: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Stock options | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | | | | | | | | | | | Total common stock equivalents | 1,919,497 | | | 1,775,667 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of securities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS because to do so would increase EPS amounts or decrease loss per share amounts for the period presented, by antidilutive securities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Leases (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Assets and Liabilities |
ROU assets and lease liabilities related to our current operating leases are as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | April 30, 2024 | April 30, 2023 | Operating lease right-of-use assets, net
| 6,252 | | 7,318 | | Current portion of operating lease liabilities
| 1,337 | | 1,208 | | | Non-current portion of operating lease liabilities | 6,093 | | 7,391 | |
|
| Summary of Future Operating Lease Payments |
Future minimum lease payments for operating leases due each fiscal year as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 2,902 | | | 2026 | 2,950 | | | 2027 | 2,916 | | | 2028 | 2,867 | | | 2029 | 2,392 | | | Thereafter | — | | | Total undiscounted liabilities | 14,027 | | | Less: Imputed interest | (6,597) | | | Present value of minimum lease payments | $ | 7,430 | |
|
| Schedule of Components of Lease Expense |
The composition of total lease cost for the years ended April 30, 2024 and 2023 were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended April 30 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | Operating lease costs | $ | 1,680 | | | $ | 1,566 | | | | | | | | | Financing lease costs: | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | 146 | | | 135 | | | | Interest on lease liabilities | 15 | | | 19 | | | | | | | | | Total lease costs | $ | 1,841 | | | $ | 1,720 | | | | | | | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAssets And Liabilities, Lessee [Text Block]
| Name: |
csbr_AssetsAndLiabilitiesLesseeTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of lessee's lease cost. Includes, but is not limited to, interest expense for finance lease, amortization of right-of-use asset for finance lease, operating lease cost, short-term lease cost, variable lease cost and sublease income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCostTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of lessee's operating lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to operating lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of Operating Subsidiaries
| Name: |
csbr_NumberofOperatingSubsidiaries |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of segments reported by the entity. A reportable segment is a component of an entity for which there is an accounting requirement to report separate financial information on that component in the entity's financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 54
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-54
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_NumberOfReportableSegments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=csbr_OperatingSubsidiariesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Narrative (Details)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Apr. 30, 2024
USD ($)
institution
|
Apr. 30, 2023
USD ($)
institution
|
Apr. 30, 2022
USD ($)
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Cash |
$ 2,618,000
|
$ 10,118,000
|
|
| Cash equivalents |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
| Number of major institutions with cash balances | institution |
3
|
3
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (7,276,000)
|
$ (5,335,000)
|
|
| Cash used in operations |
6,137,000
|
(3,972,000)
|
|
| Working capital deficit |
7,900,000
|
|
|
| Accumulated deficit |
84,593,000
|
77,317,000
|
|
| Asset impairment |
0
|
807,000
|
|
| Impairment of goodwill |
0
|
0
|
|
| Unrecognized tax benefits |
181,000
|
181,000
|
$ 181,000
|
| Income tax penalties and interest expense |
0
|
0
|
|
| (Benefit) provision for income tax |
$ (32,000)
|
68,000
|
|
| Provision adjustment |
|
(95,000)
|
|
| Capitalized software development costs |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Finite-lived intangibles |
|
0
|
|
| Minimum |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Useful life |
3 years
|
|
|
| Maximum |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Useful life |
7 years
|
|
|
| Recurring Basis |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Assets, fair value |
$ 0
|
0
|
|
| Liabilities, fair value |
0
|
0
|
|
| Nonrecurring Basis |
|
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Assets, fair value |
0
|
0
|
|
| Liabilities, fair value |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber Of Major Institutions With Cash Balances
| Name: |
csbr_NumberOfMajorInstitutionsWithCashBalances |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of asset recognized for present right to economic benefit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477796/946-210-45-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 210
-Topic 946
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477796/946-210-45-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_Cash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of impairment loss from asset representing future economic benefit arising from other asset acquired in business combination or from joint venture formation or both, that is not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long lived assets held for use (including those held for disposal by means other than sale). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 100
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482078/820-10-55-100
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsHeldForUse |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of financial and nonfinancial obligations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479170/946-210-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) to previously recorded tax expense. Includes, but is not limited to, significant settlements of income tax disputes, and unusual tax positions or infrequent actions taken by the entity, including tax assessment reversal, and IRS tax settlement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxAdjustmentsSettlementsAndUnusualProvisions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementFrequencyAxis=us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementFrequencyAxis=us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementsNonrecurringMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod in which remaining performance obligation is expected to be recognized as revenue, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=csbr_FewContractsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionStartDateAxis=2024-05-01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue - Summary of Accounts Receivable and Unbilled Services (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2022 |
| Receivables [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Accounts receivable |
$ 4,886
|
$ 3,843
|
$ 6,037
|
| Unbilled services |
5,941
|
4,993
|
4,106
|
| Total accounts receivable and unbilled services |
10,827
|
8,836
|
10,143
|
| Less: allowance for doubtful accounts and estimated credit losses |
(1,301)
|
(825)
|
(630)
|
| Total accounts receivable, net |
$ 9,526
|
$ 8,011
|
$ 9,513
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccounts Receivable, Excluding Unbilled Receivables, Current
| Name: |
csbr_AccountsReceivableExcludingUnbilledReceivablesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(3)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableGrossCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479344/326-20-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllowanceForDoubtfulAccountsReceivableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount received for services rendered and products shipped, but not yet billed, for non-contractual agreements due within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer.
