false2023FY0001305168P1YP1Yhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2023#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2023#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2023#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationshttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2023#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationsP3YP3Y00013051682023-01-012023-12-3100013051682023-06-30iso4217:USD00013051682024-02-16xbrli:shares00013051682023-12-3100013051682022-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares0001305168us-gaap:ServiceMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ServiceMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:ProductMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ProductMember2022-01-012022-12-3100013051682022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-3100013051682021-12-310001305168us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-12-310001305168arc:UDSMember2023-12-310001305168arc:UDSMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMember2022-01-012022-12-31xbrli:pure0001305168us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168stpr:CAus-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMemberus-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168stpr:CAus-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMemberus-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:ThreeLargestVendorsMemberus-gaap:CostOfGoodsTotalMemberus-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:ThreeLargestVendorsMemberus-gaap:CostOfGoodsTotalMemberus-gaap:SupplierConcentrationRiskMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2021-12-310001305168us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:BuildingMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:BuildingMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001305168srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001305168srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001305168srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2023-12-310001305168arc:DigitalPrintingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:DigitalPrintingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:MPSMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:MPSMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:ScanningAndDigitalImagingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:ScanningAndDigitalImagingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ShippingAndHandlingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMemberarc:SoftwareLicensingMemberus-gaap:ProductConcentrationRiskMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMemberarc:SoftwareLicensingMemberus-gaap:ProductConcentrationRiskMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168country:US2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168country:US2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:NonUsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168country:US2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-12-310001305168country:US2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:NonUsMember2022-12-310001305168arc:UDSMember2023-12-3100013051682022-05-012022-05-310001305168arc:ChineseJointVentureMember2022-05-310001305168us-gaap:CoVenturerMember2022-05-012022-05-310001305168us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2022-12-310001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:AmendmentTo2021CreditAgreementMember2023-06-150001305168us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:AmendmentTo2021CreditAgreementMember2023-06-152023-06-150001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-04-220001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310001305168arc:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMembersrt:MinimumMemberarc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryOneMember2021-04-222021-04-220001305168arc:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMemberarc:A2021CreditAgreementMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryOneMember2021-04-222021-04-220001305168srt:MinimumMemberarc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:BaseRateMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryTwoMember2021-04-222021-04-220001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:BaseRateMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberarc:DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryTwoMember2021-04-222021-04-220001305168arc:A2021CreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-3100013051682023-12-012023-12-3100013051682020-12-310001305168srt:MinimumMember2023-12-310001305168srt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168srt:AffiliatedEntityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168srt:AffiliatedEntityMember2023-12-310001305168srt:AffiliatedEntityMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168srt:AffiliatedEntityMember2022-12-310001305168arc:ManagedPrintServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:ManagedPrintServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:ManagedPrintServicesMemberus-gaap:EquipmentMember2023-12-310001305168arc:ManagedPrintServicesMemberus-gaap:EquipmentMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember2023-12-310001305168arc:EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2023-12-310001305168arc:EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:Amended2021PlanMember2023-04-262023-04-260001305168arc:Amended2021PlanMember2023-04-260001305168arc:A2014InventivePlanAnd2005StockPlanMember2021-04-290001305168srt:MinimumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168srt:MaximumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:RangeOneMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:RangeOneMember2023-12-310001305168arc:RangeTwoMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:RangeTwoMember2023-12-310001305168arc:RangeThreeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:RangeThreeMember2023-12-310001305168arc:RangeFourMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:RangeFourMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-31arc:boardOfDirectMember0001305168us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168us-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-31arc:boardOfDirectorMember0001305168us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-12-310001305168us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-12-310001305168us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001305168arc:EligibleEmployeesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001305168arc:HighlyCompensatedEmployeesMember2023-01-012023-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
_______________________________________
Form 10-K
_______________________________________
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2023
or
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-32407
_______________________________________
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its Charter)
_______________________________________
| | | | | |
| Delaware | 20-1700361 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
12657 Alcosta Blvd, Suite 200
San Ramon, California 94583
(925) 949-5100
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant’s principal executive offices)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | ARC | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
Large accelerated filer ¨ Accelerated filer ý Non-accelerated filer ¨ Smaller reporting company ☒
Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ý
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ý
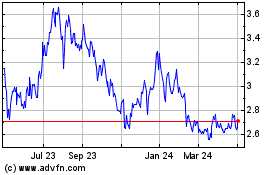
Based on the closing price of $3.24 of the registrant’s Common Stock on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2023 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter), the aggregate market value of the voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant on that date was approximately $117,924,128.
As of February 16, 2024, there were 42,765,875 shares of the Registrant’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, are incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K in Part III as indicated therein.
_______________________________________
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2023
Table of Contents
Page
| | | | | |
| PART I | |
| Item 1. Business | |
| Item 1A. Risk Factors | |
| Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments | |
| Item 1C. Cybersecurity | |
| Item 2. Properties | |
| Item 3. Legal Proceedings | |
| Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures | |
| PART II | |
| Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | |
| Item 6. [Reserved.] | |
| Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | |
| Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | |
| Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | |
| Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | |
| Item 9A. Controls and Procedures | |
| Item 9B. Other Information | |
| Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdiction that Prevent Inspections | |
| PART III | |
| Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | |
| Item 11. Executive Compensation | |
| Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | |
| Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | |
| Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services | |
| PART IV | |
| Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule | |
| Item 16. Form 10-K Summary | |
| Signatures | |
| |
| |
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
2023 ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, “ARC Document Solutions,” “ARC,” “the Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” refer to ARC Document Solutions, Inc., a Delaware corporation, and its consolidated subsidiaries, unless the context otherwise dictates.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. All statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this report are statements that could be deemed forward-looking statements, including without limitation statements with respect to expectations regarding the impact of the future cash flows, and capital requirements, the impact of foreign exchange rate movements on sales and net income, and the Company's anticipated effective tax rate, and statements of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements.
In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “intend,” “plan,” “project,” “target,” “likely,” “will,” “would,” “could,” and other similar language, whether in the negative or affirmative. The forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are only predictions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and should not be relied upon as of any subsequent date. Such statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions described in the section titled “Risk Factors” under Part I, Item 1A below and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Because forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified, you should not rely on these forward-looking statements as indicative of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in our forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Some of the key factors that could cause actual results to differ from our expectations are listed below:
•A significant portion of our revenue across all of our product and services is generated from customers in the architectural, engineering, construction and building owner/operator industry, or AEC/O. Any decline in that industry could adversely affect our future revenue and profitability.
•Because a significant portion of our overall costs are fixed, our earnings are highly sensitive to changes in revenue.
•We derive a significant percentage of net sales from within the State of California and our business could be disproportionately harmed by an economic downturn or natural disaster affecting California.
•Our growth strategy depends, in part, on our ability to successfully market and execute several different, but related, service offerings. Failure to do so could impede our future growth and adversely affect our competitive position.
•We are dependent upon our vendors to continue to supply us equipment, parts, supplies, and services at comparable terms and price levels as the business grows.
•Our failure to protect our customers’ confidential information against security breaches could damage our reputation, harm our business and adversely affect our results of operation.
•Our failure to adequately protect the proprietary aspects of our technology solutions may cause us to lose market share.
•Our failure to comply with laws related to privacy and data security could adversely affect our financial condition.
•Our information technology and telecommunications systems are susceptible to damage, breach or interruption.
•Added risks are associated with our international operations.
•Our business could suffer if we fail to attract, retain, and successfully integrate skilled personnel.
•The market prices of our common stock is volatile, and is impacted by factors other than our financial performance, which could cause the value of an investment in our stock to decline.
•Changes in tax laws and interpretations could adversely affect our business.
•Our debt instruments impose certain restrictions on our ability to operate which in turn could negatively affect our ability to respond to business and market conditions and therefore could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
•If the interest rates on our borrowings increase, our access to capital and net income could be adversely affected.
•We may be exposed to employment-related claims and costs and periodic litigation that could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
All future written and verbal forward-looking statements attributable to us or any person acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained or referred to in this section. We undertake no obligation, and specifically disclaim any obligation, to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. You should, however, consult further disclosures we make in future filings of our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, and Current Reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments thereto, as well as our proxy statements.
TRADEMARKS AND TRADE NAMES
We own or have rights to a number of trademarks, service marks, and trade names that we use in conjunction with the operation of our business, including the name and design mark “ARC Document Solutions,” “ABACUS,” “METAPRINT,” “PlanWell,” “PlanWell PDS,” “Riot Creative Imaging,” “SKYSITE,” and various design marks associated therewith. In addition, we own or have rights to various trademarks, service marks, and trade names that we use regionally in conjunction with our operations. This report also includes trademarks, service marks and trade names of other companies.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Our Company
ARC Document Solutions Inc. is a digital printing company. We provide digital printing and document-related services to customers in a growing variety of industries. Our primary services are:
•digital printing of general and specialized business documents such as those found in marketing and advertising, engineering and construction and other industries, as well as producing highly-customized display graphics of all types and sizes;
•acquiring, placing and managing ARC-certified office printing equipment with proprietary device tracking and print management software at our customers’ offices and job sites;
•scanning documents, indexing them and adding digital search features for use in digital document management, document archives and facilities management, as well as providing other digital imaging services; and,
•reselling digital printing equipment and supplies.
Each of these services frequently include additional logistics services in the form of distributing and delivering finished documents, installing display graphics, or the digital storage of graphic files.
While our production equipment and services are technologically sophisticated, we have also invested heavily in developing technology applications that improve digital printing and document management process, increase the efficiency of print networks, and provide features that enhance data security. We believe the use of this technology by our customers creates a more valuable relationship.
Our services, technology and national footprint create economies of scale and production efficiency across geographical boundaries for customers who prefer to work with a single supplier for their digital printing needs. We believe these single-source capabilities provide us with a material advantage over our competition in local and regional markets.
We serve more than 35,000 active customers in a wide variety of markets including retail, technology, energy, education, hospitality, public utilities, and others. We also perform work for a majority of the largest design, engineering, and construction-oriented firms in North America. Our largest customers are served by an enterprise sales force called Global Solutions. No individual customer accounts for more than 2.5% of our overall revenue.
We believe that no other public company in the U.S. offers the particular set of services we do. We believe we are the largest digital printing provider to the architectural, engineering and construction industry, or AEC, as measured by revenue, number of customers, and number of service centers.
Our employees are generally long-tenured, highly-experienced, and cross-trained. They provide our services from 146 service centers located throughout North America and in select locations around the world. All of our service centers can provide the complete array of our general services, but each service center varies in scale, size of labor force and capacity based on the size and needs of its particular market.
Our primary operational objective is to drive as much customer work through our service center network as is practical in order to leverage our production infrastructure, a capable and efficient workforce, and production-grade equipment.
Our services can be customized to meet the needs of individual customers, as well as address the needs of a broad industry, and we believe we have an excellent reputation for service and reliability. Because of our reputation for high level of service and the benefits that our technology brings to our customers, we find that we are able to charge a reasonable premium for our offering.
Importantly, we don't believe that we should be compared to conventional printers. We do not produce high-volume, low-margin, commodity offset or lithographic printing, but rather provide short-run, customized, high-quality digital printing services. As such, we believe the customers, end-products, production equipment, labor utilization and economic models of conventional printers are materially different than ours.
ARC was organized as a limited liability company under the name American Reprographics Holdings L.L.C. in 1997. In 2005, we reorganized as a Delaware corporation in connection with our initial public offering under the name American
Reprographics Company. At the end of 2012 we formally changed our corporate name to “ARC Document Solutions, Inc.,” leaving our New York Stock Exchange ticker symbol “ARC” unchanged. We are headquartered in San Ramon, California. We conduct our operations through our wholly-owned subsidiary, ARC Document Solutions, LLC, a Texas limited liability company, and its affiliates. In the years following our inception, our business grew through acquisitions, but for more than a decade acquisitions have not been a focal point for growth.
Principal Products and Services
Specifically, our offerings include:
Digital Printing: We print documents of any size in color and black and white on a variety of materials including plain paper, vinyl, fabric, metal, wood and other three-dimensional substrates. While we can and do print high-page count work such as manuals or catalogs, the documents we typically produce are usually characterized by their high-quality production, low-volume and quick turnaround, and are produced using highly-sophisticated digital printing equipment.
Managed Print Services: We acquire and manage digital printing equipment and place it in our customers' facilities for their use, based on a service level agreement, or SLA. We lease or own the equipment ourselves, while our customers pay for what they use. Per-use minimum charges are often part of our SLAs. We operate more than 10,000 managed print services, or MPS, locations, ranging in size from one or two pieces of equipment in a single office, to hundreds of pieces equipment in offices around the world. We also provide proprietary software to our customers that are designed to control their print expenses and connect their remote employees with their offices and ARC print centers nationwide. This software is developed and integrated by ARC.
Scanning and Digital Imaging: We scan hard-copy small format or large format documents in color or black and white, typically providing them to our customers as searchable PDF files. We also use our patented optical character recognition technology to make documents searchable, and we host them on proprietary applications for use as part of our ARC Facilities solutions. The types of documents that we scan include office files, construction plans and other small or large documents. We also process, distribute and print-on-demand images we capture for our customers. Our large, centralized Scanning and Digital Imaging centers are compliant with the Health Insurability Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, so we can convert documents that include protected health information, or PHI. Our unique software creates efficient search tags on scanned data for easy search and retrieval. We offer Cloud-based document management software and other digital hosting services to our customers or make files available for our customers to host themselves.
Equipment and Supplies Sales: We sell equipment and supplies to a small segment of our customer base. We also provide ancillary services such as equipment service and maintenance, often as a way to generate recurring revenue in addition to a one-time sale. In addition, we offer certified used equipment available for sale or for use in our MPS offering.
Operations
The majority of our products and services are available from each of our service centers. As noted earlier, our primary operational objective is to optimize our business performance by driving as much customer work through our service center network as is practical, leveraging our production infrastructure, workforce, and production-grade equipment. All our production centers are digitally connected and we operate standard software and systems to support seamless movement of customers digital data and print anywhere within the ARC system.
In addition, we can provide many of our services in our customers’ offices. Our geographic presence is concentrated in the U.S., with additional service centers in Canada, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), China, India, and the United Kingdom. Our origin as a company was in California, and the initial expansion of our business was concentrated there. We derive approximately 30% of our total revenue from the products and services delivered in California.
All of our production facilities are connected via a Software-Defined Wide Area Network, or SD-WAN. Our cloud offerings are hosted by Amazon Web Services. We employ a combination of proprietary and industry-leading technologies to provide redundancy, backup and security of all data in our systems. All of our technology operations are designed to meet ISO 29001 standards for data security, and several of our service centers are HIPAA-compliant allowing us to manage document conversions and other scanning tasks involving protected health information, or PHI.
In response to the pandemic, most of our corporate, financial and administrative staff have been working entirely or partially from home, while our service center staff continue to work in our facilities and adhere to strict safety and health protocols.
Seasonality is a small part of our business, with sales of Digital Printing for construction clients influenced by seasonality and building cycles. Sales of display graphics are affected by retail trends, marketing calendars, advertising campaigns and branding initiatives, as well as the marketing and communication needs of our office and real estate development clients.
MPS sales are driven by the generation of office documents and our customers' desire to improve business processes and reduce print-related costs. Scanning and Digital Imaging sales are influenced primarily by the desire for document workflow improvements. Equipment and Supplies sales are driven by purchasing cycles of individual customers, as well as by new features and advancements from equipment manufacturers.
Strategic Focus
Our strategic focus areas include driving profitable growth, optimizing our business performance, and returning value to our stockholders.
Driving profitable growth: We intend to expand the markets and industries we serve while leveraging our long-term relationships with existing customers. Our outside sales efforts are focused on developing new customers and markets that are identified and targeted by our centralized corporate marketing team. Account-based sales have been generally shifted to in-house service centers where work is performed, existing customer relationships are strongest, and additional contacts within these accounts can be easily discovered.
Optimizing our business performance: We intend to leverage our service centers and cross-trained workforce to create efficiencies in our operations, lower our costs, and provide exceptional service to our customers. We believe that the more work we are able to drive through our service centers, the greater our efficiencies become.
Returning value to our stockholders: We intend to continue focusing our capital allocation strategy on benefiting our stockholders by using our cash flows to fund our dividend program and repurchase shares of our common stock in the open market.
Human Capital Management
We employed approximately 1,900 people as of December 31, 2023. Approximately 70% of our employees are located in the U.S. Approximately 98% of our team are full-time employees, with 60% representing non-exempt roles working in production functions. There are 14 engineers employed in our corporate headquarters in San Ramon, California, to develop, maintain, and support our proprietary software solutions. We also operate a technology center in Kolkata, India, with approximately 200 employees at that location who, in addition to supporting our San Ramon technology team, also support our research and development efforts. Approximately 90 service employees and managers work in our service centers in Canada, 50 in the United Kingdom, and another 200 in India, United Arab Emirates and China. None of our employees are currently represented by labor unions.
We have long embraced inclusion, diversity and equity in our workforce from the top down. Two of our four board members are women. Our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Operating Officer and our Chief Technology Officer are Southeast Asian, our Chief Financial Officer is Hispanic, and our Corporate Counsel and Corporate Secretary is a woman. Similar racial and gender diversity is represented across our workforce.
We believe our success is a direct result of the contributions and commitment of our employees. In 2023, ARC adjusted its compensation plans throughout the year to help facilitate employee retention. We also make profit-sharing and incentive plans part of most employees' compensation package. We believe that profit-sharing plans in particular encourage team efforts and cohesion within local and regional employee groups.
Our employee benefit offerings include price-competitive, high-quality medical insurance plans that include incentives for physical fitness, and we offer mental health and other employee assistance programs.
Our Customers
We serve more than 35,000 active customers in a wide variety of markets. No single customer accounted for 2.5% or more of our sales in 2023. The size of our customers is wide-ranging, from local restaurant owners and construction subcontractors to international retailers, regional energy companies, and some of the country’s largest school districts. We frequently sell products and services from across our portfolio to a single customer, particularly when working with larger customers. In
addition, we often sell similar services to different companies within the same industry. Payment terms for account-based customers typically do not exceed 30 days.
The types of Digital Printing customers we sell to span a wide variety of industries that include but are not limited to:
•advertising/media/marketing/promotional/graphic design departments,
•building owners and real estate developers,
•design, engineering and construction professionals,
•office management & IT departments responsible for print and document management,
•facilities management staff in schools, hospitals and other institutions,
•procurement departments in businesses of all kinds,
•small business owners,
•retail merchandising departments, and
•city/county/state municipalities.
The local markets we serve through our service centers are often highly fragmented with a wide variety of specialized, geographically-differentiated business practices. Larger regional, national and international customers often consolidate the purchasing and the acquisition of our services through a single corporate department. We serve these larger customers through our enterprise sales force which we refer to as our Global Solutions.
Competition
The level of competition that we face varies in each of our markets, but we believe our service level, the breadth of our offerings, price, quality, responsiveness, and convenience to the customer are common competitive elements in any market.
We often compete with single-service firms, e.g., quick printers, copier dealers or scanning bureaus, but we do not know of any other firm that currently provides the full suite of services we offer.
Local copy shops and self-serve franchises are often aggressive competitors for digital printing business, but rarely offer the breadth of document management and logistics services that we do.
There are several companies in each major metropolitan market that provide MPS and related print services, but we believe these companies cannot provide the same or similar integrated services and technology that we offer.
Likewise, there are small and regional scanning companies in many of the markets where we compete, but few have the infrastructure, footprint, stewardship guarantees, and privacy certifications that we do.
With regard to large national and international customers, we know of no other document solutions companies in the U.S. with the national presence and global reach that we have established for each of our primary services.
We believe that we have a strong competitive position in the markets and industries that we serve for the following reasons:
•Broad expertise in specialized digital printing, finishing and installation.
•Capabilities in a wide variety of digital printing formats including large-format, small-format, black and white, color, as well as print capabilities on conventional substrates (paper and paper-based products) and unconventional substrates (vinyl, fabric, plastic, metal, three-dimensional structures, etc.).
•Strong domain expertise in printing specialty documents, especially in the architectural, engineering and construction industries.
•Long-standing positive customer relationships in every industry we serve.
•High-ranking organic search engine statistics for our primary services.
•Long-term contracts with high-profile, enterprise-level customers that can be leveraged for referral work.
•A large North American service center footprint of 134 facilities, with additional market presence in Canada, China, the UAE, India, the U.K. and other select international locations.
•The variety of equipment brands we make available to our customers as compared to the single brands offered by competing equipment manufacturers.
•We believe we are the only national company that integrates digital printing and document production at (1) customer sites (onsite offerings), (2) a national network of service centers (offsite offerings), and (3) digital management of documents in the cloud (cloud-based offerings).
Suppliers and Vendors
We purchase or lease equipment for use in our production facilities and at our customers’ sites. We also purchase paper, toner and other consumables for the operation of our equipment. As a high-volume purchaser, we believe we receive favorable prices as compared to other service providers. Price increases are typically passed on to customers.
Our primary vendors of equipment, maintenance services, and digital printing supplies include Hewlett Packard, Canon Solutions America (Océ), and Xerox.
Purchases from these vendors during 2023 comprised approximately 35% of our total purchases of inventory and supplies. Although there are a limited number of suppliers that could supply our inventory, we believe any shortfalls from existing suppliers could be filled by other suppliers on comparable terms.
Proprietary Rights
We rely on a combination of copyright, trademark and trade secret laws, license agreements, nondisclosure and non-competition agreements, reseller agreements, customer contracts, and technical measures to establish and protect our rights in our proprietary technology. We also rely on a variety of technologies that are licensed from third parties to perform key functions.
We have registered “ARC Document Solutions,” “ARC,” as well as our historical name and logo, “American Reprographics Company,” as trademarks in the U.S. with the United States Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO. We have registered “PlanWell”, “PlanWell PDS”, “Riot Creative Imaging”, “ABACUS” and "SKYSITE” as trademarks with the USPTO and in other countries. We have registered three patents which relate to systems and methods for optimizing data transfers and synchronization of information that enable our facilities management solution. We do not own any other registered trademarks, service marks, or patents, that are material to our business.
For a discussion of the risks associated with our proprietary rights, see Item 1A, "Risk Factors - Our failure to adequately protect the proprietary aspects of our technology solutions may cause us to lose market share."
Regulatory Matters
Data Privacy and Security
Aspects of our business involve collecting, processing, disclosing, storing, and transmitting personal data, which are subject to certain privacy policies, contractual obligations, and laws, regulations, and directives relating to privacy and data protection. We store a substantial amount of customer and employee data, including personal data, on our networks and other systems and the cloud offerings we operate. In addition, the types of data subject to protection as personal data in the United States, and elsewhere have been expanding. In recent years, the collection and use of personal data by companies have come under increased regulatory and public scrutiny, especially in relation to the collection and processing of sensitive data, such as healthcare, biometric, genetic, financial services, and children’s data, precise location data, and data regarding a person’s race or ethnic origins, political opinions, or religious beliefs. For example, in the United States, protected health information is subject HIPAA, which can provide for civil and criminal penalties for noncompliance. Entities (such as us) that engage in receiving, maintaining, or transmitting protected health information provided by covered entities and other business associates are subject to enforcement under HIPAA. Our access to protected health information triggers obligations to comply with certain privacy rules and data security requirements under HIPAA.
There are a broad variety of other data protection laws in the United States that are applicable to our activities, and a wide range of enforcement agencies at both the state and federal levels that can review companies for privacy and data security concerns based on general consumer protection laws. The Federal Trade Commission and state Attorneys General all are aggressive in reviewing privacy and data security protections for consumers. New laws also are being considered at both the state and federal levels. A broad range of legislative measures also have been introduced at the federal level. Accordingly, failure to comply with federal and state laws (both those currently in effect and future legislation) regarding privacy and security of personal information could expose us to fines and penalties under such laws. In the event of a security breach, we also may have obligations to notify our customers or other parties or individuals about this breach, and this can lead to significant costs and the risk of potential enforcement and/or litigation. There is also a threat of consumer class actions related to these laws and the overall protection of personal data. Even if we are not determined to have violated these laws, government investigations into these issues typically require the expenditure of significant resources and generate negative publicity, which could harm our reputation and our business.
In the United States there also are specific state laws that may impact our business activities. For example, the state of California adopted a comprehensive privacy law, the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”), which took effect in January 2020 and became enforceable in July 2020. We have been and will continue to be required to devote substantial resources to implement and maintain compliance with the CCPA, and noncompliance could result in regulatory investigations and fines or private litigation. Moreover, in November 2020, California voters approved a privacy law, the California Privacy Rights Act, or CPRA, which amends the CCPA to create privacy rights and obligations in California. More than 12 other states already have passed similar state privacy laws, which already have gone into effect or will go into effect in the future. In addition, the state of Washington passed the My Health My Data Act in 2023 which specifically regulates health information that is not otherwise regulated by the HIPAA rules. Other states have already passed similar laws and other states may do so in the future. All of these privacy laws may impact our business activities and our relationships with business partners, customers and service providers.
Furthermore, the U.S. Congress is considering comprehensive privacy legislation. At this time, it is unclear whether Congress will pass such a law and if so, when and what it will require and prohibit. Moreover, it is not clear whether any such legislation would give the FTC any new authority to impose civil penalties for violations of the Federal Trade Commission Act in the first instance, whether Congress will grant the FTC rulemaking authority over privacy and information security, or whether Congress will vest some or all privacy and data security regulatory authority and enforcement power in a new agency, akin to EU data protection authorities.
Environmental
Our operations are subject to numerous laws and regulations governing environmental protection and occupational health and safety matters. Under these laws and regulations, we may be liable for, among other things, the cost of investigating and remediating contamination, regardless of fault or actions on our part. The amount of any such expense or related natural resource damages for which we may be held responsible could be substantial. For example, we are currently performing environmental remediation at a property we acquired as part of a business acquisition in the 1990s located in California. For additional discussion regarding the property and our estimated current estimated expenses see the discussion in Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The estimate of our final remediation expenses may change over time because of the varying costs of currently available cleanup techniques, unpredictable contaminant reduction rates associated with available cleanup techniques and the difficulty of determining in advance the nature and full extent of contamination. Based on our experience to date, we do not currently anticipate any material adverse effect on our business or consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows as a result of future compliance with existing environmental laws and regulations. However, evolving statutory and regulatory standards, their interpretation, more vigorous enforcement policies of regulatory agencies, or stricter or different interpretations of existing statutory and regulatory standards, may require additional expenditures by us, which may be material. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not incur significant environmental compliance costs in the future.
Available Information
We use our corporate website, www.e-arc.com, as a channel for routine distribution of important information, including news releases, analyst presentations and financial information. The information on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K or into any other report or document we file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission or SEC. We file with, or furnish, to the SEC Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those reports, as well as proxy statements and annual reports to stockholders, and, from time to time, other documents. The reports and other documents filed with or furnished to the SEC are available to investors on or through our corporate website free of charge as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file them with or furnish them to the SEC. The SEC maintains an internet site located at http://www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. Our SEC filings and other documents pertaining to the conduct of our business can be found on the “Investors” section of our website available at ir.e-arc.com. These documents are available in print to any stockholder who requests a copy by writing or by calling ARC Document Solutions.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
The risks and uncertainties set forth below, as well as other risks and uncertainties described elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K including in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” or in other filings with the SEC, could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and the trading price of our common stock. Additional risks and uncertainties that are not currently known to us or that are not currently believed by us to be material may also harm our business operations and financial results. Because of the following risks and uncertainties, as well as other factors affecting our financial condition and operating results, past financial performance should not be considered to be a reliable indicator of future performance, and investors should not use historical trends to anticipate results or trends in future periods.
Risks Related to Our Business
A significant portion of our revenue across all of our product and services is generated from customers in the AEC/O industry. Any decline in that industry could adversely affect our future revenue and profitability.
We estimate that customers in the AEC/O industry accounted for approximately 50% of our net sales in 2023; therefore, our results largely depend on the strength of that industry. Our historical operating results reflect the cyclical and variable nature of the AEC/O industry. We believe that the AEC/O industry generally experiences downturns several months after a downturn in the general economy, and that there may be a similar delay in the recovery of the AEC/O industry following a recovery of the general economy. A downturn in the AEC/O industry would diminish demand for all of our products and services, and would therefore negatively affect our revenues and have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition.
We derive a significant percentage of net sales from within the State of California and our business could be disproportionately harmed by an economic downturn or natural disaster affecting California.
We derived approximately 30% of our net sales in 2023 from our operations in California. Accordingly, we are sensitive to economic factors affecting business activity in California, including general and local economic conditions, declines in specific industries, macroeconomic trends, political factors affecting commerce and economic development, and natural disasters (including drought, earthquakes and wildfires) the intensity and frequency of which are being exacerbated by climate change. Any adverse developments affecting California could have a disproportionately negative effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our growth strategy depends, in part, on our ability to successfully market and execute several different, but related, service offerings. Failure to do so could impede our future growth and adversely affect our competitive position.
As part of our growth strategy, we intend to continue to offer and grow a variety of service offerings that are relatively new to the company. Our efforts will be affected by our ability to acquire new customers for our new service offerings as well as sell the new service offerings to existing customers. If we fail to procure new customers or sell these services to our existing customers, our growth may be adversely affected and we may incur operating losses as a result of a failure to realize revenue from the investments made in new service offerings.
Because a significant portion of our overall costs are fixed, our earnings are highly sensitive to changes in revenue.
Our network of service centers, equipment and related support activities involves substantial fixed costs which cannot be adjusted quickly to respond to declines in demand for our services. We estimate that approximately 23% of our overall costs were fixed in 2023. As a consequence, our results of operations are subject to relatively high levels of volatility and our earnings could deteriorate rapidly in the face of declining revenues because our ability to reduce fixed costs in the short-term is limited. If we fail to manage our fixed costs appropriately, or to maintain adequate cash reserves to cover such costs, we may suffer material adverse effects on our results of operations and financial condition.
We are dependent upon our vendors to continue to supply us with equipment, parts, supplies, and services at comparable terms and price levels as the business grows.
Our access to equipment, parts, supplies, and services depends upon our relationships with, and our ability to purchase these items on competitive terms from our principal vendors. These vendors are not required to use us to distribute their equipment and are generally free to change the prices and other terms at which they sell to us. In addition, we compete with the selling efforts of some of these vendors. Our reliance on a limited number of principal vendors presents various risks. These include the risk that an interruption in our relationships with our principal vendors for any reason, such as a natural catastrophe, epidemics, pandemics, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, or actions taken in regard to increased tariffs on goods produced in
certain countries such as China, we may not be able to develop an alternate source without incurring material additional costs and substantial delays. Significant deterioration in relationships with, or in the financial condition of, these significant vendors could have an adverse effect on our ability to sell equipment as well as our ability to provide effective service and technical support to our customers. If one of these vendors terminates or significantly curtails its relationship with us, or if one of these vendors ceases operations, we would be forced to expand our relationships with our other existing vendors or seek out new relationships with previously unused vendors.
Our failure to adequately protect the proprietary aspects of our technology solutions may cause us to lose market share.
Our success depends on our ability to protect and preserve the proprietary aspects of our technology products. We rely on a combination of patent, copyright, trademark and trade secret protection, confidentiality agreements, license and subscription agreements, and technical measures to establish and protect our rights in our proprietary technologies. These protections, however, may be inadequate. It is also possible that our intellectual property rights could be challenged, invalidated or circumvented, allowing others to use our intellectual property to our competitive detriment. Furthermore, we may, from time to time, be subject to intellectual property litigation which can be expensive, a burden on management’s time and our Company’s resources, and the outcome of any such litigation may be uncertain.
Competition in our industry and innovation by our competitors may hinder our ability to execute our business strategy and adversely affect our profitability.
The markets for our products and services are highly competitive, with competition primarily at local and regional levels. We compete primarily based on the level and quality of customer service, technological leadership, and price. Our future success depends, in part, on our ability to continue to improve our service and product offerings, and develop and integrate new technology solutions. In addition, current and prospective customers may decide to perform certain services themselves instead of outsourcing these services to us. These competitive pressures could adversely affect our sales and consolidated results of operations.
Changes in laws or regulations relating to privacy or the collection, processing, disclosure, storage, localization, or transmission of personal data, or any actual or perceived failure by us to comply with such laws and regulations, contractual obligations, or applicable privacy policies, could materially adversely affect our business
Aspects of our business involve collecting, processing, disclosing, storing, and transmitting personal data, which are subject to certain privacy policies, contractual obligations, and laws, regulations, and directives relating to privacy and data protection. We store a substantial amount of customer and employee data, including personal data, on our networks and other systems and the cloud offerings we operate. In addition, the types of data subject to protection as personal data in the United States, and elsewhere have been expanding. In recent years, the collection and use of personal data by companies have come under increased regulatory and public scrutiny, especially in relation to the collection and processing of sensitive data, such as healthcare, biometric, genetic, financial services, and children’s data, precise location data, and data regarding a person’s race or ethnic origins, political opinions, or religious beliefs. For example, in the United States, protected health information is subject to HIPAA, which can provide for civil and criminal penalties for noncompliance. Entities (such as us) that engage in receiving, maintaining, or transmitting protected health information provided by covered entities and other business associates are subject to enforcement under HIPAA. Our access to protected health information triggers obligations to comply with certain privacy rules and data security requirements under HIPAA.
In addition to potential enforcement by the United States Department of Health and Human Services for potential HIPAA violations, we are also potentially subject to privacy enforcement from the FTC. The FTC has been particularly focused on certain activities related to the processing of sensitive data, including the unpermitted processing of health and genetic data through its recent enforcement actions and is expanding the types of privacy violations that it interprets to be “unfair” under Section 5 of the FTC Act, as well as the types of activities it views to trigger the Health Breach Notification Rule (which the FTC also has the authority to enforce). We will need to account for the FTC’s evolving rules and guidance for proper privacy and data security practices in order to mitigate our risk for a potential enforcement action, which may be costly. If we are subject to a potential FTC enforcement action, we may be subject to a settlement order that requires us to adhere to very specific privacy and data security practices, which may impact our business. We may also be required to pay fines as part of a settlement (depending on the nature of the alleged violations). If we violate any consent order that we reach with the FTC, we may be subject to additional fines and compliance requirements. We face risks of similar enforcement from State Attorneys General and, potentially, other regulatory agencies.
Any systems failure or security breach that results in the release of, or unauthorized access to, personal data, or any failure or perceived failure by us or our third-party service providers to comply with applicable privacy policies, contractual obligations, or any applicable laws or regulations relating to privacy or data protection, could result in proceedings against us by domestic or foreign government entities or others, including private plaintiffs in litigation. Such proceedings could result in
the imposition of sanctions, fines, penalties, liabilities, government orders, and/or orders requiring that we change our data practices, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, reputation, and financial condition.
State privacy laws in the United States also may impact our business operations. The state of California has adopted a comprehensive privacy law, the CCPA, which took effect in January 2020 and became enforceable in July 2020. We have been required to devote substantial resources to implement and maintain compliance with the CCPA, and noncompliance could result in regulatory investigations and fines or private litigation. Moreover, in November 2020, California voters approved a privacy law, the CPRA, which amends the CCPA to create additional privacy rights and obligations in California, and went into effect on January 1, 2023. Numerous other states have passed laws similar to the CCPA, which will go into effect in 2023 and beyond. More states may follow. These laws may impose additional costs and obligations on us. The Securities and Exchange Commission also has issued new regulations related to cybersecurity that may require additional reporting and other compliance obligations, as well as creating additional risks related to public notifications concerning cyber incidents.
Furthermore, the U.S. Congress is considering comprehensive privacy legislation. At this time, it is unclear whether Congress will pass such a law and if so, when and what it will require and prohibit. Moreover, it is not clear whether any such legislation would give the FTC any new authority to impose civil penalties for violations of the Federal Trade Commission Act in the first instance, whether Congress will grant the FTC rulemaking authority over privacy and information security, or whether Congress will vest some or all privacy and data security regulatory authority and enforcement power in a new agency, akin to EU data protection authorities.
Complying with these and other changing requirements could cause us to incur substantial costs or pay substantial fines or penalties, require us to change our business practices, require us to take on more onerous obligations in our contracts, or limit our ability to provide certain services in certain jurisdictions, any of which could materially adversely affect our business and operating results. New laws or regulations restricting or limiting the collection or use of mobile data could also reduce demand for certain of our offerings or require changes to our business practices, which could materially adversely affect our business and operating results.
If we or our third-party service providers experience a disruption due to a cybersecurity attack or security breach and unauthorized parties obtain access to our customers’ or vendors’ data, our data, our networks or other systems, or the cloud offerings we operate, our offerings may be perceived as not being secure, our reputation may be harmed, demand for our offerings may be reduced, our operations may be disrupted, we may incur significant legal and financial liabilities, and our business could be materially adversely affected
As part of our business, we process, store, and transmit our customers’ and vendors’ data as well as our own, including in our networks and other systems and the cloud offerings we operate. Security breaches may occur due to technological error, computer viruses, or third-party action, including intentional misconduct by computer hackers or state actors, physical break-ins, industrial espionage, fraudulent inducement of employees, customers, or channel partners to disclose sensitive information such as usernames or passwords, and employee, customer, or channel partner error or malfeasance. A security breach could result in unauthorized access to or disclosure, modification, misuse, loss, or destruction of our customers’, prospects’, vendors’, or channel partners’ data, our data (including our proprietary information, intellectual property, or trade secrets), our networks or other systems, or the cloud offerings we operate. Third parties may also conduct attacks designed to prevent access to critical data or systems through ransomware or temporarily deny customers access to our cloud environments.
We, and our service providers, may in the future experience attempts by third parties to identify and exploit software and service vulnerabilities, penetrate or bypass our security measures, and gain unauthorized access to our or our customers’ or service providers’ cloud environments, networks, and other systems. Security measures that we or our third-party service providers have implemented may not be effective against all current or future security threats. Because there are many different security breach techniques and such techniques continue to evolve, we may be unable to anticipate, detect, or mitigate attempted security breaches and implement adequate preventative measures.
Any security breach, ransomware attack, or successful denial of service attack could result in a loss of customer confidence in the security of our offerings and damage to our brand, reduce the demand for our offerings, disrupt our normal business operations, require us to spend material resources to investigate or correct the breach, require us to notify affected customers or individuals and/or applicable regulators and others, provide identity theft protection services to individuals, expose us to legal liabilities, including litigation, regulatory enforcement actions, and indemnity obligations, and materially adversely affect our revenues and operating results. Our software services operate in conjunction with and are dependent on third-party products and components across a broad ecosystem. If there is a security vulnerability in one of these products or components, and if there is a security exploit targeting it, we could face increased costs, liability claims, customer dissatisfaction, reduced revenue, or harm to our reputation or competitive position. Our insurance policies may not be adequate to compensate us for the
potential losses arising from any cybersecurity breach or incident. In addition, such insurance may not be available to us in the future on economically reasonable terms, or at all. Further, our insurance may not cover all claims made against us and could have high deductibles in any event, and defending a suit, regardless of its merit, could be costly and divert management attention.
These risks will increase as we continue to grow the scale of our Digital Printing and Scanning and Digital Imaging services and process, store, and transmit increasingly large amounts of our customers’, vendors’, and our own data. In particular, as remote working conditions have led businesses to increasingly rely on virtual environments and communication systems, there has been an increase in cyberattacks and other malicious activities.
Damage or disruption to our facilities, including our technology center, could impair our ability to effectively provide our services and may have a significant effect on our revenues, expenses and financial condition.
