Pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3)
Registration No. 333-257632
PROSPECTUS

Samsara Luggage, Inc.
361,596
Shares of Common Stock
This prospectus relates to the offer and sale,
from time to time, of up to 361,596 shares of the common stock of Samsara Luggage, Inc. (the “Company,” “Samsara,”
“we,” “us” and “our”) by those stockholders named in the section of this prospectus entitled “Selling
Stockholders.” The shares of common stock being offered by the selling stockholders (the “Shares”) may be issued upon
the conversion of certain convertible notes (the “Convertible Notes”) (and accrued interest thereon) issued pursuant to a
Securities Purchase Agreement that we entered into with the selling stockholder on June 7, 2021 (the “Purchase Agreement’).
We
are not selling any shares of common stock in this offering, and we will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares by the selling
stockholder.
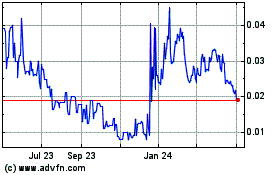
Our common stock is quoted on the OTCQB under
the symbol “SAML.” On August 23, 2021, the last reported sale price of our common stock on the OTCQB was $2.98 per share,
and we had approximately 1,447,955 shares of common stock outstanding.
The
selling stockholder may offer all or part of the shares for resale from time to time through public or private transactions, at either
prevailing market prices or at privately negotiated prices.
This
prospectus provides a general description of the securities being offered. You should carefully read this entire prospectus and the registration
statement of which it forms a part before you invest in any securities.
Investing
in our securities involves risks. You should review carefully the risks and uncertainties described under the heading “Risk
Factors” on page 5.
Neither
the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined
if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this prospectus is
September 3, 2021
Table
of Contents
PROSPECTUS
SUMMARY
This
summary highlights selected information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all the information that
you should consider before investing in the common stock. You should carefully read the entire prospectus. In particular, attention should
be directed to the sections entitled “Risk Factors,” “Business,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis
of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and related notes thereto contained herein before
making an investment decision.
Business
Overview
Samsara
Luggage is a leading travel and lifestyle direct-to-consumer brand that develops smart travel products that are unique to the vast global
marketplace. Samsara’s products are designed to create a world where travel isn’t a hassle but rather an effortless experience.
The Company’s forward-thinking creative team of engineers and designers analyzed the standard travel experience to understand the
solutions they could develop to alleviate many common travel headaches. By combining unmatched quality materials, functional design features
and innovative technology, Samsara created a line of travel products that make travel seamless, safer and more convenient.
Samsara’s
first-generation Carry-on is equipped with smart features, including IoT technology that provides a layer of convenience for travelers
and protects them from theft and hackers that may install malware and ransomware in key public locations in airports, hotels and beyond.
As part of its commitment to providing value for its tech-savvy customers and competing in the everchanging travel landscape, Samsara
incorporates the latest technology into its travel products. With the upcoming launch of its Next Generation Carry-on, Samsara is aiming
to be the first to market a suitcase with a secure Wi-Fi Hotspot feature travelers can access globally. This new collection is scheduled
to launch at the end of the year 2021, pending no further delay due to COVID-19.
To
address the new needs of travelers due to the coronavirus pandemic, Samsara Luggage launched the Nano Weekender, a smart travel bag that
is treated with bacteriostatic nanotechnology protection that prevents colonies of bacteria from developing on the fabric. Samsara Luggage
also launched the Essentials by Samsara travel safety kit to provide commuters with an added layer of safety. Each kit contained
protective items including a reusable facemask, hand sanitizer, disposable gloves, and alcohol wipes. These kits are sold individually
and gifted to customers with purchase of the Carry-on Aluminum suitcase or Nano Weekender bag.
All of Samsara’s products are compliant
with Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and aviation regulations.
Samsara
launched Sarah & Sam (sarah-sam.com) a fashion and lifestyle collection in the fourth quarter of the 2020 fiscal year. Sarah& Sam is a part of Samsara Direct, a new business model initiated in response to the travel restrictions enforced due to the coronavirus
pandemic. Samsara Direct leverages the company’s established digital assets and manufacturing and fulfillment supply chain capabilities
offer additional consumer products that are in demand and relevant to the changing needs of the market.
Corporate
Information
Our
principal executive offices are located at One University Plaza, Suite 505, Hackensack, NJ 07601 and our telephone number is (877) 421-1574.
The
Offering
This
prospectus relates to the offer and sale from time to time of up to 361,596 shares of our common stock, $0.0001 par value per share (the
“Common Stock”) by the selling stockholder, that may be issued upon conversion of the Convertible Notes.
The
selling stockholder under this prospectus is offering for sale up to 361,596 shares of our Common Stock. On June 7, 2021, we entered
into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”) with the selling stockholder. Pursuant to the Agreement, the selling
stockholder has agreed to purchase from us up to an aggregate of $1,250,000 worth of Convertible Notes of our Common Stock from time
to time in three installments. The first installment of $500,000 was issued on June 7, 2021. The second installment of $500,000 will
be issued no later than one day following the date that the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part is filed. The
third installment of $250,000 will be issued no later than one day following the date that the registration statement of which this prospectus
forms a part of is declared effective.
Except
as described in this prospectus, the selling stockholder is entitled to convert at its option the outstanding and unpaid amounts of the
Convertible Notes into fully paid and nonassessable shares of Common Stock at the lower of the $8.188 or 80% of the lowest Volume Weighted
Average Price of our Common Stock. The selling stockholder may not assign or transfer its rights and obligations under the Purchase Agreement
without the prior written consent of the Company.
As of August 23, 2021, there were 1,447,955
shares of our Common Stock outstanding, of which 1,099,063 shares were held by non-affiliates. If the selling stockholder converts the
Convertible Notes, the ownership position of the shareholders prior to the conversion would be diluted. If the selling stockholder converts
the Convertible Notes into all of the 361,596 shares being registered under the registration statement of which this prospectus forms
a part, such shares would represent 16.65% of all of our then outstanding shares and 22.89% of the then total number of shares held by
non-affiliates (assuming no further issuances). Under the terms of a Registration Rights Agreement entered into with the selling stockholder
at the same time as the Purchase Agreement, we must register with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission 361,596 shares of Common
Stock underlying the Convertible Notes for resale by the selling stockholder under the Purchase Agreement, however, the Convertible Notes
may be converted into more than the 361,596 shares of our Common Stock being offered under this prospectus. The number of shares ultimately
offered for resale by the selling stockholder depends upon the number of Convertible Notes we sell to it under the Purchase Agreement,
the market price of our Common Stock (subject to a floor and ceiling if we are not in default of the Convertible Notes) and the interest
accrued on the Convertible Notes at the time of conversion.
Issuances
of our Common Stock upon conversion of the Convertible Notes will not affect the rights or privileges of our existing stockholders, except
that the economic and voting interests of each of our existing stockholders will be diluted as a result of any such issuance. Although
the number of shares of Common Stock that our existing stockholders own will not decrease, the shares owned by our existing stockholders
will represent a smaller percentage of our total outstanding shares after any such issuance to the selling stockholder.
|
Common
Stock offered by selling stockholder:
|
|
361,596
of the shares that may be issued to the selling stockholder pursuant to the Purchase Agreement
upon the conversion of Convertible Notes and accrued interest thereon and subsequently resold
in this offering.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common
Stock outstanding:
|
|
1,447,955 shares
as of August 23, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common
Stock outstanding after the offering:
|
|
1,809,551,
assuming the selling stockholder converts the Convertible Notes (and the full year of accrued
interest thereon) into all of the shares being registered in the registration statement of
which this prospectus forms a part.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount:
|
|
The
Convertible Notes are convertible by the selling stockholder upon issuance. The conversion
price will be the lesser of (i) $8.188 and (ii) 80% of the lowest daily volume
weighted average prices of the Company’s Common Stock (as reported by Bloomberg Financial
Markets) (“VWAP”) during the last ten (10) trading days immediately preceding
the date of such conversion.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest
Rate:
|
|
The
rate of interest on the Convertible Notes will be 10% per annum.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use
of Proceeds:
|
|
We
will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares by the selling stockholder. As of the
date hereof, we have received $500,000 from the sale of a Convertible Note to the selling
stockholder under the Purchase Agreement. Within one day from the filing of the registration
statement of which this prospectus forms a part, we will receive another $500,000 from the
sale of Convertible Notes to the selling stockholder. Within one day from the effective date
of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, we will receive up to
another $250,000 from the sale of Convertible Notes to the selling stockholder. These proceeds
will be used for general corporate and working capital or other purposes that our Board of
Directors deems to be in our best interest. As of the date of this prospectus, we cannot
specify with certainty the particular uses for the net proceeds we may receive. Accordingly,
we will retain broad discretion over the use of these proceeds, if any.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quotation
of Common Stock:
|
|
Our Common Stock is listed for quotation on
the OTCQB under the symbol “SAML.”
|
|
Dividend
policy:
|
|
We
currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of
our business. Therefore, we do not currently anticipate paying cash dividends on our Common
Stock.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Risk
factors:
|
|
An
investment in our company is highly speculative and involves a significant degree of risk. See “Risk Factors” and other
information included in this prospectus for a discussion of factors you should carefully consider before deciding to invest in shares
of our Common Stock.
|
SPECIAL
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
We
have made statements under the captions “Risk Factors,” “Use of Proceeds,” “Management’s Discussion
and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation,” “Business” and elsewhere in this prospectus that are
forward-looking statements. You can identify these statements by forward-looking words such as “may,” “will,”
“expect,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate” and similar terminology. Additionally,
many of these risks and uncertainties are currently amplified by and will continue to be amplified by, or in the future may be amplified
by, the coronavirus (“COVID-19”) outbreak, the continued restrictions that have been placed on travel in many countries as
a result of the outbreak and the adverse impact on the global economy from the outbreak.
Forward-looking
statements address, among other things:
|
|
●
|
the
risks and other factors described under the caption “Risk Factors” under Item 1 of this Registration Statement;
|
|
|
●
|
the
COVID-19 outbreak and resulting economic conditions, which had, and is expected to continue to have, a significant impact on our
operations, including an unprecedented decline in demand, as well as its current, and uncertain future impact, including but not
limited to, its effect on the ability or desire of people to travel due to travel restrictions, and other restrictions and orders,
which is expected to continue to impact our results, operations, outlooks, plans, goals, growth, cash flows, liquidity, and stock
price;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
the
significant decline in travel demand because of COVID-19, including the current and any future disruptions in airline passenger traffic.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our
future operating results;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our
business prospects;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
any
contractual arrangements and relationships with third parties;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
the
dependence of our future success on the general economy;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
any
possible financings; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
the
adequacy of our cash resources and working capital.
|
We
believe it is important to communicate our expectations to our investors. However, there may be events in the future that we are not
able to accurately able to predict or which we do not fully control that will cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed
or implied by our forward-looking statements. These include the factors listed under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this
prospectus.
Although
we believe that our expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels
of activity, performance, or achievements. Our forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this prospectus, and we assume no
duty to update them or to explain why actual results may differ.
Except
as otherwise indicated by the context, references in this Registration Statement to “Company,” “Samsara,” “we,”
“us” and “our” are references to SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC. All references to “USD” or United States Dollar
refer to the legal currency of the United States of America.
RISK
FACTORS
Investing
in our securities involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider and evaluate all of the information included and incorporated
by reference or deemed to be incorporated by reference in this prospectus. Our business, results of operations or financial condition
could be adversely affected by any of these risks or by additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently
consider immaterial.
Risks
Related to COVID-19
The
COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected our business and is expected to continue to materially affect our business, financial condition,
results of operations and/or cash flows for an extended period. Governmental authorities have taken and continue to take measures to
address the outbreak, including restrictions on travel and other orders, including partial shelter-in-place orders. The pandemic is a
highly fluid and rapidly evolving situation and we cannot anticipate with any certainty the length, scope or severity of such restrictions
in the jurisdiction that we operate.
The
full impact that COVID-19 will have on our business cannot be predicted at this time due to numerous uncertainties, including the duration
and severity of the outbreak, future mutations in the virus that causes COVID-19, increases or spikes in the number of cases, the availability
of vaccines and effectiveness of actions taken to contain the disease, the length of time it takes for rental volume and pricing to return
and normal economic and operating conditions to resume, and other factors. This impact could include, but is not limited to, those discussed
below:
|
|
●
|
Changes
in our revenues and customer demand: Our revenues and profitability were materially impacted
during 2020 compared to prior years, and we expect they will continue to be adversely affected.
Although we believe that travel will increase due to wider vaccine usage and availability,
we cannot predict whether and when volumes will increase to historic levels. Our business
is highly dependent on travel and both for commercial and leisure purposes.
|
|
|
●
|
Our
workforce: The COVID-19 outbreak has caused us to reduce production of our luggage line as
we seek to keep our costs in line with demand.
|
|
|
●
|
The
adequacy of our cash flow and earnings and other conditions may affect our liquidity: We
have taken a number of actions as a result of COVID-19 that have increased our long-term
debt. As we manage through the effects of the pandemic, our level of indebtedness may further
increase. There is no guarantee that debt financings will be available in the future to fund
our obligations or will be available on terms consistent with our expectations.
|
Risks
Related to our Company
Samsara
has a limited operating history, has incurred significant operating losses since its inception and expects to incur significant losses
for the foreseeable future. Samsara may never generate significant revenue or become profitable or, if Samsara achieves profitability,
it may not be able to sustain it.
Samsara
has a limited operating history and has generated limited revenues to date. Samsara is dependent upon additional capital resources for
the continuation of its planned principal operations, which are subject to significant risks and uncertainties, including failing to
secure funding to expand commercialization of its products or failing to profitably operate the business.
Samsara has incurred significant operating losses
since its inception. Samsara’s net losses were $1,140,000 and $3,142,000 for the years ended December 31, 2020, and December 31,
2019, respectively. As of December 31, 2020, Samsara had an accumulated deficit of $6,376,000. Substantially all of Samsara’s losses
have resulted from expenses incurred in connection with its research and development programs and from general and administrative costs
associated with Samsara’s operations. Samsara expects to continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future and anticipates these
losses will increase substantially as Samsara continues to develop and commercialize its products.
To
become and remain profitable, Samsara must succeed in developing and commercializing products that generate significant revenue. This
will require Samsara to be successful in a range of challenging activities, including manufacturing, and marketing and selling products.
Samsara may never succeed in these activities and, even if it does, may never generate revenues that are significant enough to achieve
profitability. In addition, Samsara has not yet demonstrated an ability to successfully overcome many of the risks and uncertainties
frequently encountered by companies in new and rapidly evolving fields. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with
smart luggage product development, Samsara is unable to accurately predict the timing or amount of increased expenses or when, or if,
Samsara will be able to achieve profitability. Even if Samsara does achieve profitability, it may not be able to sustain or increase
profitability on a quarterly or annual basis. Samsara’s failure to become and remain profitable would depress the value of Samsara
and could impair its ability to raise capital, expand its business, maintain its research and development efforts, diversify its product
candidates or even continue its operations. A decline in the value of Samsara could also cause stockholders to lose all or part of their
investment.
The
report of Samsara’s independent registered public accounting firm expresses substantial doubt about the ability of Samsara to continue
as a going concern.
Samsara’s
independent registered public accounting firm indicated in its report on Samsara’s financial statements for the period ended December
31, 2020, that conditions exist that raise substantial doubt about Samsara’s ability to continue as a “going concern.”
A going concern paragraph included in Samsara’s independent registered public accounting firm’s report on its consolidated
financial statements could impair investor perceptions and Samsara’s ability to finance its operations through the sale of equity,
incurring debt, or other financing alternatives. Samsara’s ability to continue as a going concern will depend upon many factors
beyond Samsara’s control including the availability and terms of future funding. If Samsara is unable to achieve its goals and
raise the necessary funds to finance its operations, its business would be jeopardized, and Samsara may not be able to continue.
Samsara
will require substantial additional financing to achieve its goals, and a failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed and on
acceptable terms, or at all, could force Samsara to delay, limit, reduce or terminate its product development programs, commercialization
efforts or other operations.
Samsara
expects its expenses to increase in connection with its ongoing activities. Samsara also expects to incur significant commercialization
expenses related to product manufacturing, marketing, sales and distribution. Samsara cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary
to successfully complete the development and commercialization of its products. Furthermore, following the completion of the Merger,
Samsara will incur the additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, Samsara will need to obtain substantial
additional funding in connection with its continuing operations. If Samsara is unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms,
Samsara could be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate its research and development programs or any future commercialization efforts.
Samsara
has based its estimates on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and Samsara could use its capital resources sooner than it currently
expects. Samsara’s operating plans and other demands on its cash resources may change as a result of many factors currently unknown
to Samsara, and Samsara may need to seek additional funds sooner than planned, through public or private equity or debt financings or
other capital sources, including potentially government funding, collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements. In addition,
Samsara may seek additional capital due to favorable market conditions or strategic considerations even if Samsara believes it has sufficient
funds for its current or future operating plans. Attempting to secure additional financing may divert Samsara’s management from
its day-to-day activities, which may adversely affect Samsara’s ability to develop its product.
Samsara’s
future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
|
|
●
|
the
costs and timing of manufacturing for Samsara’s products, including commercial manufacturing of its products;
|
|
|
●
|
the
costs of obtaining, maintaining and enforcing Samsara’s intellectual property rights;
|
|
|
●
|
Samsara’s
efforts to enhance operational systems and hire additional personnel to satisfy its obligations as a public company, including enhanced
internal controls over financial reporting;
|
|
|
●
|
the
costs associated with hiring additional personnel and consultants as Samsara’s research and development activities increase;
|
|
|
●
|
the
timing and amount of the milestone or other payments Samsara must make to the licensors and other third parties from whom Samsara
have licensed or acquired technology;
|
|
|
●
|
the
costs and timing of establishing or securing sales and marketing capabilities for its products;
|
|
|
●
|
Samsara’s
ability to achieve market acceptance and adequate market share and revenue for its products; and
|
|
|
●
|
the
terms and timing of establishing and maintaining collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements.
|
In
addition, Samsara’s products may not achieve commercial success.
Accordingly,
Samsara will need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve its business objectives. Adequate additional financing may not
be available to Samsara on acceptable terms, or at all. In addition, Samsara may seek additional capital due to favorable market conditions
or strategic considerations, even if Samsara believes it has sufficient funds for its current or future operating plans.
Raising
additional capital may cause dilution to Samsara’s stockholders, restrict Samsara’s operations or require Samsara to relinquish
rights to its technologies or product candidates.
Until
such time, if ever, as Samsara can generate substantial product revenues, Samsara expects to finance its cash needs through equity offerings,
debt financings or other capital sources, including potentially government funding, collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements.
To the extent that Samsara raises additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, existing stockholders’
ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect
stockholders’ rights as a common stockholder. Debt financing and preferred equity financing, if available, may involve agreements
that include covenants limiting or restricting Samsara’s ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making
capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If
Samsara raises funds through future collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements, Samsara may have to relinquish valuable
rights to its future revenue streams or products or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to Samsara and/or that may reduce
the value of Samsara’s Common Stock.
Risks
Relating to Samsara’s Strategy and Industry
Samsara’s
success depends on independent contractors to manufacture and supply Samsara with its smart luggage products, and to label, package,
and ship these products.
Samsara
has retained third party manufacturers to manufacture and supply Samsara with its smart luggage products. Samsara relies on independent
contractors for the supply of its smart luggage products and for the labeling, packaging, and shipping of these products. Samsara may
not be successful in developing relationships with these independent contractors. In addition, these third-party contractors may not
dedicate sufficient resources or give sufficient priority to satisfying Samsara’s requirements or needs. There is limited history
upon which to base any assumption as to the likelihood that Samsara will prove successful in selecting qualified third-party independent
contractors or in negotiating any agreements with them. If Samsara is unsuccessful in addressing these risks, its results of operations
could be adversely affected.
Samsara
does not have long term commitments from suppliers and other independent contractors.
Samsara
may experience shortages of supplies and inventory because Samsara orders goods and services via purchase orders and has not signed long-term
contracts with its suppliers. Samsara currently utilizes the services of two manufacturers in China, one for the manufacture of the suitcase
and the other for the manufacture of the smart unit. In addition, Samsara utilizes the services of two contractors, one in China and
one in the United States, for the provision of order fulfillment services. Samsara’s success is dependent on Samsara’s ability
to timely provide its customers with Samsara’s smart luggage products. Although Samsara directly markets these products, Samsara
is dependent on its suppliers and other independent contractors for the manufacture and supply of Samsara’s smart luggage products
and for the labeling, packaging, and shipment of these products. No assurance can be given that Samsara will enter into agreements with
other suppliers for the supply of its smart luggage products at acceptable levels of quality and price, or with other independent contractors
who will provide Samsara with order fulfillment services at acceptable levels of quality and price. While Samsara currently has and anticipates
continuing to have good relationships with its suppliers and other independent contractors, if Samsara is unable to secure additional
sources of supply or order fulfillment services from one or more independent contractors on a timely basis and on acceptable terms, Samsara’s
results of operations could be adversely affected.
The
selling of smart luggage products is subject to current governmental regulations.
Several
aspects of Samsara’s smart luggage products, including its battery, locks and LED lights, are subject to the requirements of federal
law relating to aviation and homeland security, as well as international regulation of electronic devices. Part 15 of the FCC Rules requires
operation of electronic equipment not to cause harmful interference and to accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation. The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) recommends that only TSA approved locks be used on luggage,
to avoid risk of TSA agents breaking the lock for inspection. The European Union requires all electronic devices to comply with the Restriction
of Hazardous Substances (ROHS) regulations which restricts the use of specific hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic
products. BS EN 62471 gives universal best-practice recommendations for the photobiological safety of electric lamps and lighting systems,
including LED lights. This standard specifies exposure limits, measurement techniques and classification systems to control photobiological
and light hazards. The EU radio equipment directive establishes a regulatory framework for placing radio equipment on the market, setting
requirements for safety and health, electromagnetic compatibility, and the efficient use of the radio spectrum.
Additionally,
smart luggage products are subject to airline regulations applicable to manufacturing materials, size and weight. While Samsara believes
that it is and will be in substantial compliance with the laws and regulations which regulate its business, the failure to comply with
any of these laws or regulations, or the imposition of new laws or regulations could negatively impact Samsara’s proposed business.
Samsara
faces intense competition and many of its competitors have substantially greater resources than Samsara has.
Samsara
operates in a highly competitive environment. In addition, the competition in the market for smart luggage products may intensify. There
are numerous well-established companies based in the United States with longer operating histories, significantly greater resources and
name recognition, and a larger base of distributors and retailers. In addition, there are smaller entrepreneurial companies who are developing
products that will compete with the smart luggage products that Samsara currently sells. As a result, these competitors may have greater
credibility with Samsara’s potential customers. They also may be able to adopt more aggressive pricing policies and devote greater
resources to the development, promotion, and sale of their products. These competitors may make it difficult for Samsara to market and
sell its products and compete in the smart luggage market, which could harm Samsara’s business.
Samsara
depends on market acceptance of its smart luggage products. If these products do not gain market acceptance, Samsara’s ability
to compete will be adversely affected.
Samsara’s
success depends in large part on Samsara’s ability to successfully market its smart luggage products. No assurances can be given
that Samsara will be able to successfully market its smart luggage products or achieve consumer acceptance. Moreover, failure to successfully
commercialize its smart luggage products on a timely and cost-effective basis will have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s
ability to compete in its targeted market.
Failure
to meet customers’ expectations or deliver expected performance could result in losses and negative publicity, which would harm
Samsara’s business.
If
the smart luggage products which Samsara sells fail to perform in the manner expected by its customers, then Samsara’s revenues
may be delayed or lost due to adverse customer reaction. In addition, negative publicity about Samsara and its products could adversely
affect Samsara’s ability to attract or retain customers. Furthermore, disappointed customers may initiate claims for damages against
Samsara, regardless of Samsara’s responsibility for their disappointment.
Samsara
needs to retain key personnel to support its services and ongoing operations.
The
marketing and sale of Samsara’s smart luggage products will continue to place a significant strain on Samsara’s limited personnel,
management, and other resources. Samsara’s future success depends upon the continued services of its executive officers and the
hiring of key employees and contractors who have critical industry experience and relationships that Samara will need to rely on to implement
its business plan. The loss of the services of any of Samsara’s officers or the lack of availability of other skilled personnel
would negatively impact Samsara’s ability to market and sell its smart luggage products, which could adversely affect Samsara’s
financial results and impair Samsara’s growth.
If
Samsara cannot build and maintain strong brand loyalty to its products, its business may suffer.
Samsara
believes that the importance of brand recognition will increase as more companies produce smart luggage products. Development and awareness
of Samsara’s brand will depend largely on Samsara’s ability to successfully advertise and market its products. If Samsara
is unsuccessful, its products may not be able to gain widespread acceptance among consumers. A failure to develop Samsara’s smart
luggage products sufficiently could have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Samsara
may incur losses as a result of claims that may be brought against Samsara due to defective products or as a result of product recalls.
While
Samsara is not aware of any claims having been brought in connection with Samsara’s smart luggage products, Samsara may be liable
if the use of Samsara’s products causes injury, illness, or death. Samsara also may be required to withdraw or recall some of its
products if they are damaged or defective. A significant product liability judgment against Samsara or a widespread product withdrawal
or recall could have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business and financial condition.
If
a third party asserts that Samsara’s infringes upon its proprietary rights, Samsara could be required to redesign its products,
change suppliers, pay significant royalties, or enter into license agreements.