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnbilledReceivablesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
Accounts Receivable, Unbilled Services and Deferred Revenue - Summary of Deferred Revenue (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Receivables [Abstract] |
|
|
| Deferred revenue |
$ 12,094
|
$ 12,776
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Property and Equipment - Summary of Property and Equipment (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
$ 16,112
|
$ 15,816
|
| Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(10,391)
|
(8,630)
|
| Property and equipment, net |
$ 5,721
|
$ 7,186
|
| Finance lease, right-of-use asset, statement of financial position [Extensible Enumeration] |
Property and equipment, net
|
Property and equipment, net
|
| Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
$ 246
|
$ 246
|
| Computer equipment and software |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
2,152
|
2,102
|
| Laboratory equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
11,506
|
10,390
|
| Capitalized software development costs |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
1,888
|
1,888
|
| Assets in progress |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
3
|
1,079
|
| Leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total property and equipment |
$ 317
|
$ 111
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates line item in statement of financial position that includes finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated depreciation and amortization, of property, plant, and equipment and finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ComputerEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_OtherMachineryAndEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_AssetUnderConstructionMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_LeaseholdImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
Property and Equipment - Narrative (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2022 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
$ 1,900,000
|
$ 2,200,000
|
|
| Finance lease, depreciation and amortization expenses |
1,700,000
|
2,100,000
|
|
| Assets under finance lease |
1,000,000
|
1,000,000
|
|
| Disposed of lab equipment |
|
0
|
|
| Accumulated depreciation |
10,391,000
|
8,630,000
|
|
| Loss on disposal of equipment |
435,000
|
0
|
|
| Servicing asset |
1,900,000
|
|
|
| Servicing asset at fair value, amount |
|
807,000
|
|
| Hosting arrangement, amortization expense |
0
|
630,000
|
|
| Finance lease, depreciation and amortization expense |
146,000
|
135,000
|
|
| 2022 Finance Lease |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Finance lease costs |
$ 370,000
|
|
$ 370,000
|
| Present value of minimum future obligations interest rate |
3.25%
|
|
|
| Finance lease, depreciation and amortization expense |
$ 75,000
|
72,000
|
|
| Interest on finance lease liability |
6,000
|
8,000
|
|
| 2023 Finance Lease |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Finance lease costs |
$ 368,000
|
368,000
|
|
| Present value of minimum future obligations interest rate |
3.50%
|
|
|
| Finance lease, depreciation and amortization expense |
$ 71,000
|
63,000
|
|
| Interest on finance lease liability |
9,000
|
11,000
|
|
| Finance Leased Assets |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Depreciation |
$ 146,000
|
$ 135,000
|
|
| Capitalized software development costs |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Useful life |
3 years
|
|
|
| Laboratory Equipment |
|
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Disposed of lab equipment |
$ 542,000
|
|
|
| Accumulated depreciation |
107,000
|
|
|
| Loss on disposal of equipment |
$ 435,000
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent Value Minimum Future Obligations Interest Rate
| Name: |
csbr_PresentValueMinimumFutureObligationsInterestRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478777/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period that reflects the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over the assets' useful lives. Includes production and non-production related depreciation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Depreciation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense recognized in the current period that allocates the cost of tangible assets, intangible assets, or depleting assets to periods that benefit from use of the assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 48
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-48
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 49
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-49
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationDepletionAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest paid on finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseInterestPaymentOnLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for capitalized implementation cost from hosting arrangement that is service contract. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-SubTopic 40
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476168/350-40-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_HostingArrangementServiceContractImplementationCostExpenseAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation and amortization from plant, property, and equipment and right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of divestiture of long-lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentDisposals |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate amount of servicing assets that are subsequently measured at fair value and servicing assets that are subsequently measured using the amortization method. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 860
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481260/860-50-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ServicingAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of an asset representing net future revenue from contractually specified servicing fees, late charges, and other ancillary revenues, in excess of future costs related to servicing arrangements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 860
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481229/860-50-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 860
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481260/860-50-45-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 860
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481260/860-50-45-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 860
-SubTopic 50
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481260/860-50-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ServicingAssetAtFairValueAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