Our IT systems are an important part of our operations. We currently store customer data on a variety of servers, including servers hosted by Amazon Web Services and at our technology center located in San Ramon, California near known earthquake fault zones. Although we have redundant systems and offsite backup procedures in place, interruption in service, damage to or destruction of our technology center or a disruption of our data storage processes resulting from sustained process abnormalities, human error, acts of terrorism, violence, war or a natural disaster, such as fire, earthquake or flood, could result in delays, in reduced levels of customer service and have a material adverse effect on the markets in which we operate and on our business operations.
Although we currently maintain general property damage insurance, if we incur losses from uninsured events, we could incur significant expenses which would adversely affect our results of operations, cash flows and financial condition.
Catastrophic events, including global pandemics such as the COVID-19 pandemic, could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and/or financial condition.
The occurrence of a major earthquake, fire, flood or other weather events, power loss, telecommunications failure, software or hardware malfunctions, pandemics (including the COVID-19 pandemic), cyber-attack, war, terrorist attack or other catastrophic event that our disaster recovery plans do not adequately address, could adversely affect our employees, our systems, our ability to produce and distribute our products, and our reputation.
A catastrophic event resulting in the destruction or disruption of our workforce, our systems, our ability to produce and distribute our products, any of our data centers or our critical business or information technology systems could adversely affect our ability to conduct normal business operations and our operating results or cash flows. The adverse effects of any such catastrophic event would be exacerbated if experienced at the same time as another unexpected and adverse event, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Added risks are associated with our international operations.
We have international operations in China, India, the United Kingdom, Canada, and United Arab Emirates. Approximately 12% of our revenues for 2023 were derived from our international operations, with approximately 3% derived from China. We anticipate that future sales to international customers will continue to account for a significant percentage of our revenues. Risks associated with international sales and operations include, but are not limited to:
a.Political and economic instability, including the war between Ukraine and Russia, the conflict in Israel and neighboring regions and potential hostilities between China and Taiwan;
b.International terrorism;
c.Global economic sanctions and export controls, including U.S. export controls related to China, sanctions related to Russia, and increased scrutiny of exports of digital imaging and other products;
d.Failure to comply with anti-bribery legislation, including the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act;
e.Changes in legal and regulatory requirements, including complex trade compliance regulations;
f.U.S. and foreign government policy changes affecting the markets for our products;
g.Changes in tax laws and tariffs;
h.Additional deterioration in U.S. - China and U.S. - Russia relations;
i.Difficulties in protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights;
j.Failure to comply with the foreign data protection laws;
k.New and emerging non-U.S. regulations relating to environmental, social and governance and corporate social responsibility matters, which could be costly to comply with;
l.Transportation, including piracy in international waters;
m.Currency exchange rate fluctuations; and
n.Challenges relating to managing a global workforce with diverse cultures, backgrounds and labor laws.
The impact of these factors is difficult to predict, but one or more of them could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. Certain international contracts may also include industrial cooperation agreements requiring specific in-country purchases, investments, manufacturing agreements or other financial obligations, known as offset obligations, and may provide for penalties if we fail to meet such requirements.
Our business could suffer if we fail to attract, retain, and successfully integrate skilled personnel.
We believe that our ability to attract, retain, and successfully integrate qualified personnel is critical to our success. As we continue to place more emphasis on document management and storage technology, our need to hire and retain software and other technology-focused personnel has increased, and can be expected to continue to increase. Competition for such personnel, particularly in the San Francisco Bay Area, is intense. If we lose key personnel and/or are unable to recruit qualified personnel, our ability to manage and grow our business will be adversely affected. In addition, the loss of the services of one or more members of our senior management team would disrupt our business and impede our ability to successfully execute our business strategy.
We may be exposed to employment-related claims and periodic litigation that could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We are subject to a number of risks inherent to our status as an employer, including claims of misconduct or negligence on the part of our employees, claims by our employees and former employees of discrimination or harassment; claims relating to violations of wage, hour and other workplace regulations; and claims relating to employee benefits, entitlements to employee benefits, or errors in the calculation or administration of such benefits.
If we experience significant incidents in any of the above-described areas, we could face substantial out-of-pocket losses, or fines. In addition, such claims may give rise to litigation, which may be time consuming, distracting and costly, and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Environmental, health, and safety laws and regulations, and the costs of compliance, could materially adversely affect our financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Our operations are subject to numerous laws and regulations governing environmental protection and occupational health and safety matters. Under these laws and regulations, we may be liable for, among other things, the cost of investigating and remediating contamination, regardless of fault or actions on our part. The amount of any such expense or related natural resource damages for which we may be held responsible could be substantial. We have incurred, and in the future may continue to incur, liability under environmental statutes and regulations with respect to the contamination detected at sites we own or operate (including contamination caused by prior owners and operators of such sites, abutters or other persons) and the sites at which we have disposed of hazardous substances. For example, we are currently performing environmental remediation at a property we acquired as part of a business acquisition in the 1990’s located in California. As of December 31, 2023, we have established a reserve totaling $4.5 million with respect to certain presently estimated environmental remediation costs. For additional discussion regarding the property and our estimated expenses see the discussion under the caption “Site Remediation Obligation” within Part II, Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The estimate of our final remediation expenses may change over time because of the varying costs of currently available cleanup techniques, unpredictable contaminant reduction rates associated with available cleanup techniques and the difficulty of determining in advance the nature and full extent of contamination. Based on our experience to date, we do not currently anticipate any material adverse effect on our business or consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows as a result of future compliance with existing environmental laws and regulations. However, evolving statutory and regulatory standards, their interpretation, more vigorous enforcement policies of regulatory agencies, or stricter or different interpretations of existing statutory and regulatory standards, may require additional expenditures by us, which may be material. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not incur significant environmental compliance costs in the future.
Changes in tax laws and interpretations could adversely affect our business.
We are subject to income and other taxes in the U.S. and in numerous foreign jurisdictions. Our domestic and foreign tax provisions are dependent on the jurisdictions in which profits are determined to be earned and taxed. Additionally, the amount of tax provision is subject to our interpretation of applicable tax laws in the jurisdictions in which we operate. A number of factors influence our effective tax rate, including changes in tax laws and treaties as well as the interpretation of existing laws and rules. Federal, state, and local governments and administrative bodies within the U.S., which represents a majority of our
operations, and other foreign jurisdictions have implemented, or are considering, a variety of broad tax, trade, and other regulatory reforms that may impact us.
Results of tax examinations may adversely affect our future results of operations.
We are subject to various tax examinations on an ongoing basis. Adverse results of tax examinations for income, payroll, value added, sales-based and other taxes may require future material tax payments if we are unable to sustain our position with the relevant jurisdiction. Where appropriate, we have made accruals for these matters which are reflected in our Consolidated Balance Sheets and Statements of Operations.
Risks Related to Our Indebtedness
Our debt instruments impose certain restrictions on our ability to operate which in turn could negatively affect our ability to respond to changing business and market conditions and therefore could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
As of December 31, 2023, we had $62.2 million in outstanding short and long-term borrowings under our credit facilities, and finance leases, excluding trade payables and operating leases. The terms of the agreements under which this indebtedness was incurred may limit or restrict, among other things, our ability to incur certain additional debt, make certain restricted payments, consummate certain asset sales, and enter into certain transactions with affiliates.
We are also required to maintain a total leverage ratio and fixed charge coverage ratio under our credit agreement with U.S. Bank National Association, dated April 22, 2021, or the 2021 Credit Agreement, as amended on June 15, 2023. Our inability to meet these ratios could result in the acceleration of the repayment of the outstanding obligations under the 2021 Credit Agreement, the termination of the lenders’ commitment to provide our revolving line of credit thereunder, the increase in our effective cost of funds or the cross-default of other credit arrangements. As a result, our ability to operate may be restricted and our ability to respond to business and market conditions may be limited, which could have an adverse effect on our business and operating results.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The market prices of our common stock is volatile, and may be impacted by factors other than our financial performance, which could cause the value of an investment in our common stock to decline.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate substantially due to a variety of factors, many of which are beyond our control. Between January 1, 2023, and December 31, 2023, the closing price of our common stock fluctuated from a low of $2.65 to a high of $3.84 per share.
In the past, stockholders have sometimes instituted securities class action litigation against companies following periods of volatility in the market price of their securities. Any similar litigation against us could result in substantial costs, divert management's attention as well as our other resources and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
There can be no assurance that we will continue to declare dividends or repurchase shares of our common stock.
Our Board of Directors has declared quarterly dividends in the past. Our ability to continue to pay quarterly dividends and to repurchase shares of our common stock is subject to capital availability and periodic determinations by our Board of Directors that dividends and repurchases of shares of our common stock are in the best interests of our stockholders and in compliance with applicable laws. Our dividend payments and repurchases of shares of our common stock may change from time to time. Management currently intends to continue quarterly dividends, and repurchases of shares of our common stock, subject to approval by our Board of Directors, but we cannot provide any assurance as to the timing, sustainability, or any particular amounts of future dividends and repurchases of shares of our common stock. A suspension in our dividend payments or repurchases of shares of our common stock could have a negative effect on the price of our common stock and would have a negative effect on returns on investment to our stockholders.
Our third amended and restated by-laws provide that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware (or, if the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, then the federal district court for the District of Delaware) is the exclusive forum for certain litigation that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for such disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees
Our amended and restated by-laws provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware (or, if the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, then the federal district court for the District of Delaware) shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the corporation, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any current or former director, officer, other employee or stockholder of the corporation to the corporation or the corporation’s stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware or as to which the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware confers jurisdiction on the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware, or (iv) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of our Certificate of Incorporation or our bylaws or governed by the internal affairs doctrine. This exclusive forum provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Securities Act, the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction.
The choice of forum provision may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and other employees. Alternatively, if a court were to find the choice of forum provision contained in our third amended and restated by-laws to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such action in other jurisdictions.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
We believe that cybersecurity is important to how we operate as a company and as such we focus on defining and managing our cybersecurity risk. With the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape and continual emergence of new threats, our Board of Directors, Audit Committee, and senior management team ensure that significant resources are devoted to cybersecurity risk management and the technologies, processes and people that support it. We have steadily increased companywide awareness to strengthen our cybersecurity risk management practice and processes. We employ a risk-based cybersecurity program that leverages the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework and is designed to protect, detect, identify, and respond to cybersecurity risks and incidents. We regularly assess critical areas of our cybersecurity program to identify cybersecurity strengths and weaknesses and provide valuable insights for mitigating cyber risks.
Our cybersecurity team monitors networks and systems for potential signs of suspicious activity by utilizing, among other things, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication, and encryption. Additionally, our cybersecurity program includes a security Incident Management policy to ensure that consistent, methodical, and timely incident response process is completed by the designated response team. The designated cybersecurity incident response team is responsible for managing and coordinating our cybersecurity incident response efforts. The incident management workflow with assigned duties and responsibilities streamlines the incident response and helps improve and mitigate the overall incident impact.
We engage cybersecurity consultants, and other third parties to enhance our cybersecurity practices. We conduct penetration testing, vulnerability, and other assessments with the assistance of these third parties. These tests and assessments
enhance our cybersecurity program. We also use third-party service providers to support our operations and technology initiatives. We evaluate third-party service providers from a cybersecurity risk landscape.
Our Board of Directors oversees management’s processes for identifying and mitigating risks, including risks pertaining to cybersecurity. On a periodic basis, senior executives, including our Chief Technology Officer (CTO) present to the Board of Directors details of our cybersecurity initiatives and program and any incidents deemed to have a business impact, even if the impact is not material for us. The Board of Directors along with all committee members participate in discussions regarding cybersecurity risks.
Our Information Technology and Security organization is managed by our Chief Technology Officer who has overall responsibility for monitoring and managing cybersecurity threats and incidents and for implementing cybersecurity policies, programs, procedures, and strategies. The Chief Technology Officer has vast experience in providing cyber security oversight.
Despite the continuous risk faced by the Company, we have suffered no incidents that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition. Notwithstanding the exhaustive approach we take to cybersecurity, we may not be successful in preventing or mitigating a cybersecurity incident that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. While we maintain cybersecurity insurance and have never had a cybersecurity claim, the costs related to cybersecurity threats or disruptions may not be fully insured. See Item 1A. “Risk Factors” for a discussion of cybersecurity risks.
Item 2. Properties
At the end of 2023, we operated 146 service centers, of which 126 were in the United States, eight were in Canada, six were in China, three were in the United Kingdom, two were in India, and one was in United Arab Emirates. We also occupied a technology center in Kolkata, India, as well as other facilities, including our executive offices located in San Ramon, California.
In total, the Company occupied approximately 1.0 million square feet as of December 31, 2023.
We lease nearly all of our service centers, and each of our administrative facilities and our technology centers. In addition to the facilities that are owned, our fixed assets are comprised primarily of machinery and equipment, vehicles, and computer equipment. We believe that our facilities are adequate and appropriate for the purposes for which they are currently used in our operations and are well maintained.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
We are involved, and will continue to be involved, in legal proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including commercial and employment-related lawsuits. Some of these lawsuits purport or may be determined to be class actions and seek substantial damages, and some may remain unresolved for several years. We establish accruals for specific legal proceedings when it is considered probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Our evaluation of whether a loss is reasonably probable is based on our assessment and consultation with legal counsel regarding the ultimate outcome of the matter. As of December 31, 2023, we have accrued for the potential impact of loss contingencies that are probable and reasonably estimable. We do not currently believe that the ultimate resolution of any of these matters will have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows. However, the results of these matters cannot be predicted with certainty, and an unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows.
For additional discussion regarding certain environmental proceedings see the discussion in Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock, par value $0.001, is listed on the New York Stock Exchange or NYSE under the stock symbol “ARC”.
Holders
As of February 16, 2024, the approximate number of stockholders of record of our common stock was 126. Because many of the shares of our common stock are held by brokers and other institutions on behalf of stockholders, we are unable to estimate the total number of beneficial owners represented by these stockholders of record.
Dividends
In December 2023, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.05 per share of common stock that is payable on February 29, 2024 to stockholders of record as of January 31, 2024. The timing, declaration and payment of future dividends, however, falls within the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon many factors, such as our financial condition and earnings, the capital requirements of our business, restrictions imposed by applicable law and our debt agreements and any other factors the Board of Directors deems relevant from time to time.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table presents information regarding repurchases of our common stock for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except for price per share) | | (a) Total Number of
Shares Purchased (1) | | (b) Average Price Paid per Share ($) | | (c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | | (d) Approximate Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under The Plans or Programs (1) |
| Period | | | | | | | | |
| October 1, 2023—October 31, 2023 | | — | | | | | — | | | $ | 8,676 | |
| November 1, 2023—November 30, 2023 | | 158 | | | $ | 2.80 | | | 158 | | | $ | 8,234 | |
| December 1, 2023—December 31, 2023 | | 74 | | | $ | 2.99 | | | 74 | | | $ | 8,013 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Total repurchases during the fourth quarter of 2023 | | 232 | | | | | 232 | | | |
(1) On February 23, 2023, we announced that our Board of Directors expanded the repurchase program we previously announced on May 1, 2019 by an additional $5.0 million for an aggregate program size of $20.0 million through March 31, 2026. Under the repurchase program, purchases of shares of common stock may be made from time to time in the open market, or in privately negotiated transactions, in compliance with applicable state and federal securities laws. The timing and amounts of any purchases will be based on market conditions and other factors including price, regulatory requirements, and capital availability. The stock repurchase program does not obligate us to acquire any specific number of shares in any period, and may be expanded, extended, modified or discontinued at any time without prior notice.
Item 6. [Reserved.]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Business Summary
ARC Document Solutions Inc. is a digital printing company. We provide digital printing and document-related services to customers in a growing variety of industries. Our primary services are:
•digital printing of general and specialized business documents such as those found in marketing and advertising, engineering and construction and other industries, as well as producing highly-customized display graphics of all types and sizes;
•acquiring, placing and managing ARC-certified office printing equipment with proprietary device tracking and print management software at our customers’ offices and job sites;
•scanning documents, indexing them and adding digital search features for use in digital document management, document archives and facilities management, as well as providing other digital imaging services; and,
•reselling digital printing equipment and supplies.
Each of these services frequently include additional logistics services in the form of distributing and delivering finished documents, installing display graphics, or the digital storage of graphic files.
For a more complete description of our business, and product and service offerings, see Part I, Item 1 - "Business" - of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Costs and Expenses
Our cost of sales consists primarily of materials (paper, toner and other consumables), labor, and “indirect costs.” Indirect costs consist primarily of equipment expenses related to our MPS locations (typically our customers’ offices and job sites) and our service centers. Facilities and equipment expenses include maintenance, repairs, rents, insurance, and depreciation. Paper is the largest component of our material cost; however, the impact of paper pricing on our operating margins is mitigated, and in some cases eliminated, as it is often passed on to our customers. We closely monitor material cost as a percentage of net sales to measure volume and waste, and we maintain low levels of inventory. We also track labor utilization, or net sales per employee, to measure productivity and determine staffing levels.
The effects of the 2022 global supply chain disruptions on our business eased in 2023. The supply chain disruptions for us were primarily confined to price increases. As noted above, price increases are often passed on to our customers. Our labor costs have increased moderately as we sought to retain valuable employees and competed for new hires in 2023. While these increases had an effect on our results of operations, we believe our cost optimization initiatives allowed us to mitigate their impact and will allow us to continue to manage them in future periods.
Historically, our capital expenditure requirements have varied based on our need for printing equipment in our MPS locations and service centers. Over the past several years, the pandemic has reduced the number of employees in our customers’ locations, which has, in turn, reduced the need for equipment. We believe this equipment trend has become permanent and, as a result, we think our past two years of capital expenditures are more indicative of our future capital needs than our longer-term history suggests.
Because our relationships with credit providers allow us to obtain attractive lease rates, we have historically chosen to lease rather than purchase most of our equipment. Due in part to the rising cost of capital in 2023, we have adjusted our historical equipment acquisition strategy and used more of our available cash to purchase equipment during the prior year to reduce the impact of interest expense on our operating results.
Research and development costs consist mainly of the salaries, leased building space, and computer equipment related to our data storage and development centers in San Ramon, California and Kolkata, India. Such costs are primarily recorded to cost of sales.
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic adversely impacted our financial performance from 2020 to 2022, but we expect that its acute impact is behind us. We believe, however, that the reduced in office presence of employees brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic are permanent. As a result, our MPS business has been and remains under pressure as most employers have left work-from-home policies in place and less equipment is needed to support them in typical office spaces. By contrast, we believe work-from-home and hybrid work practices benefit our scanning business because employees need access to documents, regardless of where they are working, and document scanning is the first step in making them accessible in the cloud.
Uncertainty around the potential disruption to our business related to the COVID-19 pandemic and its effect on the U.S. economy and our clients’ ongoing business operations has diminished, but we remain watchful and prepared to alter our business operations to protect employees and customers.
Market Review
We believe the expanding list of industries we serve are generally growing and offer ongoing sales opportunities for our services.
Demand for digital printing appears high across our customer base, and includes environmental graphics, marketing and promotional work. We believe that the desire to communicate visually—and especially in color—is growing in all areas of commerce, in office environments, in educational venues, and in public spaces of all kinds. While office capacity has fluctuated in recent years due to work-from-home and hybrid work policies, we have experienced minimal desire among our customers to completely abandon in office work, and we have many customers who have expressed a desire to make work spaces more inviting and engaging for the people who occupy them.
While the demand for MPS has declined from its peak, we believe it remains sought after by many clients, due to our flexible print network capacity, use of certified used equipment to reduce hardware costs, and ability to create efficiencies in the printing environment through our software and services. Unlike MPS, work-from-home and other remote document access requirements increase demand for scanning and digital imaging services.
In 2023, construction activity was constrained by higher interest rates and continuing labor shortages. The volume of construction plan printing fell alongside the reduction in construction activity. While we expect building activity to increase as interest rates ease, we do not expect the use of construction plan printing to be commensurate with it.
Economic inflation in the U.S., Canada and abroad has materially affected our business over the past year, primarily in the form of higher labor and raw material costs. Price increases in materials continue to be passed on to our customers, as well as some of the labor cost increases. Supply chain disruptions, other than price increases, have largely resolved in 2023, and we believe we remain reasonably protected from them due to the wide variety of suppliers we have developed relationships with over our history.
Results of Operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | 2023 Versus 2022 | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Increase (decrease) | | |
| (In millions, except percentages) | 2023 (1) | | 2022 (1) | | | | $ (1) | | % | | | | |
| Digital Printing | $ | 170.1 | | | $ | 174.8 | | | | | $ | (4.7) | | | (2.7) | % | | | | |
| MPS | 74.8 | | | 75.8 | | | | | (1.0) | | | (1.3) | % | | | | |
| Scanning and Digital Imaging | 20.3 | | | 17.4 | | | | | 3.0 | | | 17.0 | % | | | | |
| Total services sales | $ | 265.2 | | | $ | 267.9 | | | | | $ | (2.7) | | | (1.0) | % | | | | |
| Equipment and Supplies sales | 16.0 | | | 18.1 | | | | | (2.1) | | | (11.5) | % | | | | |
| Total net sales | $ | 281.2 | | | $ | 286.0 | | | | | $ | (4.8) | | | (1.7) | % | | | | |
| Gross profit | $ | 94.4 | | | $ | 96.0 | | | | | $ | (1.6) | | | (1.7) | % | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | $ | 76.3 | | | $ | 77.5 | | | | | $ | (1.2) | | | (1.6) | % | | | | |
| Amortization of intangibles | $ | — | | | $ | 0.1 | | | | | $ | (0.1) | | | (57.7) | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Site remediation expense | $ | 4.0 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 4.0 | | | — | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense, net | $ | 1.6 | | | $ | 1.8 | | | | | $ | (0.2) | | | (9.1) | % | | | | |
| Income tax provision | $ | 4.4 | | | $ | 5.8 | | | | | $ | (1.4) | | | (24.8) | % | | | | |
| Net income attributable to ARC | $ | 8.2 | | | $ | 11.1 | | | | | $ | (2.9) | | | (25.8) | % | | | | |
Adjusted net income attributable to ARC (2) | $ | 11.8 | | | $ | 12.0 | | | | | $ | (0.2) | | | (1.8) | % | | | | |
| Cash flows provided by operating activities | $ | 36.6 | | | $ | 37.2 | | | | | $ | (0.6) | | | (1.7) | % | | | | |
EBITDA (2) | $ | 31.9 | | | $ | 39.1 | | | | | $ | (7.3) | | | (18.5) | % | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA (2) | $ | 38.1 | | | $ | 40.9 | | | | | $ | (2.8) | | | (6.8) | % | | | | |
(1)Column does not foot due to rounding.
(2)Non-GAAP financial measure. See "Non-GAAP Financial Measures" following "Results of Operations" for definitions, reconciliations and more information related to our Non-GAAP disclosures.
The following table provides information on the percentages of certain items of selected financial data as a percentage of net sales for the periods indicated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As Percentage of Net Sales |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 (1) | | 2022 (1) | | |
| Net Sales | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | |
| Cost of sales | 66.4 | | | 66.4 | | | |
| Gross profit | 33.6 | | | 33.6 | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 27.1 | | | 27.1 | | | |
| Amortization of intangibles | — | | | — | | | |
| | | | | |
| Site remediation expense | 1.4 | | | — | | | |
| Income from operations | 5.0 | | | 6.4 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Interest expense, net | 0.6 | | | 0.6 | | | |
| Income before income tax provision | 4.4 | | | 5.8 | | | |
| Income tax provision | 1.6 | | | 2.0 | | | |
| Net income | 2.9 | | | 3.8 | | | |
| Loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | 0.1 | | | 0.1 | | | |
| Net income attributable to ARC | 2.9 | % | | 3.9 | % | | |
| | | | | |
EBITDA (2) | 11.3 | % | | 13.7 | % | | |
Adjusted EBITDA (2) | 13.6 | % | | 14.3 | % | | |
(1)Column does not foot due to rounding.
(2)Non-GAAP financial measure. See "Non-GAAP Financial Measures" following "Results of Operations" for definitions, reconciliations and more information related to our Non-GAAP disclosures.
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2023 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2022
Net Sales
Net sales in 2023 decreased 1.7%, compared to 2022. The decrease in net sales was primarily driven by the decrease in sales from Digital Printing and Equipment & Supplies, partially offset by the year-over-year increase in sales from Scanning and Digital Imaging services.
Digital Printing. Sales of Digital Printing services in 2023 decreased by $4.7 million, or 2.7%, compared to 2022. Year-over-year sales increased in digital color graphic printing from new and existing customers, and we experienced continuing demand for digital color graphic printing across most of our customer base. This growth was offset by the decrease of sales in digital plan printing for construction, which we attribute to less activity and lower spending on new building projects due to higher interest rates and increased costs of capital. Digital Printing services represented 60% and 61% of total net sales for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
MPS. Sales of MPS services in 2023 decreased by $1.0 million, or 1.3%, compared to 2022. Fewer employees returning to the workplace after the pandemic has generally constrained onsite print volumes. Revenues from MPS sales represented approximately 27% of total net sales for both 2023 and 2022.
The number of MPS locations has decreased to approximately 10,440 locations as of December 31, 2023 from 10,720 as of December 31, 2022.
Scanning and Digital Imaging. Year-over-year sales of Scanning and Digital Imaging services increased by $3.0 million, or 17.0%, in 2023, compared to 2022. The increase in sales of our Scanning and Digital Imaging services was primarily attributable to growing demand for paper-to-digital document conversions used in day-to-day business operations, and the creation of digital archives to replace long-term warehoused paper document storage. We are expanding operational capacity in this service line, and plan to continue to drive an expansion of our addressable market for Scanning and Digital Imaging services with increased marketing activity, as well as by targeting building owners and facility managers that require on-demand access to their legacy documents to operate their assets efficiently. We believe that, with the expansion of the markets and industries we serve and the desire of our existing customers to have digital access to documents, our Scanning and Digital Imaging services will continue to grow in the future.
Equipment and Supplies. Equipment and Supplies sales decreased by $2.1 million, or 11.5%, in 2023, compared to 2022. The decrease was primarily driven by the ongoing economic slowdown in China, which decreased sales from UNIS Document Solutions Co. Ltd, or UDS, our Chinese joint venture. Equipment and Supplies sales continue to decline in the U.S. as well. We attribute the decrease in sales to our customers' reluctance to acquire equipment while interest rates remain high and, in certain markets including China, economic activity remains depressed. Equipment and Supplies sales derived from UDS, were $1.7 million in 2023, as compared to $2.5 million in 2022. Equipment and Supplies sales represented approximately 6% of total net sales for 2023 for 2022, respectively.
Gross Profit
Gross profit decreased to $94.4 million in 2023, compared to $96.0 million in 2022. Despite a sales decrease of $4.8 million in 2023, gross profit decreased by just $1.6 million. Gross margin remained flat at 33.6% in 2023, compared to 2022. Gross margin stability was driven by improved efficiency in our cost structure and a reduction in depreciation expense of $2.6 million. Offsetting these cost reductions were increased labor expenses related to the growth in Scanning and Digital Imaging Services, as well as wage inflation pressures across our workforce during 2023.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased by $1.2 million, or 1.6%, in 2023 compared to 2022. The decrease was primarily driven by lower commission and bonus accruals due to the decline in net sales and net income attributable to us.
Amortization of Intangibles
Amortization of intangibles decreased to less than $0.1 million in 2023 as compared to $0.1 million in 2022, primarily due to the completed amortization of certain customer relationships related to historical acquisitions.
Site Remediation Expense
We are currently involved in a site remediation obligation due to a former gas station that had been situated on a property we obtained as part of a business acquisition in the late 1990s. In 2020, the local County's Department of Environmental Health, or CDEH, approved our remedial clean-up plan, hence a liability on an undiscounted basis for $0.6 million for costs attributable to our clean-up plan was established. Additional review conducted in the fourth quarter of 2023 identified certain additional potential risks arising out of a structure on a neighboring property. As a result, in December of 2023, the CDEH requested that an alternative remedial plan be developed and submitted by March 12, 2024, to address the structural aspects of the site. We are in the process of finalizing an alternative plan with the guidance and expertise of an environmental consulting firm engaged expressly for this purpose. The additional concerns identified in December 2023 require more complex remediation measures for a longer duration than those contained in the plan approved by the CDEH in 2020. In light of the expected increase in expenses associated with remediating the site we have increased the reserve by approximately $4.0 million, reflecting a total reserve on an undiscounted basis of $4.5 million as of December 31, 2023. We have accrued probable and reasonably estimable costs for the resolution of the obligation based upon types of remediation efforts currently anticipated, the volume of contaminants in the impacted areas, regulatory oversight and other costs. The history of this site remediation obligation is summarized in Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Interest Expense, Net
Net interest expense totaled $1.6 million in 2023, compared to $1.8 million in 2022. The decrease in 2023 compared to 2022 was due to the continuing reduction of our overall debt, partially offset by increases in interest rates.
Income Taxes
We recorded an income tax provision of $4.4 million in relation to pretax income of $12.5 million for 2023, which resulted in an effective income tax rate of 35.2%. In addition to recurring state and foreign taxes and certain nondeductible expenses, our effective income tax rate for 2023 was impacted by an expiration of tax credits which were offset by a change in valuation allowances against those and other certain deferred tax assets and stock based compensation forfeitures. Excluding the impact of those expirations and valuation allowances, stock based compensation forfeitures and other discrete items, our effective income tax rate for the consolidated company would have been 29.2% and our effective income tax rate attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. would have been 29.1%.
We recorded an income tax provision of $5.8 million in relation to pretax income of $16.6 million for 2022, which resulted in an effective income tax rate of 35.1%. In addition to recurring state and foreign taxes and certain nondeductible expenses, our effective income tax rate for 2022 was primarily impacted by a change in valuation allowances against certain deferred tax assets and stock-based compensation forfeitures. Excluding the impact of valuation allowances, stock based compensation forfeitures and other discrete items, our effective income tax rate for the consolidated company would have been 29.4% and our effective income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. would have been 29.1%.
Noncontrolling Interest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest represents 35% of the income of our Chinese joint venture with UDS and its subsidiaries, which together comprise our Chinese joint-venture operations.
Impact of Inflation
Rising costs for raw materials, such as paper, inks and toners were largely passed on to customers through price increases during 2022 and 2023, moderating the impact of inflation on our financial results. As these inflationary pressures continue, however, the increased cost of labor, materials, and other indirect costs require close and active management to avoid material impacts to our cost structure.
Net Income Attributable to ARC
Net income attributable to us was $8.2 million in 2023, as compared to $11.1 million in 2022. The decrease in net income attributable to us in 2023 was primarily driven by the increase in the site remediation reserve, net of taxes, noted above.
EBITDA
EBITDA margin and Adjusted EBITDA margin is not a recognized measure under GAAP. When analyzing our operating performance, investors should use EBITDA margin and Adjusted EBITDA in addition to, and not as an alternative for, operating income or any other performance measure presented in accordance with GAAP. It is a measure we use to measure our
performance and liquidity. We believe EBITDA margin and Adjusted EBITDA reflect an additional way of viewing aspects of our operations that, when viewed with our GAAP results, provides a more complete understanding of factors and trends affecting our business. We believe the measure is used by investors and is a useful indicator to measure our performance. Because not all companies use identical calculations, our presentation of EBITDA margin and Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies. See Non-GAAP Financial Measures below for additional discussion.
EBITDA margin decreased to 11.3% in 2023 from 13.7% in 2022. Excluding the effect of the site remediation expense and stock-based compensation, adjusted EBITDA margin decreased slightly to 13.6% in 2023 from 14.3% in 2022. The decrease is largely attributable to lower sales and an increase in labor costs.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
EBITDA, EBITDA margin, Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted EBITDA margin, adjusted net income and adjusted earnings per share presented in this report are supplemental measures of our performance that are not required by or presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America or GAAP. These measures are not measurements of our financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered as alternatives to net income, net income margin, income from operations, diluted earnings per share or any other performance measures presented in accordance with GAAP or as an alternative to cash flows from operating, investing or financing activities as a measure of our liquidity. We have presented these measures because we consider them important supplemental measures of our performance and liquidity. We believe investors may also find these measures meaningful, given how our management makes use of them. The following is a discussion of our use of these measures.
EBITDA represents net income before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. EBITDA margin is a non-GAAP measure calculated by dividing EBITDA by net sales.
We use EBITDA and EBITDA margin to measure and compare the performance of our operating divisions. Our operating divisions financial performance includes all of the operating activities except debt and taxation which are managed at the corporate level for U.S. operating divisions. We use EBITDA and EBITDA margin to compare the performance of our operating divisions and to measure performance for determining consolidated-level compensation. In addition, we use EBITDA and EBITDA margin to evaluate potential acquisitions and potential capital expenditures.
EBITDA and EBITDA margin have limitations as analytical tools, and should not be considered in isolation, or as a substitute for analysis of our results as reported under GAAP. Some of these limitations are as follows:
•They do not reflect our cash expenditures, or future requirements for capital expenditures and contractual commitments;
•They do not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for, our working capital needs;
•They do not reflect the significant interest expense, or the cash requirements necessary, to service interest or principal payments on our debt;
•Although depreciation and amortization are non-cash charges, the assets being depreciated and amortized will often have to be replaced in the future, and EBITDA does not reflect any cash requirements for such replacements; and
•Other companies, including companies in our industry, may calculate these measures differently than we do, limiting their usefulness as comparative measures.
Because of these limitations, EBITDA and related ratios should not be considered as measures of discretionary cash available to us to invest in business growth or to reduce our indebtedness. We compensate for these limitations by relying primarily on our GAAP results and using EBITDA and EBITDA margin only as supplements.
Our presentation of adjusted net income and adjusted EBITDA is an attempt to provide meaningful comparisons to our historical performance for our existing and future investors. The unprecedented changes in our end markets over the past several years have required us to take measures that are unique in our history and specific to individual circumstances. Comparisons inclusive of these actions make normal financial and other performance patterns difficult to discern under a strict GAAP presentation. Each non-GAAP presentation, however, is explained in detail in the reconciliation tables below.
Specifically, we have presented adjusted net income attributable to ARC and adjusted earnings per share attributable to ARC stockholders for 2023 and 2022 to reflect the exclusion of the site remediation expense and changes in the valuation allowances related to certain deferred tax assets and other discrete tax items. This presentation facilitates a meaningful comparison of our operating results for 2023 and 2022. We believe these changes were the result of items which are not indicative of our actual operating performance.
We have presented adjusted EBITDA for 2023 and 2022 to exclude the site remediation expense as it is not indicative of our ongoing operations. We have presented adjusted EBITDA for 2023 and 2022 to also exclude stock-based compensation expense, as it is consistent with the definition of adjusted EBITDA in our Credit Agreement; therefore, we believe this information is useful to investors assessing our financial performance. We calculate adjusted EBITDA margin by dividing adjusted EBITDA by net sales.
The following is a reconciliation of cash flows provided by operating activities to EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (In thousands) | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Cash flows provided by operating activities | $ | 36,583 | | | $ | 37,227 | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | (4,798) | | | 1,128 | | | |
| Non-cash expenses | (6,078) | | | (7,140) | | | |
| Income tax provision | 4,387 | | | 5,832 | | | |
| Interest expense, net | 1,633 | | | 1,796 | | | |
| Loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | 161 | | | 304 | | | |
| | | | | |
| EBITDA | $ | 31,888 | | | $ | 39,147 | | | |
The following is a reconciliation of net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders to EBITDA and adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (In thousands) | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | $ | 8,235 | | | $ | 11,094 | | | |
| Interest expense, net | 1,633 | | | 1,796 | | | |
| Income tax provision | 4,387 | | | 5,832 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 17,633 | | | 20,425 | | | |
| EBITDA | 31,888 | | | 39,147 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Site remediation expense | 4,000 | | | — | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | 2,232 | | | 1,773 | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 38,120 | | | $ | 40,920 | | | |
The following is a reconciliation of net income margin attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders to EBITDA margin and adjusted EBITDA margin:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2023 (1) | | 2022 (1) | | |
| Net income margin attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | | 2.9 | % | | 3.9 | % | | |
| Interest expense, net | | 0.6 | | | 0.6 | | | |
| Income tax provision | | 1.6 | | | 2.0 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 6.3 | | | 7.1 | | | |
| EBITDA margin | | 11.3 | | | 13.7 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Site remediation expense | | 1.4 | | | — | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | | 0.8 | | | 0.6 | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA margin | | 13.6 | % | | 14.3 | % | | |
(1)Column does not foot due to rounding.
The following is a reconciliation of net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders to adjusted net income and adjusted earnings per share attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| (In thousands, except per share data) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | | $ | 8,235 | | | $ | 11,094 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Site remediation expense | | 4,000 | | | — | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income tax benefit related to above item | | (1,018) | | | — | | | |
| Deferred tax valuation allowance and other discrete tax items | | 567 | | | 905 | | | |
| Adjusted net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | | $ | 11,784 | | | $ | 11,999 | | | |
| Actual: | | | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | 0.19 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | |
| Diluted | | $ | 0.19 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | |
| Diluted | | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
| Adjusted: | | | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | 0.28 | | | $ | 0.28 | | | |
| Diluted | | $ | 0.27 | | | $ | 0.28 | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | |
| Diluted | | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our principal sources of cash have been cash flows from operations and borrowings under our debt and lease agreements. Our recent historical uses of cash have been for ongoing operations, payment of principal and interest on outstanding debt obligations, capital expenditures, dividends and stock repurchases.
We continually assess our capital allocation strategy, including decisions relating to dividends, repurchase shares of our common stock, capital expenditures, and debt pay-downs. The timing, declaration and payment of future dividends, however, falls within the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition and earnings, the capital requirements of our business, restrictions imposed by applicable law and the terms of any of our debt agreements and any other factors the Board of Directors deems relevant from time to time.
In February 2023, our Board of Directors approved a stock repurchase program that authorized us to purchase up to $20.0 million of our outstanding common stock through March 31, 2026. Purchases may be made from time to time in the open market at prevailing market prices or in privately negotiated transactions. During the year ended December 31, 2023 we repurchased 1.0 million shares of our common stock for a total purchase price of $3.2 million. During the year ended December 31, 2022 we repurchased 0.6 million shares of our common stock for a total purchase price of $1.7 million.
Total cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 was $56.1 million. Of this amount, $5.7 million was held in foreign countries, with $2.6 million held in China. Repatriation of some of our cash and cash equivalents in foreign countries could be subject to delay for local country approvals and could have potential adverse tax consequences. As a result of holding cash and cash equivalents outside of the U.S., our financial flexibility may be reduced.
Supplemental information pertaining to our historical sources and uses of cash is presented as follows and should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and notes thereto included elsewhere in this report.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| (In thousands) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | 36,583 | | | $ | 37,227 | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | $ | (10,389) | | | $ | (5,574) | | | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | | $ | (22,637) | | | $ | (34,155) | | | |
Operating Activities
Cash flows from operations are primarily driven by sales and the net profit generated from these sales, excluding non-cash charges.
The decrease in cash flows from operations in 2023 was primarily due to the decrease in net income partially offset by the improvement in our collection of accounts receivables.
Days sales outstanding, or DSO was 47 days as of December 31, 2023 as compared to 51 days as of December 31, 2022. We are closely managing cash collections.
DSO is calculated by taking the respective years December 31st, accounts receivable balance divided by the net sales during the fourth quarter of that year multiplied by the number of total days in a quarter.
