0001053369
false
FY
NV
NJ
2010-09-30
2025-08-31
0001053369
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
2022-09-30
0001053369
2023-06-20
0001053369
2023-03-31
0001053369
2022-03-31
0001053369
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
ELTP:SeriesJPreferredStockMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
ELTP:SeriesJPreferredStockMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
ELTP:SeriesJPreferredStockMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
ELTP:SeriesJPreferredStockMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
ELTP:SeriesJPreferredStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NewDrugApplicationsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NewDrugApplicationsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:AbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:AbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:LandBuildingsAndImprovementsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:LandBuildingsAndImprovementsMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LaboratoryManufacturingWarehouseAndTransportationEquipmentMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LaboratoryManufacturingWarehouseAndTransportationEquipmentMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:OfficeEquipmentAndSoftwareMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:OfficeEquipmentAndSoftwareMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PatentApplicationCostsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PatentApplicationCostsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:ANDAAcquisitionCostsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:ANDAAcquisitionCostsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PatentApplicationCostsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PatentApplicationCostsMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:ANDAAcquisitionCostsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:ANDAAcquisitionCostsMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsSeriesANotesMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NJEDABondsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NJEDABondsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NJEDABondsMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NJEDABondsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsSeriesANotesMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsSeriesANotesMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsCurrentMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsCurrentMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsNoncurrentMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NjedaBondsNoncurrentMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NJEDABondsMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
us-gaap:PrimeRateMember
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
2022-04-01
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember
2022-04-01
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember
us-gaap:PrimeRateMember
2022-04-01
2022-04-02
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMember
2023-06-02
0001053369
srt:BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMember
2023-06-02
2023-06-02
0001053369
ELTP:EastWestBankMember
us-gaap:MortgagesMember
2022-06-28
2022-07-02
0001053369
ELTP:EWBMortgageLoanMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember
2022-06-28
2022-07-02
0001053369
srt:MinimumMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:MinimumMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
srt:MaximumMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:MaximumMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:LoansPayableMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:TAGIPharmaMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:TAGIPharmaMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:WarehouseMember
us-gaap:PropertySubjectToOperatingLeaseMember
2010-07-01
0001053369
srt:WarehouseMember
us-gaap:PropertySubjectToOperatingLeaseMember
ELTP:July2014ModificationAgreementMember
2014-07-31
0001053369
ELTP:PompanoOfficeLeaseMember
us-gaap:PropertySubjectToOperatingLeaseMember
2020-10-31
0001053369
2020-10-01
2020-10-31
0001053369
ELTP:PompanoOfficeLeaseMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PompanoOfficeLeaseMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2017-04-27
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:MinimumMember
2019-12-04
0001053369
srt:MaximumMember
2019-12-04
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2020-08-24
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
srt:ChiefExecutiveOfficerMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2017-04-28
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2017-04-28
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember
2017-04-28
2017-04-28
0001053369
ELTP:NasratHakimMember
ELTP:SeriesJWarrantsMember
2017-04-28
2017-04-28
0001053369
ELTP:SeriesJWarrantsMember
2017-04-28
2017-04-28
0001053369
ELTP:SeriesJWarrantsMember
2017-04-28
0001053369
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputSharePriceMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputSharePriceMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member
us-gaap:WarrantMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:LincolnParkMember
2020-07-08
2020-07-08
0001053369
ELTP:LincolnParkMember
2020-07-08
0001053369
srt:DirectorMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
srt:DirectorMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PresidentAndChiefExecutiveOfficerAndOtherEmployeesMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PresidentAndChiefExecutiveOfficerAndOtherEmployeesMember
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PresidentAndChiefExecutiveOfficerAndOtherEmployeesMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
2020-04-01
2021-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomersMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerOneMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerTwoMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomersMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerOneMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerTwoMember
us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomersMember
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomersMember
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerOneMember
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:CustomerTwoMember
us-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember
us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SuppliersMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SuppliersMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SupplierOneMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SupplierTwoMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SupplierThreeMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:PurchasesMember
us-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember
ELTP:SupplierFourMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:BusinessSegmentMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
ELTP:BusinessSegmentMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember
2022-04-01
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember
2021-04-01
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
2022-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember
2023-03-31
0001053369
us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember
2022-03-31
iso4217:USD
xbrli:shares
iso4217:USD
xbrli:shares
xbrli:pure
utr:sqft
ELTP:Integer
UNITED
STATES
SECURITIES
AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON,
D.C. 20549
FORM
10-K
☒
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
FOR
THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED MARCH 31, 2023
OR
☐
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
COMMISSION
FILE NUMBER: 001-15697
| ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. |
| (Exact
Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter) |
| NEVADA |
|
22-3542636 |
(State
or other jurisdiction of
incorporation
or organization) |
|
(I.R.S.
Employer
Identification
No.) |
165
LUDLOW AVENUE
NORTHVALE,
NEW JERSEY |
|
07647 |
| (Address
of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip
Code) |
| (201)
750-2646 |
| (Registrant’s
telephone number, including area code) |
Securities
registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
| Title
of each class |
|
Trading
Symbol |
|
Name
of each exchange on which registered |
| Common
Stock, par value $0.001 per share |
|
ELTP |
|
OTCQB |
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act
of 1934. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2)
has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule
405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant
was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company,
or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller
reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large
accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated
filer |
☐ |
| Non-accelerated
filer |
☒ |
Smaller
reporting company |
☒ |
| |
|
Emerging
growth company |
☐ |
If
an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying
with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness
of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C.7262(b)) by the registered
public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate
by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously
issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements
that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during
the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The
aggregate market value of Common Stock held by non-affiliates at September 30, 2022, the last business day of the registrant’s
most recently completed second fiscal quarter was $40,556,603.
The
number of shares of the registrant’s Common Stock outstanding as of June 20, 2023 was 1,013,915,081.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE: Portions of the Proxy Statement for
the registrant’s 2023 Annual Meeting of Shareholders which is to be filed subsequent to the date hereof are incorporated by reference
into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
FORWARD
LOOKING STATEMENTS
This
Annual Report on Form 10-K and the documents incorporated herein contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning
of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Such forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties
and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of the Company, or industry results, to be materially
different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. When used in
this report, statements that are not statements of current or historical fact are forward-looking statements, and include, without limitation,
estimated future results of operations, estimates of future revenues, future expenses, future net income and future net income per share,
as well as statements regarding future financing activities, the impact of the novel strain of coronavirus referred to as COVID-19 on
the health and welfare of our employees and on our business, including any response to COVID-19 such as anticipated return to historical
purchasing decisions by customers, the economic impact of COVID-19, changes in consumer spending, decisions to engage in certain medical
procedures, future governmental orders that could impact our operations and the ability of our manufacturing facilities and suppliers
to fulfill their obligations to us, and any other statements that refer to our expected, estimated or anticipated future results. Without
limiting the foregoing, the words “plan”, “intend”, “may,” “will,” “expect,”
“believe”, “could,” “would”, “continue”, “pursue”, “anticipate,”
“estimate,” “forecast”, “contemplate”, “envisage”, “project”, or “continue”
or the negative other variations thereof, or similar expressions or other variations or comparable terminology are intended to identify
such forward-looking statements. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in this report regarding our financial
position, business strategy and plans or objectives for future operations are forward-looking statements. Without limiting the broader
description of forward-looking statements above, we specifically note, without limitation, that statements regarding the preliminary
nature of the clinical program results and the potential for further product development, that involve known and unknown risks, delays,
uncertainties and other factors not under our control, the requirement of substantial future testing, clinical trials, regulatory reviews
and approvals by the Food and Drug Administration and other regulatory authorities prior and subsequent to the commercialization of products
under development and those currently related to commercial operations, our ability to fund all of our activities and our ability to
manufacture and sell any products, gain market acceptance earn a profit from sales or licenses of any drugs or our ability to discover
new drugs in the future are all forward-looking in nature.
In
addition, because these statements reflect our current views concerning future events, these forward-looking statements involve risks
and uncertainties including, without limitation, the risks related to the impact of COVID-19 (such as, without limitation, the scope
and duration of the pandemic and the resulting economic crisis and levels of unemployment, governmental actions and restrictive measures
implemented in response, material delays and cancellations of certain medical procedures, potential manufacturing and supply chain disruptions
and other potential impacts to the business as a result of COVID-19) and the other risks and uncertainties more fully described under
the caption “Risk Factors” in Part I, Item 1A of this document. These risks and uncertainties, many of which are outside
of our control, and any other risks and uncertainties that we are not currently able to predict or identify, individually or in the aggregate,
could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows and could cause our actual
results to differ materially and adversely from those expressed in forward-looking statements contained or incorporated by reference
in this document. Additionally, the prolonged impact of COVID-19 could heighten the impact of one or more of such risk factors.
We
do not undertake any obligation to update our forward-looking statements after the date of this document for any reason, even if new
information becomes available or other events occur in the future, except as may be required under applicable securities law. You are
advised to consult any further disclosures we make on related subjects in our reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission
(the “SEC”). Also, please note that in Part 1, Item 1A, we provide a cautionary discussion of the risks, uncertainties and
possibly inaccurate assumptions relevant to our business. These are factors that, individually or in the aggregate, we think could cause
our actual results to differ materially from expected and historical results. We note these factors for investors as permitted by Section
27A of the Securities Act and Section 27E of the Exchange Act. You are notified and should understand that it is not possible to predict
or identify all such factors and consequently should not consider this to be a complete, all-inclusive discussion of all potential risks
or uncertainties.
Table
of Contents
PART I
ITEM
1. BUSINESS
General
Elite
Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Company”, “Elite”, “Elite Pharmaceuticals”, the
“registrant”, “we”, “us” or “our”) was incorporated on October 1, 1997 under the laws
of the State of Delaware, and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Elite Laboratories, Inc. (“Elite Labs”), was incorporated on August
23, 1990 under the laws of the State of Delaware. On January 5, 2012, Elite Pharmaceuticals was reincorporated under the laws of the
State of Nevada.
We
are a specialty pharmaceutical company principally engaged in the development and manufacture of oral, controlled-release products, and
the manufacture of generic pharmaceuticals. Our strategy includes developing generic versions of controlled-release drug products with
high barriers to entry.
We
occupy manufacturing, warehouse, laboratory and office space at 165 Ludlow Avenue and 135 Ludlow Avenue in Northvale, NJ (the “Northvale
Facility”). The Northvale Facility operates under Current Good Manufacturing Practice (“cGMP”) and is a United States
Drug Enforcement Agency (“DEA”) registered facility for research, development, and manufacturing. Our website address is
www.elitepharma.com.
Strategy
We
focus our efforts on the following areas: (i) manufacturing of a line of generic pharmaceutical products with approved Abbreviated New
Drug Applications (“ANDAs”); (ii) development of additional generic pharmaceutical products; (iii) development of the other
product candidates in our pipeline including products co-developed with partners; (iv) commercial exploitation of our product candidates either by sales
under our own label, license and the collection of royalties, or through the manufacture of our formulations; and (v) development of
new products for sale under our own label, and the expansion of our licensing agreements with other pharmaceutical companies, including
co-development projects, joint ventures and other collaborations.
We
continue to evaluate opportunities for the development of various types of drug products, including branded drug products which require
New Drug Applications (“NDAs”) under Section 505(b)(1) or 505(b)(2) of the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration
Act of 1984 (the “Drug Price Competition Act”) as well as generic drug products which require ANDAs.
We
believe that our business strategy enables us to reduce its risk by having a diverse product portfolio.
Commercial
Products
We
own, license, manufacture, sell or receive royalties from the following products currently being sold commercially:
| Product |
|
Branded
Product Equivalent |
|
Therapeutic
Category |
|
Launch
Date |
| Phentermine
HCl 37.5mg tablets (“Phentermine 37.5mg”) |
|
Adipex-P® |
|
Bariatric |
|
April
2011 |
| Phendimetrazine
Tartrate 35mg tablets (“Phendimetrazine 35mg”) |
|
Bontril® |
|
Bariatric |
|
November
2012 |
| Phentermine
HCl 15mg and 30mg capsules (“Phentermine 15mg” and “Phentermine 30mg”) |
|
Adipex-P® |
|
Bariatric |
|
April
2013 |
| Naltrexone
HCl 50mg tablets (“Naltrexone 50mg”) |
|
Revia® |
|
Pain |
|
September
2013 |
| Isradipine
2.5mg and 5mg capsules (“Isradipine 2.5mg” and “Isradipine 5mg”) |
|
N/A |
|
Cardiovascular |
|
January
2015 |
| Trimipramine
Maleate Immediate Release 25mg, 50mg and 100mg capsules (“Trimipramine 25mg”, “Trimipramine 50mg”, “Trimipramine
100mg”) |
|
Surmontil® |
|
Antidepressant |
|
May
2017 |
| Dextroamphetamine
Saccharate, Amphetamine Aspartate, Dextroamphetamine Sulfate, Amphetamine Sulfate Immediate Release 5mg, 7.5mg, 10mg, 12.5mg, 15mg,
20mg and 30mg tablets (“Amphetamine IR 5mg”, “Amphetamine IR 7.5mg”, “Amphetamine IR 10mg”, “Amphetamine
IR 12.5mg”, “Amphetamine IR 15mg”, “Amphetamine IR 20mg” and “Amphetamine IR 30mg”) |
|
Adderall® |
|
Central
Nervous System (“CNS”) Stimulant |
|
April
2019 |
| Dantrolene
Sodium Capsules 25mg, 50mg and 100mg (“Dantrolene 25mg”, “Dantrolene 50mg”, “Dantrolene 100mg”) |
|
Dantrium® |
|
Muscle
Relaxant |
|
June
2019 |
| Dextroamphetamine
Saccharate, Amphetamine Aspartate, Dextroamphetamine Sulfate, Amphetamine Sulfate Extended Release 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 20mg, 25mg, and
30mg capsules (“Amphetamine ER 5mg”, “Amphetamine ER 10mg”, “Amphetamine ER 15mg”, “Amphetamine
ER 20mg”, “Amphetamine ER 25mg”, and “Amphetamine ER 30mg”) |
|
Adderall
XR® |
|
Central
Nervous System (“CNS”) Stimulant |
|
March
2020 |
| Loxapine
Succinate 5mg, 10mg, 25mg and 50gm capsules (“Loxapine 5mg”, “Loxapine 10mg”, “Loxapine 25mg”,
and Loxapine 50mg”) |
|
Loxapine® |
|
Antipsychotic |
|
May
2021 |
Note:
Phentermine 37.5mg is also referred to as “Phentermine Tablets”. Phentermine 15mg and Phentermine 30mg are collectively and
individually referred to as “Phentermine Capsules”. Phendimetrazine 35mg is also referred to as “Phendimetrazine Tablets”.
Naltrexone 50mg is also referred to as “Naltrexone Tablets”. Isradipine 2.5mg and Isradipine 5mg are collectively and individually
referred to as “Isradipine Capsules”. Trimipramine 25mg, Trimipramine 50mg, and Trimipramine 100mg are collectively and individually
referred to as “Trimipramine Capsules”. Amphetamine IR 5mg, Amphetamine IR 7.5mg, Amphetamine IR 10mg, Amphetamine IR 12.5mg,
Amphetamine IR 15mg, Amphetamine IR 20mg and Amphetamine IR 30mg are collectively and individually referred to as “Amphetamine
IR Tablets”. Dantrolene 25mg, Dantrolene 50mg and Dantrolene 100mg are collectively and individually referred to as “Dantrolene
Capsules”. Amphetamine ER 5mg, Amphetamine ER 10mg, Amphetamine ER 15mg. Amphetamine ER 20mg, Amphetamine ER 25mg and Amphetamine
ER 30mg are collectively and individually referred to as “Amphetamine ER Capsules”. Loxapine 5gm, Loxapine 10mg, Loxapine
25mg and Loxapine 50mg are collectively and individually referred to as “Loxapine Capsules”.
Phentermine
37.5mg
The
approved ANDA for Phentermine 37.5mg was acquired pursuant to an asset purchase agreement with Epic Pharma LLC (“Epic”) dated
September 10, 2010 (the “Phentermine Purchase Agreement”).
Sales
and marketing rights for Phentermine 37.5mg are included in the licensing agreement between the Company and Precision Dose Inc. (“Precision
Dose”) dated September 10, 2010 (the “Precision Dose License Agreement”). Please see the section below titled “Precision
Dose License Agreement” for further details of this agreement.
Phentermine
37.5mg is currently being manufactured by Elite and distributed by TAGI under the Precision Dose License Agreement.
Phendimetrazine
Tartrate 35mg
The
ANDA for Phendimetrazine was acquired by Elite in 2013.
Phendimetrazine
35mg is currently a commercial product being manufactured at the Northvale Facility and distributed by Elite Labs.
Phentermine
15mg and Phentermine 30mg
Phentermine
15mg capsules and Phentermine 30mg capsules were developed by the Company, with Elite receiving approval from the United States Food
and Drug Administration (“FDA”) of the related ANDA in September 2012.
Sales
and marketing rights for Phentermine 15mg and Phentermine 30mg are included in the Precision Dose License Agreement. Please see the section
below titled “Precision Dose License Agreement” for further details of this agreement.
Phentermine
15mg and Phentermine 30mg are currently being manufactured by Elite and distributed by TAGI under the Precision Dose License Agreement.
Phentermine 37.5mg
The ANDA for Phentermine was acquired by Elite in 2013.
Phentermine 37.5mg is currently a commercial product being manufactured at the Northvale Facility and distributed
by Elite Labs.
Naltrexone
50mg
The
ANDA for Naltrexone 50mg was acquired by Elite in 2010.
Sales
and marketing rights for Naltrexone 50mg are included in the Precision Dose License Agreement. Please see the section below titled “Precision
Dose License Agreement” for further details of this agreement. Naltrexone 50mg is currently being manufactured by Elite and
distributed by TAGI under the Precision Dose License Agreement.
Isradipine
2.5mg and Isradipine 5mg
The
approved ANDAs for Isradipine 2.5mg and Isradipine 5mg were acquired by Elite in 2013
Isradipine
2.5mg and Isradipine 5mg are commercial products being manufactured by Elite at the Northvale Facility and distributed by
Elite Labs.
Trimipramine
25mg, Trimipramine 50mg and Trimipramine 100mg
The
approved ANDA for Trimipramine was acquired by Elite in 2017.
Trimipramine
25mg, Trimipramine 50mg and Trimipramine 100mg are a commercial product being manufactured by Elite at the Northvale Facility
and distributed by Elite Labs.
Amphetamine
IR Tablets
On
December 10, 2018, the Company received approval from the FDA for Amphetamine IR Tablets, a generic version of Adderall®, an immediate-release
mixed salt of a single entity Amphetamine product (Dextroamphetamine Saccharate, Amphetamine Aspartate, Dextroamphetamine Sulfate, Amphetamine
Sulfate) with strengths of 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 12.5 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg tablets. The product is a central nervous system stimulant
and is indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Narcolepsy.
Amphetamine
IR Tablets are currently a commercial product being manufactured by Elite and distributed by Elite Labs.
Dantrolene
Capsules
The
approved ANDAs for Dantrolene 25mg, Dantrolene 50mg and Dantrolene 100mg were acquired by Elite in 2013. Dantrolene Capsules are a commercial product being manufactured by Elite at the Northvale Facility and distributed by Elite Labs.
Amphetamine
ER Capsules
On
December 12, 2019, the Company received approval from the FDA for Amphetamine ER Capsules, a generic version of Adderall XR®, an
extended-release mixed salt of a single entity Amphetamine product (Dextroamphetamine Saccharate, Amphetamine Aspartate, Dextroamphetamine
Sulfate, Amphetamine Sulfate) with strengths of 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 20mg, 25mg, and 30 mg tablets. The product is a central nervous system
stimulant and is indicated for the treatment of ADHD and Narcolepsy.
Amphetamine
ER Capsules are currently a commercial product being manufactured by Elite and distributed by Elite Labs.
Loxapine
Capsules
The
approved ANDA for Loxapine was acquired by Elite in 2013. Loxapine Succinate 5, 10, 25 and 50 mg are commercial products being
manufactured by Elite at the Northvale Facility, launched commercially in May 2021 and distributed by Burel Pharmaceuticals, Inc, an
affiliate of Prasco, LLC (“Burel”), on an exclusive basis.
Products
Under FDA Review
SequestOx™
- Immediate Release Oxycodone with sequestered Naltrexone
SequestOx™
is our abuse-deterrent candidate for the management of moderate to severe pain where the use of an opioid analgesic is appropriate. SequestOx™
is an immediate-release Oxycodone Hydrochloride containing sequestered Naltrexone which incorporates 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 20mg and 30mg doses
of oxycodone into capsules.
In
January 2016, the Company submitted a 505(b)(2) New Drug Application for SequestOx™, after receiving a waiver of the $2.3 million
filing fee from the FDA. In March 2016, the Company received notification of the FDA’s acceptance of this filing and that such
filing has been granted priority review by the FDA with a target action under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (“PDUFA”)
of July 14, 2016.
On
July 15, 2016, the FDA issued a Complete Response Letter, or CRL, regarding the NDA. The CRL stated that the review cycle for the SequestOx™
NDA is complete and the application is not ready for approval in its present form.
On
July 7, 2017, the Company reported topline results from a pivotal bioequivalence fed study for or SequestOx™. The mean Tmax (the
amount of time that a drug is present at the maximum concentration in serum) of SequestOx™ was 4.6 hr. with a range of 0.5 hr.
to 12 hr. and the mean Tmax of the comparator, Roxicodone®, was 3.4 hr. with a range of 0.5 hr. to 12 hr. A key objective for the
study was to determine if the reformulated SequestOx™ had a similar Tmax to the comparator when taken with a high fat meal. Based
on these results, the Company paused clinical trials for this formulation of SequestOx™. On January 30, 2018, the Company reported
positive topline results from a pilot study conducted for a modified SequestOx™ wherein, based on the results of this pilot study,
the modified SequestOx™ formulation is expected to achieve bioequivalence with a Tmax range equivalent to the reference product
when conducted in a pivotal trial under fed conditions. The Company has provided the pilot data to the FDA, requesting clarification
as to the requirements for resubmission of the NDA. The FDA has provided guidance for repeated bio-equivalence studies in order to bridge
the new formulation to the original SequestOx™ studies and also extended our filing fee waiver until July 2023. Due to the prohibitive
cost of such repeated bio-equivalence studies and the uncertain commercial viability given the regulatory and competitive landscape,
the Company has paused development of this product candidate.
There
can be no assurances of the Company conducting future clinical trials, or if such trials are conducted, there can be no assurances of
the success of any future clinical trials, or if such trials are successful, there can be no assurances that an intended future resubmission
of the NDA product filing, if made, will be accepted by or receive marketing approval from the FDA. In addition, even if marketing authorization
is received, there can be no assurances that there will be future revenues or profits, or that any such future revenues or profits would
be in amounts that provide adequate return on the significant investments made to secure this marketing authorization.
Generic Products Filed
Currently the Company has filed a generic antimetabolite ANDA and a generic dopamine agonist ANDA and these products
are under review by the FDA. The Company also submitted an ANDA for pain management and intends to provide supplemental data in Q3 2023
to complete the filing.
Approved
Products Not Yet Commercialized
Acetaminophen
and Codeine Phosphate
The
Company received approval on September 10, 2019 from the FDA of an ANDA for a generic version of Tylenol® with Codeine (acetaminophen
and codeine phosphate) 300mg/7.5mg, 300mg/15mg, 300mg/30mg and 300mg/60mg tablets. Acetaminophen with codeine is a combination medication
indicated for the management of mild to moderate pain, where treatment with an opioid is appropriate and for which alternative treatments
are inadequate. Acetaminophen with codeine products have annual U.S. sales of approximately $45 million according to IQVIA (formerly
QuintilesIMS Health Data). The Company is not pursuing licensing deals for any opioids at this time until the market changes. The Company
will wait for the market to stabilize before pursuing these opportunities.
There
can be no assurances in relation to any of the above approved products not yet commercialized, that there will be future revenues of
profits, or that any such future revenues or profits would be in amounts that provide adequate return on the significant investments
made to secure these marketing authorizations.
Doxycycline Hyclate Tablets
The
Company received approval in April 2022 from the FDA of an ANDA for a generic version of an antibiotic product. According to QVIA (formerly
QuintilesIMS Health) data, the branded product for this antibiotic and its equivalents had total annual U.S. sales of approximately $85
million for the twelve months ending September 30, 2019. The product is jointly owned by Elite and Praxgen
Pharmaceuticals LLC,
formerly SunGen Pharma LLC, (“Praxgen”).
Discontinued
and Transferred Products
As
part of standard operating practices, the Company, from time to time, as relevant, conducts evaluations of all ANDAs owned, consisting,
without limitation, of ANDAs acquired or approved prior to the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023 (“Fiscal 2023”) and ANDAs
acquired or approved during the Fiscal 2023. Such evaluations include, without limitation, costs and benefits relating to each ANDA owned,
with such costs including those fees required under the FDA’s Generic Drug User Fee Amendment (“GDUFA”) which is significantly
influenced by the number of ANDAs owned, and other costs and benefits taking into consideration various specific market factors for each
ANDA. Those ANDAs with a cost/benefit profile not consistent with management criteria for continuation are identified for disposition
and effort is made to determine the optimal course of action to achieve disposition of the ANDA.
Licensing,
Manufacturing and Development Agreements
Precision
Dose License Agreement
On
September 10, 2010, we executed a License Agreement with Precision Dose (the “Precision Dose License Agreement”) to market
and distribute Phentermine 37.5mg, Phentermine 15mg, Phentermine 30mg, Hydromorphone 8mg, Naltrexone 50mg, and certain additional products
that require approval from the FDA, through its wholly-owned subsidiary, TAGI, in the United States, Puerto Rico and Canada. Phentermine
37.5mg was launched in April 2011. Hydromorphone 8mg was launched in March 2012. Phentermine 15mg and Phentermine 30mg were launched
in April 2013. Naltrexone 50mg was launched in September 2013. Precision Dose will have the exclusive right to market these products
in the United States and Puerto Rico and a non-exclusive right to market the products in Canada.
Pursuant
to the Precision Dose License Agreement, Elite will receive a license fee and milestone payments. The license fee will be computed as
a percentage of the gross profit, as defined in the Precision Dose License Agreement, earned by Precision Dose as a result of sales of
the products. The license fee is payable monthly for the term of the Precision Dose License Agreement. The milestone payments will be
paid in six installments. The first installment was paid upon execution of the Precision Dose License Agreement. The remaining installments
are to be paid upon FDA approval and initial shipment of the products to Precision Dose. The term of the Precision Dose License Agreement
is 15 years and may be extended for 3 successive terms, each of 5 years.
Marketing
License with Epic Pharma LLC
On
November 21, 2020 we entered into a license, manufacturing and supply agreement with Epic Pharma LLC (“Epic”) to market the
two Elite generic products described below in the United States (the “Epic Pharma License”).
Beginning
on May 23, 2021 and continuing until the agreement terminates, Epic has exclusive marketing rights to Trimipramine Capsules and Isradipine
Capsules. The products are manufactured by Elite for Epic on a cost-plus basis. In addition to the purchase prices for the products,
Elite also receives license fees of 50% of gross profits or greater, with such being defined as net sales less the price paid to Elite
for the products, distribution fees of less than 10% and shipping costs. This license was terminated as of March 31, 2023.
Marketing
License with Prasco, LLC and Burel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
On
February 14, 2020, and as amended on July 30, 2020, the Company entered into a license, manufacturing and supply agreement with Prasco,
LLC and its affiliate Burel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Burel”) to market generic Loxapine Succinate capsules in the United States
(the “Burel License”). Burel sales for the product began in May 2021.
Under
the agreement, Burel has exclusive marketing rights to Loxapine. The product is manufactured by Elite, and the Company receives manufacturing
fees and license fees of 50% of gross profits or greater, with such being defined as net sales less the price paid to Elite for the products,
distribution fees of less than 10% and shipping costs. This agreement was terminated as of March 31, 2023.
On April 5, 2023, the Company entered into a non-exclusive license agreement to manufacture, supply and distribute
with Prasco, LLC and its affiliate Burel to distribute generic mixed amphetamine extended-release capsules in the United States (the “New
Burel License”). The term of the agreement is two years from January 1, 2024 or the date of the first commercial sale, whichever
occurs first.
Strategic
Marketing Alliances with Lannett Company Inc.
The
Company has entered into two separate license, supply and distribution agreements with Lannett Company Inc. (“Lannett”).
The first agreement, dated March 6, 2019, relates to products that were co-developed with Praxgen (the “Lannett-Praxgen Product
Alliance”). The second agreement, dated April 9, 2019, relates to products that were solely developed by Elite (the “Lannett-Elite
Product Alliance”). Both agreements are collectively and individually referred to as the “Lannett Alliance”).
Pursuant
to Lannett-Praxgen Product Alliance with Lannett, Lannett will be the exclusive U.S. distributor for Amphetamine IR Tablets and Amphetamine
ER Capsules. Elite manufactures these products, which are purchased, marketed and distributed by Lannett under the Lannett label. In
addition to the purchase prices for the products, Elite will receive license fees well in excess of 50% of net profits, which will be
shared equally with Praxgen, pursuant to the Praxgen Agreement. Net profits are defined as net sales less the price paid to Elite for
the products, distribution fees (less than 10%) and shipping costs. The Lannett-Praxgen Product Alliance has an initial term of three
years and automatically renews for one year periods absent prior written notice of non-renewal. In addition to customary termination
provisions, the Agreement permits Lannett to terminate with regard to a product on at least three months’ prior written notice
if it determines to stop marketing and selling such product, and it permits Elite to terminate with regard to a product if at any time
after the first twelve months from the first commercial sale, the average license fee paid by Lannett for such product is less than $100,000
for a six month sales period. In addition to manufacturing fees and license fees, Lannett also paid a $750,000 milestone, upon the March
2020 commercial launch of Amphetamine ER Capsules. This milestone payment was earned during March 2020 and was shared equally by Elite
and Praxgen, pursuant to the Praxgen Agreement.
Pursuant
to the Lannett-Elite Product Alliance, Elite manufactures for Lannett’s purchase, marketing, and distribution of Dantrolene Capsules
under the Lannett label. In addition to the purchase prices for the products, Elite will receive license fees well in excess of 50% of
gross profits. Gross profits are defined as net sales less the price paid to Elite for the products, distribution fees (less than 10%)
and shipping costs. Lannett will have exclusive marketing rights to Dantrolene Capsules. The Lannett-Elite Product Alliance has an initial
term of three years and automatically renews for one year periods absent prior written notice of non-renewal. In addition to customary
termination provisions, the Agreement permits Lannett to terminate with regard to a product on at least three months’ prior written
notice if it determines to stop marketing and selling such product, and it permits Elite to terminate with regard to a product if at
any time after the first twelve months from the first commercial sale, the average license fee paid by Lannett for such product is less
than $100,000 for a six month sales period. In addition to manufacturing fees and license fees.
Please
also note that in May 2020, Praxgen, under an asset purchase agreement, assigned its rights and obligations under the Praxgen Agreement
for Amphetamine IR and Amphetamine ER to Mikah. The ANDAs for Amphetamine IR and Amphetamine ER are now registered under Elite’s
name. Mikah will now be Elite’s partner with respect to Amphetamine IR and ER and will assume all the rights and obligations for
these products from Praxgen.
All agreements with Lannett were terminated as of March 31, 2023.
Pyros Agreement
On November 21, 2022, the Company entered into an agreement with Pyros Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
(“Pyros”) pursuant to which the Company sold to Pyros its rights in and to the Company’s approved abbreviated new drug
applications (ANDAs) for its generic Sabril drug. The Company sold its rights to Pyros for $1,000,000, which was recorded as gain on sale
of ANDA during the year ended March 31, 2023. There is no further action required by the Company regarding the rights which would
affect future periods.
In conjunction with the sale of its Product to Pyros, the Company executed a Manufacturing and Supply agreement (the
“Pyros Agreement”) with Pyros. Under the terms of the Pyros Agreement, the Company will receive an agreed-upon price per drug
for the manufacturing and packaging of Sabril over a term of three years. Revenue per the Pyros Agreement will be recognized as control
of the manufactured and supplied drugs is transferred to Pyros (at the time of delivery).
Products
Under Development
Elite’s
research and development activities include developing its proprietary abuse deterrent technology and the development of a range of abuse
deterrent opioid products that utilize this technology or other approaches to abuse deterrence.
Elite’s
proprietary abuse-deterrent technology utilizes the pharmacological approach to abuse deterrence and consists of a multi-particulate
capsule which contains an opioid agonist in addition to naltrexone, an opioid antagonist used primarily in the management of alcohol
dependence and opioid dependence. When this product is taken as intended, the naltrexone is designed to pass through the body
unreleased while the opioid agonist releases over time providing therapeutic pain relief for which it is prescribed. If the
multi-particulate beads are crushed or dissolved, the opioid antagonist, naltrexone, is designed to release. The absorption of the
naltrexone is intended to block the euphoria by preferentially binding to the same receptors in the brain as the opioid agonist and
thereby reducing the incentive for abuse or misuse by recreational drug abusers.
We
filed an NDA for the first product to utilize our abuse deterrent technology, Immediate Release Oxycodone 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 20mg and 30mg
with sequestered Naltrexone (collectively and individually referred to as “SequestOx™”), on January 14, 2016. Please
see “Filed products under FDA review; SequestOx™ - Immediate Release Oxycodone with sequestered Naltrexone” above and
please note that continued development of this product is currently paused.
The
Company is currently not selling and is evaluating the market place when deciding to proceed with the above listed filed application.
Please
note that, while the FDA is required to review applications within certain timeframes, during the review process, the FDA frequently
requests that additional information be submitted. The effect of such requests and subsequent submissions can significantly extend the
time for the FDA review process. Until a product is actually approved, there can be no assurances that the information requested and
submitted will be considered adequate by the FDA to justify approval. The packaging and labeling of our approved products are also subject
to FDA regulation. Based on the foregoing, it is impossible to anticipate the amount of time that will be needed to obtain FDA approval
and to commercialize a product, if approved. In addition, there can be no assurances of the Company filing the required application(s)
with the FDA or of the FDA approving such application(s) if filed. The Company’s ability to successfully develop and commercialize
products incorporating its abuse deterrent technology is subject to a high level of risk as detailed in “Item 1A-Risk Factors-Risks
Related to our Business” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Abuse-Deterrent
and Sustained Release Opioids
The
abuse-deterrent opioid products utilize our patented abuse-deterrent technology that is based on a pharmacological approach. These products
are combinations of a narcotic agonist formulation intended for use in patients with pain, and an antagonist, formulated to deter abuse
of the drug. Both, agonist, and antagonist, have been on the market for a number of years and sold separately in various dose strengths.
The
Company is currently not selling opioids and is evaluating the market place when deciding to proceed with the above listed filed applications.
Patents
The Company owns the following patents:
| PATENT |
|
EXPIRATION
DATE |
| U.S.
patent 8,182,836 |
|
March
2024 |
| U.S.
patent 8,425,933 |
|
March
2025 |
| U.S.
patent 8,703,186 |
|
March
2025 |
| Canadian
patent 2,521,655 |
|
April
2023 |
| Canadian
patent 2,541,371 |
|
April
2024 |
| U.S.
patent 9,056,054 |
|
June
2030 |
| U.S.
patent 10,213,388 |
|
June
2030 |
We
intend to apply for patents for other products in the future; however, there can be no assurance that any of the pending applications
or other applications which we may file will be granted. We have also filed corresponding foreign applications for key patents.
Prior
to the enactment in the United States of new laws adopting certain changes mandated by the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (“GATT”),
the exclusive rights afforded by a U.S. Patent were for a period of 17 years measured from the date of grant. Under GATT, the term of
any U.S. Patent granted on an application filed subsequent to June 8, 1995 terminates 20 years from the date on which the patent application
was filed in the United States or the first priority date, whichever occurs first. Future patents granted on an application filed before
June 8, 1995, will have a term that terminates 20 years from such date, or 17 years from the date of grant, whichever date is later.
Under
the Drug Price Competition Act, a U.S. product patent or use patent may be extended for up to five years under certain circumstances
to compensate the patent holder for the time required for FDA regulatory review of the product. Such benefits under the Drug Price Competition
Act are available only to the first approved use of the active ingredient in the drug product and may be applied only to one patent per
drug product. There can be no assurance that we will be able to take advantage of this law.
Also,
different countries have different procedures for obtaining patents, and patents issued by different countries provide different degrees
of protection against the use of a patented invention by others. There can be no assurance, therefore, that the issuance to us in one
country of a patent covering an invention will be followed by the issuance in other countries of patents covering the same invention,
or that any judicial interpretation of the validity, enforceability, or scope of the claims in a patent issued in one country will be
similar to the judicial interpretation given to a corresponding patent issued in another country. Furthermore, even if our patents are
determined to be valid, enforceable, and broad in scope, there can be no assurance that competitors will not be able to design around
such patents and compete with us using the resulting alternative technology.
Trademarks
SequestOx™
is a trademark owned by Elite.
We
currently plan to license at least some of our products to other entities in the marketing of pharmaceuticals but may also sell products
under our own brand name in which case we may register trademarks for those products.
Elite sells its own products under an “Elite Labs” label.
Other
Business Factors and Details
Government
Regulation and Approval
The
design, development, manufacturing, and marketing of pharmaceutical compounds, on which our success depends, are intensely regulated
by governmental regulatory agencies, in particular the FDA and DEA. Non-compliance with applicable requirements can result in fines and
other judicially imposed sanctions, including product seizures, injunction actions and criminal prosecution based on products or manufacturing
practices that violate statutory requirements. In addition, administrative remedies can involve voluntary withdrawal of products, as
well as the refusal of the FDA to approve ANDAs and NDAs. The FDA also has the authority to withdraw approval of drugs in accordance
with statutory due process procedures.
Before
a drug may be marketed, it must be approved by the FDA either through an NDA or an ANDA, each of which is discussed below.
NDAs
and NDAs under Section 505(b)(2) of the Drug Price Competition Act
The
FDA approval procedure for an NDA is generally a two-step process. During the initial product development stage, an investigational new
drug application (“IND”) for each product is filed with the FDA. The IND contains results of animal and in vitro studies
assessing the toxicology, pharmacokinetic, pharmacological, and pharmacodynamics characteristics of the product candidate; chemistry,
manufacturing, and controls information; and any available human data or literature to support the use of the product candidate. A 30-day
waiting period after the filing of each IND is required by the FDA prior to the commencement of initial clinical testing. If the FDA
does not comment on or question the IND within such 30-day period, initial clinical studies may begin. If, however, the FDA has comments
or questions, they must be answered to the satisfaction of the FDA before initial clinical testing may begin. In some instances, this
process could result in substantial delay and expense. Clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases that may overlap
or be combined:
Phase
One: The product candidate is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or patients with the target disease or condition.
These studies are designed to test the safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, and distribution of the investigational product
in humans, the side effects associated with increasing doses, and, if possible, to gain early evidence on effectiveness. In the case
of some products for severe or life-threatening diseases, especially when the product may be too inherently toxic to ethically administer
to healthy volunteers, the initial human testing;
Phase
Two: The product candidate is administered to a limited patient population with a specified disease or condition to evaluate the
preliminary efficacy, optimal dosages, and dosing schedule and to identify possible adverse side effects and safety risks. Multiple Phase
2 clinical trials may be conducted to obtain information prior to beginning;
Phase
Three: The product candidate is administered to an expanded patient population to further evaluate dosage, to provide statistically
significant evidence of clinical efficacy and to further test for safety, generally at multiple geographically dispersed clinical trial
sites. These clinical trials are intended to establish the overall risk.
Concurrent
with clinical trials, companies usually complete additional animal studies and must also develop additional information about the chemistry
and physical characteristics of the drug and finalize a process for manufacturing the product in commercial quantities in accordance
with cGMP requirements. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of the product candidate
and, among other things, the manufacturer must develop methods for testing the identity, strength, quality, and purity of the final drug.
In addition, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested, and stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the product
candidate does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
Assuming
successful completion of all required testing in accordance with all applicable regulatory requirements, the results of product development
nonclinical and clinical trials, along with descriptions of the manufacturing process, analytical tests conducted on the chemistry of
the drug, proposed labeling and other relevant information are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA requesting approval to market the
product. The submission of an NDA is subject to the payment of substantial user fees; a waiver of such fees may be obtained under certain
limited circumstances.
The
FDA reviews an NDA to determine, among other things, whether a product is safe and effective for its intended use and whether its manufacturing
is cGMP-compliant to assure and preserve the product’s identity, strength, quality, and purity. Under the Prescription Drug User
Fee Act, or PDUFA, guidelines that are currently in effect, the FDA has a goal of ten months from the date of “filing” of
a standard NDA for a new molecular entity to review and act on the submission. This review typically takes 12 months from the date the
NDA is submitted to FDA because the FDA has approximately two months to make a “filing” decision after the application is
submitted. The FDA conducts a preliminary review of all NDAs within the first 60 days after submission, before accepting them for filing,
to determine whether they are sufficiently complete to permit substantive review The FDA may request additional information rather than
accept an NDA for filing. In this event, the NDA must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application is
also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing.
The
FDA may refer an application for a novel drug to an advisory committee. An advisory committee is a panel of independent experts, including
clinicians and other scientific experts, that reviews, evaluates and provides a recommendation as to whether the application should be
approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations
carefully when making decisions.
Before
approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect the facility or facilities where the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve
an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP and adequate to assure
consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect
one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCPs. If the FDA determines that the application, manufacturing process, or manufacturing
facilities are not acceptable, it will outline the deficiencies in the submission and often will request additional testing or information.
Notwithstanding the submission of any requested additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy
the regulatory criteria for approval.
After
the FDA evaluates an NDA, it will issue an approval letter or a Complete Response Letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing
of the drug with prescribing information for specific indications. A Complete Response Letter indicates that the review cycle of the
application is complete, and the application will not be approved in its present form. A Complete Response Letter usually describes the
specific deficiencies in the NDA identified by the FDA and may require additional clinical data, such as an additional pivotal Phase
3 clinical trial or other significant and time-consuming requirements related to clinical trials, nonclinical studies, or manufacturing.
If a Complete Response Letter is issued, the sponsor must resubmit the NDA, addressing all of the deficiencies identified in the letter,
or withdraw the application. Even if such data and information are submitted, the FDA may decide that the NDA does not satisfy the criteria
for approval.
If
regulatory approval of a product is granted, such approval will be granted for particular indications and may entail limitations on the
indicated uses for which such product may be marketed. For example, the FDA may approve the NDA with a REMS to ensure the benefits of
the product outweigh its risks. A REMS is a safety strategy to manage a known or potential serious risk associated with a medicine and
to enable patients to have continued access to such medicines by managing their safe use. It could include medication guides, physician
communication plans, or elements to assure safe use, such as restricted distribution methods, patient registries, and other risk minimization
tools. The FDA also may offer conditional approval subject to, among other things, changes to proposed labeling or the development of
adequate controls and specifications. Once approved, the FDA may withdraw the product approval if compliance with pre- and post-marketing
requirements is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the marketplace. The FDA may also require one or more Phase
4 post-market studies and surveillance to further assess and monitor the product’s safety and effectiveness after commercialization,
and may limit further marketing of the product based on the results of these post-marketing studies. In addition, new government requirements,
including those resulting from new legislation, may be established, or the FDA’s policies may change, which could impact the timeline
for regulatory approval or otherwise impact ongoing development programs.
The
FDA closely regulates the marketing, labeling, advertising, and promotion of drug products. A company can make only those claims relating
to safety and efficacy that are approved by the FDA and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. The FDA and other agencies
actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses. Failure to comply with these requirements can
result in, among other things, adverse publicity, warning letters, corrective advertising, and potential civil and criminal penalties.
Physicians may prescribe, in their independent professional medical judgment, legally available products for uses that are not described
in the product’s labeling and that differ from those tested by us and approved by the FDA. Physicians may believe that such off-label
uses are the best treatment for many patients in varied circumstances. The FDA does not regulate the behavior of physicians in their
choice of treatments. The FDA does, however, restrict manufacturer’s communications on the subject of off-label use of their products.
The federal government has levied large civil and criminal fines against companies for alleged improper promotion of off-label use and
has enjoined companies from engaging in off-label promotion. The FDA and other regulatory agencies have also required that companies
enter into consent decrees or permanent injunctions under which specified promotional conduct is changed or curtailed. However, companies
may share truthful and not misleading information that is otherwise consistent with a product’s FDA-approved labeling.
Whether
or not FDA approval has been obtained, approval of the product by comparable regulatory authorities in any foreign country must be obtained
prior to the commencement of marketing of the product in that country. We intend to conduct all marketing in territories other than the
United States through other pharmaceutical companies based in those countries. The approval procedure varies from country to country,
can involve additional testing, and the time required may differ from that required for FDA approval. Although there are some procedures
for unified filings for certain European countries, in general each country has its own procedures and requirements, many of which are
time consuming and expensive. Thus, there can be substantial delays in obtaining required approvals from both the FDA and foreign regulatory
authorities after the relevant applications are filed. After such approvals are obtained, further delays may be encountered before the
products become commercially available.
NDAs
under Section 505(b)(2)
Section
505(b)(2) NDAs may provide an alternate path to FDA approval for new or improved formulations or new uses of previously approved products.
Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from clinical trials
not conducted by, or for, the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. The FDA may then approve the
new product candidate for all, or some, of the label indications for which the referenced product has been approved, as well as for any
new indication sought by the Section 505(b)(2) applicant.
To
the extent that the Section 505(b)(2) applicant is relying on the FDA’s findings of safety and effectiveness for an already approved
product, the applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the approved product in the Orange Book to
the same extent that an ANDA applicant would. Thus approval of a Section 505(b)(2) NDA can be stalled until all the listed patents claiming
the referenced product have expired; until any non-patent exclusivity, such as exclusivity for obtaining approval of a NCE, listed in
its publication “Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations,” also referred to as the “Orange
Book,” for the referenced product has expired; and, in the case of a Paragraph IV certification and subsequent patent infringement
suit, until the earlier of 30 months, settlement of the lawsuit or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the Section
505(b)(2) applicant. In the interim period, the FDA may grant tentative approval. Tentative approval indicates that the FDA has determined
that the applicant meets the standards for approval as of the date that the tentative approval is granted. Final regulatory approval
can only be granted if the FDA is assured that there is no new information that would affect final regulatory/ approval.
ANDAs
To
obtain approval of a generic drug, an applicant must submit an abbreviated new drug application, or ANDA, to the agency. An ANDA is a
comprehensive submission that contains, among other things, data and information pertaining to the active pharmaceutical ingredient,
bioequivalence, drug product formulation, specifications and stability of the generic drug, as well as analytical methods, manufacturing
process validation data and quality control procedures. ANDAs are “abbreviated” because they cannot include preclinical and
clinical data to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. Instead, in support of such applications, a generic manufacturer must rely on
the preclinical and clinical testing previously conducted for a drug product previously approved under an NDA, known as the reference
listed drug, or RLD.
In
order for an ANDA to be approved, the FDA must find that the generic version is identical to the RLD with respect to the active ingredients,
the route of administration, the dosage form, the strength of the drug and the conditions of use of the drug. At the same time, the FDA
must also determine that the generic drug is “bioequivalent” to the innovator drug. Under the statute, a generic drug is
bioequivalent to a RLD if “the rate and extent of absorption of the drug do not show a significant difference from the rate and
extent of absorption of the listed drug.” Upon approval of an ANDA, the FDA indicates whether the generic product is “therapeutically
equivalent” to the RLD in the Orange Book. Physicians and pharmacists consider a therapeutic equivalent generic drug to be fully
substitutable for the RLD. In addition, by operation of certain state laws and numerous health insurance programs, the FDA’s designation
of therapeutic equivalence often results in substitution of the generic drug without the knowledge or consent of either the prescribing
physician or patient.
When
an ANDA applicant submits its application to the FDA, it is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the reference
product in the FDA’s Orange Book. Specifically, the ANDA applicant must certify that: (i) the required patent information has not
been filed; (ii) the listed patent has expired; (iii) the listed patent has not expired, but will expire on a particular date and approval
is sought after patent expiration; or (iv) the listed patent is invalid or will not be infringed by the new product.
If
the follow-on applicant does not challenge the innovator’s listed patents, FDA will not approve the ANDA application until all
the listed patents claiming the referenced product have expired. A certification that the new product will not infringe the already approved
product’s listed patents, or that such patents are invalid, is called a Paragraph IV certification. If the follow-on applicant
has provided a Paragraph IV certification to the FDA, the applicant must also send notice of the Paragraph IV certification to the NDA
and patent holders once the ANDA has been accepted for filing by the FDA. The NDA and patent holders may then initiate a patent infringement
lawsuit in response to the notice of the Paragraph IV certification. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit within 45 days of the
receipt of a Paragraph IV certification automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA until the earlier of 30 months, expiration
of the patent, settlement of the lawsuit, or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the ANDA applicant.
In
May 1992, Congress enacted the Generic Drug Enforcement Act of 1992, which allows the FDA to impose debarment and other penalties on
individuals and companies that commit certain illegal acts relating to the generic drug approval process. In some situations, the Generic
Drug Enforcement Act requires the FDA to not accept or review ANDAs for a period of time from a company or an individual that has committed
certain violations. It also provides for temporary denial of approval of applications during the investigation of certain violations
that could lead to debarment and also, in more limited circumstances, provides for the suspension of the marketing of approved drugs
by the affected company. Lastly, the Generic Drug Enforcement Act allows for civil penalties and withdrawal of previously approved applications.
Neither we nor any of our employees have ever been subject to debarment. We do not believe that we receive any services from any debarred
person.
Controlled
Substances
The
federal Controlled Substances Act of 1970, or CSA, and its implementing regulations establish a “closed system” of regulations
for controlled substances. The CSA imposes registration, security, recordkeeping and reporting, storage, manufacturing, distribution,
importation, exportation, disposal and other requirements under the oversight of the Drug Enforcement Agency, or DEA. The DEA is the
federal agency responsible for regulating controlled substances, and requires those individuals or entities that manufacture, import,
export, distribute, research, or dispense controlled substances to comply with the regulatory requirements in order to prevent the diversion
of controlled substances to illicit channels of commerce.
The
DEA categorizes controlled substances into one of five schedules — Schedule I, II, III, IV or V — with
varying qualifications for listing in each schedule. Schedule I substances by definition have a high potential for abuse, have no currently
accepted medical use in treatment in the United States and lack accepted safety for use under medical supervision. Pharmaceutical products
having a currently accepted medical use that are otherwise approved for marketing may be listed as Schedule II, III, IV or V substances,
with Schedule II substances presenting the highest potential for abuse and physical or psychological dependence, and Schedule V substances
presenting the lowest relative potential for abuse and dependence. The regulatory requirements are more restrictive for Schedule II substances
than Schedule III-V substances.
Facilities
that manufacture, distribute, import or export any controlled substance must register annually with the DEA. The DEA registration is
specific to the particular location, activity(ies) and controlled substance schedule(s). For example, separate registrations are required
for importation and manufacturing activities, and each registration authorizes which schedules of controlled substances the registrant
may handle. Certain coincident activities are permitted without obtaining a separate DEA registration, however, such as distribution
of controlled substances by the manufacturer that produces them.