Although
presently Samsara is not aware of any such claims, a third party may assert that Samsara’s smart luggage products violate its intellectual
property rights. As the number of smart luggage products increases, infringement claims may become more common. Any claims against Samsara,
regardless of their merit, could:
|
|
●
|
Be
expensive and time-consuming to defend;
|
|
|
●
|
Result
in negative publicity;
|
|
|
●
|
Force
Samsara to stop selling its products;
|
|
|
●
|
Divert
management’s attention and Samsara’s other resources; and
|
|
|
●
|
Require
Samsara to enter into royalty or licensing agreements in order to obtain the right to sell its products, which right may not be available
on terms acceptable to Samsara, if at all.
|
In
addition, Samsara’s believes that any successful challenge to its use of a trademark or domain name could substantially diminish
Samsara’s ability to conduct business in a particular market or jurisdiction and thus could decrease Samsara’s revenues and/or
result in losses to Samsara’s business.
Samsara
relies on third parties to conduct many of its activities. Any failure by a third-party to conduct these activities and other requirements
and in a timely manner may delay or prevent Samsara’s ability to commercialize its products.
Samsara
is dependent on third parties to perform certain activities. Specifically, Samsara has used and relied on, these third parties for the
manufacture of its luggage products, and for order fulfillment services. While Samsara has signed purchase orders governing the activities
of its third-party contractors, Samsara has limited influence over their actual performance. There is no guarantee that any such third
parties will devote adequate time and resources to such activities or perform as contractually required. If any of these third parties
fail to meet expected deadlines, adhere to Samsara’s requirements, or otherwise performs in a substandard manner, Samsara’s
ability to fulfill customer orders for products may be undermined. In addition, many of the third parties with whom Samsara contracts
may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including Samsara’s competitors, for whom they may also be conducting
development activities that could harm Samsara’s competitive position.
If
any of Samsara’s relationships with these third parties terminate, Samsara may not be able to enter into arrangements with alternative
third parties or do so on commercially reasonable terms.
In
addition, Samsara may be unable to establish any agreements with third-party manufacturers or to do so on acceptable terms. Even if Samsara
is able to establish agreements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails additional risks, including:
|
|
●
|
failure
of third-party manufacturers to comply with regulatory requirements and maintain quality assurance;
|
|
|
●
|
breach
of the manufacturing agreement by the third-party;
|
|
|
●
|
failure
to manufacture Samsara’s product according to Samsara’s specifications;
|
|
|
●
|
failure
to manufacture Samsara’s product according to Samsara’s schedule, or at all;
|
|
|
●
|
misappropriation
of Samsara’s proprietary information, including Samsara’s trade secrets and know-how; and
|
|
|
●
|
termination
or nonrenewal of the agreement by the third-party at a time that is costly or inconvenient for Samsara.
|
Any
performance failure on the part of Samsara’s existing or future manufacturers could delay product development, and any related
remedial measures may be costly or time consuming to implement. Samsara does not currently have arrangements in place for redundant supply
or a second source for all required raw materials used in the manufacture of Samsara’s products. If Samsara’s current third-party
manufacturers cannot perform as agreed, Samsara may be required to replace such manufacturers and Samsara may be unable to replace them
on a timely basis or at all. Samsara’s current and anticipated future dependence upon others for the manufacture of Samsara’s
products may adversely affect Samsara’s future profit margins and Samsara’s ability to commercialize any products on a timely
and competitive basis.
Samsara’s
reliance on third parties requires Samsara to share its trade secrets, which increases the possibility that Samsara’s trade secrets
will be misappropriated or disclosed.
Because
Samsara currently relies on third parties to manufacture its products, Samsara must, at times, share its proprietary technology and confidential
information, including trade secrets, with them. Samsara seeks to protect its proprietary technology, in part, by entering into confidentiality
agreements, consulting agreements or other similar agreements with its advisors, employees, consultants and contractors prior to beginning
research or disclosing proprietary information. These agreements typically limit the rights of the third parties to use or disclose Samsara’s
confidential information. Despite the contractual provisions employed when working with third parties, the need to share trade secrets
and other confidential information increases the risk that such trade secrets may become known by Samsara’s competitors, are intentionally
or inadvertently incorporated into the technology of others or are disclosed or used in violation of these agreements. Given that Samsara’s
proprietary position is based, in part, on Samsara’s know-how and trade secrets, and despite Samsara’s efforts to protect
its trade secrets, a competitor’s discovery of Samsara’s proprietary technology and confidential information or other unauthorized
use or disclosure would impair Samsara’s competitive position and may have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business,
financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Samsara
may seek to enter into collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements and may not be successful in doing so, and even if Samsara
is, it may not realize the benefits of such relationships.
Samsara
may seek to enter into collaborations, joint ventures, licenses and other similar arrangements for the development or commercialization
of Samsara’s products, due to capital costs required to develop or commercialize the products or manufacturing constraints. Samsara
may not be successful in its efforts to establish such collaborations for Samsara’s products. In addition, Samsara faces significant
competition in seeking appropriate strategic partners, and the negotiation process can be time consuming and complex. Further, any future
collaboration agreements may restrict Samsara from entering into additional agreements with potential collaborators. Samsara cannot be
certain that, following a strategic transaction or license, Samsara will achieve an economic benefit that justifies such transaction.
Even
if Samsara is successful in its efforts to establish such collaborations, the terms that Samsara agrees upon may not be favorable to
Samsara, and Samsara may not be able to maintain such collaborations.
In
addition, any potential future collaborations may be terminable by Samsara’s strategic partners, and Samsara may not be able to
adequately protect its rights under these agreements. Furthermore, strategic partners may negotiate for certain rights to control decisions
regarding the development and commercialization of Samsara’s products, if approved, and may not conduct those activities in the
same manner as Samsara would. Any termination of collaborations Samsara enters in the future, or any delay in entering into collaborations
related to Samsara’s products, could delay the development and commercialization of Samsara’s products and reduce their competitiveness
if they reach the market, which could have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business, financial condition and results of
operations.
Business
disruptions could seriously harm Samsara’s future revenue and financial condition and increase its costs and expenses.
Samsara’s
operations could be subject to earthquakes, power shortages, telecommunications failures, water shortages, floods, hurricanes, typhoons,
fires, extreme weather conditions, medical epidemics and other natural or manmade disasters or business interruptions, for which Samsara
is predominantly self-insured. Samsara relies on third- party manufacturers to produce Samsara’s products whose operations may
be disrupted by a man-made or natural disaster or other business interruption. The occurrence of any of these business disruptions could
seriously harm Samsara’s operations and financial condition and increase its costs and expenses.
Samsara
is subject to U.S. and certain foreign export and import controls, sanctions, embargoes, anti-corruption laws and anti-money laundering
laws and regulations. Compliance with these legal standards could impair Samsara’s ability to compete in domestic and international
markets. Samsara could face criminal liability and other serious consequences for violations, which could harm its business.
Samsara
is subject to export control and import laws and regulations, including the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, U.S. Customs regulations,
and various economic and trade sanctions regulations administered by the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Controls,
and anti-corruption and anti-money laundering laws and regulations, including the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended,
the U.S. domestic bribery statute contained in 18 U.S.C. § 201, the U.S. Travel Act, the USA PATRIOT Act, and other state and national
anti-bribery and anti-money laundering laws in the countries in which Samsara conducts activities. Anti-corruption laws are interpreted
broadly and prohibit companies and their employees, agents, clinical research organizations, contractors and other collaborators and
partners from authorizing, promising, offering, providing, soliciting or receiving, directly or indirectly, improper payments or anything
else of value to recipients in the public or private sector. Samsara can be held liable for the corrupt or other illegal activities of
its employees, agents, contractors and other collaborators and partners, even if Samsara does not explicitly authorize or have actual
knowledge of such activities. Any violations of the laws and regulations described above may result in substantial civil and criminal
fines and penalties, imprisonment, the loss of export or import privileges, debarment, tax reassessments, breach of contract and fraud
litigation, reputational harm and other consequences.
Samsara
may engage in strategic transactions that could impact its liquidity, increase its expenses and present significant distractions to Samsara’s
management.
From
time to time, Samsara may consider strategic transactions, such as acquisitions of companies, asset purchases and licensing arrangements.
Any future transactions could increase Samsara’s near- and long-term expenditures, result in potentially dilutive issuances of
Samsara’s equity securities, including its Common Stock, or the incurrence of debt, contingent liabilities, amortization expenses
or acquired in-process research and development expenses, any of which could affect Samsara’s financial condition, liquidity and
results of operations. Additional potential transactions that Samsara may consider in the future include a variety of business arrangements,
including spin-offs, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, restructurings, divestitures, business combinations and investments. Future
acquisitions may also require Samsara to obtain additional financing, which may not be available on favorable terms or at all. These
transactions may never be successful and may require significant time and attention of management. In addition, the integration of any
business that Samsara may acquire in the future may disrupt Samsara’s existing business and may be a complex, risky and costly
endeavor for which Samsara may never realize the full benefits of the acquisition. Accordingly, although there can be no assurance that
Samsara will undertake or successfully complete any additional transactions of the nature described above, any additional transactions
that Samsara does complete could have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business, results of operations, financial condition
and prospects.
If
Samsara fails to comply with its obligations in the agreements under which it licenses intellectual property rights from third parties,
or otherwise experiences disruptions in its business relationships with its licensors, Samsara could lose license rights that are important
to its business.
Samsara
is a party to several license agreements under which it is granted rights to intellectual property that are important to its business
and Samsara may enter into additional license agreements in the future. These license agreements impose, and Samsara expects that any
future license agreements where Samsara licenses intellectual property will impose, on Samsara, various development, regulatory and/or
commercial diligence obligations, payment of milestones and/or royalties and other obligations. If Samsara fails to comply with its obligations
under these agreements, or Samsara is subject to bankruptcy-related proceedings, the licensor may have the right to terminate the license,
in which event Samsara would not be able to market products covered by the license.
Samsara
may need to obtain licenses from third parties to advance its research or allow commercialization of its products, and Samsara cannot
provide any assurances that third-party patents do not exist which might be enforced against Samsara’s products in the absence
of such a license. Samsara may fail to obtain any of these licenses on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. Even if Samsara is able
to obtain a license, it may be non-exclusive, thereby giving Samsara’s competitors access to the same technologies licensed to
Samsara. In that event, Samsara may be required to expend significant time and resources to develop or license replacement technology.
If Samsara is unable to do so, Samsara may be unable to develop or commercialize the affected products, which could materially harm Samsara’s
business and the third parties owning such intellectual property rights could seek either an injunction prohibiting Samsara’s sales,
or, with respect to Samsara’s sales, an obligation on Samsara’s part to pay royalties and/or other forms of compensation.
Licensing of intellectual property is of critical importance to Samsara’s business and involves complex legal, business and scientific
issues. Disputes may arise between Samsara and its licensors regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
|
|
●
|
the
scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues;
|
|
|
●
|
whether
and the extent to which Samsara’s technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject
to the licensing agreement;
|
|
|
●
|
Samsara’s
right to sublicense patents and other rights to third parties;
|
|
|
●
|
Samsara’s
diligence obligations with respect to the use of the licensed technology in relation to its development and commercialization of
Samsara’s products, and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations;
|
|
|
●
|
Samsara’s
right to transfer or assign the license; and
|
|
|
●
|
the
ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by Samsara’s licensors
and Samsara and its partners.
|
If
disputes over intellectual property that Samsara has licensed prevent or impair Samsara’s ability to maintain its current licensing
arrangements on acceptable terms, Samsara may not be able to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates,
which would have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business.
Samsara’s
commercial success depends significantly on its ability to operate without infringing the patents and other proprietary rights of third
parties. Claims by third parties that Samsara infringes their proprietary rights may result in liability for damages or prevent or delay
Samsara’s developmental and commercialization efforts.
Samsara’s
commercial success depends in part on avoiding infringement of the patents and proprietary rights of third parties. However, Samsara’s
or its licensee’s research, development and commercialization activities may be subject to claims that Samsara or its licensee
infringes or otherwise violates patents or other intellectual property rights owned or controlled by third parties. Other entities may
have or obtain patents or proprietary rights that could limit Samsara’s or its licensee’s ability to make, use, sell, offer
for sale or import Samsara’s products, or impair Samsara’s competitive position. There is a substantial amount of litigation,
both within and outside the United States, involving patent and other intellectual property rights. Numerous third-party U.S. and foreign
issued patents and pending patent applications exist in the fields in which Samsara is developing products.
Because
patent applications are maintained as confidential for a certain period of time, until the relevant application is published Samsara
may be unaware of third-party patents that may be infringed by commercialization of any of Samsara’s products, and Samsara cannot
be certain that Samsara was the first to file a patent application related to a product candidate or technology. Moreover, because patent
applications can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending patent applications that may later result in issued patents
that Samsara’s products may infringe. In addition, identification of third-party patent rights that may be relevant to Samsara’s
technology is difficult because patent searching is imperfect due to differences in terminology among patents, incomplete databases and
the difficulty in assessing the meaning of patent claims. In addition, third parties may obtain patents in the future and claim that
use of Samsara’s technologies infringes upon these patents. Any claims of patent infringement asserted by third parties would be
time consuming and could:
|
|
●
|
result
in costly litigation that may cause negative publicity;
|
|
|
●
|
divert
the time and attention of Samsara’s technical personnel and management;
|
|
|
●
|
cause
development delays;
|
|
|
●
|
subject
Samsara to an injunction preventing Samsara from making, using, selling, offering for sale, or importing Samsara products;
|
|
|
●
|
prevent
Samsara from commercializing any of its products until the asserted patent expires or is held finally invalid or not infringed in
a court of law;
|
|
|
●
|
require
Samsara to develop non-infringing technology, which may not be possible on a cost-effective basis;
|
|
|
●
|
subject
Samsara to significant liability to third parties; or
|
|
|
●
|
require
Samsara to enter into royalty or licensing agreements, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, or
which might be non-exclusive, which could result in Samsara’s competitors gaining access to the same technology.
|
Although
no third-party has asserted a claim of patent infringement against Samsara as of the date of this prospectus, others may hold proprietary
rights that could prevent Samsara’s products from being marketed. Any patent-related legal action against Samsara claiming damages
and seeking to enjoin activities relating to Samsara’s products could subject Samsara to potential liability for damages, including
treble damages if Samsara were determined to have willfully infringed, and require Samsara to obtain a license to manufacture or develop
its products. Defense of these claims, regardless of their merit, would involve substantial litigation expense and would be a substantial
diversion of employee resources from Samsara’s business. Samsara cannot predict whether it would prevail in any such actions or
that any license required under any of these patents would be made available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. Moreover, even
if Samsara or its future strategic partners were able to obtain a license, the rights may be nonexclusive, which could result in Samsara’s
competitors gaining access to the same intellectual property. In addition, Samsara cannot be certain that it could redesign its products
to avoid infringement, if necessary. Accordingly, an adverse determination in a judicial or administrative proceeding, or the failure
to obtain necessary licenses, could prevent Samsara from developing and commercializing its products, which could harm Samsara’s
business, financial condition and operating results.
Parties
making claims against Samsara may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than Samsara can because
they have substantially greater resources. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual
property litigation or administrative proceedings, there is a risk that some of Samsara’s confidential information could be compromised
by disclosure. In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material
adverse effect on Samsara’s ability to raise additional funds or otherwise have a material adverse effect on Samsara’s business,
results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
If
Samsara is unable to protect the confidentiality of its trade secrets, its business and competitive position would be harmed.
In
addition, Samsara relies on the protection of its trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information
to maintain Samsara’s competitive position. Although Samsara has taken steps to protect its trade secrets and unpatented know-how,
including entering into confidentiality agreements with third parties, and confidential information and inventions agreements with employees,
consultants and advisors, Samsara cannot provide any assurances that all such agreements have been duly executed, and any of these parties
may breach the agreements and disclose Samsara’s proprietary information, including its trade secrets, and Samsara may not be able
to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is
difficult, expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the United States
are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets.
Moreover,
third parties may still obtain this information or may come upon this or similar information independently, and Samsara would have no
right to prevent them from using that technology or information to compete with Samsara. If any of these events occurs or if Samsara
otherwise loses protection for its trade secrets, the value of this information may be greatly reduced and Samsara’s competitive
position would be harmed. If Samsara does not apply for patent protection prior to such publication or if Samsara cannot otherwise maintain
the confidentiality of its proprietary technology and other confidential information, then Samsara’s ability to obtain patent protection
or to protect its trade secret information may be jeopardized.
Risks
Related to the Company’s Common Stock
An
active, liquid and orderly market for the Company’s Common Stock may not develop, and you may not be able to resell your Common
Stock at or above the purchase price.
Samsara’s Common Stock is quoted on
the OTCQB. An active trading market for the Company’s Common Stock has not developed and may never develop or be sustained. The
lack of an active market may impair an investor’s ability to sell its shares at the time it wishes to sell them or at a price that
it considers reasonable. An inactive market may also impair the Company’s ability to raise capital by selling shares and may impair
the Company’s ability to acquire other businesses or technologies using the Company’s shares as consideration, which, in
turn, could materially adversely affect the Company’s business.
The trading price of the shares of the Company’s Common Stock could be highly volatile, and purchasers of the Company’s Common
Stock could incur substantial losses.
The
Company’s stock price is likely to be volatile. The stock market in general has experienced extreme volatility that has often been
unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. As a result of this volatility, investors may not be able to sell their
Common Stock at or above their purchase price. The market price for the Company’s Common Stock may be influenced by those factors
discussed in this “Risk Factors” section and many others, including:
|
|
●
|
the
success or failure of the Company’s efforts to acquire, license or develop additional products;
|
|
|
●
|
innovations
or new products developed by the Company or its competitors;
|
|
|
●
|
announcements
by the Company or its competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments;
|
|
|
●
|
manufacturing,
supply or distribution delays or shortages;
|
|
|
●
|
any
changes to the Company’s relationship with any manufacturers, suppliers, licensors, future collaborators or other strategic
partners;
|
|
|
●
|
achievement
of expected product sales and profitability;
|
|
|
●
|
variations
in the Company’s financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to the Company;
|
|
|
●
|
trading
volume of the Company’s Common Stock;
|
|
|
●
|
an
inability to obtain additional funding;
|
|
|
●
|
sales
of the Company’s stock by insiders and stockholders;
|
|
|
●
|
general
economic, industry and market conditions other events or factors, many of which are beyond the Company’s control;
|
|
|
●
|
additions
or departures of key personnel; and
|
|
|
●
|
intellectual
property, product liability or other litigation against the Company.
|
Samsara
does not currently intend to pay dividends on its Common Stock, and, consequently, investors’ ability to achieve a return on your
investment will depend on appreciation, if any, in the price of the Company’s Common Stock.
Samsara
has never declared or paid any cash dividend on its Common Stock. Samsara currently anticipates that it will retain future earnings for
the development, operation and expansion of the Company’s business and does not anticipate declaring or paying any cash dividends
for the foreseeable future. Any return to stockholders will therefore be limited to the appreciation of their stock. There is no guarantee
that shares of the Company’s Common Stock will appreciate in value or even maintain the price at which stockholders have purchased
their shares.
Sales
of a substantial number of shares of the Company’s Common Stock by the Company’s stockholders in the public market could
cause the Company’s stock price to fall.
Sales
of a substantial number of shares of the Company’s Common Stock in the public market or the perception that these sales might occur
could significantly reduce the market price of the Company’s Common Stock and impair the Company’s ability to raise adequate
capital through the sale of additional equity securities.
If
the Company fails to maintain proper and effective internal control over financial reporting, the Company’s ability to produce
accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, investors may lose confidence in the Company’s financial reporting
and the trading price of the Company’s Common Stock may decline.
Pursuant
to Section 404 of Sarbanes-Oxley, the Company’s management is required to report upon the effectiveness of the Company’s
internal control over financial reporting. Additionally, if the Company reaches an accelerated filer threshold, the Company’s independent
registered public accounting firm will be required to attest to the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial
reporting. The rules governing the standards that must be met for management to assess the Company’s internal control over financial
reporting are complex and require significant documentation, testing and possible remediation. To comply with the requirements of being
a reporting company under the Exchange Act, the Company will need to upgrade its information technology systems; implement additional
financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures; and hire additional accounting and finance staff. If the Company
or, if required, its auditors are unable to conclude that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective,
investors may lose confidence in the Company’s financial reporting and the trading price of the Company’s Common Stock may
decline.
The
Company cannot assure its investors that there will not be material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in the Company’s internal
control over financial reporting in the future. Any failure to maintain internal control over financial reporting could severely inhibit
the Company’s ability to accurately report its financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. If the Company is unable
to conclude that its internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if the Company’s independent registered public
accounting firm determines the Company has a material weakness or significant deficiency in the Company’s internal control over
financial reporting once that firm begin its Section 404 reviews, investors may lose confidence in the accuracy and completeness of the
Company’s financial reports, the market price of the Company’s Common Stock could decline, and the Company could be subject
to sanctions or investigations by the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Failure to remedy any material weakness in the Company’s
internal control over financial reporting, or to implement or maintain other effective control systems required of public companies,
could also restrict the Company’s future access to the capital markets.
USE
OF PROCEEDS
We
will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares by the selling stockholder. As of the date hereof, we received $500,000 from the
sale of a Convertible Note to the selling stockholder under the Purchase Agreement. Within one day from the date we file the registration
statement of which this prospectus forms a part, we will receive another $500,000 from the sale of Convertible Notes to the selling stockholder.
Within one day from the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, we will receive up to another
$1,250,000 from the sale of Convertible Notes to the selling stockholder. These proceeds will be used for general corporate and working
capital or other purposes that our Board of Directors deems to be in our best interest. As of the date of this prospectus, we cannot
specify with certainty the particular uses for the net proceeds we may receive. Accordingly, we will retain broad discretion over the
use of these proceeds, if any.
Amount
of Proceeds from Sale of Convertible Notes
Shortly
after the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, we will have sold an aggregate of $1,250,000
of Convertible Notes. We may be required to make additional payments to the selling stockholder. These additional fees could total up
to $375,000, in which case we would have net proceeds from the sale of the Convertible Notes equal to $808,150. The following table set
out the payments we have made and may have to make in connection with the sale of $1,250,000 of Convertible Notes.
|
Interest
Payments (1)
|
|
$
|
125,000
|
|
|
Redemption
Premium (2)
|
|
$
|
62,500
|
|
|
Maximum
Liquidated Damages (3)
|
|
$
|
187,500
|
|
|
Total:
|
|
$
|
375,000
|
|
|
(1)
|
The
convertible notes mature in one year and bear interest at a rate of 10% per annum.
|
|
(2)
|
If
we redeem the convertible notes, we must pay an amount equal to the principal amount being redeemed plus a redemption premium equal
to 5% of the outstanding principal amount being redeemed plus outstanding and accrued interest.
|
|
(3)
|
In
the event the registration statements is not timely filed or declared effective, we must pay to the selling stockholder a cash amount
equal to 2% of the outstanding principal balance of the Notes as liquidated damages and not as a penalty. Liquidated damages shall
be capped at 15% of the principal of the Convertible Debentures.
|
We
have not made, and do not need to make, any payments to any affiliate of the Selling Shareholder, or any person with whom the Selling
Shareholder has a contractual relationship.
The
following sets forth upon the issuance of $1,250,000 of Convertible Notes, the gross proceeds paid or payable to us in connection with
our issuance of the Convertible Notes, all payments that have been made or that may be required to be made by us in connection with the
issuance of the Convertible Notes, our resulting net proceeds and the combined total possible profit to be realized as a result of any
conversion discounts regarding the Common Stock underlying the Convertible Notes.
|
Gross proceeds to the Company
|
|
$
|
1,250,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All payments that have been made or that may be required to be made by the Company to the Selling Shareholder in the first year of the convertible notes
|
|
$
|
375,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net proceeds to the Company if we make all such payments to the Selling Shareholder
|
|
$
|
875,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All payments that have been made or that may be required to be made by the Company to the Selling Shareholder in the first year of the convertible notes as a percentage of net proceeds
|
|
|
30
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The combined total possible profit to be realized as a result of any conversion discounts regarding the securities underlying the convertible notes (1)
|
|
$
|
312,501
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The combined total possible profit to be realized as a result of any conversion discounts regarding the securities underlying the convertible notes as a percentage of net proceeds
|
|
|
26.41
|
%
|
|
|
(1)
|
As
calculated in “Selling Stockholder - Potential Profits to Selling Stockholder” using
the date of issuance as the conversion date for the first tranche and the other tranches.
The actual profit as a result of the conversion discount cannot be calculated until conversion
as the conversion price depends on market conditions at and before conversion, and it may
be significantly greater.
|
DETERMINATION
OF OFFERING PRICE
The
selling stockholder will offer Common Stock at the prevailing market prices or privately negotiated price. The offering price of our
Common Stock does not necessarily bear any relationship to our book value, assets, past operating results, financial condition or any
other established criteria of value. Our Common Stock may not trade at market prices in excess of the offering price as prices for Common
Stock in any public market will be determined in the marketplace and may be influenced by many factors, including the depth and liquidity.
PLAN
OF DISTRIBUTION
The
Common Stock held by the selling stockholder may be sold or distributed from time to time by the selling stockholder directly to one
or more purchasers or through brokers, dealers, or underwriters who may act solely as agents at market prices prevailing at the time
of sale, at prices related to the prevailing market prices, at negotiated prices, or at fixed prices, which may be changed on any stock
exchange, market or trading facility on which the shares are traded or in private transactions. The sale of the selling stockholder’s
Common Stock offered by this prospectus may be affected in one or more of the following methods:
|
|
●
|
ordinary brokerage
transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
transactions involving
cross or block trades;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
a
purchase by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
an exchange
distribution in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
in privately
negotiated transactions;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
broker-dealers
may agree with the selling stockholders to sell a specified number of such shares at a stipulated price per share;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
“at
the market” into an existing market for the Common Stock;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
through the
writing of options on the shares;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
a combination
of any such methods of sale; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
any other
method permitted pursuant to applicable law.
|
In
order to comply with the securities laws of certain states, if applicable, the shares of the selling stockholder may be sold only through
registered or licensed brokers or dealers. In addition, in certain states, such shares may not be sold unless they have been registered
or qualified for sale in the state or an exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and complied with.