We have presented DSO because we consider it an important metric as it is a valuable indicator of the efficiency of the business and quality of our cash flows. We believe investors may also find this metric meaningful given the importance of cash flows from operations and management's ability to efficiently manage our working capital.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was primarily related to capital expenditures. We incurred capital expenditures totaling $10.8 million and $5.9 million, in 2023 and 2022, respectively. The year-over-year increase in capital expenditures is driven primarily by our decision to enter into fewer leases and acquire more equipment outright in 2023 due to increasing interest rates.
Financing Activities
Net cash of $22.6 million used in financing activities in 2023 primarily relates to payments on our finance leases, dividends, and repurchases of shares of our common stock, partially offset by proceeds from stock option exercises. Our need for printing equipment has significantly decreased over the past several years, resulting in a decrease of $4.2 million in our finance lease liability as of December 31, 2023 compared to the balance in the prior year. This reduction in the finance lease liability will also drive a further reduction in 2024 payments for financed leases.
Our cash position, working capital, and debt obligations as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are shown below and should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Balance Sheets and notes thereto contained elsewhere in this report.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | | |
| (In Thousands) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 56,093 | | | $ | 52,561 | | | |
| Working capital | | $ | 37,495 | | | $ | 34,906 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Borrowings from revolving credit facility | | $ | 40,000 | | | $ | 40,000 | | | |
| Various finance leases | | 22,236 | | | 26,474 | | | |
| Total debt obligations | | $ | 62,236 | | | $ | 66,474 | | | |
The increase of $2.6 million in working capital in 2023 was primarily driven by the increase in cash of $3.5 million and $2.7 million decrease in the current portion of our finance lease liability, partially offset by a $3.0 million decrease in accounts receivable and an increase in accounts payable over 2022. To manage our working capital, we chiefly focus on our DSO and monitor the aging of our accounts receivable, as receivables are the most significant element of our working capital.
We believe that our current cash and cash equivalents balance of $56.1 million, the availability under our 2021 Credit Agreement, the availability under our equipment lease lines, and cash flows provided by operations should be adequate to cover the next twelve months and beyond of working capital needs, debt requirements consisting of scheduled principal and interest payments, and planned capital expenditures, to the extent such items are known or are reasonably determinable based on current business and market conditions. See “Debt Obligations” section for further information related to our 2021 Credit Agreement.
A significant portion of our revenue across all of our product and services is generated from customers in the AEC/O industry. As a result, our operating results and financial condition can be significantly affected by economic factors that influence the AEC/O industry, including the disruptions in the capital markets, economic sanctions and economic slowdowns or
recessions, rising inflation, public health crises, like the COVID-19 pandemic, and interest rates fluctuations. Additionally, a general economic downturn may adversely affect the ability of our customers and suppliers to obtain financing for significant operations and purchases, and to perform their obligations under their agreements with us. We believe that credit constraints in the financial markets could result in a decrease in, or cancellation of, existing business, could limit new business, and could negatively affect our ability to collect our accounts receivable on a timely basis.
We have not been actively seeking growth through acquisition since 2009, but will consider acquisitions that we feel add value to the overall company.
Debt Obligations
Credit Agreement
On June 15, 2023, we entered into an amendment, or the Amendment, to our Credit Agreement dated as of April 22, 2021, or the 2021 Credit Agreement, with U.S. Bank National Association, as administrative agent and the lenders part thereto. The Amendment, among other things, modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement to replace the relevant benchmark provisions from the London Interbank Offered Rate to the forward-looking term rate based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, or SOFR. The Amendment also modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement relating to the payment of dividends and stock repurchases made by us and the related component calculations included in the fixed charge coverage ratio that we are required to maintain. After giving effect to the Amendment, we are permitted to repurchase up to $10.0 million of shares of our common stock in any twelve-month period and all such permitted stock repurchases will be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. In addition, we are permitted to make other restricted payments that are not stock repurchases, such as the payment of dividends, of up to $12.0 million during any twelve-month period which will also be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. The making of stock repurchases and the payment of dividends and other restricted payments is subject, in each case, to pro forma compliance with the financial covenants and other customary conditions set forth in the 2021 Credit Agreement.
The 2021 Credit Agreement provides for the extension of revolving loans in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $70 million and replaces the Credit Agreement dated as of November 20, 2014, as amended, or the 2014 Credit Agreement. The obligation under the 2021 Credit Agreement matures on April 22, 2026.
As of December 31, 2023, our borrowing availability under the Revolving Loan commitment was $27.8 million, after deducting outstanding letters of credit of $2.2 million and an outstanding Revolving Loan balance of $40.0 million.
Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement bear interest, in the case of Term SOFR loans, at a per annum rate equal to the applicable Term SOFR (which rate shall not be less than zero), plus a margin ranging from 1.25% to 1.75%, based on our Total Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement). Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement that are not Term SOFR loans bear interest at a per annum rate equal to the Alternate Base Rate (as such terms is defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement) plus a margin ranging from 0.25% to 0.75%, based on our Total Leverage Ratio. As of December 31, 2023, one month Term SOFR loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement accrued interest at 6.8%. We pay certain recurring fees with respect to the 2021 Credit Agreement, including administration fees to the administrative agent.
Subject to certain exceptions, including, in certain circumstances, reinvestment rights, the loans extended under the 2021 Credit Agreement are subject to customary mandatory prepayment provisions with respect to: the net proceeds from certain asset sales; the net proceeds from certain issuances or incurrences of debt (other than debt permitted to be incurred under the terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement); the net proceeds from certain issuances of equity securities; and net proceeds of certain insurance recoveries and condemnation events.
The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary representations and warranties, subject to limitations and exceptions, and customary covenants restricting the ability (subject to various exceptions) we and our subsidiaries to: incur additional indebtedness (including guarantee obligations); incur liens; sell certain property or assets; engage in mergers or other fundamental changes; consummate acquisitions; make investments; pay dividends, other distributions or repurchase equity interest of us or our subsidiaries; change the nature of their business; prepay or amend certain indebtedness; engage in certain transactions with affiliates; amend our organizational documents; or enter into certain restrictive agreements. In addition, the 2021 Credit Agreement contains financial covenants which requires we maintain (i) at all times, a Total Leverage Ratio in an amount not to exceed 2.75 to 1.00; and (ii) a Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement), as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, an amount not less than 1.15 to 1.00. We were in compliance with our covenants as of December 31, 2023.
The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary events of default, including with respect to: nonpayment of principal, interest, fees or other amounts; failure to perform or observe covenants; material inaccuracy of a representation or warranty
when made; cross-default to other material indebtedness; bankruptcy, insolvency and dissolution events; inability to pay debts; monetary judgment defaults; actual or asserted invalidity or impairment of any definitive loan documentation, repudiation of guaranties or subordination terms; certain ERISA related events; or a change of control.
The obligations of our subsidiary that is the borrower under the 2021 Credit Agreement are guaranteed by us and each of our other United States domestic subsidiaries. The 2021 Credit Agreement and any interest rate protection and other hedging arrangements provided by any lender party to the credit facility or any affiliate of such a lender are secured on a first priority basis by a perfected security interest in substantially all of our and each guarantor’s assets (subject to certain exceptions).
Credit Agreement
The following table sets forth the outstanding balance, borrowing capacity and applicable interest rate under Credit Agreement.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2023 |
| | Balance | | Available
Borrowing
Capacity | | Interest
Rate |
| | | (Dollars in thousands) |
| | | | | | |
Revolving Loans (1) | | $ | 40,000 | | | $ | 27,844 | | | 6.8 | % |
| | | | | | |
(1) Revolving Loan available borrowing capacity, net of $2.2 million of outstanding standby letters of credit as of December 31, 2023.
Finance Leases
As of December 31, 2023, we had $22.2 million of finance lease obligations outstanding, with a weighted average interest rate of 5.5% and maturities between 2024 and 2029.
Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases. We lease machinery, equipment, and office and operational facilities under non-cancelable operating lease agreements. Certain lease agreements for our facilities generally contain renewal options and provide for annual increases in rent based on the local Consumer Price Index. Refer to Note 7, Leasing, for the schedule of our future minimum operating lease payments as of December 31, 2023.
Legal Proceedings. We are involved, and will continue to be involved, in legal proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including commercial and employment-related lawsuits. Some of these lawsuits purport or may be determined to be class actions and seek substantial damages, and some may remain unresolved for several years. We establish accruals for specific legal proceedings when it is considered probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. We evaluate whether a loss is reasonably probable based on our assessment and consultation with legal counsel regarding the ultimate outcome of the matter. As of December 31, 2023, we have accrued for the potential impact of loss contingencies that are probable and reasonably estimable. We do not currently believe that the ultimate resolution of any of these matters will have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows. However, the results of these matters cannot be predicted with certainty, and an unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows.
Site Remediation Obligation. As part of a business acquisition in the 1990’s, we purchased a site located in California where a former commercial gas station had operated from 1939 until approximately 1986. Prior to our acquisition, the gas station was demolished and its underground storage tanks were removed.
Environmental monitoring of the property was conducted from 1987 through 2017 under the oversight of the local County's Department of Environmental Health (CDEH) and it eventually revealed petroleum products in the soil, groundwater, and the air in between soil particles. As a result, a Corrective Action Implementation Plan (CAIP) detailing remedial clean-up methods at the site was required to be submitted in 2020. Accordingly, we recorded a liability on an undiscounted basis of $0.6 million in 2020, the estimated cost, to remediate the site.
The 2020 CAIP was approved by the CDEH, but based on additional site data, the department requested a submission of addenda to the CAIP to address other site conditions. The additional review conducted in the fourth quarter of 2023 identified certain potential risks arising out of a structure on a neighboring property. As a result, in December of 2023, the CDEH requested that an alternative remedial plan be developed and submitted by March 12, 2024, to address the structural aspects of the site. We are in the process of finalizing an alternative plan with the guidance and expertise of an environmental consulting firm engaged expressly for this purpose. The additional concerns identified in 2023 require that the new plan be designed in a
way that is significantly more expensive than the original plan, is more complicated, and will result in a longer duration to remediate the site.
The Consolidated Balance Sheets include a liability on an undiscounted basis for the site remediation of $4.5 million as of December 31, 2023, of which $2.2 million is classified as a current liability, and $0.6 million as of December 31, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the liability represents our estimate of the probable cleanup, investigation, and remediation costs based on available information. We anticipate that most of this liability will be paid out over seven years, but some costs maybe be paid out over a longer period.
The estimate of our final remediation expenses may change over time because of the varying costs of currently available cleanup techniques, unpredictable contaminant reduction rates associated with available cleanup techniques, and the difficulty of determining in advance the nature and full extent of contamination. However, evolving statutory and regulatory standards, their interpretation, more vigorous enforcement policies of regulatory agencies, or stricter or different interpretations of existing statutory and regulatory standards, may require additional expenditures, which may be material. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not incur significant additional environmental compliance costs in the future.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our management prepares financial statements in conformity with GAAP. When we prepare these consolidated financial statements, we are required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments, including those related to accounts receivable, inventories, deferred tax assets, goodwill and intangible assets, long-lived assets and leases. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for our judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. To the extent that there are material differences between these estimates and actual results, our future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows will be affected. We believe that the accounting policies discussed below are critical to understanding our historical and future performance, as these policies relate to the more significant areas involving management's judgments and estimates.
Goodwill Impairment
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, we assess goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired. At September 30, 2023, the Company performed its annual assessment and determined that goodwill was not impaired.
Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017, we elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04 which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test.
We determine the fair value of our reporting units using an income approach. Under the income approach, we determined fair value based on estimated discounted future cash flows of each reporting unit. Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including revenue growth rates and EBITDA margins, discount rates and future market conditions, among others. The level of judgement and estimation is inherently higher in these uncertain economic times.
The results of the latest annual goodwill impairment test, as of September 30, 2023, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) | Number of
Reporting
Units | | Representing
Goodwill of |
| No goodwill balance | 6 | | | $ | — | |
| | | |
Fair value of reporting units exceeds their carrying values by more than 15% | 1 | | | 121,051 | |
| 7 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
Based upon a sensitivity analysis, a reduction of approximately 50 basis points of projected EBITDA in 2023 and beyond, assuming all other assumptions remain constant, would result in no further impairment of goodwill.
Based upon a separate sensitivity analysis, a 50 basis point increase to the weighted average cost of capital would result in
no further impairment of goodwill.
Given the uncertain economic times and the changing document and printing needs of our customers and the uncertainties regarding the effect on our business, there can be no assurance that the estimates and assumptions made for purposes of our goodwill impairment testing in 2023 will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. If our assumptions, including forecasted EBITDA of certain reporting units, are not achieved, then we may be required to record goodwill impairment charges in future periods, whether in connection with our next annual impairment testing in the third quarter of 2024, or on an interim basis, if any such change constitutes a triggering event (as defined under ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other) outside of the quarter when we regularly perform our annual goodwill impairment test. It is not possible at this time to determine if any such future impairment charge would result or, if it does, whether such charge would be material.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to our customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that we are expected to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. We applied practical expedients related to unsatisfied performance obligations for (i) contracts with an original expected length of one year or less and (ii) contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue at the amount to which it has the right to invoice for services performed.
Digital Printing consists of professional services and software services to (i) reproduce and distribute large-format and small-format documents in either black and white or color, or Ordered Prints and (ii) specialized graphic color printing. Substantially, all the Company’s revenue from Digital Printing comes from professional services to reproduce Ordered Prints. Sales of Ordered Prints are initiated through a customer order or quote and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the re-produced Ordered Prints. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Ordered Prints are delivered to the customer’s site or handed to the customer for walk in orders. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue.
MPS consists of placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in the customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities. MPS relieves the Company’s customers of the burden of purchasing print equipment and related supplies and maintaining print devices and print networks, and shifts their costs to a “per-use” basis. MPS is supported by our hosted proprietary technology, Abacus®, which allows our customers to capture, control, manage, print, and account for their documents. Under its MPS contracts, the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge”. MPS sales are driven by the ongoing print needs of the Company’s customers at their facilities. Upon the issuance of ASC 842, Leases, the Company concluded that certain of its MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. See Note 7, Leasing, for additional information.
Scanning and Digital Imaging combines software and professional services to facilitate the capture, management, access and retrieval of documents and information that have been produced in the past. Scanning and Digital Imaging may include our hosted SKYSITE software and facilities solution to organize, search and retrieve documents, as well as the provision of services that include the capture and conversion of hardcopy and electronic documents into digital files, or Scanned Documents, and their cloud-based storage and maintenance. Sales of Scanning and Digital Imaging professional services, which represent substantially all revenue for this business line, are initiated through a customer order or proposal and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the digital files. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Scanned Documents are delivered to the customer either through SKYSITE, our facilities solution or through other electronic media. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue.
Equipment and Supplies sales consist of reselling printing, imaging, and related equipment, or Goods, to customers primarily in architectural, engineering and construction firms. Sales of Equipment and Supplies are initiated through a customer order and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligations under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the Goods. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Goods are delivered to the customer’s site. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring
goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. We have experienced minimal customer returns or refunds and does not offer a warranty on equipment that it is reselling.
Leases
We recognize lease assets and corresponding lease liabilities for all operating and finance leases on our Consolidated Balance Sheets, excluding short-term leases (leases with terms of 12 months or less) as described under ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). Some of our long-term operating lease agreements include options to extend, which are also factored into the recognition of their respective assets and liabilities when appropriate based on management’s assessment of the probability that the options will be exercised. Lease payments are discounted using the rate implicit in the lease, or, if not readily determinable, a third-party secured incremental borrowing rate based on information available at lease commencement. Additionally, certain of our lease agreements include escalating rents over the lease terms which, under Topic 842, results in rent being expensed on a straight-line basis over the life of the lease that commences on the date we have the right to control the property. Finance leases were not impacted by the adoption of ASC 842, as finance lease liabilities and the corresponding ROU assets were already recorded in the balance sheet under the previous guidance, ASC 840. For additional information about the impact of the adoption of ASC 842, see Note 7, Leasing.
Site Remediation Obligation
We are currently involved in a site remediation obligation due to a former gas station that had been situated on a property we obtained as part of a business acquisition in the late 1990s. We have accrued estimates of the probable and reasonably estimable costs for the resolution of the obligation based upon types of remediation efforts currently anticipated, the volume of contaminants in the impacted areas, regulatory oversight and other costs.
Our current estimates of future environmental cleanup and remediation liabilities related to the site may change over time due to various factors, including but not limited to, the nature and extent of required future cleanup and removal activities, and the extent and duration of regulatory oversight, among other things. The final outcome of any regulatory inquiries and requirements cannot be predicted with certainty, and unfavorable or unexpected outcomes could result in additional costs that could be material to our results of operations during any particular year of the remediation process. See Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion on environmental matters.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial and tax reporting purposes. Such amounts are adjusted, as appropriate, to reflect changes in tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. Changes in tax laws or accounting standards and methods may affect recorded deferred taxes in future periods.
When establishing a valuation allowance, we consider future sources of taxable income such as future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards and tax planning strategies. A tax planning strategy is an action that: is prudent and feasible; an enterprise ordinarily might not take but would take to prevent an operating loss or tax credit carryforward from expiring unused; and would result in realization of deferred tax assets. In the event we determine that its deferred tax assets, more likely than not, will not be realized in the future, the valuation adjustment to the deferred tax assets will be charged to earnings in the period in which we make such a determination. We have a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023.
In future quarters we will continue to evaluate our historical results for the preceding twelve quarters and our future projections to determine whether we will generate sufficient taxable income to utilize our deferred tax assets, and whether a valuation allowance is required.
We calculate our current and deferred tax provision based on estimates and assumptions that could differ from the actual results reflected in income tax returns filed in subsequent years. Adjustments based on filed returns are recorded when identified.
Income taxes have not been provided on certain undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because such earnings are considered to be permanently reinvested.
The amount of taxable income or loss we report to the various tax jurisdictions is subject to ongoing audits by federal, state and foreign tax authorities. We estimate of the potential outcome of any uncertain tax issue is subject to management’s assessment of relevant risks, facts, and circumstances existing at that time. We use a more-likely-than-not threshold for
financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We record a liability for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and tax position taken or expected to be taken on its tax return. To the extent that our assessment of such tax positions changes, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. We report tax-related interest and penalties as a component of income tax expense.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to our Consolidated Financial Statements for disclosure on recently adopted accounting pronouncements and those not yet adopted.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are a smaller reporting company, as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, and are not required to provide the information required under this item.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Our financial statements and the accompanying notes that are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed under Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” and are set forth beginning on page F-1 immediately following the signature pages of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or the Exchange Act are recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer (our principal executive officer) and our Chief Financial Officer (our principal financial officer), as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act as of December 31, 2023. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer concluded that as of December 31, 2023, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or 15(d)-15(f) of the Exchange Act). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based upon the framework in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on that evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Crowe LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the fiscal year 2023 consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes to internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2023, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
Adoption or Termination of Trading Arrangements
None of our directors or officers (as defined in Rule 16a-1(f)) adopted or terminated a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement or a non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement (as defined in Item 408(c) of Regulation S-K) during the three months ended December 31, 2023.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Certain information regarding our executive officers is included below. All other information regarding directors, executive officers and corporate governance required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the applicable information in the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, or 2024 Annual Meeting, which will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after our fiscal year end of December 31, 2023, and is set forth under “Nominees for Director,” “Corporate Governance Profile,” “Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports” and in other applicable sections in the proxy statement.
Information about our Executive Officers
The following sets forth certain information regarding all of our executive officers as of February 28, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar | | 70 | | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Director |
| Jorge Avalos | | 48 | | Chief Financial Officer |
| Rahul K. Roy | | 64 | | Chief Technology Officer |
| Dilantha Wijesuriya | | 62 | | President and Chief Operating Officer |
Kumarakulasingam (“Suri”) Suriyakumar co-founded the Company in 1989 and has served as ARC Document Solution’s Chief Executive Officer since June 1, 2007. He served as the Company’s Chief Operating Officer from 1991 until his appointment as Chief Executive. He also served as President from 1991 until June of 2022. On July 24, 2008, Mr. Suriyakumar was appointed Chairman of ARC’s Board of Directors. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Suriyakumar was employed with Aitken Spence & Co. LTD, a highly diversified conglomerate and one of the five largest corporations in Sri Lanka.
Jorge Avalos was appointed Chief Financial Officer of ARC Document Solutions in January of 2015. From 2011 to his appointment as CFO, Mr. Avalos was Chief Accounting Officer and Vice President Finance of ARC. Mr. Avalos joined the Company in June 2006 as the Company’s Director of Finance and became the Company’s Corporate Controller in December 2006, and Vice President, Corporate Controller in December of 2010. Prior to joining the company, Mr. Avalos was employed with Vendare Media Group, an online network and social media company, as its controller. From September 1998 through March 2005, Mr. Avalos was employed in a variety of audit and management roles with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP.
Rahul K. Roy joined ARC Document Solutions as its Chief Technology Officer in September 2000. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Roy was the founder, President and Chief Executive Officer of MirrorPlus Technologies, Inc., which developed software for the reprographics industry, from August 1993 until it was acquired by the Company in 1999. Mr. Roy also served as the Chief Operating Officer of InPrint, a provider of printing, software, duplication, packaging, assembly, and distribution services to technology companies, from 1993 until it was acquired by the Company in 1999.
Dilantha “Dilo” Wijesuriya joined Ford Graphics, a former division of ARC Document Solutions, in January 1991. He subsequently became president of that division in 2001, and became a Company regional operations head in 2004, a position he retained until his appointment as the Company’s Senior Vice President, National Operations in August 2008. Mr. Wijesuriya was appointed Chief Operating Officer in 2011 and made President in June of 2022. Prior to his employment with the Company, Mr. Wijesuriya was a divisional manager with Aitken Spence & Co. LTD, a highly diversified conglomerate and one of the five largest corporations in Sri Lanka.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the applicable information in the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting and is set forth under “Executive Compensation.”
The information in the section of the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting captioned “Compensation Committee Report” is incorporated by reference herein but shall be deemed furnished, not filed and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing we make under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Exchange Act.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the applicable information in the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting and is set forth under “Beneficial Ownership of Voting Securities” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information.”
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the applicable information in the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting and is set forth under “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Corporate Governance Profile.”
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting and is set forth under “Auditor Fees.”
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
| | |
(1) Financial Statements |
|
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm - Armanino LLP (PCAOB ID: 32) |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm - Crowe LLP (PCAOB ID: 173) |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
| Consolidated Statements of Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
All other schedules have been omitted as the required information is not present or is not present in amounts sufficient to require submission of the schedule, or because the information required is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
See Item 15(b) below.
(b) Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed herewith as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or are incorporated by reference to exhibits previously filed with the SEC:
Index to Exhibits
| | | | | | | | |
| Number | | Description |
| |
| 3.1 | | |
|
| |
| 3.2 | | | |
| |
| 3.3 | | |
|
| |
| 4.2 | | | |
| | |
| 10.1 | | | |
| |
| 10.2 | | |
|
| |
| 10.3 | | | |
| |
| 10.4 | | |
|
| |
| 10.5 | | | |
| |
| 10.6 | | | |
| |
| 10.7 | | | |
| |
| 10.8 | | | |
| |
| 10.9 | | | |
| |
| 10.10 | | | |
| | |
| 10.11 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| |
| 10.12 | | | Lease Agreement, for the premises commonly known as 934 and 940 Venice Boulevard, Los Angeles, CA, dated November 19, 1997, by and between American Reprographics Company, L.L.C. (formerly Ford Graphics Group, L.L.C.) and Sumo Holdings LA, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Reg. No. 333-119788), as filed on October 15, 2004). |
| |
| 10.13 | | | Amendment to Lease for the premises commonly known as 934 and 940 Venice Boulevard, Los Angeles, CA, effective as of August 2, 2005, by and between Sumo Holdings LA, LLC, Landlord and American Reprographics Company, L.L.C. (formerly known as Ford Graphics Group, L.L.C.) Tenant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed on November 14, 2005 |
| |
| 10.14 | | | |
| |
| 10.15 | | | |
| |
| 10.16 | | | Indemnification Agreement, dated April 10, 2000, among American Reprographics Company, L.L.C., American Reprographics Holdings, L.L.C., ARC Acquisition Co., L.L.C., Mr. Chandramohan, Mr. Suriyakumar, Micro Device, Inc., Dieterich-Post Company, ZS Ford L.P., and ZS Ford L.L.C. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Reg. No. 333-119788), as filed on October 15, 2004). |
| | |
| 10.17 | | | |
| |
| 10.18 | | | |
| |
| 10.19 | | | |
| |
| 10.20 | | | |
| |
| 10.21 | | | |
| | |
| 10.22 | | | |
| | |
| 10.23 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| 10.24 | | | |
| | |
| 10.25 | | | |
| | |
| 10.27 | | | |
| | |
| 10.29 | | | |
| | |
| 10.30 | | | |
| | |
| 10.31 | | | |
| | |
| 10.33 | | | |
| | |
| 10.36 | | | |
| | |
| 10.37 | | | |
| | |
| 10.38 | | | |
| | |
| 10.39 | | | |
| | |
| 10.41 | | | |
| | |
| 10.42 | | | |
| | |
| 10.43 | | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.44 | | | |
| | |
| 10.45 | | | |
| | |
| 10.46 | | | |
| | |
| 10.47 | | | |
| | |
| 10.48 | | | |
| | |
| 10.49 | | | |
| | |
| 10.50 | | |
|
| | |
| 16.1 | | | |
| | |
| 21.1 | | | |
| | |
| 23.1 | | | |
| | |
| 23.2 | | | |
| | |
| 31.1 | | | |
| |
| 31.2 | | | |
| |
| 32.1 | | | |
| |
| 32.2 | | | |
| | |
| 97.1 | | |
| | |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document * |
| | | | | | | | |
| |
| 101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema * |
| |
| 101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase * |
| |
| 101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase * |
| |
| 101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase * |
| |
| 101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase * |
| | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within the Inline XBRL document) |
| | |
| * | | Filed herewith |
| | |
| ^ | | Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or agreement |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
Not applicable.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC. |
| |
| By: | | /s/ KUMARAKULASINGAM SURIYAKUMAR |
| | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
Date: February 29, 2024
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | |
/s/ KUMARAKULASINGAM SURIYAKUMAR Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar | | Chairman and
Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 29, 2024 |
| | |
/s/ JORGE AVALOS Jorge Avalos | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | February 29, 2024 |
| | | | |
/s/ TRACEY LUTTRELL Tracey Luttrell | | Director, Corporate Counsel and Corporate Secretary | | February 29, 2024 |
| | | | |
/s/ BRADFORD L. BROOKS
Bradford L. Brooks | | Director | | February 29, 2024 |
| | |
/s/ CHERYL COOK Cheryl Cook | | Director | | February 29, 2024 |
| | |
/s/ MARK W. MEALY Mark W. Mealy | | Director | | February 29, 2024 |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | | |
| | | |
| Armanino LLP (PCAOB ID: 32) | | F-2 | |
| | | |
| | | |
Crowe LLP (PCAOB ID: 173) | | F-3 | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | F-5 | |
| |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | F-6 | |
| |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | F-7 | |
| |
| Consolidated Statements of Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | F-8 | |
| |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | F-9 | |
| |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | | F-10 | |
| |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of ARC Document Solutions, Inc.:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. and Subsidiaries (collectively the "Company" or “ARC”) as of December 31, 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, stockholders' equity, and cash flows, for the year ended December 31, 2022, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements").
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2022, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2022, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for Opinion
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audit of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
We began serving as the Company’s auditors in 2020. In 2023, we became the predecessor auditor.
/s/ ArmaninoLLP
San Francisco, California
February 23, 2023
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Stockholders and the Board of Directors of ARC Document Solutions, Inc.
San Ramon, California
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. (the "Company") as of December 31, 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, equity, and cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework: (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2023 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework: (2013) issued by COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit of the financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
Critical audit matters are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. We determined that there are no critical audit matters.
/s/ Crowe LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2023.
San Francisco, California
February 29, 2024
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, | | December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 56,093 | | | $ | 52,561 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowances for credit losses of $1,857 and $1,947 | 35,775 | | | 38,748 | |
| Inventory | 8,818 | | | 8,610 | |
| | | |
| Prepaid expenses | 3,988 | | | 4,018 | |
| Other current assets | 3,978 | | | 3,540 | |
| Total current assets | 108,652 | | | 107,477 | |
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $229,122 and $231,913 | 40,925 | | | 40,214 | |
| Right-of-use assets from operating leases | 32,838 | | | 28,163 | |
| Goodwill | 121,051 | | | 121,051 | |
| Other intangible assets, net | 162 | | | 208 | |
| | | |
| Deferred income taxes, net | 4,383 | | | 7,993 | |
| Other assets | 2,113 | | | 2,209 | |
| Total assets | $ | 310,124 | | | $ | 307,315 | |
| Liabilities and Equity | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 24,175 | | | $ | 22,972 | |
| Accrued payroll and payroll-related expenses | 9,401 | | | 11,235 | |
| Accrued expenses | 18,787 | | | 16,882 | |
| Current operating lease liabilities | 9,924 | | | 9,924 | |
| Current portion of finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | |
| Total current liabilities | 71,157 | | | 72,571 | |
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | |
| Long-term debt and finance leases | 53,366 | | | 54,916 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 52 | | | — | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 2,467 | | | 199 | |
| Total liabilities | 154,399 | | | 151,025 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 6) | | | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | |
| ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders’ equity: | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value, 25,000 shares authorized; 0 shares issued and outstanding | — | | | — | |
Common stock, $0.001 par value, 150,000 shares authorized; 52,526 and 51,400 shares issued and 42,783 and 43,101 shares outstanding | 52 | | | 51 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 136,460 | | | 132,952 | |
| Retained earnings | 44,144 | | | 44,416 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (4,200) | | | (4,187) | |
| 176,456 | | | 173,232 | |
Less cost of common stock in treasury, 9,743 and 8,299 shares | 22,390 | | | 18,877 | |
| Total ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders’ equity | 154,066 | | | 154,355 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | 1,659 | | | 1,935 | |
| Total equity | 155,725 | | | 156,290 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 310,124 | | | $ | 307,315 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended
December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Service sales | $ | 265,160 | | | $ | 267,891 | | | |
| Equipment and Supplies sales | 16,041 | | | 18,119 | | | |
| Total net sales | 281,201 | | | 286,010 | | | |
| Cost of sales | 186,800 | | | 190,013 | | | |
| Gross profit | 94,401 | | | 95,997 | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 76,333 | | | 77,544 | | | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 41 | | | 97 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Site remediation expense | 4,000 | | | — | | | |
| Income from operations | 14,027 | | | 18,356 | | | |
| Other income, net | (67) | | | (62) | | | |
| | | | | |
| Interest expense, net | 1,633 | | | 1,796 | | | |
| Income before income tax provision | 12,461 | | | 16,622 | | | |
| Income tax provision | 4,387 | | | 5,832 | | | |
| Net income | 8,074 | | | 10,790 | | | |
| Loss attributable to noncontrolling interest | 161 | | | 304 | | | |
| Net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | $ | 8,235 | | | $ | 11,094 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.19 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.19 | | | $ | 0.26 | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | |
| Basic | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | |
| Diluted | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended
December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Net income | $ | 8,074 | | | $ | 10,790 | | | |
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax | (128) | | | (2,104) | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (128) | | | (2,104) | | | |
| Comprehensive income | 7,946 | | | 8,686 | | | |
| Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest | (276) | | | (722) | | | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders | $ | 8,222 | | | $ | 9,408 | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | ARC Document Solutions, Inc. Stockholders | | | | |
| | Common Stock | | | | | | Accumulated | | | | | | |
| Shares | | Par
Value | | Additional Paid-in
Capital | | Retained
Earnings | | Other Comprehensive
(Loss) Income | | Common Stock in
Treasury | | Noncontrolling
Interest | | Total |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | 50,584 | | | $ | 50 | | | $ | 129,881 | | | $ | 41,768 | | | $ | (2,501) | | | $ | (16,771) | | | $ | 6,565 | | | $ | 158,992 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 152 | | | | | 1,773 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,773 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 45 | | | | | 98 | | | | | | | | | | | 98 | |
| Stock options exercised | 619 | | | 1 | | | 1,200 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury shares | | | | | | | | | | | (2,106) | | | | | (2,106) | |
Cash dividends - common stock ($0.20 per share) | | | | | | | (8,446) | | | | | | | | | (8,446) | |
| Distribution to noncontrolling interest | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,908) | | | (3,908) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | 11,094 | | | (1,686) | | | | | (722) | | | 8,686 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | 51,400 | | | $ | 51 | | | $ | 132,952 | | | $ | 44,416 | | | $ | (4,187) | | | $ | (18,877) | | | $ | 1,935 | | | $ | 156,290 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 270 | | | | | 2,232 | | | | | | | | | | | 2,232 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 51 | | | | | 133 | | | | | | | | | | | 133 | |
| Stock options exercised | 805 | | | 1 | | | 1,143 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,144 | |
| Treasury shares | | | | | | | | | | | (3,513) | | | | | (3,513) | |
Cash dividends - common stock ($0.20 per share) | | | | | | | (8,507) | | | | | | | | | (8,507) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | 8,235 | | | (13) | | | | | (276) | | | 7,946 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | 52,526 | | | $ | 52 | | | $ | 136,460 | | | $ | 44,144 | | | $ | (4,200) | | | $ | (22,390) | | | $ | 1,659 | | | $ | 155,725 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 8,074 | | | $ | 10,790 | | | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | 351 | | | 320 | | | |
| Depreciation | 17,592 | | | 20,328 | | | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 41 | | | 97 | | | |
| Amortization of deferred financing costs | 67 | | | 61 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | 2,232 | | | 1,773 | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | 5,016 | | | 4,927 | | | |
| Deferred tax valuation allowance | (1,326) | | | 264 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other non-cash items, net | (262) | | | (205) | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | 2,783 | | | (195) | | | |
| Inventory | (243) | | | 62 | | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 9,391 | | | 9,746 | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | (7,133) | | | (10,741) | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 36,583 | | | 37,227 | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | (10,752) | | | (5,881) | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other | 363 | | | 307 | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (10,389) | | | (5,574) | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | |
| Proceeds from stock option exercises | 1,144 | | | 1,201 | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 133 | | | 98 | | | |
| Share repurchases | (3,513) | | | (2,106) | | | |
| Distribution to noncontrolling interest | — | | | (3,908) | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Payments on long-term debt agreements and finance leases | (11,860) | | | (14,736) | | | |
| Borrowings under revolving credit facilities | 162,000 | | | 154,000 | | | |
| Payments under revolving credit facilities | (162,000) | | | (160,250) | | | |
| Payment of deferred financing costs | (23) | | | (6) | | | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends paid | (8,518) | | | (8,448) | | | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (22,637) | | | (34,155) | | | |
| Effect of foreign currency translation on cash balances | (25) | | | (866) | | | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 3,532 | | | (3,368) | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 52,561 | | | 55,929 | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 56,093 | | | $ | 52,561 | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 1,715 | | | $ | 1,837 | | | |
| Income taxes paid, net | $ | 903 | | | $ | 167 | | | |
| Noncash financing activities: | | | | | |
| Finance lease obligations incurred | $ | 7,764 | | | $ | 9,482 | | | |
| Operating lease obligations incurred | $ | 14,478 | | | $ | 8,687 | | | |
| Declared unpaid dividends | $ | 2,144 | | | $ | 2,106 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(In thousands, except per share data or where otherwise noted)
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
ARC Document Solutions Inc. is a digital printing company. We provide digital printing and document-related services to customers in a growing variety of industries. ARC offers Digital Printing services, Managed Print Services ("MPS"), and Scanning and Digital Imaging services. In addition, ARC also sells Equipment and Supplies. The Company conducts its operations through its wholly-owned operating subsidiary, ARC Document Solutions, LLC, a Texas limited liability company, and its affiliates.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis and relies on historical experience and various other factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances to determine such estimates. Actual results could differ from those estimates and such differences may be material to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Risk and Uncertainties
The Company generates a significant portion of its revenue from sales of services and products to customers in the architectural, engineering, construction and building owner/operator ("AEC/O") industry. As a result, the Company's results largely depend on the strength of that industry. The Company's historical operating results reflect the cyclical and variable nature of the AEC/O industry. ARC believes that the AEC/O industry generally experiences downturns several months after a downturn in the general economy, and that there may be a similar delay in the recovery of the AEC/O industry following a recovery of the general economy. A downturn in the AEC/O industry would diminish demand for all of the Company's products and services, and would therefore negatively affect the Company's revenues and have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, operating results and financial condition.
As part of the Company's growth strategy, ARC intends to continue to expand the market and industries it services and increase sales of a variety of service offerings that utilize ARC's existing production methods and infrastructure, but that are relatively new to the Company. The success of the Company’s efforts will be affected by its ability to acquire new customers for the Company’s new service offerings, as well as to sell the new service offerings to existing customers. The Company’s inability to successfully market and execute these relatively new service offerings could significantly affect its business and reduce its long-term revenue, resulting in an adverse effect on its results of operations and financial condition.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Cash Equivalents
Cash equivalents include demand deposits and short-term investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased.
The Company maintains its cash deposits at numerous banks located throughout the United States, Canada, India, United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom and China, which at times, may exceed federally insured limits. UNIS Document Solutions, Co. Ltd., ("UDS"), the Company’s joint venture in China, held $2.6 million and $3.2 million of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risk on cash and cash equivalents.
Concentrations of Credit Risk and Significant Vendors
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade receivables are limited due to a large, diverse customer base. No individual customer represented more than 2.5% of net sales during 2023 and 2022.
The Company has geographic concentration risk as sales in California, as a percent of total sales, were approximately 30% and 31% for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
The Company contracts with various suppliers. Although there are a limited number of suppliers that could supply the Company’s inventory, management believes any shortfalls from existing suppliers could be absorbed by its existing suppliers or from other suppliers on comparable terms. However, a change in suppliers could cause a delay in sales and adversely affect results.
Purchases from the Company’s three largest vendors during 2023 and 2022 comprised approximately 35% of the Company’s total purchases of inventory and supplies.
Allowance for Credit Losses
The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of the financial condition of its customers, monitors collections and payments from customers, and generally does not require collateral. The Company provides for the possible inability to collect accounts receivable by recording an allowance for credit losses. The Company writes off accounts receivable balances when it is considered uncollectible. The Company estimates the allowance for credit losses based on historical experience, aging of accounts receivable, and information regarding the credit worthiness of its customers. Additionally, the Company provides an allowance for returns and discounts based on historical experience. The allowance for credit losses activity was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | Charges to
Cost and
Expenses | | Deductions (1) | | Balance at
End of
Period |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | $ | 1,947 | | | $ | 351 | | | $ | (441) | | | $ | 1,857 | |
| Year ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | $ | 2,104 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | (477) | | | $ | 1,947 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
(1) Deductions represent uncollectible accounts written-off net of recoveries.
Inventories
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (determined on a first-in, first-out basis; or average cost) or net realizable value. Inventories primarily consist of materials for use and resale in digital printing, and equipment for resale. On an ongoing basis, inventories are reviewed and adjusted for estimated obsolescence or unmarketable inventories to reflect the lower of cost or net realizable value. Charges to write-down inventory to realizable value are recorded as an increase in cost of sales.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial and tax reporting purposes. Such amounts are adjusted, as appropriate, to reflect changes in tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce the Company's deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. Changes in tax laws or accounting standards and methods may affect recorded deferred taxes in future periods.