The
DEA inspects all manufacturing facilities to review security, recordkeeping, reporting and handling prior to issuing a controlled substance
registration. The specific security requirements vary by the type of business activity and the schedule and quantity of controlled substances
handled. The most stringent requirements apply to manufacturers of Schedule I and Schedule II substances. Required security measures
commonly include background checks on employees and physical control of controlled substances through storage in approved vaults, safes
and cages, and through use of alarm systems and surveillance cameras. Once registered, manufacturing facilities must maintain records
documenting the manufacture, receipt and distribution of all controlled substances. Manufacturers must submit periodic reports to the
DEA of the distribution of Schedule I and II controlled substances, Schedule III narcotic substances, and other designated substances.
Registrants must also report any controlled substance thefts or significant losses, and must obtain authorization to destroy or dispose
of controlled substances.
For
drugs manufactured in the United States, the DEA establishes annually an aggregate quota for the amount of substances within Schedules
I and II that may be manufactured or produced in the United States based on the DEA’s estimate of the quantity needed to meet legitimate
medical, scientific, research and industrial needs. The quotas apply equally to the manufacturing of the active pharmaceutical ingredient
and production of dosage forms. The DEA may adjust aggregate production quotas, and individual manufacturing or procurement quotas from
time to time, although the DEA has substantial discretion in whether or not to make such adjustments for individual companies. The DEA
quota system was amended in 2018 to require sponsors to strengthen controls over diversion of controlled substances, controls and limits
the availability and production of controlled substances in Schedule I or II.
Federal
laws have been enacted to address the national epidemics of prescription opioid abuse and illicit opioid use. In 2016, the Comprehensive
Addiction and Recovery Act (“CARA”), was enacted to address the national epidemics of prescription opioid abuse and heroin
use. CARA expands the availability of naloxone for law enforcement and other first responders, forms an interagency task force to develop
best practices for pain management with opioid medications and provides resources to improve state monitoring of opioids. The Substance
Use-Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act (“SUPPORT Act”), which
was signed into law in November 2018, includes a number of measures directed towards regulation and improvement of treatment for substance
use-disorder and increased coverage by CMS of medically-assisted treatment options. In addition, the SUPPORT Act requires HHS to report
to Congress on existing barriers to access to abuse-deterrent opioid formulations by Medicare Part C and D beneficiaries
The
states also maintain separate controlled substance laws and regulations, including licensing, recordkeeping, security, distribution,
and dispensing requirements. State authorities, including Boards of Pharmacy, regulate use of controlled substances in each state. Failure
to maintain compliance with applicable requirements, particularly as manifested in the loss or diversion of controlled substances, can
result in enforcement action that could have a material adverse effect on business, operations and financial conditions. The DEA may
seek civil penalties, refuse to renew necessary registrations, or initiate proceedings to revoke those registrations. In certain circumstances,
violations could lead to criminal prosecution.
Other
Healthcare Laws and Compliance Requirements
Our
activities are subject to various federal and state fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute,
the federal civil False Claims Act, and laws and regulations pertaining to limitations on and reporting of healthcare provider payments
(physician sunshine laws). These laws and regulations are interpreted and enforced by various federal, state and local authorities including
CMS, the Office of Inspector General for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the U.S. Department of Justice, individual
U.S. Attorney offices within the Department of Justice, and state and local governments. These laws include:
| ● | the
U.S. federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons or entities
from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or paying any remuneration,
directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward either
the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, lease, order, or arranging for or recommending
the purchase, lease or order of, any good or service, for which payment may be made, in whole
or in part, under federal healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. A person or
entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate
it in order to have committed a violation; |
| | | |
| |
● |
the
U.S. civil False Claims Act (which can be enforced through “qui tam,” or whistleblower actions, by private citizens on
behalf of the federal government), prohibits any person from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented
false or fraudulent claims for payment of government funds or knowingly making, using or causing to be made or used, a false record
or statement material to an obligation to pay money to the government or knowingly and improperly avoiding, decreasing or concealing
an obligation to pay money to the U.S. federal government; |
| |
|
|
| |
● |
U.S.
federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, which imposes criminal liability and amends provisions
on the reporting, investigation, enforcement, and penalizing of civil liability for, among other things, knowingly and willfully
executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program, or knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing
or covering up a material fact or making any materially false statement, in connection with the delivery of, or payment for healthcare
benefits, items or services by a healthcare benefit program, which includes both government and privately funded benefits programs;
similar to the U.S. federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific
intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation; |
| |
|
|
| |
● |
state
laws and regulations, including state anti-kickback and false claims laws, that may apply to our business practices, including but
not limited to, research, distribution, sales and marketing arrangements and claims involving healthcare items or services reimbursed
by any third-party payer, including private insurers; state laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical
industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the U.S. federal government,
or otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers and other potential referral sources; and state laws and
regulations that require drug manufacturers to file reports relating to pricing and marketing information, which requires tracking
gifts and other remuneration and items of value provided to healthcare professionals and entities; and |
| |
|
|
| |
● |
the
Physician Payments Sunshine Act, implemented as the Open Payments program, and its implementing regulations, requires certain manufacturers
of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies that are reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid, or the Children’s Health
Insurance Program to report annually to CMS information related to certain payments made in the preceding calendar year and other
transfers of value to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their
immediate family members; beginning in 2022, applicable manufacturers are required to report such information regarding payments
and transfers of value provided, as well as ownership and investment interests held, during the previous year to physician assistants,
nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse anesthetists, and certified nurse-midwives. |
Violations
of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, may subject us to significant civil, criminal and administrative
sanctions including penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment, and exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare
and Medicaid, and/or adverse publicity.
Moreover,
government entities and private litigants have asserted claims under state consumer protection statutes against pharmaceutical companies
for alleged false or misleading statements in connection with the marketing, promotion and/or sale of pharmaceutical products, including
state investigations and litigation by certain government entities regarding the marketing of opioid products.
Foreign
Corrupt Practices Act
The
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or the FCPA, generally prohibits offering, promising, giving, or authorizing others to give anything of
value, either directly or indirectly, to a non-U.S. government official in order to influence official action, or otherwise obtain or
retain business. The FCPA also requires public companies to make and keep books and records that accurately and fairly reflect the transactions
of the corporation and to devise and maintain an adequate system of internal accounting controls. Our industry is heavily regulated and
therefore involves significant interaction with public officials, including officials of non-U.S. governments. Additionally, in many
other countries, the health care providers who prescribe pharmaceuticals are employed by their government, and the purchasers of pharmaceuticals
are government entities; therefore, our dealings with these prescribers and purchasers are subject to regulation under the FCPA. Recently,
the SEC and Department of Justice have increased their FCPA enforcement activities with respect to pharmaceutical companies. Violations
could result in fines, criminal sanctions against us, our officers, or our employees, the closing down of our facilities, requirements
to obtain export licenses, cessation of business activities in sanctioned countries, implementation of compliance programs, and prohibitions
on the conduct of our business. Enforcement actions may be brought by the Department of Justice or the Securities and Exchanges Commission
(“SEC”), and recent enacted legislation has expanded the SEC’s power to seek disgorgement in all FCPA cases filed in
federal court and extended the statute of limitations in SEC enforcement actions in intent-based claims such as those under the FCPA
from five years to ten years.
Coverage
and Reimbursement
Sales
of any pharmaceutical product depend, in part, on the extent to which such product will be covered by third-party payors, such as federal,
state, and foreign government healthcare programs, commercial insurance, and managed healthcare organizations, and the level of reimbursement
for such product by third-party payors. Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any newly approved
product. Decisions regarding the extent of coverage and amount of reimbursement to be provided for any product are made on a plan-by-plan
basis. One third-party payor’s decision to cover a particular product does not ensure that other payors will also provide coverage
for the product. As a result, the coverage determination process can require manufacturers to provide scientific details, information
on cost-effectiveness, and clinical support for the use of a product to each payor separately. This can be a time-consuming process,
with no assurance that coverage and adequate reimbursement will be applied consistently or obtained in the first instance.
In
addition, third-party payors are increasingly reducing reimbursements for pharmaceutical products and related services. The U.S. government
and state legislatures have continued implementing cost-containment programs, including price controls and restrictions on coverage and
reimbursement. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the prices charged, examining the medical necessity and reviewing the
cost effectiveness of pharmaceutical products, in addition to questioning their safety and efficacy. Adoption of price controls and cost-containment
measures, and adoption of more restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could further limit sales of
any product. Decreases in third-party reimbursement for any product or a decision by a third-party payor not to cover a product could
reduce physician usage and patient demand for the product.
We
expect that additional federal, state and foreign healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit
the amounts that third-party payors, including government payors, will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in
limited coverage and reimbursement and reduced demand for our products, once approved, or additional pricing pressures.
Compliance
with Environmental Laws
We
are subject to comprehensive federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations that govern, among other things, air polluting
emissions, waste water discharges, solid and hazardous waste disposal, and the remediation of contamination associated with current or
past generation handling and disposal activities, including the past practices of corporations as to which we are the legal successor
or in possession. We do not expect that compliance with such environmental laws will have a material effect on our capital expenditures,
earnings, or competitive position in the foreseeable future. There can be no assurance, however, that future changes in environmental
laws or regulations, administrative actions or enforcement actions, or remediation obligations arising under environmental laws will
not have a material adverse effect on our capital expenditures, earnings, or competitive position.
Competition
We
have competition with respect to our principal areas of operation. We develop and manufacture generic products, products using controlled-release
drug technology, products utilizing abuse deterrent technologies, and we develop and market (either on our own or by license to other
companies) generic and proprietary controlled-release and abuse deterrent pharmaceutical products. In both areas, our competition consists
of those companies which develop controlled release, abuse deterrent drugs and alternative drug delivery systems. We do not represent
a significant presence in the pharmaceutical industry.
An
increasing number of pharmaceutical companies have become interested in the development and commercialization of products incorporating
advanced or novel drug delivery systems. Some of the major pharmaceutical companies have invested and are continuing to invest significant
resources in the development of their own drug delivery systems and technologies and some have invested funds in such specialized drug
delivery companies. Many of these companies have greater financial and other resources as well as more experience than we do in commercializing
pharmaceutical products. Certain companies have a track record of success in developing controlled-release drugs. Significant among these
are, without limitation, Pfizer, Sandoz (a Novartis company), Mylan Laboratories, Inc., Endo Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Teva Pharmaceuticals
Industries Ltd., Amneal Laboratories, Inc., Mallinckrodt, and Aurobindo. Each of these companies has developed expertise in certain types
of drug delivery systems, although such expertise does not carry over to developing a controlled-release version of all drugs. Such companies
may develop new drug formulations and products or may improve existing drug formulations and products more efficiently than we can. In
addition, almost all of our competitors have vastly greater resources than we do. While our product development capabilities and, if
obtained, patent protection may help us to maintain our market position in the field of advanced drug delivery, there can be no assurance
that others will not be able to develop such capabilities or alternative technologies outside the scope of our patents, if any, or that
even if patent protection is obtained, such patents will not be successfully challenged in the future.
In
addition to competitors that are developing products based on drug delivery technologies, there are also companies that have announced
that they are developing opioid abuse-deterrent products that might compete directly or indirectly with Elite’s products. These
include, but are not limited to Pfizer Inc., Collegium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Purdue Pharma LP.
We
also face competition in the generic pharmaceutical market. The principal competitive factors in the generic pharmaceutical market include:
(i) introduction of other generic drug manufacturers’ products in direct competition with our products under development, (ii)
introduction of authorized generic products in direct competition with any of our products under development, particularly if such products
are approved and sold during exclusivity periods, (iii) consolidation among distribution outlets through mergers and acquisitions and
the formation of buying groups, (iv) ability of generic competitors to quickly enter the market after the expiration of patents or exclusivity
periods, diminishing the amount and duration of significant profits, (v) the willingness of generic drug customers, including wholesale
and retail customers, to switch among pharmaceutical manufacturers, (vi) pricing pressures and product deletions by competitors, (vii)
a company’s reputation as a manufacturer and distributor of quality products, (viii) a company’s level of service (including
maintaining sufficient inventory levels for timely deliveries), (ix) product appearance and labelling and (x) a company’s breadth
of product offerings.
Sources
and Availability of Raw Materials; Manufacturing
A
significant portion of our raw materials may be available only from foreign sources. Foreign sources can be subject to the special risks
of doing business abroad, including:
| |
● |
Greater
possibility for disruption due to transportation or communication problems; |
| |
● |
The
relative instability of some foreign governments and economies; |
| |
● |
Interim
price volatility based on labor unrest, materials or equipment shortages, export duties, restrictions on the transfer of funds, or
fluctuations in currency exchange rates; and, |
| |
● |
Uncertainty
regarding recourse to a dependable legal system for the enforcement of contracts and other rights. |
While
we currently obtain the raw materials that we need from over 20 suppliers, some materials used in our products are currently available
from only one supplier or a limited number of suppliers. The FDA requires identification of raw material suppliers in applications for
approval of drug products. If raw materials were unavailable from a specified supplier, FDA approval of a new supplier could delay the
manufacture of the drug involved.
We
have acquired pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment for manufacturing our products. We have registered our facilities with the FDA and
the DEA.
Our
Reporting Segments
We
currently operate in two segments, which are products whose marketing approvals were secured via an ANDA and products whose marketing
approvals were secured via an NDA. ANDA products are referred to as generic pharmaceuticals and NDA products are referred to as branded
pharmaceuticals. For the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 revenue from our ANDA segment were $34.2 million and $32.3 million, respectively.
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 revenue from our NDA segment were $0.0 million and $0.0 million, respectively.
Segment
information is consistent with the financial information regularly reviewed by our chief operating decision maker, who we have determined
to be the chief executive office, for the purposes of making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance of the Company.
There are currently no intersegment revenues. Asset information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating
decision maker does not review this information by segment.
Employees
As
of June 15, 2023, we had 53 full time employees. Full-time employees are engaged in operations, administration, research, and development.
None of our employees is represented by a labor union and we have never experienced a work stoppage. We believe our relationship with
our employees to be good. However, our ability to achieve our financial and operational objectives depends in large part upon our continuing
ability to attract, integrate, retain, and motivate highly qualified personnel, and upon the continued service of our senior management
and key personnel.
ITEM
1A. RISK FACTORS
An
investment in the Company’s securities involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described below
as well as other information provided to you in this report, including information in the section of this document entitled “Forward
Looking Statements.” The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones facing us. Additional risks and uncertainties
not presently known to us or that we currently believe are immaterial may also impair our business operations. If any of the following
risks actually occur, our business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected, the value of
our Common Stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment.
In
addition to the other information contained in this report, the following risk factors should be considered carefully in evaluating an
investment in us and in analyzing our forward-looking statements.
Risk
Factor Summary
The
following is a summary of the risk factors contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K that could adversely affect our business, ability
to operate, financial condition, results of operation, equity and cash flows. This summary does not address all of the risks that we
face and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the more detailed descriptions included below. In addition to this summary, we
strongly encourage you to carefully review the full risk factors in their entirety.
Business
Related Risks
| |
● |
The
pharmaceutical industry is highly competitive. |
| |
● |
Natural
disasters and associated supply chain effects. |
| |
● |
Interruptions
in operations at our sole facility could have a material adverse effect on our business. |
| |
● |
We
may sell, withdraw or discontinue manufacture of certain products. |
| |
● |
We
may fail to successfully identify, develop, and commercialize new products. |
| |
● |
Our
operations could be disrupted by failure of our information systems or cyber-attacks. |
| |
● |
Delays
in product development may result in failure to achieve adequate return on investment. |
| |
● |
Our
business is dependent on market perceptions, social and political pressures, including public concern over the abuse of opioids. |
| |
● |
Unstable
economic conditions may adversely affect our business. |
| |
● |
We
depend on qualified scientific and technical personnel and our ability to attract and retained such. |
| |
● |
Unsuccessful
collaboration or licensing arrangements could limit revenues and product development. |
Financial
and Liquidity Related Risks
| |
● |
We
have a relatively limited operating history and our operating results could fluctuate significantly. |
| |
● |
Our
ability to fund operations is uncertain and we may require additional financing to meet objectives. |
| |
● |
We
have substantial indebtedness which may adversely affect our financial condition. |
| |
● |
There
is a risk of impairment of significant intangible assets on our balance sheet. |
| |
● |
GAAP
requires estimates, judgements and assumptions which inherently contain uncertainties. |
Legal
and Regulatory Risks
| |
● |
The
pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated which creates uncertainty and substantial compliance costs. |
| |
● |
Our
business may be adversely affected by legislation or healthcare regulatory reform and initiatives. |
| |
● |
Use
of generics may be limited through legislative, regulatory or efforts of pharmaceutical companies. |
| |
● |
New
tariffs and evolving trade policy between the US and other countries may adversely affect our business. |
| |
● |
The
DEA could limit the availability of active ingredients used in many of our products. |
| |
● |
Changes
in FDA approval requirements may prevent or delay approval of new products. |
| |
● |
We
received a CRL from the FDA indicating that the SequestOx™ NDA is not ready for approval. |
| |
● |
Regulatory
factors may cause us to be unable to manufacture products or face interruptions in our manufacturing process. |
| |
● |
Agreements
between branded pharmaceutical companies and generic pharmaceutical companies are facing increased government scrutiny in the United
States and Internationally. |
Litigation
and Liability Related Risks
| |
● |
We
may not be able to obtain or maintain adequate insurance coverages. |
| |
● |
Litigation,
product liability claims, product recalls, government investigations and other significant legal proceedings are common in the pharmaceutical
industry. |
| |
● |
We
are subject to various fraud and abuse laws which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational
harm, and diminished profits and future earnings. |
| |
● |
Our
products contain controlled substances which may subject us to increased litigation risk and regulation. |
| |
● |
Mandatory
REMS programs could increase the cost, burden, and liability associated with the commercialization of certain products. |
| |
● |
Illegal
distribution and third party sale of counterfeit versions of our products could have a detrimental effect on our reputation and business. |
Structural
and Organizational Risks
| |
● |
Provisions
of our Articles of Incorporation could deter a change of management and discourage offers to acquire us. |
Intellectual
Property Related Risks
| |
● |
Our
ability to protect intellectual property rights and successfully defend third party allegations of intellectual property infringement
is vital to our business and uncertain. |
Risks
Related to our Common Shares
| |
● |
Dilution
from issuance of shares to Lincoln Park, Directors, Employees, Consultants or upon exercise of warrants and options or the perception
that dilution may occur could cause the price per share of common stock to fall. |
| |
● |
Our
common stock is a penny stock, quoted on the OTC bulletin board, with rules in place that could limit trading and liquidity of our
shares, increased transaction costs that could adversely affect our price per share. |
| |
● |
Shareholder
activism could negatively affect us. |
| |
● |
Our
stock price has been volatile. |
| |
● |
Capital
raises through sales of securities may cause substantial dilution to existing shareholders. |
| |
● |
Issuance
of shares of common or preferred stock could make achieving a change of control more difficult. |
| |
● |
We
have no plans to pay regular dividends or conduct ordinary share purchases. |
Business
Related Risks
The
pharmaceutical industry is highly competitive.
The
pharmaceutical industry is highly competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change, and we may be unable to compete
effectively, which could impair our ability to implement our business model. Competitive factors faced include, without limitation, product
development, safety, efficacy, commercialization, marketing, promotion, product quality, cost-effectiveness, reputation, service, patient
convenience, access to scientific and technical information, and ability to manage operations in an economic environment that has been severely
impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, the pharmaceutical industry is undergoing rapid and significant technological
change, and we expect competition to intensify as technical advances in each field are made and become more widely known. An increasing
number of pharmaceutical companies have been or are becoming interested in the development and commercialization of products incorporating
advanced or novel drug delivery systems. We expect that competition in the field of drug delivery will increase in the future as other
specialized research and development companies begin to concentrate on this aspect of the business. Some of the major pharmaceutical
companies have invested and are continuing to invest significant resources in the development of their own drug delivery systems and
technologies and some have invested funds in specialized drug delivery companies. Many of our competitors have longer operating histories
and, they, and future competitors, may have greater financial, research and development, marketing, and other resources than we do. Furthermore,
recent trends in this industry include market consolidation, which may further concentrate financial, technical, market and other strengths
and resources with the result being a further increase competitive pressures existent in this industry. Such companies may develop new
formulations and products, or may improve existing ones, more efficiently than we can. Our success, if any, will depend in part on our
ability to keep pace with the changing technology in the fields in which we operate.
As
we expand our presence in the generic pharmaceuticals market our product candidates may face intense competition from brand-name companies
that have taken aggressive steps to thwart competition from generic companies. In particular, brand-name companies continue to sell or
license their products directly or through licensing arrangements or strategic alliances with generic pharmaceutical companies (so-called
“authorized generics”). No significant regulatory approvals are required for a brand-name company to sell directly or through
a third party to the generic market, and brand-name companies do not face any other significant barriers to entry into such market. In
addition, such companies continually seek to delay generic introductions and to decrease the impact of generic competition, using tactics
which include, without limitation:
| |
● |
Obtaining
new patents on drugs whose original patent protection is about to expire; |
| |
● |
Filing
patent applications that are more complex and costly to challenge; |
| |
● |
Filing
suits for patent infringement that automatically delay approval from the FDA; |
| |
● |
Filing
citizens’ petitions with the FDA contesting approval of the generic versions of products due to alleged health and safety issues; |
| |
● |
Developing
controlled-release or other “next-generation” products, which often reduce demand for the generic version of the existing
product for which we may be seeking approval; |
| |
● |
Changing
product claims and product labeling; |
| |
● |
Developing
and marketing as over-the-counter products those branded products which are about to face generic competition; and, |
| |
● |
Making
arrangements with managed care companies and insurers to reduce the economic incentives to purchase generic pharmaceuticals. |
These
strategies may increase the costs and risks associated with our efforts to introduce our generic products under development and may delay
or prevent such introduction altogether.
In
addition, sales of our products may be adversely affected by the continuing consolidation within the retail and wholesale pharmaceutical
markets. Our products, whether sold directly by the Company or through third parties that are licensed to market and distribute our products
are sold in large part to a market that is comprised of a relatively few retail drug chains, wholesalers, and managed care organizations,
with such entities continuing to undergo consolidation. Such consolidation may provide these customers or our products with additional
purchasing leverage, and consequently, may increase the pricing pressures faced by us. Additionally, the emergence of large buying groups
representing independent retail pharmacies, and the prevalence and influence of managed care organizations and similar institutions,
enable those groups to extract price discounts on our products and our revenues and quarterly results comparisons may also be affected
by fluctuations in the buying patterns of retail chains, major distributors, and other trade buyers.
Furthermore,
policies regarding returns, rebates, allowances and chargebacks, and marketing programs adopted by wholesalers may reduce our revenues
in future fiscal periods. Based on industry practice, generic drug manufacturers have liberal return policies and have been willing to
give customers post-sale inventory allowances. Such industry practices apply to the current sales of our products by our marketing partners,
which in turn effect profit splits and license fees received, and they will also affect prospective future sales made directly by Company.
Under
these arrangements, from time to time, customers are given credits on our generic products that are held by them in inventory after there
is a decrease in the market prices of the same generic products due to competitive pricing. Therefore, if new competitors enter the marketplace
and significantly lower the prices of any of their competing products, the price of our products would also likely be reduced. As a result,
we, or are marketing partners, would be obligated to provide credits to our customers who are then holding inventories of such products,
which could reduce sales revenue, profit splits, license fees and gross margin for the period the credit is provided. Like most competitors
in this market, our marketing partners, or us in the case of prospective direct sales made by the Company, also give credits for chargebacks
to wholesalers that have contracts with our marketing partners, or us, prospectively, for their sales to hospitals, group purchasing
organizations, pharmacies, or other customers. A chargeback is the difference between the price the wholesaler pays and the price that
the wholesaler’s end-customer pays for a product. Although, our marketing partners establish, and prospectively we would also establish
reserves based on prior experience and best estimates of the impact that these policies may have in subsequent periods, we cannot ensure
that such reserves established are adequate or that actual product returns, rebates, allowances, and chargebacks will not exceed estimates.
Differences between established reserves and actual amounts of such credits and charges, could result in a material adverse effect on
our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flow and stock price.
The
existence and occurrence of any of the above could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations,
cash flow, ability to operate and stock price.
Natural
disasters could cause closures of our facilities and disrupt our operations.
Furthermore,
the occurrence of one or more unexpected events, including fires, tornadoes, tsunamis, hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and other
forms of severe hazards in the United States or in other countries in which we or our suppliers operate or are located could
adversely affect our operations and financial performance. We have lost power or had to shut down operations as a result of extreme
weather and natural disasters, most notably Superstorm Sandy. These types of unexpected events could result in physical damage to
and complete or partial closure of one or more of distribution centers or manufacturing facilities, or the temporary or long-term
disruption in the supply of products, and/or disruption of our ability to deliver products to customers. Further, the long-term
effects of climate change on general economic conditions and the pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution industry in
particular are unclear, and changes in the supply, demand or available sources of energy and the regulatory and other costs
associated with energy production and delivery may affect the availability or cost of goods and services, including natural
resources, necessary to run our businesses. Existing insurance arrangements may not provide protection for the costs that may arise
from such events, particularly if such events are catastrophic in nature or occur in combination. Any long-term disruption in our
ability to service our customers from one or more distribution centers or outsourcing facilities could have a material adverse
effect on our operations, our business, results of operations and stock price.
Interruptions
in operations at our sole facility could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If
our manufacturing facility or the facilities of any of our suppliers fail to comply with regulatory requirements or encounter other
manufacturing difficulties, it could adversely affect our ability to manufacture and supply products. All facilities and
manufacturing processes used for the manufacture of pharmaceutical products are subject to inspection by regulatory agencies at any
time and must be operated in conformity with current good manufacturing practice (“cGMP”) and, in the case of controlled
substances, DEA regulations. Compliance with the FDA’s cGMP and DEA requirements applies to both drug products seeking
regulatory approval and to approved drug products. In complying with cGMP requirements, pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities must
continually expend significant time, money and effort in production, recordkeeping, quality assurance and quality control so that
their products meet applicable specifications and other requirements for product safety, efficacy and quality. Failure to comply
with applicable legal requirements subjects us, our manufacturing facilities and the facilities of our third-party suppliers to
possible legal or regulatory action, including, without limitation, shutdown, which may adversely affect our ability to supply the
product. Additionally, our manufacturing facilities, and those of our third party suppliers may face other significant disruptions
due to labor strikes, failure to reach acceptable agreement with labor unions, infringement of intellectual property rights,
vandalism, natural disaster, pandemics, storm or other environmental damage, civil or political unrest, export or import
restrictions or other events. Were we not able to manufacture products at our manufacturing facilities or were our third party
suppliers unable to manufacture products at their facilities because of regulatory, business or any other reasons, the manufacture
and marketing of these products would be interrupted. This could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of
operation, financial condition, cash flows, competitive position and ability to operate.
Furthermore,
all of our manufacturing operations are conducted at the Northvale Facility and any delays or unanticipated expenses in connection with
the operation at the Northvale Facility, resulting in a significant disruption at this facility, even on a short-term basis, whether
due to, without limitation, an adverse quality or compliance observation, including a total or partial suspension of production and/or
distribution by regulatory authorities, an act of God, civil or political unrest, force majeure situation or other events could impair
our ability to produce and ship products on a timely basis, and could, among other consequences, subject us to exposure to claims from
customers. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and
cash flows.
We
may sell, withdraw or discontinue manufacture of certain products.
We
may discontinue the manufacture and distribution of certain existing products, which may adversely affect our business, results of operations,
financial condition, and cash flows. As part of regular evaluations of product performance, we may determine that it is in our best interest
to discontinue the manufacture and distribution of certain of our products. We cannot guarantee that we have correctly forecasted, or
will correctly forecast in the future, the appropriate products to discontinue or that a decision to discontinue various products is
prudent if market conditions change. In addition, there can be no assurances that the discontinuance of products will reduce operating
expense or not cause the incurrence of material charges associated with such a decision. Furthermore, the discontinuance of existing
products, entails various risks, including, without limitation, the ability to find a purchaser for such products, if there is a decision
to sell the product, as well as the risk that the purchase price obtained will not be equal to at least the book value of the net assets
relating to such products. Other risks associated with a product discontinuance, include, without limitation, managing the expectations
of and maintaining good relations with our customers who previously purchased a discontinued product from us, and the effects such would
have on future sales to these customers. We may also incur significant liabilities and costs associated with our product discontinuance.
In
addition, we may, from time to time, sell and/or withdraw approved ANDAs if we determine that the costs of maintaining such ANDAs is
excessive when compared to their actual current value and their perceived value and place in our strategic plans.
Although
our expectations are to engage only in the sale or withdrawal of ANDAs if they advance or otherwise support our overall strategy, any
such ANDA sale by definition reduces the size and scope of our business, with a direct correlation to opportunities with respect to certain
markets, products or therapeutic categories.
All
of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and ability
to operate.
We
may fail to successfully identify, develop and commercialize new products.
Elite’s
product pipeline, including the paused development of its abuse deterrent opioid products, are in various stages of development. Prior
to commercialization, product development must be completed that could include scale-up, clinical studies, regulatory filing, regulatory
review, approval by the FDA, and/or other development steps. Development is subject to risks. We cannot assure you that development will
be successful, or that during development unexpected delays might occur or additional costs might be incurred.
In
order to obtain FDA approval to market a new drug product, we must demonstrate proof of safety and effectiveness in humans. To meet these
requirements, we must conduct extensive preclinical testing and “adequate and well-controlled” clinical trials. Conducting
clinical trials is a lengthy, time-consuming, and expensive process. Completion of necessary clinical trials may take several years or
more. Delays associated with product candidates for which we are directly conducting preclinical or clinical trials may cause us to incur additional
operating expenses. The commencement and rate of completion of clinical trials may be delayed by many factors, including, without limitation,
for example:
| |
● |
Ineffectiveness
of our product candidate or perceptions by physicians that the product candidate is not safe or effective for a particular indication; |
| |
● |
Inability
to manufacture sufficient quantities of the product candidate for use in clinical trials; |
| |
● |
Delay
or failure in obtaining approval of our clinical trial protocols from the FDA or institutional review boards; |
| |
● |
Slower
than expected rate of patient recruitment and enrollment; |
| |
● |
Inability
to adequately follow and monitor patients after treatment; |
| |
● |
Difficulty
in managing multiple clinical sites; |
| |
● |
Unforeseen
safety issues; |
| |
● |
Government
or regulatory delays; and, |
| |
● |
Clinical
trial costs that are greater than we currently anticipate. |
Even
if we achieve positive interim results in clinical trials, these results do not necessarily predict final results, and positive results
in early trials may not be indicative of success in later trials. A number of companies in the pharmaceutical industry have suffered
significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials, even after achieving promising results in earlier trials. Negative or inconclusive
results or adverse medical events during a clinical trial could cause us to repeat or terminate a clinical trial or require us to conduct
additional trials. We do not know whether our existing or any future clinical trials will demonstrate safety and efficacy sufficiently
to result in marketable products. Our clinical trials may be suspended at any time for a variety of reasons, including if the FDA or
we believe the patients participating in our trials are exposed to unacceptable health risks or if the FDA finds deficiencies in the
conduct of these trials.
Failures
or perceived failures in our clinical trials will directly delay our product development and regulatory approval process, damage our
business prospects, make it difficult for us to establish collaboration and partnership relationships, and negatively affect our reputation
and competitive position in the pharmaceutical community.
Our
ability to sustain current operations, engender business growth, achieve current and future revenues and profitability, significantly
depends on our ability to successfully identify, develop, obtain regulatory approval, commercialize and market new pharmaceutical products,
including, without limitation, our own products as well as those that may be developed in partnership with other entities, such as those
that were previously developed with Praxgen pursuant to a now terminated product development agreement. As a result, we must continually
develop, test and manufacture new products, which must meet regulatory standards to receive requisite marketing authorizations.
The
process of developing and obtaining regulatory approvals for new products is time-consuming, costly and inherently unpredictable. There
are direct, indirect, known and unknown risks inherent in the development of pharmaceuticals, including, without limitation, product candidates
which initially show promise in preliminary pharmacological or marketing studies, but fail to yield the positive results consistent with
initial indications. Product candidates we may develop may not receive the marketing authorizations necessary for us to market them and, if approved,
we may be unable to successfully commercialize them on a timely basis or at all, or if commercialized, revenues and profits achieved
from the sale of such products might not reach levels that provide sufficient return on those costs incurred during the commercialization
process.
The
successful commercialization of a product is subject to a number of factors, including:
| |
● |
The
timely filing of any NDA, ANDA or other regulatory submission applicable to our product candidates; |
| |
● |
Any
adverse development or perceived adverse development with respect to the applicable regulatory agency’s review of such regulatory
submission and approval for the indication sought; |
| |
● |
The
effectiveness, ease of use and safety of our products as compared to existing products; |
| |
● |
Customer
demand and the willingness of physicians and customers to adopt our products over products with which they may have more loyalty
or familiarity and overcoming any biases towards our products; |
| |
● |
The
cost of our product compared to alternative products and the pricing and commercialization strategies of our competitors; |
| |
● |
The
success of our launch and marketing efforts; |
| |
● |
Adverse
publicity about us, our products, our competitors and their products or the industry as a whole or favorable publicity about competitors; |
| |
● |
The
advent of new and innovative alternative products; and |
| |
● |
Any
unforeseen issues or adverse developments in connection with a product and any resulting litigation or regulatory scrutiny and harm
to our reputation or the reputation or acceptance of the product in the market. |
In
addition, there are many risks associated with developing, commercializing and marketing new products that are beyond our control. For
example, without limitation, our collaboration partner(s) may decide to make substantial changes to a product’s formulation or
design, may experience financial difficulties or may have limited financial resources. Any of the foregoing may delay the development,
commercialization and/or marketing of new products. In addition, if a codeveloper on a new product terminates our collaboration agreement
or does not perform under the agreement, we may experience delays and additional costs in developing and marketing that product, with
no assurances of us having the resources that may be required to overcome such delays or additional costs that were beyond our control.
We
conduct research and development to enable us to manufacture and market pharmaceutical products in accordance with specific government
regulations. Our drug development efforts relating to SequestOx™, which are currently paused, and certain generics are focused
on technically difficult-to-formulate products and/or products that require advanced manufacturing technology. Typically, expenses related
to research, development, and regulatory approval of compounds for SequestOx™, which is a branded pharmaceutical product, the development
of which is currently paused, are significantly greater than those expenses associated with generic products. Expanded research and development
efforts are required, resulting in increased research expenses. Because of the inherent risk associated with research and development
efforts in the healthcare industry, particularly with respect to new drugs, our research and development expenditures may not result
in the successful regulatory approval and introduction of new pharmaceutical products and failure in the development of any new product
can occur at any point in the process, including late in the process after substantial investment. Also, after we submit a regulatory
application, the relevant governmental health authority may require that we conduct additional studies, including, for example, studies
to assess the product’s interaction with alcohol. As a result, we may be unable to reasonably predict the total research and development
costs to develop a particular product and there is a significant risk that the funds we invest in research and development will not generate
financial returns. In addition, our operating results and financial condition may fluctuate as the amount we spend to research and develop,
commercialize, acquire or license new products, technologies and businesses changes. Much of the preceding occurred with the development
of SequestOx™, which has not received marketing approval from the FDA, for which continued development has been paused and with
material adverse effects on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and ability to operate resulting in
the past, as well as the risk remaining for the future.
Because
of these risks, our research and development efforts may not result in any commercially viable products. Any delay in, or termination
of, preclinical or clinical trials will delay the filing of our drug applications with the FDA and, ultimately, our ability to commercialize
product candidates and generate product revenues. If a significant portion of these development efforts are not successfully completed,
required regulatory approvals are not obtained, or any approved products are not commercially successful, our business, financial condition,
and results of operations may be materially harmed.
Our
operations could be disrupted by failure of our information systems or cyber-attacks.
Our
operations could be disrupted if our information systems fail, if we are unsuccessful in implementing necessary upgrades or if we are
subject to cyber-attacks. Our business depends on the efficient and uninterrupted operation of our computer and communications systems
and networks, hardware and software systems and our other information technology. We collect and maintain information, which includes
confidential and proprietary information as well as personal information regarding our customers and employees, in digital form. Data
maintained in digital form is subject to risk of cyber-attacks, which are increasing in frequency and sophistication. Cyber-attacks could
include the deployment of harmful malware, viruses, worms, and other means to affect service reliability and threaten data confidentiality,
integrity and availability. Despite our efforts to monitor and safeguard our systems to prevent data compromise, the possibility of a
future data compromise cannot be eliminated entirely, and risks associated with intrusion, tampering, and theft remain. In addition,
we do not have insurance coverage with respect to system failures or cyber- attacks. A failure of our systems, or an inability to successfully
expand the capacity of these systems, or an inability to successfully integrate new technologies into our existing systems could have
a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows.
We
also have outsourced significant elements of our information technology infrastructure to third parties, some of which may be outside
the U.S. Accordingly, significant elements of our information technology infrastructure, require our management of multiple independent
vendor relationships with third parties who may or could have access to our confidential information. The size and complexity of our
information technology systems, and those of our third-party vendors with whom we contract, make such systems potentially vulnerable
to service interruptions. The size and complexity of our and our vendors’ systems and the large amounts of confidential information
that is present on them also makes them potentially vulnerable to security breaches from inadvertent or intentional actions by our employees,
partners, or vendors, or from attacks by malicious third parties.
The
Company and its vendors’ sophisticated information technology operations are spread across multiple, sometimes inconsistent, platforms,
which pose difficulties in maintaining data integrity across systems. The ever-increasing use and evolution of technology, including
cloud-based computing, creates opportunities for the unintentional or improper dissemination or destruction of confidential information
stored in the Company’s systems.
Any
breach of our security measures or the accidental loss, inadvertent disclosure, unapproved dissemination, misappropriation or misuse
of trade secrets, proprietary information or other confidential information, whether as a result of theft, hacking, fraud, trickery or
other forms of deception, or for any other cause, could enable others to produce competing products, use our proprietary technology or
information and/or adversely affect our business position. Further, any such interruption, security breach, loss or disclosure of confidential
information could result in financial, legal, business and reputational harm to our company and could have a material adverse effect
on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and stock price.
Delays
in generic product development may result in failure to achieve adequate return on investment.
The
time necessary to develop generic drugs may adversely affect whether, and the extent to which, we receive a return on our capital. The
development process for generic products, including, without limitation, drug formulation, testing, and FDA review and approval, often
takes three or more years. We must also successfully address any challenges brought by the owner of the listed patent. This process requires
that we expend considerable capital to pursue activities that do not yield an immediate or near-term return. Also, because of the significant
time necessary to develop a product, the actual market for a product at the time it is available for sale may be significantly less than
the originally projected market for the product. If this were to occur, our potential return on our investment in developing the product,
if approved for marketing by the FDA, would be adversely affected and we may never receive a return on our investment in the product.
It is also possible for the manufacturer of the brand-name product for which we are developing a generic drug to obtain approvals from
the FDA to switch the brand-name drug from the prescription market to the OTC market. If this were to occur, we would be prohibited from
marketing our product other than as an OTC drug, in which case revenues could be substantially less than we anticipated.
Our
business is dependent on market perceptions, social and political pressures, including public concern over the abuse of opioids.
Market
acceptance of our products among physicians, patients, health care payors and the medical community, is a key component of commercial
success and if such is not achieved, our business will be adversely affected. The degree of market acceptance of any of our approved
products among physicians, patients, health care payors and the medical community will depend on a number of factors, including, without
limitation:
| |
● |
Acceptable
evidence of safety and efficacy; |
| |
● |
Relative
convenience and ease of administration; |
| |
● |
The
prevalence and severity of any adverse side effects; |
| |
● |
Availability
of alternative treatments; |
| |
● |
Pricing
and cost effectiveness; |
| |
● |
Effectiveness
of sales and marketing strategies; and, |
| |
● |
Ability
to obtain sufficient third-party coverage or reimbursement. |
If
we are unable to achieve market acceptance for our products, then such products will not be commercially successful, and our business
will be adversely affected.
Some
of these factors are not within our control, and our products may not achieve expected levels of market acceptance. Additionally, continuing
and increasingly sophisticated studies of the proper utilization, safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products are being conducted
by the industry, government agencies and others which can call into question the utilization, safety, and efficacy of previously marketed
products. In some cases, studies have resulted, and may in the future result, in the discontinuance of product marketing or other risk
management programs such as the need for a patient registry.
We
may also experience downward pressure on the price of our products due to social or political pressure to lower the cost of drugs, which
would reduce our revenue and future profitability.
Public
concern over the abuse of opioid medications, including increased legal and regulatory action, could also negatively affect our business.
While Elite has de-emphasized its programs with respect to opioids and will continue to focus on products other than opioids, certain
governmental and regulatory agencies, as well as state and local jurisdictions, are focused on the abuse of opioid medications in the
United States. State and local governmental agencies may investigate us as a manufacturer and/or distributor of medicines containing
opioids or in conjunction with their investigation of other pharmaceutical wholesale distributors, and others in the supply chain that
have a direct or indirect connection to our operations in relation to the distribution of opioid medications. In addition, multiple lawsuits
have been filed against other pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors alleging, among other claims, that they failed to provide
effective controls and procedures to guard against the diversion of controlled substances, acted negligently by distributing controlled
substances to pharmacies that serve individuals who abuse controlled substances, and failed to report suspicious orders of controlled
substances in accordance with regulations. Additional governmental entities have indicated an intent to sue these other manufacturers
and distributors. While no such actions have been taken against us, the immediate effect on the Company has been an inability to commercialize
and market three opioid products approved during fiscal years prior to the twelve months ended March 31, 2021 and a cessation of orders
for another two other opioid products that had been marketed by our marketing partners. During the year ended March 31, 2020, we disposed
of four approved ANDA’s for opioid products. As of March 31, 2023, we continue to hold one approved ANDA for an opioid product
that, while approved by the FDA, has not been launched commercially. Further, defense against any such opioid related lawsuits could
be cost-prohibitive resulting in an adverse material effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and
stock price. Similar allegations made against us, even without litigation, could also negatively affect our business in various ways,
including through increased costs and harm to our reputation. In addition, an adverse resolution of any lawsuit or investigation could
also have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flows and stock price.
Market
perceptions of our business are important to us, especially market perceptions of the safety and quality of our products. If any of our
products or similar products that other companies distribute are subject to market withdrawal, recall, or are proven to be, or are claimed
to be, harmful to consumers, then this could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition,
and cash flows. Furthermore, due to the importance of market perceptions, negative publicity associated with product quality, illness
or other adverse effects resulting from, or perceived to be resulting from, our products, or similar products made by other companies,
could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows.
Any
or all of the above could result in a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flow,
ability to operate and stock price.
Unstable
economic conditions may adversely affect our business.
The
global economy has undergone a period of significant volatility, especially during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to diminished
credit availability, declines in consumer confidence, and increases in unemployment rates. There remains caution about the stability
of the U.S. economy, and we cannot assure that further deterioration in the financial markets will not occur. These economic conditions
have resulted in, and could lead to further, reduced consumer spending related to healthcare in general and pharmaceutical products in
particular.
In
addition, we have exposure to many different industries and counterparties, including our partners under our alliance and collaboration
agreements, suppliers of raw chemical materials, drug wholesalers and other customers that may be affected by an unstable economic environment.
Any economic instability may affect these parties’ ability to fulfil their respective contractual obligations to us, cause them
to limit or place burdensome conditions upon future transactions with us or drive us and our competitors to decrease prices, each of
which could materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition, cash flows and stock price.
We
depend on qualified scientific and technical personnel and our ability to attract and retain such personnel.
Because
of the specialized scientific nature of our business, we are highly dependent upon our ability to continue to attract and retain qualified
scientific and technical personnel. We are not aware of any pending, significant losses of scientific or technical personnel. Loss of
the services of, or failure to recruit, key scientific and technical personnel, however, would be significantly detrimental to our product-development
programs. As a result of our small size and limited financial and other resources, it may be difficult for us to attract and retain qualified
officers and qualified scientific and technical personnel.
In
addition, marketing of our branded product, SequestOx™, if approved, will require much greater use of a direct sales force compared
to marketing of our generic products, should we reinstate development and successfully commercialize this product. Our ability to realize
significant revenues from marketing and sales activities depends on our ability or the ability of our partners to attract and retain
qualified sales personnel. Competition for qualified sales personnel is intense. Any failure to attract or retain qualified sales personnel
could negatively impact our sales revenue and have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition,
cash flows and stock price.
We
have entered into employment agreements with our executive officers and certain other key employees. We do not maintain “Key
Man” life insurance on any executives.
Unsuccessful
collaboration or licensing arrangements could limit revenues and product development.
We
have entered into several collaborations and licensing arrangements for the development of products. However, there can be no assurance
that any of these agreements will result in FDA approvals, or that we will be able to market any such products, if approved, at a profit.
Collaboration and licensing arrangements pose the following risks:
| |
● |
Collaborations
and licensing arrangements may be terminated, in which case we will experience increased operating expenses and capital requirements
if we elect to pursue further development of the related product candidate; |
| |
● |
Collaborators
and licensees may delay clinical trials and prolong clinical development, under-fund a clinical trial program, stop a clinical trial,
or abandon a product candidate; |
| |
● |
Expected
revenue might not be generated because milestones may not be achieved, and product candidates may not be developed; |
| |
● |
Collaborators
and licensees could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that could compete with our future products; |
| |
● |
The
terms of our contracts with current or future collaborators and licensees may not be favorable to us in the future; |
| |
● |
A
collaborator or licensee with marketing and distribution rights to one or more of our products may not commit enough resources to
the marketing and distribution of our products, limiting our potential revenues from the commercialization of a product; |
| |
● |
Disputes
may arise delaying or terminating the research, development, or commercialization of our product candidates, or result in significant
and costly litigation or arbitration; and, |
| |
● |
One
or more third-party developers could obtain approval for a similar product prior to the collaborator or licensee resulting in unforeseen
price competition in connection with the development product. |
Any
or all of the above could result in a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flow,
ability to operate and stock price.
Financial
and Liquidity Risks
We
have a relatively limited operating history and our operating results could fluctuate significantly.
Our
revenues and operating results may vary significantly from year-to-year and quarter-to-quarter as well as in comparison to the corresponding
quarter of the preceding year. Variations may result from one or more factors, including, without limitation:
| |
● |
Effects
of a global pandemic or similar situation, including, without limitation the COVID-19 pandemic that emerged in 2020, with such effects
to include actions taken by the Company, its suppliers, partners, competitors, other entities involved in the industry, other entities,
and any laws, regulations, executive orders or other governmental/regulatory actions taken in relation to such a pandemic or similar
circumstance; |
| |
● |
Timing
of approval of applications filed with the FDA; |
| |
● |
Timing
of process validation, product launches and market acceptance of products launched; |
| |
● |
Changes
in the amounts spent to research, develop, acquire, license or promote new and existing products; |
| |
● |
Results
of clinical trial programs; |
| |
● |
Serious
or unexpected health or safety concerns with our products, brand products which we have genericized, products currently under development
or any other product candidates; |
| |
● |
Introduction
of new products by others that render our products obsolete or non-competitive; |
| |
● |
The
ability to maintain selling prices and gross margin on our products; |
| |
● |
Mix
of product manufactured and sold due to each product having different gross margins; |
| |
● |
The
cost and outcome of litigation, in the event that such occurs in relation to, without limitation, intellectual property issues, regulatory
or other matters; |
| |
● |
The
ability to comply with complex and numerous governmental regulations and regulatory authorities which oversee and regulate many aspects
of our business and operations; |
| |
● |
Changes
in coverage and reimbursement policies of health plans and other health insurers, including changes to Medicare, Medicaid, and similar
state programs, especially in relation to those products that are currently manufactured, under development or identified for future
development by the Company; |
| |
● |
Increases
in the cost of raw materials contained within our products; |
| |
● |
Manufacturing
and supply interruptions, including product rejections or recalls due to failure to comply with manufacturing specifications; |
| |
● |
Timing
of revenue recognition relating to our licensing and other agreements; |
| |
● |
The
ability to avoid infringing the intellectual property of others; |
| |
● |
The
ability to protect our intellectual property from being acquired by other entities; |
| |
● |
Our
ability to manage growth and integrate acquired products and assets successfully; and |
| |
● |
The
addition or loss of customers. |
A
negative variation in one, many or all of the above factors could, may or will have a material adverse effect on Elite’s business,
results of operations, financial condition, and cash flow and ability to operate in the future, depending on the nature and magnitude
of the variation(s).
In
addition, although we have been in operation since 1990, we have a relatively short operating history, have only achieved profitability
for the first time during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2021 and limited financial data upon which you may evaluate our business and
prospects. There can be no assurances of our ability to sustain current profitability. Additionally, in certain years prior to the year
ended March 31, 2021, the auditor’s opinion on our financials was qualified with respect to there being substantial doubt as to
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern due to continued losses not being sufficiently offset by operating revenues.
A failure to generate sufficient revenues to offset related costs of operations will have a material adverse effect on our business,
results of operations, financial condition, cash flow and ability to operate.
Furthermore,
our business model is likely to continue to evolve as we attempt to expand our product offerings and our presence in the generic pharmaceutical
market. As a result, our potential for future profitability must be considered in view of the risks, uncertainties, expenses, and difficulties
frequently encountered by companies that are attempting to move into new markets and continuing to innovate with new and unproven technologies.
Some of these risks relate to our potential inability to:
| |
● |
Develop
new products; |
| |
● |
Obtain
regulatory approval of our products; |
| |
● |
Manage
our growth, control expenditures and align costs with revenues; |
| |
● |
Attract,
retain, and motivate qualified personnel; and respond to competitive developments. |
| |
● |
Sustain
operations during a global pandemic or similar situation, such as the COVID-19 global pandemic first identified in 2020. |
If
we do not effectively address the risks we face, our business model may become unworkable and we may not achieve or sustain profitability
or successfully develop any products, resulting in a material adverse effect on Elite’s business, results of operations, financial
condition, and cash flow and ability to operate in the future.
Our
ability to fund operations is uncertain and we may require additional financing to meet objectives.
Our
ability to fund our operations, maintain liquidity and meet our financing obligations is reliant on our operations, which are subject
to significant risks and uncertainties. We rely on cash generated by operations as well as access to financial markets, such as the equity
line with Lincoln Park and equipment financings, to fund our commercial, product development and other operations, maintain liquidity
and meet our financial obligations. Amounts available under the equity line with Lincoln Park have a strong and direct correlation to
the Company’s publicly traded price per share and volumes. There can be no assurances of our traded price per share and volumes
being at sufficient levels to provide adequate funding from the equity line with Lincoln Park. In addition, there can be no assurances
of our ability to secure equipment financing, resulting in an increased risk of our inability to achieve critical or necessary facility
upgrades.