The
selling stockholder may also sell shares of Common Stock under Rule 144 promulgated under the Securities Act, if available, or any other
exemption available under the Securities Act rather than under this prospectus. In addition, the selling stockholder may transfer the
shares of Common Stock by other means not described in this prospectus.
The
selling stockholder may also sell the shares directly to market makers acting as principals and/or broker-dealers acting as agents for
themselves or their customers. Such broker-dealers may receive compensation in the form of discounts, concessions or commissions from
the selling stockholder and/or the purchasers of shares for whom such broker-dealers may act as agents or to whom they sell as principal
or both, which compensation as to a particular broker-dealer might be in excess of customary commissions. Market makers and block purchasers
purchasing the shares will do so for their own account and at their own risk. It is possible that the selling stockholder will attempt
to sell shares of Common Stock in block transactions to market makers or other purchasers at a price per share which may be below the
then market price. The selling stockholder cannot assure that all or any of the shares offered in this prospectus will be issued to,
or sold by, it.
Brokers,
dealers or agents participating in the distribution of the shares held by the selling stockholder as agents may receive compensation
in the form of commissions, discounts, or concessions from the selling stockholder and/or purchasers of the Common Stock for whom the
broker-dealers may act as agent. The selling stockholder may agree to indemnify any agent, dealer or broker-dealer that participates
in transactions involving sales of the shares if liabilities are imposed on that person under the Securities Act.
The
selling stockholder acquired the securities offered hereby in the ordinary course of business and has advised us that they have not entered
into any agreements, understandings or arrangements with any underwriters or broker-dealers regarding the sale of their shares of
Common Stock, nor is there an underwriter or coordinating broker acting in connection with a proposed sale of shares of Common Stock
by the selling stockholder. If we are notified by the selling stockholder that any material arrangement has been entered into with a
broker-dealer for the sale of shares of Common Stock, if required, we will file a supplement to this prospectus.
We
may suspend the sale of shares by the selling stockholder pursuant to this prospectus for certain periods of time for certain reasons,
including if the prospectus is required to be supplemented or amended to include additional material information.
If
the selling stockholder use this prospectus for any sale of the shares of Common Stock, it will be subject to the prospectus delivery
requirements of the Securities Act.
Regulation
M
The
anti-manipulation rules of Regulation M under the Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) may apply to sales
of our Common Stock and activities of the selling stockholder.
We
have advised the selling stockholder that while it is engaged in a distribution of the shares included in this prospectus it is required
to comply with Regulation M promulgated under the Exchange Act. With certain exceptions, Regulation M precludes the selling stockholder,
any affiliated purchasers, and any broker-dealer or other person who participates in the distribution from bidding for or purchasing
or attempting to induce any person to bid for or purchase any security which is the subject of the distribution until the entire distribution
is complete. Regulation M also prohibits any bids or purchases made in order to stabilize the price of a security in connection with
the distribution of that security. All of the foregoing may affect the marketability of the shares offered hereby this prospectus.
DESCRIPTION
OF SECURITIES
General
We are authorized by our articles of incorporation
to issue an aggregate of 7,500,000,000 shares of Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of which 1,447,955 were outstanding as of
August 23, 2021, and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock of which none were outstanding as of that date.
This
prospectus contains only a summary of the Common Stock the selling stockholder is offering.
The
following summary of the terms of our Common Stock and preferred stock, respectively, may not be complete and is subject to, and qualified
in its entirety by reference to, the terms and provisions of our Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (the “Articles
of Incorporation”) and our Bylaws, as amended (the “Bylaws”). You should refer to, and read this summary together with,
our amended and restated articles of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws to review all of the terms of our Common Stock and
preferred stock, respectively, that may be important to you.
Common
Stock
Holders
of our Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share held of record on each matter submitted to a vote of stockholders. Except
as otherwise expressly provided by the laws of the State of Nevada, or by the Articles of Incorporation at any and all meetings of the
stockholders of the Corporation there must be present, either in person or by proxy, stockholders owning a majority of the issued and
outstanding shares of the capital stock of the Corporation entitled to vote at said meeting. At any meeting of stockholders at which
a quorum is not present, the holders of, or proxies for, a majority of the stock, which is represented at such meeting, may adjourn the
meeting from time to time, without notice other than announcement at the meeting, until a quorum shall be present or represented.
To the
extent permitted by law, the Board shall have full power and discretion, subject to the provisions of the Articles of Incorporation,
to determine what, if any, dividends or distributions shall be declared and paid or made. Dividends may be paid in cash, in property,
or in shares of capital stock, subject to the provisions of the Articles of Incorporation. Before payment of any dividend, there may
be set aside out of any funds of the Company available for dividends such sums as the Directors think proper as a reserve or reserves
to meet contingencies, or for equalizing dividends, or for repairing or maintaining any property of the Company, or for such other purpose
as the Directors think conducive to the interests of the Company. The Directors may modify or abolish any such reserve in the manner
in which it was created.
Articles
of Incorporation and Bylaws
Our
articles of incorporation are silent as to cumulative voting rights in the election of our directors. Nevada law requires the existence
of cumulative voting rights to be provided for by a corporation’s articles of incorporation. In the event that a few stockholders
end up owning a significant portion of our issued and outstanding Common Stock, the lack of cumulative voting would make it more difficult
for other stockholders to replace our Board of Directors or for a third party to obtain control of us by replacing our Board of Directors.
Our articles of incorporation and bylaws do not contain any explicit provisions that would have an effect of delaying, deferring or preventing
a change in control of us.
Transfer
Agent and Registrar
The
transfer agent and registrar for our Common Stock is Worldwide Stock Transfer, LLC, 1 University Plaza Dr., #505, Hackensack, NJ 07601,
Phone: (201) 820-2008.
Listing
The shares of our Common Stock are quoted
on the OTCQB under the symbol SAML. On August 23, 2021, the last reported sale price per share for our Common Stock on the OTCQB market
as reported was $2.98.
THE
PURCHASE AGREEMENT
The
selling stockholders under this prospectus is offering for resale up to 361,596 shares of our Common Stock that may be issued upon conversion
of the Convertible Notes. On June 7, 2021, we entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with
the selling stockholder. Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, the selling stockholder has agreed to purchase from us up to an aggregate
of $1,250,000 (the “Purchase Price”) worth of Convertible Notes from time to time.
We
sold $500,000 worth of Convertible Notes to the selling stockholder on June 7, 2021, and we expect to sell an additional $500,000 within
three days of filing the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part and an additional $250,000 within three days of
the SEC’s declaration of effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The conversion price
will the lesser of (i) $8.188 and (ii) 80% of the lowest daily volume weighted average prices of the Company’s Common
Stock (as reported by Bloomberg Financial Markets) (“VWAP”) during the last ten (10) trading days immediately preceding the
date of such conversion. The Convertible Notes contemplated in the Purchase Agreement have a maturity date of one (1) year. The rate
of interest on the Convertible Notes will be 10% per annum.
We,
in our sole discretion, may redeem in cash any and all amounts owed under the Convertible Notes prior to Maturity by providing the selling
stockholder with five business days advance notice. In such a case, we would pay a redemption premium equal to 20% of the principal amount
being redeemed.
In
the event registration statements are not timely filed or declared effective, then the Company shall pay to the selling stockholder a
cash amount within three business days of the end of each month equal to 2% of the outstanding principal balance of the Notes as liquidated
damages and not as a penalty. Liquidated damages shall be capped at fifteen 15% of the Purchase Price paid by the selling stockholder.
As of August 23, 2021, there were 1,447,955
shares of our Common Stock outstanding, of which 1,099,063 shares were held by non-affiliates. If the selling stockholder converts the
Convertible Notes, the ownership position of the shareholders prior to the conversion would be diluted. If the selling stockholder converts
the Convertible Notes into all of the 361,596 shares being registered under the registration statement of which this prospectus forms
a part, such shares would represent 16.65% of all of our then outstanding shares and 22.89% of the then total number of shares held by
non-affiliates (assuming no further issuances). Under the terms of a Registration Rights Agreement entered into with the selling stockholder
at the same time as the Purchase Agreement, we must register with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission 361,596 shares of Common
Stock underlying the Convertible Notes for resale by the selling stockholder Under the Purchase Agreement, however, the Convertible Notes
may be converted into more than the 361,596 shares of our Common Stock being offered under this prospectus. The number of shares ultimately
offered for resale by the selling stockholder depends upon the number of Convertible Notes we sell to it under the Purchase Agreement,
the market price of our Common Stock and if we are in default on the Convertible Notes.
Issuances
of Convertible Notes in this offering will not affect the rights or privileges of our existing stockholders, except that the economic
and voting interests of each of our existing stockholders will be diluted as a result of any conversion of such notes. Although the number
of shares of Common Stock that our existing stockholders own will not decrease, the shares owned by our existing stockholders will represent
a smaller percentage of our total outstanding shares after any such issuance to the Equity Purchaser.
SELLING
STOCKHOLDER
The shares of Common Stock being offered by
the selling stockholder are those issuable to the selling stockholder upon conversion of the Convertible Notes. We are registering the
shares of Common Stock in order to permit the selling stockholder to offer the shares for resale from time to time.
The table below lists the selling stockholders
and other information regarding the beneficial ownership (as determined under Section 13(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as
amended, and the rules and regulations thereunder) of the shares of Common Stock held by the selling stockholder. The second column lists
the number of shares of Common Stock beneficially owned by the selling stockholders as of August 27, 2021, assuming conversion of the
Convertible Notes but taking account of any limitations on conversion and exercise set forth therein.
The
third column lists the shares of Common Stock being offered by this prospectus by the selling stockholder and does not take in account
any limitations on conversion of the Convertible Notes set forth therein.
The
fourth column assumes the sale of all of the shares offered by the selling stockholder pursuant to this prospectus.
Under
the terms of the Convertible Notes and the Purchase Agreement, the selling stockholder may not convert the Convertible Notes such that
selling stockholder or any of its affiliates would beneficially own a number of shares of our Common Stock which would exceed 9.99%.
The number of shares in the second column reflects these limitations. The selling stockholder may sell all, some or none of its shares
in this offering. See “Plan of Distribution.”
|
Name
of Selling Stockholder
|
|
Number
of Shares of Common Stock Owned Prior to Offering
|
|
|
Maximum
Number of Shares of Common Stock to
be Sold Pursuant
to this Prospectus (2)
|
|
|
Number
of Shares of Common Stock Owned After Offering (3)
|
|
|
Which
May Be
Sold in
This Offering as A Percentage of Currently
Outstanding Shares (4)
|
|
|
Percentage
of Shares of Common Stock Owned After the Offering (5)
|
|
|
YA
II PN, LTD. (1)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
361,596
|
|
|
|
414,157
|
|
|
|
16.65
|
%
|
|
|
22.89
|
%
|
|
(1)
|
YA
II PN, Ltd (“YA”) is the investor under the Purchase Agreement. Yorkville Advisors Global, LP (“Yorkville LP”)
is YA II PN, Ltd.’s. investment manager and Yorkville Advisors Global II, LLC (“Yorkville LLC”) is the General
Partner of Yorkville LP. All investment decisions for YA are made by Yorkville LLC’s President and Managing Member, Mr. Mark
Angelo. The address of YA is 1012 Springfield Avenue, Mountainside, NJ 07092, Attention: Mark Angelo, Portfolio Manager.
|
|
(2)
|
Includes
shares of Common Stock underlying the Convertible Notes that may held by the selling stockholder that are covered by this prospectus,
including any such securities that, due to contractual restrictions, may not be exercisable if such conversion or put would result
in beneficial ownership greater than 9.99%.
|
|
(3)
|
Represents
the difference between the maximum number of shares into which the principal and interest on the Convertible Notes may be converted
and the shares being registered under the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
|
|
(4)
|
Assumes
that the total number of our issued and outstanding Common Stock remains unchanged at 1,447,955 prior to the issuance of the common
shares underlying the Convertible Notes. If all of the shares are sold pursuant to this offering and the total number of our issued
and outstanding common shares otherwise remains unchanged at 361,596, such shares sold in this offering shall equal approximately
16.65% of the then issued outstanding shares of our Common Stock.
|
|
(5)
|
Assumes
that the total number of our issued and outstanding common shares remains unchanged at 1,447,955 prior to the issuance of the common
shares underlying the Convertible Notes, that the selling stockholder exercises its right to convert all of the principal and interest
on the Convertible Notes at $3.32 and that it sells all of the shares offered pursuant to this prospectus.
|
Additional
Selling Stockholder Information
|
Number
of Shares outstanding prior to the Convertible Notes transaction held by persons other than the Selling Shareholders, affiliates
of the Company, and affiliates of the Selling Shareholder
|
|
|
1,099,063
|
|
|
Number
of Shares registered for resale by the Selling Shareholder or affiliates of the Selling Shareholder in prior registration statements
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
Number
of Shares registered for resale by the Selling Shareholder or affiliates of the Selling Shareholder that continue to be held by the
Selling Shareholder or affiliates of the Selling Shareholder
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
Number
of Shares that have been sold in registered resale transactions by the Selling Shareholder or affiliates of the Selling Shareholder
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
Number
of Shares registered for resale on behalf of the Selling Shareholder or affiliates of the Selling Shareholder in the current transaction
|
|
|
1,099,063
|
|
BUSINESS
Formation
Samsara
Luggage, Inc. (the “Company” or “Samsara”) was incorporated on May 7, 2007 under the name, “Darkstar Ventures,
Inc.” under the laws of the State of Nevada. From the date of its formation until May 2011, the Company did not have any business
activity except for the development of its website and locating companies through which it could offer products. Once its proprietary
website was officially launched in July 2011, the Company engaged in the business of marketing eco-friendly health and wellness products,
such as air and water filtration systems, organic baby products, and eco-friendly beds and linens through affiliate marketing arrangements.
On
May 14, 2015, the founder of the Company, Chizkiyau Lapin, sold all of his shares of Common Stock of the Company, then constituting 51%
of the issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock of the Company, to Mr. Avraham Bengio. Beginning in April 2016, the Company began
to focus, through its wholly owned Israeli subsidiary, Bengio Urban Renewal Ltd. (“Bengio Urban Renewal”), in the area of
real estate development, particularly on the urban renewal market in Israel. As a result of the business activities of Bengio Urban Renewal,
the Company’s Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended July 31, 2016, which was filed on November 14, 2016, stated that the Company
was no longer a “shell” company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Reverse
Stock Split
On
March 17, 2021, the Company filed a Certificate of Change with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada (the “Certificate
of Change”) to affect a reverse split of Company’s Common Stock at a ratio of 1-for-7,000 (the “Reverse Stock Split”).
The Reverse Stock Split took effect at the open of business on Tuesday, March 23, 2021. As a result of the Reverse Stock Split, each
seven thousand (7,000) pre-split shares of Common Stock outstanding were automatically combined into one (1) new share of Common Stock
without any action on the part of the holders, and the number of outstanding shares of Common Stock was reduced from 5,995,825,131 shares
to 856,647 shares.
Merger
Transaction
On
November 12, 2019, the Company completed its merger with the Delaware corporation that was previously known as “Samsara Luggage,
Inc.” (“Samsara Delaware”) in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May
10, 2019, (the “Merger Agreement”) by and among the Company, Samsara Delaware, and Avraham Bengio, pursuant to which Samsara
Delaware merged with and into the Company, with the Company being the surviving corporation (the “Merger”). Following the
completion of the Merger, the business of the Company going forward became the business of Samsara Delaware prior to the Merger, namely,
the development and sale of smart luggage products.
The
Company filed (1) Articles of Merger with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company amended its Articles of
Incorporation to change the Company’s name from “Darkstar Ventures, Inc.” to “Samsara Luggage, Inc.” (the
“Name Change”); and (2) a Certificate of Amendment with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company
increased the number of authorized shares of Common Stock of the Company from 2,000,000,000 shares of Common Stock to 5,000,000,000 shares
of Common Stock.
In
connection with the Merger, the Company and Avraham Bengio entered into an Assignment and Assumption Agreement pursuant to which the
Company sold 100% of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s wholly-owned Israeli subsidiary, Bengio Urban Renewal and
all of the Company’s interest in Bengio Urban Renewal (including all debts and liabilities owed by the Company to Bengio Urban
Renewal and the debts of Bengio Urban Renewal to the Company) to Avraham Bengio, the former CEO and principal shareholder of the Company
(prior to the Merger).
At
the effective time of the Merger, each share of Common Stock of Samsara, $0.0001 par value, was converted into the right to receive 0.0654
shares of the Company’s Common Stock, such that the shareholders of Samsara Delaware were issued new shares of the Company representing
approximately 80% of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s Common Stock following the completion of the Merger. The
exchange rate was determined through arms-length negotiations between the Company and Samsara Delaware.
On
November 13, 2019, the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”) amended Section 3 of Article VII of the bylaws of
the Company to change the fiscal year end-date of the Company from July 31 to December 31.
On
October 5, 2020, the Company’s stockholders approved amending the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number
of authorized shares of Common Stock from 5,000,000,000 to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”). On November
3, 2020, the Company effected the Authorized Capital Increase by filing with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada a Certificate
of Amendment amending the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of Common Stock from
5,000,000,000 to 7,500,000,000.
Address
and Market for Securities
Our
principal executive offices are located at the following address: One University Plaza, Suite 505, Hackensack, NJ 07601. Our telephone
number is (877) 421-1574. Our website is www.samsaraluggage.com.
Our Common Stock is quoted on the OTCQB under
the symbol “SAML.” On August 23, 2021, the closing price for shares of our Common Stock as reported on the OTCQB was $2.98
per share.
Bankruptcy,
Receivership or Similar Proceeding
We
have never declared bankruptcy, have never been in receivership, and have never been involved in any legal actions or proceedings.
Transactions
during 2020
Convertible
Loan Agreement (YA II PN, Ltd.)
On
September 3, 2020, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YA II PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”),
pursuant to which the Investor will invest an aggregate amount of $220,000 in two tranches, and the Company will issue convertible debentures
and warrants to the Investor. The first tranche of the investment in the amount of $150,000 will be provided upon signature of the SPA.
The second tranche in the amount of $70,000 was provided on October 7, 2020. The funds are expected to be used to finance Samsara’s
working capital and other general corporate needs.
Each
tranche of the investment will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable after two years. Each tranche
of the investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the
lower of (a) $0.003 per share, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted average price for the Company’s Common
Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date.
As
part of the transaction, the Company issued to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 2,619 shares of Common Stock, at an
exercise price equal to $0.003. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment
or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant
being exercised.
The
Company undertook to increase its authorized shares of Common Stock to at least 7,000,000,000 within 90 days of the closing.
The
SPA and the convertible debentures contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the convertible debentures
by the maturity date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s right to convert
the convertible debentures into shares of Common Stock.
On
April 19, 2021, the Investor exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $40,000
and the accrued interest in the amount of $7,067 into 40,861 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
Convertible
Loan Agreement (Power Up Lending Group Ltd.)
On
June 26, 2020, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“Power Up SPA”) with Power Up Lending Group Ltd.
(the “Power Up”), pursuant to which Power Up agreed to provide the Company with an initial investment in the form of a convertible
loan in the principal amount of $66,700 (the “Initial Investment”). The Power Up SPA contemplates additional financing of
up to $925,000 in the aggregate, subject to the agreement of both parties. The funds are expected to be used to finance the Company’s
working capital needs.
The
convertible loan will bear interest at an annual rate of eight percent (8%) with a maturity date of June 25, 2021 (the “Maturity
Date”). The loan will be convertible after six months into shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a conversion price equal
to seventy-five percent (75%) of the average of the lowest trading price for the Company’s Common Stock during the twenty (20)
trading day period prior to the conversion date. The Company agreed to an original issue discount of $8,700 and to reimburse the Investor
for its costs in the amount of $3,000. Accordingly, the net proceeds to the Company from the Initial Investment amounted to $55,000.
The
Power Up SPA and the convertible note contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the loan amount by the
Maturity Date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of Power Up’s right to convert the loan
amount into shares of Common Stock.
On
December 28, 2020 and pursuant to the Power Up SPA, Power Up exercised its option to convert the convertible note principal in the amount
of $38,100 into 36,286 shares of Common Stock of the Company. On December 31, 2020, Power Up exercised its option to convert the convertible
note principal in the amount of $23,100 into 22,000 shares of Common Stock of the Company. On January 11, 2021, Power Up exercised its
option to convert the convertible note principal in the amount of $ 7,000 into 7,448 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
Business
Strategy
Samsara
Luggage focuses on the travel sector, specializing in high-tech smart luggage and protective travel products and accessories. The company’s
hero products are carry-on trolley suitcases with a variety of tech features. The current model is equipped with a smart unit that uses
Bluetooth technology to connect to a mobile app to send notifications when the suitcase is moving away or being opened out of sight.
The smart unit also doubles as a powerful removable battery and has an LED light that turns on automatically when it senses darkness.
This model is made of a durable and lightweight aluminum in two colorways.
The
Next Generation collection has the most advanced tech features including a GPS tracking system and Wi-Fi Hotspot. This collection will
be available in both aluminum and a sturdy polycarbonate material in a variety of colorways.
Samsara
Luggage differentiates itself in the consumer marketplace with its unique technology and the ergonomic design of the suitcase. The company
stays ahead of the competition with the most advanced tech features partnered with a design that allows the suitcase to double as a portable
desk and charging station. Tech-savvy features, functional design and quality materials distinguishes Samsara Luggage from its competitors
and in the consumer market.
Samsara
strategically sources mid-tier materials that are low-cost and abundant, yet also durable, high-quality, and luxurious. This allows the
company to attract consumers with superior products at a moderate price range. This business model also helps the company maximize its
earnings and profits.
In
2020, Samsara launched Sarah and Sam, an online fashion and lifestyle brand to create a new revenue stream during the coronavirus pandemic.
Sarah and Sam leveraged Samsara Luggage’s digital assets and supply chain capabilities to launch the new online brand that compliments
the aesthetic of Samsara Luggage. Sarah and Sam generated significant sales during the pandemic and continues to bring revenues to the
company.
Due
to COVID-19, Samsara postponed the launch of its Next-Gen line of suitcases that were presented in January 2020 at the CES exhibition.
The Company decided to make changes to its business plan and developed alternative product lines to create a new revenue stream during
the coronavirus pandemic. These new products are all sold online by Samsara’s digital unit utilizing the Company’s digital
assets.
|
|
●
|
In
March 2020, Samsara launched the “Essentials Kit” a curation of safety products for travelers and commuters to stay protected
during the pandemic.
|
|
|
●
|
In
July 2020, Samsara launched the “Nano Weekender Bag,” an overnight travel bag treated with a layer of bacteriostatic
Nano protection that prevents colonies of bacteria from developing on fabric.
|
|
|
●
|
In
the fourth quarter of 2020, Samsara expanded its D2C activities with the launch of its “Sarah & Sam” Fashion and
Lifestyle Collection on a new dedicated website: www.sarah-sam.com.
|
Research and Development
Samsara
performs research and development in the fields of materials, design, and technology to develop new features and functionality, such
as Wi-Fi hotspots, SIM cards, GPS, Bluetooth, RFID, built-in batteries, digital scaling, tracking systems, and automated locking.
Samsara’s
R&D team is also exploring ways to add new Internet of Things (IoT) components to its existing smart luggage product such as a Samsara
online community platform and integration with airline and airport systems. Additionally, Samsara’s R&D team is exploring new
composite materials to use in Samsara’s luggage products.
Samsara
works with three designers on an ongoing basis, and with NOA Labs Ltd., a Hong Kong company. Samsara’s R&D activities are overseen
by David Dahan.
Manufacturing
Samsara
utilizes two manufacturers in China to manufacture its smart luggage products, and utilizes contractors to provide order fulfilment services.
Marketing
and Sales
Samsara
Luggage is focused on conceptualizing and executing new marketing strategies that will attract a broader audience and strengthen its
marketing assets. Samsara’s current customer base includes business professionals that travel extensively for work or tech-minded
consumers that are always looking for the latest in technology and modern design. With the launch of the Next Generation collection of
suitcases we will be introducing a new price point and advanced technologies that will suit the needs of a variety of travelers that
are younger and use social media to showcase their purchases and travel adventures.
Samsara’s
marketing efforts will focus on increasing online sales and expanding its target audience to strengthen its digital assets that proved
to be an asset during the coronavirus pandemic.
Marketing
and Sales Strategy
Samsara’s
Digital Unit designs and implements a direct-to-consumer sales and marketing strategy using its hero product, the smart carry-on suitcase.
The Digital Unit creates digital assets that are an integral part of the company’s intellectual property and develops sales techniques
to advertise and sell Samsara’s products online.
In
addition, a newly established Professional Media Unit provides organic online exposure that is leveraged as “social proof”
on the Samsara website, social media platforms and all advertising assets.
These
two pillars are key to meeting the company’s sales and marketing goals.
Company
D2C Website
Samsara’s
most important digital asset is its website. The site runs on an ecommerce retail platform designed to work directly with the digital
marketing assets and supply chain system. The Digital Unit updates the site’s contents daily for search engine optimization that
will drive new traffic to the site from all over the world.
Inhouse
Lists of Identified Users
The
list of identified users Samsara has gained over time helps to increase sales from customers who return to the site after not making
a purchase on their first visit.
Mailing
Lists
The
mailing list is composed of buyers, potential customers who subscribe to receive updates and customers who responded to emails from previous
mailing lists. This list helps the company continually communicate with customers regarding upcoming promotions and new product launches.
This list helps Samsara increase its conversions and acquire repeat buyers.
Social
Media Presence – Paid and Organic
Samsara
uses its digital assets to attract its target audience who is very active on various social media platforms. Samsara’s paid and
organic posts are geared towards converting sales from social media users and increasing the company’s social following on all
the online social networks.
Building
Digital Sales Capabilities
Samsara’s
digital sales are reliant on leveraging digital assets and establishing multiple sales channels using valuable data to target potential
customers.
The
Digital Unit gathers information from all the digital activity accrued from Samsara’s advertising, public relations, and branding
initiatives. Using this information, we can use targeted algorithms to reach potential customers and achieve higher conversion rates.
