If any of the securities being registered
on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the
following box. ☒
If this Form is filed to register additional
securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities
Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment
filed pursuant to rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement
number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment
filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement
number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant
is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company.
See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,”
and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
You should carefully read all information
in the prospectus, including the financial statements and their explanatory notes under the Financial Statements prior to making
an investment decision.
This summary highlights selected information
appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. While this summary highlights what we consider to be important information about us, you
should carefully read this entire prospectus before investing in our Common Stock, especially the risks and other information we
discuss under the headings “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition
and Results of Operation” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes beginning on page F-1. Our fiscal year
end is June 30 and our fiscal years ended June 30, 2018 and 2019 are sometimes referred to herein as fiscal years 2018 and 2019,
respectively. Some of the statements made in this prospectus discuss future events and developments, including our future strategy
and our ability to generate revenue, income and cash flow. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties which
could cause actual results to differ materially from those contemplated in these forward-looking statements. See “Cautionary
Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements”. Unless otherwise indicated or the context requires otherwise, the words “we,”
“us,” “our”, the “Company” or “our Company” or “SmartMetric” refer
to SmartMetric, Inc., a Nevada corporation and its wholly-owned subsidiary, SmartMetric Australia Pty. Ltd.
Corporate History and Business Overview
SmartMetric, Inc. (“SmartMetric”
or the “Company”) was incorporated pursuant to the laws of Nevada on December 18, 2002. SmartMetric is a development
stage company engaged in the technology industry. SmartMetric’s main products are a fingerprint sensor debit card as well
as a card with a finger sensor and fully functional fingerprint reader embedded inside the card. The SmartMetric biometric cards
have a rechargeable battery allowing for portable biometric identification and card activation. This card is referred to as a biometric
card or the SmartMetric Biometric Card.
The Market for Biometric Credit Cards
According to a to a press release issued
by Goode Intelligence, an independent market research company, regarding their October 2018 report on the biometrics payment sector,
nearly 579 million biometric credit/debit cards will be in use over the next five (5) years. Goode Intelligence believes* there
is a significant market opportunity for biometric payment cards. and forecasts that by 2023 there will be almost 579 million biometric
payment cards in use around the world.
“Contactless card payments are even
outperforming mobile in many regions. Many consumers prefer to use a contactless payment card over a mobile payment equivalent
and according to Goode Intelligence research, many users would like to use cards in contactless mode for higher value transactions.
Biometric payment cards not only offer improved security by removing the PIN but also allow frictionless payments for higher value
transactions,” stated Good Intelligence.
SmartMetric engaged an outside independent
research company to survey a statistically relevant sample of Visa credit card holders in the United States. One of the questions
asked showed that nearly 67% of these credit card holders would be willing to pay $69.95 for a biometric secured credit card.
The survey asked:
Would you pay for a safer biometric secured credit card that
has a built-in fingerprint reader for your protection?
|
|
*
|
Goode Intelligence is an independent analyst and consultancy company
that provides quality advice to global decision makers in business and technology.
|
Goode Intelligence works in information
security, mobile security, authentication and identity verification, biometrics, enterprise mobility and mobile commerce sectors.
Founded in 2007 by Alan Goode and headquartered
in London, Goode. Intelligence helps both technology providers, investors and IT purchasers make strategic business decisions based
on quality research, insight and consulting.
The SmartMetric Biometric Technology
and Products
SmartMetric’s founder, Chaya Hendrick
is the originator and inventor of various miniature biometric activated cards, including the SmartMetric biometric fingerprint
activated payments card with an embedded fully functional fingerprint reader inside. the card. The card is the size and thickness
of a standard credit card. The SmartMetric biometric payments card provides for high level security for credit and debit cards
by adding biometric authentication and activation to Europay, MasterCard and Visa (“EMV”) chip cards in use around
the world. The SmartMetric biometric payments card has been manufactured to be totally interoperable with existing EMV chip card
readers, ATMs as well as banking payments infrastructure. Using the advanced electronic miniaturization by SmartMetric to make
its biometric credit/debit cards the Company has also created a multi-functional biometric building access control and logical
network access card.
Since July 1, 2018, SmartMetric has commenced
efforts towards creating a biometric health insurance card with memory for storing a person’s medical files, including medical
images. This allows a person to securely take with them their private medical files inside the card when traveling away from home.
For the first time, a person’s complete medical files can be stored in a credit card-sized card and the information is only
able to be accessed by the card holder’s own fingerprint. The company is in discussion with significant health membership
organizations concerning the offering of the SmartMetric Biometric Medical Records card to their respective members.
SmartMetric has developed its rechargeable
battery powered fingerprint reader that is of a scale that fits “inside” a standard credit or debit card. The cardholder
has stored inside the card his or her fingerprint. To activate the card the person swipes the fingerprint sensor, the sensor is
connected to an internal microprocessor that manages the fingerprint sensor fingerprint image capture and comparison matching with
the pre-stored fingerprint of the cardholder held in the internal electronic memory of the card. The card has a surface mounted
EMV chip as found on EMV banking chip cards that is activated or turned on only after a card holder’s fingerprint has been
scanned and verified using the SmartMetric miniature “in-card” biometric scanner.
There are over seven (7) billion EMV chip
cards used by banks around the world for credit cards, ATM cards and debit cards according to EMVco. SmartMetric sees this existing
user base as a natural market for its advanced biometric activated card technology for the credit and debit card market. SmartMetric
has established a network of card manufacturers and technology distributors to market its in-card biometric products to card issuing
banks and in the case of the SmartMetric biometric security card, to businesses.
SmartMetric has completed development of
its biometric card and is now actively marketing its card to major card issuing banks throughout the world in partnership with
established card distributors and dealers.
SmartMetric has also developed a multi-function
logical and physical access security card this size and thickness of a standard credit card. Utilizing the small size breakthroughs
by the Company in its biometric payments card development, SmartMetric has successfully developed a biometric security card that
is the size and thickness of a standard credit card that can easily fit inside a person’s wallet.
As with the biometric payments card, the
SmartMetric security card has an internal rechargeable battery that is used to power the card’s internal processor used in
the biometric fingerprint scan. All functions and operations of the card are subject to a valid fingerprint scan and match of the
card user.
On February 1, 2019, SmartMetric entered
into a manufacturing and license agreement with Servired, SA (“Servired”). Servired operates the major payments network
in Spain for credit and debit card transactions. Subsequently, the Servired agreement has been transferred and assumed in total
by RedSys, SA. (“RedSys”) as part of a corporate reorganization. RedSys is now the corporate entity that owns the ADVANTIS
(discussed later) credit card and debit card chip and operating software system. Regarding integration of Advantis in Redsys, Redsys
acquired from Servired, through company succession, the independent economic marketing unit of the Advantis System and the Pricenet,
SIS and SAS family programs.
The ADVANTIS EMV Chip and operating system
is currently being used by banks around the world on their debit and credit cards. 1.4 Billion cards with the ADVANTIS chip and
software operating system have been issued by their member banks worldwide.
SmartMetric is now in the process of manufacturing
its biometric credit/debit card with the ADVANTIS payments card chip and operating system. This will allow over 500 Banks worldwide,
who are already using the ADVANTIS chip and chip card operating system, to seamlessly issue this new SmartMetric – ADVANTIS
biometric credit and debit card.
Additional technological advances have
now been made on both the Company’s biometric credit/debit card and its multifunction cyber security, building access to
the biometric card.
In Card Fingerprint Matching and Verification
The SmartMetric Biometric card incorporates
a rechargeable, lithium polymer battery. This battery is rechargeable, very thin and has been designed by SmartMetric to fit inside
the SmartMetric fingerprint credit card sized card. This battery is manufactured by a third party unaffiliated with the Company
to SmartMetric’s specifications. This battery is embedded inside the card.
Other components needed for manufacture
of the SmartMetric Biometric Card include, but are not limited to, sensors, microchips, memory chips and processor chips. The ultra-thin
circuit board developed by SmartMetric has, in total, nearly 200 active and passive components. The sources and availability of
these materials are numerous, readily available and should not affect the ability of SmartMetric to meet future demand. The supply
of memory processors and passive components may be interrupted at any time based on global supply/demand issues. We have not experienced
component supply issues to date and the Company, as a matter of policy, has alternative component sources to mitigate and protect
against supply chain issues.
The biometric card has been designed to
offer the option of a built-in radio frequency transmitter for contactless access and identity verification. The RFID contactless
chip transmission is turned on using the card users fingerprint verification.
The thinness form factor of many of the
components, has also resulted in the Company having to develop its own process for high volume electronic assembly. The Company
has also successfully overcome the challenge of developing a process of encapsulating the electronics in plastic to create the
credit card sized biometric fingerprint activated card that also has an internal rechargeable battery.
Standard credit card manufacturing utilizes
machines that require high pressure and high temperature in fusing top and bottom sheets of plastic together thereby encasing any
electronics inside the card. Given the complexity of the card’s electronics and vulnerability to an assembly process involving
high heat and high pressure, damage to the electronic circuitry was a major challenge for the Company to overcome. Research and
development activities of the Company allowed the Company to achieve this ability through a trade secret process that protects
the silicon and internal battery that is mounted directly onto the card’s internal electronics circuit board.
The Security Technology Industry
SmartMetric Biometric Multi-Function Security Card
SmartMetric has developed a multi-function
logical and physical access security card this size and thickness of a standard credit card. Utilizing the small size breakthroughs
by the Company in its biometric payments card development, SmartMetric has successfully developed a biometric security card that
can easily fit inside a person’s wallet.
As with the biometric payments card, the
SmartMetric security card has an internal rechargeable battery that is used to power the card’s internal processor used in
the biometric fingerprint scan. All functions and operations of the card are subject to a valid fingerprint scan and match of the
card user.
The main features of the SmartMetric biometric security card
are:
|
|
1.
|
Logical access smartcard card chip for insertion into a card reader attached to a computer or network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.
|
RFID transceiver for physical access i.e. doorways, elevators, etc.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
Validation indicator light that glows green immediately following a fingerprint validation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Rechargeable battery to power the card
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.
|
Size and thickness of a credit card
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
Changeable security code on reverse of card for additional log on security
|
Cybersecurity and identity validation for
network access control, physical building entry and secure on-the-spot identity security is now handled by the revolutionary biometric
activated cyber and ID multi-function security card which has been developed by SmartMetric after over a decade of R&D.
From governments to the workplace, better,
stronger security is desired across the enterprise. Our new biometric multifunction security card provides a revolutionary biometric
based solution that is portable, easily integrated and backward compatible to existing backend security infrastructure.
The new multifunction biometric security
card by SmartMetric is a revolutionary leap forward in the Cyber and Access Security world according to SmartMetric.
Access management market is estimated to
grow from USD 8.09 billion in 2016 to USD 14.82 billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 12.9% between 2016 and 2021 according to a recent
research report by KBV Research in a publication titled Identity & Access Management Market – Global Forecast by Marqual
IT Solutions Pvt. Ltd (KBV Research) November 2016 KBV Research is a name owned by IT Solutions Pvt. Ltd.
Recent Developments
The COVID-19 has had an impact on SmartMetric's
final card production. While the delays are due to supply line disruption, the Company is confident that these delays will be
short-lived based on advice from our manufacturing partners, manufacturing alternatives and alternative supply lines that are
being put into place by the Company..
Sales and Marketing
SmartMetric has engaged distributors and
dealers in both North and South America. SmartMetric has entered into an agreement with Redsys the owner of the ADVANTIS credit
and debit card chip that is used in over 1.4 Billion credit/debit cards globally. RedSys/Advantis is owned by card issuing Banks.
Five hundred (500) card issuing banking organizations around the world are issuing credit and debit cards with the RedSys/ADVANTIS
chip.
SmartMetric has added the ADVANTIS credit/debit
card chip onto the SmartMetric biometric card thereby allowing the existing RedSys / ADVANTIS banks already issuing credit and
debit cards with their chip on board to now issue seamlessly the SmartMetric biometric credit / debit card. RedSys / ADVANTIS have
agreed to work closely with SmartMetric in promoting the SmartMetric card globally. RedSys / ADVANTIS is owned by some the largest
Banks in Europe and Latin America.
Intellectual Property
We rely on patents, licenses, trade secrets,
trademarks, copyright registrations and non-disclosure agreements to establish and protect our proprietary rights in our technologies
and products. A number of patents are in process (Patents Pending) that cover critical aspects of the engineering and function
of the SmartMetric biometric card. The founder of SmartMetric, Chaya Hendrick, is the inventor of these patents, and has provided
SmartMetric with an option over biometric card related pending patents invented by her.
Some of the most recent patents pending
have not been disclosed on the publicly searchable USPTO database of filed for patents and remain trade secrets within the Company.
Publishing of such patents pending will be done in due course.
Patents
SmartMetric biometric card is protected
by five (5) USPTO issued patents. Other patents are pending. Our technology is also dependent upon unpatented trade secrets. However,
trade secrets are difficult to protect. In an effort to protect our trade secrets, we have a policy of requiring our employees,
consultants and advisors to execute non-disclosure agreements. The principal shareholder of SmartMetric and technology inventor,
Chaya Hendrick, through various corporate investment vehicles and companies also owns other technologies, patents, and has financial
interest in other technology companies. Chaya Hendrick, under an executed employment agreement is not subject to any restriction
on using and owning any technology, methodology, process or invention created by Chaya Hendrick.
Government Regulation
There are currently no governmental regulations,
which have any bearing on the raw materials or the manufacturing of our payments card products. United States federal departments
such as the Department of Defense have rules and regulations concerning security features of smart cards used as identity or building
and cyber access cards. These regulations stipulate a specific licensing and testing protocol for such cards.
Banking Industry Self-Regulation
The EMV chip used in chip cards are subject
to licensing and testing by the banking-controlled body called EMVco. EMVco is an acronym standing for Europay, MasterCard and
Visa. These international payments card networks were the founding parties of EMVco.
Individual payments networks such as Visa,
Mastercard, Europay, American Express, Union Pay Dinners and JCB all have their own individual licensing and testing standards
and processes.
Research and Development
Our research and development program is
focused on ongoing development of new products built on our existing biometric card. We continue to refine our technology and develop
further improvements to our biometric card products. We have finalized our first biometric EMV payments card product. We have also
concluded the design and electronic engineering for our soon-to-be released multi-function security and access control biometric
cards. Research and development will continue as the Company continues to innovate and develop new biometric card-based products.
Future biometric card-based products the Company is now working on, include but are not limited to: (a) health insurance card with
stored in-card medical records; (b) national identity card; and (c) drivers’ licenses.
The Company has developed and is continuing
to develop its own embedded systems and application software that works with the SmartMetric Biometric Card. This development software
and systems and ongoing electronic design and development requires the company to continue to expend time and financial resources
on significant software development. Currently, the Company has electronic and software engineers working in Tel Aviv, Israel and
Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Competition
Various potential competitors have announced
products similar to that of SmartMetric’s. It is understood that “announced” is defined as a person to hold their
finger on the cards fingerprint sensor while it is in a card reader. Unlike the SmartMetric biometric card that is powered from
its own internal rechargeable battery, this other type of card does not allow the card to be used in most restaurants that need
to take the card away from the table for processing at the checkout. It also does not allow their other type of card to be used
at the vast majority of ATM’s.
Employees
As of the date of this prospectus, we have
one full time employee, our Chief Executive Officer and President, Chaya Hendrick. We primarily use direct contract hires in administration
and engineering, as is common in the information technology world. All work product developed by all of our engineers remains the
intellectual property of SmartMetric. Engineers who work for SmartMetric under contract are primarily based in Tel Aviv, Israel.
Some software engineering is conducted in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
GHS Equity Financing Agreement and Registration
Rights Agreement
On March 6, 2020, the Company entered into
an equity financing agreement, and a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”) with GHS Investments
LLC, a Nevada limited liability company. Under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS agreed to provide the Company with
up to $4,000,000 over the course of 36 months in return for shares of the Company’s common stock. The 36-month period will
commence upon effectiveness of this registration statement on Form S-1 (the “Registration Statement”) filed with the
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”).