Our
operations are also subject to many significant risks and uncertainties, as described, without limitation, in this “Risk Factors”
section, including, without limitation, those risks related to the effects of a global pandemic such as or similar to the COVID-19 pandemic,
competition in the markets in which we operate, litigation risks, government investigations, including those related to our sale, marketing
and/or distribution of prescription opioid medications in prior periods, and others. Any negative development or outcome in connection
with any or all of these risks and uncertainties could result in significant consequences, including, without limitation, one or more
of the following:
| |
● |
The
dedication of a substantial portion of our cash flows from operations to the payment of legal or related expenses, resulting in these
same funds being unavailable for other purposes, including, without limitation, debt service, operations, capital expenditures, product
development and future business opportunities; |
| |
● |
A
limitation in our ability to adjust to changing market conditions, causing us to be more vulnerable to periods of negative or impaired
growth in the general economy or in our business, resulting the company being put at a competitive disadvantage as a result of a
decreased or unavailable ability to engage in capital spending and take all other actions that would otherwise be required to ensure
growth and competitiveness; |
| |
● |
A
limitation in our ability to attract and retain key personnel; |
| |
● |
A
decrement in our debt service and compliance obligations related to certain of our outstanding debt obligations, exposing us to events
of default and reduced credit ratings, which in turn lead to increased capital costs and potential unavailability of capital; and, |
| |
● |
An
overall inability to fund our operations and liquidity needs. |
The
occurrence or possibility of one or more of these or similar events may cause us to pursue one or more significant corporate transactions
as well as other remedial measures, including refinancing all or part of our then-existing indebtedness, selling assets, reducing, delaying
or eliminating capital expenditures, seeking to raise additional capital or pursuing internal reorganizations, restructuring activities,
strategic alliances, or cost-saving initiatives. Any refinancing of our substantial indebtedness could be at significantly higher interest
rates, which will depend on both the conditions of the market as well as the Company’s finances at such time, and may also require
our compliance with covenants that could be more onerous than current, which in turn could result in the further restriction of our business
operations. Any refinancing may also increase the amount of our secured indebtedness. In addition, the terms of existing or future debt
agreements may restrict us from adopting any of the alternatives. Internal reorganizations, restructuring activities, asset sales and
cost saving initiatives may also be complex and could entail significant costs and charges or could otherwise negatively impact shareholder
value. There can also be no assurance that we will be able to accomplish any of these alternatives on terms acceptable to us, or at all,
or that even if accomplished, that the intended results and benefits would be realized.
We
most likely will require additional financing to meet our business objectives.
We
most likely will need additional funding to accomplish our plans to conduct the clinical development and commercialization of a range
of multiple abuse deterrent opioids or initiate, continue or complete the development of additional generic products already identified
for development or currently in development.
As
of March 31, 2023, we had cash on hand of approximately $7.8 million and a working capital surplus of $13.7 million, and, for the fiscal
year ended March 31, 2023, we generated income from operations totaling $3.7 million, net other income totaling $0.3 million and net
income of $3.6 million.
On
July 8, 2020, we entered into another purchase agreement (the “2020 LPC Purchase Agreement”), together with a registration
rights agreement (the “2020 LPC Registration Rights Agreement”), with Lincoln Park. Under the terms and subject to
the conditions of the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement, we have the right to sell to and Lincoln Park is obligated to purchase up to $25 million
in shares of our common stock, subject to certain limitations, from time to time, over the 36-month period commencing on July 27, 2020
and expiring on August 1, 2023.
While
growth in our current generic product line, consisting of Phentermine Tablets, Phentermine Capsules, Phendimetrazine Tablets, Naltrexone
Tablets, Isradipine Capsules, Trimipramine Capsules, Loxapine capsules, Amphetamine IR Tablets, Amphetamine ER Capsules and Dantrolene Capsules, and successful commercialization of other products in our product development pipeline,
may lead to eventual profitability, there can be no assurances of Elite becoming profitable. Furthermore, there can be no assurances
of the continuation revenues being earned from the current generic product line, no assurances of Elite’s successful commercialization
of other products in our development pipeline, and no assurances of Elite’s ability to continue as a going concern. In addition,
there can be no assurances of Elite being able to raise additional funds in a timely manner, on acceptable terms, if needed to support
commercial operations resulting in a material detrimental effect on Elite’s ability to become profitable and accordingly being
a material factor to the detriment of Elite’s ability to continue as a going concern as well as having a material adverse effect
on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flow and ability to operate in the future.
To
sustain operations and meet our business objectives we must be able to commercialize our products and other products or pipeline opportunities.
If we are unable to timely obtain additional financing, if necessary, and/or we are unable to timely generate greater revenues from our
operations, we will be required to reduce and, possibly, cease operations and liquidate our assets. No assurance can be given that we
will be able to commercialize the new opportunities or consummate such other financing or strategic alternative in the time necessary
to avoid the cessation of our operations and liquidation of our assets.
Furthermore,
the capital and credit markets have experienced extreme volatility. Disruptions in the credit markets make it harder and more expensive
to obtain funding. In the event current resources do not satisfy our needs, we may have to seek additional financing. The availability
of additional financing will depend on a variety of factors such as market conditions and the general availability of credit. Future
debt financing may not be available to us when required or may not be available on acceptable terms, and as a result we may be unable
to grow our business, take advantage of business opportunities, or respond to competitive pressures.
Please
also see the risk factor titled “Global pandemic and natural disasters”.
We
have substantial indebtedness which may adversely affect our financial condition.
We
currently have substantial indebtedness. Total liabilities as of March 31, 2023, were $11.9 million, with such amount including, without
limitation, $3.9 million in various loans, leases, and bonds payable, $0.5 million in derivative liabilities, and $7.5 million in current
payables and accruals. The consequences of this substantial indebtedness could include:
| |
● |
An
increase in our vulnerability to general economic and industry conditions, including recessions, depressions, effects of global pandemics
such as the COVID-19 pandemic, significant inflation and other financial market volatility; |
| |
● |
Exposure
to the risk of increased interest rates; |
| |
● |
The
Company being required to dedicate a substantial portion of cash flow from operations for debt service and the attendant result of
a diminished ability to fund working capital, capital expenditures and other expenses; |
| |
● |
A
limitation in our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry in which we operate; |
| |
● |
Our
being at a competitive disadvantage as compared to competitors with less indebtedness; and |
| |
● |
A
limitation in our ability to borrow additional funds that may be needed to operate and expand our business. |
In
addition, a notice of default was issued by the New Jersey Economic Development Authority in relation to prior obligations of our tax-exempt
bonds. Although we are current in our payments under these bonds, if the principal balances due under these bonds are accelerated pursuant
to the notice of default, our ability to operate in the future will be materially and adversely affected.
For
more information on the NJEDA Bonds, see Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition
and Results of Operations; Liquidity and Capital Resources; NJEDA Bonds”.
There
is a risk of impairment of significant intangible assets on our balance sheet.
We
have significant intangible assets on our balance sheet. Consequently, potential impairment of intangible assets may have an adverse
material effect on our profitability.
Intangible
assets represent a significant portion of our assets. As of March 31, 2023, intangible assets were approximately $6.3 million, or approximately
16% of our assets.
Generally
accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”) requires that intangible assets be subject to regular impairment
analysis to determine if changes in circumstances indicate that the value of the asset as recorded may not be recoverable. Such events
or changes in circumstances are an inherent risk in the pharmaceutical industry and often cannot be predicted. However, should a change
in circumstance occur, requiring the impairment of an intangible asset, the result of such an impairment may have an adverse material
effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and stock price. During the year ended March 31, 2023, we determined that circumstances indicated that the value of our intangible
assets may not be recoverable. During the year ended March 31, 2023, we recorded impairment of approximately $0.3 million of our ANDA
and patent intangible assets.
GAAP
requires estimates, judgements and assumptions which inherently contain uncertainties.
There
are inherent uncertainties involved in estimates, judgments and assumptions used in the preparation of financial statements in accordance
with GAAP. Any future changes in estimates, judgments and assumptions used or necessary revisions to prior estimates, judgments or assumptions
could lead to a restatement of our results.
The
consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are prepared in accordance with GAAP. This involves making
estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect reported amounts of assets (including intangible assets), liabilities, mezzanine equity,
stockholders’ equity, operating revenues, costs of sales, operating expenses, other income, and other expenses. Estimates, judgments,
and assumptions are inherently subject to change in the future and any necessary revisions to prior estimates, judgments or assumptions
could lead to a restatement. Any such changes could result in corresponding changes to the amounts of assets (including goodwill and
other intangible assets), liabilities, mezzanine equity, stockholders’ equity, operating revenues, costs of sales, operating expenses,
other income and other expenses.
Legal
and Regulatory Risks
The
pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated which creates uncertainty and substantial compliance costs.
The
pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated, which creates uncertainty about our ability to bring new products to market and imposes
substantial compliance costs on our business in relation to product development as well as commercial operations.
Governmental
authorities such as the FDA impose substantial requirements on the development, manufacture, holding, labelling, marketing, advertising,
promotion, distribution and sale of therapeutic pharmaceutical products through lengthy and detailed laboratory and clinical testing
and other costly and time-consuming procedures. In addition, before obtaining regulatory approvals for certain generic products, we must
conduct limited bioequivalence studies and other research to show comparability to the branded products. A failure to obtain satisfactory
results in required pre-marketing trials may prevent us from obtaining required regulatory approvals. The FDA may also require companies
to conduct post-approval studies and companies are subject to post-approval surveillance regarding their drug products and to report
adverse events. The FDA also can require companies to formulate approved Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) to help ensure
that a drug’s benefits outweigh its risks.
We
may seek FDA approval for certain product candidates through the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway. Even if we receive approval for an NDA
under Section 505(b)(2), the FDA may not take timely enforcement action against companies marketing unapproved versions of the drug;
therefore, we cannot be sure that that we will receive the benefit of any de facto exclusive marketing period or that we will fully recoup
the expenses incurred to obtain an approval. In addition, certain competitors and others have objected to the FDA’s interpretation
of Section 505(b)(2). If the FDA’s interpretation of Section 505(b)(2) is successfully challenged, this could delay or even prevent
the FDA from approving any NDA that we submit under Section 505(b)(2).
Moreover,
even if our product candidates are approved under Section 505(b)(2), the approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses
for which the products may be marketed or to other conditions of approval or may contain requirements for costly post-marketing testing
and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of the products.
The
ANDA approval process for a new product varies in time, is difficult to estimate and can vary significantly, from as little as 10 months
from the date of application, to several years or more. Furthermore, ANDA approvals, if granted, may not include all indications for
which the Company may seek to market each product.
Further,
once a product is approved or cleared for marketing, failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can result in, among other
things, suspensions or withdrawals of approvals or clearances, seizures or recalls of products, injunctions against the manufacture,
holding, distribution, marketing and sale of a product, and civil and criminal sanctions. Furthermore, changes in existing regulations
or the adoption of new regulations could prevent us from obtaining, or affect the timing of, future regulatory approvals or clearances.
Meeting regulatory requirements and evolving government standards may delay marketing of our new products for a considerable period of
time, impose costly procedures upon our activities and result in a competitive advantage to larger companies that compete against us.
Even
if regulatory approval is obtained for a particular product candidate, the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities may, nevertheless,
impose significant restrictions on the indicated uses or marketing of such products, or impose ongoing requirements for post-approval
studies. Following any regulatory approval of our product candidates, we will be subject to continuing regulatory obligations, such as
safety reporting requirements, and additional post-marketing obligations, including regulatory oversight of the promotion and marketing
of our products. If we become aware of previously unknown problems with any of our product candidates here or overseas or at our contract
manufacturers’ facilities, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions on our products, our contract manufacturers or on us, including
requiring us to reformulate our products, conduct additional clinical trials, make changes in the labelling of our products, implement
changes to or obtain re-approvals of our contract manufacturers’ facilities or withdraw the product from the market. In addition,
we may experience a significant drop in the sales of the affected products, our reputation in the marketplace may suffer and we may become
the target of lawsuits, including class action suits. Moreover, if we fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, we may
be subject to fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals, product recalls, seizure of products, operating restrictions,
and criminal prosecution. Any of these events could harm or prevent sales of the affected products or could substantially increase the
costs and expenses of commercializing and marketing these products.
Compliance
with federal and state and local law regulations, including compliance with any newly enacted regulations, requires substantial expenditures
of time, money, and effort to ensure full compliance. Failure to comply with the FDA, DEA, EPA and other governmental regulations can
result in fines, disgorgement, unanticipated compliance expenditures, recall or seizure of products, exposure to product liability claims,
total or partial suspension of production or distribution, suspension of the FDA’s review of NDAs or ANDAs, enforcement actions,
injunctions and civil or criminal prosecution, any of which could have a material and adverse effect on our business, results of operations
and financial condition.
Our
business may be adversely affected by legislation or healthcare regulatory reform and initiatives.
Our
business and financial condition may be adversely affected by legislation or regulatory reform of the healthcare system in the United
States. We cannot predict with any certainty how existing laws may be applied or how laws or legal standards may change in the future.
Current or future legislation, whether state or federal, or in any of the non-U.S. jurisdictions with authority over our suppliers, customers
or operations, may have a material effect on our business, ability to operate, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Employers
may seek to reduce costs by reducing or eliminating employer group healthcare plans or by transferring a greater portion of their healthcare
costs to their employees. Job losses, or other economic hardships, especially, but not limited to those hardships resulting from the
effects of the COVID-19 global pandemic, may also result in reduced levels of coverage for some individuals, potentially resulting in
lower healthcare coverage for themselves or their families. Furthermore, increased instability in the insurance marketplace or an increase
in uninsured Americans or others living and working in the USA may result from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 elimination of the Patient
Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA)’s requirement that individuals maintain health insurance or incur a financial penalty
and other steps taken by various governmental and other organizations to limit or end subsidies to such individuals at comparatively
lower income levels. These economic conditions may affect an individual’s ability to afford healthcare as a result of increased
premiums, co-pay or deductible obligations, greater cost sensitivity to existing co-pay or deductible obligations, lost healthcare coverage
or for other reasons. It is possible that such conditions could lead to changes in patient behavior and spending patterns that could
negatively affect prescription and usage of certain or all of our products, including, without limitation, delaying of treatment, rationing
of prescription medications, non-filling of prescriptions, reduction in the frequency of visits to healthcare facilities, utilizing alternative
therapies or foregoing healthcare insurance coverage altogether. Such changes may result in the reduced demand for any or all of our
products, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and ability
to operate as a going concern.
Furthermore,
our ability to commercialize and generate revenues and profit splits relating to the sale of our products depends, in part, on the extent
to which reimbursement for the costs of these products is available from third-party payors, including government healthcare programs,
such as Medicaid and Medicare, private health insurers and other payors. We cannot be certain that, over time, third party reimbursements
for our products will be adequate for us to maintain price levels sufficient for realization of an appropriate return on our investment.
Government payers, private insurers and other third party payers are increasingly attempting to contain healthcare costs by: (i) limiting
both coverage and the level of reimbursement (including adjusting co-pays) for drugs, (ii) refusing, in some cases, to provide any coverage
for certain uses for drugs and (iii) requiring or encouraging, through more favorable reimbursement levels or otherwise, the substitution
of generic alternatives to branded drugs. For example, government agencies or third-party payers could attempt to reduce reimbursement
for physician administered products through their interpretation of complex government price reporting obligations and payment and reimbursement
coding rules, and could attempt to reduce reimbursement for separate physician administered products that share an active ingredient
by requiring the blending of sales and pricing information in the same payment and reimbursement code.
The
unavailability of, or reduction in, the reimbursement of our products could have a material adverse effect on our business, ability to
operate as a going concern, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow.
Use
of generics may be limited through legislative, regulatory or efforts of pharmaceutical companies.
Many
pharmaceutical companies increasingly have used state and federal legislative and regulatory means to delay generic competition, which,
if successful, could limit the use of generic pharmaceuticals. These efforts have included:
| |
● |
Pursuing
new patents for existing products which may be granted just before the expiration of earlier patents, which could extend patent protection
for additional years; |
| |
● |
Using
the Citizen Petition process (for example, under 21 C.F.R. s. 10.30) to request amendments to FDA standards; |
| |
● |
Attempting
to use the legislative and regulatory process to have drugs reclassified or rescheduled or to set definitions of abuse-deterrent
formulations to protect patents and profits; and |
| |
● |
Engaging
in state-by-state initiatives to enact legislation that restricts the substitution of some generic drugs. |
| |
● |
Seeking
changes to U.S. Pharmacopeia, an organization that publishes industry recognized compendia of drug standards; |
| |
● |
Attaching
patent extension amendments to non-related federal legislation; |
| |
● |
Persuading
regulatory bodies to withdraw the approval of brand-name drugs for which the patents are about to expire and converting the market
to another product of the brand company on which longer patent protection exists; |
| |
● |
Entering
into agreements whereby other generic companies will begin to market an authorized generic at the same time or after generic competition
initially enters the market; |
| |
● |
Filing
suits for patent infringement and other claims that may delay or prevent regulatory approval, manufacture and/or scale of generic
products; and, |
| |
● |
Introducing
“next generation” products prior to the expiration of market exclusivity for the reference product, which often materially
reduces demand for the generic or the reference product for which we seek regulatory approval for a generic equivalent. |
If
pharmaceutical companies or other third parties are successful in limiting the use of generic products through these or other means,
our sales of generic products and our growth prospects may decline. A material decline in generic product sales will have a material
adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and our ability to operate.
New
tariffs and evolving trade policy between the US and other countries may adversely affect our business.
New
tariffs and evolving trade policy between the United States and other countries, including China and Mexico, may have an adverse effect
on our sourcing of critical raw materials from suppliers located outside of the United States and corresponding adverse effects on our
business and results of operations.
Some
of our suppliers, including those of critical active pharmaceutical ingredients are located outside of the United States. There is uncertainty
about the future relationship between the U.S. and various other countries, including China, with respect to trade policies, treaties,
government regulations and tariffs.
Changes
could potentially disrupt our existing supply chains and impose additional costs on our business, including costs with respect to raw
materials upon which our business depends. Furthermore, if tariffs, trade restrictions or trade barriers are placed on products such
as ours by foreign governments, it could cause us to raise prices for our products, which may result in the loss of customers. If we
are unable to pass along increased costs to our customers, our margins could be adversely affected. Additionally, it is possible that
further tariffs may be imposed that could affect imports of APIs and other materials used in our products, or our business may be adversely
impacted by retaliatory trade measures taken by other countries, including restricted access to APIs or other materials used in our products,
causing us to raise prices or make changes to our products. Further, the continued threats of tariffs, trade restrictions and trade barriers
could have a generally disruptive impact on the global economy and, therefore, negatively impact our sales. Given the volatility and
uncertainty regarding the scope and duration of these tariffs and other aspects of U.S. international trade policy, the impact on our
operations and results is uncertain and could be significant. Further governmental action related to tariffs, additional taxes, regulatory
changes or other retaliatory trade measures could occur in the future. Any of these factors could have a material adverse effect on our
business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
The
DEA could limit the availability of active ingredients used in many of our products.
The
DEA limits the availability of the active ingredients used in many of our current products and products in development, as well as the
production and distribution of these products, and, as a result, our procurement, production, and distribution quotas may not be sufficient
to meet commercial demand or complete clinical trials.
The
DEA regulates chemical compounds as Schedule I, II, III, IV or V substances, with Schedule I substances considered to present the highest
risk of substance abuse and Schedule V substances the lowest risk. The active ingredients in some of our current products and products
in development, including, without limitation, hydromorphone, methadone, phentermine, phendimetrazine and oxycodone, are listed by the
DEA as Scheduled substances under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Consequently, their manufacture, shipment, storage, sale, and
use are subject to a high degree of regulation. Furthermore, the DEA limits the availability of the active ingredients used in many of
our current products and products in development and we and/or our contract customers and suppliers, must annually apply to the DEA for
procurement quotas in order to obtain and distribute these substances. As a result, our procurement and production quotas may not be
sufficient to meet commercial demand or to complete any clinical trials we may conduct. Moreover, the DEA may adjust these quotas from
time to time during the year, although the DEA has substantial discretion in whether or not to make such adjustments. Any delay or refusal
by the DEA in establishing our quotas, or modification of our quotas, for controlled substances could delay or result in the stoppage
of our clinical trials or product launches or could cause trade inventory disruptions for those products that already been launched,
which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, cash flows and stock price.
We
received a CRL from the FDA indicating that the SequestOx™ NDA is not ready for approval.
We
received a Complete Response Letter from the FDA that indicated that our SequestOx™ NDA is not ready for approval in its present
form. We have paused further development of this product and we cannot assure that development will restart. If we are unable to obtain
approval for SequestOx™ or if we incur significant costs or delays in obtaining such approval, our return on investment in SequestOx™
will be materially adversely affected.
In
July 2016, the FDA issued a Complete Response Letter, or CRL, regarding the NDA. The CRL stated that the review cycle for the SequestOx™
NDA is complete and the application is not ready for approval in its present form. On December 21, 2016, we met with the FDA for an end-of-review
meeting to discuss steps that we could take to obtain approval of SequestOx™. Based on the FDA response, we believe there is a
path forward to address the issues cited in the CRL, with such path forward including modification of the SequestOx™ formulation,
and the successful completion of in vitro and in vivo studies. If we are unable to modify the formulation or if we are unable to successfully
complete the required studies, we will not meet the requirements specified by the FDA for resubmission of the NDA. Furthermore, there
can be no assurances given that the FDA will eventually approve our NDA. If we are unable to obtain approval for SequestOx™, we
will be unable to commercialize the product. Furthermore, in the event that the Company does receive marketing approval for SequestOx™,
there can be no assurances of the Company realizing future revenues or profits related to this product, or that any such future revenues
and profits would be in amounts that provide adequate return on the significant investments made to secure this marketing authorization.
The Company has currently paused further development of SequestOx™ due to the prohibitive cost of such and attendant risks related
thereto.
Regulatory
factors may cause us to be unable to manufacture products or face interruptions in our manufacturing process.
Our
manufacturing operations as well as our suppliers’ manufacturing operations are subject to establishment registration by the FDA
and periodic inspections by the FDA to assure compliance regarding the manufacturing of our products. If we or our suppliers do not maintain
the current registrations or if we or our partners receive notices of manufacturing and quality-related observations following inspections
by the FDA, our operating results would be materially negatively impacted.
Our
facilities, as well as those of applicable suppliers, rely on maintaining current FDA, and DEA if applicable, registration and other
license to produce and develop generic drugs and raw materials used in such operations. If we, or one of our suppliers does not successfully
renew and maintain current FDA, DEA and other required licenses, our operations and financial results would be negatively impacted. We
and our suppliers are subject to periodic inspection by the FDA, DEA and other regulatory agencies, as applicable, to assure regulatory
compliance regarding the manufacture and distribution of pharmaceutical products and raw materials. These regulatory bodies impose stringent
mandatory requirements on the manufacture and distribution of pharmaceutical products to ensure their safety and efficacy. If we or any
of our third party suppliers receive notices of manufacturing and quality-related observations and are unable to satisfactorily resolve
the issues and observations identified in a timely fashion, there could be a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition,
results of operations, cash flow and stock price.
Agreements
between branded pharmaceutical companies and generic pharmaceutical companies are facing increased government scrutiny in the United
States and Internationally.
There
are numerous and continuing litigation in which generic companies challenge the validity or enforceability of an innovator products patents
and/or the applicability of such patents to a generic applicant’s products. Settlement of such litigation is a common outcome,
with review of such agreements by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (the “FTC”) and the Antitrust Division of the Department
of Justice (the “DOJ”) being required by law. The FTC has stated publicly its view that some of these settlement agreements
violate antitrust laws and has commenced actions against the branded and generic companies that are parties to these agreements. Accordingly,
in the event of the Company being party to a settlement agreement, either as the branded, innovator product owner, or as the generic
applicant, we may receive formal or informal requests from the FTC for information about a settlement agreement and there is a risk of
the FTC or DOJ alleging a violation of antitrust laws and commencing an action against us.
Any
such action could have an adverse effect on the Company’s business, operations and financial condition.
Litigation
and Liability Related Risks
We
may not be able to obtain or maintain adequate insurance coverages.
The
cost of insurance, including directors and officer insurance, workers compensation, product liability, truck and general liability insurance
have increase significantly in recent years and may continue to increase in the future. We have increased deductibles and/or decreased
coverages to mitigate some of these costs. These insurance premium increases, as well as our increased risk due to reduced coverage and
increased deductibles could have an adverse material effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and
stock price.
We
may not have and may be unable to obtain or maintain in the future insurance, on acceptable terms, that provide adequate coverage against
potential liabilities or other losses, such as the cost of a recall or defense against claims, if any claim is brought against us, for
any reason, regardless of the merits, success or failure of such claim. In the past year, as a result of product liability and securities
litigation in the general marketplace, and a threatened claim of action against us in relation to the shareholder vote conducted in December
2019, our insurance premiums have increased significantly, while also providing no greater, and in most cases, lower levels of coverage.
The significant premium increases experienced were prior to, and accordingly did not consider, the impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic
on the legal and litigation environment in which we and all other companies operate.
The
amount of our insurance coverage is accordingly limited by our financial resources and greatly impacted by the significant premium increases
of the past year and reasonably expected further increases in the near to mid-term due to the global pandemic. Furthermore, even where
claims are submitted to insurance carriers for defenses and indemnity that are within coverage limits, there can be no assurance that
such claims will be fully covered by insurance or that the indemnitors or insurers will remain financially viable to provide reimbursement
consistent with coverage maintained.
Any
failure by us, to obtain sufficient insurance coverage, with reimbursement of claims being provided and generate sufficient cash flow,
if needed, above insurance coverage, to pay amounts due in relation to potential claims, will have a material adverse effect on our business,
financial condition, results of operations, cash flow and ability to operate as a going concern.
Litigation,
product liability claims, product recalls, government investigations and other significant legal proceedings are common in the pharmaceutical
industry.
Litigation,
product liability claims, other significant legal proceedings, government investigations and product recalls are common in the pharmaceutical
industry and can be protracted and expensive and could delay and/or prevent entry of our products into the market, which, in turn, could
have a material adverse effect on our business.
As
a business that operates in the pharmaceutical industry, we are inherently exposed to significant potential risks from lawsuits, product
liability claims, patent and proprietary rights claims, other significant proceedings, government investigations or product recalls,
including, without limitation, such matters associated with the testing, manufacturing, marketing and sale of our products. While no
such judgements have been made against us to date, some plaintiffs have received substantial damage awards or settlements against other
healthcare companies based upon various legal theories, including, without limitation, claims for injuries allegedly caused by use of
their products. Our business continues to be inherently exposed to the risk of being subject to product liability cases, as well as other
significant legal proceedings and government investigations.
For
example, we have been a manufacturer of prescription opioid medications in the past, and while we have not been subject to lawsuits,
other manufacturers of such products, as well as distributors and other sellers of such medications, have been subjects of subject of
lawsuits and have received subpoenas and other requests for information from various federal, state and local government agencies regarding
the sale, marketing and/or distribution of prescription opioid medications. Numerous claims against opioid manufacturers, have been and
may continue to be filed by or on behalf of states, counties, cities, Native American tribes, other government-related persons or entities,
hospitals, health systems, unions, health and welfare funds, other third-party payers and/or individuals. In these cases, plaintiffs
seek various remedies, including without limitation declaratory and/or injunctive relief; compensatory, punitive and/or treble damages;
restitution, disgorgement, civil penalties, abatement, attorneys’ fees, costs and/or other relief. Settlement demands may seek
significant monetary and other remedies, or otherwise be on terms that would result in material adverse effects on our business and ability
to operate as a going concern. The precedent of awards against and settlements by our competitors could also incentivize parties to bring
additional claims against us. In addition to the risks of direct expenditures for defense costs, settlements and/or judgments in connection
with these claims, proceedings and investigations, there is a possibility of loss of revenues, injunctions and disruption of business.
Furthermore, we and other manufacturers of prescription opioid medications have been, and will likely continue to be, subject to negative
publicity and press, which could harm our brand and the demand for our products. In addition, current or future regulatory and legislative
proposals could impact us and other manufacturers of prescription opioid medications. See the risk factor “Our business and financial
condition may be adversely affected by legislation” for more information.
In
addition, our current and former products may cause or appear to cause serious adverse side effects or potentially dangerous drug interactions
if misused or improperly prescribed or as a result of faulty surgical technique. Any failure to effectively identify, analyze, report
and protect adverse event data and/or to fully comply with relevant laws, rules and regulations around adverse event reporting could
expose the Company to legal proceedings, penalties, fines and/or reputational damage.
Also,
through the use of social media, plaintiff’s attorneys have a wide variety of tools to advertise their services and solicit new
clients for litigation, including using judgments and settlements obtained in litigation against us or other pharmaceutical companies
as an advertising tool. For these or other reasons, any significant product liability or mass tort litigation in which we are a defendant
could have a larger number of plaintiffs than such actions have seen historically and we could also see an increase in the number of
cases filed against us because of the increasing use of widespread and media-varied advertising. Furthermore, a ruling against other
pharmaceutical companies in product liability or mass tort litigation in which we are not a defendant could have a negative impact on
pending litigation where we are a defendant.
In
addition, in certain circumstances, such as in the case of products that do not meet approved specifications or for which subsequent
data demonstrate such products may be unsafe, ineffective or misused, it may be necessary for us to initiate voluntary or mandatory recalls
or withdraw such products from the market. Any such recall or withdrawal could result in adverse publicity, costs connected to the recall
and loss of revenue. Adverse publicity could also result in an increased number of additional product liability claims, whether or not
these claims have a basis in scientific fact. See the risk factor “Our business is dependent on market perceptions, social and
political pressures, including public concern over the abuse of opioids ” for more information.
We
are also inherently exposed to litigation concerning patents and proprietary rights which can be protracted and expensive. Companies
routinely bring litigation against applicants and allege patent infringement or other violations of intellectual property rights as the
basis for filing suit against an applicant. Elite develops, owns, and/or manufactures generic and branded pharmaceutical products and
such drug products may be subject to such litigation. Litigation often involves significant expense and can delay or prevent introduction
or sale of our products.
There
may also be situations where we use our business judgment and decide to market and sell products, notwithstanding the fact that allegations
of patent infringement(s) have not been finally resolved by the courts. The risk involved in doing so can be substantial because the
remedies available to the owner of a patent for infringement include, among other things, damages measured by the profits lost by the
patent owner and not by the profits earned by the infringer. In the case of a willful infringement, the definition of which is subjective,
such damages may be trebled. Moreover, because of the discount pricing typically involved with bioequivalent products, patented brand
products generally realize a substantially higher profit margin than bioequivalent products. An adverse decision in a case such as this
or in other similar litigation could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position and results of operations and
could cause the market value of our Common Stock to decline.
If
we are found liable in any lawsuits, including patent infringement, violation of proprietary rights, product liability claims or actions
related to our manufacture, sales, marketing or pricing practices or the sale, marketing and/or distribution of prescription opioid medications,
or if we are subject to government investigations or product recalls, it could result in the imposition of damages, including punitive
damages, fines, reputational harm, civil lawsuits, criminal penalties, interruptions of business, modification of business practices,
equitable remedies and other sanctions against us or our personnel as well as significant legal and other costs. We may also voluntarily
settle cases even if we believe that we have meritorious defenses because of the significant legal and other costs that may be required
to defend such actions. Any judgments, claims, settlements and related costs could be well in excess of any applicable insurance. As
a result, we may experience significant negative impacts on our operations. To satisfy judgments or settlements, we also may need to
seek financing, which may not be available on terms acceptable to us, or at all, when required. Judgments also could cause defaults under
our debt agreements and/or restrictions on our product use and we could incur losses as a result. Any of the risks above could have a
material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows and ability to operate as a going
concern.
The
occurrence or possibility of any such result may cause us to pursue one or more significant corporate transactions as well as other remedial
measures, including internal reorganizations, restructuring activities, strategic corporate alignments, cost saving initiatives or asset
sales. See the risk factor “Our ability to fund our operations, maintain liquidity and meet our financing obligations is reliant
on our operations, which are subject to significant risks and uncertainties” for more information. Likewise, any internal reorganizations,
restructuring activities, strategic corporate alignments, cost-saving initiatives or asset sales may be complex, could entail significant
costs and charges or could otherwise negatively impact shareholder value and there can be no assurance that we will be able to accomplish
any of these alternatives on terms acceptable to us, or at all, or that they will result in their intended benefits.
We
also may incur significant liability if it is determined that we are promoting or have in the past promoted the “off-label”
use of drugs. In jurisdictions including, without limitation, the United States, a company is not permitted to promote drugs for uses
that are not described in the product’s labelling and that differ from those that were approved or cleared by the FDA. Such users
are commonly referred to as “off-label uses”. Under what is known as the “practice of medicine”, physicians and
other healthcare practitioners may prescribe drug products for off-label or unapproved uses. While the FDA does not regulate a physician’s
choice of medications, treatments, or product uses, the FFDCA and FDA regulations significantly restrict permissible communications on
the subject of off-label uses of drug products by pharmaceutical companies. The FDA, FTC, the Office of the Inspector General of the
Department of Health and Human Services (“HHS”), the DOJ and various state Attorneys General actively enforce laws and regulations
that prohibit the promotion of off-label uses. A company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant
liability, including civil fines, criminal fines and penalties, civil damages, exclusion from federal funded healthcare programs and
potential liability under the federal False Claims Act and any applicable state false claims act. Conduct giving rise to such liability
could also form the basis for private civil litigation by third-party payers or other persons claiming to be harmed by such conduct.
Notwithstanding
the regulatory restrictions on off-label promotion, the FDA’s regulations and judicial case law allows companies to engage in some
forms of truthful, non-misleading and non-promotional speech concerning the off-label use of products. Elite believes it and its marketing
partners comply with these restrictions.
Nonetheless,
the FDA, HHS, DOJ, and/or state Attorneys General, and qui tam relators may take the position that the Company is not in compliance with
such requirements, and if such non-compliance is proven, the consequences of such may have an adverse material effect on our business,
financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and stock price.
We
are subject to various fraud and abuse laws which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational
harm and diminished profits and future earnings.
Our
activities are subject to various federal and state fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute,
the federal civil False Claims Act, and laws and regulations pertaining to limitations on and reporting of healthcare provider payments
(physician sunshine laws). These laws and regulations are interpreted and enforced by various federal, state and local authorities including
CMS, the Office of Inspector General for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the U.S. Department of Justice, individual
U.S. Attorney offices within the Department of Justice, and state and local governments. These laws include:
| |
● |
the
U.S. federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons or entities from knowingly and willfully soliciting,
offering, receiving or paying any remuneration, directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward
either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, lease, order, or arranging for or recommending the purchase, lease or
order of, any good or service, for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under federal healthcare programs such as Medicare
and Medicaid. A person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order
to have committed a violation; |
| |
●
|
the
U.S. civil False Claims Act (which can be enforced through “qui tam,” or whistleblower actions, by private citizens on
behalf of the federal government), prohibits any person from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented
false or fraudulent claims for payment of government funds or knowingly making, using or causing to be made or used, a false record
or statement material to an obligation to pay money to the government or knowingly and improperly avoiding, decreasing or concealing
an obligation to pay money to the U.S. federal government; |
| |
|
|
| |
● |
U.S.
federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, which imposes criminal liability and amends provisions
on the reporting, investigation, enforcement, and penalizing of civil liability for, among other things, knowingly and willfully
executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program, or knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing
or covering up a material fact or making any materially false statement, in connection with the delivery of, or payment for healthcare
benefits, items or services by a healthcare benefit program, which includes both government and privately funded benefits programs;
similar to the U.S. federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific
intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation; |
| |
|
|
| |
●
|
state
laws and regulations, including state anti-kickback and false claims laws, that may apply to our business practices, including but
not limited to, research, distribution, sales and marketing arrangements and claims involving healthcare items or services reimbursed
by any third-party payer, including private insurers; state laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical
industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the U.S. federal government,
or otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers and other potential referral sources; and state laws and
regulations that require drug manufacturers to file reports relating to pricing and marketing information, which requires tracking
gifts and other remuneration and items of value provided to healthcare professionals and entities; |
| |
|
|
| |
●
|
the
Physician Payments Sunshine Act, implemented as the Open Payments program, and its implementing regulations, requires certain manufacturers
of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies that are reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid, or the Children’s Health
Insurance Program to report annually to CMS information related to certain payments made in the preceding calendar year and other
transfers of value to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their
immediate family members; beginning in 2022, applicable manufacturers are required to report such information regarding payments
and transfers of value provided, as well as ownership and investment interests held, during the previous year to physician assistants,
nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse anesthetists, and certified nurse-midwives; and |
| |
|
|
| |
●
|
the
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or the FCPA, which generally prohibits offering, promising, giving, or authorizing others to give
anything of value, either directly or indirectly, to a non-U.S. government official in order to influence official action, or otherwise
obtain or retain business. The FCPA also requires public companies to make and keep books and records that accurately and fairly
reflect the transactions of the corporation and to devise and maintain an adequate system of internal accounting controls. Our industry
is heavily regulated and therefore involves significant interaction with public officials, including officials of non-U.S. governments.
Additionally, in many other countries, the health care providers who prescribe pharmaceuticals are employed by their government,
and the purchasers of pharmaceuticals are government entities; therefore, our dealings with these prescribers and purchasers are
subject to regulation under the FCPA. Recently, the SEC and Department of Justice have increased their FCPA enforcement activities
with respect to pharmaceutical companies. |
Violations
of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, may subject us to significant civil, criminal and administrative
sanctions including penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment, and exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare
and Medicaid, and/or adverse publicity. Moreover, government entities and private litigants have asserted claims under state consumer
protection statutes against pharmaceutical companies for alleged false or misleading statements in connection with the marketing, promotion
and/or sale of pharmaceutical products, including state investigations and litigation by certain government entities regarding the marketing
of opioid products.
Our
products contain controlled substances which may subject us to increased litigation risk and regulation.
Some
of our current products and products under development contain controlled substances. Misuse or abuse of such drugs can lead to physical
or other hard. The FDA and/or the DEA may impose new regulations concerning the manufacture, storage, transportation, distribution, and
sale of prescription narcotics. Such regulations may include new labelling requirements, the development and implementation of a formal
REMS, restrictions on prescription and sale of such products and mandatory reformulation in order to make abuse of such products more
difficult. In 2007, Congress passed legislation authorizing the FDA to require companies to undertake post-approval studies in order
to assess known or signaled potential serious safety risks and to make any labelling changes necessary to address safety risks. Congress
also empowered the FDA to require companies to formulate REMS to confirm a drug’s benefits exceed its risks. In 2011, the FDA issued
letters to manufacturers of long-acting and extended-release opioids requiring them to develop and submit to the FDA a post-market REMS
plan to require that training be provided to prescribers of these products and that information is provided to prescribers that they
can use in counselling patients on the risks and benefits of opioid drug use. Elite does not currently own a product that requires a
REMS plan, but some of the products in our pipeline may require a REMS plan. The federal government has also released a comprehensive
action plan to reduce prescription drug abuse, which may include proposed legislation to amended existing controlled substances laws
to require healthcare practitioners who request DEA registration to prescribe controlled substances to receive training on opioid prescribing
practices as a condition of registration. In addition, state health departments and boards of pharmacy have authority to regulate distribution
and may modify their regulations with respect to prescription narcotics in an attempt to curb abuse.
Mandatory
REMS programs could increase the cost, burden and liability associated with the commercialization of certain products.
The
FDA has imposed a class-wide REMS on all IR, ER and long acting (“LA”) opioid drug products (known as the Opioid Analgesic
REMS). The FDA continually evaluates whether the REMS program is meeting its goal of ensuring that the benefit of these drugs continue
to outweigh their risks, and whether the goals or elements of the program should be modified. If the FDA determines that additional measures
are necessary, the modification of the Opioid Analgesic REMS to impose additional or more burdensome requirements could increase the
costs associated with marketing opioid products and/or reduce the willingness of healthcare providers to prescribe those products, both
which would have a material adverse effect on the ability to successfully commercializing, or to generate sufficient revenue from, such
products.
Illegal
distribution and third party sale of counterfeit versions of our products could have a detrimental effect on our reputation and business.
Third
parties could illegally distribute and sell counterfeit versions of our products, which do not meet the rigorous manufacturing and testing
standards that our products undergo. Counterfeit products are frequently unsafe or ineffective and can be life-threatening. Counterfeit
medicines may contain harmful substances, the wrong dose of the active pharmaceutical ingredient or no active pharmaceutical ingredients
at all. However, to distributors and users, counterfeit products may be visually indistinguishable from the authentic version.
Reports
of adverse reactions to counterfeit drugs or increased levels of counterfeiting could materially affect patient confidence in the authentic
product. It is possible that adverse events caused by unsafe counterfeit products will mistakenly be attributed to the authentic product.
In addition, thefts of inventory at warehouses, plants or while in-transit, which are not properly stored, and which are sold through
unauthorized channels could adversely impact patient safety, our reputation, and our business.
Public
loss of confidence in the integrity of pharmaceutical products as a result of counterfeiting or theft could have a material adverse effect
on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Structural
and Organizational Risks
Provisions
of our Articles of Incorporation could deter a change of management and discourage offers to acquire us.
Provisions
of our Articles of Incorporation and By-Laws law may make it more difficult for someone to acquire control of us or for our shareholders
to remove existing management and might discourage a third party from offering to acquire us, even if a change in control or in Management
would be beneficial to our shareholders. For example, as discussed above, our Articles of Incorporation allows us to issue shares of
preferred stock without any vote or further action by our shareholders. Our Board of Directors has the authority to fix and determine
the relative rights and preferences of preferred stock. Our Board of Directors also has the authority to issue preferred stock without
further shareholder approval. As a result, our Board of Directors could authorize the issuance of a series of preferred stock that would
grant to holders the preferred right to our assets upon liquidation, the right to receive dividend payments before dividends are distributed
to the holders of common stock and the right to the redemption of the shares, together with a premium, prior to the redemption of our
common stock. In this regard, on November 15, 2013, we entered into a Shareholder Rights Plan and, under the Rights Plan, our Board of
Directors declared a dividend distribution of one Right for each outstanding share of our common stock and one right for each share of
Common Stock into which any of our outstanding Preferred Stock is convertible, to shareholders of record at the close of business on
that date. Each Right entitles the registered holder to purchase from us one “Unit” consisting of one one-millionth (1/1,000,000)
of a share of Series H Junior Participating preferred stock, at a purchase price of $2.10 per Unit, subject to adjustment, and may be
redeemed prior to November 15, 2023, the expiration date, at $0.000001 per Right, unless earlier redeemed by the Company. The Rights
generally are not transferable apart from the common stock and will not be exercisable unless and until a person or group acquires or
commences a tender or exchange offer to acquire, beneficial ownership of 15% or more of our common stock. However, for Mr. Hakim, our
Chief Executive Officer, the Rights Plan’s the 15% threshold excludes shares beneficially owned by him as of November 15, 2013
and all shares issuable to him pursuant to his employment agreement and the Mikah Note. Our By-Laws provide for the classification of
our Board of Directors into three classes.
Intellectual
Property Related Risks
Our
ability to protect intellectual property rights and successfully defend third party allegations of intellectual property infringement
is vital to our business and uncertain.
Our
success depends on our ability to protect our current and future products and to defend our intellectual property rights. If we fail
to protect our intellectual property adequately, competitors may manufacture and market products similar to ours.
We
currently hold six patents. We intend to file further patent applications in the future. We cannot be certain that our pending patent
applications will result in the issuance of patents. If patents are issued, third parties may sue us to challenge our patent protection,
and although we know of no reason why they should prevail, it is possible that they could. In addition to modification or revocation
of patents in legal proceedings, issued patents may later be modified or revoked by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office or by analogous
foreign offices. It is likewise possible that our patent rights may not prevent or limit our present and future competitors from developing,
using or commercializing products that are similar or functionally equivalent to our products.
In
addition, we may be required to obtain licenses to patents, or other proprietary rights of third parties, in connection with the development
and use of our products and technologies as they relate to other persons’ technologies. At such time as we discover a need to obtain
any such license, we will need to establish whether we will be able to obtain such a license on favorable terms, if at all. The failure
to obtain the necessary licenses or other rights could preclude the sale, manufacture or distribution of our products.
We
rely particularly on trade secrets, unpatented proprietary expertise and continuing innovation that we seek to protect, in part, by entering
into confidentiality agreements with licensees, suppliers, employees, and consultants. We cannot provide assurance that these agreements
will not be breached or circumvented. We also cannot be certain that there will be adequate remedies in the event of a breach. Disputes
may arise concerning the ownership of intellectual property or the applicability of confidentiality agreements. We cannot be sure that
our trade secrets and proprietary technology will not otherwise be obtained by other entities, such as government or regulatory authorities,
or become known, obtained, or independently developed by our competitors or by other entities through means beyond our control. We also
cannot be sure that, if patents are not issued with respect to products arising from research, we will be able to maintain the confidentiality
of information relating to these products. In addition, efforts to ensure our intellectual property rights can be costly, time-consuming,
and/or ultimately unsuccessful.
Furthermore,
companies that produce branded pharmaceutical products routinely bring litigation against ANDA or similar applicants that seek regulatory
approval to manufacture and market generic forms of branded products, alleging patent infringement or other violations of intellectual
property rights. Patent holders may also bring patent infringement suits against companies that are currently marketing and selling approved
generic products. Litigation often involves significant expense. Additionally, if the patents of others are held valid, enforceable and
infringed by our current products or future product candidates, we would, unless we could obtain a license from the patent holder, need
to delay selling our corresponding generic product and, if we are already selling our product, cease selling and potentially destroy
existing product stock. Additionally, we could be required to pay monetary damages or royalties to license proprietary rights from third
parties and we may not be able to obtain such licenses on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
There
may be situations in which we may make business and legal judgments to market and sell products that are subject to claims of alleged
patent infringement prior to final resolution of those claims by the courts based upon our belief that such patents are invalid, unenforceable
or are not infringed by our marketing and sale of such products. This is commonly referred to in the pharmaceutical industry as an “at-risk”
launch. The risk involved in an at-risk launch can be substantial because, if a patent holder ultimately prevails against us, the remedies
available to such holder may include, among other things, damages calculated based on the profits lost by the patent holder, which can
be significantly higher than the profits we make from selling the generic version of the product. Moreover, if a court determines that
such infringement is willful, the damages could be subject to trebling. We could face substantial damages from adverse court decisions
in such matters. We could also be at risk for the value of such inventory that we are unable to market or sell.
The
occurrence of any of the above could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash
flow and stock price.
Risks
Related to our Common Shares
Dilution
from issuance of shares to Lincoln Park, Directors, Employees, Consultants or upon exercise of warrants and options or the perception
that dilution may occur could cause the price per share of common stock to fall.
On
July 8, 2020, we entered into the Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park, pursuant to which Lincoln Park has committed to purchase up to
$25,000,000 of our common stock. Concurrently with the execution of the Purchase Agreement, we issued 5,975,857 shares of our common
stock to Lincoln Park as an initial fee for its commitment to purchase shares of our common stock under the Purchase Agreement. Furthermore,
for each additional purchase by Lincoln Park, additional commitment shares in commensurate amounts up to a total of 5,975,857 shares
will be issued based upon the relative proportion of the aggregate amount of $25,000,000 purchased by Lincoln Park. The purchase shares
that may be sold pursuant to the Purchase Agreement may be sold by us to Lincoln Park at our discretion from time to time over a 36-month
period commencing after July 27, 2020 and expiring on August 1, 2023. The purchase price for the shares that we may sell to Lincoln Park
under the Purchase Agreement will fluctuate based on the price of our common stock. Depending on market liquidity at the time, sales
of such shares may cause the trading price of our common stock to fall.
We
generally have the right to control the timing and amount of any sales of our shares to Lincoln Park. Additional sales of our common
stock, if any, to Lincoln Park will depend upon market conditions and other factors to be determined by us. Lincoln Park may ultimately
purchase all, some, or none of the shares of our common stock that may be sold pursuant to the Purchase Agreement and, after it has acquired
shares, Lincoln Park may sell all, some or none of those shares.
In
addition, as of March 31, 2023, there were outstanding warrants to purchase an aggregate of approximately 79 million shares of Common
Stock at a cash exercise price of $0.1521 per share, vested options to purchase an aggregate of approximately 15.4 million shares at a
weighted average cash exercise price of $0.07. Additional shares of Common Stock may be issuable as a result of anti-dilution provisions
in the outstanding warrants, with such provisions excluding any shares issued to Lincoln Park from consideration .
As
a result of the above discussed potential issuance of securities, such issuances by us could result in substantial dilution to the interests
of other holders of our common stock. Additionally, the sale of a substantial number of shares of our common stock to Lincoln Park or
pursuant to the conversion or exercise of outstanding shares of warrants, or the anticipation of such issuances, could make it more difficult
for us to sell equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and at a price that we might otherwise wish to effect sales.
Furthermore,
pursuant to the Company’s policies relating to the compensation of Directors, 2/3 of all director fees are paid via the issuance
of shares of Common Stock, with such shares being valued at the simple average of the closing price of the Company’s Common Stock
for each day in the period for which the director fees were incurred. In addition, members of the Company’s management, certain
employees and consultants receive a portion of their salaries or compensation via the issuance of shares Common Stock, with such shares
being valued by the same method as that used for the shares issued in payment of director fees.
The
issuance of these shares is dilutive to holders of our Common Stock, and the subsequent sale of these shares, or the perception that
the sale of these shares may occur, could cause the price of our common stock to fall.
Our
common stock is a penny stock, quoted on the OTC bulletin board, with rules in place that could limit trading and liquidity of our shares,
increased transaction costs that could adversely affect our price per share.
Our
common stock is a “low-priced” security or “penny stock” under rules promulgated under the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). In accordance with these rules, broker-dealers participating in transactions
in low-priced securities must first deliver a risk disclosure document which describes the risks associated with such stocks, the broker-dealer’s
duties in selling the stock, the customer’s rights and remedies and certain market and other information. Furthermore, the broker-dealer
must make a suitability determination approving the customer for low-priced stock transactions based on the customer’s financial
situation, investment experience and objectives. Broker-dealers must also disclose these restrictions in writing to the customer, obtain
specific written consent from the customer, and provide monthly account statements to the customer. The effect of these restrictions
will likely decrease the willingness of broker-dealers to make a market in our Common Stock, will decrease liquidity of our Common Stock
and will increase transaction costs for sales and purchases of our Common Stock as compared to other securities.
In
addition, our Common stock is quoted on the Venture Market (the “OTCQB”) which is a regulated quotation
service that displays real-time quotes, last sale prices and volume limitations in over-the-counter securities. Because trades and quotations
on the OTCQB involve a manual process, the market information for such securities cannot be guaranteed. In addition, quote information,
or even firm quotes, may not be available. The manual execution process may delay order processing and intervening price fluctuations
may result in the failure of a limit order to execute or the execution of a market order at a significantly different price. Execution
of trades, execution reporting and the delivery of legal trade confirmations may be delayed significantly. Consequently, one may not
be able to sell shares of our Common Stock at the optimum trading prices.
When
fewer shares of a security are being traded on the OTCQB, volatility of prices may increase, and price movement may outpace the ability
to deliver accurate quote information. Lower trading volumes in a security may result in a lower likelihood of an individual’s
orders being executed, and current prices may differ significantly from the price one was quoted by the OTCQB at the time of the order
entry. Orders for OTCQB securities may be cancelled or edited like orders for other securities. All requests to change or cancel an order
must be submitted to, received, and processed by the OTCQB. Due to the manual order processing involved in handling OTCQB trades, order
processing and reporting may be delayed, and an individual may not be able to cancel or edit his order. Consequently, one may not be
able to sell shares of Common Stock at the optimum trading prices.
The
dealer’s spread (the difference between the bid and ask prices) may be large and may result in substantial losses to the seller
of securities on the OTCQB if the Common Stock or other security must be sold immediately. Further, purchasers of securities may incur
an immediate “paper” loss due to the price spread. Moreover, dealers trading on the OTCQB may not have a bid price for securities
bought and sold through the OTCQB. Due to the foregoing, demand for securities that are traded through the OTCQB may be decreased or
eliminated.