Advertising
Advertising
in recognizable media outlets (Google, Facebook, etc.) and tracking sales conversions helps us identify our buyer personas to an accurate
degree. We can leverage this information to target this customer profile precisely through paid media opportunities.
|
|
-
|
Partnerships
with External Content Providers
|
|
|
o
|
Partnerships
with Affiliates.
|
|
|
-
|
Use
of Designated Mailing Lists
|
Promoting
products to target audiences and groups that offer promotional content to their extensive relevant mailing lists.
|
|
-
|
Selling
on Online Trading Platforms
|
Samsara
has established relationships with sellers in online trading platforms with affiliate programs.
Competition
Samsara’s
primary competitors offering aluminum suitcases in the carry-on luggage market include Away, Rimowa, Samsonite (Tumi), and Zero Halliburton.
|
Competitor
|
|
Product
|
|
Price
|
|
|
Features
|
|
Away
|
|
Aleon
21” Carry-On Aluminum Hardside Luggage
|
|
$
|
549
|
|
|
●
|
Dimensions:
20.9 x 15.7 x 9.0 inches, Weight: 10.6 lbs., Volume: 2098 cubic inches
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Lightweight
and extremely durable Aircraft Grade Aluminum Frame and Body with two TSA-Approved Resettable Combination Locks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Interior
Compression Packing System will keep items from shifting to the bottom, and prevent wrinkles
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
A
telescoping handle, 360-degree spinner wheels, double reinforced square corners for extra space, a fitted rubber seal makes the case
water-resistant and airtight; piano hinges extend the length of the case for added durability
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
10-year
Worry Free Warranty
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rimowa
|
|
Rimowa
Topas IATA Carry- On Luggage 21” Inch Multi-wheel 32L TSA Lock Spinner Suitcase Silver
|
|
$
|
799
|
|
|
●
|
Dimensions:
21.7 x 7.9 x 15.7 inches
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
4-wheel
spinners for smooth-rolling mobility in any direction
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
The
height-adjustable Flex-Divider system on the interior can also be set to accommodate the exact volume of your luggage and keeps your
belongings in the greatest possible order
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Integrated
in the case, the innovative TSA lock that can be opened without damage during security checks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zero
Halliburton
|
|
Zero
Halliburton Geo Aluminum 3.0
International Carry-On (Silver)
|
|
$
|
850
|
|
|
●
|
Dimensions:
15 x 8 x 21 inches
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Made
in USA from imported materials. Utilizes premium anodized aluminum that is as strong as steel but only one-fourth the weight. Innovative
and unique double-rib design provides additional strength and durability as well as optimum protection of its contents. The intuitive
3-stage dual-button handle system allows for quicker release for both left and right-handed travelers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Designed
to securely close using two TSA accepted combination locks that are integrated into the draw-bolt latches. Seals airtight with the
addition of a neoprene gasket seal around the opening’s perimeter.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
The
spinner wheels provide convenient and controlled ‘by-your-side’ mobility for easy traveling. Our superior piano hinge
is used to keep the shells of each case in alignment and adds additional strength and integrity to the seal.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
The
interior is divided into two compartments with flat panels in place to hold clothes securely and discreetly. Our signature lining
is stain-resistant and non-abrasive to clothes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Our
newly introduced ZH Global Tracking allows your case to be tracked anywhere in the world, providing additional peace of mind for
your travel.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Samsonite
|
|
Samsonite
LITE-BOX ALU SPINNER (4 WHEELS) 55CM
|
|
$
|
667
|
|
|
●
|
Dimensions:
55 x 40 x 23 cm (including handles, wheels, bottom glides, side pockets and other external parts)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Volume:
40 L
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Weight:
4.7 kg
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Warranty:
Limited 10-year global warranty
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Model:
Spinner (4 wheels)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Color:
Aluminum
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Material:
100% High-end anodized aluminum
|
Intellectual
Property
Samsara
owns a design patent on its carry-on luggage product, filed in the United States (136531) on October 3, 2017, in Europe (004385086-0001)
on October 4, 2017, in China (315400) on October 9, 2017 and in Israel (60249) on April 6, 2017. Samsara also owns registered trademarks
on the “Samsara” trade name in Europe and the US.
Government
Regulations
Several
aspects of Samsara’s smart luggage products, including its battery, locks and LED lights, are subject to the requirements of federal
law relating to aviation and homeland security, as well as international regulation of electronic devices. Part 15 of the FCC Rules requires
operation of electronic equipment not to cause harmful interference and to accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation. The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) recommends that only TSA approved locks be used on luggage,
to avoid risk of TSA agents breaking the lock for inspection. The European Union requires all electronic devices to comply with the Restriction
of Hazardous Substances (ROHS) regulations which restricts the use of specific hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic
products. BS EN 62471 gives universal best-practice recommendations for the photobiological safety of electric lamps and lighting systems,
including LED lights. This standard specifies exposure limits, measurement techniques and classification systems to control photobiological
and light hazards. The EU radio equipment directive establishes a regulatory framework for placing radio equipment on the market, setting
requirements for safety and health, electromagnetic compatibility, and the efficient use of the radio spectrum. Additionally, smart luggage
products are subject to airline regulations applicable to manufacturing materials, size and weight.
Samsara
believes that it is in substantial compliance with the laws and regulations which regulate its business, as detailed below:
Air
Travel Regulations
The
Samsara Luggage Carry-on case complies with all airline regulations applicable to manufacturing materials, size and weight. Additionally,
it incorporates all the electronic parts into one removeable unit, leaving an option for the suitcase to be completely electronic free,
if needed, in compliance with the airline regulations of January 2018, requesting passengers to remove batteries from checked-in smart
luggage.
Samsara
carry-on locks, bearing the Travel Sentry logo, meet TSA recommendations for accepted locks which can be opened by the TSA without being
broken.
Electronic
Equipment
On
March 12, 2018, Samsara received a Grant of Equipment Authorization Certification Issued Under the Authority of the Federal Communications
Commission stating that the Samsara smart unit is in compliance with the FCC part 15c (Regulating the interference of electronic equipment
during operation).
On
April 17, 2018, Samsara received a Certificate of Compliance with the European Union RoHS regulations (regulating and restricting the
use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment).
On
January 25, 2018, Samsara received an Attestation of Global Compliance with regulation EN 62471 (regulation of the photo biological safety
of lamps and lamp systems).
On
February 27, 2018, Samsara received the EU-RED (Radio Equipment Directive) Certificate of Conformity (regulating radio equipment, electromagnetic
compatibility, and the efficient use of the radio spectrum.)
Employees
Samsara
does not have any employees. All of its business activities are performed by independent contractors and third-party service providers.
MARKET
FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market
Information
Our Common Stock is listed on OTCQB under
the symbol “SAML.” The market for our Common Stock is limited, volatile and sporadic. The following table sets forth, for
the periods indicated, the high and low bid prices of our Common Stock on the OTCQB as reported by Google Finance. The following quotations
reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, markdown, or commissions, and may not reflect actual transactions. Those fiscal
quarters during which there were no sales of our Common Stock have been labeled as “n/a.”
|
|
|
High Bid
|
|
|
Low Bid
|
|
|
Fiscal Year 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 30, 2021
|
|
$
|
8.40
|
|
|
$
|
1.40
|
|
|
March 31, 2021
|
|
$
|
14.69
|
|
|
$
|
1.40
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Year 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2020
|
|
$
|
9.79
|
|
|
$
|
1.40
|
|
|
September 30, 2020
|
|
$
|
11.19
|
|
|
$
|
4.90
|
|
|
June 30, 2020
|
|
$
|
31.47
|
|
|
$
|
11.19
|
|
|
March 31, 2020
|
|
$
|
48.25
|
|
|
$
|
13.99
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Year 2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2019
|
|
$
|
244.76
|
|
|
$
|
17.48
|
|
|
September 30, 2019
|
|
$
|
55.24
|
|
|
$
|
16.78
|
|
|
June 30, 2019
|
|
$
|
174.83
|
|
|
$
|
9.79
|
|
|
March 31, 2019
|
|
$
|
16.78
|
|
|
$
|
8.39
|
|
The last reported sales
price for our shares of Common Stock on the OTCQB as of August 23, 2021, was $2.98 per share. As of August 12, 2021, we had approximately
170 shareholders who held shares of Common Stock through securities position listings.
Dividend
Policy
We
have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our Common Stock. For the foreseeable future, we intend to retain any earnings to finance
the development and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our Common Stock. Any future determination
to pay dividends will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend upon then existing conditions, including our financial
condition and results of operations, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, business prospects and other factors that the board
of directors considers relevant.
Securities
Authorized for Issuance under Compensation Plans
None.
Stock
Incentive Plan
None.
MANAGEMENT’S
DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL
CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
Samsara
Luggage, Inc. was incorporated in the State of Nevada on May 7, 2007, under the name “Darkstar Ventures, Inc.” under the
laws of the State of Nevada. Currently, the Company develops and sells smart luggage products.
Recent
Developments
Reverse
Stock Split
On
March 17, 2021, the Company filed a Certificate of Change with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada (the “Certificate
of Change”) to effect a reverse split of Company’s common stock at a ratio of 1-for-7,000 (the “Reverse Stock Split”).
The Reverse Stock Split took effect at the open of business on Tuesday, March 23, 2021. As a result of the Reverse Stock Split, each
seven thousand (7,000) pre-split shares of common stock outstanding automatically combined into one (1) new share of common stock without
any action on the part of the holders, and the number of outstanding shares common stock were reduced from 5,995,825,131 shares to 856,546
shares (subject to rounding of fractional shares).
No
fractional shares were issued in connection with the Reverse Stock Split. The Company issued one whole share of the post-Reverse Stock
Split Common Stock to any stockholder who otherwise would have received a fractional share as a result of the Reverse Stock Split.
Increase
in Authorized Share Capital
On
October 5, 2020, the Board of Directors of the Company approved, and the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our
common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, (the “Common Stock”), executed a written consent in lieu of a meeting that approved,
amending the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of Common Stock from 5,000,000,000
to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”).
On
November 3, 2020, the Company effected the Authorized Capital Increase by filing with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada a
Certificate of Amendment amending the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of Common
Stock from 5,000,000,000 to 7,500,000,000.
YAII
PN Ltd. Convertible Debentures
September
2020
On
September 3, 2020, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”),
pursuant to which the Investor invested an aggregate amount of $220,000 in two tranches, and the Company issued convertible debentures
and warrants to the Investor. The first tranche of the investment in the amount of $150,000 was provided upon signature of the SPA. The
second tranche in the amount of $70,000 was provided on October 7, 2020. The funds are expected to be used to finance the Company’s
working capital and other general corporate needs. Each tranche of the investment will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent
(10%) and will be repayable after two years. Each tranche of the investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s
Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $0.003 per share, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted
average price for the Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date.
As
part of the transaction, the Company issued to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 18,333,333 shares of Common Stock, at
an exercise price equal to $0.003. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash
payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of
the warrant being exercised.
The
Company undertook to increase its authorized shares of Common Stock to at least 7,000,000,000 within 90 days of the closing.
The
foregoing descriptions of the terms and conditions of the SPA and the convertible debentures are qualified in their entirety by reference
to the full text of the SPA and the convertible debentures.
The
Company issued the convertible debentures and the warrants under the exemptions from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the
Securities Act of 1933. The Company expect that any issuance of shares of Common Stock pursuant to the terms of the convertible debentures
and the warrants will be exempt from registration under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities
Act”), and regulations promulgated thereunder. None of these transactions involved any underwriters, underwriting discounts or
commissions, or any public offering, and the Investor had adequate access, through their relationships with the Company, to information
about the Company.
The
shares of Common Stock to be issued in the event of conversion of the convertible debentures and upon exercise of the warrants will not
be registered under the Securities Act, or any state securities laws, and may not be offered or sold in the United States absent registration
or an applicable exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act.
April
2021
On
April 6, 2021, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“Second SPA”) with the Investor, pursuant to which
the Investor will invest $150,000, and the Company will issue a convertible debenture and warrants to the Investor. The $150,000 investment
was provided upon signature of the Second SPA. The investment will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable
after two years. The investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a conversion price
equal to the lower of (a) $3.46, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted average price for the Company’s Common
Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date.
As
part of the transaction, the Company issued to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 10,838 shares of Common Stock, at an
exercise price equal to $3.46. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment
or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant
being exercised.
Financial
Overview
Critical
Accounting Policies and Estimates
This
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations discusses our financial statements, which
have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”).
In connection with the preparation of our financial statements, we were required to make assumptions and estimates about future events
and apply judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses and the related disclosures. We base our
assumptions, estimates and judgments on historical experience, current trends and other factors that management believes to be relevant
at the time our consolidated financial statements are prepared. On a regular basis, management reviews the accounting policies, assumptions,
estimates and judgments to ensure that our financial statements are presented fairly and in accordance with U.S. GAAP. However, because
future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty, actual results could differ from our assumptions and estimates,
and such differences could be material. As applicable to the consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus,
the most significant estimates and assumptions relate to the going concern assumptions and convertible loans Derivative Liabilities and
Fair Value of Financial Instruments.
Our
significant accounting policies are discussed in Note 2, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” of the notes to consolidated
financial statement, which are incorporated by reference into this prospectus. Our management believes that, as for the financial statements
for the periods included in this prospectus, the “going concern” assessment and accounting for Derivative Liabilities and
Fair Value of Financial Instruments are critical accounting policies. However, due to the early stage of operations of our Company, there
are no other accounting policies that are considered to be critical accounting policies by management.
Going
Concern Uncertainty
The
development and commercialization of our product will require substantial expenditures. We have not yet generated any material revenues
and have incurred substantial accumulated deficit and negative operating cash flows. We currently have no sources of recurring revenue
and are therefore dependent upon external sources for financing its operations. There can be no assurance that we will succeed in obtaining
the necessary financing to continue our operations. As a result, our independent registered public accounting firm has expressed substantial
doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from
the outcome of this uncertainty.
Results
of Operations
Six months ended June 30,
2021 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2020
Revenue
The Company generates revenues through
the sale and distribution of smart luggage products and sales through the Sarah & Sam fashion brand. Revenues during the six
months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $184,000 compared to $351,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2020. The decrease in
the total revenue is mainly due to the Essentials Kits sales in second quarter of 2020, that increased sales dramatically, offering
COVID essentials products that were in high demand at the beginning of the pandemic. Revenues generated exclusively by Sarah &
Sam during the six months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $150,000 with a gross profit of $80,000 which represents a gross profit
margin of 53.3%. Revenues for the second quarter ending June 30, 2021 grew by 200% with an increase in new cluster sales from its
newest vertical Sarah and Sam. Samsara launched Sarah & Sam, a fashion and lifestyle collection in the fourth quarter of
the 2020 fiscal year. Sarah & Sam is a part of Samsara Direct, a new business model initiated in response to the travel
restrictions enforced due to the coronavirus pandemic. Samsara Direct leverages the company's established digital
assets and manufacturing and fulfillment supply chain capabilities to offer additional consumer products that respond to the
changing needs of the market.
Costs of Revenue
Costs of revenue consists of the purchase
of raw materials and the cost of production. Cost of revenues during the six months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $141,000 compared
to $186,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2020. The decrease in the costs of revenue is mainly due to decrease in sales as described
above.
Gross Profit
During the six months ended June 30,
2021, Gross Profit totaled $43,000, representing a Gross Profit margin of 23.36%. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, Gross
Profit totaled $165,000, representing a Gross Profit margin of 47%.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses totaled $777,000 during
the six months ended June 30, 2021, compared to $851,000 during the six months ended June 30, 2020, representing a net decrease
of $74,000. The decrease in the operating expenses is mainly due to decrease in the research and development and selling and marketing
expenses.
Financing Income (expenses)
Financing expenses totaled $1,743,000 during
the six months ended June 30, 2021 compared to a financing income of $461,000 during the six months ended June 30, 2020 representing
a net decrease of 2,204,000. The increase in the financing expenses is mainly due to increase in the expenses in respect of warrants
issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses mostly attributed to the conversion of the warrants into
the Common Shares of the Company.
Net Profit/Loss
We realized a net loss of $2,477,000 for the
six months ended June 31, 2021, as compared to a net loss of $225,000 for the six months ended June 31, 2020, for the reasons
described above.
Three months ended June 30,
2021 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2020
Revenue
The Company generates
revenues through the sale and distribution of smart luggage products and sales through the Sarah & Sam fashion brand. Revenues during
the three months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $109,000 compared to $330,000 for the three months ended June 30, 2020.The decrease
in the total revenue is mainly due to the Essentials Kits sales in Q2 of 2020, that increased sales dramatically, offering COVID essentials
products that were in high demand at the beginning of the pandemic. Revenues generated exclusively by Sarah & Sam during the three
months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $98,000 with a gross profit of $45,000 which represents a gross profit margin of 46%.
Costs of Revenue
Costs of revenue consists
of the purchase of raw materials and the cost of production. Cost of revenues during the three months ended June 30, 2021 totaled
$104,000 compared to $172,000 for the three months ended June 30, 2020. The increase in the costs of revenue is mainly due to increase
in sales as described above.
Gross Profit
During the three months
ended June 30, 2021, Gross Profit totaled $5,000, representing a Gross Profit margin of 4.58%. During the three months ended June 30,
2020, Gross Profit totaled $158,000, representing a Gross Profit margin of 48%.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses totaled
$451,000 during the three months ended June 30, 2021, compared to $487,000 during the three months ended June 30, 2020, representing
a net decrease of $36,000. The decrease in the operating expenses is mainly due to decrease in the research and development, selling
and marketing expenses.
Financing Income (expenses)
Financing expenses totaled
$1,396,000 during the three months ended June 30, 2021 compared to a financing expenses of $58,000 during the three months ended
June 30, 2020 representing a net increase of 1,338,000. The increase in the operating expenses is mainly due to increase in the
expenses in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses. The decrease in the financing
expenses is mainly due to increase in the expenses in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest
expenses mostly attributed to the conversion of the warrants into the Common Shares of the Company.
Net Profit/Loss
We realized a net loss
of $1,842,000 for the three months ended June 31, 2021, as compared to a net loss of $387,000 for the three months ended June 31,
2020, for the reasons described above.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
Liquidity
is the ability of a company to generate funds to support its current and future operations, satisfy its obligations, and otherwise operate
on an ongoing basis. Significant factors in the management of liquidity are funds generated by operations, levels of accounts receivable
and accounts payable and capital expenditures.
As of June 30, 2021, the Company had $197,000
of cash, total current assets of $294,000, and total current liabilities of $1,166,000, creating a working capital deficit of $872,000.
As of December 31, 2020, the Company had $54,000 of cash, total current assets of $211,000 and total current liabilities of $1,127,000
creating a working capital deficit of $916,000. The decrease in our working capital deficit was mainly attributable to decrease of $46,000
in cash and cash equivalents.
Net cash used in operating activities was
$285,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2021, as compared to cash used in operating activities of $376,000 for the six months
ended June 30, 2020. The Company’s primary uses of cash have been for research and development expenses, sales and marketing
expenses, and working capital purposes.
Net cash provided by financing activities
was $428,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2021, as compared to $55,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2020.
We
have principally financed our operations through the sale of our common stock and the issuance of debt. Due to our operational losses,
we relied to a large extent on financing our cash flow requirements through issuance of common stock and debt. There can be no assurance
we will be successful in raising the necessary funds to execute our business plan.
Year
ended December 31, 2020, compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Revenue
The
Company generates revenues through the sale and distribution of smart luggage products. Revenues during the year ended December 31, 2020,
totaled $468,000, compared to $649,000 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease in the total revenue is mainly due to the fact
that the 2019 revenues included proceeds from the Company’s crowdfunding campaign.
Costs
of Revenue
Costs
of revenue consists of the purchase of raw materials and the cost of production. Cost of revenues during the year ended December 31,
2020, totaled $285,000, compared to $525,000 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease in the total revenue is mainly due to
the decrease in sales.
Gross
Profit
During
the year ended December 31, 2020, Gross Profit totaled $183,000, representing a Gross Profit margin of 39.1%. During the year ended December
31, 2019, Gross Profit totaled $124,000 representing Gross Profit margin of 19%.
Operating
Expenses
Operating
expenses totaled $1,636,000 during the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to $2,031,000 during the year ended December 31, 2019,
representing a net decrease of $395,000. The increase in the operating expenses is mainly due to increase in the growth of the Company’s
business. The decrease in the total revenue is mainly due to the decrease in sales.
Net
Loss
We
incurred a net loss of $1,140,000 for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to a net loss of $3,142,000 for the year ended December
31, 2019, for the reasons described above.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
Liquidity
is the ability of a company to generate funds to support its current and future operations, satisfy its obligations, and otherwise operate
on an ongoing basis. Significant factors in the management of liquidity are funds generated by operations, levels of accounts receivable
and accounts payable and capital expenditures.
As
of December 31, 2020, the Company has $54,000 of cash, total current assets of $211,000, and total current liabilities of $1,127,000,
creating a working capital deficit of $916,000. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had $477,000 of cash, total current assets of $616,000,
and total current liabilities of $1,810,000, creating a working capital deficit of $1,194,000.
The
decrease in our working capital deficit was mainly attributable to the decrease of $560,000 in Fair Value of the convertible component
in a convertible loan and decrease of $299,000 in Fair Value of warrants issued in convertible loan, which was mitigated by a decrease
of $423,000 in cash and cash equivalents.
Net
cash used in operating activities was $626,000 for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to cash used in operating activities
of $1,100,000 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The Company’s primary uses of cash have been for professional support, research
and development expenses, sales and marketing expenses, and working capital purposes.
Net
cash used in investing activities was $0 for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to net cash generated from investing activities
of $6,000 for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Net
cash provided by financing activities was approximately $191,000 for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to approximately $1,454,000
for the year ended December 31, 2019. We have principally financed our operations through the sale of our common stock and the issuance
of debt. Due to our operational losses, we relied to a large extent on financing our cash flow requirements through issuance of common
stock and debt. There can be no assurance we will be successful in raising the necessary funds to execute our business plan.
Necessity
of Additional Financing
Securing
additional financing is critical to implementation of our business plan. If and when we obtain the required additional financing, we
should be able to fully implement our business plan. In the event we are unable to raise any additional funds we will not be able to
pursue our business plan, and we may fail entirely. We currently have no committed sources of financing.
Going
Concern Consideration
The
above conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Our independent auditors included an explanatory
paragraph in their report on the accompanying financial statements regarding concerns about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Our financial statements contain additional note disclosures describing the circumstances that lead to this disclosure by our independent
auditors. Although we anticipate that our current operations will provide us with cash resources, we believe existing cash will not be
sufficient to fund planned operations and projects through the next 12 months. Therefore, we believe we will need to increase our sales,
attain profitability, and raise additional funds to finance our future operations. Any meaningful equity or debt financing will likely
result in significant dilution to our existing stockholders. There is no assurance that additional funds will be available on terms acceptable
to us, or at all.
To
address these risks, we must, among other things, implement and successfully execute our business and marketing strategy surrounding
our products, continually develop and upgrade our website, respond to competitive developments, lower our financing costs, and attract,
retain and motivate qualified personnel. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in addressing such risks, and the failure
to do so can have a material adverse effect on our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Seasonality
We
do not expect our sales to be impacted by seasonal demands for our products.
Obligations
and Commitments
Legal
We
are not currently involved in any legal matters arising in the normal course of business. From time to time, we could become involved
in disputes and various litigation matters that arise in the normal course of business. These may include disputes and lawsuits related
to intellectual property, licensing, contract law and employee relations matters. Periodically, we review the status of significant matters,
if any exist, and assesses its potential financial exposure. If the potential loss from any claim or legal claim is considered probable
and the amount can be estimated, we accrue a liability for the estimated loss. Legal proceedings are subject to uncertainties, and the
outcomes are difficult to predict. Because of such uncertainties, accruals are based on the best information available at the time. As
additional information becomes available, we reassess the potential liability related to pending claims and litigation.
Off-Balance
Sheet Arrangements
We
do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
MANAGEMENT
Our
directors and executive officers and their respective ages as of the date of this prospectus are as follows:
|
Name
|
|
Age
|
|
Position(s)
|
|
Atara
Dzikowski
|
|
48
|
|
Chief
Executive Officer and Director
|
|
David
Dahan
|
|
49
|
|
Chief
Technical Officer and Director
|
Atara
Dzikowski
Atara
Dzikowski served as Director and CEO of the Delaware company, Samsara Luggage, Inc., from its inception in 2017 until the Merger, and
following the Merger has served as Director and CEO of Samsara. She has served as Chairperson and CEO of Design Boxes Ltd. from 2013
to date. From 2009 to 2013, Ms. Dzikowski was Director of Development and Public Affairs of Shenkar College of Engineering, Design and
Art. She holds a Master’s in Public Administration from Clark University and a BA degree in Communication and Management from The
College of Management in Tel Aviv. Since the Merger, Atara has been employed full time by Samsara as its Chief Executive Officer.
David
Dahan
David
Dahan served as Director and CTO of the Delaware company, Samsara Luggage, Inc., from its inception in 2017 until the Merger, and following
the Merger has served as Director and CTO of Samsara. From 2015 to date, Mr. Dahan is also employed at Nova-Sight Ltd., a medical device
company developing products for diagnostics and therapy in the field of ophthalmology, as its Software Department Manager. In 2009, Mr.
Dahan co-founded Serve Africa Ltd., a holding company that provides Satellite IP connectivity communication services throughout the continent
of Africa, and from 2013 to 2017 he served as its CEO. In 2008, Mr. Dahan founded Viramedics Ltd., a Bio-Tech firm dealing with Skin
Cancer detection, working with leading medical institutes worldwide towards clinical studies and implementation, and served as its CTO
through 2009. He also serves as a consultant to companies, mainly in the software algorithm field. Mr. Dahan holds a B.Sc degree in Physics
and Computer Science from Ben Gurion University. Since the Merger, David has been employed part-time by Samsara as its Chief Technical
Officer.