When establishing a valuation allowance, the Company considers future sources of taxable income such as future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards and tax planning strategies. A tax planning strategy is an action that: is prudent and feasible; an enterprise ordinarily might not take but would take to prevent an operating loss or tax credit carryforward from expiring unused; and would result in realization of deferred tax assets. In the event the Company determines that its deferred tax assets, more likely than not, will not be realized in the future, the valuation adjustment to the deferred tax assets will be charged to earnings in the period in which the Company makes such a determination. The Company has a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023.
In future quarters the Company will continue to evaluate its historical results for the preceding twelve quarters and our future projections to determine whether this will generate sufficient taxable income to utilize the Company's deferred tax assets, and whether a valuation allowance is required.
The Company calculates current and deferred tax provision based on estimates and assumptions that could differ from the actual results reflected in income tax returns filed in subsequent years. Adjustments based on filed returns are recorded when identified.
Income taxes have not been provided on certain undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because such earnings are considered to be permanently reinvested.
The amount of taxable income or loss we report to the various tax jurisdictions is subject to ongoing audits by federal, state and foreign tax authorities. The Company estimate of the potential outcome of any uncertain tax issue is subject to management’s assessment of relevant risks, facts, and circumstances existing at that time. The Company uses a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company records a liability for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and tax position taken or expected to be taken on its tax return. To the extent that the Company's assessment of such tax positions changes, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. The Company will not report tax-related interest and penalties as a component of income tax expense.
Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | 10-20 years |
| Leasehold improvements | | 10-20 years or lease term, if shorter |
| Machinery and equipment | | 3-7 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | | 3-7 years |
Assets acquired under capital lease arrangements are included in machinery and equipment, are recorded at the present value of the minimum lease payments, and are depreciated using the straight-line method over the life of the asset or term of the lease, whichever is shorter. Expenses for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred, while renewals and betterments are capitalized. Gains or losses on the sale or disposal of property and equipment are reflected in operating income.
The Company accounts for software costs developed for internal use in accordance with ASC 350-40, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software, which requires companies to capitalize certain qualifying costs incurred during the application development stage of the related software development project. The primary use of this software is for internal use and, accordingly, such capitalized software development costs are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the economic lives of the related products not to exceed three years. The Company’s machinery and equipment (see Note 4, Property and Equipment, Net) includes $1.9 million and $1.7 million of capitalized software development costs as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, net of accumulated amortization of $24.2 million and $23.3 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Depreciation expense includes the amortization of capitalized software development costs which amounted to $0.9 million and $1.0 million, during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Software development costs for software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed are expensed as incurred until the establishment of technological feasibility, at which time those costs are capitalized until the product is available for general release to customers and amortized over the estimated life of the product. Technological feasibility is established upon the completion of a working prototype that has been certified as having no critical bugs and is a release candidate. To date, costs and time incurred between the establishment of technological feasibility and product release have not been material, and all software development costs have been charged to research and development expense in our consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss).
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company periodically assesses potential impairments of its long-lived assets in accordance with the provisions of ASC 360, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets. An impairment review is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. The Company groups its assets at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of the other assets and liabilities. The Company has determined that the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are available is the regional level, which is the operating segment level.
Factors considered by the Company include, but are not limited to, significant underperformance relative to historical or projected operating results; significant changes in the manner of use of the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall
business; and significant negative industry or economic trends. When the carrying value of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, the Company estimates the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows and eventual disposition is less than the carrying amount of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. An impairment loss is reflected as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset, based on the fair value if available, or discounted cash flows, if fair value is not available. The Company had no long-lived asset impairments in 2023 or 2022.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, the Company assesses goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired.
Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017, the Company elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04 which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test.
The Company determines the fair value of its reporting units using an income approach. Under the income approach, the Company determined fair value based on estimated discounted future cash flows of each reporting unit. Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including revenue growth rates and EBITDA margins, discount rates and future market conditions, among others. The level of judgement and estimation is inherently higher in these uncertain economic times.
Other intangible assets that have finite lives are amortized over their useful lives. Customer relationships are amortized using the accelerated method, based on customer attrition rates, over their estimated useful lives of 13 (weighted average) years.
Deferred Financing Costs
Direct costs incurred in connection with debt agreements are recorded as incurred and amortized based on the effective interest method for the Company's borrowings under its credit agreement with U.S. Bank National Association, dated April 22, 2021 (the "2021 Credit Agreement"), as amended on June 15, 2023. At December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company had $0.2 million in unamortized deferred financing costs.
Fair Values of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to their short maturities. Refer to Note 11, Fair Value Measurements, in Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for disclosures regarding fair value measurements in accordance with the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures.
Insurance Liability
The Company maintains a high deductible insurance policy for a significant portion of its risks and associated liabilities with respect to workers’ compensation. The Company’s deductible is $250 thousand per individual. The accrued liabilities associated with this program are based on the Company’s estimate of the ultimate costs to settle known claims, as well as claims incurred but not yet reported to the Company, as of the balance sheet date. The Company’s estimated liability is not discounted and is based upon an actuarial report obtained from a third party. The actuarial report uses information provided by the Company’s insurance brokers and insurers, combined with the Company’s judgments regarding a number of assumptions and factors, including the frequency and severity of claims, claims development history, case jurisdiction, applicable legislation, and the Company’s claims settlement practices.
Commitments and Contingencies
In the normal course of business, the Company estimates potential future loss accruals related to legal, workers’ compensation, tax and other contingencies. These accruals require management’s judgment on the outcome of various events based on the best available information. However, due to changes in facts and circumstances, the ultimate outcomes could differ from management’s estimates.
Site Remediation Obligation - The Company is currently involved in a site remediation obligation due to a former gas station that had been situated on a property the Company obtained as part of a business acquisition in the late 1990s. The
Company has accrued estimates of the probable and reasonably estimable costs for the resolution of the obligation based upon types of remediation efforts currently anticipated, the volume of contaminants in the impacted areas, regulatory oversight and other costs.
The Company's current estimates of future environmental cleanup and remediation liabilities related to the site may change over time due to various factors, including but not limited to, the nature and extent of required future cleanup and removal activities, and the extent and duration of regulatory oversight, among other things. The final outcome of any regulatory inquiries and requirements cannot be predicted with certainty, and unfavorable or unexpected outcomes could result in additional costs that could be material to the Company's results of operations during any particular year of the remediation process. See Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion on this site remediation obligation.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to the Company's customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company is expected to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. The Company applied practical expedients related to unsatisfied performance obligations for (i) contracts with an original expected length of one year or less and (ii) contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue at the amount to which it has the right to invoice for services performed.
Net sales of the Company’s principal services and products were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Service Sales | | | | | |
| Digital Printing | $ | 170,083 | | | $ | 174,752 | | | |
| MPS | 74,764 | | | 75,782 | | | |
| Scanning and Digital Imaging | 20,313 | | | 17,357 | | | |
| Total services sales | 265,160 | | | 267,891 | | | |
| Equipment and Supplies Sales | 16,041 | | | 18,119 | | | |
| Total net sales | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | |
Digital Printing consists of professional services and software services to (i) re-produce and distribute large-format and small-format documents in either black and white or color (“Ordered Prints”) and (ii) specialized graphic color printing. Substantially, all of the Company’s revenue from Digital Printing comes from professional services to re-produce Ordered Prints. Sales of Ordered Prints are initiated through a customer order or quote and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the re-produced Ordered Prints. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Ordered Prints are delivered to the customer’s site or handed to the customer for walk in orders. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue.
MPS consists of placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in the customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities. MPS relieves the Company’s customers of the burden of purchasing print equipment and related supplies and maintaining print devices and print networks, and shifts their costs to a “per-use” basis. MPS is supported by the Company's hosted proprietary technology, Abacus®, which allows customers to capture, control, manage, print, and account for their documents. Under its MPS contracts, the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge”. MPS sales are driven by the ongoing print needs of the Company’s customers at their facilities. Upon the issuance of ASC 842, Leases, the Company concluded that certain of its MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. See Note 7, Leasing, for additional information.
Scanning and Digital Imaging, combines software and professional services to facilitate the capture, management, access and retrieval of documents and information that have been produced in the past. Scanning and Digital Imaging includes the Company's hosted SKYSITE ® software and ARC Facilities solution to organize, search and retrieve documents, as well as the
provision of services that include the capture and conversion of hardcopy and electronic documents into digital files (“Scanned Documents”), and their cloud-based storage and maintenance. Sales of Scanning and Digital Imaging professional services, which represent substantially all revenue for the business line, are initiated through a customer order or proposal and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the digital files. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Scanned Documents are delivered to the customer either through SKYSITE, ARC Facilities, or through other electronic media. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue.
Equipment and Supplies sales consist of reselling printing, imaging, and related equipment (“Goods”) to customers primarily in architectural, engineering and construction firms. Sales of Equipment and Supplies are initiated through a customer order and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligations under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the Goods. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Goods are delivered to the customer’s site. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. The Company has experienced minimal customer returns or refunds and does not offer a warranty on equipment that it is reselling.
The Company has established contractual pricing for certain large national customer accounts (“Global Solutions”). These contracts generally establish uniform pricing at all operating segments for Global Solutions. Revenues earned from the Company’s Global Solutions are recognized in the same manner as non-Global Solutions revenues.
Included in revenues are fees charged to customers for shipping, handling, and delivery services. Such revenues amounted to $11.0 million and $11.3 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Revenues from hosted software licensing activities are recognized ratably over the term of the license. Revenues from software licensing activities comprise less than 2.5% of the Company’s consolidated revenues during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Management provides for returns, discounts and allowances based on historic experience and adjusts such allowances as considered necessary.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company’s comprehensive income (loss) includes foreign currency translation adjustments, net of taxes.
Asset and liability accounts of international operations are translated into the Company’s functional currency, U.S. dollars, at current rates. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average currency rate for the fiscal year.
Segment and Geographic Reporting
The provisions of ASC 280, Segment Reporting, require public companies to report financial and descriptive information about their reportable operating segments. The Company identifies operating segments based on the various business activities that earn revenue and incur expense and whose operating results are reviewed by the Company's Chief Executive Officer, who is the Company's chief operating decision maker. Because its operating segments have similar products and services, classes of customers, production processes, distribution methods and economic characteristics, the Company operates as a single reportable segment.
The Company recognizes revenues in geographic areas based on the location to which the product was shipped or services have been rendered. See table below for revenues and property and equipment, net, attributable to the Company’s U.S. operations and foreign operations.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | | | | | |
| Revenues from external customers | | $ | 247,474 | | | $ | 33,727 | | | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 254,559 | | | $ | 31,451 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment, net | | $ | 35,868 | | | $ | 5,057 | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 34,595 | | | $ | 5,619 | | | $ | 40,214 | | | | | | | |
Advertising and Shipping and Handling Costs
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and approximated $0.7 million during 2023 and 2022. Shipping and handling costs incurred by the Company are included in cost of sales.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company applies the Black-Scholes valuation model in determining the fair value of share-based payments to employees, which is then amortized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period.
Total stock-based compensation for 2023 and 2022, was $2.2 million and $1.8 million, respectively, and was recorded in selling, general, and administrative expenses, consistent with the classification of the underlying salaries. In accordance with ASC 718, Income Taxes, any excess tax benefit resulting from stock-based compensation, in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, are classified along with other income tax cash flows as an operating activity.
The weighted average fair value at the grant date for options issued in 2023 and 2022, was $1.28 and $0.96, respectively. The fair value of each option grant was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions for 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Weighted average assumptions used: | | | | | | |
| Risk free interest rate | | 3.7 | % | | 2.1 | % | | |
| Expected volatility | | 63.0 | % | | 56.4 | % | | |
| Expected dividend yield | | 6.4 | % | | 6.2 | % | | |
Using historical exercise data as a basis, the Company determined that the expected term for stock options issued in 2023 and 2022, was and 7.2 years and 6.7 years, respectively.
For fiscal years 2023 and 2022, expected stock price volatility is based on the Company’s historical volatility for a period equal to the expected term. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant with an equivalent remaining term. The Company accounts for forfeitures of share-based awards when they occur.
As of December 31, 2023, total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to nonvested stock-based compensation was approximately $2.7 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 1.7 years.
For additional information, see Note 9, Employee Stock Purchase Plan and Stock Plan.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development activities relate to costs associated with the design and testing of new technology or enhancements and maintenance to existing technology. Such costs are expensed as incurred are primarily recorded to cost of sales. In total, research and development amounted to $6.2 million and $6.5 million, during 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Noncontrolling Interest
The Company accounted for its investment in UDS under the purchase method of accounting, in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations. UDS has been consolidated in the Company’s financial statements from the date of acquisition. Noncontrolling interest, which represents the 35% noncontrolling interest in UDS, is reflected on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements. In May of 2022, the Company completed an $11.2 million capital distribution from its Chinese JV. As the Company is 65% owner, $7.3 million came to the Company's US operations, and 35% or $3.9 million went to the JV partner, thus resulting in a $3.9 million decrease in the Company's consolidated cash and noncontrolling interest balance sheet accounts in 2022.
Sales Taxes
The Company bills sales taxes, as applicable, to its customers. The Company acts as an agent and bills, collects, and remits the sales tax to the proper government jurisdiction. The sales taxes are accounted for on a net basis, and therefore are not included as part of the Company’s revenue.
Earnings Per Share
The Company accounts for earnings per share in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings Per Share. Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to ARC by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share is computed similarly to basic earnings per share except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if common shares subject to outstanding options and acquisition rights had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. Common share equivalents are excluded from the computation if their effect is anti-dilutive. There were 4.1 million and 3.2 million common shares excluded from the calculation of diluted net income attributable to ARC per common share as their effect would have been anti-dilutive for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company’s common share equivalents consist of stock options issued under the Company’s Stock Plan.
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding were calculated as follows for 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — basic | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | |
| Effect of dilutive stock awards | 941 | | | 1,066 | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — diluted | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Loss (Topic 326) (“ASU 2016-13”), which updates the guidance on recognition and measurement of credit losses for financial assets. The new requirements, known as the current expected credit loss model ("CECL") will require entities to adopt an impairment model based on expected losses rather than incurred losses. ASU 2016-13 must be adopted on a modified-retrospective approach. This update was effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020 including interim periods within those fiscal years. In October 2019, the FASB approved an extension for all non-SEC filers, including small reporting companies, to extend the effective date to fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Therefore, the effective date for this update was January 1, 2023. The implementation of CECL did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated statements of financial condition and results of operations.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures,” which requires public entities to disclose specific tax rate reconciliation categories, as well as income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction, amongst other disclosure enhancements. The ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The ASU can be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis. The Company is evaluating the disclosure requirements related to the new standard.
3. GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES
Goodwill
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, the Company assesses goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired. At September 30, 2023, the Company performed its assessment and determined that goodwill was not impaired.
Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017 the Company elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test.
There can be no assurance that the estimates and assumptions made for purposes of the Company's goodwill impairment analysis in 2023 will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. If the Company’s assumptions, including forecasted EBITDA of certain reporting units, are not achieved, then the Company may be required to record goodwill impairment charges in future periods, whether in connection with the Company’s next annual impairment testing in the third quarter of 2024, or on an interim basis, if any such change constitutes a triggering event (as defined under ASC 350, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other) outside of the quarter when the Company regularly performs its annual goodwill impairment test. It is not possible at this time to determine if any such future impairment charge would result or, if it does, whether such charge would be material.
The carrying amount of goodwill from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023 is summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross
Goodwill | | Accumulated
Impairment
Loss | | Net
Carrying
Amount |
| | | | | |
| January 1, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| December 31, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
Long-lived and Other Intangible Assets
The Company periodically assesses potential impairments of its long-lived assets in accordance with the provisions of ASC 360, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets. An impairment review is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. The Company groups its assets at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of the other assets and liabilities. The Company has determined that the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are available is the regional level, which is the operating segment level.
Factors considered by the Company include, but are not limited to, significant underperformance relative to historical or projected operating results; significant changes in the manner of use of the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business; and significant negative industry or economic trends. When the carrying value of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, the Company estimates the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows and eventual disposition is less than the carrying amount of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. An impairment loss is reflected as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset, based on the fair value if available, or discounted cash flows, if fair value is not available. The Company assessed potential impairments of its long lived assets as of September 30, 2023 and concluded that there was no impairment.
The following table sets forth the Company’s other intangible assets resulting from business acquisitions as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 which continue to be amortized:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount |
| Amortizable other intangible assets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Customer relationships | $ | 99,185 | | | $ | 99,178 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | 99,087 | | | $ | 99,073 | | | $ | 14 | |
| Trade names and trademarks | 20,262 | | | 20,107 | | | 155 | | | 20,281 | | | 20,087 | | | 194 | |
| $ | 119,447 | | | $ | 119,285 | | | $ | 162 | | | $ | 119,368 | | | $ | 119,160 | | | $ | 208 | |
Estimated future amortization expense of other intangible assets for each of the next five fiscal years and thereafter are as follows:
| | | | | |
| 2024 | $ | 39 | |
| 2025 | 35 | |
| 2026 | 34 | |
| 2027 | 34 | |
| 2028 | 20 | |
| Thereafter | — | |
| $ | 162 | |
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment, net consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Machinery and equipment | $ | 245,802 | | | $ | 246,262 | |
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | 21,374 | | | 23,128 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 2,871 | | | 2,737 | |
| 270,047 | | | 272,127 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation | (229,122) | | | (231,913) | |
| $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 40,214 | |
Depreciation expense was $17.6 million and $20.3 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
5. LONG-TERM DEBT
Long-term debt consists of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | |
Revolving Loans; 6.8% and 5.6% interest rate at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 40,000 | | | 40,000 | |
Various finance leases; weighted average interest rate of 5.5% and 5.1% at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively; principal and interest payable monthly through November 2029 | 22,236 | | | 26,474 | |
| | | |
| 62,236 | | | 66,474 | |
| Less current portion | (8,870) | | | (11,558) | |
| $ | 53,366 | | | $ | 54,916 | |
Credit Agreement
On June 15, 2023, the Company entered into an amendment (the "Amendment") to its Credit Agreement dated as of April
22, 2021 (the "2021 Credit Agreement") with U.S. Bank National Association, as administrative agent and the lenders part thereto. The Amendment, among other things, modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement to replace the relevant benchmark provisions from the London Interbank Offered Rate to the forward-looking term rate based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR"). The Amendment also modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement relating to the payment of dividends and stock repurchases by the Company and the related component calculations included in the fixed charge coverage ratio that the Company is required to maintain. After giving effect to the Amendment, the Company is permitted to repurchase up to $10 million of its stock in any twelve-month period and all such permitted stock repurchases will be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. In addition, the Company is permitted to make other restricted payments that are not stock repurchases, such as the payment of dividends, of up to $12 million made during any twelve-month period which will be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. The making of stock repurchases and the payment of dividends and other restricted payments is subject, in each case, to pro forma compliance with the financial covenants and other customary conditions set forth in the 2021 Credit Agreement.
The 2021 Credit Agreement provides for the extension of revolving loans in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $70 million and replaces the Credit Agreement dated as of November 20, 2014, as amended (the "2014 Credit Agreement"). The obligation under the 2021 Credit Agreement matures on April 22, 2026.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company's borrowing availability of Revolving Loans under the Revolving Loan commitment was $27.8 million, after deducting outstanding letters of credit of $2.2 million and outstanding Revolving Loans of $40.0 million.
Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement bear interest, in the case of Term SOFR loans, at a per annum rate equal to the applicable Term SOFR (which rate shall not be less than zero), plus a margin ranging from 1.25% to 1.75%, based on the Company’s Total Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement). Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement that are not Term SOFR loans bear interest at a per annum rate equal to the Alternate Base Rate (as such terms is defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement) plus a margin ranging from 0.25% to 0.75%, based on the Company’s Total Leverage Ratio. As of December 31, 2023, one month Term SOFR loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement accrued interest at 6.8%.
The Company pays certain recurring fees with respect to the 2021 Credit Agreement, including administration fees to the administrative agent.
Subject to certain exceptions, including, in certain circumstances, reinvestment rights, the loans extended under the Credit Agreement are subject to customary mandatory prepayment provisions with respect to: the net proceeds from certain asset sales; the net proceeds from certain issuances or incurrences of debt (other than debt permitted to be incurred under the terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement); the net proceeds from certain issuances of equity securities; and net proceeds of certain insurance recoveries and condemnation events of the Company.
The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary representations and warranties, subject to limitations and exceptions, and customary covenants restricting the ability (subject to various exceptions) of the Company and its subsidiaries to: incur additional indebtedness (including guarantee obligations); incur liens; sell certain property or assets; engage in mergers or other fundamental changes; consummate acquisitions; make investments; make certain distributions or repurchase equity interest of the Company or its subsidiaries; change the nature of their business; prepay or amend certain indebtedness; engage in certain transactions with affiliates; amend their organizational documents; or enter into certain restrictive agreements. In addition, the 2021 Credit Agreement contains financial covenants which requires the Company to maintain (i) at all times, a Total Leverage Ratio in an amount not to exceed 2.75 to 1.00; and (ii) a Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement), as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, an amount not less than 1.15 to 1.00. The Company was in compliance with its covenants during the year ended December 31, 2023.
The 2021 Credit Agreement allows for payment of dividends. In December 2023, the Company's Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.05 per share of common stock that is payable on February 29, 2024 to stockholders of record as of January 31, 2024. Accordingly, the Company recorded a dividend payable of $2.1 million within accrued expenses as of December 31, 2023.
The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary events of default, including with respect to: nonpayment of principal, interest, fees or other amounts; failure to perform or observe covenants; material inaccuracy of a representation or warranty when made; cross-default to other material indebtedness; bankruptcy, insolvency and dissolution events; inability to pay debts; monetary judgment defaults; actual or asserted invalidity or impairment of any definitive loan documentation, repudiation of guaranties or subordination terms; certain ERISA related events; or a change of control.
The obligations of the Company’s subsidiary that is the borrower under the 2021 Credit Agreement are guaranteed by the Company and each of the Company's other United States subsidiaries. The 2021 Credit Agreement and any interest rate
protection and other hedging arrangements provided by any lender party to the credit facility or any affiliate of such a lender are secured on a first priority basis by a perfected security interest in substantially all of the borrower’s, the Company’s and each guarantor’s assets (subject to certain exceptions).
6. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Leases. The Company leases machinery, equipment, and office and operational facilities under non-cancelable operating lease agreements. Certain lease agreements for the Company’s facilities generally contain renewal options and provide for annual increases in rent based on the local Consumer Price Index. Refer to Note 7, Leasing, for the schedule of the Company’s future minimum operating lease payments as of December 31, 2023.
Legal Proceedings. The Company is involved, and will continue to be involved, in legal proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including commercial and employment-related lawsuits. Some of these lawsuits purport or may be determined to be class actions and seek substantial damages, and some may remain unresolved for several years. The Company establishes accruals for specific legal proceedings when it is considered probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company's evaluation of whether a loss is reasonably probable is based on our assessment and consultation with legal counsel regarding the ultimate outcome of the matter. As of December 31, 2023, the Company has accrued for the potential impact of loss contingencies that are probable and reasonably estimable. The Company does not currently believe that the ultimate resolution of any of these matters will have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows. However, the results of these matters cannot be predicted with certainty, and an unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows.
Site Remediation Obligation. As part of a business acquisition in the 1990’s, the Company purchased a site located in California where a former commercial gas station had operated from 1939 until approximately 1986. Prior to the Company's acquisition, the gas station was demolished and its underground storage tanks were removed.
Environmental monitoring of the property was conducted from 1987 through 2017 under the oversight of the local County's Department of Environmental Health ("CDEH") and it eventually revealed petroleum products in the soil, groundwater, and the air in between soil particles. As a result, a Corrective Action Implementation Plan ("CAIP") detailing remedial clean-up methods at the site was required to be submitted in 2020. Accordingly, the Company recorded a liability on an undiscounted basis of $0.6 million in 2020, the estimated cost, to remediate the site.
The 2020 CAIP was approved by the CDEH, but based on additional site data, the department requested a submission of addenda to the CAIP to address other site conditions. The additional review conducted in the fourth quarter of 2023 identified certain potential risks arising out of a structure on a neighboring property. As a result, in December of 2023, the CDEH requested that an alternative remedial plan be developed and submitted by March 12, 2024, to address the structural aspects of the site. The Company is in the process of finalizing an alternative plan with the guidance and expertise of an environmental consulting firm engaged expressly for this purpose. The additional concerns identified in 2023 require that the new plan be designed in a way that is significantly more expensive than the original plan, is more complicated, and will result in a longer duration to remediate the site.
The Company's Consolidated Balance Sheets include a liability on an undiscounted basis for the site remediation of $4.5 million as of December 31, 2023, of which $2.2 million is classified as a current liability, and $0.6 million as of December 31, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the liability represents the Company's estimate of the probable cleanup, investigation, and remediation costs based on available information. The Company anticipates that most of this liability will be paid out over seven years, but some costs may be paid out over a longer period.
As noted above, the estimate of the final remediation expenses may change over time because of the varying costs of currently available cleanup techniques, unpredictable contaminant reduction rates associated with available cleanup techniques, and the difficulty of determining in advance the nature and full extent of contamination. However, evolving statutory and regulatory standards, their interpretation, more vigorous enforcement policies of regulatory agencies, or stricter or different interpretations of existing statutory and regulatory standards, may require additional expenditures by the Company, which may be material. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that the Company will not incur significant additional environmental compliance costs in the future.
7. LEASING
Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases
The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements.
The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet.
Lessee Accounting
The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842.
Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants.
The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | |
| Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | |
| Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | |
| Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | |
| Current | | | | |
| Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | |
| Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | |
| Long-term | | | | |
| Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | |
| Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | |
| Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Classification | Year Ended |
| December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | |
Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | |
| | | | |
| Finance lease cost | | | | |
| Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | |
| Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | |
| Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023.
(2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) |
| 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | |
| 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | |
| 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | |
| 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | |
| 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | |
| Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | |
| Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | |
| Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | |
| Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
(2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028.
(3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) |
| 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | |
| 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | |
| 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | |
| 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | |
| 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | |
| Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | |
| Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | |
| Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | |
| Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
(2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023.
(3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | |
| Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 |
| Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 |
| | | |
| Weighted average discount rate | | |
| Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % |
| Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | |
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | |
| Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | |
| Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Lessor Accounting
The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842.
The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842.
MPS revenue includes $68.8 million of rental income and $6.0 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2023. MPS revenue includes $70.0 million of rental income and $5.8 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company's property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, includes approximately $20 million and $23 million of equipment subject to leases with customers under the Company's MPS arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. Following termination of an MPS arrangement, the Company will place existing equipment at an alternate customer site pursuant to an MPS arrangement, at one of the Company's service centers, or dispose of the equipment.
8. INCOME TAXES
The following table includes the consolidated income tax provision for federal, state, and foreign income taxes related to the Company’s total earnings before taxes for 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Current: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | |
| State | | 215 | | | 154 | | | |
| Foreign | | 481 | | | 487 | | | |
| | 696 | | | 641 | | | |
| Deferred: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | 2,805 | | | 4,142 | | | |
| State | | 682 | | | 1,040 | | | |
| Foreign | | 204 | | | 9 | | | |
| | 3,691 | | | 5,191 | | | |
| Income tax provision | | $ | 4,387 | | | $ | 5,832 | | | |
The Company's foreign earnings before taxes were $2.0 million and $0.4 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
The Company’s US earnings before taxes were $10.5 million and $16.2 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
The consolidated deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Financial statement accruals not currently deductible | $ | 950 | | | $ | 985 | |
| Site remediation obligation | 1,149 | | | 166 | |
| | | |
| Accrued vacation | 765 | | | 754 | |
| Accrued bonuses | 543 | | | 914 | |
| Deferred revenue, net | 21 | | | 37 | |
| Fixed assets | 2,980 | | | 4,242 | |
| Right of use operating lease liabilities | 9,600 | | | 8,494 | |
| Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | 1,541 | | | 745 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 2,343 | | | 2,365 | |
| Federal tax net operating loss carryforward | 11,990 | | | 14,593 | |
| State tax net operating loss carryforward, net | 4,723 | | | 5,182 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Foreign tax net operating loss carryforward | 487 | | | 879 | |
| | | |
| Tax credits, net | 213 | | | 1,669 | |
| | | |
| Gross deferred tax assets | 37,305 | | | 41,025 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | (1,313) | | | (2,651) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 35,992 | | | $ | 38,374 | |
| | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | $ | (23,010) | | | $ | (23,197) | |
| Right of use operating lease assets | (8,547) | | | (7,184) | |
| Fixed assets | (104) | | | — | |
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 4,331 | | | $ | 7,993 | |
A reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Statutory federal income tax rate | 21 | % | | 21 | % | | |
| State taxes, net of federal benefit | 6 | | | 6 | | | |
| Foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | |
| Valuation allowance | (11) | | | 1 | | | |
| Tax credits expired | 12 | | | — | | | |
| Global intangible low taxed income | 1 | | | — | | | |
| Section 162(m) limitation | 3 | | | 2 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Stock based compensation | 1 | | | 3 | | | |
| Discrete items for federal, state and foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Effective income tax rate | 35 | % | | 35 | % | | |
In accordance with ASC 740-10, Income Taxes, the Company evaluates the need for deferred tax asset valuation allowances based on a more likely than not standard. The ability to realize deferred tax assets depends on the ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carryback or carryforward periods provided for in the tax law for each applicable tax jurisdiction. The Company considers the following possible sources of taxable income when assessing the realization of deferred tax assets:
•Future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences;
•Future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards;
•Taxable income in prior carryback years; and
•Tax-planning strategies.
The assessment regarding whether a valuation allowance is required or should be adjusted also considers all available positive and negative evidence factors, including but not limited to:
•Nature, frequency, and severity of recent losses;
•Duration of statutory carryforward periods;
•Historical experience with tax attributes expiring unused; and
•Near- and medium-term financial outlook.
The Company utilizes a rolling three years of actual and current year anticipated results as the primary measure of cumulative income/losses in recent years, as adjusted for permanent differences. The evaluation of deferred tax assets requires judgment in assessing the likely future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company's financial statements or tax returns and future profitability. The Company's accounting for deferred tax consequences represents its best estimate of those future events. Changes in the Company's current estimates, due to unanticipated events or otherwise, could have a material effect on its financial condition and results of operations. The Company has a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023.
Based on the Company’s current assessment, the remaining net deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023 are considered more likely than not to be realized. The valuation allowance of $1.3 million may be increased or reduced as conditions change or if the Company is unable to implement certain available tax planning strategies. The realization of the Company’s net deferred tax assets ultimately depends on future taxable income, reversals of existing taxable temporary differences or through a loss carry back.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had approximately $57.1 million of consolidated federal, $75.8 million of state and $2.9 million of foreign net operating loss carryforwards available to offset future taxable income, respectively. Certain
federal net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2032. Certain state net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2024. The foreign net operating loss carryforwards begin to expire in 2024. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had approximately $0.2 million of foreign tax credit carryforwards which will expire in 2024.
The Company and some of its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction, and various states and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is not under examination in any U.S. federal, state or foreign jurisdiction. Due to net operating losses, substantially all the tax years from 2011 remain open to examination by the tax authorities.
There were no unrecognized tax benefits as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 or 2022. The Company does not include interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense. The Company does not anticipate any significant changes to unrecognized tax benefits over the next 12 months. During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, no interest or penalties were required to be recognized related to unrecognized tax benefits.
9. EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Under the Company’s Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”) eligible employees may purchase up to a calendar year maximum per eligible employee of the lesser of (i) 2,500 shares of common stock, or (ii) a number of shares of common stock having an aggregate fair market value of $25 thousand as determined on the date of purchase at 85% of the fair market value of such shares of common stock on the applicable purchase date. The compensation expense in connection with the ESPP in 2023 and 2022, was $23 thousand and $17 thousand, respectively.
Employees purchased the following shares in the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| Shares purchased | 50 | | | 45 | | | |
| Average price per share | $ | 2.64 | | | $ | 2.16 | | | |
Stock Plan
On April 29, 2021, the Company's stockholders approved the Company's 2021 Incentive Plan, replacing the 2014 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended, which is the only equity incentive plan under which the Company can currently grant equity incentive awards. The 2021 Incentive Plan provides for the grant of incentive and non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock bonuses and other forms of awards granted or denominated in the Company's common stock or units of the Company's common stock, as well as cash bonus awards, to employees, directors and consultants of the Company. On April 26, 2023, the Company's stockholders approved an amendment to the 2021 Incentive Plan ("Amended 2021 Plan") to increase the aggregate number of equity incentive shares authorized for issuance by 5,000,000 shares of common stock. Under the Amended 2021 Plan, the Company is authorized to issue up to 8.5 million shares plus such additional number of shares of common stock (up to 6,132,593 shares) as is equal to the number of shares of common stock subject to awards granted under the 2014 Incentive Plan and the Company's 2005 Stock Plan, which awards expire, terminate or are otherwise surrendered, cancelled, forfeited or repurchased by the Company pursuant to a contractual repurchase right. At December 31, 2023, 5.1 million shares remain available for issuance under the Stock Plan.
Stock options granted under the Company's Stock Plan generally expire no later than ten years from the date of grant. Options generally vest and become fully exercisable over a period of three to four years from date of award, except that options granted to non-employee directors may vest over a shorter time period. The exercise price of options must be equal to at least 100% of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The Company allows for cashless exercises of vested outstanding options.
During 2023 and 2022, the Company granted options to acquire a total of 1.1 million shares and 1.7 million shares, respectively, of the Company's common stock to certain key employees with an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The granted stock options vest annually over three to four years from the grant date and expire 10 years after the date of grant.
The following is a further breakdown of the stock option activity under the Stock Plan:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price per Share | | Weighted
Average
Contractual
Life
(In years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(In thousands) |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 5,462 | | | $ | 3.56 | | | | | |
| Granted | 1,658 | | | $ | 3.11 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (618) | | | $ | 2.49 | | | | | |
| Forfeited/Canceled | (533) | | | $ | 5.31 | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 5,969 | | | $ | 3.39 | | | | | |
| Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 3.60 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (805) | | | $ | 2.60 | | | | | |
| Forfeited/Canceled | (82) | | | $ | 3.12 | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | |
| Vested or expected to vest at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | |
| Exercisable at December 31, 2023 | 3,582 | | | $ | 3.80 | | | 4.26 | | $ | 2,105 | |
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the total pretax intrinsic value (the difference between the closing stock price on December 31, 2023 and the exercise price, multiplied by the number of in-the-money options) that would have been received by the option holders had all the option holders exercised their options on December 31, 2023. This amount changes based on the fair market value of the common stock. Total intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 were $471 thousand and $292 thousand, respectively.
A summary of the Company’s non-vested stock options as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Weighted
Average Grant Date |
| Non-vested Options | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share |
| Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 2,350 | | | $ | 0.96 | |
| Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 1.28 | |
| Vested | (835) | | | $ | 0.94 | |
| Forfeited/Canceled | (15) | | | $ | 1.14 | |
| Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 2,596 | | | $ | 1.10 | |
The following table summarizes certain information concerning outstanding options at December 31, 2023:
| | | | | |
| |
| Range of Exercise Price per Share | Options Outstanding at
December 31, 2023 |
$1.14 – $2.64 | 2,218 | |
$3.20 – $4.75 | 3,196 | |
$6.16 – $7.19 | 392 | |
$8.89 – $9.09 | 372 | |
$1.14 – $9.09 | 6,178 | |
Restricted Stock
In 2023, the Company granted 0.1 million shares of restricted stock awards to certain key employees with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock awards vest annually over three years from the grant date. In addition, the Company granted approximately 30 thousand shares of restricted stock awards to each of the Company's four non-employee members of its board advisors or board of directors, with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock vests on the one-year anniversary of the grant date.
In 2022, the Company granted 0.1 million shares of restricted stock awards to certain key employees with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock awards vest annually over three years from the grant date. In addition, the Company granted approximately 16 thousand shares of restricted stock awards to each of the Company's three non-employee members of its board of directors with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock vests on the one-year anniversary of the grant date.
A summary of the Company’s non-vested restricted stock as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Weighted
Average Grant Date |
| Non-vested Restricted Stock | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share |
| Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 719 | | | $ | 2.35 | |
| Granted | 269 | | | $ | 3.31 | |
| Vested | (365) | | | $ | 2.40 | |
| Forfeited/Canceled | — | | | $ | — | |
| Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 623 | | | $ | 2.73 | |
The total fair value of restricted stock awards vested during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 was $1.1 million and $1.7 million, respectively.
10. RETIREMENT PLANS
The Company sponsors a 401(k) Plan, which covers substantially all employees of the Company who have attained age 21. Under the Company’s 401(k) Plan, eligible employees may contribute up to 75% of their annual eligible compensation (or in the case of highly compensated employees, up to 6% of their annual eligible compensation), subject to contribution limitations imposed by the Internal Revenue Service. The Company matches 20% of an employee’s contributions, up to a total of 4% of that employee’s compensation. An independent third party administers the Company’s 401(k) Plan. The Company's total expense under these plans amounted to $0.5 million and $0.4 million annually during fiscal years 2023 and 2022, respectively.
11. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
In accordance with ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, the Company has categorized its assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value into a three-level fair value hierarchy as set forth below. If the inputs used to measure fair value fall within different levels of the hierarchy, the categorization is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The three levels of the hierarchy are defined as follows:
Level 1-inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2-inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
Level 3-inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company's assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value were not material.
Fair Values of Financial Instruments. The following methods and assumptions were used by the Company in estimating the fair value of its financial instruments for disclosure purposes:
Cash equivalents: Cash equivalents are time deposits with maturity of three months or less when purchased, which are highly liquid and readily convertible to cash. Cash equivalents reported in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets were $1.2 million and $1.7 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and are carried at cost and approximate fair value due to the relatively short period to maturity of these instruments.
Short- and long-term debt and finance leases: The carrying amount of the Company’s finance leases reported in the Consolidated Balance Sheets approximates fair value based on the Company’s current incremental borrowing rate for similar types of borrowing arrangements. The carrying amount reported in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet as of
December 31, 2023 for borrowings under its Credit Agreement is $40.0 million. The Company has determined that borrowings under its Credit Agreement of $40.0 million as of December 31, 2023 approximates its fair value.
Exhibit 4.2
DESCRIPTION OF THE REGISTRANT’S SECURITIES
REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12 OF THE
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934, AS AMENDED
The common stock, par value $0.001 per share (“Common Stock”) of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. (the “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our”) is registered under Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). The following description sets forth certain general terms and provisions of our Common Stock. These description are in all respects subject to and qualified in their entirety by, and should be read in conjunction with the applicable provisions of, our Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Charter”) and our Third Amended and Restated Bylaws (the “Bylaws”), each of which is incorporated by reference as an exhibit to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of which this exhibit is a part, and by applicable law. We encourage you to read our Charter, our Bylaws and the applicable provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”) for additional information.
Authorized Capital Stock
Our authorized capital stock consists of 150,000,000 shares of Common Stock, and 25,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share (“Preferred Stock”).