Shareholder
activism could negatively affect us.
In
recent years, shareholder activism involving corporate governance, fiduciary duties of Directors and Officers, strategic direction and
operations has become increasingly prevalent. If we become the subject of such shareholder activism, their demands may disrupt our business
and divert the attention of our management, Board and employees. Also, we may incur substantial costs, including legal fees and other
expenses, related to such activist shareholder matters. Perceived uncertainties resulting from such activist shareholder matters may
result in loss of potential business opportunities with our current and potential customers and business partners, be exploited by our
competitors and make attracting and retaining qualified personnel more difficult. In addition, such shareholder activism may cause significant
fluctuations in our share price based on temporary or speculative market perceptions, uncertainties or other factors that do not necessarily
reflect the underlying fundamentals and prospects of our business.
The
effects of shareholder activism pursued against the Company could have an adverse material effect on our business, financial condition,
results of operations, cash flows and stock price.
Our
stock price has been volatile.
The
market price for the publicly traded stock of pharmaceutical companies is generally characterized by high volatility. There has been
significant volatility in the market prices for our Common Stock. For the twelve months ended March 31, 2023, the closing sale price
on the Venture Market (“OTCQB”) of our Common Stock fluctuated from a high of $0.05 per share to a low of $0.03 per share.
The price per share of our Common Stock may not exceed or even remain at current levels in the future. The market price of our Common
Stock may be affected by a number of factors, including, without limitation:
| |
● |
Results
of our clinical trials; |
| |
● |
Approval
or disapproval of our ANDAs or NDAs; |
| |
●
|
Announcements
of innovations, new products, or new patents by us or by our competitors; |
| |
● |
Announcements
of other material events; |
| |
● |
Governmental
regulation; |
| |
● |
Patent
or proprietary rights developments; |
| |
● |
Proxy
contests or litigation; |
| |
● |
News
regarding the efficacy of, safety of or demand for drugs or drug technologies; |
| |
● |
Economic
and market conditions, generally and related to the pharmaceutical industry; |
| |
● |
Healthcare
legislation; |
| |
● |
Changes
in third-party reimbursement policies for drugs; and |
| |
● |
Fluctuations
in our operating results. |
Capital
raises through sales of securities may cause substantial dilution to existing shareholders.
Any
additional financing that involves the further sale of our securities could cause existing holders of our Common Stock to experience
substantial dilution. On the other hand, if we incurred debt, we would be subject to risks associated with indebtedness, including the
risk that interest rates might fluctuate, and cash flow would be insufficient to pay principal and interest on such indebtedness.
Issuance
of shares of common or preferred stock could make achieving a change of control more difficult.
The
issuance of additional shares of our Common Stock, including those shares issued pursuant to conversion of convertible preferred shares,
or the issuance of shares of an additional series of preferred stock could be used to make a change of control of us more difficult and
expensive. Under certain circumstances, such shares could be used to create impediments to, or frustrate persons seeking to cause, a
takeover or to gain control of us. Such shares could be sold to purchasers who might side with our Board of Directors in opposing a takeover
bid that the Board of Directors determines not to be in the best interests of our shareholders. It might also have the effect of discouraging
an attempt by another person or entity through the acquisition of a substantial number of shares of our Common Stock to acquire control
of us with a view to consummating a merger, sale of all or part of our assets, or a similar transaction, since the issuance of new shares
could be used to dilute the stock ownership of such person or entity.
We
have no plans to pay regular dividends or conduct share purchases.
We
do not intend to pay any cash dividends either currently or in the foreseeable future on our common shares. Additionally, we do not intend
to conduct share repurchases either currently or in the foreseeable future.
ITEM
1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM
2. PROPERTIES
We
own a facility located at 165 Ludlow Avenue, Northvale, New Jersey (“165 Ludlow”) which contains approximately 15,000 square
feet of floor space. This real property and the improvements thereon are encumbered by a mortgage in favor of the New Jersey Economic
Development Authority (“NJEDA”) as security for a loan through tax-exempt bonds from the NJEDA to Elite. The mortgage contains
certain customary provisions including, without limitation, the right of NJEDA to foreclose upon a default by Elite. The NJEDA has declared
the payment of this bond to be in default (for more information on the NJEDA Bonds, see Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion
and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations; Liquidity and Capital Resources; NJEDA Bonds”). We are currently
using the facility as a laboratory, manufacturing, storage, distribution, and office space.
We own a facility located at 135-137 Ludlow Avenue, Northvale, New Jersey
(“135 Ludlow”) which contains approximately 35,000 square feet of floor space. This real property and the improvements thereon
are encumbered by a mortgage in favor of East West Bank.
In
October 2020, the Company entered into an operating lease for office space in Pompano Beach, Florida (the “Pompano Office Lease”).
The Pompano Office Lease is for approximately 1,275 square feet of office space, with Elite taking occupancy on November 1, 2020. The
Pompano Office includes a 3 month abatement from November 2020 through February 2021 and has a term of three years, ending on October
31, 2023.
165
Ludlow and 135 Ludlow are hereinafter referred to as the “Northvale Facility”, or, together with Pompano, the “Facilities.”
Properties
used in our operation are considered suitable for the purposes for which they are used, at the time they are placed into service, and
are believed adequate to meet our needs for the reasonably foreseeable future.
ITEM
3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
In
the ordinary course of business, we may be subject to litigation from time to time. There is no current, pending or, to our knowledge,
threatened litigation or administrative action to which we are a party or of which our property is the subject (including litigation
or actions involving our officers, directors, affiliates, or other key personnel, or holders of record or beneficially of more than 5%
of any class of our voting securities, or any associate of any such party) which in our opinion has, or is expected to have, a material
adverse effect upon our business, prospects financial condition or operations. A significant increase in the number of claims or an increase
in amounts owing under successful claims could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and
cash flows.
ITEM
4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not
Applicable.
PART
II
ITEM
5. MARKET FOR COMPANY’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market
Information
Our
Common Stock is quoted on the Venture Market (“OTCQB”) under the ticker symbol “ELTP”. The following table shows,
for the periods indicated, the high and low bid prices per share of our Common Stock as by OTCQB. Over-the-counter market
quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission and may not necessarily represent actual transactions.
| Quarter Ended | | |
High | | |
Low | |
| Fiscal Year Ending March 31, 2023 | | |
| | |
| |
| March 31, 2023 | | |
$ | 0.04 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| December 31, 2022 | | |
$ | 0.04 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| September 30, 2022 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| June 30, 2022 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Fiscal Year Ending March 31, 2022 | | |
| | | |
| | |
| March 31, 2022 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| December 31, 2021 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
$ | 0.03 | |
| September 30, 2021 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
$ | 0.04 | |
| June 30, 2021 | | |
$ | 0.06 | | |
$ | 0.05 | |
As
of June 20, 2023, the last reported sale price of our Common Stock, as reported by the OTCQB, was $0.03.
Holders
As
of June 20, 2023, there were, respectively, approximately 111 holders of record of our Common Stock.
Dividends
We
have never paid cash dividends on our Common Stock. We currently anticipate that we will retain all available funds for use in the operation
and expansion of our business.
Recent
Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Securities
Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The
following table sets forth certain information regarding Elite’s equity compensation plans as of March 31, 2023:
| Plan Category | |
Number of
securities to
be issued upon
exercise of
outstanding
options, warrants,
and rights
(a) | | |
Weighted-average
exercise price
per share of
outstanding
options, warrants,
and rights
(b) | | |
Number of
securities
remaining
available for
future issuance
under equity
compensation
plans (excluding
securities reflected
in column (a)) | |
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (1) | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 2,150,000 | |
| (1)
|
Represents
securities reserved and available for grant under the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan |
2014
Equity Incentive Plan
Our
2014 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2014 Plan”) was adopted by the Board on March 17, 2014, to attract, motivate and retain
officers, employees, consultants, and directors by issuing common stock-based incentives to directors, officers, employees, and consultants
who are selected for participation. By relating incentive compensation to increases in shareholder value, it is hoped that these individuals
will both continue in the long-term service of the Company and be motivated to experience a heightened interest and participate in the
future success of Company operations. An aggregate of 3,000,000 shares of Common Stock were initially reserved for grant and issuance pursuant to
the 2014 Plan. The 2014 Plan is administered and interpreted by our Compensation Committee (the “Administrator”). Awards
under the 2014 Plan may be granted in any one or all of the following forms: (i) incentive stock options (“ISOs”) intended
to qualify under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”); (ii) non-qualified stock options
(“NSOs”); (iii) stock appreciation rights, which may be granted in tandem with options or on a stand-alone basis; (iv) shares
of restricted stock; (v) shares of unrestricted stock; (vi) performance shares, and (vii) performance units.
Options
may not be granted under the 2014 Plan at an exercise price of less than the fair market value of the common stock on the date of grant
and the term of options cannot exceed ten years. ISOs may only be granted to persons who are employees of the Company. The exercise price
of an ISO granted to a holder of more than 10% of the common stock must be at least 110% of the fair market value of the common stock
on the date of grant, and the term of these options cannot exceed five years.
The
Administrator also may grant stock appreciation rights. Stock appreciation rights represent the right to receive upon exercise an amount
payable in cash or common stock equal to (A) the number of shares with respect to which the stock appreciation right is being exercised
multiplied by (B) the excess of (i) the fair market value of a share of common stock on the date the award is exercised over (ii) the
exercise price specified in the award agreement.
Under
the performance award component of the 2014 Plan, participants may be granted an award denominated in shares of common stock or in dollars.
Achievement of the performance targets, or multiple performance targets established by the Administrator relating to corporate, group,
unit or individual performance based upon standards set by the Administrator shall entitle the participant to payment at the full amount
or a portion of the amount specified with respect to the award, at the discretion of the Administrator based on its evaluation of the
performance of the target goals applicable to such award. Payment may be made in cash, common stock or any combination thereof, as determined
by the Administrator, and shall be adjusted in the event the participant ceases to be an employee of the Company before the end of a
performance cycle by reason of death, disability, or retirement.
Under
the stock component of the 2014 Plan, the Administrator may, in selected cases, grant to a plan participant a given number of shares
of restricted stock or unrestricted stock. Restricted stock under the 2014 Plan is common stock restricted as to sale pending fulfillment
of such vesting schedule and employment requirements as the Administrator shall determine. Prior to the lifting of the restrictions,
the participant will nevertheless be entitled to receive distributions in liquidation and dividends on, and to vote the shares of, the
restricted stock. The 2014 Plan provides for forfeiture of restricted stock for breach of conditions of grant.
The
2014 Plan also permits the board of directors (and not the Compensation Committee) to grant awards of NSOs, restricted stock or unrestricted
stock to non-employee directors. The board may authorize individual grants or adopt one or more formulas for grants of awards to the
non-employee directors. All options granted to non-employee directors must have an exercise price equal to the fair market value at the
date of grant.
The
exercise price of awards may be paid in cash, in shares of common stock (valued at fair market value at the date of exercise), by delivery
of a notice of exercise together with irrevocable instructions to a broker to deliver to the Company the proceeds of the sale of common
stock or of a loan from the broker sufficient to pay the exercise price, by having the Company withhold from shares being exercised the
number of shares having a fair market value equal to the exercise price for all shares being exercised, or by a combination of the foregoing
means of payment, as may be determined by the Administrator.
Issuer
Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
ITEM
6. [RESERVED]
ITEM
7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Management’s
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, or MD&A, is intended to provide a reader of our consolidated
financial statements with a narrative from the perspective of our management on our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity
and certain other factors that may affect our future results. You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial
condition and results of operations together with our financial statements and the related notes and other financial data included elsewhere
in this Annual Report. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report,
including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks
and uncertainties. You should review Item 1A of this Annual Report for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results
to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion
and analysis.
Results
of Operations:
Years
ended March 31, 2023 compared to March 31, 2022
Revenue,
Cost of manufacturing and Gross profit:
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
Change |
| | |
2023 | |
2022 | |
Dollars | |
Percentage |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | | |
$ | 2,235,710 | | |
| 8 | % |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | | |
| (342,713 | ) | |
| (6 | )% |
| Total revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | | |
| 1,892,997 | | |
| 6 | % |
| Cost of manufacturing | |
| 17,561,093 | | |
| 17,466,763 | | |
| 94,330 | | |
| 1 | % |
| Gross profit | |
$ | 16,594,021 | | |
$ | 14,795,354 | | |
$ | 1,798,667 | | |
| 12 | % |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Gross profit - percentage | |
| 49 | % | |
| 46 | % | |
| | | |
| | |
Total
revenues for the year ended March 31, 2023 increased by $1.9 million or 6%, to $34.2 million, as compared to $32.3 million for the prior
year, primarily due to increased revenues from Amphetamine ER Capsules and Phentermine as compared to prior year.
Manufacturing
fees increased by $2.2 million, or 8%, primarily due to manufacturing revenues increased from Amphetamine ER Capsules, as compared to
the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Licensing
fees decreased by $0.3 million, or 6%. This decrease was primarily due to licensing fees decreasing from the sales of Amphetamine IR Tablets, Naltrexone Tablets, and Isradipine as compared to the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Costs
of manufacturing consist of manufacturing and assembly costs. Our costs of revenue increased by $0.1 million or 1%, to $17.6 million as compared
to $17.5 million for the prior fiscal year. This increase was due to the increased manufacturing activities and related manufacturing
revenues during the year ended March 31, 2023, as compared to the prior year. The increase in cost of revenues of 1%, compared with the increase in manufacturing fees of 8% is due to efficiencies
gained in the manufacturing and sale of Amphetamine ER Capsules, which were launched during fiscal year 2021.
Our
gross profit margin was 49% during the year ended March 31, 2023 as compared to 46% during the comparable prior fiscal year.
Operating
expenses:
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
Change |
| | |
2023 | |
2022 | |
Dollars | |
Percentage |
| Operating expenses: | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Research and development | |
$ | 6,200,163 | | |
$ | 4,051,349 | | |
$ | 2,148,814 | | |
| 53 | % |
| General and administrative | |
| 5,122,272 | | |
| 4,464,003 | | |
| 658,269 | | |
| 15 | % |
| Non-cash compensation | |
| 39,325 | | |
| 14,353 | | |
| 24,972 | | |
| 174 | % |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| 292,807 | | |
| — | | |
| 292,807 | | |
| — | % |
| Depreciation and amortization | |
| 1,263,452 | | |
| 1,194,939 | | |
| | | |
| 68,5136 | % |
| Total operating expenses | |
$ | 12,918,019 | | |
$ | 9,724,644 | | |
$ | 3,193,375 | | |
| 33 | % |
Operating
expenses consist of research and development costs, general and administrative, non-cash compensation and depreciation and
amortization expenses. Operating expenses totaled for $12.9 million the year ended March 31, 2023, which increased approximately
$3.2 million, or 33%, from the prior year, largely due to increases of $2.1 million in research and development costs, $0.7 million in general and administrative
expenses, and $0.3 million in impairment of intangible assets. The changes in balance of each line item from the prior year are outlined
below.
Research
and development costs for the year ended March 31, 2023 were $6.2 million, an increase of $2.1 million, or 53%, from $4.1 million of such
costs for the prior year. The increase was a result of the timing and nature of product development activities during the year ended
March 31, 2023 as compared to the prior year.
General
and administrative expenses for the year ended March 31, 2023 were $5.1 million, an increase of $0.7 million, or 15%, from $4.5 million
of such costs for the prior year. The increase was due in large part to the increase in payroll-related expense and professional expense.
Non-cash
compensation expense for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 was less than $0.1 million.
Impairment of intangible assets the year ended March 31, 2023 was $0.3 million, compared with $0.0 in the prior
year. The increase was due to impairment of ANDA and patent intangible assets.
Depreciation
and amortization expenses for the year ended March 31, 2023 were $1.3 million, and remained relatively unchanged from $1.2 million of
such costs for the prior year.
As
a result of the foregoing, our income from operations for the year ended March 31, 2023 was $3.7 million, compared to income from operations
of $5.1 million for the prior year.
Other
income (expense):
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
Change |
| | |
2023 | |
2022 | |
Dollars | |
Percentage |
| Other income, net: | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments | |
$ | 415,126 | | |
$ | 1,425,409 | | |
$ | (1,010,283 | ) | |
| (71 | )% |
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs | |
| (1,112,707 | ) | |
| (191,816 | ) | |
| (920,891 | ) | |
| 480 | % |
| Gain on sale of ANDA | |
| 1,000,000 | | |
| — | | |
| 1,000,000 | | |
| — | % |
| Interest income | |
| 7,453 | | |
| 126 | | |
| 7,327 | | |
| 5,815 | % |
| Other income, net | |
$ | 309,872 | | |
$ | 1,233,719 | | |
$ | (923,847 | ) | |
| (75 | )% |
Other
income, net for the year ended the year ended March 31, 2023 was $0.3 million, a reduction of $0.9 million from the prior year. The
decrease in other income, net was due to the recognition of gain of $1,000,000 related to the sale of ANDA during the year ended
March 31, 2023. Additionally, change in fair value of derivative instruments decreased by approximately $1.0 million. Interest
expense and amortization of debt issuance costs increased by approximately $0.9 million. The change in fair value of derivative instruments is largely due to decreases in
the Company’s stock price during the year ended March 31, 2023 compared with the prior year. The change in interest expense
and amortization of debt issuance costs is largely due to interest incurred on the EWB loan of approximately $12.0 million and EWB
mortgage loan of approximately $2.6 million, entered into in April and July, 2022, respectively.
As
a result of the foregoing, our income before income taxes for the year ended March 31, 2023 was $4.0 million, compared to $6.3 million
for the prior year.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
Capital
Resources
| | |
March 31, 2023 | |
March 31, 2022 | |
Change |
| Current assets | |
$ | 21,510,297 | | |
$ | 18,861,389 | | |
$ | 2,648,908 | |
| Current liabilities | |
$ | 7,833,637 | | |
$ | 6,694,241 | | |
$ | 1,139,396 | |
| Working capital | |
$ | 13,676,660 | | |
$ | 12,167,148 | | |
$ | 1,509,512 | |
The
Company considers cash and working capital balances as several of the factors the Company uses in evaluating its performance. As of March
31, 2023, the Company had cash on hand of $7.8 million and accounts receivable to be collected within expected operating cycles of $3.1
million. The Company believes that such resources, combined with the working capital surplus of $13.7 million and the continuation of
ongoing operations, are sufficient to fund operations through the current operating cycle. For the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company
had income from operations totaling $3.7 million, net other income totaling $0.3 million and a net income of $3.6 million. The Company’s
other income and net income (loss) available to common shareholders are significantly influenced by the fluctuations in the fair value
of warrant derivatives with such fair value bearing a strong inverse correlation to the market share price of the Company’s Common
Stock.
Our
working capital (total current assets less total current liabilities) increased by $1.5 million from $12.2 million as of March 31, 2022
to $13.7 million as of March 31, 2023, with such increase being primarily related to the net income of $3.6 million and a net positive
operating cash flows of $3.3 million achieved during the year ended March 31, 2023.
Summary
of Cash Flows:
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, |
| | |
2023 | |
2022 |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | |
$ | 3,338,704 | | |
$ | 6,508,314 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | |
$ | (5,736,618 | ) | |
$ | (498,566 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | |
$ | 1,702,199 | | |
$ | (667,133 | ) |
Net
cash provided by operating activities for the year ended March 31, 2023 was $3.3 million, which included net income of $3.6 million,
offset by non-cash (income) expenses totaling $1.8 million and net increases in assets and decreases in liabilities totaling $2.0 million.
Net
cash provided by operating activities for the year ended March 31, 2022 was $6.5 million, which included net income of $8.9 million,
offset by non-cash (income) expenses totaling $1.4 million and net increases in assets and decreases in liabilities totaling $1.0 million.
Net
cash used in investing activities for the year ended March 31, 2023 was comprised of purchases of property and equipment of $5.7 million.
Net
cash used in investing activities for the year ended March 31, 2022 was comprised of purchases of property and equipment of $0.5 million.
Net
cash provided by financing activities was $1.7 million for the year ended March 31, 2023 which contained proceeds and loan payments related
to the EWB mortgage loan and equipment loans.
Net
cash used in financing activities was $0.7 million for the year ended March 31, 2022 which was offset primarily by loan payments.
Nasrat Promissory Note
In place of the EWB Term
Loan, the Company has entered into a collateralized promissory note with an individual lender with rates comparable to the EWB Term
Loan but with less restrictive covenants (a “Promissory Note”). As of June 2, 2023, a Promissory Note was placed with
Nasrat Hakim, CEO and Chairman of the Board of Directors, for $3,000,000. The Promissory Note has an interest rate of 9% for the
first year and 10% for an optional second year and the proceeds will be used for working capital and other business purposes.
East West Bank
On April 2, 2022, the Company and Elite Labs entered into a Loan and Security Agreement (the “EWB Loan Agreement”)
with East West Bank (“EWB”). Pursuant to the EWB Loan Agreement, the Company and Elite Labs received one term loan for a principal
amount of $12,000,000 (the “EWB Term Loan”) and a revolving line of credit up to $2,000,000 (the “EWB Revolver,”
together with the “EWB Term Loan,” the EWB Loans”), each of which shall be used for working capital. As of March 31,
2023, the principal and interest on the EWB Term Loan has been paid in full by the Company and the EWB Loan Agreement is terminated.
Lincoln Park Capital
July
8, 2020 Purchase Agreement
On
July 8, 2020, the Company entered into a purchase agreement (the “2020 LPC Purchase Agreement”), and a registration rights
agreement (the “2020 LPC Registration Rights Agreement”), with Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”),
pursuant to which Lincoln Park has committed to purchase up to $25.0 million of the Company’s Common Stock, $0.001 par value per
share, from time to time over the term of the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement, at the Company’s direction. The 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement expires on August 1, 2023.
During
the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company did not issue any shares of Common Stock to Lincoln Park.
NJEDA
Bonds
On
August 31, 2005, the Company successfully completed a refinancing of a prior 1999 bond issue through the issuance of new tax-exempt bonds
(the “Bonds”). The refinancing involved borrowing $4,155,000, evidenced by a 6.5% Series A Note in the principal amount of
$3,660,000 maturing on September 1, 2030 and a 9% Series B Note in the principal amount of $495,000 maturing on September 1, 2012. The
net proceeds, after payment of issuance costs, were used (i) to redeem the outstanding tax-exempt Bonds originally issued by the Authority
on September 2, 1999, (ii) refinance other equipment financing and (iii) for the purchase of certain equipment to be used in the manufacture
of pharmaceutical products. As of March 31, 2016, all of the proceeds were utilized by the Company for such stated purposes.
Interest
is payable semi-annually on March 1 and September 1 of each year. The Bonds are collateralized by a first lien on the Company’s
facility and equipment acquired with the proceeds of the original and refinanced Bonds. The related Indenture requires the maintenance
of a Debt Service Reserve Fund of $366,000 in relation to the Series A Notes.
Bond
issue costs of $354,454 were paid from the bond proceeds and are being amortized over the life of the bonds. Amortization of bond issuance
costs amounted to $14,178 for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023.
The
NJEDA Bonds require the Company to make an annual principal payment on September 1st of varying amounts as specified in the loan documents
and semi-annual interest payments on March 1st and September 1st, equal to interest due on the outstanding principal at the applicable
rate for the semi-annual period just ended.
As
of the date of filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, there are no interest or principal amounts in arrears. The Series B Notes were
retired, at par in July 2014.
Mortgage
On July 1, 2022, the East West Bank provided a mortgage loan (“EWB Mortgage Loan”) in the amount of $2.55
million for the purchase of the property at 135-137 Ludlow Avenue, which was formerly leased by the Company. The EWB Mortgage Loan
matures in 10 years and bears interest at a rate of 4.75% fixed for 5 years then adjustable at the Wall Street Journal Prime Rate (“WSJP”)
plus 0.5% with floor rate of 4.5%. The total transaction costs associated with the EWB Mortgage Loan incurred as of March 31, 2023, were
$13,251, which are being amortized on a monthly basis over ten years, beginning in July 2022.
Off-Balance
Sheet Arrangements
We
have not entered into any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our
financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues, or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures, or
capital resources that would be considered material to investors.
Effects
of Inflation
We
are subject to price risks arising from price fluctuations in the market prices of the products that we sell. Management does not believe
that inflation risk is material to our business or our consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
Critical
Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our
significant accounting policies are disclosed in Note 1 of our Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report
on Form 10-K. The following discussion addresses our most critical accounting policies, which are those that are both important to the
portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and that require significant judgment or use of complex estimates.
Segment
Information
Financial
Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 280, Segment Reporting, establishes
standards for reporting information about operating segments. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which
separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making group,
in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive
Officer, who reviews the financial performance and the results of operations of the segments prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP when
making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance of the Company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are products whose marketing approvals were secured via an Abbreviated New Drug Applications
(“ANDA”) and products whose marketing approvals were secured via a New Drug Application (“NDA”). ANDA products
are referred to as generic pharmaceuticals and NDA products are referred to as branded pharmaceuticals.
There
are currently no intersegment revenues. Asset information by operating segment is not presented since the chief operating decision maker
does not review this information by segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation of the
Company’s audited consolidated financial statements. Please see note 15 for further details.
Revenue
Recognition
The
Company generates revenue from the development of pain management products, manufacturing of a line of generic pharmaceutical products
with approved ANDA, commercialization of products either by license and the collection of royalties, or through the manufacture of formulations
and the development of new products and the expansion of licensing agreements with other pharmaceutical companies, including co-development
projects, joint ventures and other collaborations. The Company also generates revenue through its focus on the development of various
types of drug products, including branded drug products which require NDAs.
Under
ASC 606, Revenue from Contacts with Customers (“ASC 606”), the Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains control
of promised goods or services, in an amount that reflects the consideration which is expected to be received in exchange for those goods
or services. The Company recognizes revenues following the five-step model prescribed under ASC 606: (i) identify contract(s) with a
customer; (ii) identify the performance obligation(s) in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the transaction
price to the performance obligation(s) in the contract; and (v) recognize revenues when (or as) the Company satisfies a performance obligation.
The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the entity will collect the consideration it is entitled
to in exchange for the goods or services it transfers to the customer. At contract inception, once the contract is determined to be within
the scope of ASC 606, the Company assesses the goods or services promised within each contract and determines those that are performance
obligations and assesses whether each promised good or service is distinct. The Company then recognizes as revenue the amount of the
transaction price that is allocated to the respective performance obligation when (or as) the performance obligation is satisfied. Sales,
value add, and other taxes collected on behalf of third parties are excluded from revenue.
Nature
of goods and services
The
following is a description of the Company’s goods and services from which the Company generates revenue, as well as the nature,
timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and significant payment terms for each, as applicable:
a)
Manufacturing Fees
The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties, if and when the products are approved.
These products include products using controlled-release drug technology and products utilizing abuse deterrent technologies. The Company
also develops and markets (either on its own or by license to other companies) generic and proprietary controlled-release and abuse deterrent
pharmaceutical products.
The
Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains control of the Company’s product based on the contractual shipping terms of
the contract. Revenue on product are presented gross because the Company is primarily responsible for fulfilling the promise to provide
the product, is responsible to ensure that the product is produced in accordance with the related supply agreement and bears risk of
loss while the inventory is in-transit to the commercial partner. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects
to receive in exchange for transferring products to a customer.
b)
License Fees
The
Company enters into licensing and development agreements, which may include multiple revenue generating activities, including milestones
payments, licensing fees, product sales and services. The Company analyzes each element of its licensing and development agreements in
accordance with ASC 606 to determine appropriate revenue recognition. The terms of the license agreement may include payment to the Company
of licensing fees, non-refundable upfront license fees, milestone payments if specified objectives are achieved, and/or royalties on
product sales.
If
the contract contains a single performance obligation, the entire transaction price is allocated to the single performance obligation.
Contracts that contain multiple performance obligations require an allocation of the transaction price based on the estimated relative
standalone selling prices of the promised products or services underlying each performance obligation. The Company determines standalone
selling prices based on the price at which the performance obligation is sold separately. If the standalone selling price is not observable
through past transactions, the Company estimates the standalone selling price taking into account available information such as market
conditions and internally approved pricing guidelines related to the performance obligations.
The
Company recognizes revenue from non-refundable upfront payments at a point in time, typically upon fulfilling the delivery of the associated
intellectual property to the customer. For those milestone payments which are contingent on the occurrence of particular future events
(for example, payments due upon a product receiving FDA approval), the Company determined that these need to be considered for inclusion
in the calculation of total consideration from the contract as a component of variable consideration using the most-likely amount method.
As such, the Company assesses each milestone to determine the probability and substance behind achieving each milestone. Given the inherent
uncertainty of the occurrence of future events, the Company will not recognize revenue from the milestone until there is not a high probability
of a reversal of revenue, which typically occurs near or upon achievement of the event.
Significant
management judgment is required to determine the level of effort required under an arrangement and the period over which the Company
expects to complete its performance obligations under the arrangement. If the Company cannot reasonably estimate when its performance
obligations either are completed or become inconsequential, then revenue recognition is deferred until the Company can reasonably make
such estimates. Revenue is then recognized over the remaining estimated period of performance using the cumulative catch-up method.
When
determining the transaction price of a contract, an adjustment is made if payment from a customer occurs either significantly before
or significantly after performance, resulting in a significant financing component. Applying the practical expedient in ASC 606-10-32-18,
the Company does not assess whether a significant financing component exists if the period between when the Company performs its obligations
under the contract and when the customer pays is one year or less. None of the Company’s contracts contained a significant financing
component as of March 31, 2023.
In
accordance with ASC 606-10-55-65, royalties are recognized when the subsequent sale of the customer’s products occurs.
Collaborative
Arrangements
Contracts
are considered to be collaborative arrangements when they satisfy the following criteria defined in ASC 808, Collaborative Arrangements:
| |
● |
The
parties to the contract must actively participate in the joint operating activity; and, |
| |
● |
The
joint operating activity must expose the parties to the possibility of significant risk and rewards, based on whether or not the
activity is successful. |
Cash
The
Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash
equivalents consist of cash on deposit with banks and money market instruments. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents with
high-quality, U.S. financial institutions and, to date has not experienced losses on any of its balances.
Accounts
Receivable
Accounts
receivable are comprised of balances due from customers, net of estimated allowances for uncollectible accounts, if any. In determining
collectability, historical trends are evaluated, and specific customer issues are reviewed on a periodic basis to arrive at appropriate
allowances.
Inventory
Inventory
is recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value on a specific identification by lot number basis.
Long-Lived
Assets
The
Company periodically evaluates the fair value of long-lived assets, which include property and equipment and intangibles, whenever events
or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
Property
and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is provided on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the respective
assets which range from three to forty years. Major repairs or improvements are capitalized. Minor replacements and maintenance and repairs
which do not improve or extend asset lives are expensed currently.
Upon
retirement or other disposition of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and the resulting
gain or loss, if any, is recognized in income.
Intangible
Assets
The
Company capitalizes certain costs to acquire intangible assets; if such assets are determined to have a finite useful life they are amortized
on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life. Costs to acquire indefinite lived intangible assets, such as costs related to
ANDAs are capitalized accordingly.
The
Company tests its intangible assets for impairment at least annually (as of March 31st) and whenever events or circumstances change that
indicate impairment may have occurred. A significant amount of judgment is involved in determining if an indicator of impairment has
occurred. Such indicators may include, among others and without limitation: a significant decline in the Company’s expected future
cash flows; a sustained, significant decline in the Company’s stock price and market capitalization; a significant adverse change
in legal factors or in the business climate of the Company’s segments; unanticipated competition; and slower growth rates.
During the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company determined that circumstances occurred which indicated that impairment
of intangible assets may have occurred. The circumstances included a decrease in the Company’s stock price during the year ended March
31, 2023, compared with the prior year. The Company recorded impairment of approximately $0.3 million on its ANDA and patent intangible
assets during the year ended March 31, 2023.
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenditures are charged to expense as incurred.
Leases
The
Company assesses whether an arrangement is a lease or contains a lease at inception. For arrangements considered leases or that contain
a lease that is accounted for separately, the Company determines the classification and initial measurement of the right-of-use asset
and lease liability at the lease commencement date, which is the date that the underlying asset becomes available for use. The Company
has elected to account for non-lease components associated with its leases and lease components as a single lease component.
The
Company recognizes a right-of-use asset, which represents the Company’s right to use the underlying asset for the lease term, and
a lease liability, which represents the present value of the Company’s obligation to make payments arising over the lease term.
The present value of the lease payments is calculated using either the implicit interest rate in the lease or an incremental borrowing
rate.
Contingencies
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series of complex judgments
about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
Income
Taxes
Income
taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which
those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Where applicable, the Company records a valuation allowance to reduce
any deferred tax assets that it determines will not be realizable in the future.
The
Company recognizes the benefit of an uncertain tax position that it has taken or expects to take on income tax returns it files if such
tax position is more likely than not to be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position.
These tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate resolution.
The
Company operates in multiple tax jurisdictions within the United States of America. The Company remains subject to examination in all
tax jurisdiction until the applicable statutes of limitation expire. As of March 31, 2023, a summary of the tax years that remain subject
to examination in our major tax jurisdictions are: United States – Federal, 2014 and forward, and State, 2010 and forward. The
Company did not have any unrecognized tax positions for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022.
Warrants
and Preferred Shares
The
accounting treatment of warrants and preferred share series issued is determined pursuant to the guidance provided by ASC 470, Debt,
ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, as applicable. Each feature of a freestanding
financial instruments including, without limitation, any rights relating to subsequent dilutive issuances, dividend issuances, equity
sales, rights offerings, forced conversions, optional redemptions, automatic monthly conversions, dividends and exercise are assessed
with determinations made regarding the proper classification in the Company’s financial statements.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC Topic 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation. Under the fair value
recognition provisions of this topic, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award
and is recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, based on the terms of the awards. The cost
of the stock-based payments to nonemployees that are fully vested and non-forfeitable as at the grant date is measured and recognized
at that date, unless there is a contractual term for services in which case such compensation would be amortized over the contractual
term.
In
accordance with the Company’s Director compensation policy and certain employment contracts, director’s fees and a portion
of employee’s salaries are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s common stock, in lieu of cash, with the
valuation of such share being calculated on a quarterly basis and equal to the simple average closing price of the Company’s common
stock.
Earnings
(Loss) Per Share Applicable to Common Shareholders’
The
Company follows ASC 260, Earnings Per Share, which requires presentation of basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share (“EPS”)
on the face of the income statement for all entities with complex capital structures and requires a reconciliation of the numerator and
denominator of the basic EPS computation to the numerator and denominator of the diluted EPS computation. In the accompanying financial
statements, basic earnings (loss) per share is computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of shares of common
stock outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS excluded all dilutive potential shares if their effect was anti-dilutive.
Fair
Value of Financial Instruments
ASC
Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC Topic 820”) provides a framework for measuring fair value in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles.
ASC
Topic 820 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. ASC Topic 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between (1)
market participant assumptions developed based on market data obtained from independent sources (observable inputs) and (2) an entity’s
own assumptions about market participant assumptions developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (unobservable
inputs).
The
fair value hierarchy consists of three broad levels, which gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). The three levels of the fair value
hierarchy under ASC Topic 820 are described as follows:
| |
● |
Level
1 Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that are accessible at the measurement date. |
| |
● |
Level
2 Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly.
Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar
assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability;
and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
| |
● |
Level
3 Inputs that are unobservable for the asset or liability. |
The
carrying amounts of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities, such as cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses and other
current assets, accounts payable and accrued expenses, approximate their fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
Based upon current borrowing rates with similar maturities the carrying value of long-term debt approximates fair value.
Non-Financial
Assets that are Measured at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
Non-financial
assets such as intangible assets, and property and equipment are measured at fair value only when an impairment loss is recognized.
The Company recorded impairment of approximately $0.3 million on its ANDA and patent intangible assets during the year ended March 31, 2023.
Treasury
Stock
The
Company records treasury stock at the cost to acquire it and includes treasury stock as a component of shareholders’ equity (deficit).
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In
June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial
Instruments. This update requires immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses (“CECL”).
Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that
are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022
for public entities qualifying as smaller reporting companies. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact
of this update on the consolidated financial statements and does not expect a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Management
has evaluated other recently issued accounting pronouncements and does not believe that any of these pronouncements will have a significant
impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
ITEM
7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Not
Applicable.
ITEM
8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Attached
hereto and filed as a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are our Consolidated Financial Statements, beginning on page F-1.
ITEM
9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM
9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation
of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The
term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Exchange Act, refers to controls
and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits
under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and
forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required
to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s
management, including its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding
required disclosure. As required by Rules 13a-15(b) and 15d-15(b) of the Exchange Act, our management, with the participation of our
Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the
end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial
Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of March 31, 2023 at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s
Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Internal
control over financial reporting refers to the process designed by, or under the supervision of, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief
Financial Officer, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding
the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally
accepted accounting principles, and includes those policies and procedures that: (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable
detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions
are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,
and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (3)
provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s
assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Internal
control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and
operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are achieved. Further, the design
of a control system must be balanced against resource constraints, and therefore the benefits of controls must be considered relative
to their costs. Given the inherent limitations in all systems of controls, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance all
control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within a company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities
that judgments in decision making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of a simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls
can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people or by management override of the controls.
The design of any system of controls is also based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there
can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls
may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or the degree of compliance with policies or procedures may deteriorate. Accordingly,
given the inherent limitations in a cost-effective system of internal control, financial statement misstatements due to error or fraud
may occur and may not be detected. Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable, not absolute, assurance
of achieving their objectives. We conduct periodic evaluations of our systems of controls to enhance, where necessary, our control policies
and procedures.
Management
is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules
13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief
Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial
reporting. Management has used the framework set forth in the report entitled “Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013)”
published by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission to evaluate the effectiveness of our internal control
over financial reporting. Based on its evaluation, management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective
as of March 31, 2023 at the reasonable assurance level.
Changes
in internal control over financial reporting
There
were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting identified in management’s evaluation pursuant to Rules 13a-15(d)
or 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act during the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2023 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to
materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM
9B. OTHER INFORMATION
Effective as of June 28, 2023, Mark Pellegrino ceased to be employed by
the Company. The Company has begun a search for a new chief financial officer. Nasrat Hakim, the Company’s President and Chief Executive
Officer, will serve as the Company’s Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer until a new chief financial officer
is identified and hired.
ITEM
9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
None.
PART
III
ITEM
10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The
following sets forth biographical information about each of our directors and executive officers as of the date of this report:
| Name |
|
Age |
|
Position |
|
Director/Officer
Since |
|
Director
Class |
| Nasrat
Hakim |
|
62 |
|
President,
Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
August
2013 |
|
III |
| Barry
Dash, Ph. D. |
|
92 |
|
Director |
|
April
2005 |
|
II |
| Jeffrey
Whitnell |
|
67 |
|
Director |
|
October
2009 |
|
III |
| Davis
Caskey |
|
75 |
|
Director |
|
April
2016 |
|
I |
Kirko Kirkov |
|
55 |
|
Chief Commercial Officer |
|
September 2022 |
|
|
| Douglas
Plassche |
|
59 |
|
Executive
Vice President of Operations |
|
August
2013 |
|
|
The
principal occupations and employment of each Director and executive officer during the past five years is set forth below. In each instance
in which dates are not provided in connection with an individual’s business experience, such individual has held the position indicated
for at least the past five years.
Pursuant
to our amended and restated bylaws, our Board of Directors is classified into three separate classes of directors. Each
director currently holds office until the expiration of the term of his class (each for three years) and until his successor is duly
elected and qualified, or until such director’s death, resignation, or removal.
Nasrat
Hakim
Nasrat
Hakim has served as a Director, President, and Chief Executive officer since August 2013. He has been a member of the Audit Committee,
member and chairman of the nominating Committee and member of the Compensation Committee since September 2016. Mr. Hakim has more than
30 years of pharmaceutical and medical industry experience in Quality Assurance, Analytical Research and Development, Technical Services,
and Regulatory Compliance. He brings with him proven management experience, in-depth knowledge of manufacturing systems, development
knowledge in immediate and extended release formulations and extensive regulatory experience of GMP and FDA regulations. From 2004 to
2013, Mr. Hakim was employed by Actavis, Watson and Alpharma in various senior management positions. Most recently, Mr. Hakim served
as International Vice President of Quality Assurance at Actavis, overseeing 25 sites with more than 3,000 employees under his leadership.
Mr. Hakim also served as Corporate Vice President of Technical Services, Quality and Regulatory Compliance for Actavis U.S., Global Vice
President, Quality, and Regulatory Compliance for Alpharma, as well as Executive Director of Quality Unit at TheraTech, overseeing manufacturing
and research and development. In 2009, Mr. Hakim founded Mikah Pharma, LLC, a virtual, fully functional pharmaceutical company. Mr. Hakim
holds a Bachelor in Chemistry/Bio-Chemistry and Masters of Science in Chemistry from California State University at Sacramento, Sacramento,
CA; a Masters in Law with Graduate Certification in U.S. and International Taxation from St. Thomas University, School of Law, Miami,
FL.; and a Graduate Certification in Regulatory Affairs (RAC) from California State University at San Diego, San Diego, CA. Mr. Hakim’s
leadership experience (consisting of extensive experience in senior management positions, responsible for 25 global manufacturing/regulatory
sites with more than 3,000 employees under his leadership), industry experience (comprising more than 30 years of pharmaceutical and
medical industry experience served in various quality assurance, analytical research and development/technical services and compliance
positions) and academic experience (including Bachelor degrees in Chemistry and Bio-Chemistry, Masters degrees in Chemistry and Law,
with Graduate Certification in U.S. and International Taxation, and a Graduate Certification in Regulatory Affairs) led to the conclusion
that he is qualified to serve as a director.
Barry
Dash, Ph.D.
Dr.
Barry Dash has served as a Director since April 2005, member of the Audit Committee since April 2005, member of the Nominating Committee
since April 2005 and member and Chairman of the Compensation Committee since June 2007. Dr. Dash has been, since 1995, President and
Managing Member of Dash Associates, L.L.C., an independent consultant to the pharmaceutical and health industries. From 1983 to 1996
he was employed by Whitehall-Robins Healthcare, a division of American Home Products Corporation (now known as Wyeth), initially as Vice
President of Scientific Affairs, then as Senior Vice President of Scientific Affairs and then as Senior Vice President of Advanced Technologies,
during which time he personally supervised six separate departments: Medical and Clinical Affairs, Regulatory Affairs, Technical Affairs,
Research and Development, Analytical R&D and Quality Management/Q.C. Dr. Dash had been employed by the Whitehall Robins Healthcare
from 1960 to 1976, during which time he served as Director of Product Development Research, Assistant Vice President of Product Development
and Vice President of Scientific Affairs. Dr. Dash had been employed by J.B. Williams Company (Nabisco Brands, Inc.) from 1978 to 1982.
From 1976 to 1978 he was Vice President and Director of Laboratories of the Consumer Products Division of American Can Company. Dr. Dash
holds a Ph.D. from the University of Florida and M.S. and B.S. degrees from Columbia University where he was Assistant Professor at the
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences from 1956 to 1960. He is a member of the American Pharmaceutical Association, the American Association
for the Advancement of Science and the Society of Cosmetic Chemist, American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, Drug Information
Association, American Foundation for Pharmaceutical Education, and Diplomate American Board of Forensic Examiners. He is the author of
scientific publications and patents in the pharmaceutical field. Dr. Dash’s extensive education in pharmaceutical sciences and
his experience in the development of scientific products, including his experience in regulatory affairs, led to the conclusion that
he is qualified to serve as a director.
Jeffrey
Whitnell
Jeffrey
Whitnell has served as a Director since October 23, 2009, Chairman of the Audit Committee, member of the Compensation Committee
since October 2009 and designated by the Board as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined under applicable
rules under the Exchange Act. Since April 2015, Mr. Whitnell has provided financial advisory services, primarily to the healthcare
industry, including LifeWatch Services, where he served as the Vice President, Finance & Controller. From June 2010 to March
2015, Mr. Whitnell was the Chief Financial Officer for ReliefBand Medical Technologies, a medical device company. From June 2009 to
June 2010, Mr. Whitnell provided financial advisory services to various healthcare companies, including ReliefBand Medical
Technologies. From June 2004 to June 2009, Mr. Whitnell was Chief Financial Officer and Senior Vice President of Finance at Akorn,
Inc. From June 2002 to June 2004, Mr. Whitnell was Vice President of Finance and Treasurer for Ovation Pharmaceuticals (acquired by
Lundeck). From 1997 to 2001, Mr. Whitnell was Vice President of Finance and Treasurer for MediChem Research (acquired by deCODE
genetics). Prior to 1997, Mr. Whitnell held various finance positions at Akzo Nobel and Motorola. Mr. Whitnell began his career as
an auditor with Arthur Andersen & Co. He is a certified public accountant and holds an M.B.A. in Finance from the University of
Chicago Booth School of Business and a B.S. in Accounting from the University of Illinois. Mr. Whitnell’s qualifications as an
accounting and audit expert led to the conclusion that he is qualified to serve as a director.
Davis
Caskey
Davis
Caskey has served as a Director since April 2016, and a member of the Audit Committee, the nominating Committee and the Compensation
Committee since September 2016. He brings more than 40 years of pharmaceutical industry experience to this position. Mr. Caskey is currently
President & CEO of Caskey LLC, which he formed in 2013 to serve as an umbrella to manage his pharmaceutical consulting and other
business interests. From 1990 to 2013, Davis served as the operating officer of ECR Pharmaceuticals, of which he was a founding member.
HiTech Pharmacal acquired the privately held ECR in 2009 and Mr. Caskey continued in his role until retiring in 2013. At ECR, Mr. Caskey
was credited with the establishment of the company’s sales and marketing structure, its product distribution format, and the development
and management of the firm’s internal organization. His responsibilities included the oversight of drug development and regulatory
filings, product acquisitions, and acquisition of other companies. A primary focus was to conceive and develop, with the assistance of
key strategic partners, unique dosage forms and extended release formulations of products which enhance patient compliance and safety.
Prior to ECR, Mr. Caskey was employed by A.H. Robins for 18 years in various field and home office management positions. His experience
brings critical insight into the marketing and distribution of pharmaceutical products in a rapid and ever-changing competitive marketplace,
and this experience led to the conclusion that he is qualified to serve as a director. Mr. Caskey attended the University of Texas (Austin)
and Lamar University, and holds bachelor’s and master’s degrees.
Kirko Kirkov
Mr. Kirkov joined
Elite in September 2022, as an accomplished and multi-faceted leader with more than twenty years of in-depth business development
skills across international pharmaceutical organizations. Before joining Elite, Mr. Kirkov served as General Manager of Vertice
Pharma, a specialty generics pharmaceutical company, from February 2020 to present. From April 2008 to February 2020, Mr.
Kirkov was employed by Sandoz and served in positions of increasing responsibilities beginning with Country Head & Managing
Director of Bulgaria from 2008 to 2011. From 2011 to 2013, Mr. Kirkov served as Sandoz’s Business Unit Head, Branded
Prescription Generics in Russia, and most recently, from January 2013 to February 2020, served as Sandoz’s Executive Director,
Commercial Operations. Mr. Kirkov brings with him a broad range of experience in the areas of business development, operationalization of commercial strategy, and implementation of retail and wholesale channel sales operations, having overseen sales portfolios consisting of 400+
product families, and 1,500+ SKUs covering both generic and branded products.
Mr.Kirkov has a
Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering/Engineering Management from
the University of Ottawa, two Masters of Science degrees respectively in Naval Architecture and Ocean Systems Management from the Massachusetts
Institute of Technology, a Master of Science in Applied Positive Psychology and Coaching from the University of
East London, and an MBA from the University of Durham.
Douglas
Plassche
Douglas
Plassche has served as Executive Vice President of Operations since August 2013. Prior to joining the Company, from 2009 to 2013, Mr.
Plassche served as the Managing Director of the New Jersey Solid Oral Dose Operations of Actavis, overseeing 450 employees and the production
of more than 100 products. From 2007 to 2009, Mr. Plassche was the Senior Director of Manufacturing for PAR Pharmaceuticals, overseeing
200 employees and the production of more than 70 products. From 1990 – 2007, Mr. Plassche was employed by Schering-Plough, progressing
steadily through multiple disciplines, locations, and technical operations sectors with increasing levels of responsibility. Mr. Plassche
has a bachelor’s degree in Economics from Rochester University.
There
are no family relationships between any of our directors and executive officers.
Committees
of the Board
The
Board of Directors has an Audit Committee, a Compensation Committee, and a Nominating Committee.
Audit
Committee
The
members of the Audit Committee are Jeffrey Whitnell (Chairman of the Audit Committee), Dr. Barry Dash, Davis Caskey and Nasrat Hakim.
The Board of Directors has determined that Messrs. Whitnell, Dash, and Caskey are independent and Mr. Whitnell is qualified as an audit
committee financial expert. The Board of Directors has determined that Messrs. Whitnell, Dash and Caskey are independent directors as
(i) defined in Rule 10A-3(b)(1)(ii) under the Exchange Act and (ii) under Sections 803A(2) and 803B(2)(a) of the NYSE American LLC Company
Guide (although our securities are not listed on the NYSE American LLC or any other national exchange).
Nominating
Committee
The members of the Nominating Committee are Nasrat Hakim (Chairman of the Nominating Committee), Dr.
Barry Dash, and Davis Caskey. There were no material changes to the procedures by which security holders may recommend nominees to our
Board of Directors since the filing of our last Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Compensation
Committee
The members of the Compensation Committee are Dr. Barry Dash (Chairman of the Compensation Committee),
Jeffrey Whitnell, Davis Caskey and Nasrat Hakim.
Delinquent
Section 16 Reports
Section
16(a) of the Exchange Act requires the Company’s officers and directors, and persons who own more than ten percent of a registered
class of the Company’s stock, to file reports of ownership and changes in ownership with the SEC. Officers, directors and greater
than ten percent stockholders are required by SEC regulation to furnish the Company with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file.
Based solely on its review of copies of such reports and upon written representations
from each of the Company’s officers and directors, the Company believes that, for the year ended March 31, 2023, all Section 16(a)
filing requirements applicable to the Company’s officers, directors and greater than ten percent stockholders were complied with
on a timely basis, except for one Form 3 filed on June 3, 2022 by Robert Chen, which was late due to a filing code issue, and one Form
4 filed on June 26, 2023 to report an award of options to Doug Plassche on January 3, 2023, which was late due to an administrative error.
Code
of Conduct and Ethics
At
the first meeting of the Board of Directors following the annual meeting of stockholders held on June 22, 2004, and as further updated
effective July 2009, the Board of Directors adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that is applicable to the Company’s directors,
officers, and employees. A copy of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on our website at www.elitepharma.com, under
Investor Relations.
ITEM
11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Portions of the Proxy Statement for the registrant’s 2023 Annual
Meeting of Shareholders which is to be filed subsequent to the date hereof are incorporated by reference.
ITEM
12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The
following table sets forth certain information, as of June 23, 2023 (except as otherwise indicated), regarding beneficial ownership of
our Common Stock by (i) each person who is known by us to own beneficially more than 5% of each such class, (ii) each of our directors,
(iii) each of our executive officers and (iv) all our directors and executive officers as a group. As of June 23, 2023, we had 1,013,915,081
shares of Common Stock outstanding (exclusive of 0.1 million treasury shares). On any matter presented to the holders of our Common Stock
for their action or consideration at any meeting of our Shareholders, each share of Common Stock entitles the holder to one vote.