Following effectiveness of the Registration
Statement, the Company shall have the discretion to deliver puts to GHS and GHS will be obligated to purchase shares of the Company’s
common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) based on the investment amount specified in each put
notice. The maximum amount that the Company shall be entitled to put to GHS in each put notice shall not exceed two hundred percent
(200%) of the average daily trading dollar volume of the Company’s Common Stock during the ten (10) trading days preceding
the put, so long as such amount does not exceed $500,000. Pursuant to the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS and its affiliates will
not be permitted to purchase, and the Company may not put shares of the Company’s Common Stock to GHS that would result in
GHS’s beneficial ownership equaling more than 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding Common Stock. The price of each put
share shall be equal to eighty percent (80%) of the Market Price (as defined in the Equity Financing Agreement). Puts may be delivered
by the Company to GHS until the earlier of thirty-six (36) months after the effectiveness of the Registration Statement, the date
on which GHS has purchased an aggregate of $4,000,000 worth of Common Stock under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement,
or at such time that the Registration Statement is no longer in effect. Additionally, in accordance with the Equity Financing Agreement,
the Company issued GHS a convertible promissory note in the principal amount of $35,000 and a 9 month maturity date (the “Commitment
Note”), with the first $20,000 of the Commitment Note deemed earned upon execution of the Equity Financing Agreement and
the remaining $15,000 of the Commitment Note deemed earned upon payment by GHS of the Company’s legal fees.
The Registration Rights Agreement provides
that the Company shall (i) use its best efforts to file with the Commission the Registration Statement within 60 days of the date
of the Registration Rights Agreement; and (ii) have the Registration Statement declared effective by the Commission within 30 days
after the date the Registration Statement is filed with the Commission, but in no event more than 90 days after the Registration
Statement is filed.
Where to Find More Information
We make our public filings with the SEC,
including our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and all exhibits and amendments
to these reports. These materials are available on the Company’s website at www.smartmetric.com or on the SEC’s
web site, http://www.sec.gov.
Summary of the Offering
|
Shares currently outstanding:
|
|
379,523,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares being offered:
|
|
100,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares to be outstanding after the offering
|
|
479,523,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares to Offering Price per share:
|
|
The Selling Stockholder may sell all or a portion of the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices and prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices or at negotiated prices.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use of Proceeds:
|
|
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the shares of our common stock by the Selling Stockholder.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trading Symbol:
|
|
SMME
|
|
|
|
|
|
Risk Factors:
|
|
See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 11 herein and the other information in
this prospectus for a discussion of the factors you should consider before deciding to invest in shares of our common
stock.
|
SUMMARY CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The following summary consolidated statements
of operations data for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial
statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. Additionally, the six months ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 have been derived
from our unaudited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary consolidated balance sheet
data as of March 31, 2020 are derived from our consolidated financial statements that are included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The historical financial data presented below is not necessarily indicative of our financial results in future periods, and the
results for the quarter ended March 31, 2020 is not necessarily indicative of our operating results to be expected for the full
fiscal year ending June 30, 2020 or any other period. You should read the summary consolidated financial data in conjunction with
those financial statements and the accompanying notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition
and Results of Operations.” Our consolidated financial statements are prepared and presented in accordance with United States
generally accepted accounting principles, or U.S. GAAP. Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis consistent
with our audited financial statements and include all adjustments, consisting of normal and recurring adjustments that we consider
necessary for a fair presentation of the financial position and results of operations as of and for such periods.
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
10,017
|
|
|
|
6,450
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
10,017
|
|
|
|
16,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
10,017
|
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
$
|
898,380
|
|
|
$
|
884,140
|
|
|
Liability for stock to be issued
|
|
|
69,183
|
|
|
|
147,484
|
|
|
Deferred Officer’s salary
|
|
|
821,682
|
|
|
|
790,015
|
|
|
Related party interest payable
|
|
|
135,240
|
|
|
|
93,488
|
|
|
Dividends payable
|
|
|
2,489
|
|
|
|
3,123
|
|
|
Due to shareholders
|
|
|
41,343
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Shareholder loan
|
|
|
6,571
|
|
|
|
3,759
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,974,888
|
|
|
|
1,922,009
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
1,974,888
|
|
|
|
1,922,009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 4)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of discount, authorized 1,000,000 shares 128,500 and 121,700 shares issued and outstanding, respectively
|
|
|
106,580
|
|
|
|
99,278
|
|
|
Preferred Series C stock subscriptions receivable
|
|
|
(30,000
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ deficit:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred B stock, $.001 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized, 610,000 and 610,000 shares issued and outstanding
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
Common stock, $.001 par value; 600,000,000 and 300,000,000 shares authorized, 316,875,686 and 264,648,821 shares issued and outstanding, respectively
|
|
|
316,876
|
|
|
|
264,649
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
25,215,910
|
|
|
|
24,663,528
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(27,574,847
|
)
|
|
|
(26,933,463
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(2,041,451
|
)
|
|
|
(2,004,676
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and equity
|
|
$
|
10,017
|
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Three
Months
|
|
|
Three
Months
|
|
|
Nine
Months
|
|
|
Nine
Months
|
|
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer’s salary
|
|
|
47,500
|
|
|
|
47,500
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
Other general and administrative
|
|
|
93,200
|
|
|
|
121,200
|
|
|
|
375,779
|
|
|
|
369,361
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
14,090
|
|
|
|
38,949
|
|
|
|
60,796
|
|
|
|
90,084
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
154,790
|
|
|
|
207,649
|
|
|
|
579,075
|
|
|
|
601,945
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations before other expense
|
|
|
(154,790
|
)
|
|
|
(207,649
|
)
|
|
|
(579,075
|
)
|
|
|
(601,945
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(14,081
|
)
|
|
|
(13,647
|
)
|
|
|
(41,731
|
)
|
|
|
(39,468
|
)
|
|
Total Other expense
|
|
|
(14,081
|
)
|
|
|
(13,647
|
)
|
|
|
(41,731
|
)
|
|
|
(39,468
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
(620,806
|
)
|
|
|
(641,413
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
(620,806
|
)
|
|
|
(641,413
|
)
|
|
Preferred C stock dividends
|
|
|
(4,614
|
)
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
|
(20,577
|
)
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
Net loss available for common stockholders
|
|
$
|
(173,485
|
)
|
|
$
|
(225,569
|
)
|
|
$
|
(641,383
|
)
|
|
$
|
(645,686
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
|
|
307,327,958
|
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
|
285,940,273
|
|
|
|
253,891,612
|
|
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer’s salary
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
Other general and administrative
|
|
|
577,756
|
|
|
|
683,329
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
107,962
|
|
|
|
129,375
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
875,718
|
|
|
|
1,002,704
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations before other expense
|
|
|
(875,718
|
)
|
|
|
(1,002,704
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other expense:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(53,432
|
)
|
|
|
(39,084
|
)
|
|
Loss on patent impairment
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(600,000
|
)
|
|
Total other expense
|
|
|
(53,432
|
)
|
|
|
(639,084
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
Preferred stock dividends
|
|
|
(7,401
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Net loss available for common stockholders
|
|
$
|
(936,551
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.01
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
|
240,133,406
|
|
RISK FACTORS
This investment has a high degree of
risk. Before you invest you should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below and the other information in
this prospectus. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, operating results and financial condition could be
harmed and the value of our stock could go down. This means you could lose all or a part of your investment. You should
carefully consider the risks described below together with all of the other information included in our public filings before making
an investment decision with regard to our securities. The statements contained in or incorporated into this document that are not
historic facts are forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ
materially from those set forth in or implied by forward-looking statements. If any of the following events described in these
risk factors actually occur, our business, financial condition or results of operations could be harmed. In that case, the trading
price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment. Moreover, additional risks not presently
known to us or that we currently deem less significant also may impact our business, financial condition or results of operations,
perhaps materially. For additional information regarding risk factors, see “Forward-Looking Statements.”
Special Information Regarding Forward-Looking
Statements
The information herein contains forward-looking
statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934, as amended. Actual results may materially differ from those projected in the forward-looking statements as a result
of certain risks and uncertainties set forth in this report. Although management believes that the assumptions made and expectations
reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, there is no assurance that the underlying assumptions will, in fact,
prove to be correct or that actual results will not be different from expectations expressed in this report.
We desire to take advantage of the “safe
harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. This filing contains a number of forward-looking
statements that reflect management’s current views and expectations with respect to our business, strategies, products, future
results and events, and financial performance. All statements made in this filing other than statements of historical fact, including
statements addressing operating performance, clinical developments which management expects or anticipates will or may occur in
the future, including statements related to our technology, market expectations, future revenues, financing alternatives, statements
expressing general optimism about future operating results, and non-historical information, are forward looking statements. In
particular, the words “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “anticipate,” “estimate,”
“may,” variations of such words, and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements, but are not the exclusive
means of identifying such statements, and their absence does not mean that the statement is not forward-looking. These forward-looking
statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, including those discussed below. Our actual results, performance or
achievements could differ materially from historical results as well as those expressed in, anticipated, or implied by these forward-looking
statements. We do not undertake any obligation to revise these forward-looking statements to reflect any future events or circumstances.
Readers should not place undue reliance
on these forward-looking statements, which are based on management’s current expectations and projections about future events,
are not guarantees of future performance, are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions (including those described below),
and apply only as of the date of this filing. Our actual results, performance or achievements could differ materially from the
results expressed in, or implied by, these forward-looking statements. Factors which could cause or contribute to such differences
include, but are not limited to, the risks to be discussed in this Form S-1 Registration and in the press releases and other communications
to shareholders issued by us from time to time which attempt to advise interested parties of the risks and factors which may affect
our business. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new
information, future events, or otherwise. For additional information regarding forward-looking statements, see “Forward-Looking
Statements.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position
and Need to Raise Additional Capital
We have a limited operating history
as a company and may not be able to effectively operate our business.
Our limited staff and operating history
mean that there is a high degree of uncertainty regarding our ability to:
|
|
●
|
develop our technologies and proposed products;
|
|
|
●
|
identify, hire and retain the needed personnel to implement our business plan and sell our products;
|
|
|
●
|
Manage our growth and / or successfully scale our business; or
|
|
|
●
|
respond to competition.
|
No assurances can be given as to exactly
when, if at all, we will be able to fully develop, and take the necessary steps to derive any revenues from our proposed products.
Our business depends upon our ability
to keep pace with the latest technological changes, and our failure to do so could make us less competitive in our industry.
The market for our services is characterized
by rapid change and technological improvements. Failure to respond in a timely and cost-effective way to these technological developments
may result in serious harm to our business and operating results. As a result, our success will depend, in part, on our ability
to develop and market service offerings that respond in a timely manner to the technological advances of available to our customers,
evolving industry standards and changing preferences.
Raising capital may be difficult
as a result of our history of losses and limited operating history in our current stage of development.
When making investment decisions, investors
typically look at a company’s management, earnings and historical performance in evaluating the risks and operations of the
business and the business’s future prospects. Our history of losses and relatively limited operating history in our current
stage of development makes such evaluation, as well as any estimation of our future performance, substantially more difficult.
As a result, investors may be unwilling to invest in us or on terms or conditions which are acceptable. If we are unable to secure
additional financing, we may need to materially scale back our business plan and/or operations or cease operations altogether.
We are an early-stage company, have
no product revenues, are not profitable and may never be profitable.
From inception through March 31, 2020,
we have raised approximately $26,000,000 through the sale of our securities. During this same period, we have recorded an accumulated
deficit of approximately $27,574,847 million. Our net losses for the two most recent fiscal years ended June 30, 2019, and 2018
were $936,551 and $1,641,788, respectively. We have never made any sales and have never generated revenues and we anticipate none
will be generated for the foreseeable future. We expect to incur significant operating losses for the foreseeable future as we
continue the development of our products. Accordingly, we will need additional capital to fund our continuing operations and any
expansion plans. Since we do not generate any revenue, the most likely source of such additional capital is the sale of our securities.
To the extent that we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities, our stockholders are likely to experience dilution
with regard to their percentage ownership of the company, which may be significant. If we raise additional capital by incurring
debt, we could incur significant interest expense and become subject to covenants that could affect the manner in which we conduct
our business, including securing such debt obligations with our assets.
To date, we have generated only losses,
which are expected to continue for the foreseeable future.
For the nine months ended March 31, 2020
and 2019, we incurred a net loss of $620,806 and $641,413, respectively. We may not be able to achieve expected results, including
any guidance or outlook it may provide from time to time.
We may continue to incur losses and may
be unable to achieve profitability. We cannot assure you that our net losses and negative cash flow will not accelerate and surpass
our expectations nor can we assure you that we will ever generate any net income or positive cash flow.
We may not be able to continue as
a going concern if we do not obtain additional financing by December 31, 2020.
Since our inception, we have funded our
operations primarily through the sale of our securities. Our cash balance at March 31, 2020 was $0. Based on our current expected
level of operating expenditures, we expect to only be able to fund our operations through the first quarter (ending September 30,
2020) of fiscal year ending June 30, 2021, at which time we will need additional capital. Our ability to continue as a going concern
is wholly dependent upon obtaining sufficient capital to fund our operations. We have no committed sources of additional capital
and our access to capital funding is always uncertain. Accordingly, despite our ability to secure capital in the past, we cannot
assure you that we will be able to secure additional capital through financing transactions, including issuance of debt, or through
other means. In the event that we are not able to secure additional funding, we may be forced to curtail operations, cease operations
altogether or file for bankruptcy.
The COVID-19 has had an impact on SmartMetric's
final card production. While the delays are due to supply line disruption, the Company is confident that these delays will be short-lived
based on advice from our manufacturing partners, manufacturing alternatives and alternative supply lines that are being put into
place by the Company.
We entered into a royalty and licensing
agreement with Chaya Hendrick, our CEO, which requires substantial payments by us on an annual basis and additionally in the event
gross revenues are derived, which could harm our financial position.
Pursuant to a licensing and royalty agreement,
entered into on September 11, 2017 by the Company and Chaya Hendrick, our founder and CEO, we received a license to certain patents
related to our technologies until the expiration of such patents in exchange for the following : (i) Issuance of 200,000 Series
B Convertible Preferred Shares, (ii) 5% of gross revenues derived from the sale of products derived from the patents, and (iii)
annual payments beginning at $50,000 per annum, increased by 100% of each previous year (offset against 5% gross revenue royalty
payments). We believe these patents are instrumental our business plan and if we are unable to make such required payments under
the plan, Chaya Hendrick may terminate the agreement, which may materially impact our business plan. Furthermore, there can be
no assurances that we will be able to continue to meet our financial obligations under the terms of the agreement unless we are
able to raise additional capital through the sale of our securities or derive revenue from some other source.
As of March 31, 2020, we owe Chaya
Hendrick, our CEO, $790,015 in deferred salary, of which the failure to pay could result in Chaya Hendrick’s termination
of employment, the result of which would materially harm our business.
We currently have not paid $790,015 in
salary owed to Chaya Hendrick pursuant to Chaya Hendrick’s employment agreement outstanding with us as of March 31, 2020.
While Chaya Hendrick continues to support the Company and continues to operate as its CEO, President and chairman of the Board,
there can be no assurances that this will continue if we fail to back salaries and future salary owed. Additionally, as of July
1, 2017, all prior and future deferred salary owed will bear interest at a rate of 7% per annum. In the event Chaya Hendrick terminates
employment for lack of payment, the Company believes such loss would cause irreparable harm to our product development and would
materially harm our business prospects. Additionally, there can be no assurances that Chaya would not attempt to foreclose on our
assets in order to satisfy such debt obligations.
Risks Relating to our Stage of Development
and Business
Our potential competitors have significantly
greater resources than we have, which may make competing difficult.