Common Stock
The holders of our Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share held on all matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders. The holders of our Common Stock do not have any cumulative voting rights. Holders of our Common Stock are entitled to receive ratably any dividends declared by our board of directors (“Board”) out of funds legally available for that purpose, subject to any preferential dividend rights of any outstanding Preferred Stock. Our Common Stock has no preemptive rights, conversion rights or other subscription rights or redemption rights.
In the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up, holders of our Common Stock will be entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of all debts and other liabilities and any liquidation preference of any outstanding Preferred Stock. Each outstanding share of Common Stock is duly and validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable.
Preferred Stock
Our Board will have the authority, without further action by our stockholders, to issue up to 25,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock in one or more series and to fix the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions thereof. These rights, preferences and privileges could include dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, liquidation preferences, sinking fund terms and the number of shares constituting, or the designation of, such series, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of Common Stock. The issuance of our Preferred Stock could adversely affect the voting power of holders of Common Stock and the likelihood that such holders will receive dividend payments and payments upon our liquidation. In addition, the issuance of Preferred Stock could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of our company or other corporate action.
______________________________________________________________________________
No shares of Preferred Stock are outstanding as of the date of our Annual Report on Form 10-K with which this exhibit is filed as an exhibit.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Delaware Law and Provisions of our Charter and our Bylaws
Certain provisions of the DGCL and of our Charter and our Bylaws could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing another party from acquiring control of us and encouraging persons considering unsolicited tender offers or other unilateral takeover proposals to negotiate with our board of directors rather than pursue non-negotiated takeover attempts. These provisions include the items described below.
Delaware Anti-Takeover Statute
Section 203 of the DGCL is applicable to us. Section 203 of the DGCL restricts some types of transactions and business combinations between a corporation and a 15% stockholder. A 15% stockholder is generally considered by Section 203 to be a person owning 15% or more of the corporation’s outstanding voting stock. Section 203 refers to a 15% stockholder as an “interested stockholder.” Section 203 restricts these transactions for a period of three years from the date the stockholder acquires 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock. With some exceptions, unless the transaction is approved by the board of directors and the holders of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation, Section 203 prohibits significant business transactions such as:
•a merger with, disposition of significant assets to or receipt of disproportionate financial benefits by the interested stockholder, and
•any other transaction that would increase the interested stockholder’s proportionate ownership of any class or series of our capital stock.
The shares held by the interested stockholder are not counted as outstanding when calculating the two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock needed for approval.
The prohibition against these transactions does not apply if:
•prior to the time that any stockholder became an interested stockholder, the board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction in which such stockholder acquired 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock, or
•the interested stockholder owns at least 85% of our outstanding voting stock as a result of a transaction in which such stockholder acquired 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock. Shares held by persons who are both directors and officers or by some types of employee stock plans are not counted as outstanding when making this calculation.
No Written Consent of Stockholders
______________________________________________________________________________
Our Charter provides that all stockholder actions are required to be taken by a vote of the stockholders at an annual or special meeting, and that stockholders may not take any action by written consent in lieu of a meeting. This limit may lengthen the amount of time required to take stockholder actions and would prevent the amendment of our bylaws or removal of directors by our stockholders without holding a meeting of stockholders.
Special Meetings of Stockholders
Our Charter provides that special meetings of the stockholders for any purpose or purposes, unless required by law, may only be called our board of directors (the “Board”), the chairman of the board, if
any, the chief executive officer or the president. This limitation on the ability to call a special meeting could make it more difficult for stockholders to initiate actions that are opposed by the Board. These actions could include the removal of an incumbent director or the election of a stockholder nominee as a director. They could also include the implementation of a rule requiring stockholder ratification of specific defensive strategies that have been adopted by the board with respect to unsolicited takeover bids. In addition, the limited ability to call a special meeting of stockholders may make it more difficult to change the existing Board and management.
Board Vacancies
Subject to the rights of the holders of any outstanding series of preferred stock, our Charter authorizes the Board to fill vacancies, including newly created directorships, unless the Board determines by resolution that any such vacancies or newly created directorships shall be filled by the stockholders. Our Charter also provides that directors may be removed by stockholders only by affirmative vote of holders of two-thirds of the outstanding shares of voting stock.
Advance Notice Requirements
Our Bylaws establish advance notice procedures with regard to stockholder proposals relating to the nomination of candidates for election as directors or new business to be brought before meetings of our stockholders. These procedures provide that notice of stockholder proposals must be timely given in writing to our corporate secretary prior to the meeting at which the action is to be taken. Generally, to be timely, notice must be received at our principal executive offices not less than 90 days nor more than 120 days prior to the first anniversary date of the annual meeting for the preceding year. Our Bylaws specify the requirements as to form and content of all stockholders’ notices. These requirements may preclude stockholders from bringing matters before the stockholders at an annual or special meeting.
Amendment to our Charter and Bylaws
Any amendment of our Charter must first be approved by a majority of our Board, and if required by law or our Charter, must thereafter be approved by a majority of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment and a majority of the outstanding shares of each class entitled to vote thereon as a class, except that the amendment of the provisions relating to stockholder action, board composition, limitation of liability and the amendment of our Bylaws and Charter must be approved by not less than two thirds (2/3) of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment.
______________________________________________________________________________
Our Bylaws may be amended by the affirmative vote of a majority of the directors then in office, subject to any limitations set forth in the Bylaws; and may also be amended by the affirmative vote of at least two thirds (2/3) of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment.
Exclusive Forum
Our Bylaws provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware (or, if the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware does not have jurisdiction, then the federal district court for the District of Delaware) shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed to us by any current or former director, officer, other employee or stockholder to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or as to which the DGCL confers jurisdiction on the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware, or (iv) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of our Certificate of Incorporation or our Bylaws or governed by the internal affairs doctrine. This exclusive forum provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Securities Exchange Act 1934, as amended, or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction. Unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal district courts of the United States of America shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for the resolution of any claims arising under the Securities Act. Although our certificate of incorporation contains the choice of forum provisions described above, it is possible that
a court could rule that such a provision is inapplicable for a particular claim or action or that such provision is unenforceable.
Undesignated Preferred Stock
Our Charter provides for 25,000,000 authorized shares of Preferred Stock. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of convertible Preferred Stock may enable our Board to discourage an attempt to obtain control of us by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise. For example, if in the due exercise of its fiduciary obligations, our board of directors were to determine that a takeover proposal is not in the best interests of our stockholders, our Board could cause shares of convertible Preferred Stock to be issued without stockholder approval in one or more private offerings or other transactions that might dilute the voting or other rights of the proposed acquirer or insurgent stockholder or stockholder group. In this regard, our Charter grants our Board broad power to establish the rights and preferences of authorized and unissued shares of convertible Preferred Stock. The issuance of shares of convertible Preferred Stock could decrease the amount of earnings and assets available for distribution to holders of shares of Common Stock. The issuance may also adversely affect the rights and powers, including voting rights, of these holders and may have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing a change in control of us.
Stock Exchange Listing
Our Common Stock is listed on New York Stock Exchange under the trading symbol “ARC.”
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our Common Stock is Broadridge Corporate Issuer Solutions, Inc. The transfer agent and registrar’s address is 1155 Long Island Avenue, Edgewood, NY 11717, and its telephone number is 1-877-830-4932.
Exhibit 21.1
SUBSIDIARIES OF ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name of Subsidiary | | Jurisdiction of Formation | | Doing Business As |
| ARC Document Solutions India Pvt. Ltd. | | India | | |
| ARC — UK Technologies Limited | | United Kingdom | | |
| ARC Acquisition Corporation | | California | | |
| ARC Digital Canada Corp. | | British Columbia | | ARC |
| ARC Reprographics Canada Corp. | | British Columbia | | |
| Reprografia Digital de Mexico, S.A. de C.V. | | Mexico | | |
| Reprographics Fort Worth, Inc. | | Delaware | | |
| SkySite Technologies, Inc. | | Delaware | | |
| ARC Document Solutions, LLC | | Texas | | ARC |
| | | | ARC - Southern |
| | | | ARC Document Solutions |
| | | | ARC Imaging Resources |
| | | | ARC Technology Solutions |
| | | | ARC Facilities |
| | | | Planwell |
| | | | Ridgway's MD, LLC a/k/a Ridgway’s, LLC |
| | | | Riot Creative Imaging |
| | | | The Pier Group |
| Shenzhen Unis - Printing Document Solutions Co., Ltd | | People's Republic of China | | |
| UNIS Document Solutions Co., Ltd. | | People's Republic of China | | |
| | | | |
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We hereby consent to the incorporation of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. of our report dated February 23, 2023 relating to the consolidated financial statements appearing in this Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023.
/s/ ArmaninoLLP
San Ramon, California
February 29, 2024
Exhibit 23.2
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We consent to the incorporation by reference in Registration Statement Nos. 333-272376, 333-255852, 333-239256, 333-224451, 333-195757 and 333-122637 on Form S-8 and 333-132530 on Form S-3 of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. of our report dated February 29, 2024 relating to the financial statements and effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
/s/ Crowe LLP
San Francisco, California
February 29, 2024
Exhibit 31.1
CERTIFICATION OF PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER
PURSUANT TO RULE 13A-14(A) AND RULE 15D-14(A)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of ARC Document Solutions, Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
a) designed such disclosure controls and procedures or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
b) designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
c) evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
d) disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
a) all significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
b) any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal controls over financial reporting.
| | |
|
| /s/ KUMARAKULASINGAM SURIYAKUMAR |
| Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar |
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Date: February 29, 2024
Exhibit 31.2
CERTIFICATION OF PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL AND ACCOUNTING OFFICER
PURSUANT TO RULE 13A-14(A) AND RULE 15D-14(A)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Jorge Avalos, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of ARC Document Solutions, Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
a) designed such disclosure controls and procedures or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
b) designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
c) evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
d) disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
a) all significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
b) any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal controls over financial reporting.
| | |
|
| /s/ JORGE AVALOS |
| Jorge Avalos |
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
Date: February 29, 2024
Exhibit 32.1
CERTIFICATION
PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar, hereby certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, to the best of my knowledge, that:
| | | | | |
| (1) | the Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; and |
| | | | | |
| (2) | the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
| | |
|
| /s/ KUMARAKULASINGAM SURIYAKUMAR |
| Kumarakulasingam Suriyakumar |
| Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
Date: February 29, 2024
Exhibit 32.2
CERTIFICATION
PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of ARC Document Solutions, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Jorge Avalos, hereby certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, to the best of my knowledge, that:
| | | | | |
| (1) | the Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; and |
| | | | | |
| (2) | the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
| | |
|
| /s/ JORGE AVALOS |
| Jorge Avalos |
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
Date: February 29, 2024
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
Amended and Restated Executive Compensation Recovery Policy
Effective: December 1, 2023
This Compensation Recovery Policy (this “Policy”) is adopted by ARC Document Solutions, Inc. (the “Company”) in accordance with Section 303A.14 of the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) Listed Company Manual (“Section 303A.14”), which implements Rule 10D-1 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) (as promulgated pursuant to Section 954 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010). This Policy is effective as of December 1, 2023 (the “Effective Date”).
1.Definitions
(a)“Accounting Restatement” means a requirement that the Company prepare an accounting restatement due to the material noncompliance of the Company with any financial reporting requirement under the U.S. federal securities laws, including any required accounting restatement to correct an error in previously issued financial statements that is material to the previously issued financial statements, or that would result in a material misstatement if the error were corrected in the current period or left uncorrected in the current period. Changes to the Company’s financial statements that do not represent error corrections are not an Accounting Restatement, including: (A) retrospective application of a change in accounting principle; (B) retrospective revision to reportable segment information due to a change in the structure of the Company’s internal organization; (C) retrospective reclassification due to a discontinued operation; (D) retrospective application of a change in reporting entity, such as from a reorganization of entities under common control; and (E) retrospective revision for stock splits, reverse stock splits, stock dividends or other changes in capital structure.
(b)“Committee” means the Compensation Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”).
(c)“Covered Person” means a person who served as an Executive Officer at any time during the performance period for the applicable Incentive-Based Compensation. This Policy (or designated portions hereof as the case may be) will also apply to such other employees (or classes of employees), as the Committee may designate from time to time as Covered Persons.
(d)“Erroneously Awarded Compensation” means the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation that was Received that exceeds the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation that otherwise would have been Received had the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation been determined based on the restated amounts, computed without regard to any taxes paid by the Covered Person or by the Company on the Covered Person’s behalf. For Incentive-Based Compensation based on stock price or total shareholder return, where the amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation is not subject to mathematical recalculation directly from the information in an Accounting Restatement, the amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation will be based on a reasonable estimate by the Committee of the effect of the Accounting Restatement on the stock price or total shareholder return upon which the Incentive-Based Compensation was Received.
(e)“Executive Officer” means the Company’s president, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer (or if there is no such accounting officer, the controller), any vice president of the Company in charge of a principal business unit, division, or function (such as
sales, administration, or finance), any other officer who performs a significant policy-making function, or any other person (including as applicable executives of any of the Company’s parents or subsidiaries) who performs similar policy-making functions for the Company.
(f)“Financial Reporting Measures” means (A) measures that are determined and presented in accordance with the accounting principles used in preparing the Company’s financial statements, and any measures that are derived wholly or in part from such measures (whether or not such measures are presented within the Company’s financial statements or included in a filing made with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission), (B) stock price and (C) total shareholder return.
(g)“Incentive-Based Compensation” means any compensation that is granted, earned, or vested based wholly or in part upon the attainment of a Financial Reporting Measure.
(h)Incentive-Based Compensation is deemed to be “Received” in the Company’s fiscal period during which the Financial Reporting Measure specified in the applicable Incentive-Based Compensation award is attained, even if the payment or grant of the Incentive-Based Compensation occurs after the end of that period or is subject to additional time-based vesting requirements.
(i)“Recovery Period” means the three completed fiscal years immediately preceding the earlier of: (A) the date the Board, a committee of the Board, or the officer or officers of the Company authorized to take such action if Board action is not required, concludes, or reasonably should have concluded, that the Company is required to prepare an Accounting Restatement; or (B) the date a court, regulator, or other legally authorized body directs the Company to prepare an Accounting Restatement. In addition, if there is a change in the Company’s fiscal year end, the Recovery Period will also include any transition period to the extent required by Section 303A.14.
2.Recovery of Erroneously Awarded Compensation
(a)Application of Prior Policy. If the Company is required to prepare an Accounting Restatement and the provisions of Section 2(b) of this Policy are inapplicable, the Executive Compensation Recovery Policy previously adopted by the Board (the “Prior Policy”) will apply in accordance with its terms. The Prior Policy will not apply when Section 2(b) of this Policy is applicable.
(b)Application of this Policy. Subject to the terms of this Policy and the requirements of Section 303A.14, if, on or after the Effective Date, the Company is required to prepare an Accounting Restatement, the Company will attempt to recover, reasonably promptly from each Covered Person, any Erroneously Awarded Compensation that was Received by such Covered Person during the Recovery Period pursuant to Incentive-Based Compensation that is subject to this Policy.
3.Interpretation and Administration
(a)Role of the Committee. This Policy will be interpreted by the Committee in a manner that is consistent with Section 303A.14 and any other applicable law and will otherwise be interpreted in the business judgment of the Committee. All decisions and interpretations of the Committee that are consistent with Section 303A.14 will be final and binding.
(b)Compensation Not Subject to this Policy. This Policy does not apply to Incentive-Based Compensation that was Received before the Effective Date. With respect to any Covered
Person, this Policy does not apply to Incentive-Based Compensation that was Received by such Covered Person before beginning service as an Executive Officer or, if earlier, first being designated by the Committee as a Covered Person.
(c)Determination of Means of Recovery. Subject to the requirement that recovery be made reasonably promptly, the Committee will determine the appropriate means of recovery, which may vary between Covered Persons or based on the nature of the applicable Incentive-Based Compensation, and which may involve, without limitation, establishing a deferred repayment plan or setting off against current or future compensation otherwise payable to the Covered Person. Recovery of Erroneously Awarded Compensation will be made without regard to income taxes paid by the Covered Person or by the Company on the Covered Person’s behalf in connection with such Erroneously Awarded Compensation.
(d)Determination That Recovery is Impracticable. The Company is not required to recover Erroneously Awarded Compensation if a determination is made by the Committee that either (A) after the Company has made and documented a reasonable attempt to recover such Erroneously Awarded Compensation, the direct expense paid to a third party to assist in enforcing this Policy would exceed the amount to be recovered or (B) recovery of such Erroneously Awarded Compensation would likely cause an otherwise tax-qualified retirement plan, under which benefits are broadly available to employees of the Company, to fail to meet the requirements of Section 401(a)(13) or 411(a) of the Internal Revenue Code and regulations thereunder.
(e)No Indemnification or Company-Paid Insurance. The Company will not indemnify any Covered Person against the loss of Erroneously Awarded Compensation and will not pay or reimburse any Covered Person for the purchase of a third-party insurance policy to fund potential recovery obligations.
(f)Interaction with Other Clawback Provisions. The Company will be deemed to have recovered Erroneously Awarded Compensation in accordance with this Policy to the extent the Company actually receives such amounts pursuant to any other Company policy, program or agreement (including the Prior Policy), pursuant to Section 304 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or otherwise.
(g)No Limitation on Other Remedies. Nothing in this Policy will be deemed to limit the Company’s right to terminate employment of any Covered Person, to seek recovery of other compensation paid to a Covered Person, or to pursue other rights or remedies available to the Company under applicable law.
v3.24.0.1
Cover Page - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Feb. 16, 2024 |
Jun. 30, 2023 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Dec. 31, 2023
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--12-31
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
001-32407
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
ARC DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
DE
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
20-1700361
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
12657 Alcosta Blvd, Suite 200
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
San Ramon
|
|
|
| Entity Address, State or Province |
CA
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
94583
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
925
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
949-5100
|
|
|
| Title of 12(b) Security |
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share
|
|
|
| Trading Symbol |
ARC
|
|
|
| Security Exchange Name |
NYSE
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
true
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| ICFR Auditor Attestation Flag |
true
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction [Flag] |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 117,924,128
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding |
|
42,765,875
|
|
| Documents Incorporated by Reference |
Portions of the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, are incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K in Part III as indicated therein.
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2023
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0001305168
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDocuments incorporated by reference. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-23
| Name: |
dei_DocumentsIncorporatedByReferenceTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the state or province.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressStateOrProvince |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:stateOrProvinceItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(b) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b
| Name: |
dei_Security12bTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the Exchange on which a security is registered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection d1-1
| Name: |
dei_SecurityExchangeName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarExchangeCodeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTrading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.
| Name: |
dei_TradingSymbol |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:tradingSymbolItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Balance Sheets - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Current assets: |
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 56,093
|
$ 52,561
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowances for credit losses of $1,857 and $1,947 |
35,775
|
38,748
|
| Inventory |
8,818
|
8,610
|
| Prepaid expenses |
3,988
|
4,018
|
| Other current assets |
3,978
|
3,540
|
| Total current assets |
108,652
|
107,477
|
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $229,122 and $231,913 |
40,925
|
40,214
|
| Right-of-use assets from operating leases |
32,838
|
28,163
|
| Goodwill |
121,051
|
121,051
|
| Other intangible assets, net |
162
|
208
|
| Deferred income taxes, net |
4,383
|
7,993
|
| Other assets |
2,113
|
2,209
|
| Total assets |
310,124
|
307,315
|
| Current liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts payable |
24,175
|
22,972
|
| Accrued payroll and payroll-related expenses |
9,401
|
11,235
|
| Accrued expenses |
18,787
|
16,882
|
| Current operating lease liabilities |
9,924
|
9,924
|
| Current portion of finance leases |
8,870
|
11,558
|
| Total current liabilities |
71,157
|
72,571
|
| Long-term operating lease liabilities |
27,357
|
23,339
|
| Long-term debt and finance leases |
53,366
|
54,916
|
| Deferred income taxes |
52
|
0
|
| Other long-term liabilities |
2,467
|
199
|
| Total liabilities |
154,399
|
151,025
|
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 6) |
|
|
| ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value, 25,000 shares authorized; 0 shares issued and outstanding |
0
|
0
|
| Common stock, $0.001 par value, 150,000 shares authorized; 52,526 and 51,400 shares issued and 42,783 and 43,101 shares outstanding |
52
|
51
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
136,460
|
132,952
|
| Retained earnings |
44,144
|
44,416
|
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(4,200)
|
(4,187)
|
| Total stockholders equity before adjustment of treasury stock |
176,456
|
173,232
|
| Less cost of common stock in treasury, 9,743 and 8,299 shares |
22,390
|
18,877
|
| Total ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders’ equity |
154,066
|
154,355
|
| Noncontrolling interest |
1,659
|
1,935
|
| Total equity |
155,725
|
156,290
|
| Total liabilities and equity |
$ 310,124
|
$ 307,315
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after tax, of accumulated increase (decrease) in equity from transaction and other event and circumstance from nonowner source. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14A
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue received from shareholders in common stock-related transactions that are in excess of par value or stated value and amounts received from other stock-related transactions. Includes only common stock transactions (excludes preferred stock transactions). May be called contributed capital, capital in excess of par, capital surplus, or paid-in capital. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapitalCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are recognized. Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 26: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed within one year (or the normal operating cycle, if longer). Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the caption on the face of the balance sheet to indicate that the entity has entered into (1) purchase or supply arrangements that will require expending a portion of its resources to meet the terms thereof, and (2) is exposed to potential losses or, less frequently, gains, arising from (a) possible claims against a company's resources due to future performance under contract terms, and (b) possible losses or likely gains from uncertainties that will ultimately be resolved when one or more future events that are deemed likely to occur do occur or fail to occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.17)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.25)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingencies |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated impairment loss of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Goodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after valuation and LIFO reserves of inventory expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all liabilities that are recognized. Liabilities are probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of an entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 22: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19-26)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Liabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.21)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt and lease obligation, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligations |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to noncontrolling interest. Excludes temporary equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.31)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncurrent assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.24)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable preferred shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits within a future period of one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 340
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482955/340-10-05-5
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 340
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483032/340-10-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated depreciation and amortization, of property, plant, and equipment and finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal amount of stockholders' equity (deficit) items including stock value, paid in capital, retained earnings and including equity attributable to noncontrolling interests and before deducting the carrying value of treasury stock.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityBeforeTreasuryStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent and noncontrolling interest. Excludes temporary equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-23
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-5
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-5
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (i)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-8
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (d)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-8
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-5
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-1
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-17
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-3
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-3
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 40: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 41: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-15
Reference 42: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-16
Reference 43: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4I
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4I
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount allocated to previously issued common shares repurchased by the issuing entity and held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481520/505-30-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.30)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockCommonValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Balance Sheets (Parenthetical) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Statement of Financial Position [Abstract] |
|
|
| Allowance for credit losses |
$ 1,857
|
$ 1,947
|
| Accumulated depreciation |
$ 229,122
|
$ 231,913
|
| Preferred stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
25,000,000
|
25,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
| Common stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
150,000,000
|
150,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued (in shares) |
52,526,000
|
51,400,000
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
42,783,000
|
43,101,000
|
| Treasury stock, shares (in shares) |
9,743,000
|
8,299,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479344/326-20-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllowanceForDoubtfulAccountsReceivableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of preferred stock nonredeemable or redeemable solely at the option of the issuer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) issued to shareholders (includes related preferred shares that were issued, repurchased, and remain in the treasury). May be all or portion of the number of preferred shares authorized. Excludes preferred shares that are classified as debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate share number for all nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) held by stockholders. Does not include preferred shares that have been repurchased. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation and amortization from plant, property, and equipment and right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfFinancialPositionAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of previously issued common shares repurchased by the issuing entity and held in treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockCommonShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Statements of Operations - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Total net sales |
$ 281,201
|
$ 286,010
|
| Cost of sales |
186,800
|
190,013
|
| Gross profit |
94,401
|
95,997
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
76,333
|
77,544
|
| Amortization of intangible assets |
41
|
97
|
| Site remediation expense |
4,000
|
0
|
| Income from operations |
14,027
|
18,356
|
| Other income, net |
(67)
|
(62)
|
| Interest expense, net |
1,633
|
1,796
|
| Income before income tax provision |
12,461
|
16,622
|
| Income tax provision |
4,387
|
5,832
|
| Net income |
8,074
|
10,790
|
| Loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
161
|
304
|
| Net income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders |
$ 8,235
|
$ 11,094
|
| Earnings per share attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders: |
|
|
| Basic (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.19
|
$ 0.26
|
| Diluted (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.19
|
$ 0.26
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
| Basic (in shares) |
42,543
|
42,214
|
| Diluted (in shares) |
43,484
|
43,280
|
| Service sales |
|
|
| Total net sales |
$ 265,160
|
$ 267,891
|
| Equipment and Supplies sales |
|
|
| Total net sales |
$ 16,041
|
$ 18,119
|
| X |
- DefinitionLoss per share attributable to American Reprographics Company shareholders.
| Name: |
arc_CompanyShareholdersAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense charged against earnings to allocate the cost of intangible assets (nonphysical assets not used in production) in a systematic and rational manner to the periods expected to benefit from such assets. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs related to goods produced and sold and services rendered by an entity during the reporting period. This excludes costs incurred during the reporting period related to financial services rendered and other revenue generating activities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.2(a),(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfGoodsAndServicesSold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1,2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (210.5-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of Net Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4J
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4J
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of income or expense from ancillary business-related activities (that is to say, excluding major activities considered part of the normal operations of the business). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe consolidated profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, including the portion attributable to the noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4J
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4J
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-2
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProfitLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total costs related to selling a firm's product and services, as well as all other general and administrative expenses. Direct selling expenses (for example, credit, warranty, and advertising) are expenses that can be directly linked to the sale of specific products. Indirect selling expenses are expenses that cannot be directly linked to the sale of specific products, for example telephone expenses, Internet, and postal charges. General and administrative expenses include salaries of non-sales personnel, rent, utilities, communication, etc. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ProductMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Statement of Comprehensive Income [Abstract] |
|
|
| Net income |
$ 8,074
|
$ 10,790
|
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax |
|
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax |
(128)
|
(2,104)
|
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax |
(128)
|
(2,104)
|
| Comprehensive income |
7,946
|
8,686
|
| Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(276)
|
(722)
|
| Comprehensive income attributable to ARC Document Solutions, Inc. stockholders |
$ 8,222
|
$ 9,408
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income and other comprehensive income, attributable to parent entity. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income (loss) and other comprehensive income (loss), attributable to noncontrolling interests. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-20
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTaxAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income and other comprehensive income. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTaxIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax and reclassification adjustments of gain (loss) on foreign currency translation adjustments, foreign currency transactions designated and effective as economic hedges of a net investment in a foreign entity and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term-investment nature. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 220
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-10A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossForeignCurrencyTransactionAndTranslationAdjustmentNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax and reclassification adjustments of other comprehensive income (loss). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-17
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-5
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 220
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482739/220-10-55-15
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTaxPeriodIncreaseDecreaseAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe consolidated profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, including the portion attributable to the noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4J
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4J
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-2
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProfitLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfIncomeAndComprehensiveIncomeAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Statements of Equity - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
Total |
Common Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Retained Earnings |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income |
Common Stock in Treasury |
Noncontrolling Interest |
| Beginning balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2021 |
|
50,584
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Beginning balance at Dec. 31, 2021 |
$ 158,992
|
$ 50
|
$ 129,881
|
$ 41,768
|
$ (2,501)
|
$ (16,771)
|
$ 6,565
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation (in shares) |
|
152
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation |
$ 1,773
|
|
1,773
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan (in shares) |
45
|
45
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
$ 98
|
|
98
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock options exercised (in shares) |
618
|
619
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock options exercised |
$ 1,201
|
$ 1
|
1,200
|
|
|
|
|
| Treasury shares |
(2,106)
|
|
|
|
|
(2,106)
|
|
| Cash dividends - common stock |
(8,446)
|
|
|
(8,446)
|
|
|
|
| Distribution to noncontrolling interest |
(3,908)
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3,908)
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ 8,686
|
|
|
11,094
|
(1,686)
|
|
(722)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2022 |
51,400
|
51,400
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Dec. 31, 2022 |
$ 156,290
|
$ 51
|
132,952
|
44,416
|
(4,187)
|
(18,877)
|
1,935
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation (in shares) |
|
270
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation |
$ 2,232
|
|
2,232
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan (in shares) |
50
|
51
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
$ 133
|
|
133
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock options exercised (in shares) |
805
|
805
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock options exercised |
$ 1,144
|
$ 1
|
1,143
|
|
|
|
|
| Treasury shares |
(3,513)
|
|
|
|
|
(3,513)
|
|
| Cash dividends - common stock |
(8,507)
|
|
|
(8,507)
|
|
|
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ 7,946
|
|
|
8,235
|
(13)
|
|
(276)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Dec. 31, 2023 |
52,526
|
52,526
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Dec. 31, 2023 |
$ 155,725
|
$ 52
|
$ 136,460
|
$ 44,144
|
$ (4,200)
|
$ (22,390)
|
$ 1,659
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income and other comprehensive income. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTaxIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of paid and unpaid cash dividends declared for classes of stock, for example, but not limited to, common and preferred. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 405
-Topic 942
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481071/942-405-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DividendsCash |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInStockholdersEquityRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDecrease in noncontrolling interest balance from payment of dividends or other distributions by the non-wholly owned subsidiary or partially owned entity, included in the consolidation of the parent entity, to the noncontrolling interest holders. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterestDecreaseFromDistributionsToNoncontrollingInterestHolders |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued during the period as a result of an employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesEmployeeStockPurchasePlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber, after forfeiture, of shares or units issued under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes shares or units issued under employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate change in value for stock issued during the period as a result of employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueEmployeeStockPurchasePlan |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue, after forfeiture, of shares issued under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of stock issued as a result of the exercise of stock options. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.29-31)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent and noncontrolling interest. Excludes temporary equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-23
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483421/250-10-45-5
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-5
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (i)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480528/815-20-65-6
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 848
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483550/848-10-65-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 105
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479343/105-10-65-6
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-8
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (d)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482615/740-10-65-8
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479654/326-10-65-4
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480336/718-10-65-15
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-5
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-1
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-17
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-3
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-3
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 40: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 41: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-15
Reference 42: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-16
Reference 43: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4I
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4I
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the cost of common and preferred stock that were repurchased during the period. Recorded using the cost method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481549/505-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TreasuryStockValueAcquiredCostMethod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate dividends declared during the period for each share of common stock outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockDividendsPerShareDeclared |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfStockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
| Net income |
$ 8,074
|
$ 10,790
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
| Allowance for credit losses |
351
|
320
|
| Depreciation |
17,592
|
20,328
|
| Amortization of intangible assets |
41
|
97
|
| Amortization of deferred financing costs |
67
|
61
|
| Stock-based compensation |
2,232
|
1,773
|
| Deferred income taxes |
5,016
|
4,927
|
| Deferred tax valuation allowance |
(1,326)
|
264
|
| Other non-cash items, net |
(262)
|
(205)
|
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts receivable |
2,783
|
(195)
|
| Inventory |
(243)
|
62
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
9,391
|
9,746
|
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(7,133)
|
(10,741)
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
36,583
|
37,227
|
| Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
| Capital expenditures |
(10,752)
|
(5,881)
|
| Other |
363
|
307
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(10,389)
|
(5,574)
|
| Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
| Proceeds from stock option exercises |
1,144
|
1,201
|
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
133
|
98
|
| Share repurchases |
(3,513)
|
(2,106)
|
| Distribution to noncontrolling interest |
0
|
(3,908)
|
| Payments on long-term debt agreements and finance leases |
(11,860)
|
(14,736)
|
| Borrowings under revolving credit facilities |
162,000
|
154,000
|
| Payments under revolving credit facilities |
(162,000)
|
(160,250)
|
| Payment of deferred financing costs |
(23)
|
(6)
|
| Dividends paid |
(8,518)
|
(8,448)
|
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(22,637)
|
(34,155)
|
| Effect of foreign currency translation on cash balances |
(25)
|
(866)
|
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
3,532
|
(3,368)
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
52,561
|
55,929
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
56,093
|
52,561
|
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
|
|
| Cash paid for interest |
1,715
|
1,837
|
| Income taxes paid, net |
903
|
167
|
| Noncash financing activities: |
|
|
| Finance lease obligations incurred |
7,764
|
9,482
|
| Operating lease obligations incurred |
14,478
|
8,687
|
| Declared unpaid dividends |
$ 2,144
|
$ 2,106
|
| X |
- DefinitionDividends Declared And Unpaid
| Name: |
arc_DividendsDeclaredAndUnpaid |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFinance Lease Obligations Incurred
| Name: |
arc_FinanceLeaseObligationsIncurred |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionOperating Lease Obligations Incurred
| Name: |
arc_OperatingLeaseObligationsIncurred |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfFinancingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense charged against earnings to allocate the cost of intangible assets (nonphysical assets not used in production) in a systematic and rational manner to the periods expected to benefit from such assets. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period that reflects the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over the assets' useful lives. Includes production and non-production related depreciation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Depreciation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) from effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; held in foreign currencies. Excludes amounts for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 230
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_EffectOfExchangeRateOnCashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the amounts payable to vendors for goods and services received and the amount of obligations and expenses incurred but not paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in amount due within one year (or one business cycle) from customers for the credit sale of goods and services. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate value of all inventory held by the reporting entity, associated with underlying transactions that are classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInInventories |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingCapitalAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in prepaid expenses, and assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInPrepaidDeferredExpenseAndOtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash paid for interest, excluding capitalized interest, classified as operating activity. Includes, but is not limited to, payment to settle zero-coupon bond for accreted interest of debt discount and debt instrument with insignificant coupon interest rate in relation to effective interest rate of borrowing attributable to accreted interest of debt discount. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPaidNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoncashInvestingAndFinancingItemsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) included in net income that results in no cash inflow (outflow), classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNoncashIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash (inflow) outflow from investing activities classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForProceedsFromOtherInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow to reacquire common stock during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRepurchaseOfCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCash outflow in the form of capital distributions and dividends to common shareholders, preferred shareholders and noncontrolling interests. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsOfDividends |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow for loan and debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsOfFinancingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of long-lived, physical assets that are used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale; includes cash outflows to pay for construction of self-constructed assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquirePropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow to a noncontrolling interest. Includes, but not limited to, reduction of noncontrolling interest ownership. Excludes dividends paid to the noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToMinorityShareholders |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow from contractual arrangement with the lender, including but not limited to, letter of credit, standby letter of credit and revolving credit arrangements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromLinesOfCredit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow from exercise of option under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow associated with the amount received from the stock plan during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockPlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe consolidated profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, including the portion attributable to the noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4J
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4J
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 4K
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481175/810-10-55-4K
Reference 35: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-2
Reference 38: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
Reference 39: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProfitLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense (reversal of expense) for expected credit loss on accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479319/326-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProvisionForDoubtfulAccounts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow for payment of an obligation from a lender, including but not limited to, letter of credit, standby letter of credit and revolving credit arrangements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_RepaymentsOfLinesOfCredit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow for debt, mandatory redeemable security, and principal payment for finance lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a),(b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_RepaymentsOfLongTermDebtAndCapitalSecurities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the valuation allowance for a specified deferred tax asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowanceDeferredTaxAssetChangeInAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
| DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION |
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION ARC Document Solutions Inc. is a digital printing company. We provide digital printing and document-related services to customers in a growing variety of industries. ARC offers Digital Printing services, Managed Print Services ("MPS"), and Scanning and Digital Imaging services. In addition, ARC also sells Equipment and Supplies. The Company conducts its operations through its wholly-owned operating subsidiary, ARC Document Solutions, LLC, a Texas limited liability company, and its affiliates. Basis of Presentation The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis and relies on historical experience and various other factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances to determine such estimates. Actual results could differ from those estimates and such differences may be material to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Risk and Uncertainties The Company generates a significant portion of its revenue from sales of services and products to customers in the architectural, engineering, construction and building owner/operator ("AEC/O") industry. As a result, the Company's results largely depend on the strength of that industry. The Company's historical operating results reflect the cyclical and variable nature of the AEC/O industry. ARC believes that the AEC/O industry generally experiences downturns several months after a downturn in the general economy, and that there may be a similar delay in the recovery of the AEC/O industry following a recovery of the general economy. A downturn in the AEC/O industry would diminish demand for all of the Company's products and services, and would therefore negatively affect the Company's revenues and have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, operating results and financial condition. As part of the Company's growth strategy, ARC intends to continue to expand the market and industries it services and increase sales of a variety of service offerings that utilize ARC's existing production methods and infrastructure, but that are relatively new to the Company. The success of the Company’s efforts will be affected by its ability to acquire new customers for the Company’s new service offerings, as well as to sell the new service offerings to existing customers. The Company’s inability to successfully market and execute these relatively new service offerings could significantly affect its business and reduce its long-term revenue, resulting in an adverse effect on its results of operations and financial condition.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for organization, consolidation and basis of presentation of financial statements disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480424/946-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480424/946-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//810/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//205/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES Cash Equivalents Cash equivalents include demand deposits and short-term investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased. The Company maintains its cash deposits at numerous banks located throughout the United States, Canada, India, United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom and China, which at times, may exceed federally insured limits. UNIS Document Solutions, Co. Ltd., ("UDS"), the Company’s joint venture in China, held $2.6 million and $3.2 million of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risk on cash and cash equivalents. Concentrations of Credit Risk and Significant Vendors Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade receivables are limited due to a large, diverse customer base. No individual customer represented more than 2.5% of net sales during 2023 and 2022. The Company has geographic concentration risk as sales in California, as a percent of total sales, were approximately 30% and 31% for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company contracts with various suppliers. Although there are a limited number of suppliers that could supply the Company’s inventory, management believes any shortfalls from existing suppliers could be absorbed by its existing suppliers or from other suppliers on comparable terms. However, a change in suppliers could cause a delay in sales and adversely affect results. Purchases from the Company’s three largest vendors during 2023 and 2022 comprised approximately 35% of the Company’s total purchases of inventory and supplies. Allowance for Credit Losses The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of the financial condition of its customers, monitors collections and payments from customers, and generally does not require collateral. The Company provides for the possible inability to collect accounts receivable by recording an allowance for credit losses. The Company writes off accounts receivable balances when it is considered uncollectible. The Company estimates the allowance for credit losses based on historical experience, aging of accounts receivable, and information regarding the credit worthiness of its customers. Additionally, the Company provides an allowance for returns and discounts based on historical experience. The allowance for credit losses activity was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | Charges to