As
used in the table below and elsewhere in this report, the term beneficial ownership with respect to a security consists of sole or shared
voting power, including the power to vote or direct the vote, and/or sole or shared investment power, including the power to dispose
or direct the disposition, with respect to the security through any contract, arrangement, understanding, relationship, or otherwise,
including a right to acquire such power(s) during the 60 days immediately following June 23, 2023. Except as otherwise indicated, the
Shareholders listed in the table have sole voting and investment powers with respect to the shares indicated.
| Name
and Address of Beneficial Owner of Common Stock | |
Common
Stock | | |
Percent
(%) of Voting
Securities Beneficially Owned | |
| Nasrat
Hakim, President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors* | |
| 295,824,820 | (1) | |
| 29.1 | % |
| Barry
Dash, Director* | |
| 3,235,555 | (2) | |
| ** | % |
| Jeffrey
Whitnell, Director* | |
| 3,187,020 | (3) | |
| ** | % |
| Davis
Caskey, Director* | |
| 2,049,436 | (4) | |
| ** | % |
| Douglas
Plassche, Executive Vice President * | |
| 4,133,932 | (5) | |
| ** | % |
| Robert Chen | |
| — | | |
| ** | % |
| Mark Pellegrino | |
| — | | |
| ** | % |
| All
Directors and Officers as a group | |
| 308,430,763 | (6) | |
| 30.4 | % |
| *
|
The
address is c/o Elite Pharmaceuticals Inc., 165 Ludlow Avenue, Northvale, NJ 07647. |
| **
|
Less
than 1% |
| (1)
|
Includes
167,114,882 shares of Common Stock held and 49,701,277 shares of Common Stock due and owing to Mr. Hakim as of March 31, 2023 (the
latest practicable date) for compensation earned pursuant to Mr. Hakim’s employment agreement with the Company and 79,008,661
shares of Common Stock issuable upon cash exercise of the Series J Warrants with an exercise price of $0.1521 per share. |
| (2)
|
Includes
2,687,898 shares of Common Stock held and 547,657 shares of Common Stock due and owing to Dr. Dash as of March 31, 2023 (the latest
practicable date) for Directors fees accrued as of such date. |
| (3)
|
Includes
2,639,363 shares of Common Stock held and 547,657 shares of Common Stock due and owing to Mr. Whitnell as of March 31, 2023 (the
latest practicable date) for Directors fees accrued as of such date. |
| (4)
|
Includes
1,501,779 shares of Common Stock held and 547,657 shares of Common Stock due and owing to Mr. Caskey as of March 31, 2023 (the latest
practicable date) Date for Directors fees accrued as of such date. |
| (5)
|
Includes
1,133,932 shares of Common Stock held and shares of Common
Stock issuable upon cash exercise of vested options to purchase 3,000,000 shares of Common Stock and excludes 7,500,000 shares issuable upon exercise of options not vested or not
exercisable within the next 60 days. |
| (6)
|
Relates
only to current directors and officers. Includes 175,077,854 shares of Common Stock held, 51,344,248 shares of Common Stock due and
owing as of March 31, 2023 (the latest practicable date) for director’s fees and salaries accrued as of such date, 3,000,000
shares of Common Stock issuable upon cash exercise of vested options and 79,008,661 shares of Common Stock issuable upon cash exercise
of warrants at an exercise price of $0.1521 per share of Common Stock, and excludes 7,500,000 shares issuable upon exercise of options not vested or not exercisable within the next 60
days. |
ITEM
13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Certain
Related Person Transactions
In
May 2020, Praxgen, under an asset purchase agreement, assigned its rights and obligations under the Praxgen Agreement for Amphetamine
IR and Amphetamine ER to Mikah. The ANDAs for Amphetamine IR and Amphetamine ER are now registered under Elite’s name. Mikah will
now be Elite’s partner with respect to Amphetamine IR and ER and will assume all the rights and obligations for these products
from Praxgen. Mikah was founded in 2009 by Nasrat Hakim.
Director
Independence
All
related person transactions are reviewed and, as appropriate, may be approved or ratified by the Board of Directors. If a Director is
involved in the transaction, he or she may not participate in any review, approval, or ratification of such transaction. Related person
transactions are approved by the Board of Directors only if, based on all of the facts and circumstances, they are in, or not inconsistent
with, our best interests and the best interests of our stockholders, as the Board of Directors determines in good faith. The Board of
Directors takes into account, among other factors it deems appropriate, whether the transaction is on terms generally available to an
unaffiliated third-party under the same or similar circumstances and the extent of the related person’s interest in the transaction.
The Board of Directors may also impose such conditions as it deems necessary and appropriate on us or the related person in connection
with the transaction.
In
the case of a transaction presented to the Board of Directors for ratification, the Board of Directors may ratify the transaction or
determine whether rescission of the transaction is appropriate.
ITEM
14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The
Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2023 is Buchbinder Tunick & Company
LLP (“Buchbinder”).
The
following table presents fees, including reimbursements for expenses, for professional audit services rendered by Buchbinder, for the
audits of our financial statements and interim reviews of our quarterly financial statements.
| | |
Fiscal 2023 | | |
Fiscal 2022 | |
| Audit Fees | |
$ | 120,000 | | |
$ | 120,000 | |
| Audit-Related Fees | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
| Tax Fees | |
$ | 10,000 | | |
$ | 8,500 | |
Audit
Fees
Represents
fees for professional services provided for the audit of our annual financial statements, services that are performed to comply with
generally accepted auditing standards, and review of our financial statements included in our quarterly reports and services in connection
with statutory and regulatory filings.
Audit-Related
Fees
Represents
the fees for assurance and related services that were reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements.
Tax
Fees
Represents
preparation of Federal, State and Local income tax returns.
The
Audit Committee has determined that Buchbinder’s rendering of these audit-related services was compatible with maintaining auditor’s
independence. The Board of Directors considered Buchbinder to be well qualified to serve as our independent public accountants. The Committee
also pre-approved the charges for services performed in Fiscal 2023.
Pre-Approval
Procedures
The
Audit Committee pre-approves all audit related and tax services and the terms thereof (which may include providing comfort letters in
connection with securities underwriting) and non-audit services (other than non-audit services prohibited under Section 10A(g) of the
Exchange Act or the applicable rules of the SEC or the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board) to be provided to us by the independent
auditor; provided, however, the pre-approval requirement is waived with respect to the provisions of non-audit services for us if the
“de minimus” provisions of Section 10A (i)(1)(B) of the Exchange Act are satisfied. This authority to pre-approve non-audit
services may be delegated to one or more members of the Audit Committee, who shall present all decisions to pre-approve an activity to
the full Audit Committee at its first meeting following such decision.
PART
IV
ITEM
15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SCHEDULES
| (a)
|
The
following are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K |
(1)
The financial statements and schedules required to be filed by Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and listed in the Index to Consolidated
Financial Statements.
(2)
The Exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K and listed below in the “Index to Exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation
S-K.”
| (b)
|
The
Exhibits are filed with or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K |
| |
|
| (c)
|
None |
Index
to Exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K.
| Exhibit
No. |
|
Description |
| 3.1(a) |
|
Articles
of Incorporation of Elite-Nevada, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on
January 9, 2012. |
| 3.1(b) |
|
Certificate
of Designations of the Series G Convertible Preferred Stock as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on April
18, 2013, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated April 18, 2013 and filed with the SEC
on April 22, 2013. |
| 3.1(c) |
|
Certificate
of Designation of the Series H Junior Participating Preferred Stock, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2 (contained in Exhibit
1) to the Registration Statement on Form 8-A filed with the SEC on November 15, 2013. |
| 3.1(d) |
|
Certificate of Designations of the Series I Convertible Preferred Stock as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on February 6, 2014, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated February 6, 2014 and filed with the SEC on February 7, 2014. |
| 3.1(e) |
|
Certificate
of Designations of the Series J Convertible Preferred Stock as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on May 3,
2017, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated April 28, 2017 and filed with the SEC on
April 28, 2017. |
| 3.1(f) |
|
Certificate
of Amendment to Articles of Incorporation, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated June
29, 2020 and filed with the SEC on June 29, 2020. |
| 3.2(a) |
|
Amended
and Restated By-Laws of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 23, 2020
and filed with the SEC on April 23, 2020. |
| 4.1 |
|
Form
of specimen certificate for Series G Convertible Preferred Stock of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the
Current Report on Form 8-K, dated April 18, 2013 and filed with the SEC on April 22, 2013. |
| 4.2 |
|
Form
of specimen certificate for Series I Convertible Preferred Stock of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the
Current Report on Form 8-K, dated February 6, 2014 and filed with the SEC on February 7, 2014. |
| 4.3 |
|
Rights
Agreement, dated as of November 15, 2013, between the Company and American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC., incorporated
by reference to Exhibit 1 to the Registration Statement on Form 8-A filed with the SEC on November 15, 2013. |
| 4.4 |
|
Form
of Series H Preferred Stock Certificate, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 1 to the Registration Statement on Form 8-A filed with
the SEC on November 15, 2013. |
| 4.5 |
|
Warrant
to purchase shares of Common Stock issued to Nasrat Hakim dated April 28, 2017 incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current
Report on Form 8-K, dated April 28, 2017, and filed with the SEC on April 28, 2017. |
| 4.6 |
|
Description
of Common Stock, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed with the SEC on June 29, 2020 |
| 10.1 |
|
Elite
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2014 Equity Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Company’s Definitive Proxy
Statement for its Annual Meeting of Shareholders, filed with the SEC on April 3, 2014. |
| 10.2 |
|
Form
of Confidentiality Agreement (corporate), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Form SB-2. |
| 10.3 |
|
Form
of Confidentiality Agreement (employee), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Form SB-2. |
| 10.4 |
|
Loan
Agreement, dated as of August 15, 2005, between New Jersey Economic Development Authority (“NJEDA”) and the Company,
incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated August 31, 2005 and filed with the SEC on September
6, 2005. |
| 10.5 |
|
Series
A Note in the aggregate principal amount of $3,660,000.00 payable to the order of the NJEDA, incorporated by reference to Exhibit
10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated August 31, 2005 and filed with the SEC on September 6, 2005. |
| 10.19 |
|
August
1, 2013 Secured Convertible Note from the Company to Mikah Pharma LLC., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current
Report on Form 8-K, dated August 1, 2013 and filed with the SEC on August 5, 2013. |
| 10.20 |
|
August 1, 2013 Security Agreement from the Company to Mikah Pharma LLC., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated August 1, 2013 and filed with the SEC on August 5, 2013. |
| 10.21 |
|
October
15, 2013 Hakim Credit Line Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period
ended September 30, 2013. |
| 10.22 |
|
October
2, 2013 Manufacturing and Licensing Agreement with Epic Pharma LLC, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Amended Quarterly
Report on Form 10-Q/A for the period ended September 30, 2013 and filed with the SEC on April 25, 2014. Confidential Treatment granted
with respect to portions of the Agreement. |
| 10.23 |
|
February
7, 2014 Amendment to Secured Convertible Note from the Company to Mikah, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current
Report on Form 8-K, dated February 7, 2014 and filed with the SEC on February 7, 2014. |
| 10.24 |
|
Employment
Agreement with Dr. G. Kenneth Smith, dated October 20, 2014, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.82 to the Quarterly Report on
Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2014 and filed with the SEC on November 14, 2014. |
| 10.25 |
|
January
28, 2015 First Amendment to the Loan Agreement between Nasrat Hakim and Elite Pharmaceuticals dated October 15, 2013, incorporated
by reference to Exhibit 10.83 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended December 31, 2014 and filed with the SEC
on February 17, 2015. |
| 10.26 |
|
January
28, 2015 Termination of Development and License Agreement for Mikah-001 between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Mikah Pharma LLC
and Transfer of Payment, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.84 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended December
31, 2014 and filed with the SEC on February 17, 2015. |
| 10.27 |
|
June 4, 2015 License Agreement with Epic Pharma LLC, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.85 to Amendment No. 1 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015 and filed with the SEC on July 11, 2016. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.28 |
|
Amendment
No. 1 to Hakim Employment Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC
on January 29, 2016. |
| 10.29 |
|
August
24, 2016 Master Development and License Agreement between Elite and SunGen Pharma LLC. incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.44
to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2016 and filed with the SEC on November 9, 2016. (Confidential
Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.30 |
|
Purchase
Agreement between the Company and Lincoln Park Capital LLC dated May 1, 2017, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current
Report on Form 8-K, dated May 2, 2017 and filed with the SEC on May 2, 2017. |
| 10.31 |
|
Registration
Rights Agreement between the Company and Lincoln Park Capital LLC dated May 1, 2017, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to
the Current Report on Form 8-K, dated May 2, 2017 and filed with the SEC on May 2, 2017. |
| 10.32 |
|
April
28, 2017 Exchange Agreement between the Company and Nasrat Hakim, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report
on Form 8-K, dated April 28, 2017 and filed with the SEC on April 28. 2017. |
| 10.33 |
|
May
2017 Trimipramine Acquisition Agreement from Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.50 to the Annual Report on Form
10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. |
| 10.34 |
|
May
2017 Secured Promissory Note from the Company to Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.51 to the Annual Report on
Form 10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. |
| 10.35 |
|
May
2017 Security Agreement between the Company to Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.52 to the Annual Report on Form
10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. |
| 10.36 |
|
May 2017 Assignment of Supply and Distribution Agreement between Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories and Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.53 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. |
| 10.37 |
|
May
2017 Assignment of Manufacturing and Supply Agreement between Epic and Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.54 to
the Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. |
| 10.38 |
|
Supply and Distribution Agreement between Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories and Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.55 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.39 |
|
Manufacturing
and Supply Agreement between Epic and Mikah Pharma, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.56 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K,
for the period ended March 31, 2017 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2017. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions
of the Agreement). |
| 10.40 |
|
Master
Development and License Agreement For Products Between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. And SunGen dated July 6, 2017, incorporated by
reference to Exhibit 10.57 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2017 and filed with the SEC on August
9, 2017. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.41 |
|
First
Amendment to Master Development And License Agreement For Products Between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and SunGen Pharma, LLC, incorporated
by reference to Exhibit 10.59 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2017 and filed with the SEC on August
9, 2017. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.42 |
|
Second
Amendment to Master Development And License Agreement For Products Between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and SunGen Pharma, LLC, incorporated
by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2017 and filed with the SEC on August
9, 2017. (Confidential Treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.43 |
|
May
22, 2018 License, Manufacturing and Supply Agreement with Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. USA, incorporated by reference to Exhibit
10.60 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018 and filed with the SEC on June 14, 2018. (Confidential
treatment granted with respect to portions of the Agreement). |
| 10.44 |
|
August 1, 2018 Amendment to the Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. USA License, Supply and Distribution Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.44 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended December 31, 2019 and filed with the SEC on February 10, 2020. (Portions of this Agreement have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10)).of this Agreement have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10)). |
| 10.45 |
|
Development Agreement effective December 3, 2018 by and between Mikah Pharma LLC and Elite Laboratories, Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.51 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended March 31, 2019 and filed with the SEC on June 21, 2019 (portions of this Agreement have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10)). |
| 10.46 |
|
Asset Purchase Agreement dated November 13, 2019 by and between the Company and Nostrum Laboratories Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended December 31, 2019 and filed with the SEC on February 10, 2020. |
| 10.47 |
|
January 2, 2020 Amendment to the Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. USA License, Supply and Distribution Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.50 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended December 31, 2019 and filed with the SEC on February 10, 2020. (Portions of this Agreement have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10)). |
| 10.48 |
|
Asset Purchase Agreement executed January 16, 2020 by and between the Company and Nostrum Laboratories Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended December 31, 2019 and filed with the SEC on February 10, 2020. |
| 10.49 |
|
Employment Agreement with Douglas Plassche, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.52 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed with the SEC on June 14, 2021. |
| 10.50 |
|
Master Development and License Agreement for Products Between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Mikah Pharma LLC, effective as of June 10, 2021.(Portions of this Agreement have been redacted in compliance with Regulation S-K Item 601(b)(10), incorporated by reference to the 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2021 and filed with the SEC on August 16, 2021. |
| 10.51 |
|
License and Distribution Agreement by and between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Dexcel Ltd. (Or Akiva, Israel), dated December 6, 2021, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.57 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended March 31, 2022, filed with the SEC on June 29, 2022. |
| 10.52 |
|
February 18, 2022 Retention Agreement with Douglas Plassche, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended March 31, 2022, filed with the SEC on June 29, 2022. |
| 10.53 |
|
Agreement for Sale and Purchase of Real Estate, dated April 8, 2022, by and between Clyde Wesp and Margaret Wesp as trustees of the Wesp Family Joint Living Trust UTD November 19, 2015 and the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended June 30, 2022 and filed with the SEC on August 15, 2022. |
| 10.54 |
|
Loan and Security Agreement, dated April 1, 2022, by and among East West Bank, Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Elite Laboratories, Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, for the period ended June 30, 2022 and filed with the SEC on August 15, 2022. |
| 10.55 |
|
Employment Agreement, dated September 5, 2022, between Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Kirko Kirkov, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 7, 2022. |
| 21 |
|
Subsidiaries
of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 21 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended March 31, 2019 and
filed with the SEC on June 21, 2019. |
| 23.1 |
|
Consent of Buchbinder Tunick & Company LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm* |
| 31.1 |
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a)* |
| 32.1 |
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.** |
| |
|
|
| 101.INS* |
|
Inline
XBRL Instance Document |
| |
|
|
| 101.SCH* |
|
Inline
XBRL Taxonomy Schema Document |
| |
|
|
| 101.CAL* |
|
Inline
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| |
|
|
| 101.DEF* |
|
Inline
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| |
|
|
| 101.LAB* |
|
Inline
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| |
|
|
| 101.PRE* |
|
Inline
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| |
|
|
| 104 |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within the
Inline XBRL document) |
| *
|
Filed
herewith. |
| |
|
| **
|
Furnished
herewith. |
ITEM
16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant
to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed
on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. |
| |
|
|
| |
By:
|
/s/
Nasrat Hakim |
| |
|
Nasrat
Hakim |
| |
|
Chief
Executive Officer |
| |
|
|
| |
Dated:
June 29, 2023 |
Pursuant
to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant
and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
| |
|
|
|
|
| /s/
Nasrat Hakim |
|
Chief
Executive Officer, President and Chairman of the |
|
June
29, 2023 |
| |
|
Board of Directors (Principal
Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer, and Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| /s/ Barry Dash |
|
Director |
|
June 29, 2023 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| /s/
Jeffrey Whitnell |
|
Director |
|
June
29, 2023 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| /s/
Davis Caskey |
|
Director |
|
June
29, 2023 |
ELITE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED MARCH 31, 2023 AND 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING
FIRM
To
the Board of Directors and
Stockholders
of Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Subsidiary
Opinion
on the Financial Statements
We
have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Subsidiary (the “Company”) as
of March 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each
of the years in the two year period ended March 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated
financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated
financial position of the Company as of March 31, 2023 and 2022 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the
years in the two year period ended March 31, 2023 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of
America.
Basis
for Opinion
These
consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion
on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public
Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance
with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We
conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company
is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits,
we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion
on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our
audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error
or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding
the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used
and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements.
We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical
Audit Matter
The
critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated
or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial
statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter
does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit
matter below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Intangible
Assets — Refer to Notes 1 and 4 to the consolidated financial statements
Critical
Audit Matter Description
As
described in Note 1 and 4 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has capitalized costs of $6,052,189 for ANDAs and $289,039
for patents. The Company evaluates its intangible assets for impairment annually during the fourth quarter in accordance with ASC Topic
350, Intangibles, Goodwill and Other, and whenever events or circumstances change that indicate impairment may have occurred.
Management
performs a qualitative assessment of each intangible asset prior to performing a quantitative impairment test. Qualitative factors management
considers include, the current revenue, cost factors of raw material and labor, current cash flows, legal and regulatory factors and
industry and market considerations. If the qualitative assessment indicates the fair value is more likely than not less than the carrying
value a quantitative test is performed. Management performed a quantitative test on certain intangible assets using a discounted cash
flow methodology. The methods used to estimate the fair value of intangible assets involve significant assumptions. The significant assumptions
applied by management in estimating the fair value of intangible assets included income projections and discount rates. Due to the significant
estimates and assumptions management is required to make, we identified the fair value of intangible assets as a critical audit matter.
Performing audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of these estimates and assumptions required a high degree of auditor judgment
and an increased extent of effort.
How
We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit
The
primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter included:
We
obtained an understanding and evaluated the design and implementation of controls over the intangible valuation process. This included
management’s review over the assessment of the methodology, significant inputs and assumptions included in the fair value estimate,
as well as management’s review around the completeness, accuracy and reasonableness of the data used in this estimate.
Our
audit procedures assessed whether the valuation methodology used was appropriate and tested the mathematical accuracy of the valuation
model.
We
evaluated whether the assumptions used were reasonable by considering the historical revenue, current customer contracts, gross profit
percentage and cost of debt discount rates, and whether such assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the
audit.
| /s/
Buchbinder Tunick & Company LLP |
|
| |
|
| Buchbinder Tunick & Company LLP |
|
| |
|
| We
have served as the Company’s auditor since 2010. |
|
| |
|
| Little
Falls, New Jersey 07424 |
|
| |
|
| June
29, 2023 |
|
| |
|
| PCAOB
ID: 6189 |
|
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED
BALANCE SHEETS
(AUDITED)
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| ASSETS | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash | |
$ | 7,832,247 | | |
$ | 8,535,357 | |
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $-0-, respectively | |
| 3,094,549 | | |
| 3,057,913 | |
| Inventory | |
| 9,550,716 | | |
| 6,741,170 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| 1,032,785 | | |
| 526,949 | |
| Total current assets | |
| 21,510,297 | | |
| 18,861,389 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $14,586,335 and $13,348,565, respectively | |
| 10,426,158 | | |
| 5,952,992 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Intangible assets | |
| 6,341,228 | | |
| 6,634,035 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating lease - right-of-use asset | |
| 13,062 | | |
| 1,031,884 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred income tax benefit | |
| 2,171,821 | | |
| 2,171,821 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Other assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Restricted cash - debt service for NJEDA bonds | |
| 412,434 | | |
| 405,039 | |
| Security deposits | |
| 21,018 | | |
| 91,738 | |
| Total other assets | |
| 433,452 | | |
| 496,777 | |
| Total assets | |
$ | 40,896,018 | | |
$ | 35,148,898 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current liabilities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Accounts payable | |
$ | 2,446,810 | | |
$ | 1,430,985 | |
| Accrued expenses | |
| 5,047,726 | | |
| 4,693,142 | |
| Deferred revenue, current portion | |
| 13,333 | | |
| 13,333 | |
| Bonds payable, current portion, net of bond issuance costs | |
| 110,822 | | |
| 100,822 | |
| Loans payable, current portion | |
| 200,032 | | |
| 253,006 | |
| Lease obligation - operating lease, current portion | |
| 14,914 | | |
| 202,953 | |
| Total current liabilities | |
| 7,833,637 | | |
| 6,694,241 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long-term liabilities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred revenue, net of current portion | |
| 18,890 | | |
| 32,226 | |
| Bonds payable, net of current portion and bond issuance costs | |
| 1,029,018 | | |
| 1,139,848 | |
| Loans payable, net of current portion | |
| 2,532,502 | | |
| 249,046 | |
| Lease obligation - operating lease, net of current portion | |
| — | | |
| 835,893 | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| 521,711 | | |
| 936,837 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | |
| — | | |
| 38,780 | |
| Total long-term liabilities | |
| 4,102,121 | | |
| 3,232,630 | |
| Total liabilities | |
| 11,935,758 | | |
| 9,926,871 | |
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ELITE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(AUDITED)
(continued)
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Shareholders’ equity: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common stock; par value $0.001; 1,445,000,000 shares authorized; 1,014,015,081 shares issued and 1,013,915,081 shares outstanding as of March 31, 2023; 1,011,381,988 shares issued and 1,011,281,988 shares outstanding as of March 31, 2022 | |
| 1,014,019 | | |
| 1,011,385 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | |
| 164,750,980 | | |
| 164,577,227 | |
| Treasury stock; 100,000 shares as of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022; at cost | |
| (306,841 | ) | |
| (306,841 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | |
| (136,497,898 | ) | |
| (140,059,744 | ) |
| Total shareholders’ equity | |
| 28,960,260 | | |
| 25,222,027 | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | |
$ | 40,896,018 | | |
$ | 35,148,898 | |
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(AUDITED)
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Revenue: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | |
| Total revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | |
| Cost of manufacturing | |
| 17,561,093 | | |
| 17,466,763 | |
| Gross profit | |
| 16,594,021 | | |
| 14,795,354 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating expenses: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Research and development | |
| 6,200,163 | | |
| 4,051,349 | |
| General and administrative | |
| 5,122,272 | | |
| 4,464,003 | |
| Non-cash compensation through issuance of stock options | |
| 39,325 | | |
| 14,353 | |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| 292,807 | | |
| — | |
| Depreciation and amortization | |
| 1,263,452 | | |
| 1,194,939 | |
| Total operating expenses | |
| 12,918,019 | | |
| 9,724,644 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income from operations | |
| 3,676,002 | | |
| 5,070,710 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Other income, net: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments | |
| 415,126 | | |
| 1,425,409 | |
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs | |
| (1,112,707 | ) | |
| (191,816 | ) |
| Gain on sale of ANDA | |
| 1,000,000 | | |
| — | |
| Interest income | |
| 7,453 | | |
| 126 | |
| Other income, net | |
| 309,872 | | |
| 1,233,719 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | |
| (424,028 | ) | |
| 1,736,437 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net benefit for sale of state net operating losses and credits | |
| — | | |
| 857,379 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic net income per share attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Diluted net income per share attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic weighted average Common Stock outstanding | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Diluted weighted average Common Stock outstanding | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
(AUDITED)
| | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Capital | | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Deficit | | |
Equity | |
| | |
Series J Preferred Stock | | |
Common Stock | | |
Additional
Paid-In | | |
Treasury Stock | | |
Accumulated | | |
Total Shareholders’ | |
| | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Capital | | |
Shares | | |
Amount | | |
Deficit | | |
Equity | |
| Balance as of March 31, 2021 | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 1,009,276,752 | | |
$ | 1,009,279 | | |
$ | 164,407,480 | | |
| 100,000 | | |
$ | (306,841 | ) | |
$ | (148,957,989 | ) | |
$ | 16,151,929 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 8,898,245 | | |
| 8,898,245 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 14,353 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 14,353 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Shares issued in payment of salaries | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 2,105,236 | | |
| 2,106 | | |
| 155,394 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 157,500 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Balance as of March 31, 2022 | |
| — | | |
$ | — | | |
| 1,011,381,988 | | |
$ | 1,011,385 | | |
$ | 164,577,227 | | |
| 100,000 | | |
$ | (306,841 | ) | |
$ | (140,059,744 | ) | |
$ | 25,222,027 | |
| Beginning balance | |
| — | | |
$ | — | | |
| 1,011,381,988 | | |
$ | 1,011,385 | | |
$ | 164,577,227 | | |
| 100,000 | | |
$ | (306,841 | ) | |
$ | (140,059,744 | ) | |
$ | 25,222,027 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 3,561,846 | | |
| 3,561,846 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 39,325 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 39,325 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Shares issued in payment of salaries | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 1,378,608 | | |
| 1,379 | | |
| 58,621 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 60,000 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Shares issued in payment of consultants | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 1,254,485 | | |
| 1,255 | | |
| 75,807 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 77,062 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | |
| — | | |
$ | — | | |
| 1,014,015,081 | | |
$ | 1,014,019 | | |
$ | 164,750,980 | | |
| 100,000 | | |
$ | (306,841 | ) | |
$ | (136,497,898 | ) | |
$ | 28,960,260 | |
| Ending balance | |
| — | | |
$ | — | | |
| 1,014,015,081 | | |
$ | 1,014,019 | | |
$ | 164,750,980 | | |
| 100,000 | | |
$ | (306,841 | ) | |
$ | (136,497,898 | ) | |
$ | 28,960,260 | |
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(AUDITED)
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Depreciation and amortization | |
| 1,277,622 | | |
| 1,209,119 | |
| Amortization of operating leases - right-of-use assets | |
| 67,061 | | |
| 225,590 | |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| 292,807 | | |
| — | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (415,126 | ) | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred income tax benefit | |
| — | | |
| (2,171,821 | ) |
| Non-cash compensation accrued | |
| 540,000 | | |
| 767,122 | |
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options | |
| 39,325 | | |
| 14,353 | |
| Non-cash rent expense and lease accretion | |
| 803 | | |
| 1,152 | |
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Accounts receivable | |
| (36,636 | ) | |
| 438,463 | |
| Inventory | |
| (2,809,546 | ) | |
| (1,728,268 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| (435,116 | ) | |
| 209,796 | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities | |
| 1,336,566 | | |
| 314,214 | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | |
| (13,336 | ) | |
| (13,332 | ) |
| Lease obligations - operating leases | |
| (67,566 | ) | |
| (230,910 | ) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | |
| 3,338,704 | | |
| 6,508,314 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | |
| (5,736,618 | ) | |
| (498,566 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | |
| (5,736,618 | ) | |
| (498,566 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Payment of bond principal | |
| (115,000 | ) | |
| (110,000 | ) |
| Payments of loans and mortgage payable | |
| (12,240,111 | ) | |
| — | |
| Proceeds from loans and mortgage payable, net of transaction costs | |
| 14,438,985 | | |
| — | |
| Other loan payments | |
| (381,675 | ) | |
| (557,133 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | |
| 1,702,199 | | |
| (667,133 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net change in cash and restricted cash | |
| (695,715 | ) | |
| 5,342,615 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash and restricted cash, beginning of period | |
| 8,940,396 | | |
| 3,597,781 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash and restricted cash, end of period | |
$ | 8,244,681 | | |
$ | 8,940,396 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash and non-cash transactions: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash paid for interest | |
$ | 1,098,537 | | |
$ | 177,636 | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | |
$ | 424,028 | | |
$ | — | |
| Financing of equipment purchases and insurance renewal | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 244,124 | |
| Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting expenses | |
$ | 137,062 | | |
$ | 157,500 | |
| Supplemental non-cash amounts of lease liabilities arising from obtaining right of use assets | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 1,042,800 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Reconciliation of cash and restricted cash | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash | |
$ | 7,832,247 | | |
$ | 8,535,357 | |
| Restricted cash - debt service for NJEDA bonds | |
| 412,434 | | |
| 405,039 | |
| Total cash and restricted cash shown in statement of cash flows | |
$ | 8,244,681 | | |
$ | 8,940,396 | |
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Overview
Elite
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the “Company” or “Elite”) was incorporated on October 1, 1997 under the laws of the State
of Delaware, and its wholly-owned subsidiary Elite Laboratories, Inc. (“Elite Labs”) was incorporated on August 23, 1990
under the laws of the State of Delaware. On January 5, 2012, Elite Pharmaceuticals was reincorporated under the laws of the State of
Nevada. Elite Labs engages primarily in researching, developing, licensing, manufacturing, and sales of generic, oral dose pharmaceuticals. The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties and itself, if and when the products
are approved. These products include drugs that cover therapeutic areas for allergy, bariatric, attention deficit and infection. Research
and development activities are performed with an objective of developing products that will secure marketing approvals from the United
States Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), and thereafter, commercially exploiting such products.
Principles
of Consolidation
The
accompanying audited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
in the United States (“GAAP”). The audited consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its
wholly-owned subsidiary, Elite Labs. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Segment
Information
Financial
Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification 280 (“ASC 280”), Segment Reporting,
establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise
about which separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making
group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance.
The
Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive Officer, who reviews the financial performance and the results
of operations of the segments prepared in accordance with GAAP when making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance
of the Company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are products whose marketing approvals were secured via an Abbreviated New Drug Applications
(“ANDA”) and products whose marketing approvals were secured via a New Drug Application (“NDA”). ANDA products
are referred to as generic pharmaceuticals and NDA products are referred to as branded pharmaceuticals.
There
are currently no intersegment revenues. Asset information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating decision
maker does not review this information by segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation
of the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements. Please see Note 15 for further details.
Revenue
Recognition
The
Company generates revenue from manufacturing and licensing fees and direct sales to pharmaceutical distributors for pharmacies and institutions. Manufacturing fees include the development of pain management
products, manufacturing of a line of generic pharmaceutical products with approved ANDA, through the manufacture of formulations and
the development of new products. Licensing fees include the commercialization of products either by license and the collection of royalties,
or the expansion of licensing agreements with other pharmaceutical companies, including co-development projects, joint ventures and other
collaborations.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Under
ASC 606, Revenue from Contacts with Customers (“ASC 606”), the Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains
control of promised goods or services, in an amount that reflects the consideration which is expected to be received in exchange for
those goods or services. The Company recognizes revenues following the five-step model prescribed under ASC 606: (i) identify contract(s)
with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligation(s) in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the
transaction price to the performance obligation(s) in the contract; and (v) recognize revenues when (or as) the Company satisfies a performance
obligation. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the entity will collect the consideration
it is entitled to in exchange for the goods or services it transfers to the customer. At contract inception, once the contract is determined
to be within the scope of ASC 606, the Company assesses the goods or services promised within each contract and determines those that
are performance obligations and assesses whether each promised good or service is distinct. The Company then recognizes as revenue the
amount of the transaction price that is allocated to the respective performance obligation when (or as) the performance obligation is
satisfied. Sales, value add, and other taxes collected on behalf of third parties are excluded from revenue.
Nature
of goods and services
The
following is a description of the Company’s goods and services from which the Company generates revenue, as well as the nature,
timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and significant payment terms for each, as applicable:
a)
Manufacturing Fees
The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties, if, and when, the products are
approved. These products include products using controlled-release drug technology. The Company also develops and markets (either on
its own or by license to other companies) generic and proprietary controlled-release pharmaceutical products.
The
Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains control of the Company’s product based on the contractual shipping terms of
the contract. The Company is primarily responsible for fulfilling the promise to provide the product, is responsible to ensure that the
product is produced in accordance with the related supply agreement and bears risk of loss while the inventory is in-transit to the commercial
partner. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring products to a
customer.
b)
License Fees
The
Company enters into licensing and development agreements, which may include multiple revenue generating activities, including milestones
payments, licensing fees, product sales and services. The Company analyzes each element of its licensing and development agreements in
accordance with ASC 606 to determine appropriate revenue recognition. The terms of the license agreement may include payment to the Company
of licensing fees, non-refundable upfront license fees, milestone payments if specified objectives are achieved, and/or royalties on
product sales.
If
the contract contains a single performance obligation, the entire transaction price is allocated to the single performance obligation.
Contracts that contain multiple performance obligations require an allocation of the transaction price based on the estimated relative
standalone selling prices of the promised products or services underlying each performance obligation. The Company determines standalone
selling prices based on the price at which the performance obligation is sold separately. If the standalone selling price is not observable
through past transactions, the Company estimates the standalone selling price taking into account available information such as market
conditions and internally approved pricing guidelines related to the performance obligations.
The
Company recognizes revenue from non-refundable upfront payments at a point in time, typically upon fulfilling the delivery of the associated
intellectual property to the customer. For those milestone payments which are contingent on the occurrence of particular future events
(for example, payments due upon a product receiving FDA approval), the Company determined that these need to be considered for inclusion
in the calculation of total consideration from the contract as a component of variable consideration using the most-likely amount method.
As such, the Company assesses each milestone to determine the probability and substance behind achieving each milestone. Given the inherent
uncertainty of the occurrence of future events, the Company will recognize revenue from the milestone when there is not a high probability
of a reversal of revenue, which typically occurs near or upon achievement of the event.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Significant
management judgment is required to determine the level of effort required under an arrangement and the period over which the Company
expects to complete its performance obligations under the arrangement. If the Company cannot reasonably estimate when its performance
obligations either are completed or become inconsequential, then revenue recognition is deferred until the Company can reasonably make
such estimates. Revenue is then recognized over the remaining estimated period of performance using the cumulative catch-up method.
When
determining the transaction price of a contract, an adjustment is made if payment from a customer occurs either significantly before
or significantly after performance, resulting in a significant financing component. Applying the practical expedient in ASC 606-10-32-18,
the Company does not assess whether a significant financing component exists if the period between when the Company performs its obligations
under the contract and when the customer pays is one year or less. None of the Company’s contracts contained a significant financing
component as of March 31, 2023.
In
accordance with ASC 606-10-55-65, royalties are recognized when the subsequent sale of the customer’s products occurs.
c)
Direct Sales
The
Company will begin direct sales of products under the Company’s own label beginning on April 1, 2023. License agreements will remain
in place for select products. With this transition, however, a large portion of the manufacturing and license fees now reported will
be replaced with revenues from direct sales of pharmaceutical products to distributors for pharmacies and institutions.
Disaggregation
of revenue
In
the following table, revenue is disaggregated by type of revenue generated by the Company. The table also includes a reconciliation of
the disaggregated revenue with the reportable segments:
SCHEDULE
OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| NDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Licensing fees | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
| Total NDA revenue | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| ANDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | |
| Total ANDA revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | |
| Total revenue | |
$ | 34,155,114 | | |
$ | 32,262,117 | |
Selected
information on reportable segments and reconciliation of operating income by segment to income (loss) from operations before income taxes
are disclosed within Note 15.
Cash
The
Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash
equivalents consist of cash on deposit with banks and money market instruments. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents with
high-quality, U.S. financial institutions and, to date has not experienced losses on any of its balances.
Restricted
Cash
As
of March 31, 2023, and March 31, 2022, the Company had $412,434 and $405,039, of restricted cash, respectively, related to debt service
reserve in regard to the New Jersey Economic Development Authority (“NJEDA”) bonds (see Note 5).
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Accounts
Receivable
Accounts
receivable are comprised of balances due from customers, net of estimated allowances for uncollectible accounts. In determining collectability,
historical trends are evaluated, and specific customer issues are reviewed on a periodic basis to arrive at appropriate allowances.
Inventory
Inventory
is recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value on specific identification by lot number basis.
Long-Lived
Assets
The
Company periodically evaluates the fair value of long-lived assets, which include property and equipment and intangibles, whenever events
or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
Property
and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is provided on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the respective
assets which range from three to forty years. Major repairs or improvements are capitalized. Minor replacements and maintenance and repairs
which do not improve or extend asset lives are expensed currently.
Upon
retirement or other disposition of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and the resulting
gain or loss, if any, is recognized in income.
Intangible
Assets
The
Company capitalizes certain costs to acquire intangible assets; if such assets are determined to have a finite useful life they are amortized
on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life. Costs to acquire indefinite lived intangible assets, such as costs related to
ANDAs and patents are capitalized accordingly.
The
Company tests its intangible assets for impairment at least annually (as of March 31st) and whenever events or circumstances change that
indicate impairment may have occurred. A significant amount of judgment is involved in determining if an indicator of impairment has
occurred. Such indicators may include, among others and without limitation: a significant decline in the Company’s expected future
cash flows; a sustained, significant decline in the Company’s stock price and market capitalization; a significant adverse change
in legal factors or in the business climate of the Company’s segments; unanticipated competition; and slower growth rates.
For
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company determined indicators of impairment have occurred and recorded impairment expense of $292,807 on its ANDAs and patents.
Please
also see Note 4 for further details on intangible assets.
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenditures are charged to expense as incurred.
Contingencies
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s condensed
consolidated financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series
of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Income
Taxes
Income
taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which
those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Where applicable, the Company records a valuation allowance to reduce
any deferred tax assets that it determines will not be realizable in the future.
The
Company recognizes the benefit of an uncertain tax position that it has taken or expects to take on income tax returns it files if such
tax position is more likely than not to be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position.
These tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate resolution.
The
Company operates in multiple tax jurisdictions within the United States of America. The Company remains subject to examination in
all tax jurisdiction until the applicable statutes of limitation expire. As of March 31, 2023, a summary of the tax years that
remain subject to examination in our major tax jurisdictions are: United States – Federal, 2019 and forward, and State, 2016
and forward. The Company did not record unrecognized tax positions for the years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Warrants
and Preferred Shares
The
accounting treatment of warrants and preferred share series issued is determined pursuant to the guidance provided by ASC 470, Debt,
ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, as applicable. Each feature of a
freestanding financial instrument including, without limitation, any rights relating to subsequent dilutive issuances, dividend issuances,
equity sales, rights offerings, forced conversions, optional redemptions, automatic monthly conversions, dividends and exercise is assessed
with determinations made regarding the proper classification in the Company’s financial statements.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation. Under the fair value
recognition provisions, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized
as an expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, based on the terms of the awards. The cost of the stock-based
payments to nonemployees that are fully vested and non-forfeitable as at the grant date is measured and recognized at that date, unless
there is a contractual term for services in which case such compensation would be amortized over the contractual term.
In
accordance with the Company’s Director compensation policy and certain employment contracts, director’s fees and a portion
of employee’s salaries are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s Common Stock (“Common Stock”),
in lieu of cash, with the valuation of such share being calculated on a quarterly basis and equal to the average closing price of the
Company’s Common Stock.
Sale
of ANDA
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company entered into an agreement with Pyros Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Pyros”) pursuant
to which the Company sold to Pyros its rights in and to the Company’s approved abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) for its
generic Sabril drug. The Company sold such rights to Pyros for $1,000,000, which was recorded as gain on sale of ANDA during the year
ended March 31, 2023. There is no further action required by the Company regarding the rights which would affect future periods.
In
conjunction with the sale of its Product to Pyros, the Company executed a Manufacturing and Supply agreement (the “Pyros Agreement”)
with Pyros. Under the terms of the Pyros Agreement, the Company will receive an agreed-upon price per drug for the manufacturing and
packaging of Sabril over a term of three years. Revenue per the Pyros Agreement will be recognized as control of the manufactured and
supplied drugs is transferred to Pyros (at the time of delivery).
Earnings
Per Share Attributable to Common Shareholders’
The
Company follows ASC 260, Earnings Per Share, which requires presentation of basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”)
on the face of the income statement for all entities with complex capital structures and requires a reconciliation of the numerator and
denominator of the basic EPS computation to the numerator and denominator of the diluted EPS computation. In the accompanying financial
statements, basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding
during the period. The computation of diluted net income per share does not include the conversion of securities that would have an antidilutive
effect.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
following is the computation of earnings per share applicable to common shareholders for the periods indicated:
SCHEDULE
OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Numerator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| Effect of dilutive instrument on net income | |
| (415,126 | ) | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Net income - diluted | |
$ | 3,146,720 | | |
$ | 7,472,836 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Denominator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - basic | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options and convertible securities | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - diluted | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income per share | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| Diluted | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
Fair
Value of Financial Instruments
ASC
820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”) provides a framework for measuring fair value in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles.
ASC
820 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between (1) market
participant assumptions developed based on market data obtained from independent sources (observable inputs) and (2) an entity’s
own assumptions about market participant assumptions developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (unobservable
inputs).
The
fair value hierarchy consists of three broad levels, which gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). The three levels of the fair value
hierarchy under ASC 820 are described as follows:
| ● | Level
1 – Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
that are accessible at the measurement date. |
| ● | Level
2 – Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for
the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs include quoted prices
for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar
assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that
are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived principally from or
corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
| ● | Level
3 – Inputs that are unobservable for the asset or liability. |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Measured
on a Recurring Basis
The
following table presents information about our liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, aggregated by the level in the
fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fell:
SCHEDULE
OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| | |
| | |
Fair Value Measurement Using | |
| | |
Amount at Fair Value | | |
Level 1 | | |
Level 2 | | |
Level 3 | |
| March 31, 2023 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 521,711 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 521,711 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| March 31, 2022 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 936,837 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 936,837 | |
See
Note 11 for specific inputs used in determining fair value.
The
carrying amounts of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities, such as cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses and other
current assets, accounts payable and accrued expenses, approximate their fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
Based upon current borrowing rates with similar maturities the carrying value of long-term debt approximates fair value.
Non-Financial
Assets that are Measured at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
Non-financial
assets such as intangible assets, and property and equipment are measured at fair value only when an impairment loss is recognized. The
Company did not record an impairment charge related to these assets in the periods presented.
Treasury
Stock
The
Company records treasury stock at the cost to acquire it and includes treasury stock as a component of shareholders’ equity.
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In
June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial
Instruments. This update requires immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses (“CECL”).
Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that
are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022
for public entities qualifying as smaller reporting companies. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact
of this update on the consolidated financial statements and does not expect a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Management
has evaluated other recently issued accounting pronouncements and does not believe that any of these pronouncements will have a significant
impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
NOTE
2. INVENTORY
Inventory
consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF INVENTORY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Finished goods | |
$ | 2,352,330 | | |
$ | 159,808 | |
| Work-in-progress | |
| 1,791,311 | | |
| 1,203,204 | |
| Raw materials | |
| 5,407,075 | | |
| 5,378,158 | |
| Inventory, net | |
$ | 9,550,716 | | |
$ | 6,741,170 | |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property
and equipment consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Land, building and improvements | |
$ | 10,768,181 | | |
$ | 5,456,524 | |
| Laboratory, manufacturing, warehouse and transportation equipment | |
| 13,364,512 | | |
| 13,017,731 | |
| Office equipment and software | |
| 395,563 | | |
| 373,601 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | |
| 484,237 | | |
| 453,701 | |
| Property and equipment, gross | |
| 25,012,493 | | |
| 19,301,557 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | |
| (14,586,335 | ) | |
| (13,348,565 | ) |
| Property and equipment, net | |
$ | 10,426,158 | | |
$ | 5,952,992 | |
Depreciation
expense was $1,237,770 and $1,194,939 for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
NOTE
4. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The
following table summarizes the Company’s intangible assets:
SCHEDULE
OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS
| | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Impairment | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (176,645 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 289,039 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| (116,162 | ) | |
| — | | |
| 6,052,189 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (292,807 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,341,228 | |
| | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Reductions | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | * |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 465,684 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 6,168,351 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
5. ACCRUED EXPENSES
As
of March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s accrued expenses consisted of the following:
SUMMARY
OF ACCRUED EXPENSES
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Salaries and fees payable in common stock | |
$ | 4,125,000 | | |
$ | 3,625,000 | |
| Income tax | |
| 414,989 | | |
| 414,989 | |
| Consultant contract fees | |
| 193,333 | | |
| 153,333 | |
| Audit fees | |
| 125,000 | | |
| 140,000 | |
| Director dues | |
| 70,000 | | |
| 90,000 | |
| Employee bonuses | |
| — | | |
| 143,000 | |
| Other accrued expenses | |
| 119,404 | | |
| 126,820 | |
| Total accrued expenses | |
$ | 5,047,726 | | |
$ | 4,693,142 | |
NOTE
6. NJEDA BONDS
During
August 2005, the Company refinanced a bond issue occurring in 1999 through the issuance of Series A and B Notes tax-exempt bonds (the
“NJEDA Bonds” and/or “Bonds”). During July 2014, the Company retired all outstanding Series B Notes, at par,
along with all accrued interest due and owed.
In
relation to the Series A Notes, the Company is required to maintain a debt service reserve. The debt service reserve is classified as
restricted cash on the accompanying audited consolidated balance sheets. The NJEDA Bonds require the Company to make an annual principal
payment on September 1st based on the amount specified in the loan documents and semi-annual interest payments on March 1st and September
1st, equal to interest due on the outstanding principal. The annual interest rate on the Series A Note is 6.5%. The NJEDA Bonds are collateralized
by a first lien on the Company’s facility and equipment acquired with the proceeds of the original and refinanced bonds.
The
following tables summarize the Company’s bonds payable liability:
SCHEDULE
OF BONDS PAYABLE LIABILITY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Gross bonds payable | |
| | | |
| | |
| NJEDA Bonds - Series A Notes | |
$ | 1,245,000 | | |
$ | 1,360,000 | |
| Less: Current portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
| (125,000 | ) | |
| (115,000 | ) |
| Long-term portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
$ | 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Bond offering costs | |
$ | 354,454 | | |
$ | 354,454 | |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | |
| (249,294 | ) | |
| (235,124 | ) |
| Bond offering costs, net | |
$ | 105,160 | | |
$ | 119,330 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portions of bonds payable | |
$ | 125,000 | | |
$ | 115,000 | |
| Less: Bonds offering costs to be amortized in the next 12 months | |
| (14,178 | ) | |
| (14,178 | ) |
| Current portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 110,822 | | |
$ | 100,822 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable | |
| 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| Less: Bond offering costs to be amortized subsequent to the next 12 months | |
| (90,982 | ) | |
| (105,152 | ) |
| Long term portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 1,029,018 | | |
$ | 1,139,848 | |
Amortization
expense was $14,178
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022,
respectively. As of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022, interest payable was $6,744 and $7,367,
respectively. Interest expense was $6,744 and $7,367 for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Maturities
of bonds for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF MATURITIES OF BONDS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 125,000 | |
| 2025 | |
| 130,000 | |
| 2026 | |
| 140,000 | |
| 2027 | |
| 150,000 | |
| Thereafter | |
| 700,000 | |
| Total | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
NOTE
7. LOANS PAYABLE
On
April 2, 2022, the Company and Elite Labs entered into a Loan and Security Agreement (the “EWB Loan Agreement”) with East
West Bank (“EWB”). Pursuant to the EWB Loan Agreement, the Company and Elite Labs received one term loan for a principal
amount of $12,000,000 (the “EWB Term Loan”) and a revolving line of credit up to $2,000,000 (the “EWB Revolver,”
together with the “EWB Term Loan,” the EWB Loans”), each of which shall be used for working capital. The EWB Term Loan
bears interest at a rate of 9.73% (1.73% plus the prime rate (“Prime”)) and is repayable over five years, maturing on May
1, 2027. The EWB Revolver bears interest at a rate of (8.87% (0.87% plus Prime)) and matures on May 1, 2027. The total transaction costs
associated with the EWB Term Loan incurred as of March 31, 2023, were $40,120, which are being amortized on a monthly basis over five years,
beginning in April 2022. The EWB Loans are secured by a security interest in the personal property of the Company and Elite Labs. The
EWB Loan Agreement contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants include, but are not limited to, maintaining
maximum leverage ratios of 3.50 to 1.00, minimum liquidity of $5,000,000, minimum cash of $1,000,000, a fixed charge coverage ratio of
1.25 to 1.00 and restrictions on mergers or sales of assets and debt borrowings. As of March 31, 2023, the principal and interest
on the EWB Term Loan has been paid in full by the Company and the EWB Loan Agreement is terminated.
In place of the EWB Term Loan, the Company has entered into a collateralized promissory note with individual lenders
with rates comparable to the EWB Term Loan but with less restrictive covenants (a “Promissory Note”). As of June 2, 2023,
a Promissory Note was placed with Nasrat Hakim, CEO and Chairman of the Board of Directors, for $3,000,000. The Promissory Note has an
interest rate of 9% for the first year and 10% for an optional second year and the proceeds will be used for working capital and other
business purposes.