We compete against numerous companies,
many of which have substantially greater resources than we have. Several such competitors have large teams of engineers and scientists
that attempt to develop products and technologies similar to ours. Companies such as Gemalto, Giesecke & Devrient, IDEMIA,
as well as others, have substantially greater financial, research, manufacturing and marketing resources than we do. As a result,
such competitors may find it easier to compete in our industry and bring competing products to market.
Our business depends upon our ability
to keep pace with the latest technological changes, and our failure to do so could make us less competitive in our industry.
The market for our services is characterized
by rapid change and technological improvements. Failure to respond in a timely and cost-effective way to these technological developments
may result in serious harm to our business and operating results. As a result, our success will depend, in part, on our ability
to develop and market service offerings that respond in a timely manner to the technological advances of available to our customers,
evolving industry standards and changing preferences.
Our key personnel and directors are
critical to our business, and such key personnel may not remain with our company in the future.
We depend on the continued employment of
our President and CEO, Chaya Henrick and technical contracted personnel. If any of these key personnel were to leave and not be
replaced with sufficiently qualified and experienced personnel, our business could be adversely affected. In particular, our current
strategy to penetrate the market for contactless logical access identification and transaction solutions is heavily dependent on
the vision, leadership and experience of our President and CEO, Chaya Hendrick.
Our continued success will depend, to a
significant extent, upon the performance and contributions of Chaya Henrick and upon our ability to attract motivate and retain
highly qualified management personnel and employees. We depend on Chaya Henrick to effectively manage our business in a highly
competitive environment. If one or more of our key officers join a competitor or form a competing company, we may experience interruptions
in product development, delays in bringing products to market, difficulties in our relationships with customers and loss of additional
personnel, which could significantly harm our business, financial condition, operating results and projected growth.
We currently employ a part-time Chief Financial
Officer, Mr. Jay Needelman, who is also a member of the Board. The loss of services of any of our key management personnel, whether
through resignation or other causes, the reduced services of our part-time Chief Financial Officer, or the inability to attract
qualified personnel as needed, could prevent us from adequately executing our business strategy.
Rapid technological changes could
make our services or products less attractive.
The smart card, biometric identification
and personal identification industries are characterized by rapid technological change, frequent new product innovations, changes
in customer requirements and expectations and evolving industry standards. If we are unable to keep pace with these changes, our
business may be harmed. Products using new technologies, or emerging industry standards, could make our technologies less attractive.
If addition, we may face unforeseen problems when developing our products, which could harm our business. Furthermore, our competitors
may have access to technologies not available to us, which may enable them to produce products of greater interest to consumers
or at a more competitive cost.
Sales of our products depend on the
development of emerging applications in their target markets and on diversifying and expanding our customer base in new markets
and geographic regions, all of which may be financially burdensome or unsuccessful.
Our intent is to market and sell our products
primarily to the private sector while addressing emerging applications that have not yet reached a stage of mass adoption or deployment.
The market for some of these solutions (electronic biometric fingerprinting) is at an early stage of deployment in the private
sector compared to other forms of services that try to identify a person through simpler means (by their name, social security
number, etc.) Additionally, we have a strategy of expanding sales of existing products into new geographic markets. Our target
market initially will be South America and Australia. In the event that we are unable to adequately develop our applications or
gain traction in these emerging markets, or that the cost of the foregoing is too great, our business may be harmed.
Continuing disruption in the global
financial markets may adversely impact customers and customer spending patterns.
Continuing disruption in the global financial
markets as a result of the ongoing global financial uncertainty may cause consumers, businesses and governments to defer purchases
in response to tighter credit, decreased cash availability and declining consumer confidence. Accordingly, demand for our products
could decrease and differ materially from their current expectations. Further, some of our customers may require substantial financing
in order to fund their operations and make purchases from us. The inability of these customers to obtain sufficient credit to finance
purchases of our products and meet their payment obligations to us or possible insolvencies of our customers could result in decreased
customer demand, an impaired ability for us to collect on outstanding accounts receivable, significant delays in accounts receivable
payments, and significant write-offs of accounts receivable, each of which could adversely impact our financial results.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we are not able to adequately protect our intellectual
property, we may not be able to compete effectively.
Our ability to compete depends in part
upon the strength of our proprietary rights in our technologies, brands and content. The efforts we have taken to protect our intellectual
property and proprietary rights may not be sufficient or effective at stopping unauthorized use of our intellectual property and
proprietary rights. In addition, effective trademark, patent, copyright and trade secret protection may not be available or cost-effective
in every country in which our products are made available. There may be instances where we are not able to fully protect or utilize
our intellectual property in a manner that maximizes competitive advantage. If we are unable to protect our intellectual property
and proprietary rights from unauthorized use, the value of our products may be reduced, which could negatively impact our business.
Our inability to obtain appropriate protections for our intellectual property may also allow competitors to enter our markets and
produce or sell the same or similar products. In addition, protecting our intellectual property and other proprietary rights is
expensive and diverts critical managerial resources. If any of the foregoing were to occur, or if we are otherwise unable to protect
our intellectual property and proprietary rights, our business and financial results could be adversely affected. If we are forced
to resort to legal proceedings to enforce our intellectual property rights, the proceedings could be burdensome and expensive.
In addition, our proprietary rights could be at risk if we are unsuccessful in, or cannot afford to pursue, those proceedings.
We may incur substantial costs as
a result of litigation or other proceedings relating to patent and other intellectual property rights and we may be unable to protect
our rights to, or use of, our technology.
Some or all of our patent applications
may not issue as patents, or the claims of any issued patents may not afford meaningful protection for our technologies or products.
In addition, patents issued to us or our licensors, if any, may be challenged and subsequently narrowed, invalidated or circumvented.
Patent litigation is widespread in our industry and could harm our business. Litigation might be necessary to protect our patent
position or to determine the scope and validity of third-party proprietary rights. If we choose to go to court to stop someone
else from using the inventions claimed in our patents, that individual or company would have the right to ask the court to rule
that such patents are invalid and/or should not be enforced against that third party. These lawsuits are costly and we may not
have the required resources to pursue such litigation or to protect our patent rights. In addition, there is a risk that the court
might decide that these patents are not valid and that we do not have the right to stop the other party from using the inventions.
There is also the risk that, even if the validity of these patents is upheld, the court could refuse to stop the other party on
the grounds that such other party’s activities do not infringe on our rights contained in these patents.
Furthermore, a third party may claim that
we are using inventions covered by their patent rights and may go to court to stop us from engaging in our normal operations and
activities, including making or selling our product candidates. These lawsuits are costly and could materially increase our operating
expenses and divert the attention of managerial and technical personnel. There is a risk that a court would decide that we are
infringing the third party’s patents and would order us to stop the activities covered by the patents. In addition, there
is a risk that a court would order us to pay the other party damages for having violated the other party’s patents. It is
not always clear to industry participants, including us, which patents cover various types of products or methods of use. The coverage
of patents is subject to interpretation by the courts, and the interpretation is not always uniform.
Because some patent applications in the
United States may be maintained in secrecy until the patents are issued, patent applications in the United States and many foreign
jurisdictions are typically not published until eighteen months after filing, and publications in the scientific literature often
lag behind actual discoveries, we cannot be certain that others have not filed patent applications for technology covered by our
issued patents or that we were the first to invent the technology. Our competitors may have filed, and may in the future file,
patent applications covering technology similar to ours. Any such patent application may have priority over our patent applications
and could further require us to obtain rights to issued patents covering such technologies.
If another party has filed a United States
patent application on inventions similar to ours, we may have to participate in an interference or other proceeding in the U.S.
Patent and Trademark Office, or the PTO, or a court to determine priority of invention in the United States. The costs of these
proceedings could be substantial, and it is possible that such efforts would be unsuccessful, resulting in a loss of our United
States patent position with respect to such inventions.
Some of our competitors may be able to
sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources.
In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material adverse effect
on our ability to raise the capital necessary to continue our operations.
Risks Relating to Market Approval and
Government Regulations
Compliance with regulation of corporate
governance and public disclosure diverts time and attention away from revenue generating activities.
Our management team invests significant
time and financial resources to comply with existing standards for public companies, which has lead to management’s time
and attention away from developing our business to compliance activities which could have an adverse effect on our business.
Our technology relies on our ability
to gain the acceptance and approval of large banking / credit card institutions, the failure to do so may materially harm our business.
In the event that our SmartMetric Biometric
Card does not gain acceptance/approval amongst the large card issuing institutions in the United States and abroad, our cards will
not be provided for use to customers. We currently have no plans to open our own bank/credit card issuing institution and accordingly,
we plan to rely on our ability to have our products accepted within the banking/credit card industries. Our failure to do so will
have a material impact on our ability to generate revenues and continue to operate our business.
Risks Relating to the Development and
Manufacturing of Our Products
We currently rely on third party
manufacturers and suppliers for certain components of our product; with such parties being, to some extent, outside of our control.
We currently have limited internal manufacturing
capability and intend to rely on third party contract manufacturers or suppliers for the foreseeable future. Accordingly, factors
outside of our control may result in material manufacturing delays and product shortages, which could delay or otherwise negatively
impact our manufacturing and product development plans. Should we be forced to manufacture our proposed products, we cannot give
any assurance that we would be able to develop internal manufacturing capabilities. In the event that we seek third party suppliers
or alternative manufacturers, they may require us to purchase a minimum amount of materials or could require other unfavorable
terms. Any such event could materially impact our business prospects and could delay the development and manufacturing of our products.
Moreover, we cannot give any assurance that the contract manufacturers or suppliers that we select will be able to supply our products
in a timely or cost-effective manner or in accordance with our specifications.
We have a limited number of suppliers
of key components and may experience difficulties in obtaining components for which there is significant demand, which would materially
impact our business prospects.
We rely upon a limited number of suppliers
for some key components of our products. Our reliance on a limited number of suppliers may expose us to various risks including,
without limitation, an inadequate supply of components, price increases, late deliveries and poor component quality. In addition,
some of the basic components we use in our products, such as biometric fingerprint devices and various smart card technologies
may at any time be in great demand. This could result in components not being available to us in a timely manner or at all, particularly
if larger companies have ordered more significant volumes of those components, or in higher prices being charged for components.
Disruption or termination of the supply of components or software used in our products could delay shipments of these products.
The following delays/factors from our third-party suppliers could have a material adverse effect on our business and operating
results and could also damage relationships with current and prospective customers:
|
|
●
|
Difficulties in staffing;
|
|
|
●
|
Adequate resources of qualified technicians, engineers/assemblers, and programmers;
|
|
|
●
|
Potentially adverse tax consequences;
|
|
|
●
|
Unexpected changes in regulatory requirements;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Tariffs and other trade barriers;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Export controls;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Political and economic instability; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
Late delivery of our products.
|
We utilize third party manufacturing
plants for silicon for the manufacturing our products, which, in the event of growth would need to use large quantities of silicon,
for which raw material shortages may occur.
While we currently use silicon in our products,
and no shortage currently exists of these materials, there can be no assurances that there will not be a shortage in the future,
which may materially impact our manufacturing capabilities, growth prospects, and ability to generate revenue in the future.
Risks Related to our Securities
Our board of directors has broad
discretion to issue additional securities.
We are authorized under our certificate
of incorporation to issue up to 605,000,000 shares consisting of 600,000,000 shares of common stock and 5,000,000 “blank
check” shares of preferred stock. Shares of our blank check preferred stock provide the Board with broad authority to determine
voting, dividend, conversion, and other rights. As of July 30, 2020, we have issued and outstanding 379,523,000 shares of common
stock; 610,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock that are convertible into 30,500,000 shares of common stock at the
election of the holder; and 121,700 shares of shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock that are convertible into 16,901,408
shares of common stock. Additionally, we have 28,153,406 shares of common stock reserved upon the exercise of outstanding purchase
warrants. Accordingly, as of July 30, 2020, we are entitled to issue up to 220,477,000 additional shares of common stock, and
4,390,000 additional shares of “blank check” preferred stock. Our board may generally issue those common and preferred
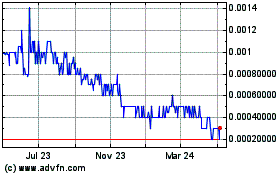
shares, or convertible securities to purchase those shares, without further approval by our shareholders. Any additional preferred
shares we may issue could have such rights, preferences, privileges, and restrictions as may be designated from time-to-time by
our board, including preferential dividend rights, voting rights, conversion rights, redemption rights and liquidation provisions.
It is likely that we will issue additional
securities to raise capital in order to further our business plans. It is also likely that we will issue additional securities
to directors, officers, employees and consultants as compensatory grants in connection with their services. Any issuances could
be made at a price that reflects a discount to, or a premium from, the then-current market price of our common stock. These issuances
would dilute the percentage ownership interest of our current shareholders, which would have the effect of reducing your influence
on matters on which our stockholders vote and might dilute the net tangible book value per share of our common stock.
If securities or industry analysts
do not publish research or reports or if they publish unfavorable research or reports, an active market for our common stock may
not develop and the price of our common stock could decline.
We are a small company which is relatively
unknown to stock analysts, stockbrokers, institutional investors and others in the investment community that generate or influence
sales volume. Even if we come to the attention of such persons, they may be reluctant to follow or recommend an unproven company
such as ours until such time as we became more seasoned and viable. Generally, the trading market for a company’s securities
depends in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish. We currently have limited research coverage
by securities and industry analysts. As a consequence, there may be periods of time when trading activity in our shares is minimal
or non-existent, as compared to a seasoned issuer with significant research coverage. We cannot give you any assurance that a broader
or more active public trading market for our common stock will develop or if developed, will be sustained, or that current trading
levels could be sustained or not diminish. In addition, in the event any analyst downgrades our securities, the price of our shares
would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases to cover us or fails to publish regular reports on us, interest in
the purchase of our securities could decrease, which could cause the price of our common stock and its trading volume, if any,
to decline.
Our common stock may be considered
a “penny stock,” and may be subject to additional sale and trading regulations that may make it more difficult to sell.
Our common stock may be considered a “penny
stock.” The principal result or effect of being designated a penny stock is that securities broker-dealers participating
in sales of our common stock may be subject to the penny stock regulations set forth in Rules 15g-2 through 15g-9 promulgated under
the Exchange Act. For example, Rule 15g-2 requires broker-dealers dealing in penny stocks to provide potential investors with a
document disclosing the risks of penny stocks and to obtain a manually signed and dated written receipt of the document at least
two business days before effecting any transaction in a penny stock for the investor’s account. Moreover, Rule 15g-9 requires
broker-dealers in penny stocks to approve the account of any investor for transactions in such stocks before selling any penny
stock to that investor. This procedure requires the broker-dealer to (i) obtain from the investor information concerning his or
her financial situation, investment experience and investment objectives; (ii) reasonably determine, based on that information,
that transactions in penny stocks are suitable for the investor and that the investor has sufficient knowledge and experience as
to be reasonably capable of evaluating the risks of penny stock transactions; (iii) provide the investor with a written statement
setting forth the basis on which the broker-dealer made the determination in (ii) above; and (iv) receive a signed and dated copy
of such statement from the investor, confirming that it accurately reflects the investor’s financial situation, investment
experience and investment objectives. Compliance with these requirements may make it more difficult and time consuming for holders
of our common stock to resell their shares to third parties or to otherwise dispose of them in the market or otherwise.
Our CEO and Chairman, as the sole
holder of our Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, controls our company.