Cost and
Expenses | | Deductions (1) | | Balance at
End of
Period | | Year ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | | Allowance for credit losses | $ | 1,947 | | | $ | 351 | | | $ | (441) | | | $ | 1,857 | | | Year ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | Allowance for credit losses | $ | 2,104 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | (477) | | | $ | 1,947 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Deductions represent uncollectible accounts written-off net of recoveries. Inventories Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (determined on a first-in, first-out basis; or average cost) or net realizable value. Inventories primarily consist of materials for use and resale in digital printing, and equipment for resale. On an ongoing basis, inventories are reviewed and adjusted for estimated obsolescence or unmarketable inventories to reflect the lower of cost or net realizable value. Charges to write-down inventory to realizable value are recorded as an increase in cost of sales. Income Taxes Deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial and tax reporting purposes. Such amounts are adjusted, as appropriate, to reflect changes in tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce the Company's deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. Changes in tax laws or accounting standards and methods may affect recorded deferred taxes in future periods. When establishing a valuation allowance, the Company considers future sources of taxable income such as future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards and tax planning strategies. A tax planning strategy is an action that: is prudent and feasible; an enterprise ordinarily might not take but would take to prevent an operating loss or tax credit carryforward from expiring unused; and would result in realization of deferred tax assets. In the event the Company determines that its deferred tax assets, more likely than not, will not be realized in the future, the valuation adjustment to the deferred tax assets will be charged to earnings in the period in which the Company makes such a determination. The Company has a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023. In future quarters the Company will continue to evaluate its historical results for the preceding twelve quarters and our future projections to determine whether this will generate sufficient taxable income to utilize the Company's deferred tax assets, and whether a valuation allowance is required. The Company calculates current and deferred tax provision based on estimates and assumptions that could differ from the actual results reflected in income tax returns filed in subsequent years. Adjustments based on filed returns are recorded when identified. Income taxes have not been provided on certain undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because such earnings are considered to be permanently reinvested. The amount of taxable income or loss we report to the various tax jurisdictions is subject to ongoing audits by federal, state and foreign tax authorities. The Company estimate of the potential outcome of any uncertain tax issue is subject to management’s assessment of relevant risks, facts, and circumstances existing at that time. The Company uses a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company records a liability for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and tax position taken or expected to be taken on its tax return. To the extent that the Company's assessment of such tax positions changes, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. The Company will not report tax-related interest and penalties as a component of income tax expense. Property and Equipment, net Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | Buildings | | 10-20 years | | Leasehold improvements | | 10-20 years or lease term, if shorter | | Machinery and equipment | | 3-7 years | | Furniture and fixtures | | 3-7 years |
Assets acquired under capital lease arrangements are included in machinery and equipment, are recorded at the present value of the minimum lease payments, and are depreciated using the straight-line method over the life of the asset or term of the lease, whichever is shorter. Expenses for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred, while renewals and betterments are capitalized. Gains or losses on the sale or disposal of property and equipment are reflected in operating income. The Company accounts for software costs developed for internal use in accordance with ASC 350-40, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software, which requires companies to capitalize certain qualifying costs incurred during the application development stage of the related software development project. The primary use of this software is for internal use and, accordingly, such capitalized software development costs are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the economic lives of the related products not to exceed three years. The Company’s machinery and equipment (see Note 4, Property and Equipment, Net) includes $1.9 million and $1.7 million of capitalized software development costs as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, net of accumulated amortization of $24.2 million and $23.3 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Depreciation expense includes the amortization of capitalized software development costs which amounted to $0.9 million and $1.0 million, during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Software development costs for software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed are expensed as incurred until the establishment of technological feasibility, at which time those costs are capitalized until the product is available for general release to customers and amortized over the estimated life of the product. Technological feasibility is established upon the completion of a working prototype that has been certified as having no critical bugs and is a release candidate. To date, costs and time incurred between the establishment of technological feasibility and product release have not been material, and all software development costs have been charged to research and development expense in our consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss). Impairment of Long-Lived Assets The Company periodically assesses potential impairments of its long-lived assets in accordance with the provisions of ASC 360, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets. An impairment review is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. The Company groups its assets at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of the other assets and liabilities. The Company has determined that the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are available is the regional level, which is the operating segment level. Factors considered by the Company include, but are not limited to, significant underperformance relative to historical or projected operating results; significant changes in the manner of use of the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business; and significant negative industry or economic trends. When the carrying value of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, the Company estimates the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows and eventual disposition is less than the carrying amount of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. An impairment loss is reflected as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset, based on the fair value if available, or discounted cash flows, if fair value is not available. The Company had no long-lived asset impairments in 2023 or 2022. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, the Company assesses goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired. Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017, the Company elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04 which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. The Company determines the fair value of its reporting units using an income approach. Under the income approach, the Company determined fair value based on estimated discounted future cash flows of each reporting unit. Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including revenue growth rates and EBITDA margins, discount rates and future market conditions, among others. The level of judgement and estimation is inherently higher in these uncertain economic times. Other intangible assets that have finite lives are amortized over their useful lives. Customer relationships are amortized using the accelerated method, based on customer attrition rates, over their estimated useful lives of 13 (weighted average) years. Deferred Financing Costs Direct costs incurred in connection with debt agreements are recorded as incurred and amortized based on the effective interest method for the Company's borrowings under its credit agreement with U.S. Bank National Association, dated April 22, 2021 (the "2021 Credit Agreement"), as amended on June 15, 2023. At December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company had $0.2 million in unamortized deferred financing costs. Fair Values of Financial Instruments The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to their short maturities. Refer to Note 11, Fair Value Measurements, in Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for disclosures regarding fair value measurements in accordance with the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures. Insurance Liability The Company maintains a high deductible insurance policy for a significant portion of its risks and associated liabilities with respect to workers’ compensation. The Company’s deductible is $250 thousand per individual. The accrued liabilities associated with this program are based on the Company’s estimate of the ultimate costs to settle known claims, as well as claims incurred but not yet reported to the Company, as of the balance sheet date. The Company’s estimated liability is not discounted and is based upon an actuarial report obtained from a third party. The actuarial report uses information provided by the Company’s insurance brokers and insurers, combined with the Company’s judgments regarding a number of assumptions and factors, including the frequency and severity of claims, claims development history, case jurisdiction, applicable legislation, and the Company’s claims settlement practices. Commitments and Contingencies In the normal course of business, the Company estimates potential future loss accruals related to legal, workers’ compensation, tax and other contingencies. These accruals require management’s judgment on the outcome of various events based on the best available information. However, due to changes in facts and circumstances, the ultimate outcomes could differ from management’s estimates. Site Remediation Obligation - The Company is currently involved in a site remediation obligation due to a former gas station that had been situated on a property the Company obtained as part of a business acquisition in the late 1990s. The Company has accrued estimates of the probable and reasonably estimable costs for the resolution of the obligation based upon types of remediation efforts currently anticipated, the volume of contaminants in the impacted areas, regulatory oversight and other costs. The Company's current estimates of future environmental cleanup and remediation liabilities related to the site may change over time due to various factors, including but not limited to, the nature and extent of required future cleanup and removal activities, and the extent and duration of regulatory oversight, among other things. The final outcome of any regulatory inquiries and requirements cannot be predicted with certainty, and unfavorable or unexpected outcomes could result in additional costs that could be material to the Company's results of operations during any particular year of the remediation process. See Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion on this site remediation obligation. Revenue Recognition Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to the Company's customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company is expected to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. The Company applied practical expedients related to unsatisfied performance obligations for (i) contracts with an original expected length of one year or less and (ii) contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue at the amount to which it has the right to invoice for services performed. Net sales of the Company’s principal services and products were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Service Sales | | | | | | | Digital Printing | $ | 170,083 | | | $ | 174,752 | | | | | MPS | 74,764 | | | 75,782 | | | | | Scanning and Digital Imaging | 20,313 | | | 17,357 | | | | | Total services sales | 265,160 | | | 267,891 | | | | | Equipment and Supplies Sales | 16,041 | | | 18,119 | | | | | Total net sales | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | |
Digital Printing consists of professional services and software services to (i) re-produce and distribute large-format and small-format documents in either black and white or color (“Ordered Prints”) and (ii) specialized graphic color printing. Substantially, all of the Company’s revenue from Digital Printing comes from professional services to re-produce Ordered Prints. Sales of Ordered Prints are initiated through a customer order or quote and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the re-produced Ordered Prints. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Ordered Prints are delivered to the customer’s site or handed to the customer for walk in orders. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. MPS consists of placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in the customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities. MPS relieves the Company’s customers of the burden of purchasing print equipment and related supplies and maintaining print devices and print networks, and shifts their costs to a “per-use” basis. MPS is supported by the Company's hosted proprietary technology, Abacus®, which allows customers to capture, control, manage, print, and account for their documents. Under its MPS contracts, the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge”. MPS sales are driven by the ongoing print needs of the Company’s customers at their facilities. Upon the issuance of ASC 842, Leases, the Company concluded that certain of its MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. See Note 7, Leasing, for additional information. Scanning and Digital Imaging, combines software and professional services to facilitate the capture, management, access and retrieval of documents and information that have been produced in the past. Scanning and Digital Imaging includes the Company's hosted SKYSITE ® software and ARC Facilities solution to organize, search and retrieve documents, as well as the provision of services that include the capture and conversion of hardcopy and electronic documents into digital files (“Scanned Documents”), and their cloud-based storage and maintenance. Sales of Scanning and Digital Imaging professional services, which represent substantially all revenue for the business line, are initiated through a customer order or proposal and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the digital files. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Scanned Documents are delivered to the customer either through SKYSITE, ARC Facilities, or through other electronic media. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. Equipment and Supplies sales consist of reselling printing, imaging, and related equipment (“Goods”) to customers primarily in architectural, engineering and construction firms. Sales of Equipment and Supplies are initiated through a customer order and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligations under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the Goods. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Goods are delivered to the customer’s site. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. The Company has experienced minimal customer returns or refunds and does not offer a warranty on equipment that it is reselling. The Company has established contractual pricing for certain large national customer accounts (“Global Solutions”). These contracts generally establish uniform pricing at all operating segments for Global Solutions. Revenues earned from the Company’s Global Solutions are recognized in the same manner as non-Global Solutions revenues. Included in revenues are fees charged to customers for shipping, handling, and delivery services. Such revenues amounted to $11.0 million and $11.3 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively. Revenues from hosted software licensing activities are recognized ratably over the term of the license. Revenues from software licensing activities comprise less than 2.5% of the Company’s consolidated revenues during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. Management provides for returns, discounts and allowances based on historic experience and adjusts such allowances as considered necessary. Comprehensive Income (Loss) The Company’s comprehensive income (loss) includes foreign currency translation adjustments, net of taxes. Asset and liability accounts of international operations are translated into the Company’s functional currency, U.S. dollars, at current rates. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average currency rate for the fiscal year. Segment and Geographic Reporting The provisions of ASC 280, Segment Reporting, require public companies to report financial and descriptive information about their reportable operating segments. The Company identifies operating segments based on the various business activities that earn revenue and incur expense and whose operating results are reviewed by the Company's Chief Executive Officer, who is the Company's chief operating decision maker. Because its operating segments have similar products and services, classes of customers, production processes, distribution methods and economic characteristics, the Company operates as a single reportable segment. The Company recognizes revenues in geographic areas based on the location to which the product was shipped or services have been rendered. See table below for revenues and property and equipment, net, attributable to the Company’s U.S. operations and foreign operations. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | | | | | | | Revenues from external customers | | $ | 247,474 | | | $ | 33,727 | | | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 254,559 | | | $ | 31,451 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | | | | | | | Property and equipment, net | | $ | 35,868 | | | $ | 5,057 | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 34,595 | | | $ | 5,619 | | | $ | 40,214 | | | | | | | |
Advertising and Shipping and Handling Costs Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and approximated $0.7 million during 2023 and 2022. Shipping and handling costs incurred by the Company are included in cost of sales. Stock-Based Compensation The Company applies the Black-Scholes valuation model in determining the fair value of share-based payments to employees, which is then amortized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period. Total stock-based compensation for 2023 and 2022, was $2.2 million and $1.8 million, respectively, and was recorded in selling, general, and administrative expenses, consistent with the classification of the underlying salaries. In accordance with ASC 718, Income Taxes, any excess tax benefit resulting from stock-based compensation, in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, are classified along with other income tax cash flows as an operating activity. The weighted average fair value at the grant date for options issued in 2023 and 2022, was $1.28 and $0.96, respectively. The fair value of each option grant was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Weighted average assumptions used: | | | | | | | | Risk free interest rate | | 3.7 | % | | 2.1 | % | | | | Expected volatility | | 63.0 | % | | 56.4 | % | | | | Expected dividend yield | | 6.4 | % | | 6.2 | % | | |
Using historical exercise data as a basis, the Company determined that the expected term for stock options issued in 2023 and 2022, was and 7.2 years and 6.7 years, respectively. For fiscal years 2023 and 2022, expected stock price volatility is based on the Company’s historical volatility for a period equal to the expected term. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant with an equivalent remaining term. The Company accounts for forfeitures of share-based awards when they occur. As of December 31, 2023, total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to nonvested stock-based compensation was approximately $2.7 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 1.7 years. For additional information, see Note 9, Employee Stock Purchase Plan and Stock Plan. Research and Development Expenses Research and development activities relate to costs associated with the design and testing of new technology or enhancements and maintenance to existing technology. Such costs are expensed as incurred are primarily recorded to cost of sales. In total, research and development amounted to $6.2 million and $6.5 million, during 2023 and 2022, respectively. Noncontrolling Interest The Company accounted for its investment in UDS under the purchase method of accounting, in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations. UDS has been consolidated in the Company’s financial statements from the date of acquisition. Noncontrolling interest, which represents the 35% noncontrolling interest in UDS, is reflected on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements. In May of 2022, the Company completed an $11.2 million capital distribution from its Chinese JV. As the Company is 65% owner, $7.3 million came to the Company's US operations, and 35% or $3.9 million went to the JV partner, thus resulting in a $3.9 million decrease in the Company's consolidated cash and noncontrolling interest balance sheet accounts in 2022. Sales Taxes The Company bills sales taxes, as applicable, to its customers. The Company acts as an agent and bills, collects, and remits the sales tax to the proper government jurisdiction. The sales taxes are accounted for on a net basis, and therefore are not included as part of the Company’s revenue. Earnings Per Share The Company accounts for earnings per share in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings Per Share. Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to ARC by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share is computed similarly to basic earnings per share except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if common shares subject to outstanding options and acquisition rights had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. Common share equivalents are excluded from the computation if their effect is anti-dilutive. There were 4.1 million and 3.2 million common shares excluded from the calculation of diluted net income attributable to ARC per common share as their effect would have been anti-dilutive for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company’s common share equivalents consist of stock options issued under the Company’s Stock Plan. Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding were calculated as follows for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — basic | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | | | Effect of dilutive stock awards | 941 | | | 1,066 | | | | | Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — diluted | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Loss (Topic 326) (“ASU 2016-13”), which updates the guidance on recognition and measurement of credit losses for financial assets. The new requirements, known as the current expected credit loss model ("CECL") will require entities to adopt an impairment model based on expected losses rather than incurred losses. ASU 2016-13 must be adopted on a modified-retrospective approach. This update was effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020 including interim periods within those fiscal years. In October 2019, the FASB approved an extension for all non-SEC filers, including small reporting companies, to extend the effective date to fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Therefore, the effective date for this update was January 1, 2023. The implementation of CECL did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated statements of financial condition and results of operations. Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures,” which requires public entities to disclose specific tax rate reconciliation categories, as well as income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction, amongst other disclosure enhancements. The ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The ASU can be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis. The Company is evaluating the disclosure requirements related to the new standard.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES |
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES Goodwill In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, the Company assesses goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired. At September 30, 2023, the Company performed its assessment and determined that goodwill was not impaired. Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017 the Company elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. There can be no assurance that the estimates and assumptions made for purposes of the Company's goodwill impairment analysis in 2023 will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. If the Company’s assumptions, including forecasted EBITDA of certain reporting units, are not achieved, then the Company may be required to record goodwill impairment charges in future periods, whether in connection with the Company’s next annual impairment testing in the third quarter of 2024, or on an interim basis, if any such change constitutes a triggering event (as defined under ASC 350, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other) outside of the quarter when the Company regularly performs its annual goodwill impairment test. It is not possible at this time to determine if any such future impairment charge would result or, if it does, whether such charge would be material. The carrying amount of goodwill from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023 is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Gross
Goodwill | | Accumulated
Impairment
Loss | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | | | | | | | January 1, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
Long-lived and Other Intangible Assets The Company periodically assesses potential impairments of its long-lived assets in accordance with the provisions of ASC 360, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets. An impairment review is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. The Company groups its assets at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of the other assets and liabilities. The Company has determined that the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are available is the regional level, which is the operating segment level. Factors considered by the Company include, but are not limited to, significant underperformance relative to historical or projected operating results; significant changes in the manner of use of the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business; and significant negative industry or economic trends. When the carrying value of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, the Company estimates the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows and eventual disposition is less than the carrying amount of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. An impairment loss is reflected as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset, based on the fair value if available, or discounted cash flows, if fair value is not available. The Company assessed potential impairments of its long lived assets as of September 30, 2023 and concluded that there was no impairment. The following table sets forth the Company’s other intangible assets resulting from business acquisitions as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 which continue to be amortized: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | Amortizable other intangible assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | Customer relationships | $ | 99,185 | | | $ | 99,178 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | 99,087 | | | $ | 99,073 | | | $ | 14 | | | Trade names and trademarks | 20,262 | | | 20,107 | | | 155 | | | 20,281 | | | 20,087 | | | 194 | | | $ | 119,447 | | | $ | 119,285 | | | $ | 162 | | | $ | 119,368 | | | $ | 119,160 | | | $ | 208 | |
Estimated future amortization expense of other intangible assets for each of the next five fiscal years and thereafter are as follows: | | | | | | | 2024 | $ | 39 | | | 2025 | 35 | | | 2026 | 34 | | | 2027 | 34 | | | 2028 | 20 | | | Thereafter | — | | | $ | 162 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//350/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET Property and equipment, net consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Machinery and equipment | $ | 245,802 | | | $ | 246,262 | | | Buildings and leasehold improvements | 21,374 | | | 23,128 | | | Furniture and fixtures | 2,871 | | | 2,737 | | | 270,047 | | | 272,127 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (229,122) | | | (231,913) | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 40,214 | |
Depreciation expense was $17.6 million and $20.3 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//360/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-6
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LONG-TERM DEBT
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| LONG-TERM DEBT |
LONG-TERM DEBT Long-term debt consists of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | | Revolving Loans; 6.8% and 5.6% interest rate at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 40,000 | | | 40,000 | | Various finance leases; weighted average interest rate of 5.5% and 5.1% at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively; principal and interest payable monthly through November 2029 | 22,236 | | | 26,474 | | | | | | | 62,236 | | | 66,474 | | | Less current portion | (8,870) | | | (11,558) | | | $ | 53,366 | | | $ | 54,916 | |
Credit Agreement On June 15, 2023, the Company entered into an amendment (the "Amendment") to its Credit Agreement dated as of April 22, 2021 (the "2021 Credit Agreement") with U.S. Bank National Association, as administrative agent and the lenders part thereto. The Amendment, among other things, modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement to replace the relevant benchmark provisions from the London Interbank Offered Rate to the forward-looking term rate based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR"). The Amendment also modifies certain terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement relating to the payment of dividends and stock repurchases by the Company and the related component calculations included in the fixed charge coverage ratio that the Company is required to maintain. After giving effect to the Amendment, the Company is permitted to repurchase up to $10 million of its stock in any twelve-month period and all such permitted stock repurchases will be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. In addition, the Company is permitted to make other restricted payments that are not stock repurchases, such as the payment of dividends, of up to $12 million made during any twelve-month period which will be excluded from the calculation of the fixed charge coverage ratio. The making of stock repurchases and the payment of dividends and other restricted payments is subject, in each case, to pro forma compliance with the financial covenants and other customary conditions set forth in the 2021 Credit Agreement.
The 2021 Credit Agreement provides for the extension of revolving loans in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $70 million and replaces the Credit Agreement dated as of November 20, 2014, as amended (the "2014 Credit Agreement"). The obligation under the 2021 Credit Agreement matures on April 22, 2026. As of December 31, 2023, the Company's borrowing availability of Revolving Loans under the Revolving Loan commitment was $27.8 million, after deducting outstanding letters of credit of $2.2 million and outstanding Revolving Loans of $40.0 million. Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement bear interest, in the case of Term SOFR loans, at a per annum rate equal to the applicable Term SOFR (which rate shall not be less than zero), plus a margin ranging from 1.25% to 1.75%, based on the Company’s Total Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement). Loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement that are not Term SOFR loans bear interest at a per annum rate equal to the Alternate Base Rate (as such terms is defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement) plus a margin ranging from 0.25% to 0.75%, based on the Company’s Total Leverage Ratio. As of December 31, 2023, one month Term SOFR loans borrowed under the 2021 Credit Agreement accrued interest at 6.8%. The Company pays certain recurring fees with respect to the 2021 Credit Agreement, including administration fees to the administrative agent. Subject to certain exceptions, including, in certain circumstances, reinvestment rights, the loans extended under the Credit Agreement are subject to customary mandatory prepayment provisions with respect to: the net proceeds from certain asset sales; the net proceeds from certain issuances or incurrences of debt (other than debt permitted to be incurred under the terms of the 2021 Credit Agreement); the net proceeds from certain issuances of equity securities; and net proceeds of certain insurance recoveries and condemnation events of the Company. The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary representations and warranties, subject to limitations and exceptions, and customary covenants restricting the ability (subject to various exceptions) of the Company and its subsidiaries to: incur additional indebtedness (including guarantee obligations); incur liens; sell certain property or assets; engage in mergers or other fundamental changes; consummate acquisitions; make investments; make certain distributions or repurchase equity interest of the Company or its subsidiaries; change the nature of their business; prepay or amend certain indebtedness; engage in certain transactions with affiliates; amend their organizational documents; or enter into certain restrictive agreements. In addition, the 2021 Credit Agreement contains financial covenants which requires the Company to maintain (i) at all times, a Total Leverage Ratio in an amount not to exceed 2.75 to 1.00; and (ii) a Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Credit Agreement), as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, an amount not less than 1.15 to 1.00. The Company was in compliance with its covenants during the year ended December 31, 2023. The 2021 Credit Agreement allows for payment of dividends. In December 2023, the Company's Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.05 per share of common stock that is payable on February 29, 2024 to stockholders of record as of January 31, 2024. Accordingly, the Company recorded a dividend payable of $2.1 million within accrued expenses as of December 31, 2023. The 2021 Credit Agreement contains customary events of default, including with respect to: nonpayment of principal, interest, fees or other amounts; failure to perform or observe covenants; material inaccuracy of a representation or warranty when made; cross-default to other material indebtedness; bankruptcy, insolvency and dissolution events; inability to pay debts; monetary judgment defaults; actual or asserted invalidity or impairment of any definitive loan documentation, repudiation of guaranties or subordination terms; certain ERISA related events; or a change of control. The obligations of the Company’s subsidiary that is the borrower under the 2021 Credit Agreement are guaranteed by the Company and each of the Company's other United States subsidiaries. The 2021 Credit Agreement and any interest rate protection and other hedging arrangements provided by any lender party to the credit facility or any affiliate of such a lender are secured on a first priority basis by a perfected security interest in substantially all of the borrower’s, the Company’s and each guarantor’s assets (subject to certain exceptions).
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for information about short-term and long-term debt arrangements, which includes amounts of borrowings under each line of credit, note payable, commercial paper issue, bonds indenture, debenture issue, own-share lending arrangements and any other contractual agreement to repay funds, and about the underlying arrangements, rationale for a classification as long-term, including repayment terms, interest rates, collateral provided, restrictions on use of assets and activities, whether or not in compliance with debt covenants, and other matters important to users of the financial statements, such as the effects of refinancing and noncompliance with debt covenants. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//470/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES Operating Leases. The Company leases machinery, equipment, and office and operational facilities under non-cancelable operating lease agreements. Certain lease agreements for the Company’s facilities generally contain renewal options and provide for annual increases in rent based on the local Consumer Price Index. Refer to Note 7, Leasing, for the schedule of the Company’s future minimum operating lease payments as of December 31, 2023. Legal Proceedings. The Company is involved, and will continue to be involved, in legal proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including commercial and employment-related lawsuits. Some of these lawsuits purport or may be determined to be class actions and seek substantial damages, and some may remain unresolved for several years. The Company establishes accruals for specific legal proceedings when it is considered probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company's evaluation of whether a loss is reasonably probable is based on our assessment and consultation with legal counsel regarding the ultimate outcome of the matter. As of December 31, 2023, the Company has accrued for the potential impact of loss contingencies that are probable and reasonably estimable. The Company does not currently believe that the ultimate resolution of any of these matters will have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows. However, the results of these matters cannot be predicted with certainty, and an unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, or cash flows. Site Remediation Obligation. As part of a business acquisition in the 1990’s, the Company purchased a site located in California where a former commercial gas station had operated from 1939 until approximately 1986. Prior to the Company's acquisition, the gas station was demolished and its underground storage tanks were removed. Environmental monitoring of the property was conducted from 1987 through 2017 under the oversight of the local County's Department of Environmental Health ("CDEH") and it eventually revealed petroleum products in the soil, groundwater, and the air in between soil particles. As a result, a Corrective Action Implementation Plan ("CAIP") detailing remedial clean-up methods at the site was required to be submitted in 2020. Accordingly, the Company recorded a liability on an undiscounted basis of $0.6 million in 2020, the estimated cost, to remediate the site. The 2020 CAIP was approved by the CDEH, but based on additional site data, the department requested a submission of addenda to the CAIP to address other site conditions. The additional review conducted in the fourth quarter of 2023 identified certain potential risks arising out of a structure on a neighboring property. As a result, in December of 2023, the CDEH requested that an alternative remedial plan be developed and submitted by March 12, 2024, to address the structural aspects of the site. The Company is in the process of finalizing an alternative plan with the guidance and expertise of an environmental consulting firm engaged expressly for this purpose. The additional concerns identified in 2023 require that the new plan be designed in a way that is significantly more expensive than the original plan, is more complicated, and will result in a longer duration to remediate the site. The Company's Consolidated Balance Sheets include a liability on an undiscounted basis for the site remediation of $4.5 million as of December 31, 2023, of which $2.2 million is classified as a current liability, and $0.6 million as of December 31, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the liability represents the Company's estimate of the probable cleanup, investigation, and remediation costs based on available information. The Company anticipates that most of this liability will be paid out over seven years, but some costs may be paid out over a longer period. As noted above, the estimate of the final remediation expenses may change over time because of the varying costs of currently available cleanup techniques, unpredictable contaminant reduction rates associated with available cleanup techniques, and the difficulty of determining in advance the nature and full extent of contamination. However, evolving statutory and regulatory standards, their interpretation, more vigorous enforcement policies of regulatory agencies, or stricter or different interpretations of existing statutory and regulatory standards, may require additional expenditures by the Company, which may be material. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that the Company will not incur significant additional environmental compliance costs in the future.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//450/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480327/954-440-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| LEASING |
LEASING Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements. The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. Lessee Accounting The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Assets | | | | | | Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | | | Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | | | Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | | | Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | | | | | | | | Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | | | | | Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | | | Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | | | Long-term | | | | | | Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | | | Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | | | Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | Year Ended | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | | Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | | | | | | | | Finance lease cost | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | | | Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | | | Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | | | Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023. (2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | | | Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 | | Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 | | | | | | Weighted average discount rate | | | | Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | | | Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | | | Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | | | Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Lessor Accounting The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. MPS revenue includes $68.8 million of rental income and $6.0 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2023. MPS revenue includes $70.0 million of rental income and $5.8 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company's property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, includes approximately $20 million and $23 million of equipment subject to leases with customers under the Company's MPS arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. Following termination of an MPS arrangement, the Company will place existing equipment at an alternate customer site pursuant to an MPS arrangement, at one of the Company's service centers, or dispose of the equipment.
|
| LEASING |
LEASING Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements. The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. Lessee Accounting The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Assets | | | | | | Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | | | Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | | | Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | | | Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | | | | | | | | Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | | | | | Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | | | Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | | | Long-term | | | | | | Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | | | Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | | | Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | Year Ended | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | | Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | | | | | | | | Finance lease cost | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | | | Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | | | Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | | | Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023. (2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | | | Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 | | Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 | | | | | | Weighted average discount rate | | | | Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | | | Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | | | Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | | | Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Lessor Accounting The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. MPS revenue includes $68.8 million of rental income and $6.0 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2023. MPS revenue includes $70.0 million of rental income and $5.8 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company's property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, includes approximately $20 million and $23 million of equipment subject to leases with customers under the Company's MPS arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. Following termination of an MPS arrangement, the Company will place existing equipment at an alternate customer site pursuant to an MPS arrangement, at one of the Company's service centers, or dispose of the equipment.
|
| LEASING |
LEASING Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements. The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. Lessee Accounting The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Assets | | | | | | Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | | | Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | | | Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | | | Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | | | | | | | | Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | | | | | Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | | | Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | | | Long-term | | | | | | Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | | | Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | | | Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | Year Ended | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | | Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | | | | | | | | Finance lease cost | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | | | Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | | | Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | | | Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023. (2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | | | Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 | | Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 | | | | | | Weighted average discount rate | | | | Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | | | Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | | | Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | | | Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Lessor Accounting The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. MPS revenue includes $68.8 million of rental income and $6.0 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2023. MPS revenue includes $70.0 million of rental income and $5.8 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company's property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, includes approximately $20 million and $23 million of equipment subject to leases with customers under the Company's MPS arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. Following termination of an MPS arrangement, the Company will place existing equipment at an alternate customer site pursuant to an MPS arrangement, at one of the Company's service centers, or dispose of the equipment.
|
| LEASING |
LEASING Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements. The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. Lessee Accounting The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Assets | | | | | | Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | | | Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | | | Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | | | Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | | | | | | | | Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | | | | | Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | | | Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | | | Long-term | | | | | | Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | | | Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | | | Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | Year Ended | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | | Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | | | | | | | | Finance lease cost | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | | | Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | | | Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | | | Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023. (2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | | | Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 | | Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 | | | | | | Weighted average discount rate | | | | Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | | | Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | | | Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | | | Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Lessor Accounting The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. MPS revenue includes $68.8 million of rental income and $6.0 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2023. MPS revenue includes $70.0 million of rental income and $5.8 million of service income for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company's property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, includes approximately $20 million and $23 million of equipment subject to leases with customers under the Company's MPS arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. Following termination of an MPS arrangement, the Company will place existing equipment at an alternate customer site pursuant to an MPS arrangement, at one of the Company's service centers, or dispose of the equipment.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for finance leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of lessee's finance lease and maturity analysis of finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeFinanceLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for operating leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of operating lease and maturity analysis of operating lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure of lessor's direct financing leases. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//842-30/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LessorDirectFinancingLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for lessor's operating leases. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//842-30/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeasesOfLessorDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
INCOME TAXES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INCOME TAXES |
INCOME TAXES The following table includes the consolidated income tax provision for federal, state, and foreign income taxes related to the Company’s total earnings before taxes for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Current: | | | | | | | | Federal | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | | State | | 215 | | | 154 | | | | | Foreign | | 481 | | | 487 | | | | | | 696 | | | 641 | | | | | Deferred: | | | | | | | | Federal | | 2,805 | | | 4,142 | | | | | State | | 682 | | | 1,040 | | | | | Foreign | | 204 | | | 9 | | | | | | 3,691 | | | 5,191 | | | | | Income tax provision | | $ | 4,387 | | | $ | 5,832 | | | |
The Company's foreign earnings before taxes were $2.0 million and $0.4 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company’s US earnings before taxes were $10.5 million and $16.2 million for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The consolidated deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | | Financial statement accruals not currently deductible | $ | 950 | | | $ | 985 | | | Site remediation obligation | 1,149 | | | 166 | | | | | | | Accrued vacation | 765 | | | 754 | | | Accrued bonuses | 543 | | | 914 | | | Deferred revenue, net | 21 | | | 37 | | | Fixed assets | 2,980 | | | 4,242 | | | Right of use operating lease liabilities | 9,600 | | | 8,494 | | | Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | 1,541 | | | 745 | | | Stock-based compensation | 2,343 | | | 2,365 | | | Federal tax net operating loss carryforward | 11,990 | | | 14,593 | | | State tax net operating loss carryforward, net | 4,723 | | | 5,182 | | | | | | | | | | | Foreign tax net operating loss carryforward | 487 | | | 879 | | | | | | | Tax credits, net | 213 | | | 1,669 | | | | | | | Gross deferred tax assets | 37,305 | | | 41,025 | | | Less: valuation allowance | (1,313) | | | (2,651) | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | 35,992 | | | $ | 38,374 | | | | | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | $ | (23,010) | | | $ | (23,197) | | | Right of use operating lease assets | (8,547) | | | (7,184) | | | Fixed assets | (104) | | | — | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | 4,331 | | | $ | 7,993 | |
A reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Statutory federal income tax rate | 21 | % | | 21 | % | | | | State taxes, net of federal benefit | 6 | | | 6 | | | | | Foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | Valuation allowance | (11) | | | 1 | | | | | Tax credits expired | 12 | | | — | | | | | Global intangible low taxed income | 1 | | | — | | | | | Section 162(m) limitation | 3 | | | 2 | | | | | | | | | | | Stock based compensation | 1 | | | 3 | | | | | Discrete items for federal, state and foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Effective income tax rate | 35 | % | | 35 | % | | |
In accordance with ASC 740-10, Income Taxes, the Company evaluates the need for deferred tax asset valuation allowances based on a more likely than not standard. The ability to realize deferred tax assets depends on the ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carryback or carryforward periods provided for in the tax law for each applicable tax jurisdiction. The Company considers the following possible sources of taxable income when assessing the realization of deferred tax assets: •Future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences; •Future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards; •Taxable income in prior carryback years; and •Tax-planning strategies. The assessment regarding whether a valuation allowance is required or should be adjusted also considers all available positive and negative evidence factors, including but not limited to: •Nature, frequency, and severity of recent losses; •Duration of statutory carryforward periods; •Historical experience with tax attributes expiring unused; and •Near- and medium-term financial outlook. The Company utilizes a rolling three years of actual and current year anticipated results as the primary measure of cumulative income/losses in recent years, as adjusted for permanent differences. The evaluation of deferred tax assets requires judgment in assessing the likely future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company's financial statements or tax returns and future profitability. The Company's accounting for deferred tax consequences represents its best estimate of those future events. Changes in the Company's current estimates, due to unanticipated events or otherwise, could have a material effect on its financial condition and results of operations. The Company has a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023. Based on the Company’s current assessment, the remaining net deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023 are considered more likely than not to be realized. The valuation allowance of $1.3 million may be increased or reduced as conditions change or if the Company is unable to implement certain available tax planning strategies. The realization of the Company’s net deferred tax assets ultimately depends on future taxable income, reversals of existing taxable temporary differences or through a loss carry back. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had approximately $57.1 million of consolidated federal, $75.8 million of state and $2.9 million of foreign net operating loss carryforwards available to offset future taxable income, respectively. Certain federal net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2032. Certain state net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2024. The foreign net operating loss carryforwards begin to expire in 2024. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had approximately $0.2 million of foreign tax credit carryforwards which will expire in 2024. The Company and some of its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction, and various states and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is not under examination in any U.S. federal, state or foreign jurisdiction. Due to net operating losses, substantially all the tax years from 2011 remain open to examination by the tax authorities. There were no unrecognized tax benefits as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 or 2022. The Company does not include interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense. The Company does not anticipate any significant changes to unrecognized tax benefits over the next 12 months. During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, no interest or penalties were required to be recognized related to unrecognized tax benefits.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income taxes. Disclosures may include net deferred tax liability or asset recognized in an enterprise's statement of financial position, net change during the year in the total valuation allowance, approximate tax effect of each type of temporary difference and carryforward that gives rise to a significant portion of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets, utilization of a tax carryback, and tax uncertainties information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//740/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482526/740-270-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN |
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under the Company’s Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”) eligible employees may purchase up to a calendar year maximum per eligible employee of the lesser of (i) 2,500 shares of common stock, or (ii) a number of shares of common stock having an aggregate fair market value of $25 thousand as determined on the date of purchase at 85% of the fair market value of such shares of common stock on the applicable purchase date. The compensation expense in connection with the ESPP in 2023 and 2022, was $23 thousand and $17 thousand, respectively.