On
July 1, 2022, the EWB provided a mortgage loan (“EWB Mortgage Loan”) in the amount of $2.55 million for the purchase of the
property at 135-137 Ludlow Avenue, which was formerly a lease held by the Company. The EWB Mortgage Loan matures in 10 years and bears
interest at a rate of 4.75% fixed for 5 years then adjustable at WSJP plus 0.5% with floor rate of 4.5%. The total transaction costs
associated with the EWB Mortgage Loan incurred as of March 31, 2023, were $13,251, which are being amortized on a monthly basis over
ten years, beginning in July 2022. The EWB Mortgage Loan contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants
include maintaining a minimum debt coverage ratio of 1.50 to 1.00 tested annually and a minimum trailing 12-month debt coverage ratio
of 1.50 to 1.00. As of March 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with each financial covenant.
Loans
payable consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF LOANS PAYABLE
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Mortgage loan payable 4.75% interest and maturing June 2032 | |
$ | 2,472,923 | | |
$ | — | |
| Equipment and insurance financing loans payable, between 7.10% and 12.02% interest and maturing between September 2023 and October 2025 | |
| 259,611 | | |
| 502,052 | |
| Less: Current portion of loans payable | |
| (200,032 | ) | |
| (253,006 | ) |
| Long-term portion of loans payable | |
$ | 2,532,502 | | |
$ | 249,046 | |
The
interest expense associated with the loans and mortgage payable was $1,013,874
and $62,845
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Loan
and mortgage principal payments for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF LOAN PRINCIPAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 200,032 | |
| 2025 | |
| 182,181 | |
| 2026 | |
| 115,330 | |
| 2027 | |
| 86,064 | |
| 2028 and thereafter | |
| 2,148,927 | |
| Total | |
$ | 2,732,534 | |
NOTE
8. DEFERRED REVENUE
Deferred
revenues in the aggregate amount of $32,223 as of March 31, 2023, were comprised of a current component of $13,333 and a long-term component
of $18,890. Deferred revenues in the aggregate amount of $45,559 as of March 31, 2022, were comprised of a current component of $13,333
and a long-term component of $32,226. These line items represent the unamortized amounts of a $200,000 advance payment received for a
TAGI Pharma (“TAGI”) licensing agreement with a fifteen-year term beginning in September 2010 and ending in August 2025.
These advance payments were recorded as deferred revenue when received and are earned, on a straight-line basis over the life of the
licenses. The current component is equal to the amount of revenue to be earned during the 12-month period immediately subsequent to the
balance sheet date and the long-term component is equal to the amount of revenue to be earned thereafter.
NOTE
9. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s condensed
consolidated financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series
of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
Operating
Leases
The
Company entered into an operating lease for a portion of a one-story warehouse, located at 135 Ludlow Avenue, Northvale, New Jersey (the
“135 Ludlow Ave. lease”). The 135 Ludlow Ave. lease is for approximately 15,000 square feet of floor space and began on July
1, 2010. During July 2014, the Company modified the 135 Ludlow Ave. lease in which the Company was permitted to occupy the entire 35,000
square feet of floor space in the building (“135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease”).
The
135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease includes an initial term, which expired on December 31, 2016 with two tenant renewal options of five years
each, at the sole discretion of the Company. On June 22, 2016, the Company exercised the first of these renewal options, with such option
including a term that begins on January 1, 2017 and expires on December 31, 2021. On June 30, 2021, the Company exercised the second
of the renewal options, with such option including a term that begins on January 1, 2022 and expires on December 31, 2026.
The
135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease property required significant leasehold improvements and qualifications, as a prerequisite, for its intended
future use. Manufacturing, packaging, warehousing and regulatory activities are currently conducted at this location. The Ludlow Ave.
lease was terminated on July 1, 2022, when the Company purchased the underlying property.
In
October 2020, the Company entered into an operating lease for office space in Pompano Beach, Florida (the “Pompano Office Lease”).
The Pompano Office Lease is for approximately 1,275 square feet of office space, with Elite taking occupancy on November 1, 2020. The
Pompano Office includes a 3 month abatement from November 2020 through February 2021 and has a term of three years, ending on October
31, 2023.
The
Company assesses whether an arrangement is a lease or contains a lease at inception. For arrangements considered leases or that contain
a lease that is accounted for separately, the Company determines the classification and initial measurement of the right-of-use asset
and lease liability at the lease commencement date, which is the date that the underlying asset becomes available for use. The Company
has elected to account for non-lease components associated with its leases and lease components as a single lease component.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
Company recognizes a right-of-use asset, which represents the Company’s right to use the underlying asset for the lease term, and
a lease liability, which represents the present value of the Company’s obligation to make payments arising over the lease term.
The present value of the lease payments is calculated using either the implicit interest rate in the lease or an incremental borrowing
rate.
Lease
assets and liabilities are classified as follows on the condensed consolidated balance sheet:
SCHEDULE
OF LEASE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| Lease | |
Classification | | |
As of March 31, 2023 | |
| Assets | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Operating lease – right-of-use asset | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| Total leased assets | |
| | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long-term | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease, net of current portion | | |
| — | |
| Total lease liabilities | |
| | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
Rent
expense is recorded on the straight-line basis. Rent expense under the 135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease for the years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022 was $58,248 and $229,563, respectively. Rent expense under the Pompano Office Lease for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022
was $25,638 and $23,430, respectively. Rent expense is recorded in general and administrative expense in the audited consolidated statements
of operations.
The
table below shows the future minimum rental payments, exclusive of taxes, insurance and other costs, under the Pompano Office Lease:
SCHEDULE
OF FUTURE MINIMUM RENTAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 15,214 | |
| 2025 | |
| — | |
| 2026 | |
| — | |
| 2027 | |
| — | |
| Thereafter | |
| — | |
| Total future minimum lease payments | |
| 15,214 | |
| Less: interest | |
| (300 | ) |
| Present value of lease payments | |
$ | 14,914 | |
The
weighted-average remaining lease term and the weighted-average discount rate of our lease was as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF WEIGHTED-AVERAGE REMAINING LEASE TERM AND THE WEIGHTED-AVERAGE DISCOUNT RATE
| Lease Term and Discount Rate | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| Remaining lease term (years) | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 0.6 | |
| | |
| | |
| Discount rate | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 6 | % |
The
Company has an obligation for the restoration of its leased facility and the removal or dismantlement of certain property and equipment
as a result of its business operation in accordance with ASC 410, Asset Retirement and Environmental Obligations – Asset Retirement
Obligations. The Company records the fair value of the asset retirement obligation in the period in which it is incurred. The Company
increases, annually, the liability related to this obligation. The liability is accreted to its present value each period and the capitalized
cost is depreciated over the useful life of the related asset. Upon settlement of the liability, the Company records either a gain or
loss. As of March 31, 2023, and March 31, 2022, the Company had a liability of $0 and $38,780, respectively, recorded as a component
of other long-term liabilities.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
10. PREFERRED STOCK
Series
J convertible preferred stock
On
April 28, 2017, the Company created the Series J Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series J Preferred”) in conjunction with the
Certificate of Designations (“Series J COD”). A total of 50 shares of Series J Preferred were authorized, zero shares are
issued and outstanding, with a stated value of $1,000,000 per share and a par value of $0.01 as of March 31, 2023.
On
April 27, 2017, a total of 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred were issued pursuant to an exchange agreement (the “Exchange Agreement”)
with Hakim, a related party and the Company’s President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors. The Exchange
Agreement provided for Hakim to exchange 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock for 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred and warrants to
purchase 79,008,661 shares of Common Stock at $0.1521 per share. The aggregate stated value of the Series J Preferred issued was equal
to the aggregate value of the shares of Common Stock exchanged, with such value of each share of Common Stock exchanged being equal to
the closing price of the Common Stock on April 27, 2017. In connection with the Exchange Agreement, the Company also issued warrants
to purchase 79,008,661 shares of Common Stock at $0.1521 per share, and such warrants are classified as liabilities on the accompanying
audited consolidated balance sheet as of March 31, 2023 (See Note 11).
An
amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of shares of Common Stock the Company is authorized
to issue from 995,000,000 shares to 1,445,000,000 shares was approved at the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders held on December
4, 2019. Prior to the approval of the increase in the number of authorized shares, there were insufficient authorized shares if the Series
J Preferred Stock were converted. As a result, the shares were classified in mezzanine equity. After the approval of the increase in
the number of authorized shares, there are now sufficient authorized shares in the event of a full conversion of Series J Preferred Stock.
With the approval of the increase in the number of authorized shares, there is no longer the presumption that a cash settlement will
be required. Therefore, the Series J Preferred was reclassified from mezzanine equity to permanent equity at its carrying amount of $13,903,960
on the consolidated balance sheets as of March 31, 2023 and 2022.
On
June 23, 2020, the Company held a Special Meeting of Shareholders, with such including a proposal for shareholders to again vote on the
above referenced amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation. This proposal was also passed by shareholder vote.
On
August 24, 2020, Hakim converted the 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred into 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock at a conversion price
of $0.1521 per share.
NOTE
11. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS
The
Company evaluates and accounts for its freestanding instruments in accordance with ASC 815, Accounting for Derivative Instruments
and Hedging Activities.
The
Company issued warrants, with a term of ten years, to affiliates in connection with an exchange agreement dated April 28, 2017, as further
described in this note below.
The
Company has 79,008,661 total warrant shares outstanding with a weighted average exercise price of $0.1521 as of March 31, 2023 and 2022.
On
April 28, 2017, the Company entered into an Exchange Agreement with Hakim, the Chairman of the Board, President, and Chief Executive
Officer of the Company, pursuant to which the Company issued to Hakim 24.0344 shares of its Series J Preferred and warrants to purchase
an aggregate of 79,008,661 shares of its Common Stock (the “Series J Warrants” and, along with the Series J Preferred issued
to Hakim, the “Securities”) in exchange for 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock owned by Hakim. The fair value of the Series
J Warrants was determined to be $6,474,674 upon issuance at April 28, 2017.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
Series J Warrants are exercisable for a period of 10 years from the date of issuance, commencing April 28, 2020. The initial exercise
price is $0.1521 per share and the Series J Warrants can be exercised for cash or on a cashless basis. The exercise price is subject
to adjustment for any issuances or deemed issuances of Common Stock or Common Stock equivalents at an effective price below the then
exercise price. Such exercise price adjustment feature prohibits the Company from being able to conclude the warrants are indexed to
its own stock and thus such warrants are classified as liabilities and measured initially and subsequently at fair value. The Series
J Warrants also provide for other standard adjustments upon the happening of certain customary events.
The
fair value of the Series J Warrants was calculated using a Black-Scholes model instead of a Monte Carlo Simulation because the probability
with the shareholder approval provisions was no longer a factor. The following assumptions were used in the Black-Scholes model to calculate
the fair value of the Series J Warrants:
SCHEDULE
OF FAIR VALUE OF WARRANTS ISSUED
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Fair value of the Company’s Common Stock | |
$ | 0.0290 | | |
$ | 0.0350 | |
| Volatility | |
| 74.37 | % | |
| 76.55 | % |
| Initial exercise price | |
$ | 0.1521 | | |
$ | 0.1521 | |
| Warrant term (in years) | |
| 4.1 | | |
| 5.1 | |
| Risk free rate | |
| 3.55 | % | |
| 2.40 | % |
The
changes in warrants (Level 3 financial instruments) measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the year ended March 31, 2023 were
as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF CHANGES IN WARRANTS MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| Balance at March 31, 2021 | |
$ | 2,362,246 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2022 | |
$ | 936,837 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (415,126 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | |
$ | 521,711 | |
NOTE
12. SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Lincoln
Park Capital Transaction - July 8, 2020 Purchase Agreement
On
July 8, 2020, the Company entered into a purchase agreement (the “2020 LPC Purchase Agreement”), and a registration rights
agreement (the “2020 LPC Registration Rights Agreement”), with Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”),
pursuant to which Lincoln Park has committed to purchase up to $25.0 million of the Company’s Common Stock, $0.001 par value per
share, from time to time over the term of the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement, at the Company’s direction.
The
Company did not issue any shares of its Common Stock pursuant to the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement during the years ended March 31,
2023 and 2022. In addition, there were no shares issued to Lincoln Park as additional commitment shares, pursuant to the 2020 LPC
Agreement. The 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement will expire on August 1, 2023.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Summary
of Common Stock Activity
During
the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company issued 2,633,093 and 2,105,236 shares of Common Stock, respectively, with such issuances
of Common Stock being summarized as follows:
SCHEDULE OF COMMON STOCK ACTIVITY
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively | |
| 1,011,381,988 | | |
| 1,009,276,752 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting fees | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| Common Stock issued during the fiscal year | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 1,014,015,081 | | |
| 1,011,381,988 | |
NOTE
13. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
Part
of the compensation paid by the Company to its Directors and employees consists of the issuance of Common Stock or via the granting of
options to purchase Common Stock.
Stock-based
Director Compensation
The
Company’s Director compensation policy, instituted in October 2009 and further revised in January 2016, includes provisions that
a portion of director’s fees are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s Common Stock, in lieu of cash, with
the valuation of such shares being calculated on quarterly basis and equal to the average closing price of the Company’s Common
Stock.
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company accrued director’s fees totaling $90,000, which will be paid via cash payments totaling
$30,000 and the issuance of 1,753,686 shares of Common Stock.
Stock-based
Employee/Consultant Compensation
Employment
contracts with the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees and engagement contracts with certain
consultants include provisions for a portion of each employee’s salaries or consultant’s fees to be paid via the issuance
of shares of the Company’s Common Stock, in lieu of cash, with the valuation of such shares being calculated on a quarterly basis
and equal to the average closing price of the Company’s Common Stock.
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company accrued salaries totaling $540,000 owed
to the Company’s President, Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees which will be paid via the issuance of 14,956,851 shares
of Common Stock. As of March 31, 2023, the Company owed its President, Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees’
salaries totaling $4,335,000 which
will be paid via the issuance of 68,264,667 shares
of Common Stock.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Options
Under
its 2014 Stock Option Plan and prior options plans, the Company may grant stock options to officers, selected employees, as well as members
of the Board of Directors and advisory board members. All options have generally been granted at a price equal to or greater than the
fair market value of the Company’s Common Stock at the date of the grant. Generally, options are granted with a vesting period
of up to three years and expire ten years from the date of grant. A summary of the activity of Company’s 2014 Stock Option Plan
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
SCHEDULE OF STOCK OPTION PLAN
| | |
Shares Underlying Options | | |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | | |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years) | | |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2021 | |
| 5,900,000 | | |
$ | 0.13 | | |
| 3.7 | | |
$ | 6,000 | |
| Granted | |
| 500,000 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (750,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2022 | |
| 5,650,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.8 | | |
$ | — | |
| Granted | |
| 15,530,000 | | |
$ | 0.03 | | |
| 10.0 | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (5,810,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | |
| 15,370,000 | | |
$ | 0.07 | | |
| 7.4 | | |
$ | — | |
| Exercisable at March 31, 2023 | |
| 4,182,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.2 | | |
$ | — | |
The
aggregate intrinsic value for outstanding options is calculated as the difference between the exercise price of the underlying awards
and the quoted price of the Company’s Common Stock as of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 of $0.03 and $0.03, respectively. As
of March 31, 2023, there was $205,340 in unrecognized stock-based compensation expense that will be recognized over a 1.5 year period.
NOTE
14. CONCENTRATIONS AND CREDIT RISK
Revenues
Two
customers accounted for approximately 96% of the Company’s revenues for the year ended March 31, 2023. These two customers accounted
for approximately 85% and 11% of revenues each, respectively.
Two
customers accounted for approximately 95% of the Company’s revenues for the year ended March 31, 2022. These two customers accounted
for approximately 84% and 11% of revenues each, respectively.
Accounts
Receivable
One
customer accounted for approximately 96% of the Company’s accounts receivable as of March 31, 2023.
Two
customers accounted for approximately 91% of the Company’s accounts receivable as of March 31, 2022. These two customers accounted
for approximately 78% and 13% of accounts receivable each, respectively.
Purchasing
One
supplier accounted for approximately 34% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for the year ended March 31, 2023.
Four
suppliers accounted for more than 69% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for the year ended March 31, 2022. These four
suppliers accounted for approximately 51%, 7%, 6%, and 5% of purchases each, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
15. SEGMENT RESULTS
FASB
ASC 280-10-50 requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach is based on
the way a company’s management organized segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance.
Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which
management disaggregates a company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are ANDAs for generic products and NDAs for branded products. The Company identified
its reporting segments based on the marketing authorization relating to each and the financial information used by its chief operating
decision maker to make decisions regarding the allocation of resources to and the financial performance of the reporting segments.
Asset
information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating decision maker does not review this information by
segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation of the Company’s audited consolidated
financial statements.
The
following represents selected information for the Company’s reportable segments:
SCHEDULE OF SELECTED INFORMATION FOR REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
| | | |
| | |
| ANDA | |
| 10,393,857 | | |
| 10,744,005 | |
| NDA | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
The
table below reconciles the Company’s operating income by segment to income from operations before provision for income taxes as
reported in the Company’s audited consolidated statement of operations:
SCHEDULE
OF OPERATING INCOME BY SEGMENT TO INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating income by segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
| Corporate unallocated costs | |
| (3,581,468 | ) | |
| (3,696,881 | ) |
| Interest income | |
| 7,453 | | |
| 126 | |
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs | |
| (1,112,707 | ) | |
| (191,816 | ) |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| (292,807 | ) | |
| — | |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | |
| (1,263,452 | ) | |
| (1,194,939 | ) |
| Significant non-cash items | |
| (580,128 | ) | |
| (781,475 | ) |
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments | |
| 415,126 | | |
| 1,425,409 | |
NOTE
16. RELATED PARTY AGREEMENTS WITH MIKAH PHARMA, LLC
In
May 2020, Praxgen, pursuant to an asset purchase agreement, assigned its rights and obligations under the Praxgen Agreement for Amphetamine
IR and Amphetamine ER to Mikah Pharma LLC (“Mikah”). The ANDAs for Amphetamine IR and Amphetamine ER are now registered under
Elite’s name. Mikah will now be Elite’s partner with respect to Amphetamine IR and ER and will assume all the rights and
obligations for these products from Praxgen. Mikah was founded in 2009 by Nasrat Hakim, a related party and the Company’s President,
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board.
In
June 2021, the Company entered into a development and license agreement with Mikah, pursuant to which Mikah will engage in the research,
development, sales and licensing of generic pharmaceutical products. In addition, Mikah will collaborate to develop and commercialize
generic products including formulation development, analytical method development, manufacturing, sales and marketing of generic products.
Initially two generic products were identified for the parties to develop.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
17. INCOME TAXES
The
components of the income taxes benefit (expense) are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF COMPONENTS OF INCOME TAXES BENEFIT (EXPENSE)
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
$ | 784,577 | | |
$ | 1,160,715 | |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| 2,171,821 | |
| Benefit of net operating loss carryforward | |
| (784,577 | ) | |
| (1,160,715 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| (424,028 | ) | |
| (435,384 | ) |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | |
$ | (424,028 | ) | |
$ | 1,736,437 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
| Net benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
The
major components of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of March 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows (amounts in thousands of dollars):
SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | 17,613 | | |
$ | 21,180 | |
| Tax credits | |
| 4,993 | | |
| 4,764 | |
| Valuation allowance | |
| (20,434 | ) | |
| (23,772 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and liabilities | |
$ | 2,172 | | |
$ | 2,172 | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 747 | |
| Valuation Allowance | |
| — | | |
| (747 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and
liabilities | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
At
March 31, 2023 and 2022, a 90%
and 90% valuation allowance is provided, respectively, as it is uncertain if the deferred tax assets will provide total future
benefits because of the uncertainty about the Company’s ability to generate the future taxable income necessary to use the net
operating loss carry forwards.
The
company believes that temporary timing differences between accrual and payment of income taxes are not material to the financial position
of the Company.
As
of March 31, 2023, Elite has a federal net operating loss carry forward of $83.9 million,
which have not expired. During 2022, the Company was able to release a portion of its valuation allowance as it determined future
profits will offset a portion of its valuation allowance. During 2022, the Company recorded a tax benefit of $2.2 million
as a result of this change in judgment. There is no change in the net deferred tax asset for 2023. Absent the above mentioned
allowance, at March 31, 2023, the Company’s federal and state income taxes due were $0.0 million
and $0.4 million,
respectively.
Exhibit 31.1
CERTIFICATION BY PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER, PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER AND PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING OFFICER
I, Nasrat Hakim, certify that:
| |
1. |
I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2023 of Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the “Registrant”) |
| |
|
|
| |
2. |
Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; |
| |
|
|
| |
3. |
Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; |
| |
|
|
| |
4. |
I am responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the Registrant and have: |
| |
a. |
Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the Registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
| |
|
|
| |
b. |
Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
| |
|
|
| |
c. |
Evaluated the effectiveness of the Registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
| |
|
|
| |
d. |
Disclosed in this report any change in the Registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the Registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the Registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
| |
5. |
I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the Registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the Registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
| |
a. |
All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the Registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
| |
|
|
| |
b. |
Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the Registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
| Date: June 29, 2023 |
/s/
Nasrat Hakim |
| |
Nasrat Hakim
Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman of the Board of Directors
(Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
Exhibit 32.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Elite Pharmaceuticals,
Inc. (the “Registrant”) on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2023 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the
“Report”), I, Nasrat Hakim, Chief Executive Officer of the Registrant, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S. C. Section 1350, as adopted
pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
The Report fully complies with the requirements of
Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; and
Information contained in the Form 10-K fairly presents,
in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Registrant.
| Date: June 29, 2023 |
/s/
Nasrat Hakim |
| |
Nasrat Hakim
Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman of the Board of Directors
(Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
This certification has been furnished solely pursuant
to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
A signed original of this written statement required
by Section 906 has been provided to Elite Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and will be retained by Elite Pharmaceuticals Inc. and furnished to the
Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request.
v3.23.2
Cover - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Jun. 20, 2023 |
Sep. 30, 2022 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Mar. 31, 2023
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2023
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--03-31
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
001-15697
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0001053369
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
22-3542636
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
NV
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
165
LUDLOW AVENUE
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
NORTHVALE
|
|
|
| Entity Address, State or Province |
NJ
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
07647
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
(201)
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
750-2646
|
|
|
| Title of 12(b) Security |
Common
Stock, par value $0.001 per share
|
|
|
| Trading Symbol |
ELTP
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Non-accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
true
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 40,556,603
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding |
|
1,013,915,081
|
|
| Documents Incorporated by Reference [Text Block] |
Portions of the Proxy Statement for
the registrant’s 2023 Annual Meeting of Shareholders which is to be filed subsequent to the date hereof are incorporated by reference
into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
|
|
|
| ICFR Auditor Attestation Flag |
true
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction [Flag] |
false
|
|
|
| Auditor Name |
Buchbinder Tunick & Company LLP
|
|
|
| Auditor Location |
Little
Falls, New Jersey 07424
|
|
|
| Auditor Firm ID |
6189
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDocuments incorporated by reference. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-23
| Name: |
dei_DocumentsIncorporatedByReferenceTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the state or province.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressStateOrProvince |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:stateOrProvinceItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(b) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b
| Name: |
dei_Security12bTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTrading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.
| Name: |
dei_TradingSymbol |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:tradingSymbolItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
Consolidated Balance Sheets - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Current assets: |
|
|
| Cash |
$ 7,832,247
|
$ 8,535,357
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $-0-, respectively |
3,094,549
|
3,057,913
|
| Inventory |
9,550,716
|
6,741,170
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,032,785
|
526,949
|
| Total current assets |
21,510,297
|
18,861,389
|
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $14,586,335 and $13,348,565, respectively |
10,426,158
|
5,952,992
|
| Intangible assets |
6,341,228
|
6,634,035
|
| Operating lease - right-of-use asset |
13,062
|
1,031,884
|
| Deferred income tax benefit |
2,171,821
|
2,171,821
|
| Other assets: |
|
|
| Restricted cash - debt service for NJEDA bonds |
412,434
|
405,039
|
| Security deposits |
21,018
|
91,738
|
| Total other assets |
433,452
|
496,777
|
| Total assets |
40,896,018
|
35,148,898
|
| Current liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts payable |
2,446,810
|
1,430,985
|
| Accrued expenses |
5,047,726
|
4,693,142
|
| Deferred revenue, current portion |
13,333
|
13,333
|
| Bonds payable, current portion, net of bond issuance costs |
110,822
|
100,822
|
| Loans payable, current portion |
200,032
|
253,006
|
| Lease obligation - operating lease, current portion |
14,914
|
202,953
|
| Total current liabilities |
7,833,637
|
6,694,241
|
| Long-term liabilities: |
|
|
| Deferred revenue, net of current portion |
18,890
|
32,226
|
| Bonds payable, net of current portion and bond issuance costs |
1,029,018
|
1,139,848
|
| Loans payable, net of current portion |
2,532,502
|
249,046
|
| Lease obligation - operating lease, net of current portion |
|
835,893
|
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants |
521,711
|
936,837
|
| Other long-term liabilities |
|
38,780
|
| Total long-term liabilities |
4,102,121
|
3,232,630
|
| Total liabilities |
11,935,758
|
9,926,871
|
| Shareholders’ equity: |
|
|
| Common stock; par value $0.001; 1,445,000,000 shares authorized; 1,014,015,081 shares issued and 1,013,915,081 shares outstanding as of March 31, 2023; 1,011,381,988 shares issued and 1,011,281,988 shares outstanding as of March 31, 2022 |
1,014,019
|
1,011,385
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
164,750,980
|
164,577,227
|
| Treasury stock; 100,000 shares as of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022; at cost |
(306,841)
|
(306,841)
|
| Accumulated deficit |
(136,497,898)
|
(140,059,744)
|
| Total shareholders’ equity |
28,960,260
|
25,222,027
|
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
$ 40,896,018
|
$ 35,148,898
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of excess of issue price over par or stated value of stock and from other transaction involving stock or stockholder. Includes, but is not limited to, additional paid-in capital (APIC) for common and preferred stock. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapital |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are recognized. Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 26: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed within one year (or the normal operating cycle, if longer). Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value, after the effects of master netting arrangements, of a financial liability or contract with one or more underlyings, notional amount or payment provision or both, and the contract can be net settled by means outside the contract or delivery of an asset, expected to be settled after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Includes assets not subject to a master netting arrangement and not elected to be offset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483466/210-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after valuation and LIFO reserves of inventory expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all liabilities that are recognized. Liabilities are probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of an entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 22: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19-26)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Liabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.21)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation due after one year or beyond the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 21: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 201.5-02(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 22: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 201.5-02(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 23: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 201.5-02(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesNoncurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of portion of long-term loans payable due within one year or the operating cycle if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LoansPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of loans payable (with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle if longer), excluding current portion. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermLoansPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(10))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.24)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits in future periods, and amount of other assets that are expected to be realized or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseAndOtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480842/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents restricted as to withdrawal or usage, classified as noncurrent. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-SubTopic 210
-Topic 954
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480632/954-210-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of the portion of long-term, collateralized debt obligations due within one year or the operating cycle, if longer. Such obligations include mortgage loans, chattel loans, and any other borrowings secured by assets of the borrower. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SecuredDebtCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying amount of collateralized debt obligations with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle, if longer, excluding the current portion. Obligations include, but not limited to, mortgage loans, chattel loans, and other borrowings secured by assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SecuredLongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of an asset, typically cash, provided to a counterparty to provide certain assurance of performance by the entity pursuant to the terms of a written or oral agreement, such as a lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SecurityDeposit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount allocated to treasury stock. Treasury stock is common and preferred shares of an entity that were issued, repurchased by the entity, and are held in its treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481520/505-30-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.29,30)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
Consolidated Balance Sheets (Parenthetical) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Statement of Financial Position [Abstract] |
|
|
| Allowance for doubtful accounts receivable, current |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| Accumulated depreciation |
$ 14,586,335
|
$ 13,348,565
|
| Common stock, par value |
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized |
1,445,000,000
|
1,445,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued |
1,014,015,081
|
1,011,381,988
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding |
1,013,915,081
|
1,011,281,988
|
| Treasury stock, shares |
100,000
|
100,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479344/326-20-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllowanceForDoubtfulAccountsReceivableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfFinancialPositionAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of previously issued common shares repurchased by the issuing entity and held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockCommonShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
Consolidated Statements of Operations - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Revenue: |
|
|
| Manufacturing fees |
$ 29,187,573
|
$ 26,951,863
|
| Licensing fees |
4,967,541
|
5,310,254
|
| Total revenue |
34,155,114
|
32,262,117
|
| Cost of manufacturing |
17,561,093
|
17,466,763
|
| Gross profit |
16,594,021
|
14,795,354
|
| Operating expenses: |
|
|
| Research and development |
6,200,163
|
4,051,349
|
| General and administrative |
5,122,272
|
4,464,003
|
| Non-cash compensation through issuance of stock options |
39,325
|
14,353
|
| Impairment of intangible assets |
292,807
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
1,263,452
|
1,194,939
|
| Total operating expenses |
12,918,019
|
9,724,644
|
| Income from operations |
3,676,002
|
5,070,710
|
| Other income, net: |
|
|
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments |
415,126
|
1,425,409
|
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs |
(1,112,707)
|
(191,816)
|
| Gain on sale of ANDA |
1,000,000
|
|
| Interest income |
7,453
|
126
|
| Other income, net |
309,872
|
1,233,719
|
| Income before income taxes |
3,985,874
|
6,304,429
|
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
(424,028)
|
1,736,437
|
| Net benefit for sale of state net operating losses and credits |
|
857,379
|
| Net income attributable to common shareholders |
$ 3,561,846
|
$ 8,898,245
|
| Basic net income per share attributable to common shareholders |
$ 0.00
|
$ 0.01
|
| Diluted net income per share attributable to common shareholders |
$ 0.00
|
$ 0.01
|
| Basic weighted average Common Stock outstanding |
1,012,911,346
|
1,010,607,713
|
| Diluted weighted average Common Stock outstanding |
1,012,911,346
|
1,010,607,713
|
| X |
- DefinitionRevenue from licensing fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_RevenueFromLicensingFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRevenue from manufacturing fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_RevenueFromManufacturingFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate cost of goods produced and sold and services rendered during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe current period expense charged against earnings on long-lived, physical assets not used in production, and which are not intended for resale, to allocate or recognize the cost of such assets over their useful lives; or to record the reduction in book value of an intangible asset over the benefit period of such asset; or to reflect consumption during the period of an asset that is not used in production. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the fair value of derivatives recognized in the income statement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4A
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480434/815-10-50-4A
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeGainLossOnDerivativeNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, excluding oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnDispositionOfAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total of expenses of managing and administering the affairs of an entity, including affiliates of the reporting entity, which are not directly or indirectly associated with the manufacture, sale or creation of a product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1,2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (210.5-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest income or expense, including any amortization and accretion (as applicable) of discounts and premiums, including consideration of the provisions for loan, lease, credit, and other related losses. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.12)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestIncomeExpenseAfterProvisionForLoanLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accretion (amortization) of purchase discount (premium) of interest income on nonoperating securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentIncomeInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of income or expense from ancillary business-related activities (that is to say, excluding major activities considered part of the normal operations of the business). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpenseAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Includes selling, general and administrative expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpensesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process whether intended for sale or the entity's use, during the reporting period charged to research and development projects, including the costs of developing computer software up to the point in time of achieving technological feasibility, and costs allocated in accounting for a business combination to in-process projects deemed to have no alternative future use. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482916/730-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 730
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482517/912-730-25-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenuesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders' Equity - USD ($)
|
Preferred Stock [Member]
Series J Preferred Stock [Member]
|
Common Stock [Member] |
Additional Paid-in Capital [Member] |
Treasury Stock, Common [Member] |
Retained Earnings [Member] |
Total |
| Beginning balance at Mar. 31, 2021 |
|
$ 1,009,279
|
$ 164,407,480
|
$ (306,841)
|
$ (148,957,989)
|
$ 16,151,929
|
| Beginning balance, shares at Mar. 31, 2021 |
|
1,009,276,752
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
| Net income |
|
|
|
|
8,898,245
|
8,898,245
|
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options |
|
|
14,353
|
|
|
14,353
|
| Shares issued in payment of salaries |
|
$ 2,106
|
155,394
|
|
|
157,500
|
| Shares issued in payment of salaries, shares |
|
2,105,236
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Mar. 31, 2022 |
|
$ 1,011,385
|
164,577,227
|
$ (306,841)
|
(140,059,744)
|
25,222,027
|
| Ending balance, shares at Mar. 31, 2022 |
|
1,011,381,988
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
| Net income |
|
|
|
|
3,561,846
|
3,561,846
|
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options |
|
|
39,325
|
|
|
39,325
|
| Shares issued in payment of salaries |
|
$ 1,379
|
58,621
|
|
|
60,000
|
| Shares issued in payment of salaries, shares |
|
1,378,608
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares issued in payment of consultants |
|
$ 1,255
|
75,807
|
|
|
77,062
|
| Shares issued in payment of consultants, shares |
|
1,254,485
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Mar. 31, 2023 |
|
$ 1,014,019
|
$ 164,750,980
|
$ (306,841)
|
$ (136,497,898)
|
$ 28,960,260
|
| Ending balance, shares at Mar. 31, 2023 |
|
1,014,015,081
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase to additional paid-in capital (APIC) for recognition of cost for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-13
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidInCapitalSharebasedCompensationRequisiteServicePeriodRecognitionValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued which are neither cancelled nor held in the treasury.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued in lieu of cash for services contributed to the entity. Number of shares includes, but is not limited to, shares issued for services contributed by vendors and founders.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesIssuedForServices |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of new stock issued during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesNewIssues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of stock issued in lieu of cash for services contributed to the entity. Value of the stock issued includes, but is not limited to, services contributed by vendors and founders.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueIssuedForServices |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the value of new stock issued during the period. Includes shares issued in an initial public offering or a secondary public offering. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueNewIssues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
| Net income |
$ 3,561,846
|
$ 8,898,245
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
1,277,622
|
1,209,119
|
| Amortization of operating leases - right-of-use assets |
67,061
|
225,590
|
| Impairment of intangible assets |
292,807
|
|
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants |
(415,126)
|
(1,425,409)
|
| Deferred income tax benefit |
|
(2,171,821)
|
| Non-cash compensation accrued |
540,000
|
767,122
|
| Non-cash compensation through the issuance of employee stock options |
39,325
|
14,353
|
| Non-cash rent expense and lease accretion |
803
|
1,152
|
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts receivable |
(36,636)
|
438,463
|
| Inventory |
(2,809,546)
|
(1,728,268)
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
(435,116)
|
209,796
|
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
1,336,566
|
314,214
|
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits |
(13,336)
|
(13,332)
|
| Lease obligations - operating leases |
(67,566)
|
(230,910)
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
3,338,704
|
6,508,314
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(5,736,618)
|
(498,566)
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(5,736,618)
|
(498,566)
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
| Payment of bond principal |
(115,000)
|
(110,000)
|
| Payments of loans and mortgage payable |
(12,240,111)
|
|
| Proceeds from loans and mortgage payable, net of transaction costs |
14,438,985
|
|
| Other loan payments |
(381,675)
|
(557,133)
|
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
1,702,199
|
(667,133)
|
| Net change in cash and restricted cash |
(695,715)
|
5,342,615
|
| Cash and restricted cash, beginning of period |
8,940,396
|
3,597,781
|
| Cash and restricted cash, end of period |
8,244,681
|
8,940,396
|
| Supplemental disclosure of cash and non-cash transactions: |
|
|
| Cash paid for interest |
1,098,537
|
177,636
|
| Cash paid for income taxes |
424,028
|
|
| Financing of equipment purchases and insurance renewal |
|
244,124
|
| Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting expenses |
137,062
|
157,500
|
| Supplemental non-cash amounts of lease liabilities arising from obtaining right of use assets |
|
1,042,800
|
| Reconciliation of cash and restricted cash |
|
|
| Cash |
7,832,247
|
8,535,357
|
| Restricted cash - debt service for NJEDA bonds |
412,434
|
405,039
|
| Total cash and restricted cash shown in statement of cash flows |
$ 8,244,681
|
$ 8,940,396
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccrued compensation non cash.
| Name: |
ELTP_AccruedCompensationNonCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNon cash rent expenses and lease accretion.
| Name: |
ELTP_NoncashRentExpenseAndLeaseAccretion |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSupplemental noncash amounts of lease liabilities arising from obtaining right of use assets.
| Name: |
ELTP_SupplementalNoncashAmountsOfLeaseLiabilitiesArisingFromObtainingRightOfUseAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including, but not limited to, disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsIncludingDisposalGroupAndDiscontinuedOperations |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense recognized in the current period that allocates the cost of tangible assets, intangible assets, or depleting assets to periods that benefit from use of the assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationDepletionAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the fair value of derivatives recognized in the income statement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4A
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480434/815-10-50-4A
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeGainLossOnDerivativeNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the amounts payable to vendors for goods and services received and the amount of obligations and expenses incurred but not paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in amount due within one year (or one business cycle) from customers for the credit sale of goods and services. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482312/912-310-45-11
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInContractWithCustomerLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate value of all inventory held by the reporting entity, associated with underlying transactions that are classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInInventories |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingCapitalAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in prepaid expenses, and assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInPrepaidDeferredExpenseAndOtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash paid for interest, excluding capitalized interest, classified as operating activity. Includes, but is not limited to, payment to settle zero-coupon bond for accreted interest of debt discount and debt instrument with insignificant coupon interest rate in relation to effective interest rate of borrowing attributable to accreted interest of debt discount. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPaidNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoncashInvestingAndFinancingItemsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of debt that an Entity assumes in acquiring a business or in consideration for an asset received in a noncash (or part noncash) acquisition. Noncash is defined as transactions during a period that affect recognized assets or liabilities but that do not result in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. "Part noncash" refers to that portion of the transaction not resulting in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoncashOrPartNoncashAcquisitionDebtAssumed1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of periodic reduction over lease term of carrying amount of right-of-use asset from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAssetAmortizationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of long-lived, physical assets that are used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale; includes cash outflows to pay for construction of self-constructed assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquirePropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow from a borrowing supported by a written promise to pay an obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromNotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow from the repayment of a long-term debt instrument issued, secured by a first mortgage deed of trust, containing a pledge of real property. The lender has the highest claim on the property in case of default. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_RepaymentsOfFirstMortgageBond |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow for a borrowing supported by a written promise to pay an obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_RepaymentsOfNotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow for the payment of debt classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_RepaymentsOfOtherDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents restricted as to withdrawal or usage, classified as noncurrent. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-SubTopic 210
-Topic 954
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480632/954-210-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe fair value of stock issued in noncash financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssued1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for option under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockOptionPlanExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
NOTE
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Overview
Elite
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the “Company” or “Elite”) was incorporated on October 1, 1997 under the laws of the State
of Delaware, and its wholly-owned subsidiary Elite Laboratories, Inc. (“Elite Labs”) was incorporated on August 23, 1990
under the laws of the State of Delaware. On January 5, 2012, Elite Pharmaceuticals was reincorporated under the laws of the State of
Nevada. Elite Labs engages primarily in researching, developing, licensing, manufacturing, and sales of generic, oral dose pharmaceuticals. The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties and itself, if and when the products
are approved. These products include drugs that cover therapeutic areas for allergy, bariatric, attention deficit and infection. Research
and development activities are performed with an objective of developing products that will secure marketing approvals from the United
States Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), and thereafter, commercially exploiting such products.
Principles
of Consolidation
The
accompanying audited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
in the United States (“GAAP”). The audited consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its
wholly-owned subsidiary, Elite Labs. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Segment
Information
Financial
Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification 280 (“ASC 280”), Segment Reporting,
establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise
about which separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making
group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance.
The
Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive Officer, who reviews the financial performance and the results
of operations of the segments prepared in accordance with GAAP when making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance
of the Company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are products whose marketing approvals were secured via an Abbreviated New Drug Applications
(“ANDA”) and products whose marketing approvals were secured via a New Drug Application (“NDA”). ANDA products
are referred to as generic pharmaceuticals and NDA products are referred to as branded pharmaceuticals.
There
are currently no intersegment revenues. Asset information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating decision
maker does not review this information by segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation
of the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements. Please see Note 15 for further details.
Revenue
Recognition
The
Company generates revenue from manufacturing and licensing fees and direct sales to pharmaceutical distributors for pharmacies and institutions. Manufacturing fees include the development of pain management
products, manufacturing of a line of generic pharmaceutical products with approved ANDA, through the manufacture of formulations and
the development of new products. Licensing fees include the commercialization of products either by license and the collection of royalties,
or the expansion of licensing agreements with other pharmaceutical companies, including co-development projects, joint ventures and other
collaborations.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Under
ASC 606, Revenue from Contacts with Customers (“ASC 606”), the Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains
control of promised goods or services, in an amount that reflects the consideration which is expected to be received in exchange for
those goods or services. The Company recognizes revenues following the five-step model prescribed under ASC 606: (i) identify contract(s)
with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligation(s) in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the
transaction price to the performance obligation(s) in the contract; and (v) recognize revenues when (or as) the Company satisfies a performance
obligation. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the entity will collect the consideration
it is entitled to in exchange for the goods or services it transfers to the customer. At contract inception, once the contract is determined
to be within the scope of ASC 606, the Company assesses the goods or services promised within each contract and determines those that
are performance obligations and assesses whether each promised good or service is distinct. The Company then recognizes as revenue the
amount of the transaction price that is allocated to the respective performance obligation when (or as) the performance obligation is
satisfied. Sales, value add, and other taxes collected on behalf of third parties are excluded from revenue.
Nature
of goods and services
The
following is a description of the Company’s goods and services from which the Company generates revenue, as well as the nature,
timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and significant payment terms for each, as applicable:
a)
Manufacturing Fees
The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties, if, and when, the products are
approved. These products include products using controlled-release drug technology. The Company also develops and markets (either on
its own or by license to other companies) generic and proprietary controlled-release pharmaceutical products.
The
Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains control of the Company’s product based on the contractual shipping terms of
the contract. The Company is primarily responsible for fulfilling the promise to provide the product, is responsible to ensure that the
product is produced in accordance with the related supply agreement and bears risk of loss while the inventory is in-transit to the commercial
partner. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring products to a
customer.
b)
License Fees
The
Company enters into licensing and development agreements, which may include multiple revenue generating activities, including milestones
payments, licensing fees, product sales and services. The Company analyzes each element of its licensing and development agreements in
accordance with ASC 606 to determine appropriate revenue recognition. The terms of the license agreement may include payment to the Company
of licensing fees, non-refundable upfront license fees, milestone payments if specified objectives are achieved, and/or royalties on
product sales.
If
the contract contains a single performance obligation, the entire transaction price is allocated to the single performance obligation.
Contracts that contain multiple performance obligations require an allocation of the transaction price based on the estimated relative
standalone selling prices of the promised products or services underlying each performance obligation. The Company determines standalone
selling prices based on the price at which the performance obligation is sold separately. If the standalone selling price is not observable
through past transactions, the Company estimates the standalone selling price taking into account available information such as market
conditions and internally approved pricing guidelines related to the performance obligations.
The
Company recognizes revenue from non-refundable upfront payments at a point in time, typically upon fulfilling the delivery of the associated
intellectual property to the customer. For those milestone payments which are contingent on the occurrence of particular future events
(for example, payments due upon a product receiving FDA approval), the Company determined that these need to be considered for inclusion
in the calculation of total consideration from the contract as a component of variable consideration using the most-likely amount method.
As such, the Company assesses each milestone to determine the probability and substance behind achieving each milestone. Given the inherent
uncertainty of the occurrence of future events, the Company will recognize revenue from the milestone when there is not a high probability
of a reversal of revenue, which typically occurs near or upon achievement of the event.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Significant
management judgment is required to determine the level of effort required under an arrangement and the period over which the Company
expects to complete its performance obligations under the arrangement. If the Company cannot reasonably estimate when its performance
obligations either are completed or become inconsequential, then revenue recognition is deferred until the Company can reasonably make
such estimates. Revenue is then recognized over the remaining estimated period of performance using the cumulative catch-up method.
When
determining the transaction price of a contract, an adjustment is made if payment from a customer occurs either significantly before
or significantly after performance, resulting in a significant financing component. Applying the practical expedient in ASC 606-10-32-18,
the Company does not assess whether a significant financing component exists if the period between when the Company performs its obligations
under the contract and when the customer pays is one year or less. None of the Company’s contracts contained a significant financing
component as of March 31, 2023.
In
accordance with ASC 606-10-55-65, royalties are recognized when the subsequent sale of the customer’s products occurs.
c)
Direct Sales
The
Company will begin direct sales of products under the Company’s own label beginning on April 1, 2023. License agreements will remain
in place for select products. With this transition, however, a large portion of the manufacturing and license fees now reported will
be replaced with revenues from direct sales of pharmaceutical products to distributors for pharmacies and institutions.
Disaggregation
of revenue
In
the following table, revenue is disaggregated by type of revenue generated by the Company. The table also includes a reconciliation of
the disaggregated revenue with the reportable segments:
SCHEDULE
OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| NDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Licensing fees | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
| Total NDA revenue | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| ANDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | |
| Total ANDA revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | |
| Total revenue | |
$ | 34,155,114 | | |
$ | 32,262,117 | |
Selected
information on reportable segments and reconciliation of operating income by segment to income (loss) from operations before income taxes
are disclosed within Note 15.
Cash
The
Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash
equivalents consist of cash on deposit with banks and money market instruments. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents with
high-quality, U.S. financial institutions and, to date has not experienced losses on any of its balances.
Restricted
Cash
As
of March 31, 2023, and March 31, 2022, the Company had $412,434 and $405,039, of restricted cash, respectively, related to debt service
reserve in regard to the New Jersey Economic Development Authority (“NJEDA”) bonds (see Note 5).
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Accounts
Receivable
Accounts
receivable are comprised of balances due from customers, net of estimated allowances for uncollectible accounts. In determining collectability,
historical trends are evaluated, and specific customer issues are reviewed on a periodic basis to arrive at appropriate allowances.
Inventory
Inventory
is recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value on specific identification by lot number basis.
Long-Lived
Assets
The
Company periodically evaluates the fair value of long-lived assets, which include property and equipment and intangibles, whenever events
or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
Property
and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is provided on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the respective
assets which range from three to forty years. Major repairs or improvements are capitalized. Minor replacements and maintenance and repairs
which do not improve or extend asset lives are expensed currently.
Upon
retirement or other disposition of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and the resulting
gain or loss, if any, is recognized in income.
Intangible
Assets
The
Company capitalizes certain costs to acquire intangible assets; if such assets are determined to have a finite useful life they are amortized
on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life. Costs to acquire indefinite lived intangible assets, such as costs related to
ANDAs and patents are capitalized accordingly.
The
Company tests its intangible assets for impairment at least annually (as of March 31st) and whenever events or circumstances change that
indicate impairment may have occurred. A significant amount of judgment is involved in determining if an indicator of impairment has
occurred. Such indicators may include, among others and without limitation: a significant decline in the Company’s expected future
cash flows; a sustained, significant decline in the Company’s stock price and market capitalization; a significant adverse change
in legal factors or in the business climate of the Company’s segments; unanticipated competition; and slower growth rates.
For
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company determined indicators of impairment have occurred and recorded impairment expense of $292,807 on its ANDAs and patents.
Please
also see Note 4 for further details on intangible assets.
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenditures are charged to expense as incurred.
Contingencies
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s condensed
consolidated financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series
of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Income
Taxes
Income
taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which
those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Where applicable, the Company records a valuation allowance to reduce
any deferred tax assets that it determines will not be realizable in the future.
The
Company recognizes the benefit of an uncertain tax position that it has taken or expects to take on income tax returns it files if such
tax position is more likely than not to be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position.
These tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate resolution.
The
Company operates in multiple tax jurisdictions within the United States of America. The Company remains subject to examination in
all tax jurisdiction until the applicable statutes of limitation expire. As of March 31, 2023, a summary of the tax years that
remain subject to examination in our major tax jurisdictions are: United States – Federal, 2019 and forward, and State, 2016
and forward. The Company did not record unrecognized tax positions for the years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Warrants
and Preferred Shares
The
accounting treatment of warrants and preferred share series issued is determined pursuant to the guidance provided by ASC 470, Debt,
ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, as applicable. Each feature of a
freestanding financial instrument including, without limitation, any rights relating to subsequent dilutive issuances, dividend issuances,
equity sales, rights offerings, forced conversions, optional redemptions, automatic monthly conversions, dividends and exercise is assessed
with determinations made regarding the proper classification in the Company’s financial statements.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation. Under the fair value
recognition provisions, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized
as an expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, based on the terms of the awards. The cost of the stock-based
payments to nonemployees that are fully vested and non-forfeitable as at the grant date is measured and recognized at that date, unless
there is a contractual term for services in which case such compensation would be amortized over the contractual term.
In
accordance with the Company’s Director compensation policy and certain employment contracts, director’s fees and a portion
of employee’s salaries are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s Common Stock (“Common Stock”),
in lieu of cash, with the valuation of such share being calculated on a quarterly basis and equal to the average closing price of the
Company’s Common Stock.
Sale
of ANDA
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company entered into an agreement with Pyros Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Pyros”) pursuant
to which the Company sold to Pyros its rights in and to the Company’s approved abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) for its
generic Sabril drug. The Company sold such rights to Pyros for $1,000,000, which was recorded as gain on sale of ANDA during the year
ended March 31, 2023. There is no further action required by the Company regarding the rights which would affect future periods.
In
conjunction with the sale of its Product to Pyros, the Company executed a Manufacturing and Supply agreement (the “Pyros Agreement”)
with Pyros. Under the terms of the Pyros Agreement, the Company will receive an agreed-upon price per drug for the manufacturing and
packaging of Sabril over a term of three years. Revenue per the Pyros Agreement will be recognized as control of the manufactured and
supplied drugs is transferred to Pyros (at the time of delivery).
Earnings
Per Share Attributable to Common Shareholders’
The
Company follows ASC 260, Earnings Per Share, which requires presentation of basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”)
on the face of the income statement for all entities with complex capital structures and requires a reconciliation of the numerator and
denominator of the basic EPS computation to the numerator and denominator of the diluted EPS computation. In the accompanying financial
statements, basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding
during the period. The computation of diluted net income per share does not include the conversion of securities that would have an antidilutive
effect.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
following is the computation of earnings per share applicable to common shareholders for the periods indicated:
SCHEDULE
OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Numerator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| Effect of dilutive instrument on net income | |
| (415,126 | ) | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Net income - diluted | |
$ | 3,146,720 | | |
$ | 7,472,836 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Denominator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - basic | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options and convertible securities | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - diluted | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income per share | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| Diluted | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
Fair
Value of Financial Instruments
ASC
820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”) provides a framework for measuring fair value in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles.
ASC
820 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between (1) market
participant assumptions developed based on market data obtained from independent sources (observable inputs) and (2) an entity’s
own assumptions about market participant assumptions developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (unobservable
inputs).
The
fair value hierarchy consists of three broad levels, which gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). The three levels of the fair value
hierarchy under ASC 820 are described as follows:
| ● | Level
1 – Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
that are accessible at the measurement date. |
| ● | Level
2 – Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for
the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs include quoted prices
for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar
assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that
are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived principally from or
corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
| ● | Level
3 – Inputs that are unobservable for the asset or liability. |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Measured
on a Recurring Basis
The
following table presents information about our liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, aggregated by the level in the
fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fell:
SCHEDULE
OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| | |
| | |
Fair Value Measurement Using | |
| | |
Amount at Fair Value | | |
Level 1 | | |
Level 2 | | |
Level 3 | |
| March 31, 2023 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 521,711 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 521,711 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| March 31, 2022 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 936,837 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 936,837 | |
See
Note 11 for specific inputs used in determining fair value.