Chaya Hendrick, our CEO and Chairman, holds
(via shares in her name or shares in the name of an entity she controls - Applied Cryptography, Inc. (“ACI”)) all 610,000
shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock outstanding. The outstanding shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock are
entitled to vote on any matter with the holders of Common Stock voting together as one (1) class and shall have that number of
votes (identical in every other respect to the voting rights of the holder of common stock entitled to vote at any regular or special
meeting of Stockholders) equal to that number of common shares which is not less than 51% of the vote required to approve any action,
which Nevada law provides may or must be approved by vote or consent of the common shares or the holders of other securities entitled
to vote, if any. Each share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock is convertible, at the option of the holder, into fifty (50)
shares of Common Stock upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and for purposes of determining a quorum of a shareholder meeting,
the outstanding shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock shall be deemed the equivalent of 51% of all shares of the Company’s
Common Stock entitled to vote at such meetings. Accordingly, Ms. Hendrick can (without the approval of our other shareholders)
elect our entire Board and determine the outcome of various matters submitted to shareholders for approval, including fundamental
corporate transactions. Voting control by Ms. Hendrick may discourage certain types of transactions involving an actual or potential
change in control of us, including transactions in which the holders of our common stock might receive a premium for their shares
over prevailing market prices.
Failure to maintain effective internal
controls in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act could have a material adverse effect on our business and operating
results and stockholders could lose confidence in our financial reporting.
Effective internal controls are necessary
for us to provide reliable financial reports and effectively prevent fraud. If we cannot provide reliable financial reports or
prevent fraud, our operating results could be harmed. Failure to achieve and maintain an effective internal control environment,
regardless of whether we are required to maintain such controls, could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported
financial information, which could have a material adverse effect on our stock price. The Company’s management assessed the
design and operating effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2019 based on the framework set
forth in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
In connection with the assessment described above, management identified control deficiencies that represented a material weakness
at June 30, 2019.
We have not paid dividends on our
common stock in the past and do not expect to pay dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. Any return on investment
may be limited to the value of our common stock.
No cash dividends have been paid on our
common stock. We expect that any income received from operations will be devoted to our future operations and growth. We do not
expect to pay cash dividends on our common stock in the near future. Payment of dividends would depend upon our profitability at
the time, cash available for those dividends, and other factors as our Board may consider relevant. If we do not pay dividends,
our common stock may be less valuable because a return on an investor’s investment will only occur if our stock price appreciates.
The requirements of being a public
company may strain our resources, divert management’s attention and affect our ability to attract and retain qualified board
members.
The Exchange Act requires, among other
things, that we file annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and financial condition. The Sarbanes-Oxley
Act requires, among other things, that we maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls for financial
reporting. For example, Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 requires that our management report on, and our independent
auditors attest to, the effectiveness of our internal controls structure and procedures for financial reporting. Section 404 compliance
may divert internal resources and will take a significant amount of time and effort to complete. We may not be able to successfully
complete the procedures and certification and attestation requirements of Section 404 by the time we will be required to do so.
If we fail to do so, or if in the future our chief executive officer, chief financial officer or independent registered public
accounting firm determines that our internal controls over financial reporting are not effective as defined under Section 404,
we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Furthermore, investor perceptions
of our company may suffer, and this could cause a decline in the market price of our common stock. Irrespective of compliance with
Section 404, any failure of our internal controls could have a material adverse effect on our stated results of operations and
harm our reputation. If we are unable to implement these changes effectively or efficiently, it could harm our operations, financial
reporting or financial results and could result in an adverse opinion on internal controls from our independent auditors. We may
need to hire a number of additional employees with public accounting and disclosure experience in order to meet our ongoing obligations
as a public company, which will increase costs. Our management team and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount
of time to new compliance initiatives and to meeting the obligations that are associated with being a public company, which may
divert attention from other business concerns, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition
and results of operations. In addition, because our management team has limited experience managing a public company, we may not
successfully or efficiently manage our transition into a public company.
Risks Related to the Offering
Our existing stockholders may experience
significant dilution from the sale of our common stock pursuant to the GHS financing agreement.
The sale of our common stock to GHS Investments
LLC in accordance with the Financing Agreement may have a dilutive impact on our shareholders. As a result, the market price of
our common stock could decline. In addition, the lower our stock price is at the time we exercise our put options, the more shares
of our common stock we will have to issue to GHS in order to exercise a put under the Financing Agreement. If our stock price decreases,
then our existing shareholders would experience greater dilution for any given dollar amount raised through the offering.
The perceived risk of dilution may cause
our stockholders to sell their shares, which may cause a decline in the price of our common stock. Moreover, the perceived risk
of dilution and the resulting downward pressure on our stock price could encourage investors to engage in short sales of our common
stock. By increasing the number of shares offered for sale, material amounts of short selling could further contribute to progressive
price declines in our common stock.
GHS Investments LLC will pay less than
the then-prevailing market price of our common stock which could cause the price of our common stock to decline.
Our common stock to be issued under the
GHS Financing Agreement will be purchased at a twenty percent (20%) discount, or eighty percent (80%) of the lowest trading price
for the Company’s common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading days immediately preceding the date on which
the Company delivers a put notice to GHS.
GHS has a financial incentive to sell our
shares immediately upon receiving them to realize the profit between the discounted price and the market price. If GHS sells our
shares, the price of our common stock may decrease. If our stock price decreases, GHS may have further incentive to sell such shares.
Accordingly, the discounted sales price in the Financing Agreement may cause the price of our common stock to decline.
We may not have access to the full amount
under the financing agreement.
The lowest closing price of the Company’s
common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading day period immediately preceding the filing of this Registration Statement
was approximately $0.014. At that price we would be able to sell shares to GHS under the Financing Agreement at the discounted
price of $0.0112. At that discounted price, the 100,000,000 shares would only represent $1,120,000, which is below the full amount
of the Financing Agreement.
We Needed Additional Capital, and the
Sale of Additional Shares, Equity and Debt Securities Resulted in Additional Dilution to Our Stockholders.
We recently required additional cash resources
due to changed business conditions or other future developments. These resources were insufficient to satisfy our cash requirements,
so we sold additional equity or debt securities or obtained one or more credit facilities. The sale of these securities resulted
in additional dilution to our shareholders. The future sale of additional equity securities could result in additional dilution
to our stockholders and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights
as a Common Stockholder. The incurrence of indebtedness would result in increased debt service obligations and could result in
operating and financing covenants that would restrict our operations. It is uncertain whether financing will be available in amounts
or on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
If we raise additional funds through government grants, collaborations,
strategic alliances, licensing arrangements or marketing and distribution arrangements, we may have to relinquish valuable rights
to our technologies, future revenue stream or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise
additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product
development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market products that we would otherwise prefer
to develop and market ourselves.
In order for the Company to continue its
business operations and provide growth to its shareholders, the Company requires financing in the form of debt, equity, credit
and other forms of financing. The Company’s issuance of additional convertible promissory notes, common stock purchase warrants,
or common stock will continue to increase the amount of shares of common stock issued and outstanding and thereby dilute our shareholders.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING
STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains forward-looking
statements. Forward-looking statements give our current expectations or forecasts of future events. You can identify these statements
by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties
and include statements regarding, among other things, our projected revenue growth and profitability, our growth strategies and
opportunity, anticipated trends in our market and our anticipated needs for working capital. They are generally identifiable by
use of the words “may,” “will,” “should,” “anticipate,” “estimate,”
“plans,” “potential,” “projects,” “continuing,” “ongoing,” “expects,”
“management believes,” “we believe,” “we intend” or the negative of these words or other variations
on these words or comparable terminology. These statements may be found under the sections entitled “Management’s Discussion
and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Business,” as well as in this prospectus
generally. In particular, these include statements relating to future actions, prospective products, market acceptance, future
performance or results of current and anticipated products, sales efforts, expenses, and the outcome of contingencies such as legal
proceedings and financial results.
Examples of forward-looking statements
in this prospectus include, but are not limited to, our expectations regarding our business strategy, business prospects, operating
results, operating expenses, working capital, liquidity and capital expenditure requirements. Important assumptions relating to
the forward-looking statements include, among others, assumptions regarding demand for our products, the cost, terms and availability
of components, pricing levels, the timing and cost of capital expenditures, competitive conditions and general economic conditions.
These statements are based on our management’s expectations, beliefs and assumptions concerning future events affecting us,
which in turn are based on currently available information. These assumptions could prove inaccurate. Although we believe that
the estimates and projections reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may prove to be incorrect.
Important factors that could cause actual
results to differ materially from the results and events anticipated or implied by such forward-looking statements include, but
are not limited to:
|
|
●
|
increased levels of competition;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
changes in the market acceptance of our products;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
changes in political, economic or regulatory conditions generally and in the markets in which we operate;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our relationships with our key customers;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our ability to retain and attract senior management and other key employees;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our ability to quickly and effectively respond to new technological developments;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
our ability to protect our trade secrets or other proprietary rights, operate without infringing upon the proprietary rights
of others and prevent others from infringing on the proprietary rights of the Company; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
other risks, including those described in the “Risk Factors” discussion of this prospectus.
|
We operate in a very competitive and rapidly
changing environment. New risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for us to predict all of those risks, nor can we assess
the impact of all of those risks on our business or the extent to which any factor may cause actual results to differ materially
from those contained in any forward-looking statement. The forward-looking statements in this prospectus are based on assumptions
management believes are reasonable. However, due to the uncertainties associated with forward-looking statements, you should not
place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements. Further, forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are
made, and unless required by law, we expressly disclaim any obligation or undertaking to publicly update any of them in light of
new information, future events, or otherwise.
USE OF PROCEEDS
We will not receive any proceeds from the
sale of the shares of our common stock by the Selling Stockholder.
DETERMINATION OF OFFERING PRICE
We have not set an offering price for the
shares registered hereunder, as the only shares being registered are those sold pursuant to the GHS Financing Agreement. GHS may
sell all or a portion of the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices and prevailing market prices at the
time of sale, at varying prices or at negotiated prices.
DILUTION
Not applicable. The shares registered under
this registration statement are not being offered for purchase. The shares are being registered on behalf of our selling shareholder
pursuant to the GHS Financing Agreement.
SELLING SECURITY HOLDER
The Selling Stockholder identified in
this prospectus may offer and sell up to 100,000,000 shares of our common stock, which consists of shares of common stock to be
sold by GHS pursuant to the Financing Agreement. If issued presently, the shares of common stock registered for resale by GHS
would represent approximately 26.40% of our issued and outstanding shares of common stock as of July 30, 2020. Additionally, as
of the date hereof, the 100,000,000 shares of our common stock registered for resale herein would represent approximately 34.44%
of the Company’s public float.
We may require the Selling Stockholder
to suspend the sales of the shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus upon the occurrence of any event
that makes any statement in this prospectus or the related registration statement untrue in any material respect or that requires
the changing of statements in those documents in order to make statements in those documents not misleading.
The Selling Stockholder identified in the
table below may from time to time offer and sell under this prospectus any or all of the shares of common stock described under
the column “Shares of Common Stock Being Offered” in the table below.
GHS will be deemed to be an underwriter
within the meaning of the Securities Act. Any profits realized by the Selling Stockholder may be deemed to be underwriting commissions.
Information concerning the Selling Stockholder
may change from time to time and, if necessary, we will amend or supplement this prospectus accordingly. We cannot give an estimate
as to the number of shares of common stock that will actually be held by the Selling Stockholder upon termination of this offering,
because the Selling Stockholder may offer some or all of the common stock under the offering contemplated by this prospectus or
acquire additional shares of common stock. The total number of shares that may be sold, hereunder, will not exceed the number of
shares offered, hereby. Please read the section entitled “Plan of Distribution” in this prospectus.
The manner in which the Selling Stockholder
acquired or will acquire shares of our common stock is discussed below under “The Offering.”
The following table sets forth the name
of the Selling Stockholder, the number of shares of our common stock beneficially owned by the Selling Stockholder before this
offering, the number of shares to be offered for the Selling Stockholder’s account and the number and (if one percent or
more) the percentage of the class to be beneficially owned by such stockholder after completion of the offering. The number of
shares owned are those beneficially owned, as determined under the rules of the SEC, and such information is not necessarily indicative
of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under such rules, beneficial ownership includes any shares of our common stock as
to which a person has sole or shared voting power or investment power and any shares of common stock which the person has the right
to acquire within 60 days, through the exercise of any option, warrant or right, through conversion of any security or pursuant
to the automatic termination of a power of attorney or revocation of a trust, discretionary account or similar arrangement, and
such shares are deemed to be beneficially owned and outstanding for computing the share ownership and percentage of the person
holding such options, warrants or other rights, but are not deemed outstanding for computing the percentage of any other person.
Beneficial ownership percentages are calculated based on 379,523,000 shares of our common stock outstanding as of July 30, 2020.
Unless otherwise set forth below, (a) the
persons and entities named in the table have sole voting and sole investment power with respect to the shares set forth opposite
the Selling Stockholder’s name, subject to community property laws, where applicable, and (b) no Selling Stockholder had
any position, office or other material relationship within the past three years, with us or with any of our predecessors or affiliates.
The number of shares of common stock shown as beneficially owned before the offering is based on information furnished to us or
otherwise based on information available to us at the timing of the filing of the registration statement of which this prospectus
forms a part.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Shares to be Owned by Selling Stockholder After the Offering and Percent of Total Issued and Outstanding Shares
|
|
|
Name
of Selling Stockholder
|
|
Shares Owned by the Selling
Stockholder before the Offering
(1)
|
|
|
Shares of Common Stock Being Offered
|
|
|
# of Shares
(2)
|
|
|
% of Class
(2)
|
|
|
GHS Investments LLC (3)
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
(4
|
)
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
0
|
%
|
Notes:
|
(1)
|
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with Securities and Exchange Commission rules and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to shares of common stock. Shares of common stock subject to options, warrants and convertible debentures currently exercisable or convertible, or exercisable or convertible within 60 days, are counted as outstanding. The actual number of shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the convertible debentures is subject to adjustment depending on, among other factors, the future market price of our common stock, and could be materially less or more than the number estimated in the table.
|
|
(2)
|
Because the Selling Stockholder may offer and sell all or only some portion of the 100,000,000 shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus and may acquire additional shares of our common stock in the future, we can only estimate the number and percentage of shares of our common stock that any of the Selling Stockholder will hold upon termination of the offering.
|
|
(3)
|
Mark Grober exercises voting and dispositive power with respect to the shares of our common stock that are beneficially owned by GHS Investments LLC.
|
|
(4)
|
Consists of up to 100,000,000 shares of common stock to be sold by GHS pursuant to the Financing Agreement.
|
THE OFFERING
On March 6, 2020, we entered into an Equity
Financing Agreement with GHS Investments LLC GHS. Although we are not mandated to sell shares under the Financing Agreement, the
Equity Financing Agreement gives us the option to sell to GHS, up to $4,000,000 worth of our common stock until thirty six (36)
months after an effective Registration Statement registering such shares of common stock. The $4,000,000 was stated as the total
amount of available funding in the Financing Agreement because this was the maximum amount that GHS agreed to offer us in funding.
There is no assurance the market price of our common stock will increase in the future. The number of common shares that remain
issuable may not be sufficient, dependent upon the share price, to allow us to access the full amount contemplated under the Financing
Agreement. Based on the lowest closing price of our common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading day period preceding the
filing date of this registration statement was approximately $0.009, the registration statement covers the offer and possible sale
of $720,000 worth of our shares.
The purchase price of the common stock
will be set at eighty percent (80%) of the lowest trading price of the common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading day
period immediately preceding the date on which the Company delivers a put notice to GHS. In addition, there is an ownership limit
for GHS of 4.99%.
GHS is not permitted to engage in short
sales involving our common stock during the term of the commitment period. In accordance with Regulation SHO, however, sales of
our common stock by GHS after delivery of a put notice of such number of shares reasonably expected to be purchased by GHS under
a put will not be deemed a short sale.