csbr_FinanceLeaseAxis=csbr_A2022FinanceLeaseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
csbr_FinanceLeaseAxis=csbr_A2023FinanceLeaseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=csbr_FinanceLeasedAssetsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_EquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments for finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates line item in statement of financial position that includes finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 270
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482964/270-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (ee)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=csbr_PharmacologyServicesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ProductAndServiceOtherMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=csbr_PersonalizedOncologyServicesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionFor an entity that discloses a concentration risk in relation to quantitative amount, which serves as the "benchmark" (or denominator) in the equation, this concept represents the concentration percentage derived from the division. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-21
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-20
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskPercentage1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_EntityWideRevenueMajorCustomerLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_SalesRevenueNetMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_CustomerConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=csbr_OneCustomerMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_AccountsReceivableMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionCollaboration Arrangement Royalty Fee
| Name: |
csbr_CollaborationArrangementRoyaltyFee |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCollaboration Arrangement, Royalty Fee, Percent Of Contract Price
| Name: |
csbr_CollaborationArrangementRoyaltyFeePercentOfContractPrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
csbr_CommitmentsAndContingenciesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense related to royalty payments under a contractual arrangement such as payment for mineral and drilling rights and use of technology or intellectual property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_RoyaltyExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
Stock-based Payments - Narrative (Details) - USD ($)
|
|
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
|
Dec. 12, 2013 |
Feb. 18, 2011 |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2021 |
Mar. 29, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2022 |
Mar. 01, 2021 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
$ 1,118,000
|
$ 864,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Grants in period, weighted average grant date fair value (in dollars per share) |
|
|
$ 3.75
|
$ 4.31
|
|
|
|
|
| Share repurchase program, authorized amount |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 5,000,000
|
|
|
| Treasury stock (in shares) |
|
|
120,300
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Treasury stock average price (in dollars per share) |
|
|
$ 5.73
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Treasury stock approximate value |
|
|
$ 708,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Remaining repurchase amount |
|
|
$ 4,300,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Equity Incentive Plan 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of shares available for grant (in shares) |
|
|
1,300,000
|
|
|
|
2,000,000
|
|
| Expiration term of awards |
|
|
10 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Strike price as percent of market value |
|
|
100.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Equity Incentive Plan 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Number of shares available for grant (in shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0
|
| Expiration term of awards |
|
|
10 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Strike price as percent of market value |
|
|
100.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Equity Incentive Plan 2010 | Maximum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares granted, net of forfeitures (in shares) |
|
30,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Vested percent |
25.00%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Independent Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Term of option to purchase |
5 years
|
|
|
|
10 years
|
|
|
|
| Stock options award shares to purchase common stock (in shares) |
8,333
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual base compensation mount |
|
|
|
|
$ 100,000
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Board of Directors Chairman |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Term of option to purchase |
5 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual base compensation mount |
|
|
|
|
150,000
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Chairperson of a Committee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Term of option to purchase |
5 years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock options award shares to purchase common stock (in shares) |
16,667
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock option award shares to purchase unregistered common stock (in shares) |
1,667
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Maximum | Independent Directors | Options and Cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual base compensation mount |
|
|
|
|
35,000
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Maximum | Chairperson of a Committee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual base compensation mount |
|
|
|
|
120,000
|
|
|
|
| Director Compensation Plan | Minimum | Chairperson of a Committee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Annual base compensation mount |
|
|
|
|
$ 110,000
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-Based Compensation, Annual Base Compensation Amount
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationAnnualBaseCompensationAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage of stock vested for share based compensation arrangement by share based payment award options during the period.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Term of Option to Purchase
| Name: |
csbr_SharebasedCompensationArrangementbySharebasedPaymentAwardTermofOptiontoPurchase |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares to purchase common stock option awards during the reporting period.