Committees
of the Board of Directors
The
Company does not have a separately constituted audit committee, compensation committee, nominating committee, executive committee or
any other committee of the Board of Directors. As such, the entire Board of Directors acts as Samsara’s audit committee.
Audit
Committee Financial Expert
The
Company does not have any member who qualifies as an audit committee financial expert. Samsara believes that the cost of retaining such
a financial expert at this time is prohibitive. Further, because the Company is still in an early development stage, Samsara believes
the services of an audit committee financial expert are not necessary at this time.
Term
of Office
Each
director is elected by the Board and serves until his or her successor is elected and qualified, unless he or she resigns or is removed
earlier. Each of our officers is elected by the Board to a term of one (1) year and serves until his or her successor is duly elected
and qualified, or until he or she is earlier removed from office or resigns.
Involvement
in Certain Legal Proceedings
None
of our directors, executive officers or control persons has been involved in any of the following events during the past five years:
(i) any bankruptcy petition filed by or against any business of which such person was a general partner or executive officer either at
the time of the bankruptcy or within two years prior to that time; (ii) any conviction in a criminal proceeding or being subject to a
pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offences); (iii) being subject to any order, judgment or decree,
not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring,
suspending or otherwise limiting his involvement in any type of business, securities or banking activities; or (iv) being found by a
court of competent jurisdiction (in a civil action), the SEC or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated a federal or
state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended or vacated.
Code
of Ethics
We
have not adopted a code of corporate conduct.
Compliance
with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires our
directors and officers, and the persons who beneficially own more than 10% of our common stock, to file reports of ownership and changes
in ownership with the SEC. Copies of all filed reports are required to be furnished to us pursuant to Rule 16a-3 promulgated under
the Exchange Act. Based solely on the reports received by us and on the representations of the reporting persons, we believe that
these persons have complied with all applicable filing requirements during the year ended December 31, 2020.
TRANSACTIONS
WITH RELATED PERSONS
Described
below are any transactions occurring during the fiscal year ending December 31, 2020 to which the Company was a party and in which a
director, executive officer, holder of more than 5% of the outstanding capital stock of the Company, or any member of such person’s
immediate family had or will have a direct or indirect material interest:
Bengio
Urban Spin-Off Transaction
In
connection with the Merger, the Company and Bengio entered into an Assignment and Assumption Agreement dated November 12, 2019, pursuant
to which the Company sold 100% of the issued and outstanding shares of Bengio Urban, and all of the Company’s interest in
Bengio Urban (including all debts and liabilities owed by the Company to Bengio Urban and the debts of Bengio Urban to the Company) to
Avraham Bengio, our former CEO and sole director.
Review,
Approval or Ratification of Transactions with Related Persons
Although
we adopted a Code of Ethics, we still rely on our Board to review related party transactions on an ongoing basis to prevent conflicts
of interest. Our Board reviews a transaction in light of the affiliations of the director, officer or employee and the affiliations of
such person’s immediate family. Transactions are presented to our Board for approval before they are entered into or, if this is
not possible, for ratification after the transaction has occurred. If our Board finds that a conflict of interest exists, then it will
determine the appropriate remedial action, if any. Our Board approves or ratifies a transaction if it determines that the transaction
is consistent with the best interests of the Company.
Director
Independence
The
Company is not subject to listing requirements of any national securities exchange or national securities association and, as a result,
the Company is not at this time required to have a board comprised of a majority of “Independent Directors.” The Company
does not believe that any of the directors of the Company meet the definition of “independent” as promulgated by the rules
and regulations of NASDAQ.
EXECUTIVE
COMPENSATION
The
following table shows, for the twelve months ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, compensation awarded or paid to, or earned
by, our Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Technical Officer, and our Chief Financial Officer:
|
SUMMARY
COMPENSATION TABLE
|
|
|
Name
|
|
Year
|
|
|
Salary
($)
|
|
|
Bonus
($)
|
|
|
Stock
Awards
($)
|
|
|
Option
Awards
($)
|
|
|
Non-Equity
Incentive Plan
Compensation
($)
|
|
|
Nonqualified
Deferred
Compensation
Earnings
($)
|
|
|
All
Other
Compensation
($)
|
|
|
Total
($)
|
|
|
Atara
Dzikowski(1)
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
(CEO)
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
David
Dahan(2)
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
(CTO)
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
From
January 1, 2018 until the effective date of the Merger, November 12, 2019, Atara Dzikowski
served as the CEO of the Delaware company, Samsara Luggage, Inc.
|
|
|
(2)
|
From
January 1, 2018 until the effective date of the Merger, November 12, 2019, David Dahan served
as CTO of the Delaware company, Samsara Luggage, Inc.
|
Employment
Contracts
On
September 22, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Ms. Dzikowski pursuant to which Ms. Dzikowski receives an annual salary
of $100,000.
Option/SAR
Grants
Samsara
does not currently have a stock option plan. No individual grants of stock options, whether or not in tandem with stock appreciation
rights known as SARs or freestanding SARs have been made to any executive officer or any Director since inception; accordingly, no stock
options have been granted or exercised by any of the officers or Directors since Samsara was founded.
Long-Term
Incentive Plans and Awards
The
Company does not have any long-term incentive plans that provide compensation intended to serve as incentive for performance. No individual
grants or agreements regarding future payouts under non-stock price-based plans have been made to any executive officer or any director
or any employee or consultant since Samsara’s inception; accordingly, no future payouts under non-stock price-based plans or agreements
have been granted or entered into or exercised by any of the officers or Directors or employees or consultants since Samsara was founded.
Potential
Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control
We
currently have no plans or arrangements in respect of payments to our executive officers in the event of termination of employment (as
a result of resignation, retirement, or change of control) or a change of responsibilities following a change of control.
Retirement
Benefits
There
are currently no arrangements or plans in which we provide pension, retirement or similar benefits for our Directors and Officers.
Compensation
of Directors
We
have no arrangement to compensate directors for their services in their capacity as Directors. Directors are not paid for meetings attended.
However, we intend to review and consider future proposals regarding board compensation. All travel and lodging expenses associated with
corporate matters are reimbursed by us, if and when incurred.
Compensation
Committee
We
do not have a separate compensation committee. Instead, our Board reviews and approves executive compensation policies and practices,
reviews salaries and bonuses for other officers, administers our stock option plans and other benefit plans, if any, and considers other
matters that may be brought forth to it.
Risk
Management Considerations
We
believe that our compensation policies and practices for our employees, including our executive officers, do not create risks that are
reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our Company.
BENEFICIAL
OWNERSHIP OF PRINCIPAL STOCKHOLDERS, OFFICERS AND DIRECTORS
As of August 23, 2021, we had 1,447,955 shares
of Common Stock outstanding. The following table sets forth, as of August 23, 2021, certain information with respect to the beneficial
ownership of our Common Stock by each stockholder known by us to be the beneficial owner of more than 5 percent of our Common Stock,
as well as by each of our current Directors and executive officers, and by all of the Company’s Directors and executive officers
as a group.
Each
person has sole voting and investment power with respect to the shares of Common Stock, except as otherwise indicated. Beneficial ownership
consists of a direct interest in the shares of Common Stock, except as otherwise indicated.
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
|
Number of Shares Owned
|
|
|
Percent
|
|
|
Atara Dzikowski (Director and CEO)
|
|
|
130,909
|
|
|
|
9.04
|
%
|
|
David Dahan (Director and CTO)
|
|
|
130,909
|
|
|
|
9.04
|
%
|
|
Directors and officers as a group (2 persons)
|
|
|
261,818
|
|
|
|
18.08
|
%
|
Change
in Control
We
are unaware of any contract or other arrangement the operation of which may at a subsequent date result in a change of control of our
Company.
Securities
Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
None.
Long-Term
Incentive Plans and Awards
We
do not have any long-term incentive plans that provide compensation intended to serve as incentive for performance. No individual grants
or agreements regarding future payouts under non-stock price-based plans have been made to any executive officer or any director or any
employee or consultant since our inception; accordingly, no future payouts under non-stock price-based plans or agreement s have been
granted or entered into or exercised by our officer or director or employees or consultants since we were founded.
Grants
of Plan-Based Awards Table
None
of our named executive officers received any grants of stock, option awards or other plan-based awards during the fiscal period ended
December 31, 2020. The Company has no activity with respect to these awards.
Options
Exercised and Stock Vested Table
None
of our named executive officers exercised any stock options, and no restricted stock units if any, held by our named executive officers
vested during the fiscal period ended December 31, 2020. The Company has no activity with respect to these awards.
Outstanding
Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End Table
None
of our named executive officers had any outstanding stock or option awards as of December 31, 2020. The Company has not issued any awards
to its named executive officers. The Company and its board may grant awards as it sees fit to its employees as well as key consultants
and other outside professionals.
Non-Cumulative
Voting
The
holders of our shares of Common Stock do not have cumulative voting rights, which means that the holders of more than 50% of such outstanding
shares, voting for the election of Directors, can elect all of the Directors to be elected, if they so choose. In such event, the holders
of the remaining shares will not be able to elect any of our Directors.
DISCLOSURE
OF COMMISSION POSITION ON INDEMNIFICATION FOR
SECURITIES ACT LIABILITIES
Our
Bylaws require us to indemnify any of our officers or directors, and certain other persons, under certain circumstances against all expenses
and liabilities incurred or suffered by such persons because of a lawsuit or similar proceeding to which the person is made a party by
reason of a his being a director or officer of the Company or our subsidiaries, unless that indemnification is prohibited by law. We
may also purchase and maintain insurance for the benefit of any officer which may cover claims for which we could not indemnify a director
or officer. We have been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission, indemnification of our officers, directors
and controlling persons under these provisions, or otherwise, is against public policy and is unenforceable.
Insofar
as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), may be permitted
to directors, officers or persons controlling us pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, we have been advised that in the
opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act,
and is therefore unenforceable.
EXPERTS
Our
financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 have been included in the registration
statement in reliance upon the report of Ilanit Halperin CPA, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
WHERE
YOU CAN FIND ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
We
are a reporting company and file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. We have
filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the securities we are offering under
this prospectus. This prospectus does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement and the exhibits to
the registration statement. For further information with respect to us and the securities we are offering under this prospectus, we refer
you to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed as a part of the registration statement. You may read and copy
the registration statement, as well as our reports, proxy statements and other information, at the SEC’s Public Reference Room
at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You can request copies of these documents by writing to the SEC and paying a fee for the
copying cost. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for more information about the operation of the Public Reference Room. The SEC maintains
an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically
with the SEC, where our SEC filings are also available. The address of the SEC’s web site is http://www.sec.gov.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
INDEX
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
BALANCE SHEETS
(U.S.
dollars in thousands except share and per share data)
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
|
|
Unaudited
|
|
|
Audited
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
197
|
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
Accounts Receivables
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
97
|
|
|
|
153
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
294
|
|
|
|
211
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and Equipment, net
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
|
298
|
|
|
|
215
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade payable
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
125
|
|
|
Accrued Expense
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
74
|
|
|
Related party payables
|
|
|
162
|
|
|
|
126
|
|
|
Convertible notes and short-term loans (Note 3)
|
|
|
139
|
|
|
|
289
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt
issue costs (Note 3)
|
|
|
641
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan (Note
3)
|
|
|
104
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,166
|
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES
|
|
|
1,166
|
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock subscribed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, authorized 7,500,000,000 shares, $0.0001 par value; 1,360,881
issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2021 and 786,700 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020.
|
|
|
136
|
|
|
|
78
|
|
|
Additional paid in capital
|
|
|
8,528
|
|
|
|
6,385
|
|
|
Services receivable
|
|
|
(679
|
)
|
|
|
(999
|
)
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(8,853
|
)
|
|
|
(6,376
|
)
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(868
|
)
|
|
|
(912
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
298
|
|
|
|
215
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Unaudited)
(U.S.
dollars in thousands except share and per share data)
|
|
|
Six Months Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from sales of products
|
|
|
184
|
|
|
|
351
|
|
|
|
109
|
|
|
|
330
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of sales of products
|
|
|
141
|
|
|
|
186
|
|
|
|
104
|
|
|
|
172
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
|
|
43
|
|
|
|
165
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
158
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development expenses
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
140
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
105
|
|
|
Selling and marketing expenses
|
|
|
161
|
|
|
|
187
|
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
105
|
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
616
|
|
|
|
524
|
|
|
|
351
|
|
|
|
277
|
|
|
TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
777
|
|
|
|
851
|
|
|
|
451
|
|
|
|
487
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING LOSS
|
|
|
(734
|
)
|
|
|
(686
|
)
|
|
|
(446
|
)
|
|
|
(329
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest and amortization of issuance cost on note and short-term loan
|
|
|
(94
|
)
|
|
|
(84
|
)
|
|
|
(22
|
)
|
|
|
(51
|
)
|
|
Income in respect of warrants issued
and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses
|
|
|
(1,649
|
)
|
|
|
545
|
|
|
|
(1,374
|
)
|
|
|
(7
|
)
|
|
TOTAL FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
|
|
(1,743
|
)
|
|
|
461
|
|
|
|
(1,396
|
)
|
|
|
(58
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET LOSS
|
|
|
(2,477
|
)
|
|
|
(225
|
)
|
|
|
(1,842
|
)
|
|
|
(387
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per basic and diluted share
|
|
|
(2.56
|
)
|
|
|
(0.45
|
)
|
|
|
(1.69
|
)
|
|
|
(0.77
|
)
|
|
Weighted average number of basic and diluted common shares
outstanding
|
|
|
966,289
|
|
|
|
505,134
|
|
|
|
1,090,199
|
|
|
|
505,134
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited)
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Six Months Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(2,477
|
)
|
|
|
(225
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash used
in operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of services receivable
|
|
|
320
|
|
|
|
360
|
|
|
Interest on convertible note and short-term loan and amortization
of issuance cost
|
|
|
62
|
|
|
|
75
|
|
|
Issuance of shares for services
|
|
|
70
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Expenses in respect of warrants issued and convertible component
in convertible loan, net interest expenses
|
|
|
1,649
|
|
|
|
(545
|
)
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
56
|
|
|
|
(48
|
)
|
|
Accounts recievables
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
Related parties, net
|
|
|
36
|
|
|
|
7
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
(5
|
)
|
|
|
(2
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Used by Operating Activities
|
|
|
(285
|
)
|
|
|
(376
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from Convertible loans, net of issuance cost
|
|
|
628
|
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
Prepayments of loans
|
|
|
(200
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
428
|
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash
|
|
|
143
|
|
|
|
(321
|
)
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
|
477
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
|
197
|
|
|
|
156
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Issuance of Common stock due to exercise of converted loans
|
|
|
1,944
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Issuance of Common stock against Accounts Payables
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
1 – GENERAL
|
|
A.
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC. (THE “COMPANY”)
|
The
Company was incorporated on May 7, 2007 under the name, “Darkstar Ventures, Inc.” under the laws of the State of Nevada.
The Company is a global smart luggage and smart travel brand. Samsara Luggage unveiled its Next Generation smart carry-on at
the 2020 Consumer Electronics Show (CES). The Next Generation is the first to market a Wi-Fi Hotspot technology for travelers to access
a secured network globally. Samsara Luggage also launched Essentials by Samsara, a safety kit providing commuters with a new layer
of safety with protective items like facemasks, hand sanitizer, disposable gloves and alcohol wipes. These kits are sold individually
and gifted to customers with purchase of the Carry-on Aluminum suitcase or Smart Weekender bag.
During
the last quarter of 2020, Samsara launched Sarah & Sam Fashion and Lifestyle Collection. Sarah& Sam is a part of Samsara
Direct business model prompted by the travel limitations due to the coronavirus pandemic, leveraging the company’s established
digital assets and manufacturing and fulfillment supply chain capabilities to offer additional consumer products that respond to the
changing needs of the market.
On
November 12, 2019, the Company completed its merger with the Delaware corporation that was previously known as “Samsara Luggage,
Inc.” (“Samsara Delaware”) in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May
10, 2019, (the “Merger Agreement”) by and among the Company, Samsara Delaware, and Avraham Bengio, pursuant to which Samsara
Delaware merged with and into the Company, with the Company being the surviving corporation (the “Merger”). Following the
completion of the Merger, the business of the Company going forward became the business of Samsara Delaware prior to the Merger, namely,
designing, manufacturing, and selling high quality luggage products to meet the evolving needs of frequent travelers and also seeking
to present new technologies within the aluminum luggage industry, including an aluminum “smart” suitcase.
The
Common Stock listed on the OTC Pink Marketplace, previously trading through the close of business on November 11, 2019 under the ticker
symbol “DAVC,” commenced trading on the OTC Pink Marketplace under the ticker symbol “SAML” on November 12, 2019.
The Common Stock has a new CUSIP number, 79589J101.
On
October 5, 2020 the Board of Directors of the Company has approved, and the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our
common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”), have executed a written consent in lieu of a special meeting
approving to amend the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock from 5,000,000,000
to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”).
The
accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As of June 30, 2021,
the Company had approximately $197 in cash and cash equivalents, approximately $872 in deficit of working capital and an accumulated
deficit of approximately $8,853. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon raising capital from financing transactions and revenue from
operations. Management anticipates their business will require substantial additional investments that have not yet been secured. Management
is continuing in the process of fund raising in the private equity and capital markets as the Company will need to finance future activities.
These financial statements do not include any adjustments that may be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
On
March 22, 2021, the Company completed a reverse stock split of its common stock. As a result of the reverse stock split, the following
changes have occurred (i) every seven thousand shares of common stock have been combined into one share of common stock; (ii) the number
of shares of common stock underlying each common stock option or common stock warrant have been proportionately decreased on a 7,000-for-1
basis, and the exercise price of each such outstanding stock option and common warrant has been proportionately increased on a 7,000
-for-1 basis. Accordingly, all option numbers, share numbers, warrant numbers, share prices, warrant prices, exercise prices and losses
per share have been adjusted within these consolidated financial statements, on a retroactive basis, to reflect this 7,000 -for-1 reverse
stock split.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Unaudited
Interim Financial Statements
The
accompanying unaudited financial statements include the accounts of the Company, prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally
accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Article 10 of U.S. Securities
and Exchange Commission Regulation S-X. Accordingly, they do not include all the information and footnotes required by generally accepted
accounting principles for complete financial statements. In the opinion of management, the financial statements presented herein have
not been audited by an independent registered public accounting firm but include all material adjustments (consisting of normal recurring
adjustments) which are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair statement of the financial condition, results of operations
and cash flows for the for six-months ended June 30, 2021. However, these results are not necessarily indicative of results for any other
interim period or for the year ended December 31, 2021. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the
Company to make certain estimates and assumptions for the reporting periods covered by the financial statements. These estimates and
assumptions affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. Actual amounts could differ from these estimates.
Certain
information and footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
have been omitted pursuant to the rules of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). The accompanying unaudited
condensed financial statements should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and notes thereto included in our Annual Report
on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020, filed with the SEC on March 30, 2021 (the “Annual Report”). For
further information, reference is made to the financial statements and footnotes thereto included in the Company’s Annual Report
on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of unaudited condensed financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and
assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, certain revenues and expenses, and disclosure of contingent assets
and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Estimates are used when
accounting for Warrants and Convertible Note and Going Concern.
Derivative and Fair Value of Financial
Instruments
Fair value accounting requires bifurcation
of embedded derivative instruments such as conversion features in convertible debt or equity instruments and measurement of their fair
value for accounting purposes. In assessing the convertible debt instruments, management determines if the convertible debt host instrument
is conventional convertible debt and further if there is a beneficial conversion feature requiring measurement. If the instrument is
not considered conventional convertible debt under ASC 470, the Company will continue its evaluation process of these instruments as
derivative financial instruments under ASC 815.
Once determined, derivative liabilities are
adjusted to reflect fair value at each reporting period end, with any increase or decrease in the fair value being recorded in results
of operations as an adjustment to fair value of derivatives.
Fair value of certain of the Company’s
financial instruments including cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses, notes payables, and other accrued liabilities
approximate cost because of their short maturities. The Company measures and reports fair value in accordance with ASC 820, “Fair
Value Measurements and Disclosure” defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in accordance with generally
accepted accounting principles and expands disclosures about fair value measurements.
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
Fair value, as defined in ASC 820, is the
price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at
the measurement date. The fair value of an asset should reflect its highest and best use by market participants, principal (or most advantageous)
markets, and an in-use or an in-exchange valuation premise. The fair value of a liability should reflect the risk of nonperformance,
which includes, among other things, the Company’s credit risk.
Valuation techniques are generally classified
into three categories: the market approach; the income approach; and the cost approach. The selection and application of one or more
of the techniques may require significant judgment and are primarily dependent upon the characteristics of the asset or liability, and
the quality and availability of inputs. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under ASC 820 must maximize the use of observable
inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. ASC 820 also provides fair value hierarchy for inputs and resulting measurement as
follows:
Level 1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active
markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Quoted prices for similar assets
or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; inputs
other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated
by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities; and
Level 3: Unobservable inputs for the asset
or liability that are supported by little or no market activity, and that are significant to the fair values.
Fair value measurements are required to be
disclosed by the Level within the fair value hierarchy in which the fair value measurements in their entirety fall. Fair value measurements
using significant unobservable inputs (in Level 3 measurements) are subject to expanded disclosure requirements including a reconciliation
of the beginning and ending balances, separately presenting changes during the period attributable to the following: (i) total gains
or losses for the period (realized and unrealized), segregating those gains or losses included in earnings, and a description of where
those gains or losses included in earning are reported in the statement of income.
The Company’s financial assets and liabilities
that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis by level within the fair value hierarchy are as follows:
|
|
|
Balance as of June 30, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible
loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
641
|
|
|
|
641
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
104
|
|
|
|
104
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
745
|
|
|
|
745
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2020
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible
loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No.
2020-06, Debt - Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging Contracts in Entity s Own Equity
(Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity s Own Equity. ASU 2020-06 will simplify
the accounting for convertible instruments by reducing the number of accounting models for convertible debt instruments and convertible
preferred stock. Limiting the accounting models results in fewer embedded conversion features being separately recognized from the host
contract as compared with current GAAP. Convertible instruments that continue to be subject to separation models are (1) those with embedded
conversion features that are not clearly and closely related to the host contract, that meet the definition of a derivative, and that
do not qualify for a scope exception from derivative accounting and (2) convertible debt instruments issued with substantial premiums
for which the premiums are recorded as paid-in capital. ASU 2020-06 also amends the guidance for the derivatives scope exception
for contracts in an entity’s own equity to reduce form-over-substance-based accounting conclusions. ASU 2020-06 will be effective
for public companies for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption
is permitted, but no earlier than fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, including interim periods within those fiscal years.
The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of ASU 2020-06 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial
statement presentation or disclosures.
Other new pronouncements issued but not effective
as of June 30, 2021 are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
NOTE 3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES
|
|
A.
|
On June 5, 2019, the
Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”), pursuant
to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with a convertible loan in the aggregate amount of $1,100,000 in three tranches,
and the Company agreed to issue convertible debentures and a warrant to the Investor.
|
The first tranche of the convertible
debentures in the amount of $200,000 was provided upon execution of the SPA. The second tranche in the amount of $300,000 was provided
on October 23, 2019 upon the Company filing of a Registration Statement on Form S-4 in connection with the Merger with Samsara Delaware.
The third tranche in the amount of $600,000 was provided on November 18, 2019 upon consummation of the Merger with Samsara Delaware and
the fulfillment of all conditions required for the Merger. The Company incurred issuance cost of $100,000 with connection to those convertible
debentures.
Each tranche of the loan will bear
interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%). The principal amount together with the accrued and unpaid interest will be repayable
after two years. Each tranche of the loan together with the accrued and unpaid interest (or any portion at the discretion of the Investor)
will be convertible at any time six months following the issuance date, into shares of Company’s common stock at a conversion price
equal to the lower of $0.003 per share or 80% of the lowest volume-weighted average price (VWAP) of Company’s share during the
period of 10 days preceding the conversion date.
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED
CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
On January 14, 2021 and pursuant
to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $50 and the accrued interest
in the amount of $4 into 38,303 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $64.
On February 11, 2021 and pursuant
to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $55 and the accrued interest
in the amount of $3 into 16,713 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $216.
On April 19, 2021 and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $40 and the accrued interest
in the amount of $7 into 40,861 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $62.
On May 12, 2021 and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $60 and the accrued interest
in the amount of $2 into 44,202 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $103.
On May 17, 2021 and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $65 into 48,316 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $85.
On May 20, 2021 and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $65 into 50,611 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $171.
On May 21, 2021 and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $70 into 54,386 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $280.
On May 24, 2021, and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $70 into 54,407 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $322.
On May 24, 2021, and pursuant to
the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the remainder of the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $15 and accrued
interest of $11 into 11,647 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $68.
As of June 30, 2021 this loan was
paid in full.
In accordance with ASC 815-15-25
the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair value as its fair value can
be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The Company recorded finance expenses
in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible component fair value over the
face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting gains or losses shown in
the statements of operations.
The fair value of the convertible
component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the fair value of the derivative and
to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the data and assumptions used
as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.40
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.43
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
330
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
In addition, the Company issued
to the Investor a warrant to purchase 13,095 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $21.00. The warrants may be exercised
within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrants shares having a value
equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The Company considered the provisions
of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with respect to the detachable Warrants
that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise” and variable exercise
price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which the Company subsequently
issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to the Company’s own
stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition. In subsequent periods,
the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in the consolidated statement
of operations.