In addition, we must deliver the other
required documents, instruments and writings required. GHS is not required to purchase the put shares unless:
|
|
●
|
Our registration statement with respect to the resale of the shares of common stock delivered in connection with the applicable
put shall have been declared effective;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
We shall have obtained all material permits and qualifications required by any applicable state for the offer and sale of the
registrable securities; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
We shall have filed all requisite reports, notices, and other documents with the SEC in a timely manner.
|
As we draw down on the equity line of credit,
shares of our common stock will be sold into the market by GHS. The sale of these shares could cause our stock price to decline.
In turn, if our stock price declines and we issue more puts, more shares will come into the market, which could cause a further
drop in our stock price. You should be aware that there is an inverse relationship between the market price of our common stock
and the number of shares to be issued under the equity line of credit. If our stock price declines, we will be required to issue
a greater number of shares under the equity line of credit. We have no obligation to utilize the full amount available under the
equity line of credit.
Neither the Equity Financing Agreement
nor any of our rights or GHS’s rights thereunder may be assigned to any other person.
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
The Selling Stockholder named above and
any of its pledgees and successors-in-interest may, from time to time, sell any or all of their shares of common stock on the OTCQB
or any other stock exchange, market or trading facility on which the shares of our common stock are traded or in private transactions.
These sales may be at fixed prices and prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices or at negotiated prices.
The Selling Stockholder may use any one or more of the following methods when selling shares:
|
|
●
|
ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the shares as agent but may position and resell a portion of the
block as principal to facilitate the transaction;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
privately negotiated transactions;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
broker-dealers may agree with the Selling Stockholder to sell a specified number of such shares at a stipulated price per share;
or
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
a combination of any such methods of sale.
|
Broker-dealers engaged by the Selling Stockholder
may arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the Selling
Stockholder (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of shares, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated,
but, except as set forth in a supplement to this prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary
brokerage commission in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction a markup or markdown in compliance
with FINRA IM-2440.
GHS is an underwriter within the meaning
of the Securities Act of 1933 and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters”
within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such
broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions
or discounts under the Securities Act of 1933. GHS has informed us that it does not have any written or oral agreement or understanding,
directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the common stock of our company. Pursuant to a requirement by FINRA, the
maximum commission or discount to be received by any FINRA member or independent broker-dealer may not be greater than 8% of the
gross proceeds received by us for the sale of any securities being registered pursuant to Rule 415 promulgated under the Securities
Act of 1933.
Discounts, concessions, commissions and
similar selling expenses, if any, attributable to the sale of shares will be borne by the Selling Stockholder. The selling stockholder
may agree to indemnify any agent, dealer, or broker-dealer that participates in transactions involving sales of the shares if liabilities
are imposed on that person under the Securities Act of 1933.
We are required to pay certain fees and
expenses incurred by us incident to the registration of the shares covered by this prospectus. We have agreed to indemnify the
Selling Stockholder against certain losses, claims, damages and liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of
1933. We will not receive any proceeds from the resale of any of the shares of our common stock by the Selling Stockholder. We
may, however, receive proceeds from the sale of our common stock under the Financing Agreement with GHS. Neither the Financing
Agreement with GHS nor any rights of the parties under the Financing Agreement with GHS may be assigned or delegated to any other
person.
We have entered into an agreement with
GHS to keep this prospectus effective until GHS has sold all of the common shares purchased by it under the Financing Agreement
and has no right to acquire any additional shares of common stock under the Financing Agreement.
The resale shares will be sold only through
registered or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the
resale shares may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an exemption from
the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations
under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale shares may not simultaneously engage
in market making activities with respect to the common stock for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M,
prior to the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the Selling Stockholder will be subject to applicable provisions of
the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing
of purchases and sales of shares of the common stock by the Selling Stockholder or any other person. We will make copies of this
prospectus available to the Selling Stockholder.
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES TO BE REGISTERED
General
We are authorized to issue an aggregate
of six hundred million (600,000,000) shares of common stock, $0.001 par value per share and five million (5,000,000) shares of
preferred stock, $0.001 par value per share, in one or more series and to fix the voting powers, preferences and other rights
and limitations of the preferred stock. As July 30, 2020, we had 379,523,000 shares of common stock outstanding and 5,000,000
shares of Preferred Stock outstanding.
Each share of common stock shall have one
(1) vote per share. Our common stock does not provide a preemptive, subscription or conversion rights and there are no redemption
or sinking fund provisions or rights. Our common stockholders are not entitled to cumulative voting for election of Board of Directors.
Dividends
We have not paid any dividends on our common
stock since our inception and do not intend to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future.
The declaration of any future cash dividends
is at the discretion of our Board and depends upon our earnings, if any, our capital requirements and financial position, our general
economic conditions, and other pertinent conditions. It is our present intention not to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable
future, but rather to reinvest earnings, if any, in our business operations.
Warrants
As of March 31, 2020, there were 30,079,406
warrants outstanding to purchase shares of our common stock at a price per share ranging between $0.05 to $1.00.
Options
The Company has not granted any options since inception.
Transfer Agent
Our transfer agent is Worldwide Stock Transfer,
LLC, 1 University Plaza Dr #505, Hackensack, NJ 07601. Their phone number is 201-820-2008.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under
Equity Compensation Plans
2017 Equity Compensation Plan
On October 12, 2017, the Board approved
the SmartMetric, Inc. 2017 Equity Compensation Plan (the “2017 Plan”) whereby 23,500,000 shares of common stock were
authorized for issuance under the plan to employees, directors and consultants. The plan permits the grant of incentive stock options,
nonstatutory stock options, restricted stock, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock units, performance units, performance
shares and other stock based awards.
As of July 30, 2020, no shares of our
common stock were issued to our employees, directors and consultants, pursuant to the 2017 Plan.
2018 Professional/Consultant Compensation
Plan
On May 2, 2018, the Board approved the
plan to, among other things, make available 20,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share,
for stock-based awards thereunder (the “2018 Plan”).
As of July 30, 2020, no shares of our
common stock were issued as stock-based awards pursuant to the 2018 Plan.
Preferred Stock
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock
On December 11, 2009, the Company filed
a Certificate of Designation with the State of Nevada, to designate 500,000 shares of preferred stock as Series B Convertible Preferred
Stock (the “Series B Convertible Preferred Stock”). Effective November 5, 2014, the number of shares designated as
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock was increased to 5,000,000 shares. Each share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock has
a par value of $0.001, and a stated value equal to $5.00 (“Stated Value”). Holders of the Series B Convertible Preferred
Stock are entitled to receive dividends or other distributions with the holders of the common stock of the Company on an as converted
basis when, as, and if declared by the directors of the Company. Holders of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock are entitled
to convert each share of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock into fifty (50) shares of common stock. Upon any liquidation,
dissolution or winding-up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, holders of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock
are entitled to receive out of the assets, whether capital or surplus, of the Company an amount equal to the Stated Value, pro
rata with the holders of the common stock.
As of July 30, 2020, the Company had 5,000,000
shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.001, authorized, and 610,000 shares of Class B preferred stock issued
and outstanding.
Series C Preferred Stock
On January 14, 2019, the Company filed
a Certificate of Designation with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada, which established 1,000,000 shares of Series C
Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series C Preferred Stock”), par value $0.001 per share, having such designations,
rights and preferences as set forth in the Certificate of Designation, as determined by the Board in its sole discretion, in accordance
with the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws. The Certificate of Designation became effective with the State
of Nevada upon filing.
The shares of Series C Preferred Stock
have a stated value of $1.00 per share, are convertible into Common Stock at a price per share equal to 71% of the average of the
lowest two (2) closing prices of the Common Stock during the fifteen (15) Trading Day (as defined in the Certificate of Designation)
period ending on the last complete Trading Day prior to the Conversion Date (as defined in the Certificate of Designation) (the
“Conversion Price”), and earn dividends at the rate of 10% per annum. Upon an Event of Default (as defined in the Certificate
of Designation), the Series C Preferred Stock earn dividends at the rate of 22% per annum.
The shares of Series C Preferred Stock
do not have voting rights, and rank: (a) senior with respect to dividend rights and rights of liquidation with the Common Stock;
(b) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation with respect to the Company’s Series B Preferred Stock; and
(c) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation to all existing indebtedness of the Company.
The Company may redeem the Series C Preferred
Stock in accordance with the terms of the Certificate of Designation prior to the one hundred eightieth (180th) day
following the date of issuance of the Series C Preferred Stock.
The Company sold 70,000 shares of Series
C Preferred Stock on January 15, 2019 for gross proceeds of $63,000 and sold 51,700 shares of Series C Preferred Stock on June
14, 2019 for gross proceeds of $47,000. For the nine month period ended March 31, 2020, there were 164,500 Preferred C shares issued
for net proceeds of $135,000 and 157,700 Preferred C shares converted to 11,980,203 shares of common stock.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Various Provisions
of Nevada Law
Provisions of the Nevada Revised Statutes,
our articles of incorporation, as amended, and bylaws could make it more difficult to acquire us by means of a tender offer, a
proxy contest or otherwise, or to remove incumbent officers and directors. These provisions, summarized below, would be expected
to discourage certain types of takeover practices and takeover bids our Board may consider inadequate and to encourage persons
seeking to acquire control of us to first negotiate with us. We believe that the benefits of increased protection of our ability
to negotiate with the proponent of an unfriendly or unsolicited proposal to acquire or restructure us will outweigh the disadvantages
of discouraging takeover or acquisition proposals because, among other things, negotiation of these proposals could result in an
improvement of their terms.
Amendments to our Articles of Incorporation
and Bylaws
Under the Nevada Revised Statutes, our
articles of incorporation may not be amended by stockholder action alone.
Nevada
Anti-Takeover Statute
We
may be subject to Nevada’s Combination with Interested Stockholders Statute (Nevada Corporation Law Sections 78.411-78.444)
which prohibits an “interested stockholder” from entering into a “combination” with the corporation, unless
certain conditions are met. An “interested stockholder” is a person who, together with affiliates and associates,
beneficially owns (or within the prior two years, did beneficially own) 10% or more of the corporation’s capital stock entitled
to vote.
Limitations
on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors
The
Nevada Revised Statutes limits or eliminates the personal liability of directors to corporations and their stockholders for monetary
damages for breaches of directors’ fiduciary duties as directors.
The
limitation of liability and indemnification provisions under the Nevada Revised Statues and in our articles of incorporation and
bylaws may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against directors for breach of their fiduciary duties. These provisions
may also have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such
an action, if successful, might otherwise benefit us and our stockholders. However, these provisions do not limit or eliminate
our rights, or those of any stockholder, to seek non-monetary relief such as injunction or rescission in the event of a breach
of a director’s fiduciary duties. Moreover, the provisions do not alter the liability of directors under the federal securities
laws. In addition, your investment may be adversely affected to the extent that, in a class action or direct suit, we pay the
costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
Authorized
but Unissued Shares
Our
authorized but unissued shares of Common Stock and preferred stock will be available for future issuance without stockholder approval,
except as may be required under the listing rules of any stock exchange on which our Common Stock is then listed. We may use additional
shares for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings to raise additional capital, corporate acquisitions
and employee benefit plans. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of Common Stock and preferred stock could render more
difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of us by means of a proxy contest, tender offer, merger or otherwise.
Penny
Stock Considerations
Our
shares will be “penny stocks” as that term is generally defined in the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 to mean equity
securities with a price of less than $5.00 per share. Thus, our shares will be subject to rules that impose sales practice and
disclosure requirements on broker-dealers who engage in certain transactions involving a penny stock. Under the penny stock regulations,
a broker-dealer selling a penny stock to anyone other than an established customer must make a special suitability determination
regarding the purchaser and must receive the purchaser’s written consent to the transaction prior to the sale, unless the
broker-dealer is otherwise exempt.
In
addition, under the penny stock regulations, the broker-dealer is required to:
|
|
●
|
Deliver,
prior to any transaction involving a penny stock, a disclosure schedule prepared by the
Securities and Exchange Commission relating to the penny stock market, unless the broker-dealer
or the transaction is otherwise exempt;
|
|
|
●
|
Disclose
commissions payable to the broker-dealer and our registered representatives and current
bid and offer quotations for the securities;
|
|
|
●
|
Send
monthly statements disclosing recent price information pertaining to the penny stock
held in a customer’s account, the account’s value, and information regarding
the limited market in penny stocks; and
|
|
|
●
|
Make
a special written determination that the penny stock is a suitable investment for the
purchaser and receive the purchaser’s written agreement to the transaction, prior
to conducting any penny stock transaction in the customer’s account.
|
Because
of these regulations, broker-dealers may encounter difficulties in their attempt to sell shares of our common stock, which may
affect the ability of selling shareholders or other holders to sell their shares in the secondary market and have the effect of
reducing the level of trading activity in the secondary market. These additional sales practice and disclosure requirements could
impede the sale of our securities, if our securities become publicly traded. In addition, the liquidity for our securities may
be decreased, with a corresponding decrease in the price of our securities. Our shares in all probability will be subject to such
penny stock rules and our shareholders will, in all likelihood, find it difficult to sell their securities.
INTERESTS
OF NAMED EXPERTS AND COUNSEL
The
consolidated financial statements for the Company for the year ended June 30, 2019 included in this prospectus have been audited
by Prager Metis CPAs, LLC, an independent registered public accounting firm. The consolidated financial statements for the Company
for the year ended June 30, 2018 included in this prospectus have been audited by AMC Auditing, an independent registered public
accounting firm. The consolidated financial statements included in this prospectus are incorporated herein in reliance upon such
reports given upon the authority of said firms as experts in auditing and accounting.
The
legality of the shares offered under this registration statement will be passed upon by Lucosky Brookman LLP.
INFORMATION
WITH RESPECT TO THE REGISTRANT
Corporate
History and Overview
SmartMetric,
Inc. (“SmartMetric” or the “Company”) was incorporated pursuant to the laws of Nevada on December 18,
2002. SmartMetric is a development stage company engaged in the technology industry. SmartMetric’s main products are a fingerprint
sensor debit card as well as a card with a finger sensor and fully functional fingerprint reader embedded inside the card.
The SmartMetric biometric cards have a rechargeable battery allowing for portable biometric identification and card activation.
This card is referred to as a biometric card or the SmartMetric Biometric Card.
The
Market for Biometric Credit Cards
According
to a to a press release issued by Goode Intelligence, an independent market research company, regarding their October 2018 report
on the biometrics payment sector, nearly 579 million biometric credit/debit cards will be in use over the next five (5) years.
Goode Intelligence believes* there is a significant market opportunity for biometric payment cards. and forecasts that by 2023
there will be almost 579 million biometric payment cards in use around the world.
“Contactless
card payments are even outperforming mobile in many regions. Many consumers prefer to use a contactless payment card over a mobile
payment equivalent and according to Goode Intelligence research, many users would like to use cards in contactless mode for higher
value transactions. Biometric payment cards not only offer improved security by removing the PIN but also allow frictionless payments
for higher value transactions,” stated Good Intelligence.
SmartMetric
engaged an outside independent research company to survey a statistically relevant sample of Visa credit card holders in the United
States. One of the questions asked showed that nearly 67% of these credit card holders would be willing to pay $69.95 for a biometric
secured credit card.
The
survey asked:
Would
you pay for a safer biometric secured credit card that has a built-in fingerprint reader for your protection?
|
|
*
|
Goode
Intelligence is an independent analyst and consultancy company that provides quality advice
to global decision makers in business and technology.
|
Goode
Intelligence works in information security, mobile security, authentication and identity verification, biometrics, enterprise
mobility and mobile commerce sectors.
Founded
in 2007 by Alan Goode and headquartered in London, Goode. Intelligence helps both technology providers, investors and IT purchasers
make strategic business decisions based on quality research, insight and consulting.