The
carrying amounts of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities, such as cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses and other
current assets, accounts payable and accrued expenses, approximate their fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
Based upon current borrowing rates with similar maturities the carrying value of long-term debt approximates fair value.
Non-Financial
Assets that are Measured at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
Non-financial
assets such as intangible assets, and property and equipment are measured at fair value only when an impairment loss is recognized. The
Company did not record an impairment charge related to these assets in the periods presented.
Treasury
Stock
The
Company records treasury stock at the cost to acquire it and includes treasury stock as a component of shareholders’ equity.
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In
June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial
Instruments. This update requires immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses (“CECL”).
Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that
are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022
for public entities qualifying as smaller reporting companies. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact
of this update on the consolidated financial statements and does not expect a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Management
has evaluated other recently issued accounting pronouncements and does not believe that any of these pronouncements will have a significant
impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INVENTORY
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Inventory Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INVENTORY |
NOTE
2. INVENTORY
Inventory
consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF INVENTORY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Finished goods | |
$ | 2,352,330 | | |
$ | 159,808 | |
| Work-in-progress | |
| 1,791,311 | | |
| 1,203,204 | |
| Raw materials | |
| 5,407,075 | | |
| 5,378,158 | |
| Inventory, net | |
$ | 9,550,716 | | |
$ | 6,741,170 | |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for inventory. Includes, but is not limited to, the basis of stating inventory, the method of determining inventory cost, the classes of inventory, and the nature of the cost elements included in inventory. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//330/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
NOTE
3. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property
and equipment consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Land, building and improvements | |
$ | 10,768,181 | | |
$ | 5,456,524 | |
| Laboratory, manufacturing, warehouse and transportation equipment | |
| 13,364,512 | | |
| 13,017,731 | |
| Office equipment and software | |
| 395,563 | | |
| 373,601 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | |
| 484,237 | | |
| 453,701 | |
| Property and equipment, gross | |
| 25,012,493 | | |
| 19,301,557 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | |
| (14,586,335 | ) | |
| (13,348,565 | ) |
| Property and equipment, net | |
$ | 10,426,158 | | |
$ | 5,952,992 | |
Depreciation
expense was $1,237,770 and $1,194,939 for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//360/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-6
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INTANGIBLE ASSETS
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
NOTE
4. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The
following table summarizes the Company’s intangible assets:
SCHEDULE
OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS
| | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Impairment | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (176,645 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 289,039 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| (116,162 | ) | |
| — | | |
| 6,052,189 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (292,807 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,341,228 | |
| | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Reductions | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | * |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 465,684 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 6,168,351 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | |
| * | Patent
application costs were incurred in relation to the Company’s abuse deterrent opioid
technology. Amortization of the patent costs will begin upon the issuance of marketing authorization
by the FDA. Amortization will then be calculated on a straight-line basis through the expiry
of the related patent(s). |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//350/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
ACCRUED EXPENSES
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Payables and Accruals [Abstract] |
|
| ACCRUED EXPENSES |
NOTE
5. ACCRUED EXPENSES
As
of March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s accrued expenses consisted of the following:
SUMMARY
OF ACCRUED EXPENSES
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Salaries and fees payable in common stock | |
$ | 4,125,000 | | |
$ | 3,625,000 | |
| Income tax | |
| 414,989 | | |
| 414,989 | |
| Consultant contract fees | |
| 193,333 | | |
| 153,333 | |
| Audit fees | |
| 125,000 | | |
| 140,000 | |
| Director dues | |
| 70,000 | | |
| 90,000 | |
| Employee bonuses | |
| — | | |
| 143,000 | |
| Other accrued expenses | |
| 119,404 | | |
| 126,820 | |
| Total accrued expenses | |
$ | 5,047,726 | | |
$ | 4,693,142 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for accounts payable and accrued liabilities at the end of the reporting period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a),20,24)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
NJEDA BONDS
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| NJEDA BONDS |
NOTE
6. NJEDA BONDS
During
August 2005, the Company refinanced a bond issue occurring in 1999 through the issuance of Series A and B Notes tax-exempt bonds (the
“NJEDA Bonds” and/or “Bonds”). During July 2014, the Company retired all outstanding Series B Notes, at par,
along with all accrued interest due and owed.
In
relation to the Series A Notes, the Company is required to maintain a debt service reserve. The debt service reserve is classified as
restricted cash on the accompanying audited consolidated balance sheets. The NJEDA Bonds require the Company to make an annual principal
payment on September 1st based on the amount specified in the loan documents and semi-annual interest payments on March 1st and September
1st, equal to interest due on the outstanding principal. The annual interest rate on the Series A Note is 6.5%. The NJEDA Bonds are collateralized
by a first lien on the Company’s facility and equipment acquired with the proceeds of the original and refinanced bonds.
The
following tables summarize the Company’s bonds payable liability:
SCHEDULE
OF BONDS PAYABLE LIABILITY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Gross bonds payable | |
| | | |
| | |
| NJEDA Bonds - Series A Notes | |
$ | 1,245,000 | | |
$ | 1,360,000 | |
| Less: Current portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
| (125,000 | ) | |
| (115,000 | ) |
| Long-term portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
$ | 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Bond offering costs | |
$ | 354,454 | | |
$ | 354,454 | |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | |
| (249,294 | ) | |
| (235,124 | ) |
| Bond offering costs, net | |
$ | 105,160 | | |
$ | 119,330 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portions of bonds payable | |
$ | 125,000 | | |
$ | 115,000 | |
| Less: Bonds offering costs to be amortized in the next 12 months | |
| (14,178 | ) | |
| (14,178 | ) |
| Current portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 110,822 | | |
$ | 100,822 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable | |
| 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| Less: Bond offering costs to be amortized subsequent to the next 12 months | |
| (90,982 | ) | |
| (105,152 | ) |
| Long term portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 1,029,018 | | |
$ | 1,139,848 | |
Amortization
expense was $14,178
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022,
respectively. As of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022, interest payable was $6,744 and $7,367,
respectively. Interest expense was $6,744 and $7,367 for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Maturities
of bonds for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF MATURITIES OF BONDS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 125,000 | |
| 2025 | |
| 130,000 | |
| 2026 | |
| 140,000 | |
| 2027 | |
| 150,000 | |
| Thereafter | |
| 700,000 | |
| Total | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for information about short-term and long-term debt arrangements, which includes amounts of borrowings under each line of credit, note payable, commercial paper issue, bonds indenture, debenture issue, own-share lending arrangements and any other contractual agreement to repay funds, and about the underlying arrangements, rationale for a classification as long-term, including repayment terms, interest rates, collateral provided, restrictions on use of assets and activities, whether or not in compliance with debt covenants, and other matters important to users of the financial statements, such as the effects of refinancing and noncompliance with debt covenants. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//470/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
LOANS PAYABLE
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| LOANS PAYABLE |
NOTE
7. LOANS PAYABLE
On
April 2, 2022, the Company and Elite Labs entered into a Loan and Security Agreement (the “EWB Loan Agreement”) with East
West Bank (“EWB”). Pursuant to the EWB Loan Agreement, the Company and Elite Labs received one term loan for a principal
amount of $12,000,000 (the “EWB Term Loan”) and a revolving line of credit up to $2,000,000 (the “EWB Revolver,”
together with the “EWB Term Loan,” the EWB Loans”), each of which shall be used for working capital. The EWB Term Loan
bears interest at a rate of 9.73% (1.73% plus the prime rate (“Prime”)) and is repayable over five years, maturing on May
1, 2027. The EWB Revolver bears interest at a rate of (8.87% (0.87% plus Prime)) and matures on May 1, 2027. The total transaction costs
associated with the EWB Term Loan incurred as of March 31, 2023, were $40,120, which are being amortized on a monthly basis over five years,
beginning in April 2022. The EWB Loans are secured by a security interest in the personal property of the Company and Elite Labs. The
EWB Loan Agreement contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants include, but are not limited to, maintaining
maximum leverage ratios of 3.50 to 1.00, minimum liquidity of $5,000,000, minimum cash of $1,000,000, a fixed charge coverage ratio of
1.25 to 1.00 and restrictions on mergers or sales of assets and debt borrowings. As of March 31, 2023, the principal and interest
on the EWB Term Loan has been paid in full by the Company and the EWB Loan Agreement is terminated.
In place of the EWB Term Loan, the Company has entered into a collateralized promissory note with individual lenders
with rates comparable to the EWB Term Loan but with less restrictive covenants (a “Promissory Note”). As of June 2, 2023,
a Promissory Note was placed with Nasrat Hakim, CEO and Chairman of the Board of Directors, for $3,000,000. The Promissory Note has an
interest rate of 9% for the first year and 10% for an optional second year and the proceeds will be used for working capital and other
business purposes.
On
July 1, 2022, the EWB provided a mortgage loan (“EWB Mortgage Loan”) in the amount of $2.55 million for the purchase of the
property at 135-137 Ludlow Avenue, which was formerly a lease held by the Company. The EWB Mortgage Loan matures in 10 years and bears
interest at a rate of 4.75% fixed for 5 years then adjustable at WSJP plus 0.5% with floor rate of 4.5%. The total transaction costs
associated with the EWB Mortgage Loan incurred as of March 31, 2023, were $13,251, which are being amortized on a monthly basis over
ten years, beginning in July 2022. The EWB Mortgage Loan contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants
include maintaining a minimum debt coverage ratio of 1.50 to 1.00 tested annually and a minimum trailing 12-month debt coverage ratio
of 1.50 to 1.00. As of March 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with each financial covenant.
Loans
payable consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF LOANS PAYABLE
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Mortgage loan payable 4.75% interest and maturing June 2032 | |
$ | 2,472,923 | | |
$ | — | |
| Equipment and insurance financing loans payable, between 7.10% and 12.02% interest and maturing between September 2023 and October 2025 | |
| 259,611 | | |
| 502,052 | |
| Less: Current portion of loans payable | |
| (200,032 | ) | |
| (253,006 | ) |
| Long-term portion of loans payable | |
$ | 2,532,502 | | |
$ | 249,046 | |
The
interest expense associated with the loans and mortgage payable was $1,013,874
and $62,845
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Loan
and mortgage principal payments for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF LOAN PRINCIPAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 200,032 | |
| 2025 | |
| 182,181 | |
| 2026 | |
| 115,330 | |
| 2027 | |
| 86,064 | |
| 2028 and thereafter | |
| 2,148,927 | |
| Total | |
$ | 2,732,534 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//470/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
DEFERRED REVENUE
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Deferred Revenue |
|
| DEFERRED REVENUE |
NOTE
8. DEFERRED REVENUE
Deferred
revenues in the aggregate amount of $32,223 as of March 31, 2023, were comprised of a current component of $13,333 and a long-term component
of $18,890. Deferred revenues in the aggregate amount of $45,559 as of March 31, 2022, were comprised of a current component of $13,333
and a long-term component of $32,226. These line items represent the unamortized amounts of a $200,000 advance payment received for a
TAGI Pharma (“TAGI”) licensing agreement with a fifteen-year term beginning in September 2010 and ending in August 2025.
These advance payments were recorded as deferred revenue when received and are earned, on a straight-line basis over the life of the
licenses. The current component is equal to the amount of revenue to be earned during the 12-month period immediately subsequent to the
balance sheet date and the long-term component is equal to the amount of revenue to be earned thereafter.
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred revenues disclosure [Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_DeferredRevenuesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_DisclosureDeferredRevenueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
NOTE
9. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s condensed
consolidated financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series
of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
Operating
Leases
The
Company entered into an operating lease for a portion of a one-story warehouse, located at 135 Ludlow Avenue, Northvale, New Jersey (the
“135 Ludlow Ave. lease”). The 135 Ludlow Ave. lease is for approximately 15,000 square feet of floor space and began on July
1, 2010. During July 2014, the Company modified the 135 Ludlow Ave. lease in which the Company was permitted to occupy the entire 35,000
square feet of floor space in the building (“135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease”).
The
135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease includes an initial term, which expired on December 31, 2016 with two tenant renewal options of five years
each, at the sole discretion of the Company. On June 22, 2016, the Company exercised the first of these renewal options, with such option
including a term that begins on January 1, 2017 and expires on December 31, 2021. On June 30, 2021, the Company exercised the second
of the renewal options, with such option including a term that begins on January 1, 2022 and expires on December 31, 2026.
The
135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease property required significant leasehold improvements and qualifications, as a prerequisite, for its intended
future use. Manufacturing, packaging, warehousing and regulatory activities are currently conducted at this location. The Ludlow Ave.
lease was terminated on July 1, 2022, when the Company purchased the underlying property.
In
October 2020, the Company entered into an operating lease for office space in Pompano Beach, Florida (the “Pompano Office Lease”).
The Pompano Office Lease is for approximately 1,275 square feet of office space, with Elite taking occupancy on November 1, 2020. The
Pompano Office includes a 3 month abatement from November 2020 through February 2021 and has a term of three years, ending on October
31, 2023.
The
Company assesses whether an arrangement is a lease or contains a lease at inception. For arrangements considered leases or that contain
a lease that is accounted for separately, the Company determines the classification and initial measurement of the right-of-use asset
and lease liability at the lease commencement date, which is the date that the underlying asset becomes available for use. The Company
has elected to account for non-lease components associated with its leases and lease components as a single lease component.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
Company recognizes a right-of-use asset, which represents the Company’s right to use the underlying asset for the lease term, and
a lease liability, which represents the present value of the Company’s obligation to make payments arising over the lease term.
The present value of the lease payments is calculated using either the implicit interest rate in the lease or an incremental borrowing
rate.
Lease
assets and liabilities are classified as follows on the condensed consolidated balance sheet:
SCHEDULE
OF LEASE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| Lease | |
Classification | | |
As of March 31, 2023 | |
| Assets | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Operating lease – right-of-use asset | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| Total leased assets | |
| | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long-term | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease, net of current portion | | |
| — | |
| Total lease liabilities | |
| | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
Rent
expense is recorded on the straight-line basis. Rent expense under the 135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease for the years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022 was $58,248 and $229,563, respectively. Rent expense under the Pompano Office Lease for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022
was $25,638 and $23,430, respectively. Rent expense is recorded in general and administrative expense in the audited consolidated statements
of operations.
The
table below shows the future minimum rental payments, exclusive of taxes, insurance and other costs, under the Pompano Office Lease:
SCHEDULE
OF FUTURE MINIMUM RENTAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 15,214 | |
| 2025 | |
| — | |
| 2026 | |
| — | |
| 2027 | |
| — | |
| Thereafter | |
| — | |
| Total future minimum lease payments | |
| 15,214 | |
| Less: interest | |
| (300 | ) |
| Present value of lease payments | |
$ | 14,914 | |
The
weighted-average remaining lease term and the weighted-average discount rate of our lease was as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF WEIGHTED-AVERAGE REMAINING LEASE TERM AND THE WEIGHTED-AVERAGE DISCOUNT RATE
| Lease Term and Discount Rate | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| Remaining lease term (years) | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 0.6 | |
| | |
| | |
| Discount rate | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 6 | % |
The
Company has an obligation for the restoration of its leased facility and the removal or dismantlement of certain property and equipment
as a result of its business operation in accordance with ASC 410, Asset Retirement and Environmental Obligations – Asset Retirement
Obligations. The Company records the fair value of the asset retirement obligation in the period in which it is incurred. The Company
increases, annually, the liability related to this obligation. The liability is accreted to its present value each period and the capitalized
cost is depreciated over the useful life of the related asset. Upon settlement of the liability, the Company records either a gain or
loss. As of March 31, 2023, and March 31, 2022, the Company had a liability of $0 and $38,780, respectively, recorded as a component
of other long-term liabilities.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//450/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480327/954-440-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
PREFERRED STOCK
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Equity [Abstract] |
|
| PREFERRED STOCK |
NOTE
10. PREFERRED STOCK
Series
J convertible preferred stock
On
April 28, 2017, the Company created the Series J Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series J Preferred”) in conjunction with the
Certificate of Designations (“Series J COD”). A total of 50 shares of Series J Preferred were authorized, zero shares are
issued and outstanding, with a stated value of $1,000,000 per share and a par value of $0.01 as of March 31, 2023.
On
April 27, 2017, a total of 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred were issued pursuant to an exchange agreement (the “Exchange Agreement”)
with Hakim, a related party and the Company’s President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors. The Exchange
Agreement provided for Hakim to exchange 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock for 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred and warrants to
purchase 79,008,661 shares of Common Stock at $0.1521 per share. The aggregate stated value of the Series J Preferred issued was equal
to the aggregate value of the shares of Common Stock exchanged, with such value of each share of Common Stock exchanged being equal to
the closing price of the Common Stock on April 27, 2017. In connection with the Exchange Agreement, the Company also issued warrants
to purchase 79,008,661 shares of Common Stock at $0.1521 per share, and such warrants are classified as liabilities on the accompanying
audited consolidated balance sheet as of March 31, 2023 (See Note 11).
An
amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of shares of Common Stock the Company is authorized
to issue from 995,000,000 shares to 1,445,000,000 shares was approved at the Company’s Annual Meeting of Shareholders held on December
4, 2019. Prior to the approval of the increase in the number of authorized shares, there were insufficient authorized shares if the Series
J Preferred Stock were converted. As a result, the shares were classified in mezzanine equity. After the approval of the increase in
the number of authorized shares, there are now sufficient authorized shares in the event of a full conversion of Series J Preferred Stock.
With the approval of the increase in the number of authorized shares, there is no longer the presumption that a cash settlement will
be required. Therefore, the Series J Preferred was reclassified from mezzanine equity to permanent equity at its carrying amount of $13,903,960
on the consolidated balance sheets as of March 31, 2023 and 2022.
On
June 23, 2020, the Company held a Special Meeting of Shareholders, with such including a proposal for shareholders to again vote on the
above referenced amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation. This proposal was also passed by shareholder vote.
On
August 24, 2020, Hakim converted the 24.0344 shares of Series J Preferred into 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock at a conversion price
of $0.1521 per share.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for terms, amounts, nature of changes, rights and privileges, dividends, and other matters related to preferred stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//505/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Derivative Financial Instruments Warrants |
|
| DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS |
NOTE
11. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS
The
Company evaluates and accounts for its freestanding instruments in accordance with ASC 815, Accounting for Derivative Instruments
and Hedging Activities.
The
Company issued warrants, with a term of ten years, to affiliates in connection with an exchange agreement dated April 28, 2017, as further
described in this note below.
The
Company has 79,008,661 total warrant shares outstanding with a weighted average exercise price of $0.1521 as of March 31, 2023 and 2022.
On
April 28, 2017, the Company entered into an Exchange Agreement with Hakim, the Chairman of the Board, President, and Chief Executive
Officer of the Company, pursuant to which the Company issued to Hakim 24.0344 shares of its Series J Preferred and warrants to purchase
an aggregate of 79,008,661 shares of its Common Stock (the “Series J Warrants” and, along with the Series J Preferred issued
to Hakim, the “Securities”) in exchange for 158,017,321 shares of Common Stock owned by Hakim. The fair value of the Series
J Warrants was determined to be $6,474,674 upon issuance at April 28, 2017.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
Series J Warrants are exercisable for a period of 10 years from the date of issuance, commencing April 28, 2020. The initial exercise
price is $0.1521 per share and the Series J Warrants can be exercised for cash or on a cashless basis. The exercise price is subject
to adjustment for any issuances or deemed issuances of Common Stock or Common Stock equivalents at an effective price below the then
exercise price. Such exercise price adjustment feature prohibits the Company from being able to conclude the warrants are indexed to
its own stock and thus such warrants are classified as liabilities and measured initially and subsequently at fair value. The Series
J Warrants also provide for other standard adjustments upon the happening of certain customary events.
The
fair value of the Series J Warrants was calculated using a Black-Scholes model instead of a Monte Carlo Simulation because the probability
with the shareholder approval provisions was no longer a factor. The following assumptions were used in the Black-Scholes model to calculate
the fair value of the Series J Warrants:
SCHEDULE
OF FAIR VALUE OF WARRANTS ISSUED
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Fair value of the Company’s Common Stock | |
$ | 0.0290 | | |
$ | 0.0350 | |
| Volatility | |
| 74.37 | % | |
| 76.55 | % |
| Initial exercise price | |
$ | 0.1521 | | |
$ | 0.1521 | |
| Warrant term (in years) | |
| 4.1 | | |
| 5.1 | |
| Risk free rate | |
| 3.55 | % | |
| 2.40 | % |
The
changes in warrants (Level 3 financial instruments) measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the year ended March 31, 2023 were
as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF CHANGES IN WARRANTS MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| Balance at March 31, 2021 | |
$ | 2,362,246 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2022 | |
$ | 936,837 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (415,126 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | |
$ | 521,711 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDerivative Financial Instruments Warrants [Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_DerivativeFinancialInstrumentsWarrantsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_DisclosureDerivativeFinancialInstrumentsWarrantsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Equity [Abstract] |
|
| SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
NOTE
12. SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Lincoln
Park Capital Transaction - July 8, 2020 Purchase Agreement
On
July 8, 2020, the Company entered into a purchase agreement (the “2020 LPC Purchase Agreement”), and a registration rights
agreement (the “2020 LPC Registration Rights Agreement”), with Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”),
pursuant to which Lincoln Park has committed to purchase up to $25.0 million of the Company’s Common Stock, $0.001 par value per
share, from time to time over the term of the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement, at the Company’s direction.
The
Company did not issue any shares of its Common Stock pursuant to the 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement during the years ended March 31,
2023 and 2022. In addition, there were no shares issued to Lincoln Park as additional commitment shares, pursuant to the 2020 LPC
Agreement. The 2020 LPC Purchase Agreement will expire on August 1, 2023.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Summary
of Common Stock Activity
During
the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company issued 2,633,093 and 2,105,236 shares of Common Stock, respectively, with such issuances
of Common Stock being summarized as follows:
SCHEDULE OF COMMON STOCK ACTIVITY
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively | |
| 1,011,381,988 | | |
| 1,009,276,752 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting fees | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| Common Stock issued during the fiscal year | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 1,014,015,081 | | |
| 1,011,381,988 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-6
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480237/815-40-50-6
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(e)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//505/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 16
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-16
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityNoteDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION |
NOTE
13. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
Part
of the compensation paid by the Company to its Directors and employees consists of the issuance of Common Stock or via the granting of
options to purchase Common Stock.
Stock-based
Director Compensation
The
Company’s Director compensation policy, instituted in October 2009 and further revised in January 2016, includes provisions that
a portion of director’s fees are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s Common Stock, in lieu of cash, with
the valuation of such shares being calculated on quarterly basis and equal to the average closing price of the Company’s Common
Stock.
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company accrued director’s fees totaling $90,000, which will be paid via cash payments totaling
$30,000 and the issuance of 1,753,686 shares of Common Stock.
Stock-based
Employee/Consultant Compensation
Employment
contracts with the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees and engagement contracts with certain
consultants include provisions for a portion of each employee’s salaries or consultant’s fees to be paid via the issuance
of shares of the Company’s Common Stock, in lieu of cash, with the valuation of such shares being calculated on a quarterly basis
and equal to the average closing price of the Company’s Common Stock.
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company accrued salaries totaling $540,000 owed
to the Company’s President, Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees which will be paid via the issuance of 14,956,851 shares
of Common Stock. As of March 31, 2023, the Company owed its President, Chief Executive Officer and certain other employees’
salaries totaling $4,335,000 which
will be paid via the issuance of 68,264,667 shares
of Common Stock.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Options
Under
its 2014 Stock Option Plan and prior options plans, the Company may grant stock options to officers, selected employees, as well as members
of the Board of Directors and advisory board members. All options have generally been granted at a price equal to or greater than the
fair market value of the Company’s Common Stock at the date of the grant. Generally, options are granted with a vesting period
of up to three years and expire ten years from the date of grant. A summary of the activity of Company’s 2014 Stock Option Plan
for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
SCHEDULE OF STOCK OPTION PLAN
| | |
Shares Underlying Options | | |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | | |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years) | | |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2021 | |
| 5,900,000 | | |
$ | 0.13 | | |
| 3.7 | | |
$ | 6,000 | |
| Granted | |
| 500,000 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (750,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2022 | |
| 5,650,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.8 | | |
$ | — | |
| Granted | |
| 15,530,000 | | |
$ | 0.03 | | |
| 10.0 | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (5,810,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | |
| 15,370,000 | | |
$ | 0.07 | | |
| 7.4 | | |
$ | — | |
| Exercisable at March 31, 2023 | |
| 4,182,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.2 | | |
$ | — | |
The
aggregate intrinsic value for outstanding options is calculated as the difference between the exercise price of the underlying awards
and the quoted price of the Company’s Common Stock as of March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 of $0.03 and $0.03, respectively. As
of March 31, 2023, there was $205,340 in unrecognized stock-based compensation expense that will be recognized over a 1.5 year period.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//718/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfCompensationRelatedCostsShareBasedPaymentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
CONCENTRATIONS AND CREDIT RISK
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Risks and Uncertainties [Abstract] |
|
| CONCENTRATIONS AND CREDIT RISK |
NOTE
14. CONCENTRATIONS AND CREDIT RISK
Revenues
Two
customers accounted for approximately 96% of the Company’s revenues for the year ended March 31, 2023. These two customers accounted
for approximately 85% and 11% of revenues each, respectively.
Two
customers accounted for approximately 95% of the Company’s revenues for the year ended March 31, 2022. These two customers accounted
for approximately 84% and 11% of revenues each, respectively.
Accounts
Receivable
One
customer accounted for approximately 96% of the Company’s accounts receivable as of March 31, 2023.
Two
customers accounted for approximately 91% of the Company’s accounts receivable as of March 31, 2022. These two customers accounted
for approximately 78% and 13% of accounts receivable each, respectively.
Purchasing
One
supplier accounted for approximately 34% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for the year ended March 31, 2023.
Four
suppliers accounted for more than 69% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for the year ended March 31, 2022. These four
suppliers accounted for approximately 51%, 7%, 6%, and 5% of purchases each, respectively.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for any concentrations existing at the date of the financial statements that make an entity vulnerable to a reasonably possible, near-term, severe impact. This disclosure informs financial statement users about the general nature of the risk associated with the concentration, and may indicate the percentage of concentration risk as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 275
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//275/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RisksAndUncertaintiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SEGMENT RESULTS
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| SEGMENT RESULTS |
NOTE
15. SEGMENT RESULTS
FASB
ASC 280-10-50 requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach is based on
the way a company’s management organized segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance.
Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which
management disaggregates a company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are ANDAs for generic products and NDAs for branded products. The Company identified
its reporting segments based on the marketing authorization relating to each and the financial information used by its chief operating
decision maker to make decisions regarding the allocation of resources to and the financial performance of the reporting segments.
Asset
information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating decision maker does not review this information by
segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation of the Company’s audited consolidated
financial statements.
The
following represents selected information for the Company’s reportable segments:
SCHEDULE OF SELECTED INFORMATION FOR REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
| | | |
| | |
| ANDA | |
| 10,393,857 | | |
| 10,744,005 | |
| NDA | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
The
table below reconciles the Company’s operating income by segment to income from operations before provision for income taxes as
reported in the Company’s audited consolidated statement of operations:
SCHEDULE
OF OPERATING INCOME BY SEGMENT TO INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating income by segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
| Corporate unallocated costs | |
| (3,581,468 | ) | |
| (3,696,881 | ) |
| Interest income | |
| 7,453 | | |
| 126 | |
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs | |
| (1,112,707 | ) | |
| (191,816 | ) |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| (292,807 | ) | |
| — | |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | |
| (1,263,452 | ) | |
| (1,194,939 | ) |
| Significant non-cash items | |
| (580,128 | ) | |
| (781,475 | ) |
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments | |
| 415,126 | | |
| 1,425,409 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for reporting segments including data and tables. Reportable segments include those that meet any of the following quantitative thresholds a) it's reported revenue, including sales to external customers and intersegment sales or transfers is 10 percent or more of the combined revenue, internal and external, of all operating segments b) the absolute amount of its reported profit or loss is 10 percent or more of the greater, in absolute amount of 1) the combined reported profit of all operating segments that did not report a loss or 2) the combined reported loss of all operating segments that did report a loss c) its assets are 10 percent or more of the combined assets of all operating segments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//280/tableOfContent
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 26
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-26
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 34
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-34
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
RELATED PARTY AGREEMENTS WITH MIKAH PHARMA, LLC
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Related Party Transactions [Abstract] |
|
| RELATED PARTY AGREEMENTS WITH MIKAH PHARMA, LLC |
NOTE
16. RELATED PARTY AGREEMENTS WITH MIKAH PHARMA, LLC
In
May 2020, Praxgen, pursuant to an asset purchase agreement, assigned its rights and obligations under the Praxgen Agreement for Amphetamine
IR and Amphetamine ER to Mikah Pharma LLC (“Mikah”). The ANDAs for Amphetamine IR and Amphetamine ER are now registered under
Elite’s name. Mikah will now be Elite’s partner with respect to Amphetamine IR and ER and will assume all the rights and
obligations for these products from Praxgen. Mikah was founded in 2009 by Nasrat Hakim, a related party and the Company’s President,
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board.
In
June 2021, the Company entered into a development and license agreement with Mikah, pursuant to which Mikah will engage in the research,
development, sales and licensing of generic pharmaceutical products. In addition, Mikah will collaborate to develop and commercialize
generic products including formulation development, analytical method development, manufacturing, sales and marketing of generic products.
Initially two generic products were identified for the parties to develop.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for related party transactions. Examples of related party transactions include transactions between (a) a parent company and its subsidiary; (b) subsidiaries of a common parent; (c) and entity and its principal owners; and (d) affiliates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(g)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(e))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//850/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-6
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RelatedPartyTransactionsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INCOME TAXES
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INCOME TAXES |
NOTE
17. INCOME TAXES
The
components of the income taxes benefit (expense) are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF COMPONENTS OF INCOME TAXES BENEFIT (EXPENSE)
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
$ | 784,577 | | |
$ | 1,160,715 | |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| 2,171,821 | |
| Benefit of net operating loss carryforward | |
| (784,577 | ) | |
| (1,160,715 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| (424,028 | ) | |
| (435,384 | ) |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | |
$ | (424,028 | ) | |
$ | 1,736,437 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
| Net benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
The
major components of deferred tax assets and liabilities as of March 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows (amounts in thousands of dollars):
SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | 17,613 | | |
$ | 21,180 | |
| Tax credits | |
| 4,993 | | |
| 4,764 | |
| Valuation allowance | |
| (20,434 | ) | |
| (23,772 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and liabilities | |
$ | 2,172 | | |
$ | 2,172 | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 747 | |
| Valuation Allowance | |
| — | | |
| (747 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and
liabilities | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
At
March 31, 2023 and 2022, a 90%
and 90% valuation allowance is provided, respectively, as it is uncertain if the deferred tax assets will provide total future
benefits because of the uncertainty about the Company’s ability to generate the future taxable income necessary to use the net
operating loss carry forwards.
The
company believes that temporary timing differences between accrual and payment of income taxes are not material to the financial position
of the Company.
As
of March 31, 2023, Elite has a federal net operating loss carry forward of $83.9 million,
which have not expired. During 2022, the Company was able to release a portion of its valuation allowance as it determined future
profits will offset a portion of its valuation allowance. During 2022, the Company recorded a tax benefit of $2.2 million
as a result of this change in judgment. There is no change in the net deferred tax asset for 2023. Absent the above mentioned
allowance, at March 31, 2023, the Company’s federal and state income taxes due were $0.0 million
and $0.4 million,
respectively.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income taxes. Disclosures may include net deferred tax liability or asset recognized in an enterprise's statement of financial position, net change during the year in the total valuation allowance, approximate tax effect of each type of temporary difference and carryforward that gives rise to a significant portion of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets, utilization of a tax carryback, and tax uncertainties information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//740/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482526/740-270-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Principles of Consolidation |
Principles
of Consolidation
The
accompanying audited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
in the United States (“GAAP”). The audited consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its
wholly-owned subsidiary, Elite Labs. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
|
| Segment Information |
Segment
Information
Financial
Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification 280 (“ASC 280”), Segment Reporting,
establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise
about which separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making
group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance.
The
Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive Officer, who reviews the financial performance and the results
of operations of the segments prepared in accordance with GAAP when making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance
of the Company.
The
Company has determined that its reportable segments are products whose marketing approvals were secured via an Abbreviated New Drug Applications
(“ANDA”) and products whose marketing approvals were secured via a New Drug Application (“NDA”). ANDA products
are referred to as generic pharmaceuticals and NDA products are referred to as branded pharmaceuticals.
There
are currently no intersegment revenues. Asset information by operating segment is not presented below since the chief operating decision
maker does not review this information by segment. The reporting segments follow the same accounting policies used in the preparation
of the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements. Please see Note 15 for further details.
|
| Revenue Recognition |
Revenue
Recognition
The
Company generates revenue from manufacturing and licensing fees and direct sales to pharmaceutical distributors for pharmacies and institutions. Manufacturing fees include the development of pain management
products, manufacturing of a line of generic pharmaceutical products with approved ANDA, through the manufacture of formulations and
the development of new products. Licensing fees include the commercialization of products either by license and the collection of royalties,
or the expansion of licensing agreements with other pharmaceutical companies, including co-development projects, joint ventures and other
collaborations.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Under
ASC 606, Revenue from Contacts with Customers (“ASC 606”), the Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains
control of promised goods or services, in an amount that reflects the consideration which is expected to be received in exchange for
those goods or services. The Company recognizes revenues following the five-step model prescribed under ASC 606: (i) identify contract(s)
with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligation(s) in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the
transaction price to the performance obligation(s) in the contract; and (v) recognize revenues when (or as) the Company satisfies a performance
obligation. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the entity will collect the consideration
it is entitled to in exchange for the goods or services it transfers to the customer. At contract inception, once the contract is determined
to be within the scope of ASC 606, the Company assesses the goods or services promised within each contract and determines those that
are performance obligations and assesses whether each promised good or service is distinct. The Company then recognizes as revenue the
amount of the transaction price that is allocated to the respective performance obligation when (or as) the performance obligation is
satisfied. Sales, value add, and other taxes collected on behalf of third parties are excluded from revenue.
|
| Nature of goods and services |
Nature
of goods and services
The
following is a description of the Company’s goods and services from which the Company generates revenue, as well as the nature,
timing of satisfaction of performance obligations, and significant payment terms for each, as applicable:
a)
Manufacturing Fees
The
Company is equipped to manufacture controlled-release products on a contract basis for third parties, if, and when, the products are
approved. These products include products using controlled-release drug technology. The Company also develops and markets (either on
its own or by license to other companies) generic and proprietary controlled-release pharmaceutical products.
The
Company recognizes revenue when the customer obtains control of the Company’s product based on the contractual shipping terms of
the contract. The Company is primarily responsible for fulfilling the promise to provide the product, is responsible to ensure that the
product is produced in accordance with the related supply agreement and bears risk of loss while the inventory is in-transit to the commercial
partner. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring products to a
customer.
b)
License Fees
The
Company enters into licensing and development agreements, which may include multiple revenue generating activities, including milestones
payments, licensing fees, product sales and services. The Company analyzes each element of its licensing and development agreements in
accordance with ASC 606 to determine appropriate revenue recognition. The terms of the license agreement may include payment to the Company
of licensing fees, non-refundable upfront license fees, milestone payments if specified objectives are achieved, and/or royalties on
product sales.
If
the contract contains a single performance obligation, the entire transaction price is allocated to the single performance obligation.
Contracts that contain multiple performance obligations require an allocation of the transaction price based on the estimated relative
standalone selling prices of the promised products or services underlying each performance obligation. The Company determines standalone
selling prices based on the price at which the performance obligation is sold separately. If the standalone selling price is not observable
through past transactions, the Company estimates the standalone selling price taking into account available information such as market
conditions and internally approved pricing guidelines related to the performance obligations.
The
Company recognizes revenue from non-refundable upfront payments at a point in time, typically upon fulfilling the delivery of the associated
intellectual property to the customer. For those milestone payments which are contingent on the occurrence of particular future events
(for example, payments due upon a product receiving FDA approval), the Company determined that these need to be considered for inclusion
in the calculation of total consideration from the contract as a component of variable consideration using the most-likely amount method.
As such, the Company assesses each milestone to determine the probability and substance behind achieving each milestone. Given the inherent
uncertainty of the occurrence of future events, the Company will recognize revenue from the milestone when there is not a high probability
of a reversal of revenue, which typically occurs near or upon achievement of the event.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Significant
management judgment is required to determine the level of effort required under an arrangement and the period over which the Company
expects to complete its performance obligations under the arrangement. If the Company cannot reasonably estimate when its performance
obligations either are completed or become inconsequential, then revenue recognition is deferred until the Company can reasonably make
such estimates. Revenue is then recognized over the remaining estimated period of performance using the cumulative catch-up method.
When
determining the transaction price of a contract, an adjustment is made if payment from a customer occurs either significantly before
or significantly after performance, resulting in a significant financing component. Applying the practical expedient in ASC 606-10-32-18,
the Company does not assess whether a significant financing component exists if the period between when the Company performs its obligations
under the contract and when the customer pays is one year or less. None of the Company’s contracts contained a significant financing
component as of March 31, 2023.
In
accordance with ASC 606-10-55-65, royalties are recognized when the subsequent sale of the customer’s products occurs.
c)
Direct Sales
The
Company will begin direct sales of products under the Company’s own label beginning on April 1, 2023. License agreements will remain
in place for select products. With this transition, however, a large portion of the manufacturing and license fees now reported will
be replaced with revenues from direct sales of pharmaceutical products to distributors for pharmacies and institutions.
|
| Disaggregation of revenue |
Disaggregation
of revenue
In
the following table, revenue is disaggregated by type of revenue generated by the Company. The table also includes a reconciliation of
the disaggregated revenue with the reportable segments:
SCHEDULE
OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| NDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Licensing fees | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
| Total NDA revenue | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| ANDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | |
| Total ANDA revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | |
| Total revenue | |
$ | 34,155,114 | | |
$ | 32,262,117 | |
Selected
information on reportable segments and reconciliation of operating income by segment to income (loss) from operations before income taxes
are disclosed within Note 15.
|
| Cash |
Cash
The
Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash
equivalents consist of cash on deposit with banks and money market instruments. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents with
high-quality, U.S. financial institutions and, to date has not experienced losses on any of its balances.
|
| Restricted Cash |
Restricted
Cash
As
of March 31, 2023, and March 31, 2022, the Company had $412,434 and $405,039, of restricted cash, respectively, related to debt service
reserve in regard to the New Jersey Economic Development Authority (“NJEDA”) bonds (see Note 5).
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| Accounts Receivable |
Accounts
Receivable
Accounts
receivable are comprised of balances due from customers, net of estimated allowances for uncollectible accounts. In determining collectability,
historical trends are evaluated, and specific customer issues are reviewed on a periodic basis to arrive at appropriate allowances.
|
| Inventory |
Inventory
Inventory
is recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value on specific identification by lot number basis.
|
| Long-Lived Assets |
Long-Lived
Assets
The
Company periodically evaluates the fair value of long-lived assets, which include property and equipment and intangibles, whenever events
or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
Property
and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is provided on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the respective
assets which range from three to forty years. Major repairs or improvements are capitalized. Minor replacements and maintenance and repairs
which do not improve or extend asset lives are expensed currently.
Upon
retirement or other disposition of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and the resulting
gain or loss, if any, is recognized in income.
|
| Intangible Assets |
Intangible
Assets
The
Company capitalizes certain costs to acquire intangible assets; if such assets are determined to have a finite useful life they are amortized
on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life. Costs to acquire indefinite lived intangible assets, such as costs related to
ANDAs and patents are capitalized accordingly.
The
Company tests its intangible assets for impairment at least annually (as of March 31st) and whenever events or circumstances change that
indicate impairment may have occurred. A significant amount of judgment is involved in determining if an indicator of impairment has
occurred. Such indicators may include, among others and without limitation: a significant decline in the Company’s expected future
cash flows; a sustained, significant decline in the Company’s stock price and market capitalization; a significant adverse change
in legal factors or in the business climate of the Company’s segments; unanticipated competition; and slower growth rates.
For
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company determined indicators of impairment have occurred and recorded impairment expense of $292,807 on its ANDAs and patents.
Please
also see Note 4 for further details on intangible assets.
|
| Research and Development |
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenditures are charged to expense as incurred.
|
| Contingencies |
Contingencies
Occasionally,
the Company may be involved in claims and legal proceedings arising from the ordinary course of its business. The Company records a provision
for a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred, and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
If these estimates and assumptions change or prove to be incorrect, it could have a material impact on the Company’s condensed
consolidated financial statements. Contingencies are inherently unpredictable, and the assessments of the value can involve a series
of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| Income Taxes |
Income
Taxes
Income
taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which
those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Where applicable, the Company records a valuation allowance to reduce
any deferred tax assets that it determines will not be realizable in the future.
The
Company recognizes the benefit of an uncertain tax position that it has taken or expects to take on income tax returns it files if such
tax position is more likely than not to be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position.
These tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate resolution.
The
Company operates in multiple tax jurisdictions within the United States of America. The Company remains subject to examination in
all tax jurisdiction until the applicable statutes of limitation expire. As of March 31, 2023, a summary of the tax years that
remain subject to examination in our major tax jurisdictions are: United States – Federal, 2019 and forward, and State, 2016
and forward. The Company did not record unrecognized tax positions for the years ended March 31, 2023
and 2022.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| Warrants and Preferred Shares |
Warrants
and Preferred Shares
The
accounting treatment of warrants and preferred share series issued is determined pursuant to the guidance provided by ASC 470, Debt,
ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, as applicable. Each feature of a
freestanding financial instrument including, without limitation, any rights relating to subsequent dilutive issuances, dividend issuances,
equity sales, rights offerings, forced conversions, optional redemptions, automatic monthly conversions, dividends and exercise is assessed
with determinations made regarding the proper classification in the Company’s financial statements.
|
| Stock-Based Compensation |
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation. Under the fair value
recognition provisions, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized
as an expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, based on the terms of the awards. The cost of the stock-based
payments to nonemployees that are fully vested and non-forfeitable as at the grant date is measured and recognized at that date, unless
there is a contractual term for services in which case such compensation would be amortized over the contractual term.
In
accordance with the Company’s Director compensation policy and certain employment contracts, director’s fees and a portion
of employee’s salaries are to be paid via the issuance of shares of the Company’s Common Stock (“Common Stock”),
in lieu of cash, with the valuation of such share being calculated on a quarterly basis and equal to the average closing price of the
Company’s Common Stock.
|
| Sale of ANDA |
Sale
of ANDA
During
the year ended March 31, 2023, the Company entered into an agreement with Pyros Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Pyros”) pursuant
to which the Company sold to Pyros its rights in and to the Company’s approved abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) for its
generic Sabril drug. The Company sold such rights to Pyros for $1,000,000, which was recorded as gain on sale of ANDA during the year
ended March 31, 2023. There is no further action required by the Company regarding the rights which would affect future periods.
In
conjunction with the sale of its Product to Pyros, the Company executed a Manufacturing and Supply agreement (the “Pyros Agreement”)
with Pyros. Under the terms of the Pyros Agreement, the Company will receive an agreed-upon price per drug for the manufacturing and
packaging of Sabril over a term of three years. Revenue per the Pyros Agreement will be recognized as control of the manufactured and
supplied drugs is transferred to Pyros (at the time of delivery).
|
| Earnings Per Share Attributable to Common Shareholders |
Earnings
Per Share Attributable to Common Shareholders’
The
Company follows ASC 260, Earnings Per Share, which requires presentation of basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”)
on the face of the income statement for all entities with complex capital structures and requires a reconciliation of the numerator and
denominator of the basic EPS computation to the numerator and denominator of the diluted EPS computation. In the accompanying financial
statements, basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding
during the period. The computation of diluted net income per share does not include the conversion of securities that would have an antidilutive
effect.
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The
following is the computation of earnings per share applicable to common shareholders for the periods indicated:
SCHEDULE
OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Numerator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| Effect of dilutive instrument on net income | |
| (415,126 | ) | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Net income - diluted | |
$ | 3,146,720 | | |
$ | 7,472,836 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Denominator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - basic | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options and convertible securities | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - diluted | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income per share | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| Diluted | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
|
| Fair Value of Financial Instruments |
Fair
Value of Financial Instruments
ASC
820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”) provides a framework for measuring fair value in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles.
ASC
820 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between (1) market
participant assumptions developed based on market data obtained from independent sources (observable inputs) and (2) an entity’s
own assumptions about market participant assumptions developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (unobservable
inputs).
The
fair value hierarchy consists of three broad levels, which gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). The three levels of the fair value
hierarchy under ASC 820 are described as follows:
| ● | Level
1 – Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
that are accessible at the measurement date. |
| ● | Level
2 – Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for
the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs include quoted prices
for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar
assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that
are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived principally from or
corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
| ● | Level
3 – Inputs that are unobservable for the asset or liability. |
ELITE
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Measured
on a Recurring Basis
The
following table presents information about our liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, aggregated by the level in the
fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fell:
SCHEDULE
OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| | |
| | |
Fair Value Measurement Using | |
| | |
Amount at Fair Value | | |
Level 1 | | |
Level 2 | | |
Level 3 | |
| March 31, 2023 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 521,711 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 521,711 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| March 31, 2022 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 936,837 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 936,837 | |
See
Note 11 for specific inputs used in determining fair value.
The
carrying amounts of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities, such as cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses and other
current assets, accounts payable and accrued expenses, approximate their fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
Based upon current borrowing rates with similar maturities the carrying value of long-term debt approximates fair value.
Non-Financial
Assets that are Measured at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
Non-financial
assets such as intangible assets, and property and equipment are measured at fair value only when an impairment loss is recognized. The
Company did not record an impairment charge related to these assets in the periods presented.
|
| Treasury Stock |
Treasury
Stock
The
Company records treasury stock at the cost to acquire it and includes treasury stock as a component of shareholders’ equity.
|
| Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements |
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In
June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial
Instruments. This update requires immediate recognition of management’s estimates of current expected credit losses (“CECL”).