| Name: |
csbr_StockOptionsAwardSharesToPurchaseCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares to purchase of unregistered common stock option awards during the reporting period.
| Name: |
csbr_StockOptionsAwardSharesToPurchaseUnregisteredCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount authorized for purchase of share under share repurchase plan. Includes, but is not limited to, repurchase of stock and unit of ownership. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481520/505-30-50-4
| Name: |
srt_StockRepurchaseProgramAuthorizedAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
srt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe difference between the maximum number of shares (or other type of equity) authorized for issuance under the plan (including the effects of amendments and adjustments), and the sum of: 1) the number of shares (or other type of equity) already issued upon exercise of options or other equity-based awards under the plan; and 2) shares (or other type of equity) reserved for issuance on granting of outstanding awards, net of cancellations and forfeitures, if applicable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAvailableForGrant |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNet number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average grant-date fair value of options granted during the reporting period as calculated by applying the disclosed option pricing methodology. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod from grant date that an equity-based award expires, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardExpirationPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchase price of common stock expressed as a percentage of its fair value.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardPurchasePriceOfCommonStockPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount remaining authorized for purchase of share under share repurchase plan. Includes, but is not limited to, repurchase of stock and unit of ownership.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchaseProgramRemainingAuthorizedRepurchaseAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal cost of shares repurchased divided by the total number of shares repurchased. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockAcquiredAverageCostPerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares that have been repurchased during the period and are being held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockSharesAcquired |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the cost of common and preferred stock that were repurchased during the period. Recorded using the cost method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockValueAcquiredCostMethod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=csbr_EquityIncentivePlan2021Member |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=csbr_EquityIncentivePlan2010Member |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=csbr_DirectorCompensationPlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=csbr_IndependentDirectorsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=csbr_ChairpersonOfACommitteeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
csbr_TriggeringEventAxis=csbr_OptionsAndCashMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=csbr_TranslationalOncologySolutionsCostOfSalesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated dividend rate (a percentage of the share price) to be paid (expected dividends) to holders of the underlying shares over the option's term. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedDividendRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated measure of the maximum percentage by which a share price is expected to fluctuate during a period. Volatility also may be defined as a probability-weighted measure of the dispersion of returns about the mean. The volatility of a share price is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rates of return on the share over a specified period. That is the same as the standard deviation of the differences in the natural logarithms of the stock prices plus dividends, if any, over the period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedVolatilityRateMaximum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated measure of the minimum percentage by which a share price is expected to fluctuate during a period. Volatility also may be defined as a probability-weighted measure of the dispersion of returns about the mean. The volatility of a share price is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rates of return on the share over a specified period. That is the same as the standard deviation of the differences in the natural logarithms of the stock prices plus dividends, if any, over the period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedVolatilityRateMinimum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum risk-free interest rate assumption that is used in valuing an option on its own shares.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsRiskFreeInterestRateMaximum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe minimum risk-free interest rate assumption that is used in valuing an option on its own shares.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsRiskFreeInterestRateMinimum |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExpected term of award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Stock-based Payments - Summary of Stock Option Activity (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2022 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Options, Outstanding [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance (in shares) |
1,775,667
|
1,658,239
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
444,730
|
186,720
|
|
| Exercised (in shares) |
(155,449)
|
(36,209)
|
|
| Canceled (in shares) |
(50,535)
|
(13,874)
|
|
| Forfeited (in shares) |
(40,750)
|
(14,625)
|
|
| Expired (in shares) |
(54,166)
|
(4,584)
|
|
| Outstanding, Ending Balance (in shares) |
1,919,497
|
1,775,667
|
1,658,239
|
| Vested and expected to vest (in shares) |
1,919,497
|
1,775,667
|
|
| Exercisable (in shares) |
1,484,895
|
1,438,807
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Options, Outstanding, Weighted Average Exercise Price [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Outstanding, Beginning Balance (in usd per share) |
$ 4.80
|
$ 4.51
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Granted (in usd per share) |
6.08
|
7.22
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Exercised (in usd per share) |
2.31
|
3.21
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Canceled (in usd per share) |
4.82
|
3.93
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Forfeited (in usd per share) |
6.21
|
7.94
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Expired (in usd per share) |
12.78
|
5.40
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Outstanding, Ending Balance (in usd per share) |
5.04
|
4.80
|
$ 4.51