The
SmartMetric Biometric Technology and Products
SmartMetric’s
founder, Chaya Hendrick is the originator and inventor of various miniature biometric activated cards, including the SmartMetric
biometric fingerprint activated payments card with an embedded fully functional fingerprint reader inside. the card. The card
is the size and thickness of a standard credit card. The SmartMetric biometric payments card provides for high level security
for credit and debit cards by adding biometric authentication and activation to Europay, MasterCard and Visa (“EMV”)
chip cards in use around the world. The SmartMetric biometric payments card has been manufactured to be totally interoperable
with existing EMV chip card readers, ATMs as well as banking payments infrastructure. Using the advanced electronic miniaturization
by SmartMetric to make its biometric credit/debit cards the Company has also created a multi-functional biometric building access
control and logical network access card.
Since
July 1, 2018, SmartMetric has commenced efforts towards creating a biometric health insurance card with memory for storing a person’s
medical files, including medical images. This allows a person to securely take with them their private medical files inside the
card when traveling away from home. For the first time, a person’s complete medical files can be stored in a credit card-sized
card and the information is only able to be accessed by the card holder’s own fingerprint. The company is in discussion
with significant health membership organizations concerning the offering of the SmartMetric Biometric Medical Records card to
their respective members.
SmartMetric
has developed its rechargeable battery powered fingerprint reader that is of a scale that fits “inside” a standard
credit or debit card. The cardholder has stored inside the card his or her fingerprint. To activate the card the person swipes
the fingerprint sensor, the sensor is connected to an internal microprocessor that manages the fingerprint sensor fingerprint
image capture and comparison matching with the pre-stored fingerprint of the cardholder held in the internal electronic memory
of the card. The card has a surface mounted EMV chip as found on EMV banking chip cards that is activated or turned on only after
a card holder’s fingerprint has been scanned and verified using the SmartMetric miniature “in-card” biometric
scanner.
There
are over seven (7) billion EMV chip cards used by banks around the world for credit cards, ATM cards and debit cards according
to EMVco. SmartMetric sees this existing user base as a natural market for its advanced biometric activated card technology for
the credit and debit card market. SmartMetric has established a network of card manufacturers and technology distributors to market
its in-card biometric products to card issuing banks and in the case of the SmartMetric biometric security card, to businesses.
SmartMetric
has completed development of its biometric card and is now actively marketing its card to major card issuing banks throughout
the world in partnership with established card distributors and dealers.
SmartMetric
has also developed a multi-function logical and physical access security card this size and thickness of a standard credit card.
Utilizing the small size breakthroughs by the Company in its biometric payments card development, SmartMetric has successfully
developed a biometric security card that is the size and thickness of a standard credit card that can easily fit inside a person’s
wallet.
As
with the biometric payments card, the SmartMetric security card has an internal rechargeable battery that is used to power the
card’s internal processor used in the biometric fingerprint scan. All functions and operations of the card are subject to
a valid fingerprint scan and match of the card user.
On
February 1, 2019, SmartMetric entered into a manufacturing and license agreement with Servired, SA (“Servired”). Servired
operates the major payments network in Spain for credit and debit card transactions. Subsequently, the Servired agreement has
been transferred and assumed in total by RedSys, SA. (“RedSys”) as part of a corporate reorganization. RedSys is now
the corporate entity that owns the ADVANTIS (discussed later) credit card and debit card chip and operating software system. Regarding
integration of Advantis in Redsys, Redsys acquired from Servired, through company succession, the independent economic marketing
unit of the Advantis System and the Pricenet, SIS and SAS family programs.
The
ADVANTIS EMV Chip and operating system is currently being used by banks around the world on their debit and credit cards. 1.4
Billion cards with the ADVANTIS chip and software operating system have been issued by their member banks worldwide.
SmartMetric
is now in the process of manufacturing its biometric credit/debit card with the ADVANTIS payments card chip and operating system.
This will allow over 500 Banks worldwide, who are already using the ADVANTIS chip and chip card operating system, to seamlessly
issue this new SmartMetric – ADVANTIS biometric credit and debit card.
Additional
technological advances have now been made on both the Company’s biometric credit/debit card and its multifunction cyber
security, building access to the biometric card.
In
Card Fingerprint Matching and Verification
The
SmartMetric Biometric card incorporates a rechargeable, lithium polymer battery. This battery is rechargeable, very thin and has
been designed by SmartMetric to fit inside the SmartMetric fingerprint credit card sized card. This battery is manufactured by
a third party unaffiliated with the Company to SmartMetric’s specifications. This battery is embedded inside the card.
Other
components needed for manufacture of the SmartMetric Biometric Card include, but are not limited to, sensors, microchips, memory
chips and processor chips. The ultra-thin circuit board developed by SmartMetric has, in total, nearly 200 active and passive
components. The sources and availability of these materials are numerous, readily available and should not affect the ability
of SmartMetric to meet future demand. The supply of memory processors and passive components may be interrupted at any time based
on global supply/demand issues. We have not experienced component supply issues to date and the Company, as a matter of policy,
has alternative component sources to mitigate and protect against supply chain issues.
The
biometric card has been designed to offer the option of a built-in radio frequency transmitter for contactless access and identity
verification. The RFID contactless chip transmission is turned on using the card users fingerprint verification.
The
thinness form factor of many of the components, has also resulted in the Company having to develop its own process for high volume
electronic assembly. The Company has also successfully overcome the challenge of developing a process of encapsulating the electronics
in plastic to create the credit card sized biometric fingerprint activated card that also has an internal rechargeable battery.
Standard
credit card manufacturing utilizes machines that require high pressure and high temperature in fusing top and bottom sheets of
plastic together thereby encasing any electronics inside the card. Given the complexity of the card’s electronics and vulnerability
to an assembly process involving high heat and high pressure, damage to the electronic circuitry was a major challenge for the
Company to overcome. Research and development activities of the Company allowed the Company to achieve this ability through a
trade secret process that protects the silicon and internal battery that is mounted directly onto the card’s internal electronics
circuit board.
The
Security Technology Industry
SmartMetric
Biometric Multi-Function Security Card
SmartMetric
has developed a multi-function logical and physical access security card this size and thickness of a standard credit card. Utilizing
the small size breakthroughs by the Company in its biometric payments card development, SmartMetric has successfully developed
a biometric security card that can easily fit inside a person’s wallet.
As
with the biometric payments card, the SmartMetric security card has an internal rechargeable battery that is used to power the
card’s internal processor used in the biometric fingerprint scan. All functions and operations of the card are subject to
a valid fingerprint scan and match of the card user.
The
main features of the SmartMetric biometric security card are:
|
|
1.
|
Logical
access smartcard card chip for insertion into a card reader attached to a computer or network
|
|
|
2.
|
RFID
transceiver for physical access i.e. doorways, elevators, etc.
|
|
|
3.
|
Validation
indicator light that glows green immediately following a fingerprint validation
|
|
|
4.
|
Rechargeable
battery to power the card
|
|
|
5.
|
Size
and thickness of a credit card
|
|
|
6.
|
Changeable
security code on reverse of card for additional log on security
|
Cybersecurity
and identity validation for network access control, physical building entry and secure on-the-spot identity security is now handled
by the revolutionary biometric activated cyber and ID multi-function security card which has been developed by SmartMetric after
over a decade of R&D.
From
governments to the workplace, better, stronger security is desired across the enterprise. Our new biometric multifunction security
card provides a revolutionary biometric based solution that is portable, easily integrated and backward compatible to existing
backend security infrastructure.
The
new multifunction biometric security card by SmartMetric is a revolutionary leap forward in the Cyber and Access Security world
according to SmartMetric.
Access
management market is estimated to grow from USD 8.09 billion in 2016 to USD 14.82 billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 12.9% between
2016 and 2021 according to a recent research report by KBV Research in a publication titled Identity & Access Management Market
– Global Forecast by Marqual IT Solutions Pvt. Ltd (KBV Research) November 2016 KBV Research is a name owned by IT Solutions
Pvt. Ltd.
Biometrics
Biometric
technologies identify users by electronically capturing a specific biological or behavioral characteristic of that individual,
such as a fingerprint or voice or facial feature, and creating a unique digital identifier from that characteristic. Because this
process relies on largely unalterable human characteristics, positive identification can be achieved independent of any information
possessed by the individual seeking authorization.
The
process of identity authentication typically requires that a person present for comparison with one or more of the following factors:
|
|
●
|
Something
known such as a password, PIN or mother’s maiden name;
|
|
|
●
|
Something
carried such as a token, card, or key; or
|
|
|
●
|
something
physical such as fingerprint, voice pattern, signature motion, facial shape or other biological or behavioral characteristic.
|
Comparison
of biological and behavioral characteristics has historically been the most reliable and accurate of the three factors but has
also been the most difficult and costly to implement into a single product that can automatically verify the identity of a user
accessing a computer network or the Internet. However, recent advances in biometric collection technologies (both biometric hardware
products and their associated processing software) have increased the speed and accuracy and reduced the cost of implementing
biometrics in commercial environments. Management believes that individuals, website operators, government organizations, and
businesses will increasingly use this method of identity authentication.
Biometrics
refers to the automatic identification of a person based on his/her physiological or behavioral characteristics. This method of
identification is preferred over traditional methods involving passwords and personal identification numbers (“PINs”)
for two reasons: (i) the person to be identified is required to be physically present at the point of identification to be identification;
and (ii) identification based on biometric techniques obviates the need to remember a password or carry a token. By replacing
PINs, biometric techniques can potentially prevent unauthorized access to or fraudulent use of cellular phones, Biometric cards,
desktop PCs, workstations and computer networks. It can be used during transactions conducted via telephone and Internet (e-commerce
and e-banking). In automobiles, biometrics could replace keys-less entry devices. The SmartMetric fingerprint activated credit
card that has the fingerprint encased inside the credit card has been developed to replace the less secure PIN’s for credit
and debit cards.
PINs
and passwords may be forgotten, may be hacked and token-based methods of identification, e.g., passports and driver’s licenses,
may be forged, stolen or lost. Various types of biometric systems are being used for real-time identification, with the most popular
based on facial recognition and fingerprint matching. Other biometric systems utilize iris and retinal scanning, speech, facial
thermograms and hand geometry. Of the biometric options available to work with a credit or debit card, fingerprint scanning is
the only biometric methodology that has been successfully reduced in size to fit inside such cards.
A
biometric system is essentially a pattern recognition system, which makes a personal identification by determining the authenticity
of a specific physiological or behavioral characteristic possessed by the user. An important issue in designing a practical system
is to determine how an individual is identified.
There
are two different ways to resolve a person’s identity; verification and identification. Verification (Am I whom I claim
I am?) involves confirming or denying a person’s claimed identity. In identification, one has to establish a person’s
identity (Who am I?).
As
stated above, the SmartMetric fingerprint biometric card has been designed as a credit-card sized card embedded with an integrated
circuit, contact chip and biometric fingerprint sensor. The SmartMetric card has been designed to provide not only memory capacity,
but also computational capability along with secure non-refutable identification of the user. We believe that the self-containment
of SmartMetric’s card makes it substantially resistant to attack, as it will not need to depend upon vulnerable external
resources. Because of this characteristic, we expect that the SmartMetric biometric card may be used in different applications,
which require strong security protection and authentication.
The
physical structure of a card is specified by the International Standards Organization (“ISO”). Generally, this structure
is made up of three elements: (i) the plastic card, which is the most basic one and has the dimensions of 85.60mm x 53.98 x 0.80mm;
(ii) an electronic circuit board inlay; and (iii) a contact chip that are embedded in the card.
The
SmartMetric card has been designed to conform to ISO standards. The electronic circuit inlay is a part of, and not distinct from,
the biometric card.
The
communication line between the card and ATMs and other standard Smart Card reading devices is bi-directional serial transmission,
which conforms to ISO standards. Card commands and input data are sent to the chip that responds with status words and output
data upon the receipt of these commands and data. Information is sent in half duplex mode (transmission of data is in one direction
at a time). This protocol, together with the restriction of the bit rate, is designed to prevent data attack on the card. Other
data protection systems are utilized inside the card including advanced encryption.
In
general, the size, the thickness and bend requirements for the biometric card were designed to protect the card from being spoiled
physically.
Recent
Developments
On
January 14, 2019, the Company filed a Certificate of Designation with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada (the “Certificate
of Designation”), which established 1,000,000 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series C Preferred
Stock”), par value $0.001 per share, having such designations, rights and preferences as set forth in the Certificate of
Designation, as determined by the Board in its sole discretion, in accordance with the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation
and Bylaws. The Certificate of Designation became effective with the State of Nevada upon filing.
The
shares of Series C Preferred Stock have a stated value of $1.00 per share, are convertible into Common Stock at a price per share
equal to 71% of the average of the lowest two (2) closing prices of the Common Stock during the fifteen (15) Trading Day (as defined
in the Certificate of Designation) period ending on the last complete Trading Day prior to the Conversion Date (as defined in
the Certificate of Designation) (the “Conversion Price”), and earn dividends at the rate of 10% per annum. Upon an
Event of Default (as defined in the Certificate of Designation), the Series C Preferred Stock earn dividends at the rate of 22%
per annum.
The
shares of Series C Preferred Stock do not have voting rights, and rank: (a) senior with respect to dividend rights and rights
of liquidation with the Common Stock; (b) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation with respect to the Company’s
Series B Preferred Stock; and (c) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation to all existing indebtedness of the
Company.
The
Company may redeem the Series C Preferred Stock in accordance with the terms of the Certificate of Designation prior to the one
hundred eightieth (180th) day following the date of issuance of the Series C Preferred Stock.
The
Company sold: (i) 70,000 shares of Series C Preferred Stock on January 15, 2019 for gross proceeds of $63,000; (ii) 51,700 shares
of Series C Preferred Stock on June 14, 2019 for gross proceeds of $47,000; and (iii) 52,800 shares of Series C Preferred Stock
on August 27, 2019 for gross proceeds of $48,000.
Sales
and Marketing
SmartMetric
has engaged distributors and dealers in both North and South America. SmartMetric has entered into an agreement with Redsys the
owner of the ADVANTIS credit and debit card chip that is used in over 1.4 Billion credit/debit cards globally. RedSys/Advantis
is owned by card issuing Banks. Five hundred (500) card issuing banking organizations around the world are issuing credit and
debit cards with the RedSys/ADVANTIS chip.
SmartMetric
has added the ADVANTIS credit/debit card chip onto the SmartMetric biometric card thereby allowing the existing RedSys / ADVANTIS
banks already issuing credit and debit cards with their chip on board to now issue seamlessly the SmartMetric biometric credit
/ debit card. RedSys / ADVANTIS have agreed to work closely with SmartMetric in promoting the SmartMetric card globally. RedSys
/ ADVANTIS is owned by some the largest Banks in Europe and Latin America.
Manufacturing
The
Company designs and develops its biometric technology. Current production capacity is approximately 250,000 cards per week that
can be substantially increased over a relatively short period of time.

SmartMetric’s
President & CEO in the card lamination factory.
Intellectual
Property
We
rely on patents, licenses, trade secrets, trademarks, copyright registrations and non-disclosure agreements to establish and protect
our proprietary rights in our technologies and products. A number of patents are in process (Patents Pending) that cover critical
aspects of the engineering and function of the SmartMetric biometric card. The founder of SmartMetric, Chaya Hendrick, is the
inventor of these patents, and has provided SmartMetric with an option over biometric card related pending patents invented by
her.
Some
of the most recent patents pending have not been disclosed on the publicly searchable USPTO database of filed for patents and
remain trade secrets within the Company. Publishing of such patents pending will be done in due course.
Patents
SmartMetric
biometric card is protected by five (5) USPTO issued patents. Other patents are pending. Our technology is also dependent upon
unpatented trade secrets. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. In an effort to protect our trade secrets, we have
a policy of requiring our employees, consultants and advisors to execute non-disclosure agreements. The principal shareholder
of SmartMetric and technology inventor, Chaya Hendrick, through various corporate investment vehicles and companies also owns
other technologies, patents, and has financial interest in other technology companies. Chaya Hendrick, under an executed employment
agreement is not subject to any restriction on using and owning any technology, methodology, process or invention created by Chaya
Hendrick.