Employees purchased the following shares in the periods presented: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Shares purchased | 50 | | | 45 | | | | | Average price per share | $ | 2.64 | | | $ | 2.16 | | | |
Stock Plan On April 29, 2021, the Company's stockholders approved the Company's 2021 Incentive Plan, replacing the 2014 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended, which is the only equity incentive plan under which the Company can currently grant equity incentive awards. The 2021 Incentive Plan provides for the grant of incentive and non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock bonuses and other forms of awards granted or denominated in the Company's common stock or units of the Company's common stock, as well as cash bonus awards, to employees, directors and consultants of the Company. On April 26, 2023, the Company's stockholders approved an amendment to the 2021 Incentive Plan ("Amended 2021 Plan") to increase the aggregate number of equity incentive shares authorized for issuance by 5,000,000 shares of common stock. Under the Amended 2021 Plan, the Company is authorized to issue up to 8.5 million shares plus such additional number of shares of common stock (up to 6,132,593 shares) as is equal to the number of shares of common stock subject to awards granted under the 2014 Incentive Plan and the Company's 2005 Stock Plan, which awards expire, terminate or are otherwise surrendered, cancelled, forfeited or repurchased by the Company pursuant to a contractual repurchase right. At December 31, 2023, 5.1 million shares remain available for issuance under the Stock Plan. Stock options granted under the Company's Stock Plan generally expire no later than ten years from the date of grant. Options generally vest and become fully exercisable over a period of three to four years from date of award, except that options granted to non-employee directors may vest over a shorter time period. The exercise price of options must be equal to at least 100% of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The Company allows for cashless exercises of vested outstanding options. During 2023 and 2022, the Company granted options to acquire a total of 1.1 million shares and 1.7 million shares, respectively, of the Company's common stock to certain key employees with an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The granted stock options vest annually over three to four years from the grant date and expire 10 years after the date of grant. The following is a further breakdown of the stock option activity under the Stock Plan: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price per Share | | Weighted
Average
Contractual
Life
(In years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(In thousands) | | Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 5,462 | | | $ | 3.56 | | | | | | | Granted | 1,658 | | | $ | 3.11 | | | | | | | Exercised | (618) | | | $ | 2.49 | | | | | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (533) | | | $ | 5.31 | | | | | | | Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 5,969 | | | $ | 3.39 | | | | | | | Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 3.60 | | | | | | | Exercised | (805) | | | $ | 2.60 | | | | | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (82) | | | $ | 3.12 | | | | | | | Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | | | Vested or expected to vest at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | | | Exercisable at December 31, 2023 | 3,582 | | | $ | 3.80 | | | 4.26 | | $ | 2,105 | |
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the total pretax intrinsic value (the difference between the closing stock price on December 31, 2023 and the exercise price, multiplied by the number of in-the-money options) that would have been received by the option holders had all the option holders exercised their options on December 31, 2023. This amount changes based on the fair market value of the common stock. Total intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 were $471 thousand and $292 thousand, respectively. A summary of the Company’s non-vested stock options as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted
Average Grant Date | | Non-vested Options | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share | | Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 2,350 | | | $ | 0.96 | | | Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 1.28 | | | Vested | (835) | | | $ | 0.94 | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (15) | | | $ | 1.14 | | | Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 2,596 | | | $ | 1.10 | |
The following table summarizes certain information concerning outstanding options at December 31, 2023: | | | | | | | | | Range of Exercise Price per Share | Options Outstanding at
December 31, 2023 | $1.14 – $2.64 | 2,218 | | $3.20 – $4.75 | 3,196 | | $6.16 – $7.19 | 392 | | $8.89 – $9.09 | 372 | | $1.14 – $9.09 | 6,178 | |
Restricted Stock In 2023, the Company granted 0.1 million shares of restricted stock awards to certain key employees with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock awards vest annually over three years from the grant date. In addition, the Company granted approximately 30 thousand shares of restricted stock awards to each of the Company's four non-employee members of its board advisors or board of directors, with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock vests on the one-year anniversary of the grant date. In 2022, the Company granted 0.1 million shares of restricted stock awards to certain key employees with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock awards vest annually over three years from the grant date. In addition, the Company granted approximately 16 thousand shares of restricted stock awards to each of the Company's three non-employee members of its board of directors with a deemed issuance price per share equal to the closing price of the Company's common stock on the date the restricted stock was granted. These restricted stock vests on the one-year anniversary of the grant date. A summary of the Company’s non-vested restricted stock as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted
Average Grant Date | | Non-vested Restricted Stock | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share | | Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 719 | | | $ | 2.35 | | | Granted | 269 | | | $ | 3.31 | | | Vested | (365) | | | $ | 2.40 | | | Forfeited/Canceled | — | | | $ | — | | | Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 623 | | | $ | 2.73 | |
The total fair value of restricted stock awards vested during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 was $1.1 million and $1.7 million, respectively.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//718/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfCompensationRelatedCostsShareBasedPaymentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
RETIREMENT PLANS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Retirement Benefits [Abstract] |
|
| RETIREMENT PLANS |
RETIREMENT PLANSThe Company sponsors a 401(k) Plan, which covers substantially all employees of the Company who have attained age 21. Under the Company’s 401(k) Plan, eligible employees may contribute up to 75% of their annual eligible compensation (or in the case of highly compensated employees, up to 6% of their annual eligible compensation), subject to contribution limitations imposed by the Internal Revenue Service. The Company matches 20% of an employee’s contributions, up to a total of 4% of that employee’s compensation. An independent third party administers the Company’s 401(k) Plan. The Company's total expense under these plans amounted to $0.5 million and $0.4 million annually during fiscal years 2023 and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationAndRetirementDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for retirement benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480482/715-20-55-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (q)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//715/tableOfContent
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (o)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (p)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480126/715-20-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480266/715-60-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_PensionAndOtherPostretirementBenefitsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Fair Value Disclosures [Abstract] |
|
| FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS |
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS In accordance with ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, the Company has categorized its assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value into a three-level fair value hierarchy as set forth below. If the inputs used to measure fair value fall within different levels of the hierarchy, the categorization is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The three levels of the hierarchy are defined as follows: Level 1-inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. Level 2-inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. Level 3-inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement. As of December 31, 2023, the Company's assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value were not material. Fair Values of Financial Instruments. The following methods and assumptions were used by the Company in estimating the fair value of its financial instruments for disclosure purposes: Cash equivalents: Cash equivalents are time deposits with maturity of three months or less when purchased, which are highly liquid and readily convertible to cash. Cash equivalents reported in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets were $1.2 million and $1.7 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and are carried at cost and approximate fair value due to the relatively short period to maturity of these instruments. Short- and long-term debt and finance leases: The carrying amount of the Company’s finance leases reported in the Consolidated Balance Sheets approximates fair value based on the Company’s current incremental borrowing rate for similar types of borrowing arrangements. The carrying amount reported in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2023 for borrowings under its Credit Agreement is $40.0 million. The Company has determined that borrowings under its Credit Agreement of $40.0 million as of December 31, 2023 approximates its fair value.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for the fair value of financial instruments (as defined), including financial assets and financial liabilities (collectively, as defined), and the measurements of those instruments as well as disclosures related to the fair value of non-financial assets and liabilities. Such disclosures about the financial instruments, assets, and liabilities would include: (1) the fair value of the required items together with their carrying amounts (as appropriate); (2) for items for which it is not practicable to estimate fair value, disclosure would include: (a) information pertinent to estimating fair value (including, carrying amount, effective interest rate, and maturity, and (b) the reasons why it is not practicable to estimate fair value; (3) significant concentrations of credit risk including: (a) information about the activity, region, or economic characteristics identifying a concentration, (b) the maximum amount of loss the entity is exposed to based on the gross fair value of the related item, (c) policy for requiring collateral or other security and information as to accessing such collateral or security, and (d) the nature and brief description of such collateral or security; (4) quantitative information about market risks and how such risks are managed; (5) for items measured on both a recurring and nonrecurring basis information regarding the inputs used to develop the fair value measurement; and (6) for items presented in the financial statement for which fair value measurement is elected: (a) information necessary to understand the reasons for the election, (b) discussion of the effect of fair value changes on earnings, (c) a description of [similar groups] items for which the election is made and the relation thereof to the balance sheet, the aggregate carrying value of items included in the balance sheet that are not eligible for the election; (7) all other required (as defined) and desired information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Basis of Presentation |
Basis of Presentation The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes. The Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis and relies on historical experience and various other factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances to determine such estimates. Actual results could differ from those estimates and such differences may be material to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
|
| Risk And Uncertainties |
Risk and Uncertainties The Company generates a significant portion of its revenue from sales of services and products to customers in the architectural, engineering, construction and building owner/operator ("AEC/O") industry. As a result, the Company's results largely depend on the strength of that industry. The Company's historical operating results reflect the cyclical and variable nature of the AEC/O industry. ARC believes that the AEC/O industry generally experiences downturns several months after a downturn in the general economy, and that there may be a similar delay in the recovery of the AEC/O industry following a recovery of the general economy. A downturn in the AEC/O industry would diminish demand for all of the Company's products and services, and would therefore negatively affect the Company's revenues and have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, operating results and financial condition. As part of the Company's growth strategy, ARC intends to continue to expand the market and industries it services and increase sales of a variety of service offerings that utilize ARC's existing production methods and infrastructure, but that are relatively new to the Company. The success of the Company’s efforts will be affected by its ability to acquire new customers for the Company’s new service offerings, as well as to sell the new service offerings to existing customers. The Company’s inability to successfully market and execute these relatively new service offerings could significantly affect its business and reduce its long-term revenue, resulting in an adverse effect on its results of operations and financial condition.
|
| Cash Equivalents |
Cash Equivalents Cash equivalents include demand deposits and short-term investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased. The Company maintains its cash deposits at numerous banks located throughout the United States, Canada, India, United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom and China, which at times, may exceed federally insured limits. UNIS Document Solutions, Co. Ltd., ("UDS"), the Company’s joint venture in China, held $2.6 million and $3.2 million of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risk on cash and cash equivalents.
|
| Concentrations of Credit Risk and Significant Vendors |
Concentrations of Credit Risk and Significant Vendors Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade receivables are limited due to a large, diverse customer base. No individual customer represented more than 2.5% of net sales during 2023 and 2022. The Company has geographic concentration risk as sales in California, as a percent of total sales, were approximately 30% and 31% for 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company contracts with various suppliers. Although there are a limited number of suppliers that could supply the Company’s inventory, management believes any shortfalls from existing suppliers could be absorbed by its existing suppliers or from other suppliers on comparable terms. However, a change in suppliers could cause a delay in sales and adversely affect results.
|
| Allowance for Credit Losses |
Allowance for Credit Losses The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of the financial condition of its customers, monitors collections and payments from customers, and generally does not require collateral. The Company provides for the possible inability to collect accounts receivable by recording an allowance for credit losses. The Company writes off accounts receivable balances when it is considered uncollectible. The Company estimates the allowance for credit losses based on historical experience, aging of accounts receivable, and information regarding the credit worthiness of its customers. Additionally, the Company provides an allowance for returns and discounts based on historical experience.
|
| Inventories |
Inventories Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (determined on a first-in, first-out basis; or average cost) or net realizable value. Inventories primarily consist of materials for use and resale in digital printing, and equipment for resale. On an ongoing basis, inventories are reviewed and adjusted for estimated obsolescence or unmarketable inventories to reflect the lower of cost or net realizable value. Charges to write-down inventory to realizable value are recorded as an increase in cost of sales.
|
| Income Taxes |
Income Taxes Deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial and tax reporting purposes. Such amounts are adjusted, as appropriate, to reflect changes in tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce the Company's deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. Changes in tax laws or accounting standards and methods may affect recorded deferred taxes in future periods. When establishing a valuation allowance, the Company considers future sources of taxable income such as future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carryforwards and tax planning strategies. A tax planning strategy is an action that: is prudent and feasible; an enterprise ordinarily might not take but would take to prevent an operating loss or tax credit carryforward from expiring unused; and would result in realization of deferred tax assets. In the event the Company determines that its deferred tax assets, more likely than not, will not be realized in the future, the valuation adjustment to the deferred tax assets will be charged to earnings in the period in which the Company makes such a determination. The Company has a $1.3 million valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023. In future quarters the Company will continue to evaluate its historical results for the preceding twelve quarters and our future projections to determine whether this will generate sufficient taxable income to utilize the Company's deferred tax assets, and whether a valuation allowance is required. The Company calculates current and deferred tax provision based on estimates and assumptions that could differ from the actual results reflected in income tax returns filed in subsequent years. Adjustments based on filed returns are recorded when identified. Income taxes have not been provided on certain undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because such earnings are considered to be permanently reinvested. The amount of taxable income or loss we report to the various tax jurisdictions is subject to ongoing audits by federal, state and foreign tax authorities. The Company estimate of the potential outcome of any uncertain tax issue is subject to management’s assessment of relevant risks, facts, and circumstances existing at that time. The Company uses a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company records a liability for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and tax position taken or expected to be taken on its tax return. To the extent that the Company's assessment of such tax positions changes, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. The Company will not report tax-related interest and penalties as a component of income tax expense.
|
| Property and Equipment |
Property and Equipment, net Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | Buildings | | 10-20 years | | Leasehold improvements | | 10-20 years or lease term, if shorter | | Machinery and equipment | | 3-7 years | | Furniture and fixtures | | 3-7 years |
Assets acquired under capital lease arrangements are included in machinery and equipment, are recorded at the present value of the minimum lease payments, and are depreciated using the straight-line method over the life of the asset or term of the lease, whichever is shorter. Expenses for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred, while renewals and betterments are capitalized. Gains or losses on the sale or disposal of property and equipment are reflected in operating income. The Company accounts for software costs developed for internal use in accordance with ASC 350-40, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software, which requires companies to capitalize certain qualifying costs incurred during the application development stage of the related software development project. The primary use of this software is for internal use and, accordingly, such capitalized software development costs are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the economic lives of the related products not to exceed three years.
|
| Software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed |
Software development costs for software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed are expensed as incurred until the establishment of technological feasibility, at which time those costs are capitalized until the product is available for general release to customers and amortized over the estimated life of the product. Technological feasibility is established upon the completion of a working prototype that has been certified as having no critical bugs and is a release candidate. To date, costs and time incurred between the establishment of technological feasibility and product release have not been material, and all software development costs have been charged to research and development expense in our consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss).
|
| Impairment of Long-Lived Assets |
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets The Company periodically assesses potential impairments of its long-lived assets in accordance with the provisions of ASC 360, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets. An impairment review is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. The Company groups its assets at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of the other assets and liabilities. The Company has determined that the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are available is the regional level, which is the operating segment level. Factors considered by the Company include, but are not limited to, significant underperformance relative to historical or projected operating results; significant changes in the manner of use of the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business; and significant negative industry or economic trends. When the carrying value of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, the Company estimates the future undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows and eventual disposition is less than the carrying amount of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. An impairment loss is reflected as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset, based on the fair value if available, or discounted cash flows, if fair value is not available.
|
| Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets |
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, the Company assesses goodwill for impairment annually as of September 30, and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that goodwill might be impaired. Goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level. Goodwill is assigned to reporting units at the date the goodwill is initially recorded. Once goodwill has been assigned to reporting units, it no longer retains its association with a particular acquisition, and all of the activities within a reporting unit, whether acquired or internally generated, are available to support the value of the goodwill. In 2017, the Company elected to early-adopt ASU 2017-04 which simplifies subsequent goodwill measurement by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. The Company determines the fair value of its reporting units using an income approach. Under the income approach, the Company determined fair value based on estimated discounted future cash flows of each reporting unit. Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including revenue growth rates and EBITDA margins, discount rates and future market conditions, among others. The level of judgement and estimation is inherently higher in these uncertain economic times. Other intangible assets that have finite lives are amortized over their useful lives. Customer relationships are amortized using the accelerated method, based on customer attrition rates, over their estimated useful lives of 13 (weighted average) years.
|
| Deferred Financing Costs |
Deferred Financing Costs Direct costs incurred in connection with debt agreements are recorded as incurred and amortized based on the effective interest method for the Company's borrowings under its credit agreement with U.S. Bank National Association, dated April 22, 2021 (the "2021 Credit Agreement"), as amended on June 15, 2023.
|
| Fair Values of Financial Instruments |
Fair Values of Financial Instruments The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to their short maturities. Refer to Note 11, Fair Value Measurements, in Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for disclosures regarding fair value measurements in accordance with the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures.
|
| Insurance Liability |
Insurance Liability The Company maintains a high deductible insurance policy for a significant portion of its risks and associated liabilities with respect to workers’ compensation. The Company’s deductible is $250 thousand per individual. The accrued liabilities associated with this program are based on the Company’s estimate of the ultimate costs to settle known claims, as well as claims incurred but not yet reported to the Company, as of the balance sheet date. The Company’s estimated liability is not discounted and is based upon an actuarial report obtained from a third party. The actuarial report uses information provided by the Company’s insurance brokers and insurers, combined with the Company’s judgments regarding a number of assumptions and factors, including the frequency and severity of claims, claims development history, case jurisdiction, applicable legislation, and the Company’s claims settlement practices.
|
| Commitments and Contingencies |
Commitments and Contingencies In the normal course of business, the Company estimates potential future loss accruals related to legal, workers’ compensation, tax and other contingencies. These accruals require management’s judgment on the outcome of various events based on the best available information. However, due to changes in facts and circumstances, the ultimate outcomes could differ from management’s estimates. Site Remediation Obligation - The Company is currently involved in a site remediation obligation due to a former gas station that had been situated on a property the Company obtained as part of a business acquisition in the late 1990s. The Company has accrued estimates of the probable and reasonably estimable costs for the resolution of the obligation based upon types of remediation efforts currently anticipated, the volume of contaminants in the impacted areas, regulatory oversight and other costs. The Company's current estimates of future environmental cleanup and remediation liabilities related to the site may change over time due to various factors, including but not limited to, the nature and extent of required future cleanup and removal activities, and the extent and duration of regulatory oversight, among other things. The final outcome of any regulatory inquiries and requirements cannot be predicted with certainty, and unfavorable or unexpected outcomes could result in additional costs that could be material to the Company's results of operations during any particular year of the remediation process. See Note 6, Commitments and Contingencies - Site Remediation Obligation within Part IV, Item 15 - "Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion on this site remediation obligation.
|
| Revenue Recognition |
Revenue Recognition Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to the Company's customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company is expected to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. The Company applied practical expedients related to unsatisfied performance obligations for (i) contracts with an original expected length of one year or less and (ii) contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue at the amount to which it has the right to invoice for services performed. Digital Printing consists of professional services and software services to (i) re-produce and distribute large-format and small-format documents in either black and white or color (“Ordered Prints”) and (ii) specialized graphic color printing. Substantially, all of the Company’s revenue from Digital Printing comes from professional services to re-produce Ordered Prints. Sales of Ordered Prints are initiated through a customer order or quote and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the re-produced Ordered Prints. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Ordered Prints are delivered to the customer’s site or handed to the customer for walk in orders. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. MPS consists of placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in the customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities. MPS relieves the Company’s customers of the burden of purchasing print equipment and related supplies and maintaining print devices and print networks, and shifts their costs to a “per-use” basis. MPS is supported by the Company's hosted proprietary technology, Abacus®, which allows customers to capture, control, manage, print, and account for their documents. Under its MPS contracts, the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge”. MPS sales are driven by the ongoing print needs of the Company’s customers at their facilities. Upon the issuance of ASC 842, Leases, the Company concluded that certain of its MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842. See Note 7, Leasing, for additional information. Scanning and Digital Imaging, combines software and professional services to facilitate the capture, management, access and retrieval of documents and information that have been produced in the past. Scanning and Digital Imaging includes the Company's hosted SKYSITE ® software and ARC Facilities solution to organize, search and retrieve documents, as well as the provision of services that include the capture and conversion of hardcopy and electronic documents into digital files (“Scanned Documents”), and their cloud-based storage and maintenance. Sales of Scanning and Digital Imaging professional services, which represent substantially all revenue for the business line, are initiated through a customer order or proposal and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligation under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the digital files. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Scanned Documents are delivered to the customer either through SKYSITE, ARC Facilities, or through other electronic media. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration the Company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. Equipment and Supplies sales consist of reselling printing, imaging, and related equipment (“Goods”) to customers primarily in architectural, engineering and construction firms. Sales of Equipment and Supplies are initiated through a customer order and are governed by established terms and conditions agreed upon at the onset of the customer relationship. Revenue is recognized when the performance obligations under the terms of a contract with a customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control of the Goods. Transfer of control occurs at a specific point-in-time, when the Goods are delivered to the customer’s site. Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring goods or providing services. Taxes collected concurrent with revenue-producing activities are excluded from revenue. The Company has experienced minimal customer returns or refunds and does not offer a warranty on equipment that it is reselling. The Company has established contractual pricing for certain large national customer accounts (“Global Solutions”). These contracts generally establish uniform pricing at all operating segments for Global Solutions. Revenues earned from the Company’s Global Solutions are recognized in the same manner as non-Global Solutions revenues. Management provides for returns, discounts and allowances based on historic experience and adjusts such allowances as considered necessary.
|
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Comprehensive Income (Loss) The Company’s comprehensive income (loss) includes foreign currency translation adjustments, net of taxes. Asset and liability accounts of international operations are translated into the Company’s functional currency, U.S. dollars, at current rates. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average currency rate for the fiscal year.
|
| Segment and Geographic Reporting |
Segment and Geographic Reporting The provisions of ASC 280, Segment Reporting, require public companies to report financial and descriptive information about their reportable operating segments. The Company identifies operating segments based on the various business activities that earn revenue and incur expense and whose operating results are reviewed by the Company's Chief Executive Officer, who is the Company's chief operating decision maker. Because its operating segments have similar products and services, classes of customers, production processes, distribution methods and economic characteristics, the Company operates as a single reportable segment. The Company recognizes revenues in geographic areas based on the location to which the product was shipped or services have been rendered. See table below for revenues and property and equipment, net, attributable to the Company’s U.S. operations and foreign operations. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | | | | | | | Revenues from external customers | | $ | 247,474 | | | $ | 33,727 | | | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 254,559 | | | $ | 31,451 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | | | | | | | Property and equipment, net | | $ | 35,868 | | | $ | 5,057 | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 34,595 | | | $ | 5,619 | | | $ | 40,214 | | | | | | | |
|
| Advertising and Shipping and Handling Costs |
Advertising and Shipping and Handling Costs Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and approximated $0.7 million during 2023 and 2022. Shipping and handling costs incurred by the Company are included in cost of sales.
|
| Stock-Based Compensation |
Stock-Based Compensation The Company applies the Black-Scholes valuation model in determining the fair value of share-based payments to employees, which is then amortized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period.
|
| Research and Development Expenses |
Research and Development Expenses Research and development activities relate to costs associated with the design and testing of new technology or enhancements and maintenance to existing technology. Such costs are expensed as incurred are primarily recorded to cost of sales.
|
| Noncontrolling Interest |
Noncontrolling Interest The Company accounted for its investment in UDS under the purchase method of accounting, in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations. UDS has been consolidated in the Company’s financial statements from the date of acquisition.
|
| Sales Taxes |
Sales Taxes The Company bills sales taxes, as applicable, to its customers. The Company acts as an agent and bills, collects, and remits the sales tax to the proper government jurisdiction. The sales taxes are accounted for on a net basis, and therefore are not included as part of the Company’s revenue.
|
| Earnings Per Share |
Earnings Per Share The Company accounts for earnings per share in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings Per Share. Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to ARC by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share is computed similarly to basic earnings per share except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if common shares subject to outstanding options and acquisition rights had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. Common share equivalents are excluded from the computation if their effect is anti-dilutive.
|
| Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements and Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted |
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Loss (Topic 326) (“ASU 2016-13”), which updates the guidance on recognition and measurement of credit losses for financial assets. The new requirements, known as the current expected credit loss model ("CECL") will require entities to adopt an impairment model based on expected losses rather than incurred losses. ASU 2016-13 must be adopted on a modified-retrospective approach. This update was effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020 including interim periods within those fiscal years. In October 2019, the FASB approved an extension for all non-SEC filers, including small reporting companies, to extend the effective date to fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Therefore, the effective date for this update was January 1, 2023. The implementation of CECL did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated statements of financial condition and results of operations. Recent Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures,” which requires public entities to disclose specific tax rate reconciliation categories, as well as income taxes paid disaggregated by jurisdiction, amongst other disclosure enhancements. The ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The ASU can be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis. The Company is evaluating the disclosure requirements related to the new standard. Adoption of ASC Topic 842, Leases The Company accounts for leases under ASC 842, Leases. ASC 842 requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee accounts for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases result in the lessee recognizing a Right of Use (ROU) asset and a corresponding lease liability. For finance leases the lessee recognizes interest expense and amortization of the ROU asset, and for operating leases the lessee will recognize a straight-line total lease expense. In addition, ASC 842 changes the definition of a lease, which resulted in changes to the classification of certain service contracts with customers to lease arrangements. The Company elected certain additional practical expedients permitted by the new guidance allowing the Company to carry forward historical accounting related to lease identification and classification for existing leases upon adoption. The Company elected, for its equipment asset classes, the practical expedient that allows lessees to treat the lease and non-lease components of leases as a single lease component. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheet.
|
| Lessee Accounting |
Lessee Accounting The Company determines whether an arrangement is a lease at contract inception. The Company's material lease contracts are generally for real estate or print equipment, and the determination of whether such contracts contain leases generally does not require significant estimates or judgments. The Company’s leases that are classified as operating leases primarily consist of real estate leases. The Company’s real estate leases contain both lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for separately. The Company’s leases that are classified as finance leases primarily consist of print equipment. Certain print equipment leases have lease and non-lease components, which are accounted for as a single lease component as discussed above. Other than the election to treat the Company's fixed lease payment as a single lease component, the accounting for finance leases will remain unchanged under ASC 842. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of the Company's operating leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and are reduced by any lease incentives received. The lease terms range from one to ten years, with renewal terms that can extend the lease term from one to five years. A portion of the Company’s real estate leases are generally subject to annual changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which are treated as variable lease payments and recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments was incurred. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants.
|
| Lessor Accounting |
Lessor Accounting The Company concluded that certain of its contracts with customers contain leases under the new leasing standard and accordingly should be accounted for as operating leases upon adoption of ASC 842. Specifically, certain of the Company's MPS arrangements, which had previously been accounted for as service revenue under ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, are now accounted for as operating leases under ASC 842. The Company's MPS arrangements consists of the placement, management, and optimization of print and imaging equipment in customers' offices, job sites, and other facilities under which the Company is paid a fixed rate per unit for each print produced (per-use), often referred to as a “click charge.” Accordingly, the fixed rate per unit charged to the customer covers the use of the equipment (i.e., the lease component), as well as the additional services performed by the Company as described above (i.e., the non-lease component). Certain of the Company's MPS contracts provide the customer the option to renew or terminate the agreement, which are considered when assessing the lease term. The Company elected the practical expedient to not separate certain lease and non-lease components related to its MPS arrangements, and accounts for the combined component under ASC 842. The pattern of revenue recognition for the Company's MPS revenue has remained substantially unchanged following the adoption of ASC 842.
|
| X |
- DefinitionAdvertising and shipping and handling costs.
| Name: |
arc_AdvertisingAndShippingAndHandlingCostsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for insurance liabilities.
| Name: |
arc_InsuranceLiabilityPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
arc_NoncontrollingInterestPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRisk And Uncertainties Policy [Policy Text Block]
| Name: |
arc_RiskAndUncertaintiesPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
arc_SalesTaxesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for basis of accounting, or basis of presentation, used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS).
| Name: |
us-gaap_BasisOfAccountingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cash and cash equivalents, including the policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Other information that may be disclosed includes (1) the nature of any restrictions on the entity's use of its cash and cash equivalents, (2) whether the entity's cash and cash equivalents are insured or expose the entity to credit risk, (3) the classification of any negative balance accounts (overdrafts), and (4) the carrying basis of cash equivalents (for example, at cost) and whether the carrying amount of cash equivalents approximates fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for commitments and contingencies, which may include policies for recognizing and measuring loss and gain contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480598/954-450-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for comprehensive income.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomePolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for credit risk. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 825
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480981/942-825-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskCreditRisk |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for deferral and amortization of significant deferred charges. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredChargesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for determining the fair value of financial instruments. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 60
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 820
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482053/820-10-60-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 825
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueOfFinancialInstrumentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for goodwill and intangible assets. This accounting policy also may address how an entity assesses and measures impairment of goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of inventory accounting policy for inventory classes, including, but not limited to, basis for determining inventory amounts, methods by which amounts are added and removed from inventory classes, loss recognition on impairment of inventories, and situations in which inventories are stated above cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483489/210-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482105/912-330-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//330/tableOfContent
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 270
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482989/270-10-45-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for leasing arrangement entered into by lessee. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeasesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for leasing arrangements entered into by lessor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479773/842-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479773/842-30-50-3A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3A
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479773/842-30-50-3A
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479773/842-30-50-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_LessorLeasesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for costs it has incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483044/730-10-05-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpensePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue from contract with customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for segment reporting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for award under share-based payment arrangement. Includes, but is not limited to, methodology and assumption used in measuring cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.C.Q3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.1.Q5)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.3.Q2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.D.2.Q6)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//718/tableOfContent
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationOptionAndIncentivePlansPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for costs incurred to (1) establish the technological feasibility of a computer software product to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed; and (2) produce product masters after establishing technological feasibility. This accounting policy also may apply to purchased computer software. This policy also may address the entity's amortization policy for its capitalized computer software costs and how it evaluates such capitalized costs for impairment. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_SoftwareToBeSoldLeasedOrOtherwiseMarketedPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11B
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-11B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-6
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/otherTransitionRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 310
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_TradeAndOtherAccountsReceivablePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Allowance for Credit Losses |
The allowance for credit losses activity was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | Charges to
Cost and
Expenses | | Deductions (1) | | Balance at
End of
Period | | Year ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | | Allowance for credit losses | $ | 1,947 | | | $ | 351 | | | $ | (441) | | | $ | 1,857 | | | Year ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | Allowance for credit losses | $ | 2,104 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | (477) | | | $ | 1,947 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Deductions represent uncollectible accounts written-off net of recoveries.
|
| Schedule of Useful Lives of Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | Buildings | | 10-20 years | | Leasehold improvements | | 10-20 years or lease term, if shorter | | Machinery and equipment | | 3-7 years | | Furniture and fixtures | | 3-7 years |
Property and equipment, net consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Machinery and equipment | $ | 245,802 | | | $ | 246,262 | | | Buildings and leasehold improvements | 21,374 | | | 23,128 | | | Furniture and fixtures | 2,871 | | | 2,737 | | | 270,047 | | | 272,127 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (229,122) | | | (231,913) | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 40,214 | |
|
| Schedule of Net Sales of Principal Services and Products |
Net sales of the Company’s principal services and products were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Service Sales | | | | | | | Digital Printing | $ | 170,083 | | | $ | 174,752 | | | | | MPS | 74,764 | | | 75,782 | | | | | Scanning and Digital Imaging | 20,313 | | | 17,357 | | | | | Total services sales | 265,160 | | | 267,891 | | | | | Equipment and Supplies Sales | 16,041 | | | 18,119 | | | | | Total net sales | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | |
|
| Schedule of Segment and Geographic Reporting |
See table below for revenues and property and equipment, net, attributable to the Company’s U.S. operations and foreign operations. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | U.S. | | Foreign
Countries | | Total | | | | | | | | Revenues from external customers | | $ | 247,474 | | | $ | 33,727 | | | $ | 281,201 | | | $ | 254,559 | | | $ | 31,451 | | | $ | 286,010 | | | | | | | | | Property and equipment, net | | $ | 35,868 | | | $ | 5,057 | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 34,595 | | | $ | 5,619 | | | $ | 40,214 | | | | | | | |
|
| Schedule of Weighted Average Assumptions for Stock-Based Compensation |
The fair value of each option grant was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Weighted average assumptions used: | | | | | | | | Risk free interest rate | | 3.7 | % | | 2.1 | % | | | | Expected volatility | | 63.0 | % | | 56.4 | % | | | | Expected dividend yield | | 6.4 | % | | 6.2 | % | | |
|
| Schedule of Basic and Diluted Earnings Per Share |
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding were calculated as follows for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — basic | 42,543 | | | 42,214 | | | | | Effect of dilutive stock awards | 941 | | | 1,066 | | | | | Weighted average common shares outstanding during the period — diluted | 43,484 | | | 43,280 | | | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of disaggregation of revenue into categories depicting how nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the various types of trade accounts and notes receivable and for each the gross carrying value, allowance, and net carrying value as of the balance sheet date. Presentation is categorized by current, noncurrent and unclassified receivables. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.3,4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAccountsNotesLoansAndFinancingReceivableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of information concerning material long-lived assets (excluding financial instruments, customer relationships with financial institutions, mortgage and other servicing rights, deferred policy acquisition costs, and deferred taxes assets) located in identified geographic areas and/or the amount of revenue from external customers attributed to that country from which revenue is material. An entity may also provide subtotals of geographic information about groups of countries. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfRevenuesFromExternalCustomersAndLongLivedAssetsByGeographicalAreasTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the significant assumptions used during the year to estimate the fair value of stock options, including, but not limited to: (a) expected term of share options and similar instruments, (b) expected volatility of the entity's shares, (c) expected dividends, (d) risk-free rate(s), and (e) discount for post-vesting restrictions. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (f)(2)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedPaymentAwardStockOptionsValuationAssumptionsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Goodwill |
The carrying amount of goodwill from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023 is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Gross
Goodwill | | Accumulated
Impairment
Loss | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | | | | | | | January 1, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2022 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | $ | 405,558 | | | $ | 284,507 | | | $ | 121,051 | |
|
| Schedule of Other Intangible Assets Resulting from Business Acquisitions |
The following table sets forth the Company’s other intangible assets resulting from business acquisitions as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 which continue to be amortized: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net
Carrying
Amount | | Amortizable other intangible assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | Customer relationships | $ | 99,185 | | | $ | 99,178 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | 99,087 | | | $ | 99,073 | | | $ | 14 | | | Trade names and trademarks | 20,262 | | | 20,107 | | | 155 | | | 20,281 | | | 20,087 | | | 194 | | | $ | 119,447 | | | $ | 119,285 | | | $ | 162 | | | $ | 119,368 | | | $ | 119,160 | | | $ | 208 | |
|
| Schedule of Estimated Future Amortization Expense |
Estimated future amortization expense of other intangible assets for each of the next five fiscal years and thereafter are as follows: | | | | | | | 2024 | $ | 39 | | | 2025 | 35 | | | 2026 | 34 | | | 2027 | 34 | | | 2028 | 20 | | | Thereafter | — | | | $ | 162 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life, by either major class or business segment. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of goodwill by reportable segment and in total which includes a rollforward schedule. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfGoodwillTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the amount of amortization expense expected to be recorded in succeeding fiscal years for finite-lived intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleofFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsFutureAmortizationExpenseTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | Buildings | | 10-20 years | | Leasehold improvements | | 10-20 years or lease term, if shorter | | Machinery and equipment | | 3-7 years | | Furniture and fixtures | | 3-7 years |
Property and equipment, net consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Machinery and equipment | $ | 245,802 | | | $ | 246,262 | | | Buildings and leasehold improvements | 21,374 | | | 23,128 | | | Furniture and fixtures | 2,871 | | | 2,737 | | | 270,047 | | | 272,127 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (229,122) | | | (231,913) | | | $ | 40,925 | | | $ | 40,214 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LONG-TERM DEBT (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Long-Term Debt |
Long-term debt consists of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | | Revolving Loans; 6.8% and 5.6% interest rate at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 40,000 | | | 40,000 | | Various finance leases; weighted average interest rate of 5.5% and 5.1% at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively; principal and interest payable monthly through November 2029 | 22,236 | | | 26,474 | | | | | | | 62,236 | | | 66,474 | | | Less current portion | (8,870) | | | (11,558) | | | $ | 53,366 | | | $ | 54,916 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of long-debt instruments or arrangements, including identification, terms, features, collateral requirements and other information necessary to a fair presentation. These are debt arrangements that originally required repayment more than twelve months after issuance or greater than the normal operating cycle of the entity, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-1A
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 55
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482949/835-30-55-8
Reference 9: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 470
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480848/942-470-50-3
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-8
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-6
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDebtInstrumentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Financial Information Associated with Leases |
The tables below present financial information associated with the Company's leases as of, and the years ended, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Assets | | | | | | Operating lease assets | Right-of-use assets from operating leases | $ | 32,838 | | | $ | 28,163 | | | Finance lease assets | Property and equipment | 50,317 | | | 60,887 | | | Less accumulated depreciation | (31,139) | | | (38,607) | | | Property and equipment, net | 19,178 | | | 22,280 | | | Total lease assets | | $ | 52,016 | | | $ | 50,443 | | | | | | | | Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | | | | | Operating | Current portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,924 | | | $ | 9,924 | | | Finance | Current portion of long-term finance leases | 8,870 | | | 11,558 | | | Long-term | | | | | | Operating | Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | 27,357 | | | 23,339 | | | Finance | Long-term portion of finance leases | 13,366 | | | 14,916 | | | Total lease liabilities | | $ | 59,517 | | | $ | 59,737 | |
|
| Schedule of Lease Cost |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Classification | Year Ended | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Operating lease cost | Cost of sales | $ | 13,702 | | | $ | 12,940 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 2,951 | | | 2,813 | | Total operating lease cost (1)(2) | | $ | 16,653 | | | $ | 15,753 | | | | | | | | Finance lease cost | | | | | | Amortization of leased assets | Cost of sales | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 12,718 | | | Selling, general and administrative expenses | 560 | | | 461 | | | Interest on lease liabilities | Interest expense, net | 1,429 | | | 1,447 | | | Total finance lease cost | | 12,302 | | | 14,626 | | | Total lease cost | | $ | 28,955 | | | $ | 30,379 | |
(1) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $3,895 and $423, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2023. (2) Includes variable lease costs and short-term lease costs of $2,795 and $240, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | | | Operating leases | 4.3 | | 4.3 | | Finance leases | 3.1 | | 2.8 | | | | | | Weighted average discount rate | | | | Operating leases | 6.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | Finance leases | 5.5 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other information | Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | | | Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 14,997 | | | $ | 14,907 | | | Operating cash flows from finance leases | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 1,451 | | | Financing cash flows from finance leases | $ | 11,860 | | | $ | 14,736 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| Schedule of Operating Lease Liability Maturity |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
|
| Schedule of Financing Lease Liability Maturity |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2023) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2024 | | $ | 11,962 | | | $ | 9,883 | | | 2025 | | 9,860 | | | 6,221 | | | 2026 | | 7,789 | | | 4,625 | | | 2027 | | 6,642 | | | 2,595 | | | 2028 | | 4,283 | | | 1,015 | | | Thereafter | | 2,345 | | | 36 | | | Total | | 42,881 | | | 24,375 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 5,600 | | | 2,139 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 37,281 | | | $ | 22,236 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2023. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which expire through December 2028. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2023. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.6 million for related parties are included in 2024 through 2028. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Maturity of lease liabilities (as of December 31, 2022) | Operating Leases(1) (2) | | Finance Leases(3) | | 2023 | | $ | 11,259 | | | $ | 12,510 | | | 2024 | | 8,354 | | | 7,903 | | | 2025 | | 6,437 | | | 4,393 | | | 2026 | | 4,467 | | | 2,878 | | | 2027 | | 3,836 | | | 1,022 | | | Thereafter | | 2,983 | | | 4 | | | Total | | 37,336 | | | 28,710 | | | Less amount representing interest | | 4,073 | | | 2,236 | | | Present value of lease liability | | $ | 33,263 | | | $ | 26,474 | |
(1) Reflects payments for non-cancelable operating leases with initial terms of one year or more as of December 31, 2022. The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate. (2) The Company leased several of its facilities under lease agreements with entities owned by certain of its current and former executive officers which were due to expire in December 2023 but were renewed for another five years in the second half of 2023. The rental payments on these facilities amounted to $0.5 million during 2022. In the table above, annual rental payments of $0.5 million for related parties are included in 2023. (3) The table above does not include any legally binding minimum lease payments for leases signed but not yet commenced, and such leases are not material in the aggregate.