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Vested and Expected to Vest (in usd per share) |
5.04
|
4.80
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Exercisable (in usd per share) |
$ 4.65
|
$ 4.35
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term, Outstanding, Beginning Balance (in years) |
|
4 years 7 months 6 days
|
4 years 10 months 24 days
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life, Granted |
9 years 6 months
|
9 years 4 months 24 days
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term, Outstanding, Ending Balance (in years) |
5 years 2 months 12 days
|
4 years 7 months 6 days
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years), Vested and expected to vest |
5 years 2 months 12 days
|
4 years 7 months 6 days
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years), Exercisable |
4 years 2 months 12 days
|
3 years 9 months 18 days
|
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Outstanding, Beginning Balance |
$ 2,683
|
$ 6,131
|
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Granted |
0
|
0
|
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Outstanding, Ending Balance |
2,172
|
2,683
|
$ 6,131
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Vested and expected to vest |
2,172
|
2,683
|
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Exercisable |
$ 2,172
|
$ 2,681
|
|
| Directors and Employees |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Options, Outstanding [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance (in shares) |
1,739,336
|
1,617,324
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
444,730
|
186,720
|
|
| Exercised (in shares) |
(155,449)
|
(36,209)
|
|
| Canceled (in shares) |
(50,535)
|
(13,874)
|
|
| Forfeited (in shares) |
(40,750)
|
(14,625)
|
|
| Expired (in shares) |
(54,166)
|
0
|
|
| Outstanding, Ending Balance (in shares) |
1,883,166
|
1,739,336
|
1,617,324
|
| Vested and expected to vest (in shares) |
1,883,166
|
1,739,336
|
|
| Exercisable (in shares) |
1,481,145
|
1,436,932
|
|
| Non- Employees |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Options, Outstanding [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance (in shares) |
36,331
|
40,915
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
|
| Exercised (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
|
| Canceled (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
|
| Forfeited (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
|
| Expired (in shares) |
0
|
(4,584)
|
|
| Outstanding, Ending Balance (in shares) |
36,331
|
36,331
|
40,915
|
| Vested and expected to vest (in shares) |
36,331
|
36,331
|
|
| Exercisable (in shares) |
3,750
|
1,875
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionIntrinsic value of equity-based compensation awards granted.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOptionsAggregateIntrinsicValueGranted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards granted, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOptionsGrantInPeriodWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsCanceledInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards granted, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantedWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options that were terminated.
| Name: |
csbr_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsCanceledInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares into which fully or partially vested stock options outstanding as of the balance sheet date can be currently converted under the option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted-average price as of the balance sheet date at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance on vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options or other stock instruments for which the right to exercise has lapsed under the terms of the plan agreements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExpirationsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which the current fair value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of options outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePriceRollforward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which current fair value of underlying stock exceeds exercise price of fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingAggregateIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding that can be converted into shares under option plan. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average exercise price, at which grantee can acquire shares reserved for issuance, for fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which option holders acquired shares when converting their stock options into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options of the plan that expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExpirationsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options that were terminated. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average per share amount at which grantees can acquire shares of common stock by exercise of options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of difference between fair value of the underlying shares reserved for issuance and exercise price of vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableIntrinsicValue1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable or convertible, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=csbr_DirectorsAndEmployeesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=csbr_NonEmployeesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current foreign income tax expense (benefit) pertaining to income (loss) from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentForeignTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current state and local tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current regional, territorial, and provincial tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
v3.24.2
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes - Summary of Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Accrued liabilities |
$ 1,269
|
$ 273
|
| Operating leases |
279
|
403
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
(318)
|
(297)
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
3,792
|
4,024
|
| Capitalized research and development costs |
4,046
|
2,597
|
| Net operating loss carry-forward |
9,038
|
9,756
|
| Total deferred tax assets |
18,106
|
16,756
|
| Less: Valuation allowance |
(18,106)
|
(16,756)
|
| Net deferred tax asset |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, Tax Deferred Expense, Operating Leases
| Name: |
csbr_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseOperatingLeases |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Liabilities, Capitalized Research and Development Costs
| Name: |
csbr_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesCapitalizedResearchAndDevelopmentCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax liability attributable to deductible temporary differences from depreciation and amortization.