Under the prior model, losses were recognized only as they were incurred. The new model is applicable to all financial instruments that
are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022
for public entities qualifying as smaller reporting companies. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact
of this update on the consolidated financial statements and does not expect a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Management
has evaluated other recently issued accounting pronouncements and does not believe that any of these pronouncements will have a significant
impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisaggregation Of Revenue [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_DisaggregationOfRevenuePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSale Of Abbreviated New Drug Applications [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_SaleOfAbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTreasury Stock Policy [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_TreasuryStockPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrants And Preferred Shares [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_WarrantsAndPreferredSharesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cash and cash equivalents, including the policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Other information that may be disclosed includes (1) the nature of any restrictions on the entity's use of its cash and cash equivalents, (2) whether the entity's cash and cash equivalents are insured or expose the entity to credit risk, (3) the classification of any negative balance accounts (overdrafts), and (4) the carrying basis of cash equivalents (for example, at cost) and whether the carrying amount of cash equivalents approximates fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEntity's cash and cash equivalents accounting policy with respect to restricted balances. Restrictions may include legally restricted deposits held as compensating balances against short-term borrowing arrangements, contracts entered into with others, or company statements of intention with regard to particular deposits; however, time deposits and short-term certificates of deposit are not generally included in legally restricted deposits. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndCashEquivalentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for commitments and contingencies, which may include policies for recognizing and measuring loss and gain contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480598/954-450-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy regarding (1) the principles it follows in consolidating or combining the separate financial statements, including the principles followed in determining the inclusion or exclusion of subsidiaries or other entities in the consolidated or combined financial statements and (2) its treatment of interests (for example, common stock, a partnership interest or other means of exerting influence) in other entities, for example consolidation or use of the equity or cost methods of accounting. The accounting policy may also address the accounting treatment for intercompany accounts and transactions, noncontrolling interest, and the income statement treatment in consolidation for issuances of stock by a subsidiary. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConsolidationPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for fair value measurements of financial and non-financial assets, liabilities and instruments classified in shareholders' equity. Disclosures include, but are not limited to, how an entity that manages a group of financial assets and liabilities on the basis of its net exposure measures the fair value of those assets and liabilities.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for goodwill and intangible assets. This accounting policy also may address how an entity assesses and measures impairment of goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of inventory accounting policy for inventory classes, including, but not limited to, basis for determining inventory amounts, methods by which amounts are added and removed from inventory classes, loss recognition on impairment of inventories, and situations in which inventories are stated above cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483489/210-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482105/912-330-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//330/tableOfContent
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 270
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482989/270-10-45-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for costs it has incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483044/730-10-05-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpensePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue from contract with customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue. Includes revenue from contract with customer and from other sources. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRecognitionPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for segment reporting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for award under share-based payment arrangement. Includes, but is not limited to, methodology and assumption used in measuring cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.C.Q3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.1.Q5)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.3.Q2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.2.Q6)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//718/tableOfContent
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationOptionAndIncentivePlansPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11B
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-11B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-6
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_TradeAndOtherAccountsReceivablePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE |
In
the following table, revenue is disaggregated by type of revenue generated by the Company. The table also includes a reconciliation of
the disaggregated revenue with the reportable segments:
SCHEDULE
OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| NDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Licensing fees | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
| Total NDA revenue | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| ANDA: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Manufacturing fees | |
$ | 29,187,573 | | |
$ | 26,951,863 | |
| Licensing fees | |
| 4,967,541 | | |
| 5,310,254 | |
| Total ANDA revenue | |
| 34,155,114 | | |
| 32,262,117 | |
| Total revenue | |
$ | 34,155,114 | | |
$ | 32,262,117 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS |
The
following is the computation of earnings per share applicable to common shareholders for the periods indicated:
SCHEDULE
OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Numerator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic | |
$ | 3,561,846 | | |
$ | 8,898,245 | |
| Effect of dilutive instrument on net income | |
| (415,126 | ) | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Net income - diluted | |
$ | 3,146,720 | | |
$ | 7,472,836 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Denominator | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - basic | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options and convertible securities | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - diluted | |
| 1,012,911,346 | | |
| 1,010,607,713 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net income per share | |
| | | |
| | |
| Basic | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
| Diluted | |
$ | 0.00 | | |
$ | 0.01 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS |
The
following table presents information about our liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, aggregated by the level in the
fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fell:
SCHEDULE
OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| | |
| | |
Fair Value Measurement Using | |
| | |
Amount at Fair Value | | |
Level 1 | | |
Level 2 | | |
Level 3 | |
| March 31, 2023 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 521,711 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 521,711 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| March 31, 2022 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
$ | 936,837 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 936,837 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of disaggregation of revenue into categories depicting how nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of derivative liabilities at fair value.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDerivativeLiabilitiesAtFairValueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INVENTORY (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Inventory Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF INVENTORY |
Inventory
consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF INVENTORY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Finished goods | |
$ | 2,352,330 | | |
$ | 159,808 | |
| Work-in-progress | |
| 1,791,311 | | |
| 1,203,204 | |
| Raw materials | |
| 5,407,075 | | |
| 5,378,158 | |
| Inventory, net | |
$ | 9,550,716 | | |
$ | 6,741,170 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the carrying amount as of the balance sheet date of merchandise, goods, commodities, or supplies held for future sale or to be used in manufacturing, servicing or production process. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483489/210-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfInventoryCurrentTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT |
Property
and equipment consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Land, building and improvements | |
$ | 10,768,181 | | |
$ | 5,456,524 | |
| Laboratory, manufacturing, warehouse and transportation equipment | |
| 13,364,512 | | |
| 13,017,731 | |
| Office equipment and software | |
| 395,563 | | |
| 373,601 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | |
| 484,237 | | |
| 453,701 | |
| Property and equipment, gross | |
| 25,012,493 | | |
| 19,301,557 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | |
| (14,586,335 | ) | |
| (13,348,565 | ) |
| Property and equipment, net | |
$ | 10,426,158 | | |
$ | 5,952,992 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INTANGIBLE ASSETS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
The
following table summarizes the Company’s intangible assets:
SCHEDULE
OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS
| | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Impairment | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (176,645 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 289,039 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| (116,162 | ) | |
| — | | |
| 6,052,189 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | (292,807 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,341,228 | |
| | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| | |
Estimated Useful Life | | |
Gross Carrying Amount | | |
Additions | | |
Reductions | | |
Accumulated Amortization | | |
Net Book Value | |
| Patent application costs | * |
| * | | |
$ | 465,684 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 465,684 | |
| ANDA acquisition costs | |
| Indefinite | | |
| 6,168,351 | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| — | | |
| 6,168,351 | |
| | |
| | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 6,634,035 | |
| * | Patent
application costs were incurred in relation to the Company’s abuse deterrent opioid
technology. Amortization of the patent costs will begin upon the issuance of marketing authorization
by the FDA. Amortization will then be calculated on a straight-line basis through the expiry
of the related patent(s). |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life, by either major class or business segment. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
ACCRUED EXPENSES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Payables and Accruals [Abstract] |
|
| SUMMARY OF ACCRUED EXPENSES |
As
of March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s accrued expenses consisted of the following:
SUMMARY
OF ACCRUED EXPENSES
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Salaries and fees payable in common stock | |
$ | 4,125,000 | | |
$ | 3,625,000 | |
| Income tax | |
| 414,989 | | |
| 414,989 | |
| Consultant contract fees | |
| 193,333 | | |
| 153,333 | |
| Audit fees | |
| 125,000 | | |
| 140,000 | |
| Director dues | |
| 70,000 | | |
| 90,000 | |
| Employee bonuses | |
| — | | |
| 143,000 | |
| Other accrued expenses | |
| 119,404 | | |
| 126,820 | |
| Total accrued expenses | |
$ | 5,047,726 | | |
$ | 4,693,142 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of accrued liabilities.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAccruedLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
NJEDA BONDS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF BONDS PAYABLE LIABILITY |
The
following tables summarize the Company’s bonds payable liability:
SCHEDULE
OF BONDS PAYABLE LIABILITY
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Gross bonds payable | |
| | | |
| | |
| NJEDA Bonds - Series A Notes | |
$ | 1,245,000 | | |
$ | 1,360,000 | |
| Less: Current portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
| (125,000 | ) | |
| (115,000 | ) |
| Long-term portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) | |
$ | 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Bond offering costs | |
$ | 354,454 | | |
$ | 354,454 | |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | |
| (249,294 | ) | |
| (235,124 | ) |
| Bond offering costs, net | |
$ | 105,160 | | |
$ | 119,330 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current portions of bonds payable | |
$ | 125,000 | | |
$ | 115,000 | |
| Less: Bonds offering costs to be amortized in the next 12 months | |
| (14,178 | ) | |
| (14,178 | ) |
| Current portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 110,822 | | |
$ | 100,822 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable - net of bond offering costs | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long term portion of bonds payable | |
| 1,120,000 | | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
| Less: Bond offering costs to be amortized subsequent to the next 12 months | |
| (90,982 | ) | |
| (105,152 | ) |
| Long term portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs | |
$ | 1,029,018 | | |
$ | 1,139,848 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF MATURITIES OF BONDS |
Maturities
of bonds for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF MATURITIES OF BONDS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 125,000 | |
| 2025 | |
| 130,000 | |
| 2026 | |
| 140,000 | |
| 2027 | |
| 150,000 | |
| Thereafter | |
| 700,000 | |
| Total | |
$ | 1,245,000 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of contractual obligation by timing of payment due. Includes, but is not limited to, long-term debt obligation, lease obligation, and purchase obligation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (S-X 210.12-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
| Name: |
srt_ContractualObligationFiscalYearMaturityScheduleTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
srt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of information pertaining to short-term and long-debt instruments or arrangements, including but not limited to identification of terms, features, collateral requirements and other information necessary to a fair presentation.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDebtTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
LOANS PAYABLE (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF LOANS PAYABLE |
Loans
payable consisted of the following:
SCHEDULE
OF LOANS PAYABLE
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Mortgage loan payable 4.75% interest and maturing June 2032 | |
$ | 2,472,923 | | |
$ | — | |
| Equipment and insurance financing loans payable, between 7.10% and 12.02% interest and maturing between September 2023 and October 2025 | |
| 259,611 | | |
| 502,052 | |
| Less: Current portion of loans payable | |
| (200,032 | ) | |
| (253,006 | ) |
| Long-term portion of loans payable | |
$ | 2,532,502 | | |
$ | 249,046 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF LOAN PRINCIPAL PAYMENTS |
Loan
and mortgage principal payments for the next five years are as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF LOAN PRINCIPAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 200,032 | |
| 2025 | |
| 182,181 | |
| 2026 | |
| 115,330 | |
| 2027 | |
| 86,064 | |
| 2028 and thereafter | |
| 2,148,927 | |
| Total | |
$ | 2,732,534 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of long-debt instruments or arrangements, including identification, terms, features, collateral requirements and other information necessary to a fair presentation. These are debt arrangements that originally required repayment more than twelve months after issuance or greater than the normal operating cycle of the entity, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-1A
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 9: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 470
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480848/942-470-50-3
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-8
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-6
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDebtInstrumentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of maturity and sinking fund requirement for long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfMaturitiesOfLongTermDebtTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF LEASE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES |
Lease
assets and liabilities are classified as follows on the condensed consolidated balance sheet:
SCHEDULE
OF LEASE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| Lease | |
Classification | | |
As of March 31, 2023 | |
| Assets | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Operating lease – right-of-use asset | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| Total leased assets | |
| | | |
$ | 13,062 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Liabilities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Long-term | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating | |
| Lease obligation – operating lease, net of current portion | | |
| — | |
| Total lease liabilities | |
| | | |
$ | 14,914 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF FUTURE MINIMUM RENTAL PAYMENTS |
The
table below shows the future minimum rental payments, exclusive of taxes, insurance and other costs, under the Pompano Office Lease:
SCHEDULE
OF FUTURE MINIMUM RENTAL PAYMENTS
| Years ending March 31, | |
Amount | |
| 2024 | |
| 15,214 | |
| 2025 | |
| — | |
| 2026 | |
| — | |
| 2027 | |
| — | |
| Thereafter | |
| — | |
| Total future minimum lease payments | |
| 15,214 | |
| Less: interest | |
| (300 | ) |
| Present value of lease payments | |
$ | 14,914 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF WEIGHTED-AVERAGE REMAINING LEASE TERM AND THE WEIGHTED-AVERAGE DISCOUNT RATE |
The
weighted-average remaining lease term and the weighted-average discount rate of our lease was as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF WEIGHTED-AVERAGE REMAINING LEASE TERM AND THE WEIGHTED-AVERAGE DISCOUNT RATE
| Lease Term and Discount Rate | |
March 31, 2023 | |
| Remaining lease term (years) | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 0.6 | |
| | |
| | |
| Discount rate | |
| | |
| Operating leases | |
| 6 | % |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of weighted average remaining lease term and weighted average discount rate [Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_ScheduleOfWeightedaverageRemainingLeaseTermAndWeightedaverageDiscountRateTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of condensed balance sheet, including, but not limited to, balance sheets of consolidated entities and consolidation eliminations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Regulation S-X (SX)
-Number 210
-Section 12
-Subsection 04
-Paragraph (a)
-Publisher SEC
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfCondensedBalanceSheetTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
srt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of lessee's operating lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to operating lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| SCHEDULE OF CHANGES IN WARRANTS MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS |
The
changes in warrants (Level 3 financial instruments) measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the year ended March 31, 2023 were
as follows:
SCHEDULE
OF CHANGES IN WARRANTS MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS
| Balance at March 31, 2021 | |
$ | 2,362,246 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (1,425,409 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2022 | |
$ | 936,837 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants | |
| (415,126 | ) |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | |
$ | 521,711 | |
|
| Warrant [Member] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF FAIR VALUE OF WARRANTS ISSUED |
SCHEDULE
OF FAIR VALUE OF WARRANTS ISSUED
| | |
March 31, 2023 | | |
March 31, 2022 | |
| Fair value of the Company’s Common Stock | |
$ | 0.0290 | | |
$ | 0.0350 | |
| Volatility | |
| 74.37 | % | |
| 76.55 | % |
| Initial exercise price | |
$ | 0.1521 | | |
$ | 0.1521 | |
| Warrant term (in years) | |
| 4.1 | | |
| 5.1 | |
| Risk free rate | |
| 3.55 | % | |
| 2.40 | % |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of warrants measurement with unobservable inputs reconciliation recurring basis [Table Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_ScheduleOfWarrantsMeasurementWithUnobservableInputsReconciliationRecurringBasisTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of input and valuation technique used to measure fair value and change in valuation approach and technique for each separate class of asset and liability measured on recurring and nonrecurring basis. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 820
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisValuationTechniquesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementEquityComponentsAxis=us-gaap_WarrantMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Equity [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF COMMON STOCK ACTIVITY |
SCHEDULE OF COMMON STOCK ACTIVITY
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively | |
| 1,011,381,988 | | |
| 1,009,276,752 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting fees | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| Common Stock issued during the fiscal year | |
| 2,633,093 | | |
| 2,105,236 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 1,014,015,081 | | |
| 1,011,381,988 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of changes in the separate accounts comprising stockholders' equity (in addition to retained earnings) and of the changes in the number of shares of equity securities during at least the most recent annual fiscal period and any subsequent interim period presented is required to make the financial statements sufficiently informative if both financial position and results of operations are presented. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfStockholdersEquityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF STOCK OPTION PLAN |
SCHEDULE OF STOCK OPTION PLAN
| | |
Shares Underlying Options | | |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | | |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years) | | |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2021 | |
| 5,900,000 | | |
$ | 0.13 | | |
| 3.7 | | |
$ | 6,000 | |
| Granted | |
| 500,000 | | |
$ | 0.05 | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (750,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2022 | |
| 5,650,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.8 | | |
$ | — | |
| Granted | |
| 15,530,000 | | |
$ | 0.03 | | |
| 10.0 | | |
$ | — | |
| Forfeited and expired | |
| (5,810,000 | ) | |
$ | — | | |
| — | | |
$ | — | |
| Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | |
| 15,370,000 | | |
$ | 0.07 | | |
| 7.4 | | |
$ | — | |
| Exercisable at March 31, 2023 | |
| 4,182,000 | | |
$ | 0.14 | | |
| 2.2 | | |
$ | — | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SEGMENT RESULTS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF SELECTED INFORMATION FOR REPORTABLE SEGMENTS |
The
following represents selected information for the Company’s reportable segments:
SCHEDULE OF SELECTED INFORMATION FOR REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
| | | |
| | |
| ANDA | |
| 10,393,857 | | |
| 10,744,005 | |
| NDA | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| Operating Income by Segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF OPERATING INCOME BY SEGMENT TO INCOME FROM OPERATIONS |
The
table below reconciles the Company’s operating income by segment to income from operations before provision for income taxes as
reported in the Company’s audited consolidated statement of operations:
SCHEDULE
OF OPERATING INCOME BY SEGMENT TO INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
For the Years Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Operating income by segment | |
$ | 10,393,857 | | |
$ | 10,744,005 | |
| Corporate unallocated costs | |
| (3,581,468 | ) | |
| (3,696,881 | ) |
| Interest income | |
| 7,453 | | |
| 126 | |
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs | |
| (1,112,707 | ) | |
| (191,816 | ) |
| Impairment of intangible assets | |
| (292,807 | ) | |
| — | |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | |
| (1,263,452 | ) | |
| (1,194,939 | ) |
| Significant non-cash items | |
| (580,128 | ) | |
| (781,475 | ) |
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments | |
| 415,126 | | |
| 1,425,409 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of selected segment reporting information by reportable segment [Table Text Block]
| Name: |
ELTP_ScheduleOfSelectedSegmentReportingInformationByReportableSegmentTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the profit or loss and total assets for each reportable segment. An entity discloses certain information on each reportable segment if the amounts (a) are included in the measure of segment profit or loss reviewed by the chief operating decision maker or (b) are otherwise regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker, even if not included in that measure of segment profit or loss. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-25
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfSegmentReportingInformationBySegmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INCOME TAXES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF INCOME TAXES BENEFIT (EXPENSE) |
SCHEDULE
OF COMPONENTS OF INCOME TAXES BENEFIT (EXPENSE)
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
$ | 784,577 | | |
$ | 1,160,715 | |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| 2,171,821 | |
| Benefit of net operating loss carryforward | |
| (784,577 | ) | |
| (1,160,715 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current | |
| (424,028 | ) | |
| (435,384 | ) |
| Deferred | |
| — | | |
| — | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | |
$ | (424,028 | ) | |
$ | 1,736,437 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
| Net benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 857,379 | |
|
| SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND LIABILITIES |
SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
Year Ended March 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Federal | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | 17,613 | | |
$ | 21,180 | |
| Tax credits | |
| 4,993 | | |
| 4,764 | |
| Valuation allowance | |
| (20,434 | ) | |
| (23,772 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and liabilities | |
$ | 2,172 | | |
$ | 2,172 | |
| State | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net operating loss carry forward | |
$ | — | | |
$ | 747 | |
| Valuation Allowance | |
| — | | |
| (747 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets and
liabilities | |
$ | — | | |
$ | — | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 9
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF DISAGGREGATION OF REVENUE (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Licensing fees |
$ 4,967,541
|
$ 5,310,254
|
| Total revenue |
34,155,114
|
32,262,117
|
| Manufacturing fees |
29,187,573
|
26,951,863
|
| New Drug Applications [Member] |
|
|
| Licensing fees |
|
|
| Total revenue |
|
|
| Abbreviated New Drug Applications [Member] |
|
|
| Licensing fees |
4,967,541
|
5,310,254
|
| Total revenue |
34,155,114
|
32,262,117
|
| Manufacturing fees |
$ 29,187,573
|
$ 26,951,863
|
| X |
- DefinitionRevenue from licensing fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_RevenueFromLicensingFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRevenue from manufacturing fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_RevenueFromManufacturingFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=ELTP_NewDrugApplicationsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=ELTP_AbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE APPLICABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
|
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic |
$ 3,561,846
|
$ 8,898,245
|
| Effect of dilutive instrument on net income |
(415,126)
|
(1,425,409)
|
| Net income - diluted |
$ 3,146,720
|
$ 7,472,836
|
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - basic |
1,012,911,346
|
1,010,607,713
|
| Dilutive effect of stock options and convertible securities |
|
|
| Weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding - diluted |
1,012,911,346
|
1,010,607,713
|
| Basic |
$ 0.00
|
$ 0.01
|
| Diluted |
$ 0.00
|
$ 0.01
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) to net income used for calculating diluted earnings per share (EPS), resulting from the assumed exercise stock options, restrictive stock units (RSUs), convertible preferred stock of an employee stock ownership plan (ESOP), and other dilutive convertible securities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DilutiveSecurities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) to net income used for calculating diluted earnings per share (EPS), resulting from the assumed exercise of dilutive convertible securities excluding adjustments related to ESOP convertible preferred stock, stock options, and restrictive stock units.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DilutiveSecuritiesEffectOnBasicEarningsPerShareOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-11
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities, and addition from assumption of issuance of common shares for dilutive potential common shares; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 40
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-40
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 40
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-40
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 40
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 40
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-40
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF LIABILITIES MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants |
$ 521,711
|
$ 936,837
|
| Fair Value, Inputs, Level 1 [Member] |
|
|
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants |
|
|
| Fair Value, Inputs, Level 2 [Member] |
|
|
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants |
|
|
| Fair Value, Inputs, Level 3 [Member] |
|
|
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Derivative financial instruments - warrants |
$ 521,711
|
$ 936,837
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value, after the effects of master netting arrangements, of a financial liability or contract with one or more underlyings, notional amount or payment provision or both, and the contract can be net settled by means outside the contract or delivery of an asset, expected to be settled after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Includes assets not subject to a master netting arrangement and not elected to be offset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483466/210-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, excluding oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnDispositionOfAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment assets, including oil and gas property and timber property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfPropertyPlantEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash restricted as to withdrawal or usage. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(1)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestrictedCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF INVENTORY (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Inventory Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Finished goods |
$ 2,352,330
|
$ 159,808
|
| Work-in-progress |
1,791,311
|
1,203,204
|
| Raw materials |
5,407,075
|
5,378,158
|
| Inventory, net |
$ 9,550,716
|
$ 6,741,170
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before valuation and LIFO reserves of completed merchandise or goods expected to be sold within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryFinishedGoods |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after valuation and LIFO reserves of inventory expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before valuation and LIFO reserves of raw materials expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryRawMaterials |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before valuation and LIFO reserves of merchandise or goods in the production process expected to be completed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryWorkInProcess |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 25,012,493
|
$ 19,301,557
|
| Less: Accumulated depreciation |
(14,586,335)
|
(13,348,565)
|
| Property and equipment, net |
10,426,158
|
5,952,992
|
| Land, Buildings and Improvements [Member] |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
10,768,181
|
5,456,524
|
| Laboratory, Manufacturing, Warehouse and Transportation Equipment [Member] |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
13,364,512
|
13,017,731
|
| Office Equipment And Software [Member] |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
395,563
|
373,601
|
| Furniture and Fixtures [Member] |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 484,237
|
$ 453,701
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480842/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_LandBuildingsAndImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=ELTP_LaboratoryManufacturingWarehouseAndTransportationEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=ELTP_OfficeEquipmentAndSoftwareMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period that reflects the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over the assets' useful lives. Includes production and non-production related depreciation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Depreciation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
|
$ 6,634,035
|
$ 6,634,035
|
| Additions |
|
|
|
| Reductions |
|
(292,807)
|
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
|
0
|
0
|
| Net Book Value |
|
$ 6,341,228
|
6,634,035
|
| Reductions |
|
|
|
| Patent Application Costs [Member] |
|
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Estimated Useful Life |
[1] |
*
|
*
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
|
$ 465,684
|
$ 465,684
|
| Additions |
|
|
|
| Reductions |
|
(176,645)
|
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
|
|
|
| Net Book Value |
|
$ 289,039
|
465,684
|
| Reductions |
|
|
|
| ANDA Acquisition Costs [Member] |
|
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Estimated Useful Life |
|
Indefinite
|
Indefinite
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
|
$ 6,168,351
|
$ 6,168,351
|
| Additions |
|
|
|
| Reductions |
|
(116,162)
|
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
|
|
|
| Net Book Value |
|
$ 6,052,189
|
6,168,351
|
| Reductions |
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_EstimatedUsefulLifeOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFinite lived intangible assets impairment.
| Name: |
ELTP_FinitelivedIntangibleAssetsImpairment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_FinitelivedIntangibleAssetsReductions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccumulated amount of amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 928
-SubTopic 340
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483147/928-340-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in assets, excluding financial assets, lacking physical substance with a definite life, from an acquisition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinitelivedIntangibleAssetsAcquired1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=ELTP_PatentApplicationCostsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=ELTP_ANDAAcquisitionCostsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SUMMARY OF ACCRUED EXPENSES (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Payables and Accruals [Abstract] |
|
|
| Salaries and fees payable in common stock |
$ 4,125,000
|
$ 3,625,000
|
| Income tax |
414,989
|
414,989
|
| Consultant contract fees |
193,333
|
153,333
|
| Audit fees |
125,000
|
140,000
|
| Director dues |
70,000
|
90,000
|
| Employee bonuses |
|
143,000
|
| Other accrued expenses |
119,404
|
126,820
|
| Total accrued expenses |
$ 5,047,726
|
$ 4,693,142
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccrued consultant contract fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_AccruedConsultantContractFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable for incentive compensation awarded to employees and directors or earned by them based on the terms of one or more relevant arrangements. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedBonusesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred through that date and payable for professional fees, such as for legal and accounting services received. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedProfessionalFeesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses incurred but not yet paid classified as other, due within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred through that date and payable for statutory sales and use taxes, including value added tax. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SalesAndExciseTaxPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF BONDS PAYABLE LIABILITY (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Less: Bonds offering costs to be amortized in the next 12 months |
$ (110,822)
|
$ (100,822)
|
| Less: Bond offering costs to be amortized subsequent to the next 12 months |
(1,029,018)
|
(1,139,848)
|
| Njeda Bonds Series A Notes [Member] |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| NJEDA Bonds - Series A Notes |
1,245,000
|
1,360,000
|
| Less: Current portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) |
(125,000)
|
(115,000)
|
| Long-term portion of bonds payable (prior to deduction of bond offering costs) |
1,120,000
|
1,245,000
|
| Bond offering costs |
354,454
|
354,454
|
| Less: Accumulated amortization |
(249,294)
|
(235,124)
|
| Bond offering costs, net |
105,160
|
119,330
|
| Njeda Bonds Current [Member] |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Current portions of bonds payable |
125,000
|
115,000
|
| Less: Bonds offering costs to be amortized in the next 12 months |
(14,178)
|
(14,178)
|
| Current portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs |
110,822
|
100,822
|
| Njeda Bonds Noncurrent [Member] |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Long term portion of bonds payable |
1,120,000
|
1,245,000
|
| Less: Bond offering costs to be amortized subsequent to the next 12 months |
(90,982)
|
(105,152)
|
| Long term portion of bonds payable, net of bond offering costs |
$ 1,029,018
|
$ 1,139,848
|
| X |
- DefinitionBonds payable current gross.
| Name: |
ELTP_BondsPayableCurrentGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLong term bonds payable gross.
| Name: |
ELTP_LongTermBondsPayableGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated amortization of debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedAmortizationDeferredFinanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of debt and lease obligation, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of investment in debt security measured at fair value with change in fair value recognized in other comprehensive income (available-for-sale), investment in debt security measured at amortized cost (held-to-maturity), and investment in debt security measured at fair value with change in fair value recognized in net income (trading), classified as current.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtSecuritiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of investment in debt security measured at fair value with change in fair value recognized in other comprehensive income (available-for-sale) and investment in debt security measured at amortized cost (held-to-maturity), classified as noncurrent.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtSecuritiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before accumulated amortization, of debt issuance costs. Includes, but is not limited to, legal, accounting, underwriting, printing, and registration costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredFinanceCostsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of debt issuance costs. Includes, but is not limited to, legal, accounting, underwriting, printing, and registration costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredFinanceCostsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of the portion of long-term, collateralized debt obligations due within one year or the operating cycle, if longer. Such obligations include mortgage loans, chattel loans, and any other borrowings secured by assets of the borrower. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SecuredDebtCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying amount of collateralized debt obligations with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle, if longer, excluding the current portion. Obligations include, but not limited to, mortgage loans, chattel loans, and other borrowings secured by assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SecuredLongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=ELTP_NjedaBondsSeriesANotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=ELTP_NjedaBondsCurrentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=ELTP_NjedaBondsNoncurrentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=ELTP_NJEDABondsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
NJEDA BONDS (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Interest expense |
$ 1,112,707
|
$ 191,816
|
| NJEDA Bonds [Member] |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Amortization of Debt Issuance Costs |
14,178
|
|
| Interest Payable |
6,744
|
7,367
|
| Interest expense |
$ 6,744
|
$ 7,367
|
| Njeda Bonds Series A Notes [Member] |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Annual interest rate |
6.50%
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfFinancingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average effective interest rate during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateDuringPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (210.5-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest payable on debt, including, but not limited to, trade payables. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(15)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.15(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPayableCurrentAndNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentTypeAxis=ELTP_NJEDABondsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=ELTP_NjedaBondsSeriesANotesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF LOANS PAYABLE (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Equipment and insurance financing loans payable, between 7.10% and 12.02% interest and maturing between September 2023 and October 2025 |
$ 259,611
|
$ 502,052
|
| Less: Current portion of loans payable |
(200,032)
|
(253,006)
|
| Long-term portion of loans payable |
$ 2,532,502
|
$ 249,046
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncluding the current and noncurrent portions, aggregate carrying value as of the balance sheet date of loans payable (with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LoansPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of portion of long-term loans payable due within one year or the operating cycle if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LoansPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of loans payable (with maturities initially due after one year or beyond the operating cycle if longer), excluding current portion. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermLoansPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- DefinitionContractual interest rate for funds borrowed, under the debt agreement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateStatedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt payable, sinking fund requirement, and other securities issued that are redeemable by holder at fixed or determinable price and date, maturing in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 470
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481544/470-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtMaturitiesRepaymentsOfPrincipalInYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_LoansPayableMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
LOANS PAYABLE (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
|
|
|
12 Months Ended |
Jun. 02, 2023 |
Jul. 02, 2022 |
Apr. 02, 2022 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Interest expenses debt |
|
|
|
$ 1,013,874
|
$ 62,845
|
| East West Bank (“EWB”) [Member] | Mortgages [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt term |
|
10 years
|
|
|
|
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
|
$ 2,550,000
|
|
|
|
| Interest rate, description |
|
bears
interest at a rate of 4.75% fixed for 5 years then adjustable at WSJP plus 0.5% with floor rate of 4.5%
|
|
|
|
| Board of Directors Chairman [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes payable |
$ 3,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Description of promissory note |
The Promissory Note has an
interest rate of 9% for the first year and 10% for an optional second year and the proceeds will be used for working capital and other
business purposes
|
|
|
|
|
| Loan and Security Agreement [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Principal amount |
|
|
$ 12,000,000
|
|
|
| Debt interest rate |
|
|
9.73%
|
|
|
| Debt term |
|
|
5 years
|
|
|
| Debt maturity date |
|
|
May 01, 2027
|
|
|
| Debt issuance cost |
|
|
|
$ 40,120
|
|
| Debt instrument, description |
|
The EWB Mortgage Loan contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants
include maintaining a minimum debt coverage ratio of 1.50 to 1.00 tested annually and a minimum trailing 12-month debt coverage ratio
of 1.50 to 1.00. As of March 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with each financial covenant.
|
|
The
EWB Loan Agreement contains customary representations, warranties and covenants. These covenants include, but are not limited to, maintaining
maximum leverage ratios of 3.50 to 1.00, minimum liquidity of $5,000,000, minimum cash of $1,000,000, a fixed charge coverage ratio of
1.25 to 1.00 and restrictions on mergers or sales of assets and debt borrowings.
|
|
| Loan and Security Agreement [Member] | Prime Rate [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt interest rate |
|
|
1.73%
|
|
|
| Loan and Security Agreement [Member] | Revolving Credit Facility [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Line of credit maximum borrowing capacity |
|
|
$ 2,000,000
|
|
|
| Line of credit, interest rate |
|
|
8.87%
|
|
|
| Line of credit, maturity date |
|
|
May 01, 2027
|
|
|
| Loan and Security Agreement [Member] | Revolving Credit Facility [Member] | Prime Rate [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Line of credit, interest rate |
|
|
0.87%
|
|
|
| EWB Mortgage Loan [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt issuance cost |
|
|
|
$ 13,251
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionIdentification of the lender and information about a contractual promise to repay a short-term or long-term obligation, which includes borrowings under lines of credit, notes payable, commercial paper, bonds payable, debentures, and other contractual obligations for payment. This may include rationale for entering into the arrangement, significant terms of the arrangement, which may include amount, repayment terms, priority, collateral required, debt covenants, borrowing capacity, call features, participation rights, conversion provisions, sinking-fund requirements, voting rights, basis for conversion if convertible and remarketing provisions. The description may be provided for individual debt instruments, rational groupings of debt instruments, or by debt in total. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 470
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480848/942-470-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentDescription |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace (par) amount of debt instrument at time of issuance. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentFaceAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContractual interest rate for funds borrowed, under the debt agreement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateStatedPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDescription of the interest rate as being fixed or variable, and, if variable, identification of the index or rate on which the interest rate is based and the number of points or percentage added to that index or rate to set the rate, and other pertinent information, such as frequency of rate resets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateTerms |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDate when the debt instrument is scheduled to be fully repaid, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(2))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentMaturityDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod of time between issuance and maturity of debt instrument, in PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of debt issuance costs. Includes, but is not limited to, legal, accounting, underwriting, printing, and registration costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredFinanceCostsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense for debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.8)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDate the credit facility terminates, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityExpirationDate1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe effective interest rate during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityInterestRateDuringPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMaximum borrowing capacity under the credit facility without consideration of any current restrictions on the amount that could be borrowed or the amounts currently outstanding under the facility. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityMaximumBorrowingCapacity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDescribes when borrowings outstanding under a line of credit will convert to a term loan, and describes the repayment terms, collateral, and priority (seniority) of the term loan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityRevolvingCreditConversionToTermLoanDescription |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncluding the current and noncurrent portions, aggregate carrying amount of all types of notes payable, as of the balance sheet date, with initial maturities beyond one year or beyond the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow during the period from additional borrowings in aggregate debt. Includes proceeds from short-term and long-term debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromIssuanceOfDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
dei_LegalEntityAxis=ELTP_EastWestBankMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_MortgagesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_BoardOfDirectorsChairmanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TypeOfArrangementAxis=ELTP_LoanAndSecurityAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableRateAxis=us-gaap_PrimeRateMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CreditFacilityAxis=us-gaap_RevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TypeOfArrangementAxis=ELTP_EWBMortgageLoanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
DEFERRED REVENUE (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Defined Benefit Plan Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred revenues |
$ 32,223
|
$ 45,559
|
| Deferred revenues current component |
13,333
|
13,333
|
| Deferred revenues long-term component |
18,890
|
$ 32,226
|
| TAGI Pharma [Member] |
|
|
| Defined Benefit Plan Disclosure [Line Items] |
|
|
| Unamortized amount |
$ 200,000
|
|
| Licensing agreement beginning |
Sep. 30, 2010
|
|
| Licensing agreement ending |
Aug. 31, 2025
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionLatest date the outstanding debt instruments are required to be repaid, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentMaturityDateRangeEnd1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEarliest date the outstanding debt instruments are required to be repaid, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentMaturityDateRangeStart1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of debt premium. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-1A
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentUnamortizedPremium |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred income and obligation to transfer product and service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(26)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred income and obligation to transfer product and service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredRevenueCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred income and obligation to transfer product and service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(26)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredRevenueNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedBenefitPlanDisclosureLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF LEASE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Operating lease- right-of-use asset |
$ 13,062
|
$ 1,031,884
|
| Total leased assets |
13,062
|
|
| Lease obligation- operating lease |
14,914
|
202,953
|
| Lease obligation-operating lease, net of current portion |
|
$ 835,893
|
| Total lease liabilities |
$ 14,914
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease due after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for operating lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Details Narrative)
|
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
|
Oct. 31, 2020
ft²
|
Mar. 31, 2023
USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2022
USD ($)
|
Jul. 31, 2014
ft²
|
Jul. 01, 2010
ft²
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Operating lease, terms |
The
Pompano Office includes a 3 month abatement from November 2020 through February 2021 and has a term of three years, ending on October
31, 2023
|
The
135 Ludlow Ave. modified lease includes an initial term, which expired on December 31, 2016 with two tenant renewal options of five years
each, at the sole discretion of the Company. On June 22, 2016, the Company exercised the first of these renewal options, with such option
including a term that begins on January 1, 2017 and expires on December 31, 2021. On June 30, 2021, the Company exercised the second
of the renewal options, with such option including a term that begins on January 1, 2022 and expires on December 31, 2026.
|
|
|
|
| Lease term |
|
5 years
|
|
|
|
| Rent expense | $ |
|
$ 58,248
|
$ 229,563
|
|
|
| Other Noncurrent Liabilities [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Other long-term liabilities | $ |
|
0
|
38,780
|
|
|
| Warehouse [Member] | Property Subject to Operating Lease [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Area of land | ft² |
|
|
|
|
15,000
|
| Warehouse [Member] | Property Subject to Operating Lease [Member] | July 2014 Modification Agreement [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Area of land | ft² |
|
|
|
35,000
|
|
| Pompano Office Lease [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Rent expense | $ |
|
$ 25,638
|
$ 23,430
|
|
|
| Pompano Office Lease [Member] | Property Subject to Operating Lease [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Loss Contingencies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Area of land | ft² |
1,275
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe carrying amount of a liability for an asset retirement obligation. An asset retirement obligation is a legal obligation associated with the disposal or retirement of a tangible long-lived asset that results from the acquisition, construction or development, or the normal operations of a long-lived asset, except for certain obligations of lessees. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481999/410-20-25-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481850/410-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetRetirementObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTerm of lessee's operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseTermOfContract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-4
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-9
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_LossContingenciesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCash payments to lessor's for use of assets under operating leases. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (g)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=us-gaap_OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MortgageLoansOnRealEstateDescriptionTypeOfPropertyAxis=srt_WarehouseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertySubjectToOrAvailableForOperatingLeaseAxis=us-gaap_PropertySubjectToOperatingLeaseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TypeOfArrangementAxis=ELTP_July2014ModificationAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MortgageLoansOnRealEstateDescriptionTypeOfPropertyAxis=ELTP_PompanoOfficeLeaseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
PREFERRED STOCK (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
Aug. 24, 2020 |
Dec. 04, 2019 |
Apr. 27, 2017 |
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Warrant to purchase price per shares |
$ 0.1521
|
$ 0.1521
|
|
|
|
| Increased number of common stock shares authorized |
1,445,000,000
|
1,445,000,000
|
|
|
|
| Carrying value of Series J convertible preferred stock |
$ 13,903,960
|
$ 13,903,960
|
|
|
|
| Minimum [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Increased number of common stock shares authorized |
|
|
|
995,000,000
|
|
| Maximum [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Increased number of common stock shares authorized |
|
|
|
1,445,000,000
|
|
| Series J Convertible Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock share authorized |
50
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock shares issued |
0
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
0
|
|
|
|
|
| Convertible preferred stock stated value |
$ 1,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Convertible preferred stock par value per share |
$ 0.01
|
|
|
|
|
| Series J Convertible Preferred Stock [Member] | Nasrat Hakim [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock shares issued |
|
|
24.0344
|
|
24.0344
|
| Shares of common stock |
|
|
158,017,321
|
|
158,017,321
|
| Warrants to purchase |
79,008,661
|
|
|
|
79,008,661
|
| Price per share |
|
|
$ 0.1521
|
|
$ 0.1521
|
| Warrant to purchase price per shares |
$ 0.1521
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionConvertible preferred stock par value per share.
| Name: |
ELTP_ConvertiblePreferredStockParValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionConvertible preferred stock stated value.
| Name: |
ELTP_ConvertiblePreferredStockStatedValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_PreferredStockConversionPricePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483014/272-10-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482987/272-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfStockLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExercise price per share or per unit of warrants or rights outstanding. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightExercisePriceOfWarrantsOrRights1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of securities into which the class of warrant or right may be converted. For example, but not limited to, 500,000 warrants may be converted into 1,000,000 shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightNumberOfSecuritiesCalledByWarrantsOrRights |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued for each share of convertible preferred stock that is converted. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 16
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConvertiblePreferredStockSharesIssuedUponConversion |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) issued to shareholders (includes related preferred shares that were issued, repurchased, and remain in the treasury). May be all or portion of the number of preferred shares authorized. Excludes preferred shares that are classified as debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate share number for all nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) held by stockholders. Does not include preferred shares that have been repurchased. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable preferred shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=ELTP_SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF FAIR VALUE OF WARRANTS ISSUED (Details)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrants and Rights Outstanding, Term |
4 years 1 month 6 days
|
5 years 1 month 6 days
|
| Measurement Input, Share Price [Member] |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrants and rights outstanding, measurement input |
0.0290
|
0.0350
|
| Measurement Input, Price Volatility [Member] |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrants and rights outstanding, measurement input |
74.37
|
76.55
|
| Measurement Input, Exercise Price [Member] |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrants and rights outstanding, measurement input |
0.1521
|
0.1521
|
| Measurement Input, Risk Free Interest Rate [Member] |
|
|
| Fair Value Measurement Inputs and Valuation Techniques [Line Items] |
|
|
| Warrants and rights outstanding, measurement input |
3.55
|
2.40
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisValuationTechniquesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod between issuance and expiration of outstanding warrant and right embodying unconditional obligation requiring redemption by transferring asset at specified or determinable date or upon event certain to occur, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (bbb)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_WarrantsAndRightsOutstandingTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF CHANGES IN WARRANTS MEASURED AT FAIR VALUE ON A RECURRING BASIS (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants |
$ 415,126
|
$ 1,425,409
|
| Fair Value, Inputs, Level 3 [Member] | Warrant [Member] |
|
|
| Platform Operator, Crypto-Asset [Line Items] |
|
|
| Beginning balance |
936,837
|
2,362,246
|
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments - warrants |
(415,126)
|
(1,425,409)
|
| Ending balance |
$ 521,711
|
$ 936,837
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the fair value of derivatives recognized in the income statement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4A
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480434/815-10-50-4A
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeGainLossOnDerivativeNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of securities pledged as collateral against derivative liabilities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483444/210-20-55-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_DerivativeLiabilityFairValueOfCollateral |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinancialInstrumentAxis=us-gaap_WarrantMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS – WARRANTS (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
Apr. 28, 2017 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Exercise price |
|
$ 0.1521
|
$ 0.1521
|
| Series J Warrants [Member] |
|
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Exercise price |
$ 0.1521
|
|
|
| Warrant expiration period |
10 years
|
|
|
| Nasrat Hakim [Member] | Series J Warrants [Member] |
|
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Fair value of the warrants |
$ 6,474,674
|
|
|
| Nasrat Hakim [Member] | Series J Convertible Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Warrant shares |
|
79,008,661
|
79,008,661
|
| Warrant to purchase shares |
79,008,661
|
|
|
| Conversion of stock, shares issued |
158,017,321
|
|
|
| Chief Executive Officer [Member] | Series J Convertible Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Shares issued |
24.0344
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionWarrant expiration period.
| Name: |
ELTP_WarrantExpirationPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExercise price per share or per unit of warrants or rights outstanding. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightExercisePriceOfWarrantsOrRights1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of securities into which each warrant or right may be converted. For example, but not limited to, each warrant may be converted into two shares.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightNumberOfSecuritiesCalledByEachWarrantOrRight |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of securities into which the class of warrant or right may be converted. For example, but not limited to, 500,000 warrants may be converted into 1,000,000 shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightNumberOfSecuritiesCalledByWarrantsOrRights |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of new shares issued in the conversion of stock in a noncash (or part noncash) transaction. Noncash is defined as transactions during a period that do not result in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. "Part noncash" refers to that portion of the transaction not resulting in cash receipts or cash payments in the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConversionOfStockSharesIssued1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredCompensationArrangementWithIndividualExcludingShareBasedPaymentsAndPostretirementBenefitsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (income) related to adjustment to fair value of warrant liability. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 13
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 480
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481766/480-10-25-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAdjustmentOfWarrants |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of stock issued as of the balance sheet date, including shares that had been issued and were previously outstanding but which are now held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfWarrantOrRightAxis=ELTP_SeriesJWarrantsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=ELTP_NasratHakimMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=ELTP_SeriesJConvertiblePreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_ChiefExecutiveOfficerMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF COMMON STOCK ACTIVITY (Details) - shares
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively |
1,011,381,988
|
|
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively |
1,014,015,081
|
1,011,381,988
|
| Common Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) [Line Items] |
|
|
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively |
1,011,381,988
|
1,009,276,752
|
| Common Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting fees |
2,633,093
|
2,105,236
|
| Common Stock issued during the fiscal year |
2,633,093
|
2,105,236
|
| Common Stock issued as of March 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively |
1,014,015,081
|
1,011,381,988
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommon Stock issued in payment of Directors fees, salaries and consulting fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_CommonStockIssuedInPaymentOfDirectorsFeesSalariesAndConsultingFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-17
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeLossLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of stock issued attributable to transactions classified as other.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementEquityComponentsAxis=us-gaap_CommonStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, $ in Millions |
|
12 Months Ended |
Jul. 08, 2020 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Restructuring Cost and Reserve [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Common stock, par value per share |
|
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Common stock issued during period shares |
|
2,633,093
|
2,105,236
|
| Lincoln Park [Member] |
|
|
|
| Restructuring Cost and Reserve [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Purchase of common stock, amount |
$ 25.0
|
|
|
| Common stock, par value per share |
$ 0.001
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommon stock issued during period shares.
| Name: |
ELTP_CommonStockIssuedDuringPeriodShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCostAndReserveLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of consideration received by subsidiary or equity investee in exchange for shares of stock issued or sold. Includes amount of cash received, fair value of noncash assets received, and fair value of liabilities assumed by the investor.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SaleOfStockConsiderationReceivedPerTransaction |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessAcquisitionAxis=ELTP_LincolnParkMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF STOCK OPTION PLAN (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
Mar. 31, 2021 |
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance |
5,650,000
|
5,900,000
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Beginning Balance |
$ 0.14
|
$ 0.13
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term |
|
2 years 9 months 18 days
|
3 years 8 months 12 days
|
| Outstanding, Intrinsic Value Beginning Balance |
|
$ 6,000
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance |
15,530,000
|
500,000
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Beginning Balance |
$ 0.03
|
$ 0.05
|
|
| Outstanding, Beginning Balance |
|
(750,000)
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price, Beginning Balance |
|
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years), Granted |
10 years
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Ending Balance |
15,370,000
|
5,650,000
|
5,900,000
|
| Outstanding, Weighted Average Exercise Price, Ending Balance |
$ 0.07
|
$ 0.14
|
$ 0.13
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term |
7 years 4 months 24 days
|
|
|
| Options, Outstanding, Intrinsic Value Ending Balance |
|
|
$ 6,000
|
| Outstanding, Ending Balance |
4,182,000
|
|
|
| Outstanding, Weighted Average Exercise Price, Ending Balance |
$ 0.14
|
|
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years), Exercisable |
2 years 2 months 12 days
|
|
|
| Options, Outstanding, Intrinsic Value Ending Balance |
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years), Exercisable.
| Name: |
ELTP_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years), Granted.
| Name: |
ELTP_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTermGranted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares into which fully or partially vested stock options outstanding as of the balance sheet date can be currently converted under the option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted-average price as of the balance sheet date at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance on vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor presentations that combine terminations, the number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan or that expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresAndExpirationsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price of options that were either forfeited or expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresAndExpirationsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which the current fair value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of options outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average per share amount at which grantees can acquire shares of common stock by exercise of options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of difference between fair value of the underlying shares reserved for issuance and exercise price of vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableIntrinsicValue1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable or convertible, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Price difference between exercise price and quoted price |
$ 0.03
|
$ 0.03
|
| Unrecognized stock based compensation expense |
$ 205,340
|
|
| Recognized over period |
1 year 6 months
|
|
| Director [Member] |
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Accrued director fees |
$ 90,000
|
|
| Cash payment |
$ 30,000
|
|
| Director [Member] | Common Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Share issued of common stock |
1,753,686
|
|
| President and Chief Executive Officer and Other Employees [Member] |
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Share issued of common stock |
68,264,667
|
|
| Accrued Salaries, Current |
$ 540,000
|
|
| Other employee salary |
$ 4,335,000
|
|
| President and Chief Executive Officer and Other Employees [Member] | Common Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Share issued of common stock |
14,956,851
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash made for payment of director fees.
| Name: |
ELTP_CashMadeForPaymentOfDirectorFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPrice difference between exercise price and quoted price.
| Name: |
ELTP_PriceDifferenceBetweenExercisePriceAndQuotedPrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of the obligations incurred through that date and payable for employees' services provided. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedSalariesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredCompensationArrangementWithIndividualExcludingShareBasedPaymentsAndPostretirementBenefitsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost not yet recognized for nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average period over which cost not yet recognized is expected to be recognized for award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognizedPeriodForRecognition1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of stock issued as of the balance sheet date, including shares that had been issued and were previously outstanding but which are now held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_DirectorMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementEquityComponentsAxis=us-gaap_CommonStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=ELTP_PresidentAndChiefExecutiveOfficerAndOtherEmployeesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
CONCENTRATIONS AND CREDIT RISK (Details Narrative) - Integer
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Revenue Benchmark [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Number of customers |
2
|
2
|
| Revenue Benchmark [Member] | Customers [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
96.00%
|
95.00%
|
| Revenue Benchmark [Member] | Customer One [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
85.00%
|
84.00%
|
| Revenue Benchmark [Member] | Customer Two [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
11.00%
|
11.00%
|
| Accounts Receivable [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Number of customers |
1
|
2
|
| Accounts Receivable [Member] | Customers [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
96.00%
|
91.00%
|
| Accounts Receivable [Member] | Customer One [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
78.00%
|
| Accounts Receivable [Member] | Customer Two [Member] | Customer Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
13.00%
|
| Purchases [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Number of suppliers |
1
|
4
|
| Purchases [Member] | Suppliers [Member] | Supplier Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
34.00%
|
69.00%
|
| Purchases [Member] | Supplier One [Member] | Supplier Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
51.00%
|
| Purchases [Member] | Supplier Two [Member] | Supplier Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
7.00%
|
| Purchases [Member] | Supplier Three [Member] | Supplier Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
6.00%
|
| Purchases [Member] | Supplier Four [Member] | Supplier Concentration Risk [Member] |
|
|
| Concentration Risk [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk, percentage |
|
5.00%
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of Customers in credit risk.
| Name: |
ELTP_NumberOfCustomers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481027/954-310-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor an entity that discloses a concentration risk in relation to quantitative amount, which serves as the "benchmark" (or denominator) in the equation, this concept represents the concentration percentage derived from the division. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-21
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-20
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskPercentage1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_SalesRevenueNetMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_CustomersMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_CustomerConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_CustomerOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_CustomerTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_AccountsReceivableMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=ELTP_PurchasesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_SuppliersMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SupplierConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_SupplierOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_SupplierTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_SupplierThreeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=ELTP_SupplierFourMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF SELECTED INFORMATION FOR REPORTABLE SEGMENTS (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating Income by Segment |
$ 3,676,002
|
$ 5,070,710
|
| Abbreviated New Drug Applications [Member] |
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating Income by Segment |
10,393,857
|
10,744,005
|
| New Drug Applications [Member] |
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating Income by Segment |
|
|
| Business Segment [Member] |
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating Income by Segment |
$ 10,393,857
|
$ 10,744,005
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=ELTP_AbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=ELTP_NewDrugApplicationsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementBusinessSegmentsAxis=ELTP_BusinessSegmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF OPERATING INCOME BY SEGMENT TO INCOME FROM OPERATIONS (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating income by segment |
$ 3,676,002
|
$ 5,070,710
|
| Interest income |
7,453
|
126
|
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
(1,263,452)
|
(1,194,939)
|
| Income before income taxes |
3,985,874
|
6,304,429
|
| Operating Segments [Member] |
|
|
| Segment Reporting Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating income by segment |
10,393,857
|
10,744,005
|
| Corporate unallocated costs |
(3,581,468)
|
(3,696,881)
|
| Interest income |
7,453
|
126
|
| Interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs |
(1,112,707)
|
(191,816)
|
| Impairment of intangible assets |
(292,807)
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
(1,263,452)
|
(1,194,939)
|
| Significant non-cash items |
(580,128)
|
(781,475)
|
| Change in fair value of derivative instruments |
415,126
|
1,425,409
|
| Income before income taxes |
$ 3,985,874
|
$ 6,304,429
|
| X |
- DefinitionCorporate unallocated costs
| Name: |
ELTP_CorporateUnallocatedCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe current period expense charged against earnings on long-lived, physical assets not used in production, and which are not intended for resale, to allocate or recognize the cost of such assets over their useful lives; or to record the reduction in book value of an intangible asset over the benefit period of such asset; or to reflect consumption during the period of an asset that is not used in production. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe difference between the book value and the sale price of options, swaps, futures, forward contracts, and other derivative instruments. This element refers to the gain (loss) included in earnings. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(7)(a)(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(7)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(7)(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(7)(a)(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.13(h))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSaleOfDerivatives |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of impairment loss recognized in the period resulting from the write-down of the carrying amount of an intangible asset (excluding goodwill) to fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfIntangibleAssetsExcludingGoodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionInterest and debt related expenses associated with nonoperating financing activities of the entity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 835
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestAndDebtExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accretion (amortization) of purchase discount (premium) of interest income on nonoperating securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentIncomeInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense or loss included in net income that result in no cash flow, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNoncashExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ConsolidationItemsAxis=us-gaap_OperatingSegmentsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF INCOME TAXES BENEFIT (EXPENSE) (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Current |
$ 784,577
|
$ 1,160,715
|
| Deferred |
|
2,171,821
|
| Benefit of net operating loss carryforward |
(784,577)
|
(1,160,715)
|
| Current |
(424,028)
|
(435,384)
|
| Deferred |
|
|
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
(424,028)
|
1,736,437
|
| Benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits |
|
857,379
|
| Net benefit from sale of state net operating loss credits |
|
$ 857,379
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
ELTP_FederalBenefitOfNetOperatingLossCarryforward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ELTP_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current state and local tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current regional, territorial, and provincial tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
SCHEDULE OF COMPONENTS OF DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND LIABILITIES (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Foreign Tax Authority [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Net operating loss carry forward |
$ 17,613
|
$ 21,180
|
| Tax credits |
4,993
|
4,764
|
| Valuation Allowance |
(20,434)
|
(23,772)
|
| Deferred tax assets and liabilities |
2,172
|
2,172
|
| State and Local Jurisdiction [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Net operating loss carry forward |
|
747
|
| Valuation Allowance |
|
(747)
|
| Deferred tax assets and liabilities |
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allocation of valuation allowances and deferred tax liability, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible differences and carryforwards, without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsLiabilitiesNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of a valuation allowances, of deferred tax assets attributable to deductible tax credit carryforwards including, but not limited to, research, foreign, general business, alternative minimum tax, and other deductible tax credit carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxCreditCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.2
INCOME TAXES (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Effective Income Tax Rate Reconciliation, Change in Deferred Tax Assets Valuation Allowance, Percent |
90.00%
|
90.00%
|
| [custom:IncomeTaxBenefitByJudgement] |
|
$ 2,200,000
|
| Net deferred tax |
$ 0
|
|
| Effective Income Tax Rate Reconciliation at Federal Statutory Income Tax Rate, Amount |
0.0
|
|
| Effective Income Tax Rate Reconciliation, State and Local Income Taxes, Amount |
400,000
|
|
| Foreign Tax Authority [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards |
$ 83,900,000
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
Elite Pharmaceuticals (QB) (USOTC:ELTP)
Historical Stock Chart
From Mar 2024 to Apr 2024
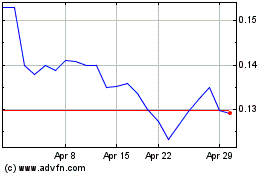
Elite Pharmaceuticals (QB) (USOTC:ELTP)
Historical Stock Chart
From Apr 2023 to Apr 2024