The warrants were estimated by third
party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair
value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
3,94
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
312
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
2.93
years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.45
|
%
|
|
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
51
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.40
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
3.43
years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
16
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
|
|
B.
|
On September 3, 2020, Samsara Luggage,
Inc. (the “Company”) entered into a second Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with the Investor, pursuant
to which the Investor will invest an aggregate amount of $220 in two tranches, and the Company will issue convertible debentures
and warrants to the Investor. The first tranche of the convertible debentures in the amount of $150 was provided upon execution of
the SPA. The second tranche in the amount of $70 was provided on October 7, 2020. Each tranche of the loan bears interest at an annual
rate of ten percent (10%). Each tranche of the investment bears interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable
after two years. Each tranche of the investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock at
a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $0.003 per share, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted average
price for the Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date. As part of the transaction,
the Company will issue to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 2,619 shares of Common Stock, at an exercise price equal
to $0.003. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment or through cashless
exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The Company has undertaken to increase its authorized shares of Common Stock to at least 7,000,000,000 within 90 days of the closing.
The SPA and the convertible debentures contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the convertible
debentures by the maturity date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s
right to convert the convertible debentures into shares of common stock.
On May 24, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA,
YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $50 into 47,247 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $281.
On May 25, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA,
YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $80 into 62,138 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $249.
On May 28, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA,
YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $70 into 57,837 shares of Common
Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $164.
On June 1, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA,
YAII exercised its option to convert the remainder of the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $20 into 15,559
shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $39.
|
As of June 30, 2021 this loan was
paid in full.
In accordance with ASC 815-15-25
the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair value as its fair value can
be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The Company recorded finance expenses
in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible component fair value over the
face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting gains or losses shown in
the statements of operations.
The fair value of the convertible
component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the fair value of the derivative and
to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.39
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.38
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.67
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.12
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
157
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED
CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
In addition, the Company issued
to the Investor a warrant to purchase 2,619 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $21.00. The warrants may be exercised
within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrants shares having a value
equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The Company considered the provisions
of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with respect to the detachable Warrants
that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise” and variable exercise
price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which the Company subsequently
issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to the Company’s own
stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition. In subsequent periods,
the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in the consolidated statement
of operations.
The warrants were estimated by third
party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair
value of the derivative at each balance sheet dates:
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
3.94
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
312
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.18
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.70
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
10
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.39
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.68
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
4
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED
CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
|
|
C.
|
On June 26, 2020, the
Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with Power Up Lending Group Ltd. (the “Investor”),
pursuant to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with an initial investment in the form of a convertible loan in the
principal amount of $67 (the “Initial Investment”). The SPA contemplates additional financing of up to $925 in the aggregate,
subject to the agreement of both parties. The funds are expected to be used to finance the Company’s working capital needs.
|
The convertible loan will bear interest
at an annual rate of eight percent (8%) with a maturity date of June 25, 2021 (the “Maturity Date”). The loan will be convertible
after six months into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to seventy-five percent (75%) of the average
of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock during the twenty (20) trading day period prior to the conversion date.
The Company agreed to an original issue discount of $9 and to reimburse the Investor for its costs in the amount of $3. Accordingly,
the net proceeds to the Company from the Initial Investment amounted to $55.
The SPA and the convertible note
contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the loan amount by the Maturity Date, and bankruptcy and insolvency
events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s right to convert the loan amount into shares of common stock.
On January 11, 2021 and pursuant
to the SPA, Power-up exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $ 7 and the accrued interest
in the amount of $ 1 into 7,448 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
As of June 30, 2021 this loan was
paid in full.
|
|
D.
|
On
April 6, 2021, the Company entered into a third Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”)
with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”), pursuant to which the Investor agreed to
provide the Company with a convertible loan in the aggregate amount of $150 and the Company
agreed to issue convertible debentures and a warrant to the Investor. The loan will bear
interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable after two years. The
investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock
at a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $3.46, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily
dollar volume-weighted average price for the Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading
days immediately preceding the conversion date.
|
In accordance with ASC 815-15-25
the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair value as its fair value can
be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The Company recorded finance expenses
in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible component fair value over the
face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting gains or losses shown in
the statements of operations.
The fair value of the convertible
component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the fair value of the derivative and
to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each of the issuance and balance sheet dates:
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the issuance date:
|
|
|
April 6,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
1.97
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
322
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
2.00
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.16
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
156
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED
CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
3.94
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
312
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.77
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.21
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
220
|
|
As part of the transaction, the
Company issued to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 10,838 shares of Common Stock, at an exercise price equal to $3.46.
The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment or through cashless exercise
by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The warrants were estimated by third
party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair
value of the derivative at each of the issuance and balance sheet dates:
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the issuance date:
|
|
|
April
6
2021
|
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
1.97
|
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
322
|
%
|
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
5.00
|
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.88
|
%
|
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
21
|
|
|
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
$3.94
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
312.2
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.77
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.82
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
43
|
|
|
|
E.
|
On June 7, 2021,
Samsara Luggage, Inc. (the “Company”) entered into a fourth Securities Purchase
Agreement (“SPA”) with the Investor, pursuant to which the Investor will invest
an aggregate amount of $1,250 in three tranches, and the Company will issue convertible debentures
and warrants to the Investor, in which each traunch is convertible into shares of the Company’s
common stock, par value $0.0001 (the “Common Stock”). The first traunch in the
principal amount of $500 was issued on June 7, 2021. The second traunch in the principal amount
of $500 will be issued within one (1) business day following the filing of a registration
statement on Form S-1 (the “Registration Statement”) under the Securities Act
of 1933, as amended, registering the Conversion Shares issuable upon conversion of the Convertible
Debentures with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The third traunch
in the principal amount of $250 will be issued within one (1) business day following
the Registration Statement having been declared effective by the SEC.
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED
CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
The Convertible Debentures bear
interest at a rate of 10% per annum (15% on default) and have a maturity date of one (1) year. The Convertible Debentures provide a conversion
right, in which any portion of the principal amount of the Convertible Debentures, together with any accrued but unpaid interest, may
be converted into the Company’s Common Stock at a conversion price equal to 80% of the lowest volume weighted average price of
the Company’s Common Stock during the ten (10) trading days immediately preceding the date of conversion, subject to adjustment.
The Convertible Debentures may not be converted into common stock to the extent such conversion would result in the Investor beneficially
owning more than 9.99% of the Company’s outstanding Common Stock (the “Beneficial Ownership Limitation”); provided,
however, that the Beneficial Ownership Limitation may be waived by the Investor upon not less than 65 days’ prior notice to the
Company. The Convertible Debentures provide the Company with a redemption right, pursuant to which the Company, upon fifteen (15) business
days’ prior notice to the Investor, may redeem, in whole or in part, outstanding principal and interest at a redemption price equal
to the principal amount being redeemed plus a redemption premium equal to 5% of the outstanding principal amount being redeemed plus
outstanding and accrued interest; however, the Investor shall have fifteen (15) business days after receipt of the Company’s redemption
notice to elect to convert all or any portion of the Convertible Debentures, subject to the Beneficial Ownership Limitation. In connection
with the Securities Purchase Agreement, the Company executed a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”)
pursuant to which it is required to file the Registration Statement with the SEC for the resale of the Conversion Shares. Pursuant to
the Registration Rights Agreement, the Company is required to meet certain obligations with respect to, among other things, the timeliness
of the filing and effectiveness of the Registration Statement. The Company is obligated to file the Registration Statement no later than
45 days after the First Closing Date and to have it declared effective by the SEC no later than 105 days after filing (the “Registration
Obligations”).
In accordance with ASC 815-15-25
the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair value as its fair value can
be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The Company recorded finance expenses
in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible component fair value over the
face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting gains or losses shown in
the statements of operations.
The fair value of the convertible
component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the fair value of the derivative and
to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet dates:
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the issuance date:
|
|
|
June 7,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
6.33
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
359
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.00
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.05
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
423
|
|
The following are the data and assumptions
used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
$
|
3.94
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
359
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.94
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.07
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
421
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
The following table presents the
changes in fair value of the level 3 liabilities for the period ended June 30, 2021:
|
|
|
Warrants
|
|
|
Convertible component
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2020
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value converted
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(484
|
)
|
|
Fair value of issued level 3 liability
|
|
|
21
|
|
|
|
578
|
|
|
Changes in fair value
|
|
|
63
|
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
Outstanding at June 30, 2021
|
|
|
104
|
|
|
|
641
|
|
NOTE 4 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Related party balances as of June
30, 2021 and December 31, 2020 consisted of the following:
Related Parties Payable
|
|
|
June 30,
2021
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Related
Parties Payable due to management fee
|
|
|
162
|
|
|
|
126
|
|
General and Administrative Expenses
|
|
|
For
the Period Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Management Fee
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
NOTE 5 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common Stock
The following summarizes the Common
Stock activity for the six months ended June 30, 2021:
|
Summary of common stock activity for the
six months ended June 30, 2021
|
|
Outstanding shares
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2020
|
|
|
786,700
|
|
|
Shares issued due to conversion of Notes.
|
|
|
549,675
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
21,658
|
|
|
Roundup shares due to reverse split.
|
|
|
2,848
|
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2021
|
|
|
1,360,881
|
|
On
January 14, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50and the accrued interest in the amount of $4 into 38,303 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of
the shares was $64.
On
January 21, 2021, the Company issued 7,383 shares of its Common Stock pursuant to a service Agreement between the Company and a service
provider. The fair market value of the shares was $20.
On
February 11, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $55 and the accrued interest in the amount of $4 into 16,713 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of
the shares was $216.
On
March 22, 2021, the Company completed a reverse stock split of its common stock. As a result of the reverse stock split, the following
changes have occurred (i) every seven thousand shares of common stock have been combined into one share of common stock; (ii) the number
of shares of common stock underlying each common stock option or common stock warrant have been proportionately decreased on a 7,000-for-1
basis, and the exercise price of each such outstanding stock option and common warrant has been proportionately increased on a 7,000
-for-1 basis. Accordingly, all option numbers, share numbers, warrant numbers, share prices, warrant prices, exercise prices and losses
per share have been adjusted within these consolidated financial statements, on a retroactive basis, to reflect this 7,000 -for-1 reverse
stock split.
On
March 23, 2021, the Company issued 2,849 shares of its Common Stock due to a reverse split rounding up differences.
On
April 19, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount
of $40 and the accrued interest in the amount of $7into 40,861 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares
was $62.
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in U.S. dollar thousands, except share
and per share data)
On May 12, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII
exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $60 and the accrued interest in the amount
of $2 into 44,202 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $103.
On
May 17, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$65 into 48,316 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $85.
On
May 20, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$65 into 50,611 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $171.
On
May 21, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$70 into 54,386 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $280.
On
May 24, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$70 into 54,407 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $322.
On May 24, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA,
YAII exercised its option to convert the remainder of the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of $15 and accrued interest
of $10 into 11,647 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $68.
On
May 24, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$50 into 47,247 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $281.
On
May 25, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$80 into 62,138 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $249.
On
May 28, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount of
$70 into 57,837 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $164.
On
June 1, 2021, and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the remainder of the Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $20 into 15,559 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market value of the shares was $39.
On
June 14, 2021, the Company issued 14,275 shares of its Common Stock pursuant to a service Agreement between the Company and a service
provider. The fair market value of the shares was $70.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
INDEX
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORT
OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
TO
THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS AND STOCKHOLDERS OF
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
Opinion
on the Financial Statements
We
have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Samsara Luggage, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, the
related statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in stockholders’ deficit and cash flows for the years in the period
ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our
opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31,
2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year in the period ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, in conformity
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going
Concern
The
accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note
1E to the financial statements, the Company has not yet generated material revenues from its operations to fund its activities and is
therefore dependent upon external sources for financing its operations. As of December 31, 2020, the Company has incurred accumulated
deficit of $6,376 thousands and negative operating cash flows. These factor among others, as discussed in Note 1E to the financial statements
raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans concerning these matters
are also described in Note 1E to the financial statements. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result
from the outcome of’ these uncertainties. This matter is also described in the “Critical Audit Matters” section of
our report.
Basis
for Opinion
These
financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s
financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board
(United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities
laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We
conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company
is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit,
we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion
on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our
audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or
fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding
the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant
estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides
a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical
audit matters
The
critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements
that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relate to accounts or disclosures that are
material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The
communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole,
and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the
accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Going
concern assessment
The
accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed
in Note 1E to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has not yet generated material revenues from its operations to fund
its activities and is therefore dependent upon external sources for financing its operations. As of December 31, 2020, the Company has
incurred accumulated deficit of $6,376 thousands and negative operating cash flows. These factor among others, as discussed in Note 1E
to the financial statements raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s
plans concerning these matters are also described in Note 1E to the financial statements. This matter is also described in the “Emphasis
of Matter – Going Concern” section of our report.
We
identified management’s assumptions used to assess the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern as a critical audit
matter due to inherent complexities and uncertainties related to the Company’s Management’s plans. Auditing these assumptions
involved especially challenging auditor judgment due to the nature and extent of audit evidence and effort required to address these
matters.
The
primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter included the following:
|
|
■
|
Assessing the reasonableness
of key assumptions underlying management’s forecast operating cash flows, including revenue growth and gross margin assumptions
and evaluating the reasonableness of management’s forecast operating cash flows
|
|
|
■
|
Evaluating the probability
that the Company will be able to reduce other operating expenditures if required
|
|
|
■
|
Assessing management’s
plans in the context of other audit evidence obtained during the audit to determine whether it supported or contradicted the conclusions
reached by management
|
|
|
■
|
Assessing the effect of
events and agreement signed after balance sheet date.
|
Fair
value measurement of Level 3 liabilities
As
discussed in Notes 2 and 3 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company entered into several Convertible Loan Agreements and
in accordance with ASC 815-15-25, the conversion feature was considered an embedded derivative instrument, and is to be recorded at its
fair value as its fair value can be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value.
The Company recorded finance expenses in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible
component fair value over the face loan amount.
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, to compute
the fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. Under accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America, these convertible component are generally classified as Level 3 convertible
component.
We
identified Level 3 convertible component as a critical audit matter because of the complex proprietary models and unobservable inputs
management uses to estimate the fair value. This evaluation required a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort,
including the need to involve our internal valuation specialists who possess significant quantitative and modeling expertise, to audit
and evaluate the appropriateness of these models and inputs.
Our
audit procedures related to the complex proprietary models and unobservable inputs used by management to estimate the fair value of Level
3 convertible component included the following, among others:
|
|
●
|
We assessed the consistency
by which management has applied significant unobservable valuation assumptions.
|
|
|
●
|
With the assistance of
our internal valuation specialists, we evaluated the appropriateness of the valuation methodologies and techniques used in determining
the fair value of Level 3 convertible component. Also, we evaluated the appropriateness of estimates of the key inputs used in determining
the fair value of the Level 3 convertible component
|
/s/
Halperin Ilanit.
Certified
Public Accountants (Isr.)
Tel
Aviv, Israel
March
30, 2021
We
have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
BALANCE
SHEETS
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
December 31,
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands,
except per share data)
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
|
477
|
|
|
Accounts Receivables
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
153
|
|
|
|
125
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
14
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
211
|
|
|
|
616
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and Equipment, net
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
|
215
|
|
|
|
621
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
125
|
|
|
|
26
|
|
|
Other current liabilities
|
|
|
74
|
|
|
|
57
|
|
|
Related party payables
|
|
|
126
|
|
|
|
105
|
|
|
Convertible notes and short-term loans (Note 3)
|
|
|
289
|
|
|
|
250
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs (Note 3)
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
|
1,053
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan (Note 3)
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
319
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
1,810
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
1,810
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (Note 4)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock subscribed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, authorized 7,500,000,000 shares, $0.0001 par value as of December 31, 2020 and 5,000,000,000 shares, $0.0001 par value as of December 31, 2019, respectively; 786,700 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020 and 505,134 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019.
|
|
|
78
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
Additional paid in capital
|
|
|
6,385
|
|
|
|
5,670
|
|
|
Services receivable
|
|
|
(999
|
)
|
|
|
(1,673
|
)
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(6,376
|
)
|
|
|
(5,236
|
)
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(912
|
)
|
|
|
(1,189
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
215
|
|
|
|
621
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
STATEMENTS
OF COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
|
|
|
Year Ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands,
except per share data)
|
|
|
Revenues from sales of products
|
|
|
468
|
|
|
|
649
|
|
|
Cost of sales
|
|
|
285
|
|
|
|
525
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
|
|
183
|
|
|
|
124
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development expenses
|
|
|
222
|
|
|
|
168
|
|
|
Selling and marketing expenses
|
|
|
328
|
|
|
|
438
|
|
|
General and administrative (Note 5)
|
|
|
1,086
|
|
|
|
1,425
|
|
|
TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
1,636
|
|
|
|
2,031
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING LOSS
|
|
|
(1,453
|
)
|
|
|
(1,907
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest on convertible loan and convertible note
|
|
|
(510
|
)
|
|
|
(314
|
)
|
|
Income (expenses) in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses (Note 3)
|
|
|
823
|
|
|
|
(921
|
)
|
|
TOTAL FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSE)
|
|
|
313
|
|
|
|
(1,235
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET LOSS
|
|
|
(1,140
|
)
|
|
|
(3,142
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and Diluted net loss per share
|
|
|
(2.07
|
)
|
|
|
(6.72
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of basic and diluted common shares outstanding
|
|
|
550,521
|
|
|
|
467,521
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
STATEMENTS
OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
(U.S.
dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
Additional
Paid-in
|
|
|
Service
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
Stockholders’
|
|
|
|
|
Shares (*)
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
Receivables
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2019
|
|
|
505,134
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
|
5,670
|
|
|
|
(1,673
|
)
|
|
|
(5,236
|
)
|
|
|
(1,189
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of shares due to conversion of Notes
|
|
|
281,566
|
|
|
|
28
|
|
|
|
715
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
743
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of services
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
674
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
674
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(1,140
|
)
|
|
|
(1,140
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2020
|
|
|
786,700
|
|
|
|
78
|
|
|
|
6,385
|
|
|
|
(999
|
)
|
|
|
(6,376
|
)
|
|
|
(912
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2018
|
|
|
369,929
|
|
|
|
37
|
|
|
|
2,676
|
|
|
|
(908
|
)
|
|
|
(2,094
|
)
|
|
|
(289
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock, net of issuance cost
|
|
|
32,738
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
497
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
500
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued of Warrants for services
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1,940
|
|
|
|
(1,940
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares Issuance of common stock for conversion of convertible note
|
|
|
9,988
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
566
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
567
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of Reverse Capitalization
|
|
|
92,479
|
|
|
|
9
|
|
|
|
(9
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of services
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
1,175
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1,175
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(3,142
|
)
|
|
|
(3,142
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2019
|
|
|
505,134
|
|
|
$
|
50
|
|
|
$
|
5,670
|
|
|
$
|
(1,673
|
)
|
|
$
|
(5,236
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,189
|
)
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
STATEMENTS
OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
|
For the Year Ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(In thousands)
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(1,140
|
)
|
|
$
|
(3,142
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash used in operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of services receivable
|
|
|
674
|
|
|
|
1,175
|
|
|
Interest on convertible note and short-term loan
|
|
|
584
|
|
|
|
258
|
|
|
Expenses in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses
|
|
|
(823
|
)
|
|
|
921
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
(28
|
)
|
|
|
58
|
|
|
Accounts Receivables
|
|
|
(4
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
14
|
|
|
|
36
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
99
|
|
|
|
26
|
|
|
Management fee due to Related party, net
|
|
|
21
|
|
|
|
16
|
|
|
Other accounts payables
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
11
|
|
|
Deferred revenue
|
|
|
(12
|
)
|
|
|
(460
|
)
|
|
Net Cash Used by Operating Activities
|
|
|
(614
|
)
|
|
|
(1,100
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investment Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of Property and Equipment
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(6
|
)
|
|
Net Cash Used by Financing Activities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(6
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repayments of Convertible note from related parties
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(56
|
)
|
|
Proceeds from loan received
|
|
|
191
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
Repayments of convertible notes, net of issuance cost of $100
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1,000
|
|
|
Repayments of long-term loans
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(40
|
)
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of shares, net of issuance cost
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
500
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
191
|
|
|
|
1,454
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash
|
|
|
(423
|
)
|
|
|
348
|
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
477
|
|
|
|
129
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
$
|
54
|
|
|
$
|
477
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
58
|
|
|
Cash paid for income taxes
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued for conversion of convertible note
|
|
$
|
223
|
|
|
$
|
567
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
1 – ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
|
|
A.
|
Samsara Luggage, Inc. (the
“Company”) was incorporated on May 7, 2007 under the name, “Darkstar Ventures, Inc.” under the laws of the
State of Nevada. From the date of its formation until May 2011, the Company did not have any business activity except for the development
of its website and locating companies through which it could offer products. Once its proprietary website was officially launched
in July 2011, the Company engaged in the business of marketing eco-friendly health and wellness products, such as air and water filtration
systems, organic baby products, and eco-friendly beds and linens through affiliate marketing arrangements. On May 14, 2015, the founder
of the Company, Chizkiyau Lapin, sold all of his shares of common stock of the Company, then constituting 51% of the issued and outstanding
shares of common stock of the Company, to Mr. Avraham Bengio. In April 2016, the Company began to focus, through its wholly-owned
Israeli subsidiary, Bengio Urban Renewal Ltd. (“Bengio Urban Renewal”), in the area of real estate development, particularly
on the urban renewal market in Israel.
|
On
March 23, 2021, the Company completed a reverse stock split of its outstanding common stock. As a result of the reverse stock split,
the following changes have occurred (i) every seven thousand shares of common stock have been combined into one share of common stock;
(ii) the number of shares of common stock underlying each common stock option or common stock warrant have been proportionately decreased
on a 7,000-for-1 basis, and the exercise price of each such outstanding stock option and common warrant has been proportionately increased
on a 7,000 -for-1 basis. Accordingly, all option numbers, share numbers, warrant numbers, share prices, warrant prices, exercise prices
and losses per share have been adjusted within these consolidated financial statements, on a retroactive basis, to reflect this 7,000
-for-1 reverse stock split.
On
November 12, 2019, the Company completed its merger with the Delaware corporation that was previously known as “Samsara Luggage,
Inc.” (“Samsara Delaware”) in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May
10, 2019, (the “Merger Agreement”) by and among the Company, Samsara Delaware, and Avraham Bengio, pursuant to which Samsara
Delaware merged with and into the Company, with the Company being the surviving corporation (the “Merger”). Following the
completion of the Merger, the business of the Company going forward became the business of Samsara Delaware prior to the Merger, namely,
designing, manufacturing, and selling high quality luggage products to meet the evolving needs of frequent travelers and also seeking
to present new technologies within the aluminum luggage industry, including an aluminum “smart” suitcase.
The
Company filed (1) Articles of Merger with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company amended its Articles of
Incorporation to change the Company’s name to “Samsara Luggage, Inc.” effective as of November 12, 2019; and (2)
a Certificate of Amendment with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company increased the number of authorized
shares of common stock of the Company from 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock to 5,000,000,000 shares of common stock effective as
of November 12, 2019.
In
connection with the Merger, the Company and Avraham Bengio entered into an Assignment and Assumption Agreement pursuant to which the
Company sold 100% of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s wholly-owned Israeli subsidiary, Bengio Urban Renewal and
all of the Company’s interest in Bengio Urban Renewal (including all debts and liabilities owed by the Company to Bengio Urban
Renewal and the debts of Bengio Urban Renewal to the Company) to Avraham Bengio, the former CEO and principal shareholder of the Company
(prior to the Merger).
At
the effective time of the Merger, each share of common stock of Samsara Delaware, $0.0001 par value, was converted into the right to
receive 0.065 shares of the Company’s common stock, such that the shareholders of Samsara Delaware were issued new shares of the
Company representing approximately 80% of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock following the completion
of the Merger. The exchange rate was determined through arms’-length negotiations between the Company and Samsara Delaware.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
1 – ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS (cont.)
Immediately
after the Merger, assuming the issuance of all of the merger consideration, there were approximately 462,407 shares of Common Stock outstanding,
of which (i) the former stockholders of Samsara Delaware owned 369,929 shares, representing approximately 80% of the outstanding shares
of Common Stock; and (ii) the Company’s stockholders immediately prior to the Merger owned 92,478 shares, representing approximately
20% of the outstanding shares of Common Stock.
The
transaction was accounted for as a reverse asset acquisition in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United
States of America (“GAAP”). Under this method of accounting, Samsara Delaware was deemed to be the accounting acquirer for
financial reporting purposes. This determination was primarily based on the facts that, immediately following the Merger: (i) Samsara
Delaware’s stockholders owned a substantial majority of the voting rights in the combined company, (ii) Samsara Delaware designated
a majority of the members of the initial board of directors of the combined company, and (iii) Samsara Delaware’s senior management
holds all key positions in the senior management of the combined company. As a result of the Recapitalization Transaction, the shareholders
of Samsara Delaware received the largest ownership interest in the Company, and Samsara Delaware was determined to be the “accounting
acquirer” in the Recapitalization Transaction. As a result, the historical financial statements of the Company were replaced with
the historical financial statements of Samsara Delaware. The number of shares prior to the reverse capitalization have been retroactively
adjusted based on the equivalent number of shares received by the accounting acquirer in the Recapitalization Transaction.
The
Common Stock listed on the OTC Pink Marketplace, previously trading through the close of business on November 11, 2019 under the ticker
symbol “DAVC,” commenced trading on the OTC Pink Marketplace under the ticker symbol “SAML” on November 12, 2019.
The Common Stock has a new CUSIP number, 79589J101. On August 24, 2021, the Company’s Common Stock began listing on the OTCQB.
On
November 13, 2019, the Board of Directors of the Company amended Section 3 of Article VII of the bylaws of the Company to change the
fiscal year end-date of the Company from July 31 to December 31.
|
|
D.
|
On October 5, 2020 the
Board of Directors of the Company has approved, and the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our common stock,
par value $0.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”), have executed a written consent in lieu of a special meeting approving
to amend the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock from 5,000,000,000
to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”).
|
The
accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As of December 31, 2020,
the Company had approximately $54 in cash and cash equivalents, approximately $916 in deficit of working capital, a stockholders’
deficiency of approximately $912 and an accumulated deficit of approximately $6,376. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the
Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon raising
capital from financing transactions and revenue from operations. Management anticipates their business will require substantial additional
investments that have not yet been secured. Management is continuing in the process of fund raising in the private equity and capital
markets as the Company will need to finance future activities. These financial statements do not include any adjustments that may be
necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The
financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US
GAAP”).