|
| X |
- DefinitionAssets And Liabilities, Lessee [Table Text Block]
| Name: |
arc_AssetsAndLiabilitiesLesseeTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of finance lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to finance lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of lessee's lease cost. Includes, but is not limited to, interest expense for finance lease, amortization of right-of-use asset for finance lease, operating lease cost, short-term lease cost, variable lease cost and sublease income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCostTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of lessee's operating lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to operating lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
INCOME TAXES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Income Tax Provision |
The following table includes the consolidated income tax provision for federal, state, and foreign income taxes related to the Company’s total earnings before taxes for 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Current: | | | | | | | | Federal | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | | State | | 215 | | | 154 | | | | | Foreign | | 481 | | | 487 | | | | | | 696 | | | 641 | | | | | Deferred: | | | | | | | | Federal | | 2,805 | | | 4,142 | | | | | State | | 682 | | | 1,040 | | | | | Foreign | | 204 | | | 9 | | | | | | 3,691 | | | 5,191 | | | | | Income tax provision | | $ | 4,387 | | | $ | 5,832 | | | |
|
| Schedule of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities |
The consolidated deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | | Financial statement accruals not currently deductible | $ | 950 | | | $ | 985 | | | Site remediation obligation | 1,149 | | | 166 | | | | | | | Accrued vacation | 765 | | | 754 | | | Accrued bonuses | 543 | | | 914 | | | Deferred revenue, net | 21 | | | 37 | | | Fixed assets | 2,980 | | | 4,242 | | | Right of use operating lease liabilities | 9,600 | | | 8,494 | | | Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | 1,541 | | | 745 | | | Stock-based compensation | 2,343 | | | 2,365 | | | Federal tax net operating loss carryforward | 11,990 | | | 14,593 | | | State tax net operating loss carryforward, net | 4,723 | | | 5,182 | | | | | | | | | | | Foreign tax net operating loss carryforward | 487 | | | 879 | | | | | | | Tax credits, net | 213 | | | 1,669 | | | | | | | Gross deferred tax assets | 37,305 | | | 41,025 | | | Less: valuation allowance | (1,313) | | | (2,651) | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | 35,992 | | | $ | 38,374 | | | | | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles | $ | (23,010) | | | $ | (23,197) | | | Right of use operating lease assets | (8,547) | | | (7,184) | | | Fixed assets | (104) | | | — | | | Net deferred tax assets | $ | 4,331 | | | $ | 7,993 | |
|
| Schedule of Effective Income Tax Rate Reconciliation |
A reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Statutory federal income tax rate | 21 | % | | 21 | % | | | | State taxes, net of federal benefit | 6 | | | 6 | | | | | Foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | Valuation allowance | (11) | | | 1 | | | | | Tax credits expired | 12 | | | — | | | | | Global intangible low taxed income | 1 | | | — | | | | | Section 162(m) limitation | 3 | | | 2 | | | | | | | | | | | Stock based compensation | 1 | | | 3 | | | | | Discrete items for federal, state and foreign taxes | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Effective income tax rate | 35 | % | | 35 | % | | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 9
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the reconciliation using percentage or dollar amounts of the reported amount of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for the year to the amount of income tax expense that would result from applying domestic federal statutory tax rates to pretax income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 12
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEffectiveIncomeTaxRateReconciliationTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Employee Share Purchases |
Employees purchased the following shares in the periods presented: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | | Shares purchased | 50 | | | 45 | | | | | Average price per share | $ | 2.64 | | | $ | 2.16 | | | |
|
| Schedule of Stock Option Plan Activity |
The following is a further breakdown of the stock option activity under the Stock Plan: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price per Share | | Weighted
Average
Contractual
Life
(In years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(In thousands) | | Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 5,462 | | | $ | 3.56 | | | | | | | Granted | 1,658 | | | $ | 3.11 | | | | | | | Exercised | (618) | | | $ | 2.49 | | | | | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (533) | | | $ | 5.31 | | | | | | | Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 5,969 | | | $ | 3.39 | | | | | | | Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 3.60 | | | | | | | Exercised | (805) | | | $ | 2.60 | | | | | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (82) | | | $ | 3.12 | | | | | | | Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | | | Vested or expected to vest at December 31, 2023 | 6,178 | | | $ | 3.54 | | | 5.99 | | $ | 2,740 | | | Exercisable at December 31, 2023 | 3,582 | | | $ | 3.80 | | | 4.26 | | $ | 2,105 | |
|
| Schedule of Non-vested Stock Options |
A summary of the Company’s non-vested stock options as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted
Average Grant Date | | Non-vested Options | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share | | Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 2,350 | | | $ | 0.96 | | | Granted | 1,096 | | | $ | 1.28 | | | Vested | (835) | | | $ | 0.94 | | | Forfeited/Canceled | (15) | | | $ | 1.14 | | | Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 2,596 | | | $ | 1.10 | |
|
| Schedule of Range of Exercise Price for Options Outstanding |
The following table summarizes certain information concerning outstanding options at December 31, 2023: | | | | | | | | | Range of Exercise Price per Share | Options Outstanding at
December 31, 2023 | $1.14 – $2.64 | 2,218 | | $3.20 – $4.75 | 3,196 | | $6.16 – $7.19 | 392 | | $8.89 – $9.09 | 372 | | $1.14 – $9.09 | 6,178 | |
|
| Schedule of Nonvested Restricted Stock Options |
A summary of the Company’s non-vested restricted stock as of December 31, 2023, and changes during the year then ended is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted
Average Grant Date | | Non-vested Restricted Stock | Shares | | Fair Market Value per Share | | Non-vested at December 31, 2022 | 719 | | | $ | 2.35 | | | Granted | 269 | | | $ | 3.31 | | | Vested | (365) | | | $ | 2.40 | | | Forfeited/Canceled | — | | | $ | — | | | Non-vested at December 31, 2023 | 623 | | | $ | 2.73 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the changes in outstanding nonvested restricted stock units. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfNonvestedRestrictedStockUnitsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the changes in outstanding nonvested shares. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfNonvestedShareActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of number, weighted-average exercise price or conversion ratio, aggregate intrinsic value, and weighted-average remaining contractual term for outstanding options that are fully vested and expected to vest. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of employee stock purchase plan activity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationEmployeeStockPurchasePlanActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure for stock option plans. Includes, but is not limited to, outstanding awards at beginning and end of year, grants, exercises, forfeitures, and weighted-average grant date fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationStockOptionsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
dei_LegalEntityAxis=arc_UDSMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionConcentration Risk, Benchmark Percentage
| Name: |
arc_ConcentrationRiskBenchmarkPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481027/954-310-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor an entity that discloses a concentration risk in relation to quantitative amount, which serves as the "benchmark" (or denominator) in the equation, this concept represents the concentration percentage derived from the division. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-21
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-20
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskPercentage1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_CustomerConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_GeographicConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=stpr_CA |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_CostOfGoodsTotalMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_SupplierConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedGoodsAndNonemployeeServicesTransactionBySupplierAxis=arc_ThreeLargestVendorsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_MovementInValuationAllowancesAndReservesRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of valuation and qualifying accounts and reserves. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-09(Column B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-09(Column E))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowancesAndReservesBalance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in valuation and qualifying accounts and reserves from charge to cost and expense. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-09(Column C)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowancesAndReservesChargedToCostAndExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in valuation and qualifying accounts and reserves. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-09(Column D))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowancesAndReservesDeductions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowancesAndReservesTypeAxis=us-gaap_AllowanceForCreditLossMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
shares in Millions |
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
May 31, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Noncontrolling Interest [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Valuation allowance |
|
$ 1,313,000
|
$ 2,651,000
|
| Deferred financing fees |
|
200,000
|
200,000
|
| Deductible insurance policy |
|
250,000
|
|
| Advertising costs |
|
700,000
|
700,000
|
| Research and development |
|
$ 6,200,000
|
$ 6,500,000
|
| Joint venture, capital cash distribution |
$ 11,200,000
|
|
|
| Proceeds from capital cash distribution |
7,300,000
|
|
|
| Decrease of noncontrolling interest |
3,900,000
|
|
|
| Common stock options excluded for anti-dilutive (in shares) |
|
4.1
|
3.2
|
| Co-venturer |
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling Interest [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Proceeds from capital cash distribution |
$ 3,900,000
|
|
|
| UDS |
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling Interest [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling interest |
|
35.00%
|
|
| Chinese Joint Venture |
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling Interest [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling interest |
35.00%
|
|
|
| Noncontrolling interest ownership percentage parent |
65.00%
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionJoint Venture, Capital Cash Distribution
| Name: |
arc_JointVentureCapitalCashDistribution |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWorkers compensation deductible per individual.
| Name: |
arc_WorkersCompensationDeductiblePerIndividual |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount charged to advertising expense for the period, which are expenses incurred with the objective of increasing revenue for a specified brand, product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 720
-SubTopic 35
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483406/720-35-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdvertisingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSecurities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) or earnings per unit (EPU) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS or EPU because to do so would increase EPS or EPU amounts or decrease loss per share or unit amounts for the period presented. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of debt issuance costs. Includes, but is not limited to, legal, accounting, underwriting, printing, and registration costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredFinanceCostsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterestLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe equity interest of noncontrolling shareholders, partners or other equity holders in consolidated entity.
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterestOwnershipPercentageByNoncontrollingOwners |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe parent entity's interest in net assets of the subsidiary, expressed as a percentage.
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterestOwnershipPercentageByParent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNet Increase or Decrease in balance of noncontrolling interest in the subsidiary during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_MinorityInterestPeriodIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow associated with the amount received by a corporation from a shareholder during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromContributedCapital |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process whether intended for sale or the entity's use, during the reporting period charged to research and development projects, including the costs of developing computer software up to the point in time of achieving technological feasibility, and costs allocated in accounting for a business combination to in-process projects deemed to have no alternative future use. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482916/730-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 730
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482517/912-730-25-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_OwnershipAxis=arc_UDSMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_OwnershipAxis=arc_ChineseJointVentureMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - Property and Equipment and Impairment of Long-Lived Assets (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Capitalized software development costs |
$ 1,900,000
|
$ 1,700,000
|
| Net of accumulated amortization |
24,200,000
|
23,300,000
|
| Depreciation expense and amortization of capitalized software development costs |
900,000
|
1,000,000
|
| Impairment of long-lived assets |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| Software |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives of other intangible assets |
3 years
|
|
| Minimum | Buildings |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
10 years
|
|
| Minimum | Leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
10 years
|
|
| Minimum | Machinery and equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
3 years
|
|
| Minimum | Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
3 years
|
|
| Maximum | Buildings |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
20 years
|
|
| Maximum | Leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
20 years
|
|
| Maximum | Machinery and equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
7 years
|
|
| Maximum | Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful lives |
7 years
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor each balance sheet presented, the amount of accumulated amortization for capitalized computer software costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalizedComputerSoftwareAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for amortization of capitalized computer software costs. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 985
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalizedComputerSoftwareAmortization1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe carrying amount of capitalized computer software costs net of accumulated amortization as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalizedComputerSoftwareNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of finite-lived intangible assets, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long lived assets held for use (including those held for disposal by means other than sale). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsHeldForUse |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_BuildingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_LeaseholdImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_MachineryAndEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of finite-lived intangible assets, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_CustomerRelationshipsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - Revenue Recognition (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
$ 281,201
|
$ 286,010
|
| Service Sales |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
265,160
|
267,891
|
| Digital Printing |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
170,083
|
174,752
|
| MPS |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
74,764
|
75,782
|
| Scanning and Digital Imaging |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
20,313
|
17,357
|
| Equipment and Supplies Sales |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
16,041
|
18,119
|
| Shipping and Handling |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total net sales |
$ 11,000
|
$ 11,300
|
| Software Licensing Activities | Product Concentration Risk | Revenue from Contract with Customer |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Concentration risk |
2.50%
|
2.50%
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor an entity that discloses a concentration risk in relation to quantitative amount, which serves as the "benchmark" (or denominator) in the equation, this concept represents the concentration percentage derived from the division. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-21
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-20
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskPercentage1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=arc_DigitalPrintingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=arc_MPSMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=arc_ScanningAndDigitalImagingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ProductMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ShippingAndHandlingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=arc_SoftwareLicensingMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ProductConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - Schedule of Segment and Geographic Reporting (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues from external customers |
$ 281,201
|
$ 286,010
|
| Property and equipment, net |
40,925
|
40,214
|
| U.S. |
|
|
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues from external customers |
247,474
|
254,559
|
| Property and equipment, net |
35,868
|
34,595
|
| Foreign Countries |
|
|
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues from external customers |
33,727
|
31,451
|
| Property and equipment, net |
$ 5,057
|
$ 5,619
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480842/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenuesFromExternalCustomersAndLongLivedAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_US |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=us-gaap_NonUsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost not yet recognized for nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average period over which cost not yet recognized is expected to be recognized for award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognizedPeriodForRecognition1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsAndMethodologyAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated dividend rate (a percentage of the share price) to be paid (expected dividends) to holders of the underlying shares over the option's term. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedDividendRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe estimated measure of the percentage by which a share price is expected to fluctuate during a period. Volatility also may be defined as a probability-weighted measure of the dispersion of returns about the mean. The volatility of a share price is the standard deviation of the continuously compounded rates of return on the share over a specified period. That is the same as the standard deviation of the differences in the natural logarithms of the stock prices plus dividends, if any, over the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedVolatilityRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe risk-free interest rate assumption that is used in valuing an option on its own shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsRiskFreeInterestRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average grant-date fair value of options granted during the reporting period as calculated by applying the disclosed option pricing methodology. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionExpected term of award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardFairValueAssumptionsExpectedTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAdditional shares included in the calculation of diluted EPS as a result of the potentially dilutive effect of share based payment arrangements using the treasury stock method. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480454/718-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-22
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-23
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-28A
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncrementalCommonSharesAttributableToShareBasedPaymentArrangements |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES - Schedule of Goodwill (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2021 |
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Goodwill impairment losses |
$ 0
|
|
|
| Gross Goodwill |
405,558,000
|
$ 405,558,000
|
$ 405,558,000
|
| Accumulated Impairment Loss |
284,507,000
|
284,507,000
|
284,507,000
|
| Net Carrying Amount |
$ 121,051,000
|
$ 121,051,000
|
$ 121,051,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated impairment loss of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Goodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accumulated impairment loss of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated impairment loss for an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillImpairedAccumulatedImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from the write-down of an asset representing the future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLES - Schedule of Other Intangible Assets Resulting from Business Acquisitions (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
$ 119,447,000
|
$ 119,368,000
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
119,285,000
|
119,160,000
|
| Net Carrying Amount |
162,000
|
208,000
|
| Impairment of long-lived assets |
0
|
0
|
| Customer relationships |
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
99,185,000
|
99,087,000
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
99,178,000
|
99,073,000
|
| Net Carrying Amount |
7,000
|
14,000
|
| Trade names and trademarks |
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
20,262,000
|
20,281,000
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
20,107,000
|
20,087,000
|
| Net Carrying Amount |
$ 155,000
|
$ 194,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccumulated amount of amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 928
-SubTopic 340
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483147/928-340-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long lived assets held for use (including those held for disposal by means other than sale). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsHeldForUse |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_CustomerRelationshipsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for asset, excluding financial asset and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach).
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with finite life expected to be recognized in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET - Schedule of Property and Equipment (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 270,047
|
$ 272,127
|
| Less accumulated depreciation |
(229,122)
|
(231,913)
|
| Property and equipment |
40,925
|
40,214
|
| Machinery and equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
245,802
|
246,262
|
| Buildings and leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
21,374
|
23,128
|
| Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 2,871
|
$ 2,737
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation and amortization from plant, property, and equipment and right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated depreciation and amortization, of property, plant, and equipment and finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before accumulated depreciation and amortization, of property, plant, and equipment and finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetBeforeAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_MachineryAndEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period that reflects the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over the assets' useful lives. Includes production and non-production related depreciation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Depreciation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LONG-TERM DEBT - Schedule of Long-Term Debt (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Various finance leases; weighted average interest rate of 5.5% and 5.1% at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively; principal and interest payable monthly through November 2029 |
$ 22,236
|
$ 26,474
|
| Long-term debt and capital lease obligations, including current maturities |
62,236
|
66,474
|
| Less current portion |
(8,870)
|
(11,558)
|
| Long-term debt and finance leases |
$ 53,366
|
$ 54,916
|
| Finance lease, weighted average interest rate |
5.50%
|
5.10%
|
| Line of Credit | Revolving Credit Facility |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revolving Loans; 6.8% and 5.6% interest rate at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively |
$ 40,000
|
$ 40,000
|
| Line of Credit | Revolving Credit Facility | 2021 Credit Agreement |
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revolving Loans; 6.8% and 5.6% interest rate at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively |
$ 40,000
|
|
| Debt instrument, interest rate, effective percentage |
6.80%
|
5.60%
|
| X |
- DefinitionEffective interest rate for the funds borrowed under the debt agreement considering interest compounding and original issue discount or premium. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateEffectivePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for finance lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt and lease obligation, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligations |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt and lease obligation, classified as current. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term debt and lease obligation, including portion classified as current.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationsIncludingCurrentMaturities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_LineOfCreditMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CreditFacilityAxis=us-gaap_RevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=arc_A2021CreditAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
LONG-TERM DEBT - Narrative (Details)
|
|
|
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
|
Jun. 15, 2023
USD ($)
|
Apr. 22, 2021
USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
$ / shares
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
$ / shares
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
$ / shares
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash dividends declared (in usd per share) | $ / shares |
|
|
$ 0.05
|
$ 0.20
|
$ 0.20
|
| Dividends payable |
|
|
$ 2,100,000
|
$ 2,100,000
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Amendment To 2021 Credit Agreement |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt, stock repurchase authorized amount |
$ 10,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt, stock repurchase authorized, period |
12 months
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt, other restricted payment authorized amount |
$ 12,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt, other restricted payment authorized period |
12 months
|
|
|
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | 2021 Credit Agreement |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Letters of credit outstanding, amount |
|
|
2,200,000
|
2,200,000
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Long-term debt |
|
|
40,000,000
|
40,000,000
|
$ 40,000,000
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit | 2021 Credit Agreement |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Line of credit facility, maximum borrowing capacity |
|
$ 70,000,000
|
|
|
|
| Line of credit, remaining borrowing capacity |
|
|
27,800,000
|
27,800,000
|
|
| Long-term debt |
|
|
$ 40,000,000
|
$ 40,000,000
|
|
| Debt instrument, interest rate, effective percentage |
|
|
6.80%
|
6.80%
|
5.60%
|
| Covenant term, total leverage ratio |
|
|
|
2.75
|
|
| Fixed charged coverage ratio |
|
|
|
1.15
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit | 2021 Credit Agreement | SOFR | Minimum | Term SOFR Loans |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt instrument, basis spread on variable rate |
|
1.25%
|
|
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit | 2021 Credit Agreement | SOFR | Maximum | Term SOFR Loans |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt instrument, basis spread on variable rate |
|
1.75%
|
|
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit | 2021 Credit Agreement | Base Rate | Minimum | Not Term SOFR Loans |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt instrument, basis spread on variable rate |
|
0.25%
|
|
|
|
| Revolving Credit Facility | Line of Credit | 2021 Credit Agreement | Base Rate | Maximum | Not Term SOFR Loans |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt Instrument [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Debt instrument, basis spread on variable rate |
|
0.75%
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Covenant Term, Total Leverage Ratio
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentCovenantTermTotalLeverageRatio |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Covenant Terms, Fixed Charged Coverage Ratio
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentCovenantTermsFixedChargedCoverageRatio |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Other Restricted Payment, Authorized Amount
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentOtherRestrictedPaymentAuthorizedAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Other Restricted Payment Authorized, Period
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentOtherRestrictedPaymentAuthorizedPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Stock Repurchase Authorized Amount
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentStockRepurchaseAuthorizedAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDebt Instrument, Stock Repurchase Authorized, Period
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentStockRepurchaseAuthorizedPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate dividends declared during the period for each share of common stock outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockDividendsPerShareDeclared |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage points added to the reference rate to compute the variable rate on the debt instrument.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentBasisSpreadOnVariableRate1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEffective interest rate for the funds borrowed under the debt agreement considering interest compounding and original issue discount or premium. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.22(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentInterestRateEffectivePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482900/835-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.12-04(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of dividends declared but unpaid on equity securities issued by the entity and outstanding. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DividendsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe total amount of the contingent obligation under letters of credit outstanding as of the reporting date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LettersOfCreditOutstandingAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMaximum borrowing capacity under the credit facility without consideration of any current restrictions on the amount that could be borrowed or the amounts currently outstanding under the facility. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityMaximumBorrowingCapacity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of borrowing capacity currently available under the credit facility (current borrowing capacity less the amount of borrowings outstanding). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityRemainingBorrowingCapacity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of unamortized premium (discount) and debt issuance cost, of long-term debt. Excludes lease obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69B
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69C
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69C
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1D
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1D
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermDebt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CreditFacilityAxis=us-gaap_RevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=arc_AmendmentTo2021CreditAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=arc_A2021CreditAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongtermDebtTypeAxis=us-gaap_LineOfCreditMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableRateAxis=arc_SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryAxis=arc_DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableRateAxis=us-gaap_BaseRateMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
arc_DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryAxis=arc_DebtInstrumentInterestRateCategoryTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Millions |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2020 |
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Liability of site remediation |
$ 4.5
|
$ 0.6
|
$ 0.6
|
| Environmental Loss Contingency, Current, Statement of Financial Position, Extensible Enumeration, Not Disclosed Flag |
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
|
| Environmental Loss Contingency, Statement of Financial Position, Extensible Enumeration, Not Disclosed Flag |
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
|
| Accrued environmental loss contingencies, current |
$ 2.2
|
|
|
| Accrual for environmental loss contingencies, payment period |
7 years
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccrual For Environmental Loss Contingencies, Payment Period
| Name: |
arc_AccrualForEnvironmentalLossContingenciesPaymentPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnvironmental Loss Contingency, Current, Statement of Financial Position, Extensible Enumeration, Not Disclosed Flag
| Name: |
arc_EnvironmentalLossContingencyCurrentStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleEnumerationNotDisclosedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnvironmental Loss Contingency, Statement of Financial Position, Extensible Enumeration, Not Disclosed Flag
| Name: |
arc_EnvironmentalLossContingencyStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleEnumerationNotDisclosedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal costs accrued as of the balance sheet date for environmental loss contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481931/410-30-50-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Subparagraph (d)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481931/410-30-50-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481899/410-30-55-16
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.Y.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480102/450-20-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481931/410-30-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccrualForEnvironmentalLossContingencies |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value of the obligation (known or estimated) arising from requirements to perform activities to remediate one or more sites, payable in twelve months or in the next operating cycle if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481899/410-30-55-11
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483076/450-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481931/410-30-50-7
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 410
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481931/410-30-50-10
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedEnvironmentalLossContingenciesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeaseDescriptionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTerm of lessee's operating lease renewal, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseRenewalTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTerm of lessee's operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseTermOfContract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING - Schedule of Financial Information Associated with Leases (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Assets |
|
|
| Right-of-use assets from operating leases |
$ 32,838
|
$ 28,163
|
| Property and equipment |
50,317
|
60,887
|
| Less accumulated depreciation |
$ (31,139)
|
$ (38,607)
|
| Finance Lease, Right-of-Use Asset, Statement of Financial Position [Extensible Enumeration] |
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $229,122 and $231,913
|
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $229,122 and $231,913
|
| Property and equipment, net |
$ 19,178
|
$ 22,280
|
| Total lease assets |
52,016
|
50,443
|
| Current |
|
|
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities |
9,924
|
9,924
|
| Current portion of finance leases |
8,870
|
11,558
|
| Long-term |
|
|
| Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities |
$ 27,357
|
$ 23,339
|
| Finance Lease, Liability, Noncurrent, Statement of Financial Position [Extensible Enumeration] |
Long-term debt and finance leases
|
Long-term debt and finance leases
|
| Long-term portion of finance leases |
$ 13,366
|
$ 14,916
|
| Total lease liabilities |
$ 59,517
|
$ 59,737
|
| X |
- DefinitionLease, Right-of-Use Asset
| Name: |
arc_LeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates line item in statement of financial position that includes noncurrent finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityNoncurrentStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated amortization of right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before accumulated amortization, of right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 842
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetBeforeAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates line item in statement of financial position that includes finance lease right-of-use asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetStatementOfFinancialPositionExtensibleList |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
enum2:enumerationSetItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesNoncurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING - Components of Lease Cost (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total operating lease cost |
$ 16,653
|
$ 15,753
|
| Interest on lease liabilities |
1,429
|
1,447
|
| Total finance lease cost |
12,302
|
14,626
|
| Total lease cost |
28,955
|
30,379
|
| Variable lease cost |
3,895
|
2,795
|
| Short-term lease cost |
423
|
240
|
| Cost of sales |
|
|
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total operating lease cost |
13,702
|
12,940
|
| Amortization of leased assets |
10,313
|
12,718
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
| Lessee, Lease, Description [Line Items] |
|
|
| Total operating lease cost |
2,951
|
2,813
|
| Amortization of leased assets |
$ 560
|
$ 461
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest expense on finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseInterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lease cost recognized by lessee for lease contract. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeaseDescriptionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of single lease cost, calculated by allocation of remaining cost of lease over remaining lease term. Includes, but is not limited to, single lease cost, after impairment of right-of-use asset, calculated by amortization of remaining right-of-use asset and accretion of lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of short-term lease cost, excluding expense for lease with term of one month or less. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShortTermLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of variable lease cost, excluded from lease liability, recognized when obligation for payment is incurred for finance and operating leases. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_CostOfSalesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING - Maturity of Lease Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Operating leases |
|
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year one |
$ 11,962
|
$ 11,259
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year two |
9,860
|
8,354
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year three |
7,789
|
6,437
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year four |
6,642
|
4,467
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year five |
4,283
|
3,836
|
| Thereafter |
2,345
|
2,983
|
| Total |
42,881
|
37,336
|
| Less amount representing interest |
5,600
|
4,073
|
| Present value of lease liability |
37,281
|
33,263
|
| Finance leases |
|
|
| Finance lease liabilities, year one |
9,883
|
12,510
|
| Finance lease liabilities, year two |
6,221
|
7,903
|
| Finance lease liabilities, year three |
4,625
|
4,393
|
| Finance lease liabilities, year four |
2,595
|
2,878
|
| Finance lease liabilities, year five |
1,015
|
1,022
|
| Thereafter |
36
|
4
|
| Total |
24,375
|
28,710
|
| Less amount representing interest |
2,139
|
2,236
|
| Present value of lease liability |
22,236
|
26,474
|
| Related Party |
|
|
| Operating leases |
|
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year one |
600
|
500
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year two |
600
|
500
|
| Operating lease liabilities, year three |
600
|
500
|
| Finance leases |
|
|
| Operating lease expense |
$ 500
|
$ 500
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilitiesPaymentsDueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments for finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for finance lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease due after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating lease expense. Excludes sublease income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilitiesPaymentsDueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionLease Weighted Average Discount Rate [Abstract]
| Name: |
arc_LeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRateAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted Average Remaining Lease Term [Abstract]
| Name: |
arc_WeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTermAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for finance lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for finance lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for operating lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of interest paid on finance lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseInterestPaymentOnLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow for principal payment on finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeasePrincipalPayments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow from operating lease, excluding payments to bring another asset to condition and location necessary for its intended use. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeasePayments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
LEASING - Additional Information, Lessor (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, net |
$ 19,178
|
$ 22,280
|
| MPS |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Rental income |
68,800
|
70,000
|
| Service income |
6,000
|
5,800
|
| MPS | Equipment Subject to Leases |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, net |
$ 20,000
|
$ 23,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization, of right-of-use asset from finance lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FinanceLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lease income from operating, direct financing, and sales-type leases. Includes, but is not limited to, variable lease payments, interest income, profit (loss) recognized at commencement, and lease payments paid and payable to lessor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479773/842-30-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=arc_ManagedPrintServicesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_EquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
INCOME TAXES - Narrative (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Foreign earnings before taxes |
$ 2,000,000
|
$ 400,000
|
| Domestic earnings (losses) before taxes |
10,500,000
|
16,200,000
|
| Valuation allowance |
1,313,000
|
2,651,000
|
| Unrecognized tax benefits |
0
|
0
|
| Unrecognized tax benefits, interest and penalties |
0
|
$ 0
|
| Federal |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating loss carryforwards |
57,100,000
|
|
| State and Local Jurisdiction |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating loss carryforwards |
75,800,000
|
|
| Foreign Tax Authority |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Operating loss carryforwards |
2,900,000
|
|
| Tax credit carryforward |
$ 200,000
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of the tax credit carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
INCOME TAXES - Schedule of Income Tax Provision (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Current: |
|
|
| Federal |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| State |
215
|
154
|
| Foreign |
481
|
487
|
| Current income tax, total |
696
|
641
|
| Deferred: |
|
|
| Federal |
2,805
|
4,142
|
| State |
682
|
1,040
|
| Foreign |
204
|
9
|
| Deferred income taxes |
3,691
|
5,191
|
| Income tax provision |
$ 4,387
|
$ 5,832
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current foreign income tax expense (benefit) pertaining to income (loss) from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentForeignTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current state and local tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current regional, territorial, and provincial tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
INCOME TAXES - Schedule of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
| Financial statement accruals not currently deductible |
$ 950
|
$ 985
|
| Site remediation obligation |
1,149
|
166
|
| Accrued vacation |
765
|
754
|
| Accrued bonuses |
543
|
914
|
| Deferred revenue, net |
21
|
37
|
| Fixed assets |
2,980
|
4,242
|
| Right of use operating lease liabilities |
9,600
|
8,494
|
| Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles |
1,541
|
745
|
| Stock-based compensation |
2,343
|
2,365
|
| Federal tax net operating loss carryforward |
11,990
|
14,593
|
| State tax net operating loss carryforward, net |
4,723
|
5,182
|
| Foreign tax net operating loss carryforward |
487
|
879
|
| Tax credits, net |
213
|
1,669
|
| Gross deferred tax assets |
37,305
|
41,025
|
| Less: valuation allowance |
(1,313)
|
(2,651)
|
| Net deferred tax assets |
35,992
|
38,374
|
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
| Goodwill and other identifiable intangibles |
(23,010)
|
(23,197)
|
| Right of use operating lease assets |
(8,547)
|
(7,184)
|
| Fixed assets |
(104)
|
0
|
| Net deferred tax assets |
$ 4,331
|
$ 7,993
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, Financial Statement Accruals Not Currently Deductible
| Name: |
arc_DeferredTaxAssetsFinancialStatementAccrualsNotCurrentlyDeductible |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, Right Of Use Operating Lease Liabilities
| Name: |
arc_DeferredTaxAssetsRightOfUseOperatingLeaseLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComponentsOfDeferredTaxAssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComponentsOfDeferredTaxLiabilitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from deferred income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsDeferredIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from intangible assets including goodwill.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGoodwillAndIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allocation of valuation allowances and deferred tax liability, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible differences and carryforwards, without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsLiabilitiesNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible domestic operating loss carryforwards. Excludes state and local operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsDomestic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible foreign operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsForeign |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible state and local operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsStateAndLocal |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from property, plant, and equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of a valuation allowances, of deferred tax assets attributable to deductible tax credit carryforwards including, but not limited to, research, foreign, general business, alternative minimum tax, and other deductible tax credit carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxCreditCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from compensated absences (includes, but not limited to, sick and personal days). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsCompensatedAbsences |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from employee bonuses. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsEmployeeBonuses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from share-based compensation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsShareBasedCompensationCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences from intangible assets including goodwill. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesGoodwillAndIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences from leasing arrangements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesLeasingArrangements |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences from property, plant, and equipment. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.0.1
v3.24.0.1
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN - Narrative (Details)
$ in Thousands |
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Apr. 26, 2023
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2023
USD ($)
boardOfDirectMember
shares
|
Dec. 31, 2022
USD ($)
boardOfDirectorMember
shares
|
Apr. 29, 2021
shares
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Percentage on market value of common stock |
|
100.00%
|
|
|
| Shares available under Stock Plan (in shares) |
|
5,100,000
|
|
|
| Expiration period |
|
10 years
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
3 years
|
|
|
| Granted (in shares) |
|
1,096,000
|
1,658,000
|
|
| Intrinsic value of options exercised | $ |
|
$ 471
|
$ 292
|
|
| Stock options exercised (in shares) |
|
805,000
|
618,000
|
|
| Restricted Stock |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Expiration period |
|
10 years
|
|
|
| Shares, granted (in shares) |
|
269,000
|
|
|
| Vested in period | $ |
|
$ 1,100
|
$ 1,700
|
|
| Restricted Stock | Key Employees |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
|
3 years
|
|
| Shares, granted (in shares) |
|
100,000
|
100,000
|
|
| Restricted Stock | Non-employee Board Members |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
1 year
|
1 year
|
|
| Shares, granted (in shares) |
|
30,000
|
16,000
|
|
| Number of awards grantees |
|
4
|
3
|
|
| Minimum |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
3 years
|
|
|
| Minimum | Restricted Stock |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
3 years
|
|
|
| Maximum |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
4 years
|
|
|
| Maximum | Restricted Stock |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Vesting period |
|
4 years
|
|
|
| ESPP |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Common stock, shares (in shares) |
|
2,500
|
|
|
| Aggregate fair market value of common stock | $ |
|
$ 25
|
|
|
| Percentage on market value of common stock |
|
85.00%
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation, expense | $ |
|
$ 23
|
$ 17
|
|
| Amended 2021 Plan |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Number of additional shares authorized (in shares) |
5,000,000
|
|
|
|
| Shares authorized under the plan (in shares) |
8,500,000
|
|
|
|
| 2014 Inventive Plan and 2005 Stock Plan |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Shares authorized under the plan (in shares) |
|
|
|
6,132,593
|
| X |
- DefinitionEmployee stock purchase plan aggregate fair market value of common stock.
| Name: |
arc_EmployeeStockPurchasePlanAggregateFairMarketValueOfCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEmployee stock purchase plan eligible number of share per employee.
| Name: |
arc_EmployeeStockPurchasePlanEligibleNumberOfSharePerEmployee |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-Based Compensation Arrangement By Share-Based Payment Award, Number Of Grantees
| Name: |
arc_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfGrantees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod over which grantee's right to exercise award under share-based payment arrangement is no longer contingent on satisfaction of service or performance condition, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, combination of market, performance or service condition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of share-based awards for which the grantee gained the right by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodTotalFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of additional shares authorized for issuance under share-based payment arrangement.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfAdditionalSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares authorized for issuance under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe difference between the maximum number of shares (or other type of equity) authorized for issuance under the plan (including the effects of amendments and adjustments), and the sum of: 1) the number of shares (or other type of equity) already issued upon exercise of options or other equity-based awards under the plan; and 2) shares (or other type of equity) reserved for issuance on granting of outstanding awards, net of cancellations and forfeitures, if applicable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAvailableForGrant |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated difference between fair value of underlying shares on dates of exercise and exercise price on options exercised (or share units converted) into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodTotalIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAn excess of the fair value of the modified award over the fair value of the award immediately before the modification. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardPlanModificationIncrementalCompensationCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod from grant date that an equity-based award expires, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardExpirationPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchase price of common stock expressed as a percentage of its fair value.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardPurchasePriceOfCommonStockPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GranteeStatusAxis=us-gaap_ShareBasedPaymentArrangementEmployeeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GranteeStatusAxis=us-gaap_ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=arc_EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=arc_Amended2021PlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=arc_A2014InventivePlanAnd2005StockPlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionStock issued during period employee stock purchase plans average price per share.
| Name: |
arc_StockIssuedDuringPeriodEmployeeStockPurchasePlansAveragePricePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
arc_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued during the period as a result of an employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesEmployeeStockPurchasePlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN - Schedule of Stock Option Plan Activity (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Shares |
|
|
| Beginning balance (in shares) |
5,969
|
5,462
|
| Granted (in shares) |
1,096
|
1,658
|
| Exercised (in shares) |
(805)
|
(618)
|
| Forfeited/Canceled (in shares) |
(82)
|
(533)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) |
6,178
|
5,969
|
| Vested or expected to vest (in shares) |
6,178
|
|
| Exercisable (in shares) |
3,582
|
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price per Share |
|
|
| Beginning balance (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.39
|
$ 3.56
|
| Granted (in dollars per share) |
3.60
|
3.11
|
| Exercised (in dollars per share) |
2.60
|
2.49
|
| Forfeited/canceled (in dollars per share) |
3.12
|
5.31
|
| Ending balance (in dollars per share) |
3.54
|
$ 3.39
|
| Vested or expected to vest (in dollars per share) |
3.54
|
|
| Exercisable (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.80
|
|
| Weighted Average Contractual Life (In years) and Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|
|
| Weighted average contractual life (in years), outstanding |
5 years 11 months 26 days
|
|
| Weighted average contractual life (in years), vested or expected to vest |
5 years 11 months 26 days
|
|
| Weighted average contractual life (in years), exercisable |
4 years 3 months 3 days
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, outstanding |
$ 2,740
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, vested or expected to vest |
2,740
|
|
| Aggregate intrinsic value, exercisable |
$ 2,105
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsAdditionalDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares into which fully or partially vested stock options outstanding as of the balance sheet date can be currently converted under the option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted-average price as of the balance sheet date at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance on vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor presentations that combine terminations, the number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan or that expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresAndExpirationsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price of options that were either forfeited or expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresAndExpirationsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which the current fair value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of options outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePriceRollforward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which current fair value of underlying stock exceeds exercise price of fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingAggregateIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding that can be converted into shares under option plan. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average exercise price, at which grantee can acquire shares reserved for issuance, for fully vested and expected to vest options outstanding. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which option holders acquired shares when converting their stock options into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average per share amount at which grantees can acquire shares of common stock by exercise of options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of difference between fair value of the underlying shares reserved for issuance and exercise price of vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableIntrinsicValue1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable or convertible, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for fully vested and expected to vest exercisable or convertible options, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, unvested options for which requisite service period has not been rendered but that are expected to vest based on achievement of performance condition, if forfeitures are recognized when they occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedAndExpectedToVestExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionGross number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average grant-date fair value of options granted during the reporting period as calculated by applying the disclosed option pricing methodology. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of non-vested options outstanding.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedNumberOfShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedNumberOfSharesRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of non-vested options forfeited.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedOptionsForfeitedNumberOfShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average grant-date fair value of non-vested options forfeited.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedOptionsForfeitedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average grant-date fair value of non-vested options outstanding.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options vested.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedNumberOfShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average grant-date fair value of options vested.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsVestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.0.1
EMPLOYEE STOCK PURCHASE PLAN AND STOCK PLAN - Schedule of Range of Exercise Price for Options Outstanding (Details) - $ / shares
shares in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
Dec. 31, 2021 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation arrangement, options, outstanding, number (in shares) |
6,178
|
5,969
|
5,462
|
| $1.14 – $2.64 |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range minimum (in dollars per share) |
$ 1.14
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range maximum (in dollars per share) |
$ 2.64
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation arrangement, options, outstanding, number (in shares) |
2,218
|
|
|
| $3.20 – $4.75 |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range minimum (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.20
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range maximum (in dollars per share) |
$ 4.75
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation arrangement, options, outstanding, number (in shares) |
3,196
|
|
|
| $6.16 – $7.19 |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range minimum (in dollars per share) |
$ 6.16
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range maximum (in dollars per share) |
$ 7.19
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation arrangement, options, outstanding, number (in shares) |
392
|
|
|
| $8.89 – $9.09 |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range minimum (in dollars per share) |
$ 8.89
|
|
|
| Range of exercise price range maximum (in dollars per share) |
$ 9.09
|
|
|
| Share-based compensation arrangement, options, outstanding, number (in shares) |
372
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe floor of a customized range of exercise prices for purposes of disclosing shares potentially issuable under outstanding stock option awards on all stock option plans and other required information pertaining to awards in the customized range. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansExercisePriceRangeLowerRangeLimit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe ceiling of a customized range of exercise prices for purposes of disclosing shares potentially issuable under outstanding stock option awards on all stock option plans and other required information pertaining to awards in the customized range. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansExercisePriceRangeUpperRangeLimit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansByExercisePriceRangeAxis=arc_RangeOneMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansByExercisePriceRangeAxis=arc_RangeTwoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansByExercisePriceRangeAxis=arc_RangeThreeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationSharesAuthorizedUnderStockOptionPlansByExercisePriceRangeAxis=arc_RangeFourMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that were forfeited during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeitedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average fair value as of the grant date of equity-based award plans other than stock (unit) option plans that were not exercised or put into effect as a result of the occurrence of a terminating event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeituresWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value at grant date for nonvested equity-based awards issued during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of non-vested equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that validly exist and are outstanding as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPer share or unit weighted-average fair value of nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes share and unit options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValueRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that vested during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value as of grant date pertaining to an equity-based award plan other than a stock (or unit) option plan for which the grantee gained the right during the reporting period, by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash in accordance with the terms of the arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost for defined contribution plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanCostRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanDisclosureLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage of employees' gross pay for which the employer contributes a matching contribution to a defined contribution plan.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanEmployerMatchingContributionPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage employer matches of the employee's percentage contribution matched.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanEmployerMatchingContributionPercentOfMatch |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMaximum percentage of employee gross pay the employee may contribute to a defined contribution plan.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedContributionPlanMaximumAnnualContributionsPerEmployeePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=arc_EligibleEmployeesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=arc_HighlyCompensatedEmployeesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.0.1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueDisclosuresAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncluding the current and noncurrent portions, aggregate carrying amount of all types of notes payable, as of the balance sheet date, with initial maturities beyond one year or beyond the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of notes payable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19,20,22)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NotesPayableFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
ARC Document Solutions (NYSE:ARC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Oct 2024 to Nov 2024
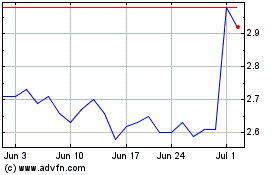
ARC Document Solutions (NYSE:ARC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Nov 2023 to Nov 2024