Government
Regulation
There
are currently no governmental regulations, which have any bearing on the raw materials or the manufacturing of our payments card
products. United States federal departments such as the Department of Defense have rules and regulations concerning security features
of smart cards used as identity or building and cyber access cards. These regulations stipulate a specific licensing and testing
protocol for such cards.
Banking
Industry Self-Regulation
The
EMV chip used in chip cards are subject to licensing and testing by the banking-controlled body called EMVco. EMVco is an acronym
standing for Europay, MasterCard and Visa. These international payments card networks were the founding parties of EMVco.
Individual
payments networks such as Visa, Mastercard, Europay, American Express, Union Pay Dinners and JCB all have their own individual
licensing and testing standards and processes.
Research
and Development
Our
research and development program is focused on ongoing development of new products built on our existing biometric card. We continue
to refine our technology and develop further improvements to our biometric card products. We have finalized our first biometric
EMV payments card product. We have also concluded the design and electronic engineering for our soon-to-be released multi-function
security and access control biometric cards. Research and development will continue as the Company continues to innovate and develop
new biometric card-based products. Future biometric card-based products the Company is now working on, include but are not limited
to: (a) health insurance card with stored in-card medical records; (b) national identity card; and (c) drivers’ licenses.
The
Company has developed and is continuing to develop its own embedded systems and application software that works with the SmartMetric
Biometric Card. This development software and systems and ongoing electronic design and development requires the company to continue
to expend time and financial resources on significant software development. Currently, the Company has electronic and software
engineers working in Tel Aviv, Israel and Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Competition
Various
potential competitors have announced products similar to that of SmartMetric’s. It is understood that “announced”
is defined as a person to hold their finger on the cards fingerprint sensor while it is in a card reader. Unlike the SmartMetric
biometric card that is powered from its own internal rechargeable battery, this other type of card does not allow the card to
be used in most restaurants that need to take the card away from the table for processing at the checkout. It also does not allow
their other type of card to be used at the vast majority of ATM’s.
Employees
As
of the date of this annual report, we have one full time employee, our Chief Executive Officer and President, Chaya Hendrick.
We primarily use direct contract hires in administration and engineering, as is common in the information technology world. All
work product developed by all of our engineers remains the intellectual property of SmartMetric. Engineers who work for SmartMetric
under contract are primarily based in Tel Aviv, Israel. Some software engineering is conducted in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Corporate
History
We
were incorporated in the State of Nevada on December 18, 2002 and our principal office is located in Las Vegas, Nevada. Since
our inception, we have invested a substantial portion of our efforts and financial resources in the development of our products.
We have generated no revenues from the sale of our products and have experienced substantial net operating losses.
Where
to Find More Information
We
make our public filings with the SEC, including our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports
on Form 8-K and all exhibits and amendments to these reports. These materials are available on the Company’s website at www.smartmetric.com or
on the SEC’s web site, http://www.sec.gov.
MARKET
PRICE OF THE REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
(a)
Common Stock
Our
common stock is quoted on the OTCQB under the symbol “SMME.”
(b)
Holders of Common Equity
As
of the date hereof, there were approximately 82 stockholders of record. An additional number of stockholders are beneficial holders
of our common stock in “street name” through banks, brokers and other financial institutions that are the record holders.
(c)
Dividend Information
We
have not paid any cash dividends to our holders of common stock. The declaration of any future cash dividends is at the discretion
of our Board and depends upon our earnings, if any, our capital requirements and financial position, our general economic conditions,
and other pertinent conditions. It is our present intention not to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future, but rather
to reinvest earnings, if any, in our business operations.
MANAGEMENT’S
DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION
You
should read the following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with financial statements
and notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that reflect
our plans, estimates and beliefs. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements.
Factors that could cause or contribute to these differences include those discussed below and elsewhere in this prospectus, particularly
in the section labeled “Risk Factors.”
We
desire to take advantage of the “safe harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995.
This filing contains a number of forward-looking statements that reflect management’s current views and expectations with
respect to our business, strategies, products, future results and events, and financial performance. All statements made in this
filing other than statements of historical fact, including statements addressing operating performance, clinical developments
which management expects or anticipates will or may occur in the future, including statements related to our technology, market
expectations, future revenues, financing alternatives, statements expressing general optimism about future operating results,
and non-historical information, are forward looking statements. In particular, the words “believe,” “expect,”
“intend,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “may,” variations of such words, and similar
expressions identify forward-looking statements, but are not the exclusive means of identifying such statements, and their absence
does not mean that the statement is not forward-looking. These forward-looking statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties,
including those discussed below. Our actual results, performance or achievements could differ materially from historical results
as well as those expressed in, anticipated, or implied by these forward-looking statements. We do not undertake any obligation
to revise these forward-looking statements to reflect any future events or circumstances.
Readers
should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which are based on management’s current expectations
and projections about future events, are not guarantees of future performance, are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions
(including those described below), and apply only as of the date of this filing. Our actual results, performance or achievements
could differ materially from the results expressed in, or implied by, these forward-looking statements. Factors which could cause
or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, the risks to be discussed in this Prospectus and in the press
releases and other communications to shareholders issued by us from time to time which attempt to advise interested parties of
the risks and factors which may affect our business. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking
statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise. For additional information regarding forward-looking
statements, see “Forward-Looking Statements.”
These
risks and factors include, by way of example and without limitation:
|
|
●
|
our
ability to successfully commercialize our products to produce a market-ready product
in a timely manner and in enough quantity;
|
|
|
●
|
absence
of contracts with customers or suppliers;
|
|
|
●
|
our
ability to maintain and develop relationships with customers and suppliers;
|
|
|
●
|
our
ability to successfully integrate acquired businesses or new brands;
|
|
|
●
|
the
impact of competitive products and pricing;
|
|
|
●
|
supply
constraints or difficulties;
|
|
|
●
|
the
retention and availability of key personnel;
|
|
|
●
|
general
economic and business conditions;
|
|
|
●
|
substantial
doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern;
|
|
|
●
|
our
need to raise additional funds in the future;
|
|
|
●
|
our
ability to successfully recruit and retain qualified personnel in order to continue our
operations;
|
|
|
●
|
our
ability to successfully implement our business plan;
|
|
|
●
|
our
ability to successfully acquire, develop or commercialize new products and equipment;
|
|
|
●
|
the
commercial success of our products;
|
|
|
●
|
intellectual
property claims brought by third parties; and
|
|
|
●
|
the
impact of any industry regulation.
|
Although
we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results,
levels of activity, or performance. Except as required by applicable law, including the securities laws of the United States,
we do not intend to update any of the forward-looking statements to conform these statements to actual results.
Readers
are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this report and in our other reports filed with
the SEC. We undertake no obligation to update or revise forward-looking statements to reflect changed assumptions, the occurrence
of unanticipated events, or changes in the future operating results over time, except as required by law. We believe that our
assumptions are based upon reasonable data derived from and known about our business and operations. No assurances are made that
actual results of operations or the results of our future activities will not differ materially from our assumptions.
As
used in this registration statement on Form S-1 and unless otherwise indicated, the terms “Company,” “we,”
“us,” and “our” refer to SmartMetric, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary, SmartMetric Australia Pty.
Ltd.
Going
Concern
The
condensed consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the carrying amounts of recorded assets
or the carrying amounts and classification of recorded liabilities that may be required should the Company be unable to continue
as a going concern.
As
shown in the accompanying consolidated financial statements the Company has incurred recurring losses of $641,383 and $645,686
for the period ending March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and has incurred a cumulative loss of $27,574,847 since inception
(December 18, 2002). The Company is currently in the development stage and has spent a substantial portion of its
time in the development of its technology.
There is no guarantee that the Company will
be able to raise enough capital or generate revenues to sustain its operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt about
the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. To mitigate this concern, management plans on continuing its relationship
with Geneva Roth Remark and the agreement to issue Preferred C shares.
Management
believes that the Company’s capital requirements will depend on many factors. These factors include the final
phase of development and mass production being successful as well as product implementation and distribution.
The
consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the carrying amounts of recorded assets or the carrying
amounts and classification of recorded liabilities that may be required should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
In
December 2019, an outbreak of a novel strain of coronavirus originated in Wuhan, China (“COVID-19”) and has since
spread worldwide, including to the Unites States, posing public health risks that have reached pandemic proportions (the “COVID-19
Pandemic”). The COVID-19 Pandemic poses a threat to the health and economic wellbeing of our employees, customers and vendors.
Like most businesses world-wide, the COVID-19 Pandemic has impacted the Company financially; however, management cannot presently
predict the scope and severity with which COVID-19 will impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash
flows.
Critical
Accounting Policies
We
have prepared our financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which
requires management to make significant judgments and estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and
disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during
the reporting period. We base these significant judgments and estimates on historical experience and other applicable assumptions
we believe to be reasonable based upon information presently available. These estimates may change as new events occur, as additional
information is obtained and as our operating environment changes. These changes have historically been minor and have been included
in the financial statements as soon as they became known. Actual results could materially differ from our estimates under different
assumptions, judgments or conditions.
All
of the Company’s significant accounting policies are discussed in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, to
our financial statements, included elsewhere in this Quarterly Report. We have identified the following as our significant accounting
policies and estimates, which are defined as those that are reflective of significant judgments and uncertainties, are the most
pervasive and important to the presentation of our financial condition and results of operations and could potentially result
in materially different results under different assumptions, judgments or conditions.
We
believe the following critical accounting policies reflect our more significant estimates and assumptions used in the preparation
of our financial statements:
Use
of Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires
management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying disclosures.
Actual results may differ from those estimates.
Research
and Development Costs - Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred. Our research and development
expenses consist primarily of expenditures for electronics design and engineering, software design and engineering, component
sourcing, component engineering, manufacturing, product trials, compensation and consulting costs.
Results
of Operations
Comparison
of the Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 and 2019
Our results of operations have varied significantly
from year to year and quarter to quarter and may vary significantly in the future. We did not have revenue for the three months
ending March 31, 2020 and 2019. Net loss for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 were $173,485 and $225,569, respectively,
resulting from the operational activities described below.
Operating
Expenses
Operating
expense totaled $154,790 and $207,649 during the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The decrease in operating
expenses is the result of the following factors.
|
|
|
Quarter Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
Change in 2020
Versus 2019
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
Operating expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer salary
|
|
$
|
47,500
|
|
|
$
|
47,500
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
(0
|
)%
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
14,090
|
|
|
|
38,949
|
|
|
|
(24,589
|
)
|
|
|
(63.8
|
)%
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
93,200
|
|
|
|
121,200
|
|
|
|
(28,000
|
)
|
|
|
(23.1
|
)%
|
|
Total operating expense
|
|
$
|
154,790
|
|
|
$
|
207,649
|
|
|
$
|
(52,859
|
)
|
|
|
(25.5
|
)%
|
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenses totaled $14,090 and $38,949 for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The decrease
of $24,589, or 63.8%, in 2020 compared to 2019 was primarily attributable to decreased engineering expenses. Our research and
development expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to engineering.
General
and Administrative
General
and administrative expenses totaled $93,200 and $121,200 for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The
decrease of $28,000 or 23.1%, in 2020 compared to 2019 was primarily the result of a decrease in consulting expenses. Our general
and administrative expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to employee compensation, legal, accounting and tax, other
professional services, and general operating expenses.
Other
Expense
Other
income (expense) totaled $14,081 and $13,647 for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
|
|
|
Quarter Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
Change in 2020
Versus 2019
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Expense
|
|
|
14,081
|
|
|
|
13,647
|
|
|
|
434
|
|
|
|
3.2
|
%
|
|
Total other expense
|
|
$
|
14,081
|
|
|
$
|
13,647
|
|
|
$
|
434
|
|
|
|
3.2
|
%
|
Interest
income (expense)
We
had net interest expense of $14,081 in the three months ended March 31, 2020 compared to $13,647 net interest expense for the
three months ended March 31, 2019. The increase of $434 was attributable to interest expenses related to accrued but unpaid salary
of our CEO pursuant to an amended and restated employment agreement entered into on July 1, 2017.
Comparison
of the Nine Months Ended March 31, 2020 and 2019
Our
results of operations have varied significantly from year to year and quarter to quarter and may vary significantly in the future.
We did not have revenue for the nine months ending March 31, 2020 and 2019. Net loss for the nine months ended March 31, 2020
and 2019 were $620,806 and $641,413, respectively, resulting from the operational activities described below.
Operating
Expenses
Operating
expense totaled $579,075 and $601,945 during the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The decrease in operating
expenses is the result of the lower research & development expenses.
|
|
|
Nine Months Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
Change in 2020
Versus 2019
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
Operating expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer salary
|
|
$
|
142,500
|
|
|
$
|
142,500
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
(0
|
)%
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
60,796
|
|
|
|
90,084
|
|
|
|
(29,288
|
)
|
|
|
(32.5
|
)%
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
375,779
|
|
|
|
369,361
|
|
|
|
6,418
|
|
|
|
1.7
|
%
|
|
Total operating expense
|
|
$
|
579,075
|
|
|
$
|
601,945
|
|
|
$
|
(22,870
|
)
|
|
|
(3.8
|
)%
|
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenses totaled $60,796 and $90,084 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The decrease
of $29,288, or 35.2%, in 2020 compared to 2019 was primarily attributable to decreased engineering expenses. Our research and
development expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to engineering.
General
and Administrative
General
and administrative expenses totaled $375,779 and $369,361 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The
increase of $6,418 or 1.7%, in 2020 compared to 2019 was primarily the result of an increase in consulting expenses. Our general
and administrative expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to employee compensation, legal, accounting and tax, other
professional services, and general operating expenses.
Other
Expense
Other
income (expense) totaled $41,731 and $39,468 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
|
|
|
Quarter Ended
March 31,
|
|
|
Change in 2020
Versus 2019
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Expense
|
|
|
41,731
|
|
|
|
39,468
|
|
|
|
2,263
|
|
|
|
5.7
|
%
|
|
Total other expense
|
|
$
|
41,731
|
|
|
$
|
39,468
|
|
|
$
|
2,263
|
|
|
|
5.7
|
%
|
Interest
income (expense)
We
had net interest expense of $41,731 in the nine months ended March 31, 2020 compared to $39,468 net interest expense for the nine
months ended March 31, 2019. The increase of $2,263 was attributable to interest expenses related to accrued but unpaid salary
of our CEO pursuant to an amended and restated employment agreement entered into on July 1, 2017.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources as of March 31, 2020
We
have incurred losses since our inception in 2002 as a result of significant expenditures for operations and research and development
and the lack of any revenue. We have an accumulated deficit of $27,574,847 as of March 31, 2020 and anticipate that we will continue
to incur additional losses for the foreseeable future. Through March 31, 2020, we have funded our operations through the private
sale of our equity securities and exercises of options and warrants, resulting in gross proceeds of approximately $27.6 million
from inception through March 31, 2020.
|
|
|
Nine months ended
March 31,
|
|
|
Change in 2020
versus 2019
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash at beginning of period
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
$
|
4,427
|
|
|
$
|
5,734
|
|
|
|
129.5
|
%
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
|
495,371
|
|
|
|
403,816
|
|
|
|
91,555
|
|
|
|
22.7
|
%
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
|
|
485,210
|
|
|
|
460,318
|
|
|
|
24,892
|
|
|
|
5.4
|
%
|
|
Cash at end of period
|
|
$
|
-0-
|
|
|
$
|
60,929
|
|
|
$
|
(60,929
|
)
|
|
|
(100.0
|
)%
|
Net
Cash Used in Operating Activities
Net
cash used in operating activities was $495,371 and $403,816 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The
increase of $91,555 in cash used during 2020 compared to 2019 was primarily attributable to an increase in consultant costs.