| Name: |
csbr_DeferredTaxLiabilityDeferredExpenseDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allocation of valuation allowances and deferred tax liability, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible differences and carryforwards, without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsLiabilitiesNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from share-based compensation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsShareBasedCompensationCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from accrued liabilities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseReservesAndAccrualsAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes - Narrative (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
Apr. 30, 2022 |
Apr. 30, 2013 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, valuation allowance |
$ 18,106
|
$ 16,756
|
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, valuation allowance, increase |
1,400
|
1,300
|
|
|
| Operating loss carryforwards |
38,600
|
41,300
|
|
|
| Operating loss, limitations on use |
432
|
|
|
$ 12,000
|
| Unrecognized tax benefits |
$ 181
|
$ 181
|
$ 181
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionOperating Loss Carryforwards, Limitations On Use, Amount
| Name: |
csbr_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLimitationsOnUseAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
csbr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the valuation allowance for a specified deferred tax asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowanceDeferredTaxAssetChangeInAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReconciliationOfUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsExcludingAmountsPertainingToExaminedTaxReturnsRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from settlements with taxing authorities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsDecreasesResultingFromSettlementsWithTaxingAuthorities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions that have been or will be taken in current period tax return. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromCurrentPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions taken in prior period tax returns. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 217
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482663/740-10-55-217
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromPriorPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Earnings Per Share - Calculations of Earnings Per Share (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share computation (dollars in thousands): |
|
|
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ (7,276)
|
$ (5,335)
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic (in shares) |
13,547,604
|
13,541,559
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, diluted (in shares) |
13,547,604
|
13,541,559
|
| Basic net (loss) per share (in usd per share) |
$ (0.54)
|
$ (0.39)
|
| Diluted net (loss) per share (in usd per share) |
$ (0.54)
|
$ (0.39)
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147476176/805-60-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 323
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478666/740-323-65-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479168/946-830-55-10
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479105/946-220-45-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147477250/944-220-S99-1
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-1
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479134/946-220-S99-3
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 34: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478524/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasicAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.2
Earnings Per Share - Summary of Potentially Dilutive Stock-based Instruments (Details) - shares
|
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total common stock equivalents |
1,919,497
|
1,775,667
|
| Stock options |
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total common stock equivalents |
1,919,497
|
1,775,667
|
| X |
- DefinitionSecurities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) or earnings per unit (EPU) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS or EPU because to do so would increase EPS or EPU amounts or decrease loss per share or unit amounts for the period presented. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147483014/272-10-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147482987/272-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfStockLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareByAntidilutiveSecuritiesAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockOptionMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=csbr_BoardMemberOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
Leases - Narrative (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Apr. 30, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating leases, rent expense |
$ 1,800
|
$ 1,900
|
| Weighted average remaining lease term (in years) |
4 years 8 months 12 days
|
5 years 8 months 12 days
|
| Weighted average discount rate, percent |
5.88%
|
5.82%
|
| Corporate Headquarters |
|
|
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating leases, rent expense |
$ 77
|
$ 83
|
| Rockville, MD |
|
|
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating leases, rent expense |
1,700
|
1,700
|
| Milan, Italy |
|
|
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating leases, rent expense |
$ 50
|
$ 98
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-7A
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeaseDescriptionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating lease expense. Excludes sublease income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for operating lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RealEstateAndAccumulatedDepreciationDescriptionOfPropertyAxis=csbr_CorporateHeadquartersMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RealEstateAndAccumulatedDepreciationDescriptionOfPropertyAxis=csbr_RockvilleMDMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RealEstateAndAccumulatedDepreciationDescriptionOfPropertyAxis=csbr_MilanItalyMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
Leases - Future Minimum Lease Payments (Details)
$ in Thousands |
Apr. 30, 2024
USD ($)
|
| Lessee, Operating Lease, Liability, Payment, Due [Abstract] |
|
| 2025 |
$ 2,902
|
| 2026 |
2,950
|
| 2027 |
2,916
|
| 2028 |
2,867
|
| 2029 |
2,392
|
| Thereafter |
0
|
| Total undiscounted liabilities |
14,027
|
| Less: Imputed interest |
(6,597)
|
| Present value of minimum lease payments |
$ 7,430
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease due after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilitiesPaymentsDueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest expense on finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseInterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lease cost recognized by lessee for lease contract. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of single lease cost, calculated by allocation of remaining cost of lease over remaining lease term. Includes, but is not limited to, single lease cost, after impairment of right-of-use asset, calculated by amortization of remaining right-of-use asset and accretion of lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org/1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
Champions Oncology (NASDAQ:CSBR)
Historical Stock Chart
From Dec 2024 to Jan 2025
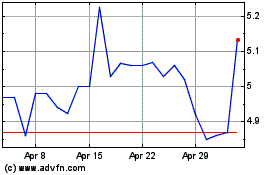
Champions Oncology (NASDAQ:CSBR)
Historical Stock Chart
From Jan 2024 to Jan 2025