Use
of Estimates
The
preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“‘US
GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and disclosure
of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during
the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates. As applicable to the financial statements, the most significant
estimates and assumptions relate to the measurement of Convertible Note and Going Concern.
Functional
currency
The
functional currency of the Company is the US dollar (“US$”), which is the currency of the primary economic environment in
which the operations of the Company are conducted.
Cash
and cash equivalents
Cash
equivalents are short-term highly liquid investments which include short term bank deposits (up to three months from date of deposit),
that are not restricted as to withdrawals or use that are readily convertible to cash with maturities of three months or less as of the
date acquired.
Inventory
Inventories
are valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Cost of raw and packaging materials, purchased products, manufactured finished
products and products in process are determined on the average cost basis. The Company regularly reviews its inventories for impairment
and reserves are established when necessary.
Property
and Equipment
Property
and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. The Company provides for depreciation and amortization
using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets, which range from three to five years. Maintenance
and repair costs are expensed as they are incurred while renewals and improvements which extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized.
At the time of retirement or disposal of property and equipment, the cost and related accumulated depreciation and amortization are removed
from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in the consolidated results of operations.
Derivative
Liabilities and Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair
value accounting requires bifurcation of embedded derivative instruments such as conversion features in convertible debt or equity instruments
and measurement of their fair value for accounting purposes. In assessing the convertible debt instruments, management determines if
the convertible debt host instrument is conventional convertible debt and further if there is a beneficial conversion feature requiring
measurement. If the instrument is not considered conventional convertible debt under ASC 470, the Company will continue its evaluation
process of these instruments as derivative financial instruments under ASC 815.
Once
determined, derivative liabilities are adjusted to reflect fair value at each reporting period end, with any increase or decrease in
the fair value being recorded in results of operations as an adjustment to fair value of derivatives.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION (cont.)
Fair
value of certain of the Company’s financial instruments including cash, accounts receivable, account payable, accrued expenses,
notes payables, and other accrued liabilities approximate cost because of their short maturities. The Company measures and reports fair
value in accordance with ASC 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosure” defines fair value, establishes a framework for
measuring fair value in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and expands disclosures about fair value investments.
Fair
value, as defined in ASC 820, is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. The fair value of an asset should reflect its highest and best use by market participants,
principal (or most advantageous) markets, and an in-use or an in-exchange valuation premise. The fair value of a liability should reflect
the risk of nonperformance, which includes, among other things, the Company’s credit risk.
Valuation
techniques are generally classified into three categories: the market approach; the income approach; and the cost approach. The selection
and application of one or more of the techniques may require significant judgment and are primarily dependent upon the characteristics
of the asset or liability, and the quality and availability of inputs. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under ASC 820
must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. ASC 820 also provides fair value hierarchy for
inputs and resulting measurement as follows:
Level
1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical assets or liabilities.
Level
2: Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in
markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived
principally from or corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities; and
Level
3: Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability that are supported by little or no market activity, and that are significant to the
fair values.
Fair
value measurements are required to be disclosed by the Level within the fair value hierarchy in which the fair value measurements in
their entirety fall. Fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs (in Level 3 measurements) are subject to expanded
disclosure requirements including a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances, separately presenting changes during the period
attributable to the following: total gains or losses for the period (realized and unrealized), segregating those gains or losses included
in earnings, and a description of where those gains or losses included in earning are reported in the statement of income.
The
Company records a debt discount related to the issuance of convertible debts that have conversion features at adjustable rates. The debt
discount for the convertible instruments is recognized and measured by allocating a portion of the proceeds as an increase in additional
paid-in capital and as a reduction to the carrying amount of the convertible instrument equal to the fair value of the conversion features.
The debt discount will be accreted by recording additional non-cash gains and losses related to the change in fair values of derivative
liabilities over the life of the convertible notes.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION (cont.)
The
Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis by level within the fair value
hierarchy are as follows:
|
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2020
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2019
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1,053
|
|
|
|
1,053
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
319
|
|
|
|
319
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
1,372
|
|
|
|
1,372
|
|
Revenue
recognition
Revenues
are recognized when delivery has occurred and there is persuasive evidence of an agreement, the fee is fixed or determinable and collection
of the related receivables is reasonably assured, and no further obligations exist. Revenues from sales of products are recognized when
title and risk and rewards for the products are transferred to the customer.
Research
and development expenses
Research
and development expenses are charged to operations as incurred.
Income
Taxes
Income
taxes are accounted for under the assets and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carry forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted
tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Use of net operating loss
carry forwards for income tax purposes may be limited by Internal Revenue Code section 382 if a change of ownership occurs.
Net
Loss Per Basic and Diluted Common Share
Basic
loss per ordinary share is computed by dividing the loss for the period applicable to ordinary shareholders, by the weighted average
number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Securities that may participate in dividends with the shares of common
stock (such as the convertible preferred) are considered in the computation of basic loss per share under the two-class method. However,
in periods of net loss, only the convertible preferred shares are considered, since such shares have a contractual obligation to share
in the losses of the Company. In computing diluted loss per share, basic loss per share is adjusted to reflect the potential dilution
that could occur upon the exercise of potential shares. Accordingly, in periods of net loss, no potential shares are considered
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION (cont.)
Stock-Based
Compensation
Share-based
payments awarded to consultants (non-employees) are accounted for in accordance with ASC Topic 505-50, “Equity-Based Payments to
Non-Employees”. However, when the Company grants to non-employees a fully vested, nonforfeitable equity instrument, such grants
are measured based on the fair value of the award at the date of grant. When the fully vested, nonforfeitable equity instruments are
granted for services to be received in future periods, the measured cost is recognized as an increase to stockholders’ equity at
the measurement date with an offsetting amount as a deduction from stockholders’ equity within the caption “Services receivable”.
Such amount is subsequently amortized to the statement of operations over the term of the services as an operating expense, as if the
Company has paid periodic payments of cash for the services received from such service provider.
Recently
Issued Accounting Standards
In
June 2016, the FASB issued an ASU that supersedes the existing impairment model for most financial assets to a current expected credit
loss model. The new guidance requires an entity to recognize an impairment allowance equal to its current estimate of all contractual
cash flows the entity does not expect to collect. The Company adopted this guidance effective January 1, 2020, with no material impact
on its consolidated financial statements
In
June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic
326) - Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. This guidance replaces the current incurred loss impairment methodology.
Under the new guidance, on initial recognition and at each reporting period, an entity is required to recognize an allowance that reflects
its current estimate of credit losses expected to be incurred over the life of the financial instrument based on historical experience,
current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts.
The
guidance became effective on January 1, 2020, including interim periods within that year and requires a modified retrospective transition
approach through a cumulative-effect adjustment to retained earnings as of the beginning of the period of adoption. Under the modified
retrospective method of adoption, prior year reported results are not restated. The Company has performed its analysis of the impact
on its financial instruments that are within the scope of this guidance and has concluded that there was no material impact to its consolidated
financial statements.
In
August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework — Changes to the
Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement” (“ASU No. 2018-13”) as part of the FASB’s broader disclosure
framework project. ASU No. 2018-13 removes, modifies and adds certain disclosures, providing greater focus on requirements that clearly
communicate the most important information to the users of the financial statements with respect to fair value measurements. The adoption
of ASU No. 2018-13 as of January 1, 2020 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In
December 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes. The amendments in
this ASU simplify the accounting for income taxes, eliminates certain exceptions to the general principles in Topic 740 and clarifies
certain aspects of the current guidance to improve consistent application among reporting entities. ASU 2019-12 is effective for fiscal
years beginning after December 15, 2021 and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2022, though early adoption
is permitted, including adoption in any interim period for which financial statements have not yet been issued. This standard is not
expected to have a material impact to the Company’s consolidated financial statements after evaluation.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION (cont.)
In
August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-06, Debt - Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives
and Hedging Contracts in Entity s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity s Own
Equity. ASU 2020-06 will simplify the accounting for convertible instruments by reducing the number of accounting models for
convertible debt instruments and convertible preferred stock. Limiting the accounting models results in fewer embedded conversion features
being separately recognized from the host contract as compared with current GAAP. Convertible instruments that continue to be subject
to separation models are (1) those with embedded conversion features that are not clearly and closely related to the host contract, that
meet the definition of a derivative, and that do not qualify for a scope exception from derivative accounting and (2) convertible debt
instruments issued with substantial premiums for which the premiums are recorded as paid-in capital. ASU 2020-06 also amends the
guidance for the derivatives scope exception for contracts in an entity’s own equity to reduce form-over-substance-based accounting
conclusions. ASU 2020-06 will be effective for public companies for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim
periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, but no earlier than fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, including
interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of ASU 2020-06 will
have on the Company’s consolidated financial statement presentation or disclosures.
Other
new pronouncements issued but not effective as of December 31, 2020 are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s
consolidated financial statements.
In
February 2016, the FASB issued a new lease accounting standard, ASU 2016-02 - “Leases”, requiring the recognition of lease
assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. This standard is effective starting January 1, 2019. The adoption of ASU 2016-02 is not
expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
In
May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09
“Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” and modified the standard thereafter. The objective of the ASU is to establish a
single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers that will supersede most
current revenue recognition guidance. The basis of the guidance is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of
promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange
for those goods and services. The Company adopted this standard as of January 1, 2018 using the modified retrospective method. See Note
2.H. to the consolidated financial statements for additional details.
On
January 5, 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, “Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. The standard
requiring changes to recognition and measurement of certain financial assets and liabilities. The standard primarily affects equity investments,
financial liabilities under the fair value option, and the presentation and disclosure requirements for financial instruments. The Company
adopted ASU 2016-01 in the first quarter of 2018 and the impact on its consolidated financial statements was not material.
In
November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18 “Restricted Cash” to provide guidance on the presentation of restricted cash in
the statement of cash flows. Currently, the statement of cash flows explained the change in cash and cash equivalents for the period.
The ASU requires that the statement of cash flows explain the change in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash for the period. The
ASU is effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2018, with early adoption permitted. The Company did not have a material effect
on the statements of cash flows as the Company’s restricted cash is not material.
In
June 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-07 “Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based
Payment Accounting.” These amendments expand the scope of Topic 718, Compensation – Stock Compensation (which currently only
includes share-based payments to employees) to include share-based payments issued to nonemployees for goods or services. Consequently,
the accounting for share-based payments to nonemployees and employees will be substantially aligned. The ASU supersedes Subtopic 505-50,
Equity – Equity-Based Payments to Non-Employees. The Company plans to adopt this standard in the first quarter of 2019. ASU 2018-07
is not expected to have an impact on Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In
August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-13, “Changes to Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurements,” which will improve
the effectiveness of disclosure requirements for recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. The standard removes, modifies,
and adds certain disclosure requirements and is effective for the Company beginning on January 1, 2020. The Company does not expect that
this standard will have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES
|
|
A.
|
On June 5, 2019, the Company
entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”), pursuant to which
the Investor agreed to provide the Company with a convertible loan in the aggregate amount of $1,100,000 in three tranches, and the
Company agreed to issue convertible debentures and a warrant to the Investor.
|
The
first tranche of the convertible debentures in the amount of $200,000 was provided upon execution of the SPA. The second tranche in the
amount of $300,000 was provided on October 23, 2019 upon the Company filing of a Registration Statement on Form S-4 in connection with
the Merger with Samsara Delaware. The third tranche in the amount of $600,000 was provided on November 18, 2019 upon consummation of
the Merger with Samsara Delaware and the fulfillment of all conditions required for the Merger. The Company incurred issuance cost of
$100,000 with connection to those convertible debentures.
Each
tranche of the loan will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%). The principal amount together with the accrued and unpaid
interest will be repayable after two years. Each tranche of the loan together with the accrued and unpaid interest (or any portion at
the discretion of the Investor) will be convertible at any time six months following the issuance date, into shares of Company’s
common stock at a conversion price equal to the lower of $0.003 per share or 80% of the lowest volume-weighted average price (VWAP) of
Company’s share during the period of 10 days preceding the conversion date.
On
December 9, 2019 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the first Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $200,000 and the accrued interest into 9,988 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
July 24, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount of
$50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $22,684 into 12,979 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 5, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $753 into 21,644 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 13, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $481 into 21,522 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
October 12, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $1,671 into 18,454 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 2, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $288 into 23,947 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 16, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $10,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $30,323 into 28,802 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 19, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $159 into 32,256 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES (cont.)
On
December 17, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $4,104 into 35,074shares of Common Stock of the Company.
In
accordance with ASC 815-15-25 the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair
value as its fair value can be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The
Company recorded finance expenses in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible
component fair value over the face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting
gains or losses shown in the statements of operations.
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the
fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the
data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0002
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.43
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2019
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0061
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
34.35
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.43
years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
1.59
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
In
addition, the Company issued to the Investor a warrant to purchase 13,095 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $0.003.
The warrants may be exercised within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of
warrants shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The
Company considered the provisions of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with
respect to the detachable Warrants that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise”
and variable exercise price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which
the Company subsequently issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to
the Company’s own stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition.
In subsequent periods, the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in
the consolidated statement of operations.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES (cont.)
The
warrants were estimated by third party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative
and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the data and assumptions used as
of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0002
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
3.43 years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2019
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0061
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
32.55
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.43 years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
1.61
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
B.
|
On September 3, 2020, Samsara
Luggage, Inc. (the “Company”) entered into a second Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with the “Investor,
pursuant to which the Investor will invest an aggregate amount of $220 in two tranches, and the Company will issue convertible debentures
and warrants to the Investor. The first tranche of the convertible debentures in the amount of $150 was provided upon execution of
the SPA. The second tranche in the amount of $70 was provided on October 7,2020. Each tranche of the loan bears interest at an annual
rate of ten percent (10%). Each tranche of the investment bears interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable
after two years. Each tranche of the investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock at
a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $0.003 per share, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted average
price for the Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date. As part of the transaction,
the Company will issue to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 2,619 shares of Common Stock, at an exercise price equal
to $0.003. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment or through cashless
exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The Company has undertaken to increase its authorized shares of Common Stock to at least 7,000,000,000 within 90 days of the closing.
The SPA and the convertible debentures contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the convertible
debentures by the maturity date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s
right to convert the convertible debentures into shares of common stock.
|
In
accordance with ASC 815-15-25 the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair
value as its fair value can be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The
Company recorded finance expenses in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible
component fair value over the face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting
gains or losses shown in the statements of operations.
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the
fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES (cont.)
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of September 3, 2020:
|
|
|
September 3,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0011
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
177.1
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
2.00
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.12
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.002
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.38
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.67
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.12
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
In
addition, the Company issued to the Investor a warrant to purchase 2,619 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $0.003.
The warrants may be exercised within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of
warrants shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The
Company considered the provisions of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with
respect to the detachable Warrants that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise”
and variable exercise price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which
the Company subsequently issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to
the Company’s own stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition.
In subsequent periods, the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in
the consolidated statement of operations.
The
warrants were estimated by third party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative
and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES (cont.)
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of September 3, 2020:
|
|
|
September,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.0011
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
177.10
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
5.00
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.24
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.002
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.68
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
|
C.
|
On June 26, 2020, the Company
entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with Power Up Lending Group Ltd. (the “Investor”), pursuant
to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with an initial investment in the form of a convertible loan in the principal
amount of $67 (the “Initial Investment”). The SPA contemplates additional financing of up to $925 in the aggregate, subject
to the agreement of both parties. The funds are expected to be used to finance the Company’s working capital needs.
|
The
convertible loan will bear interest at an annual rate of eight percent (8%) with a maturity date of June 25, 2021 (the “Maturity
Date”). The loan will be convertible after six months into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal
to seventy-five percent (75%) of the average of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock during the twenty (20)
trading day period prior to the conversion date. The Company agreed to an original issue discount of $9 and to reimburse the Investor
for its costs in the amount of $3. Accordingly, the net proceeds to the Company from the Initial Investment amounted to $55.
The
SPA and the convertible note contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the loan amount by the Maturity
Date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s right to convert the loan amount
into shares of common stock.
On
December 28, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $38,100 into 36,286 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
December 31, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $23,100 into 22,000 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES (cont.)
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the
fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the
data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
December 30,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
0.002
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
274.38
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.48
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.09
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
The
following table presents the changes in fair value of the level 3 liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2019 and as of December
31, 2020:
|
|
|
Warrants
|
|
|
Convertible
component
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2019
|
|
|
319
|
|
|
|
1,053
|
|
|
Fair value converted
|
|
|
(20
|
)
|
|
|
(151
|
)
|
|
Fair value of issued level 3 liability
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
|
127
|
|
|
Changes in fair value
|
|
|
(287
|
)
|
|
|
(536
|
)
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2020
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
|
D.
|
On August 22, 2018 the
Company (through a related company) entered into a Secured Loan and Service Agreement with an affiliated entity of Moshe Zuk (hereunder
“Zuk”) for the finance of the ongoing working capital of the Company, according to which Zuk granted the Company a loan
in the amount of $200,000. The loan bears a monthly interest at a rate of 2% paid quarterly and calculated daily. The loan was guaranteed
by the Company and by one of its shareholders.
|
In
addition, Zuk granted the Company a credit line of up to $300,000 per year. The credit line shall bear a monthly interest of 1.5% of
the utilized credit line. As of the date of this financial statements, the Company has not utilized such line of credit.
In
addition, the Company issued Zuk 395,500 shares of common stock of the Company representing 7% of the issued and outstanding shares of
the Company on a fully diluted basis, and warrants to purchase 169,500 shares of common stock of the Company representing 3% of the issued
and outstanding shares of the Company on a fully diluted basis, against payment of $50,000. The Company estimated the fair value of such
shares and warrants at a total of $334,000 of which $215,000 and $119,000 were recorded for interest expenses for the years ended December
31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
On
December 31, 2018, the balance of the Zuk loan, net of the unamortized portion of the Zuk shares and options, amounted to $7,000 and
was presented in Other Current Assets.
|
|
E.
|
On March 24, 2019, the
Company entered into a Convertible Loan Agreement with Moshe Zuk (the “Lender”). Under the agreement, the Lender provided
the Company with a loan in the amount of fifty thousand dollars ($50,000). The Company undertook to repay the loan principal, plus
annual interest of 12%, within one year. The Lender may convert the loan plus interest into shares of the Company’s common
stock at a price per share based on the lower of (a) a discount of twenty percent (20%) to the valuation of the Company at the Company’s
first financing round, or (b) a one million-dollar ($1,000,000) valuation.
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
4 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common
Stock
On
November 12, 2019, the Company completed its merger with the Samsara Delaware in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement and
Plan of Merger, dated as of May 10, 2019 by and among the Company, Samsara Delaware, and Avraham Bengio, pursuant to which Samsara Delaware
merged with and into the Company, with the Company being the surviving corporation (the “Merger”). Following the completion
of the Merger, the Company filed (1) Articles of Merger with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company amended
its Articles of Incorporation to change the Company’s name to “Samsara Luggage, Inc.” effective as of November 12,
2019; and (2) a Certificate of Amendment with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada in which the Company increased the number
of authorized shares of common stock of the Company from 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock to 5,000,000,000 shares of common stock
effective as of November 12, 2019.
On
October 5, 2020 the Board of Directors of the Company has approved, and the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our common
stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”), have executed a written consent in lieu of a special meeting approving
to amend the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock from 5,000,000,000
to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”).
Common
Stock Activity During the Years Ended December 31, 2020
At
the effective time of the Merger, each share of common stock of Samsara, $0.0001 par value, was converted into the right to receive 0.065
shares of the Company’s common stock, such that the shareholders of Samsara Delaware were issued new shares of the Company representing
approximately 80% of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock following the completion of the Merger. The
exchange rate was determined through arms’-length negotiations between the Company and Samsara Delaware. Immediately after the
Merger, assuming the issuance of all of the merger consideration, there were approximately3,236,851,080 shares of Common Stock outstanding,
of which (i) the former stockholders of Samsara Delaware owned 2,589,506,080 shares, representing approximately 80% of the outstanding
shares of Common Stock; and (ii) the Company’s stockholders immediately prior to the Merger own 92,478 shares, representing approximately
20% of the outstanding shares of Common Stock.
On
November 12, 2019, the Company issued 32,738 shares of its Common Stock in gross consideration of $500,000 pursuant to a serios securities
purchase agreements from April 2019.
On
December 9, 2019, and pursuant to the YAII Convertible Promissory Note, YAII exercised its option to convert the first Convertible Promissory
Note in the amount of $210,000 into 9,988 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
July 23, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount and
unpaid interest of $72,000 and the accrued interest into 12,979 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 5, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 into 21,644 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 13, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 into 21,552 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
October 12, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $1,671 into 18,454 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
4 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (cont.)
On
November 2, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $288 into 23,947 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 13, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $200,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $23,000 into 28,572 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 16, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $10,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $30,323 into 28,802 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 19, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $159 into 32,256 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
December 17, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $4,104 into 35,074 shares of Common Stock of the Company
On
December 28, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $38,100 into 36,286 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
December 31, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $23,100 into 22,000 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
NOTE
5 – GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES
|
|
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
|
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Professional fees
|
|
|
193
|
|
|
|
359
|
|
|
Share based compensation
|
|
|
687
|
|
|
|
883
|
|
|
Management fees
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
Other expenses
|
|
|
106
|
|
|
|
83
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,086
|
|
|
|
1,425
|
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
6 – INCOME TAXES
On
December 22, 2017, the U.S. enacted new tax reform legislation which reduced the corporate tax rate to 21% effective for tax year beginning
January 1, 2018. Under ASC 740, the effects of new tax legislation are recognized in the period which includes the enactment date. As
a result, the deferred tax assets and liabilities existing on the enactment date must be revalued to reflect the rate at which these
deferred balances will reverse. The corresponding adjustment would generally affect the Income Tax Expense (Benefit) shown on the financial
statements. However, since the company has a full valuation allowance applied against all of its deferred tax asset, there is no impact
to the Income Tax Expense for the year ending December 31, 2020.
IRC
Section 382 potentially limits the utilization of NOLs and tax credits when there is a greater than 50% change of ownership. The Company
has not performed an analysis under IRC 382 related to changes in ownership, which could place certain limits on the company’s
ability to fully utilize its NOLs and tax credits. The Company’s has added a note to its financial statements to disclose that
there may be some limitations and that an analysis has not been performed. In the interim, the Company has placed a full valuation allowance
on its NOLs and other deferred tax items.
We
recognized income tax benefits of $0 during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. When it is more likely than not that a tax asset
will not be realized through future income the Company must allow for this future tax benefit. We provided a full valuation allowance
on the net deferred tax asset, consisting of net operating loss carry forwards, because management has determined that it is more likely
than not that we will not earn income sufficient to realize the deferred tax assets during the carry forward period. Effective December
22, 2017 a new tax bill was signed into law that reduced the federal income tax rate for corporations from 35% to 21%.
The
Company has not taken a tax position that, if challenged, would have a material effect on the financial statements for the years ended
December 2020 or 2019 applicable under FASB ASC 740. We did not recognize any adjustment to the liability for uncertain tax position
and therefore did not record any adjustment to the beginning balance of accumulated deficit on the balance sheet. All tax returns for
the Company remain open.
Reconciliation
between the theoretical tax expense, assuming all income is taxed at the statutory tax rate applicable to income of the Company and the
actual tax expense as reported in the Statement of Operations, is as follows:
|
|
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Loss before taxes, as reported in the statements of operations
|
|
$
|
1,140
|
|
|
$
|
3,142
|
|
|
Federal and State statutory rate
|
|
|
21
|
%
|
|
|
21
|
%
|
|
Theoretical tax benefit on the above amount at federal statutory tax rate
|
|
|
239
|
|
|
|
660
|
|
|
Share-based compensation
|
|
|
(144
|
)
|
|
|
(247
|
)
|
|
Losses and other items for which a valuation allowance Was provided or benefit from loss carry forward
|
|
|
(95
|
)
|
|
|
(413
|
)
|
|
Actual tax income (expense)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
U.S.
dollars in thousands
|
|
|
Deferred tax assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net operating loss carry-forward
|
|
$
|
651
|
|
|
$
|
499
|
|
|
Valuation allowance
|
|
|
(651
|
)
|
|
|
(499
|
)
|
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE
6 – INCOME TAXES (cont.)
A
valuation allowance is provided when it is more likely than not that some portion of the deferred tax asset will not be realized. Management
has determined, based on its recurring net losses, lack of a commercially viable product and limitations under current tax rules, that
a full valuation allowance is appropriate.
|
|
|
U.S.
dollars in
thousands
|
|
|
Valuation allowance, December 31, 2019
|
|
$
|
499
|
|
|
Increase
|
|
|
152
|
|
|
Valuation allowance, December 31, 2020
|
|
$
|
651
|
|
The
net federal operating loss carry forward will begin expire in 2039. This carry forward may be limited upon the consummation of a business
combination under IRC Section 382.
NOTE
7 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Related
Parties Payable
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
December 31,
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Related Parties Payable due to management fee
|
|
|
126
|
|
|
|
105
|
|
General
and Administrative Expenses
|
|
|
For the Year Ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Management Fee
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
100
|
|
NOTE
8 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On
January 11, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, Power-up exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount
of $6 and the accrued interest in the amount of $2 into 7,448 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
SAMSARA LUGGAGE, INC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
BALANCE SHEETS
(U.S.
dollars in thousands except share and per share data)
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
|
|
Unaudited
|
|
|
Audited
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
Accounts Receivables
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
135
|
|
|
|
153
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
147
|
|
|
|
211
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and Equipment, net
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
|
151
|
|
|
|
215
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade payable
|
|
|
143
|
|
|
|
125
|
|
|
Accrued Expense
|
|
|
95
|
|
|
|
74
|
|
|
Related party payables
|
|
|
151
|
|
|
|
126
|
|
|
Convertible notes and short-term loans (Note 3)
|
|
|
326
|
|
|
|
289
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs (Note 3)
|
|
|
484
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan (Note 3)
|
|
|
32
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,231
|
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES
|
|
|
1,231
|
|
|
|
1,127
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock subscribed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, authorized 7,500,000,000 shares, $0.0001 par value; 859,395 issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2021 and 786,700 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020.
|
|
|
86
|
|
|
|
78
|
|
|
Additional paid in capital
|
|
|
6,685
|
|
|
|
6,385
|
|
|
Services receivable
|
|
|
(840
|
)
|
|
|
(999
|
)
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(7,011
|
)
|
|
|
(6,376
|
)
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(1,080
|
)
|
|
|
(912
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
151
|
|
|
|
215
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Unaudited)
(U.S.
dollars in thousands except share and per share data)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Revenues from sales of products
|
|
|
75
|
|
|
|
21
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of sales of products
|
|
|
37
|
|
|
|
(14
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
|
|
38
|
|
|
|
7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development expenses
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
35
|
|
|
Selling and marketing expenses
|
|
|
61
|
|
|
|
82
|
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
265
|
|
|
|
247
|
|
|
TOTAL OPERATING EXPENSES
|
|
|
326
|
|
|
|
364
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING LOSS
|
|
|
(288
|
)
|
|
|
(357
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest and amortization of issuance cost on note and short-term loan
|
|
|
(28
|
)
|
|
|
(33
|
)
|
|
Income (expenses) in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses
|
|
|
(319
|
)
|
|
|
552
|
|
|
TOTAL FINANCING INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
|
|
(347
|
)
|
|
|
519
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCOME (LOSS)
|
|
|
(635
|
)
|
|
|
162
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per basic and diluted share
|
|
|
(0.76
|
)
|
|
|
0.32
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of basic and diluted common shares outstanding
|
|
|
841,003
|
|
|
|
505,134
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
CONDENSED
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited)
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (loss)
|
|
|
(635
|
)
|
|
|
162
|
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash used in operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of services receivable
|
|
|
159
|
|
|
|
161
|
|
|
Interest on convertible note and short-term loan and amortization of issuance cost
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
|
33
|
|
|
Expenses in respect of warrants issued and convertible component in convertible loan, net interest expenses
|
|
|
319
|
|
|
|
(552
|
)
|
|
Depreciation and amortization expense
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
18
|
|
|
|
(22
|
)
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
7
|
|
|
Related parties, net
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
38
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Other Accounts payable
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(15
|
)
|
|
Net Cash Used by Operating Activities
|
|
|
(46
|
)
|
|
|
(120
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from loans payable
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Decrease in Cash
|
|
|
(46
|
)
|
|
|
(70
|
)
|
|
Cash at Beginning of Period
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
|
129
|
|
|
Cash at End of Period
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
|
59
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued for conversion of convertible note and accrued interest
|
|
|
121
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued against accounts payables
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed financial statements
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
1 – GENERAL
|
|
A.
|
Samsara
Luggage, Inc. (the “Company”)
|
The
Company was incorporated on May 7, 2007 under the name, “Darkstar Ventures, Inc.” under the laws of the State of Nevada.
The Company is a global smart luggage and smart travel brand. Samsara Luggage unveiled its Next Generation smart carry-on at
the 2020 Consumer Electronics Show (CES). The Next Generation is the first to market a Wi-Fi Hotspot technology for travelers to access
a secured network globally. Samsara Luggage also launched Essentials by Samsara, a safety kit providing commuters with a new layer
of safety with protective items like facemasks, hand sanitizer, disposable gloves and alcohol wipes. These kits are sold individually
and gifted to customers with purchase of the Carry-on Aluminum suitcase or Smart Weekender bag. During the last quarter of
2020, Samsara launched Sarah & Sam Fashion and Lifestyle Collection. Sarah& Sam is a part of Samsara Direct business
model prompted by the travel limitations due to the coronavirus pandemic, leveraging the company’s established digital assets and
manufacturing and fulfillment supply chain capabilities to offer additional consumer products that respond to the changing needs of the
market.
On
November 12, 2019, the Company completed its merger with the Delaware corporation that was previously known as “Samsara Luggage,
Inc.” (“Samsara Delaware”) in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May
10, 2019, (the “Merger Agreement”) by and among the Company, Samsara Delaware, and Avraham Bengio, pursuant to which Samsara
Delaware merged with and into the Company, with the Company being the surviving corporation (the “Merger”). Following the
completion of the Merger, the business of the Company going forward became the business of Samsara Delaware prior to the Merger, namely,
designing, manufacturing, and selling high quality luggage products to meet the evolving needs of frequent travelers and also seeking
to present new technologies within the aluminum luggage industry, including an aluminum “smart” suitcase.
The
Common Stock listed on the OTC Pink Marketplace, previously trading through the close of business on November 11, 2019 under the ticker
symbol “DAVC,” commenced trading on the OTC Pink Marketplace under the ticker symbol “SAML” on November 12, 2019.
The Common Stock has a new CUSIP number, 79589J101. On August 24, 2021, the Company’s Common Stock began listing on the OTCQB.
On
October 5, 2020 the Board of Directors of the Company has approved, and the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of our
common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”), have executed a written consent in lieu of a special meeting
approving to amend the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock from 5,000,000,000
to 7,500,000,000 (the “Authorized Capital Increase”).
The
accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As of March 31, 2021,
the Company had approximately $8 in cash and cash equivalents, approximately $1,084 in deficit of working capital, a stockholders’
deficiency of approximately $1,080 and an accumulated deficit of approximately $7,011. These conditions raise substantial doubt about
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon
raising capital from financing transactions and revenue from operations. Management anticipates their business will require substantial
additional investments that have not yet been secured. Management is continuing in the process of fund raising in the private equity
and capital markets as the Company will need to finance future activities. These financial statements do not include any adjustments
that may be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
On
March 22, 2021, the Company completed a reverse stock split of its common stock. As a result of the reverse stock split, the following
changes have occurred (i) every seven thousand shares of common stock have been combined into one share of common stock; (ii) the number
of shares of common stock underlying each common stock option or common stock warrant have been proportionately decreased on a 7,000-for-1
basis, and the exercise price of each such outstanding stock option and common warrant has been proportionately increased on a 7,000
-for-1 basis. Accordingly, all option numbers, share numbers, warrant numbers, share prices, warrant prices, exercise prices and losses
per share have been adjusted within these consolidated financial statements, on a retroactive basis, to reflect this 7,000 -for-1 reverse
stock split.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Unaudited
Interim Financial Statements
The
accompanying unaudited financial statements include the accounts of the Company, prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally
accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Article 10 of U.S. Securities
and Exchange Commission Regulation S-X. Accordingly, they do not include all the information and footnotes required by generally accepted
accounting principles for complete financial statements. In the opinion of management, the financial statements presented herein have
not been audited by an independent registered public accounting firm but include all material adjustments (consisting of normal recurring
adjustments) which are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair statement of the financial condition, results of operations
and cash flows for the for three-months ended March 31, 2021. However, these results are not necessarily indicative of results for any
other interim period or for the year ended December 31, 2021. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires
the Company to make certain estimates and assumptions for the reporting periods covered by the financial statements. These estimates
and assumptions affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. Actual amounts could differ from these estimates.
Certain
information and footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
have been omitted pursuant to the rules of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). The accompanying unaudited
condensed financial statements should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and notes thereto included in our Annual Report
on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020, filed with the SEC on March 30, 2021 (the “Annual Report”). For
further information, reference is made to the financial statements and footnotes thereto included in the Company’s Annual Report
on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Use
of Estimates
The
preparation of unaudited condensed financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States
requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, certain revenues and
expenses, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements. Actual results could differ
from those estimates. Estimates are used when accounting for Warrants and Convertible Note and Going Concern.
Derivative
and Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair
value accounting requires bifurcation of embedded derivative instruments such as conversion features in convertible debt or equity instruments
and measurement of their fair value for accounting purposes. In assessing the convertible debt instruments, management determines if
the convertible debt host instrument is conventional convertible debt and further if there is a beneficial conversion feature requiring
measurement. If the instrument is not considered conventional convertible debt under ASC 470, the Company will continue its evaluation
process of these instruments as derivative financial instruments under ASC 815.
Once
determined, derivative liabilities are adjusted to reflect fair value at each reporting period end, with any increase or decrease in
the fair value being recorded in results of operations as an adjustment to fair value of derivatives.
Fair
value of certain of the Company’s financial instruments including cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses,
notes payables, and other accrued liabilities approximate cost because of their short maturities. The Company measures and reports fair
value in accordance with ASC 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosure” defines fair value, establishes a framework for
measuring fair value in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and expands disclosures about fair value measurements.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
Fair
value, as defined in ASC 820, is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date. The fair value of an asset should reflect its highest and best use by market participants,
principal (or most advantageous) markets, and an in-use or an in-exchange valuation premise. The fair value of a liability should reflect
the risk of nonperformance, which includes, among other things, the Company’s credit risk.
Valuation
techniques are generally classified into three categories: the market approach; the income approach; and the cost approach. The selection
and application of one or more of the techniques may require significant judgment and are primarily dependent upon the characteristics
of the asset or liability, and the quality and availability of inputs. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under ASC 820
must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. ASC 820 also provides fair value hierarchy for
inputs and resulting measurement as follows:
Level
1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical assets or liabilities.
Level
2: Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in
markets that are not active; inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability; and inputs that are derived
principally from or corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities; and
Level
3: Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability that are supported by little or no market activity, and that are significant to the
fair values.
Fair
value measurements are required to be disclosed by the Level within the fair value hierarchy in which the fair value measurements in
their entirety fall. Fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs (in Level 3 measurements) are subject to expanded
disclosure requirements including a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances, separately presenting changes during the period
attributable to the following: (i) total gains or losses for the period (realized and unrealized), segregating those gains or losses
included in earnings, and a description of where those gains or losses included in earning are reported in the statement of income.
The
Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis by level within the fair value
hierarchy are as follows:
|
|
|
Balance as of March 31, 2021
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
484
|
|
|
|
484
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
32
|
|
|
|
32
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
516
|
|
|
|
516
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2020
|
|
|
|
|
Level 1
|
|
|
Level 2
|
|
|
Level 3
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value of convertible component in convertible loan, net of discounts and debt issue costs
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value of warrants issued in convertible loan
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
|
|
513
|
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
Recently
Issued Accounting Standards
In
June 2016, the FASB issued an ASU that supersedes the existing impairment model for most financial assets to a current expected credit
loss model. The new guidance requires an entity to recognize an impairment allowance equal to its current estimate of all contractual
cash flows the entity does not expect to collect. The Company adopted this guidance effective January 1, 2020, with no material impact
on its consolidated financial statements
In
June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic
326) - Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. This guidance replaces the current incurred loss impairment methodology.
Under the new guidance, on initial recognition and at each reporting period, an entity is required to recognize an allowance that reflects
its current estimate of credit losses expected to be incurred over the life of the financial instrument based on historical experience,
current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts.
The
guidance became effective on January 1, 2020, including interim periods within that year and requires a modified retrospective transition
approach through a cumulative-effect adjustment to retained earnings as of the beginning of the period of adoption. Under the modified
retrospective method of adoption, prior year reported results are not restated. The Company has performed its analysis of the impact
on its financial instruments that are within the scope of this guidance and has concluded that there was no material impact to its consolidated
financial statements.
In
August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure
Framework
— Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement” (“ASU No. 2018-13”) as part of the FASB’s
broader disclosure framework project. ASU No. 2018-13 removes, modifies and adds certain disclosures, providing greater focus on requirements
that clearly communicate the most important information to the users of the financial statements with respect to fair value measurements.
The adoption of ASU No. 2018-13 as of January 1, 2020 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Recently
Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In
December 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes. The amendments in
this ASU simplify the accounting for income taxes, eliminates certain exceptions to the general principles in Topic 740 and clarifies
certain aspects of the current guidance to improve consistent application among reporting entities. ASU 2019-12 is effective for fiscal
years beginning after December 15, 2021 and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2022, though early adoption
is permitted, including adoption in any interim period for which financial statements have not yet been issued. This standard is not
expected to have a material impact to the Company’s consolidated financial statements after evaluation.
In
August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-06, Debt - Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives
and Hedging Contracts in Entity s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity s Own
Equity. ASU 2020-06 will simplify the accounting for convertible instruments by reducing the number of accounting models for
convertible debt instruments and convertible preferred stock. Limiting the accounting models results in fewer embedded conversion features
being separately recognized from the host contract as compared with current GAAP. Convertible instruments that continue to be subject
to separation models are (1) those with embedded conversion features that are not clearly and closely related to the host contract, that
meet the definition of a derivative, and that do not qualify for a scope exception from derivative accounting and (2) convertible debt
instruments issued with substantial premiums for which the premiums are recorded as paid-in capital. ASU 2020-06 also amends the
guidance for the derivatives scope exception for contracts in an entity’s own equity to reduce form-over-substance-based accounting
conclusions. ASU 2020-06 will be effective for public companies for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, including interim
periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, but no earlier than fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, including
interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of ASU 2020-06 will
have on the Company’s consolidated financial statement presentation or disclosures.
Other
new pronouncements issued but not effective as of March 31, 2021 are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
financial statements.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
3 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES
|
|
A.
|
On
June 5, 2019, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”),
pursuant to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with a convertible loan in the aggregate amount of $1,100,000 in three
tranches, and the Company agreed to issue convertible debentures and a warrant to the Investor.
|
The
first tranche of the convertible debentures in the amount of $200,000 was provided upon execution of the SPA. The second tranche in the
amount of $300,000 was provided on October 23, 2019 upon the Company filing of a Registration Statement on Form S-4 in connection with
the Merger with Samsara Delaware. The third tranche in the amount of $600,000 was provided on November 18, 2019 upon consummation of
the Merger with Samsara Delaware and the fulfillment of all conditions required for the Merger. The Company incurred issuance cost of
$100,000 with connection to those convertible debentures.
Each
tranche of the loan will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%). The principal amount together with the accrued and unpaid
interest will be repayable after two years. Each tranche of the loan together with the accrued and unpaid interest (or any portion at
the discretion of the Investor) will be convertible at any time six months following the issuance date, into shares of Company’s
common stock at a conversion price equal to the lower of $0.003 per share or 80% of the lowest volume-weighted average price (VWAP) of
Company’s share during the period of 10 days preceding the conversion date.
On
December 9, 2019 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the first Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $200,000 and the accrued interest into 9,988 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
July 24, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount of
$50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $22,684 into 12,979 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 5, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $753 into 21,644 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
August 13, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal amount
of $75,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $481 into 21,522 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
October 12, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $1,671 into 18,454 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 2, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $288 into 23,947 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 16, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $10,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $30,323 into 28,802 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
November 19, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $159 into 32,256 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
December 17, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $45,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $4,104 into 35,074 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
January 14, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $3,625 into 38,303 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
On
February 11, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $55,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $3,496 into 16,713 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
In
accordance with ASC 815-15-25 the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair
value as its fair value can be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The
Company recorded finance expenses in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible
component fair value over the face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting
gains or losses shown in the statements of operations.
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the
fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are
the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
2.20
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
349.98
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.18
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.01
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
308
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.40
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
0.43
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
330
|
|
In
addition, the Company issued to the Investor a warrant to purchase 13,095 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $21.00.
The warrants may be exercised within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of
warrants shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The
Company considered the provisions of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with
respect to the detachable Warrants that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise”
and variable exercise price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which
the Company subsequently issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to
the Company’s own stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition.
In subsequent periods, the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in
the consolidated statement of operations.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
The
warrants were estimated by third party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative
and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet date. The following are the data and assumptions used
as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
2.20
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
251.36%
|
|
|
Expected term
|
|
3.18 years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
0.4%
|
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
0%
|
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$27
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
1.40
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
227.88%
|
|
|
Expected term
|
|
3.43 years
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
0.19%
|
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
0%
|
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$16
|
|
|
|
B.
|
On
September 3, 2020, Samsara Luggage, Inc. (the “Company”) entered into a second Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”)
with the “Investor, pursuant to which the Investor will invest an aggregate amount of $220 in two tranches, and the Company
will issue convertible debentures and warrants to the Investor. The first tranche of the convertible debentures in the amount of
$150 was provided upon execution of the SPA. The second tranche in the amount of $70 was provided on October 7, 2020. Each tranche
of the loan bears interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%). Each tranche of the investment bears interest at an annual rate
of ten percent (10%) and will be repayable after two years. Each tranche of the investment will be convertible at any time into shares
of the Company’s Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $0.003 per share, or (b) 80% of the lowest the
daily dollar volume-weighted average price for the Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding
the conversion date. As part of the transaction, the Company will issue to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 2,619
shares of Common Stock, at an exercise price equal to $0.003. The term of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant
may be exercised by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise
price of the portion of the warrant being exercised. The Company has undertaken to increase its authorized shares of Common Stock
to at least 7,000,000,000 within 90 days of the closing. The SPA and the convertible debentures contain events of default, including,
among other things, failure to repay the convertible debentures by the maturity date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that
could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s right to convert the convertible debentures into shares of common stock.
|
In
accordance with ASC 815-15-25 the conversion feature was considered embedded derivative instruments, and is to be recorded at their fair
value as its fair value can be separated from the convertible loan and its conversion is independent of the underlying note value. The
Company recorded finance expenses in respect of the convertible component in the convertible loan in the excess amount of the convertible
component fair value over the face loan amount. The conversion liability is then marked to market each reporting period with the resulting
gains or losses shown in the statements of operations.
The
fair value of the convertible component was estimated by third party appraiser using the Monte Carlo Simulation Model to compute the
fair value of the derivative and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet dates:
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet date:
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
2.20
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
251.36
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.42
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.12
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
176
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.39
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.38
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
1.67
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.12
|
%
|
|
Forfeiture rate
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Convertible component
|
|
$
|
157
|
|
In
addition, the Company issued to the Investor a warrant to purchase 2,619 shares of common stock, at an exercise price equal to $21.00.
The warrants may be exercised within 5 years from the issuance date by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the surrender of
warrants shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
The
Company considered the provisions of ASC 815-40, “Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, with
respect to the detachable Warrants that were issued to the Convertible loan, and determined that as a result of the “cashless exercise”
and variable exercise price that would adjust the number of Warrants and the exercise price of the Warrants based on the price at which
the Company subsequently issues shares or other equity-linked financial instruments, such Warrants cannot be considered as indexed to
the Company’s own stock. Accordingly, the Warrants were recognized as derivative liability at their fair value on initial recognition.
In subsequent periods, the Warrants were marked to market with the changes in fair value recognized as financing expense or income in
the consolidated statement of operations.
The
warrants were estimated by third party appraiser using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to compute the fair value of the derivative
and to mark to market the fair value of the derivative at each balance sheet dates:
The
following are the data and assumptions used as of the balance sheet dates:
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
2.20
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
251.36
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.43
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
Common stock price
|
|
|
1.39
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
227.88
|
%
|
|
Expected term
|
|
|
4.68
|
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
|
0.19
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
|
Fair Market Value of Warrants
|
|
$
|
4
|
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
|
|
C.
|
On
June 26, 2020, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with Power Up Lending Group Ltd. (the
“Investor”), pursuant to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with an initial investment in the form of a
convertible loan in the principal amount of $67 (the “Initial Investment”). The SPA contemplates additional financing
of up to $925 in the aggregate, subject to the agreement of both parties. The funds are expected to be used to finance the Company’s
working capital needs.
|
The
convertible loan will bear interest at an annual rate of eight percent (8%) with a maturity date of June 25, 2021 (the “Maturity
Date”). The loan will be convertible after six months into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal
to seventy-five percent (75%) of the average of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock during the twenty (20)
trading day period prior to the conversion date. The Company agreed to an original issue discount of $9 and to reimburse the Investor
for its costs in the amount of $3. Accordingly, the net proceeds to the Company from the Initial Investment amounted to $55.
The
SPA and the convertible note contain events of default, including, among other things, failure to repay the loan amount by the Maturity
Date, and bankruptcy and insolvency events, that could result in the acceleration of the Investor’s right to convert the loan amount
into shares of common stock.
On
December 28, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $38,100 into 36,286 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
December 31, 2020 and pursuant to the SPA, Power- Up exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal
in the amount of $23,100 into 22,000 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
On
January 11, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, Power-up exercised its option to convert the Convertible Promissory Note principal in the amount
of $ 7 and the accrued interest in the amount of $ 1 into 7,448 shares of Common Stock of the Company.
The
following table presents the changes in fair value of the level 3 liabilities for the period ended March 31, 2021:
|
|
|
Warrants
|
|
|
Convertible
component
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2020
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
493
|
|
|
Fair value converted
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(149
|
)
|
|
Fair value of issued level 3 liability
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Changes in fair value
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
|
140
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2021
|
|
|
32
|
|
|
|
484
|
|
|
|
D.
|
On
August 22, 2018 the Company (through a related company) entered into a Secured Loan and Service Agreement with an affiliated entity
of Moshe Zuk (hereunder “Zuk”) for the finance of the ongoing working capital of the Company, according to which Zuk
granted the Company a loan in the amount of $200,000. The loan bears a monthly interest at a rate of 2% paid quarterly and calculated
daily. The loan was guaranteed by the Company and by one of its shareholders. In addition, Zuk granted the Company a credit line
of up to $300,000 per year. The credit line shall bear a monthly interest of 1.5% of the utilized credit line. As of the date of
these financial statements, the Company has not utilized such line of credit.
|
|
|
E.
|
On
March 24, 2019, the Company entered into a Convertible Loan Agreement with Moshe Zuk (the “Lender”). Under the agreement,
the Lender provided the Company with a loan in the amount of fifty thousand dollars ($50,000). The Company undertook to repay the
loan principal, plus annual interest of 12%, within one year. The Lender may convert the loan plus interest into shares of the Company’s
common stock at a price per share based on the lower of (a) a discount of twenty percent (20%) to the valuation of the Company at
the Company’s first financing round, or (b) a one million-dollar ($1,000,000) valuation.
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
4 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Related
party balances at March 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020 consisted of the following:
Related
Parties Payable
|
|
|
March 31,
2021
|
|
|
December 31,
2020
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Related Parties Payable due to management fee
|
|
|
151
|
|
|
|
126
|
|
General
and Administrative Expenses
|
|
|
For the Period Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
|
(U.S.
dollars in thousands)
|
|
|
Management Fee
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
|
25
|
|
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
5 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common
Stock
The
following summarizes the Common Stock activity for the three months ended March 31, 2021:
|
Summary of common stock activity for the three months ended March 31, 2021
|
|
Outstanding
shares
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2020
|
|
|
786,700
|
|
|
Shares issued due to conversion of Notes.
|
|
|
62,464
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
7,383
|
|
|
Roundup shares due to reverse split.
|
|
|
2,849
|
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2021
|
|
|
859,395
|
|
On
January 14, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $50,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $3,625 into 38,303 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market
value of the shares was $64.
On
January 21, 2021, the Company issued 7,383 shares of its Common Stock pursuant to a service Agreement between the Company and a service
provider. The fair market value of the shares was $20.
On
February 11, 2021 and pursuant to the SPA, YAII exercised its option to convert the second Convertible Promissory Note principal in the
amount of $55,000 and the accrued interest in the amount of $3,496 into 16,713 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The fair market
value of the shares was $216.
On
March 22, 2021, the Company completed a reverse stock split of its common stock. As a result of the reverse stock split, the following
changes have occurred (i) every seven thousand shares of common stock have been combined into one share of common stock; (ii) the number
of shares of common stock underlying each common stock option or common stock warrant have been proportionately decreased on a 7,000-for-1
basis, and the exercise price of each such outstanding stock option and common warrant has been proportionately increased on a 7,000-for-1
basis. Accordingly, all option numbers, share numbers, warrant numbers, share prices, warrant prices, exercise prices and losses per
share have been adjusted within these consolidated financial statements, on a retroactive basis, to reflect this 7,000-for-1 reverse
stock split.
On
March 23, 2021, the Company issued 2,849 shares of its Common Stock due to a reverse split rounding up differences.
SAMSARA
LUGGAGE, INC.
NOTES
TO UNAUDITED CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts
in U.S. dollar thousands, except share and per share data)
NOTE
6 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On
April 6, 2021, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with YAII PN, Ltd. (the “Investor”),
pursuant to which the Investor agreed to provide the Company with a convertible loan in the aggregate amount of $150, and the Company
agreed to issue convertible debentures and a warrant to the Investor. The loan will bear interest at an annual rate of ten percent (10%)
and will be repayable after two years. The investment will be convertible at any time into shares of the Company’s Common Stock
at a conversion price equal to the lower of (a) $3.46, or (b) 80% of the lowest the daily dollar volume-weighted average price for the
Company’s Common Stock during the 10 trading days immediately preceding the conversion date. As part of the transaction, the Company
issued to the Investor warrants to purchase an aggregate of 10,838 shares of Common Stock, at an exercise price equal to $3.46. The term
of each warrant is five years from the issue date. Each warrant may be exercised by cash payment or through cashless exercise by the
surrender of warrant shares having a value equal to the exercise price of the portion of the warrant being exercised.
PROSPECTUS
361,596
Shares of Common Stock

Samsara
Luggage, Inc.
September
3, 2021
Samsara Luggage (PK) (USOTC:SAML)
Historical Stock Chart
From Mar 2024 to Apr 2024
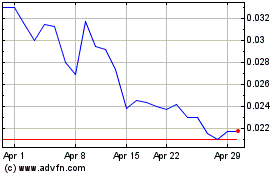
Samsara Luggage (PK) (USOTC:SAML)
Historical Stock Chart
From Apr 2023 to Apr 2024