Net
Cash Used in Investing Activities
Cash
used in investing activities was $0 and $0 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Net
Cash Provided by Financing Activities
During
the nine months ended March 31, 2020, net cash provided by financing activities was 485,210, compared to $460,318 for the nine
months ended March 31, 2019. The increase of $24,892 was due to higher sales of the Company’s securities in private placements.
We continue to seek funding through private placement sales of equity to fund our continued operations, sales and marketing and
ongoing research and development programs.
Equity
Financing Agreement
On
March 5, 2020, the Company entered into an equity financing agreement with GHS Investments, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company
(“Investor”). Pursuant to the agreement, the Company agrees the sell to the investor an indeterminate amount of shares
of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, up to an aggregate price of four million dollars ($4,000,000).
Pursuant
to the agreement, the Company is required, to within sixty (60) calendar days upon the date of execution of this Agreement, use
its best efforts to file with the SEC a Registration Statement or Registration Statements (as is necessary) on Form S-1, covering
the resale of all of the Registrable Securities, which Registration Statement(s) shall state that, in accordance with Rule 416
promulgated under the 1933 Act, such Registration Statement also covers such indeterminate number of additional shares of Common
Stock as may become issuable upon stock splits, stock dividends or similar transactions.
Per
terms of the convertible note agreement, the Company agrees to pay the investor the sum of $35,000, together with interest, on
December 5, 2020. As of the date of this filing, the Company has not yet received this money.
Year
Ended June 30, 2019 Compared to the Year Ended June 30, 2018
Our
results of operations have varied significantly from year to year and quarter to quarter and may vary significantly in the future.
We did not have revenue during the years ending June 30, 2019 and 2018. We do not anticipate generating any revenues during the
year ending June 30, 2020. Net loss for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 were $936,551 and $1,641,788, respectively, resulting
from the operational activities described below.
Operating
Expenses
Operating
expense totaled $875,718 and $1,002,704 during the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The decrease in
operating expenses is the result of the following factors.
|
|
|
Year Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
Change in 2019
Versus 2018
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
$
|
|
|
%
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
$
|
107,962
|
|
|
$
|
129,375
|
|
|
$
|
(21,413
|
)
|
|
|
(16.6
|
)%
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
577,756
|
|
|
|
683,329
|
|
|
|
(105,573
|
)
|
|
|
(15.4
|
)%
|
|
Officer salary
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(0
|
)%
|
|
Total operating expense
|
|
$
|
875,718
|
|
|
$
|
1,002,704
|
|
|
$
|
(126,986
|
)
|
|
|
(12.7
|
)%
|
Research
and Development
Research
and development expenses totaled $107,962 and $129,375 for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The decrease
of $21,143, or 16.6%, in 2019 compared to 2018 was primarily attributable to a decrease in engineering costs.
Our
research and development expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to engineering.
General
and Administrative
General
and administrative expenses totaled $577,756 and $683,329 for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The decrease
of $105,573 or 15.4%, in 2019 compared to 2018 was primarily the result of a decrease in consulting expenses.
Our
general and administrative expenses consist primarily of expenditures related to employee compensation, legal, accounting and
tax, other professional services, and general operating expenses.
Officer
salary totaled $190,000 for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources as of June 30, 2019
We
have incurred losses since our inception in 2002 as a result of significant expenditures for operations and research and development
and the lack of any revenue. We have an accumulated deficit of approximately $26.9 million as of June 30, 2019 and anticipate
that we will continue to incur additional losses for the foreseeable future. Through June 30, 2019, we have funded our operations
through the private sale of our equity securities and exercise of options and warrants, resulting in gross proceeds of approximately
$26 million. Cash and cash equivalents at June 30, 2019 were $10,161.
We
are actively seeking sources of financing to fund our continued operations and research and development programs. To raise additional
capital, we may sell shares of equity or debt securities. There can be no assurance that we will be able to complete any financing
transaction in a timely manner or on acceptable terms or otherwise. If we are not able to raise additional cash, we may be forced
to further delay, curtail, or cease development of our product candidates, or cease operations altogether.
|
|
|
Year Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash at beginning of period
|
|
$
|
4,427
|
|
|
$
|
51,695
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
|
(588,930
|
)
|
|
|
(637,997
|
)
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
|
|
594,664
|
|
|
|
590,729
|
|
|
Cash at end of period
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
$
|
4,427
|
|
Net
Cash Used in Operating Activities
Net
cash used in operating activities was $587,265 and $637,997 for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The decrease
of $50,737 in cash used during 2019 compared to 2018 was primarily attributable to lower consulting and legal expenses.
Net
Cash Used in Investing Activities
Cash
used in investing activities was $0 and $0 for years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Net
Cash Provided by Financing Activities
During
the year ended June 30, 2019, we received net proceeds of $592,999 from the sales of our securities, compared to $590,729 for
the year ended June 30, 2018. The increase was due to slightly increased private placement sales. We are actively seeking sources
of financing to fund our continued operations and research and development programs.
DIRECTORS,
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND KEY EMPLOYEES
Set
forth below are the present directors and executive officers of the Company. Except as set forth below, there are no other persons
who have been nominated or chosen to become directors, nor are there any other persons who have been chosen to become executive
officers. Other than as set forth below, there are no arrangements or understandings between any of the directors, officers and
other persons pursuant to which such person was selected as a director or an officer.
|
Name
|
|
Age
|
|
Position
with the Company
|
|
Chaya
Hendrick
|
|
63
|
|
President,
Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board
|
|
Jay
M. Needelman, CPA
|
|
52
|
|
Chief
Financial Officer, Director
|
|
Elizabeth
Ryba
|
|
68
|
|
Director
|
The
Board is comprised of only one class. All of the directors serve for a term of one year and until their successors are elected
at the Company’s annual shareholders meeting via teleconference and are qualified, subject to removal by the Company’s
shareholders.
Our
Board believes that all members of the Board and all executive officers encompass a range of talent, skill, and experience sufficient
to provide sound and prudent guidance with respect to our operations and interests. The information below with respect to our
directors and executive officers includes each individual’s experience, qualifications, attributes, and skills that led
our Board to the conclusion that he or she should serve as a director and/or executive officer.
Biographies
Set
forth below are brief accounts of the business experience during the past five years of each director, executive officer and significant
employee of the Company.
CHAYA
HENDRICK has been President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of SmartMetric since the Company’s
inception in 2002. C. Hendrick has served as President and CEO of Smart Micro Chip, Inc., an Australian corporation from 2000
to 2002. From 1999 to 2001, C. Hendrick was President and Chief Executive Officer of Smarticom Inc. and FastEcom, Inc., Australian
corporations. From 1994 to 1998, C. Hendrick served as executive officer of Applied Computing Science (Australia), an Australian
company involved in e-commerce systems, research and development. Ms. Hendrick founded Asset Developments a property development
company that created and sold regional residential land subdivisions. The last being a 1,000-acre subdivision named Claire Valley
Estates in the Canberra region of Australia. All of the property development projects were funded by C. Hendrick and were financially
profitable. C. Hendrick attended Dandenong College in Australia.
We
believe Ms. Hendrick is qualified to serve on our Board due to her extensive experience in technology development and as an executive
at technology companies.
JAY
M. NEEDELMAN, CPA, has been the Chief Financial Officer and a director of SmartMetric since 2007. Mr. Needelman
has over 20 years of experience in public accounting. A 1991 graduate of Florida State University in Tallahassee, Fl, Mr. Needelman
began his career in public accounting in Miami, Fl, in 1991. After working for two different firms, Mr. Needelman founded his
own firm in late 1992.
We
believe Mr. Needelman is qualified to serve on our Board due to his financial expertise.
ELIZABETH
RYBA has been a director of SmartMetric since April 5, 2006. From 2015 to the present, Ms. Ryba has been Vice President
of Marketing at the Design and Decoration Building in New York, one of the premier destinations for luxury interior design showrooms
in the country. From 2006 to 2015, Ms. Ryba had marketing positions at two luxury home decor brands. Ms. Ryba was a promotion
director at Hearst Publishing from 2002 through 2005. Between 2001 and 2004, Ms. Ryba was a consultant at Stratus Rewards Credit
Cards where she launched a Visa Luxury credit card where points were redeemable on private jets. Between 2000 and 2001, Ms. Ryba
worked as a Marketing Consultant for SpaFinder. From 1991 through 1999, Ms. Ryba worked at Master Card where she launched a Smart
Card in Australia. Ms. Ryba received her M.S. in Marketing from the University of Illinois, and her B.A. in English from the State
University of New York at Stony Brook.
We
believe Ms. Ryba is qualified to serve on our Board due to her extensive experience in the credit card industry as well as her
extensive experience in marketing in the luxury sector which we believe is a sector to which we may be able to sell our products.
Family
Relationships
There
are no family relationships among officers or directors of the Company.
Committees
of the Board
Our
business, property and affairs are managed by or under the direction of the Board. Members of the Board are kept informed of our
business through discussion with the chief executive and financial officers and other officers, by reviewing materials provided
to them and by participating at meetings of the Board. We have not previously had an audit committee, compensation committee or
nominations and governance committee.
Audit
Committee
We
currently do not have an acting audit committee, and our Board currently acts as our audit committee.
Audit
Committee Financial Expert
We
do not have an audit committee and thus do not have an audit committee financial expert.
Compensation
Committee
We
do not presently have a compensation committee. Our Board currently acts as our compensation committee.
Director
Independence
For
purposes of determining independence, we have adopted the definition of “independence” contained in the NASDAQ Market
Place Rules. Pursuant to the definition, the company has determined that Elizabeth Ryba qualifies as independent.
Code
of Ethics
The
Company has adopted a Code of Ethics that applies to its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer. A copy of the Company’s
code of ethics is available to any person without charge upon written request to the Company at SmartMetric, Inc., 3960 Howard
Hughes Parkway, Suite 500, Las Vegas, NV, 89109. Attn: Secretary.
Compliance
with Section 16(a) of the Securities Act of 1934
Section
16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, requires our executive officers and directors and persons who own more
than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities to file with the Securities and Exchange Commission initial statements
of beneficial ownership, reports of changes in ownership and annual reports concerning their ownership of our common stock and
other equity securities, on Form 3, 4 and 5 respectively. Executive officers, directors and greater than 10% shareholders are
required by the Securities and Exchange Commission regulations to furnish our company with copies of all Section 16(a) reports
they file.
Based
solely on our review of the copies of such reports received by us, and on written representations by our officers and directors
regarding their compliance with the applicable reporting requirements under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, we believe that,
with respect to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2019, there were no failures to file such forms in a timely fashion.
Involvement
in Certain Legal Proceedings
To
the best of our knowledge, none of our directors or executive officers has, during the past ten years:
|
|
●
|
been
convicted in a criminal proceeding or been subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other
minor offenses);
|
|
|
●
|
had
any bankruptcy petition filed by or against the business or property of the person, or of any partnership, corporation or
business association of which he was a general partner or executive officer, either at the time of the bankruptcy filing or
within two years prior to that time;
|
|
|
●
|
been
subject to any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction
or federal or state authority, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring, suspending or otherwise limiting, his involvement
in any type of business, securities, futures, commodities, investment, banking, savings and loan, or insurance activities,
or to be associated with persons engaged in any such activity;
|
|
|
●
|
been
found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the SEC or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to
have violated a federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated;
|
|
|
●
|
been
the subject of, or a party to, any federal or state judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree, or finding, not subsequently
reversed, suspended or vacated (not including any settlement of a civil proceeding among private litigants), relating to an
alleged violation of any federal or state securities or commodities law or regulation, any law or regulation respecting financial
institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement
or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order, or
any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or
|
|
|
●
|
been
the subject of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory
organization (as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Exchange Act), any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of
the Commodity Exchange Act), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority
over its members or persons associated with a member.
|
Except
as set forth in our discussion below in “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence”
none of our directors or executive officers has been involved in any transactions with us or any of our directors, executive officers,
affiliates or associates which are required to be disclosed pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC.
EXECUTIVE
COMPENSATION
General
Philosophy
Our
Board is responsible for establishing and administering the Company’s executive and director compensation.
The
following summary compensation table indicates the cash and non-cash compensation earned from the Company during the fiscal years
ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, by the current and former executive officers of the Company and each of the other two highest paid
executives or directors, if any, whose total compensation exceeded $100,000 during those periods.
Summary
Compensation Table
|
Name and Principal Position
|
|
Fiscal
Year Ended
|
|
|
Salary
($)
|
|
|
Bonus
($)
|
|
|
Stock
Awards
($)
|
|
|
Option
Awards
($)
|
|
|
Non-equity
Incentive Plan
Compensation
($)
|
|
|
Nonqualified
Deferred
Compensation
Earnings
($)
|
|
|
All Other Compensation
($)
|
|
|
Total
($)
|
|
Chaya Hendrick
(President, Chief Executive Officer, Chairman of the Board (1)
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
$
|
110,833
|
(2)
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
$
|
15,833
|
|
|
$
|
110,833
|
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
63,333
|
(3)
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
$
|
126,667
|
(4)
|
|
$
|
190,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jay Needelman
(Chief and Principal Financial Officer, Director) (7)
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
$
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
$
|
11,250
|
|
|
$
|
11,250
|
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
(1)
|
Chaya
Hendrick has been President, Chief Executive Officer and director of the Company since inception. This Summary Compensation
Table does not include the issuance of 200,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock issued to Ms. Hendrick pursuant
to an addendum to the employment agreement entered into on 9/30/2015. Each share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock is
convertible into 50 shares of Common Stock. Chaya Hendrick also has a car allowance in her employment agreement which she
has forgone for the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018.
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
|
The
Company paid Chaya Hendrick $110,833 during the fiscal year 2020, out of her total aggregate salary of $142,500, with the
remainder being accrued but unpaid. As of March 31, 2020, the Company has accrued $821,682 of unpaid salary, which includes
previously accrued but unpaid salary for periods not covered under this Summary Compensation Table.
|
|
(3)
|
The
Company paid Chaya Hendrick $63,333 for the year ended June 30, 2019 out of her total aggregate salary of $190,000, with the
remainder being accrued but unpaid. As of June 30, 2019, the Company has accrued $790,015 of unpaid salary, which includes
previously accrued but unpaid salary for periods not covered under this Summary Compensation Table.
|
|
(4)
|
Includes
$126,667 in accrued but unpaid salary for the year end June 30, 2019. As of June 30, 2019, the Company has accrued $790,015
of unpaid salary, which includes previously accrued but unpaid salary for periods not covered under this Summary Compensation
Table.
|
Outstanding
Equity Awards at Fiscal Year End
None.
Chaya
Hendrick Employment
Previous
Employment Agreement
On
July 1, 2012, the Company entered into an employment agreement (the “Prior Agreement”) with Chaya Hendrick, the Company’s
Chief Executive Officer that expired on July 1, 2017. Pursuant to the Prior Agreement, Ms. Hendrick received an annual base salary
of $190,000 per year. Ms. Hendrick was also entitled to receive a management fee equal to $50,000 per year beginning with the
Company’s fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 and each fiscal year thereafter during the term of the Agreement provided that
the Company has manufactured its first product. This fee was to increase by 25% per annum at the conclusion of each calendar year
and was based on the continued manufacturing and sales of products by the Company. As of the end of the term of the Prior Agreement,
no compensation was paid pursuant to this management fee.
Ms.
Hendrick was also entitled to participate in any and all benefit plans, from time to time, in effect for senior management, along
with vacation, sick and holiday pay in accordance with the Company’s policies established and in effect from time to time.
The Company also provided Ms. Hendrick with the use of an automobile of Ms. Hendrick’s choice at a purchase price not to
exceed $60,000. Executive’s employment with the Company was subject to termination at any time, with cause, as such terms
are defined in the Prior Agreement.
The
Prior Agreement may be terminated on 30 days’ notice by Ms. Hendrick but may only be terminated by the Company for “cause.”
In the event that Ms. Hendrick’s employment was terminated by the Company, the Company was obligated to pay to Ms. Hendrick
an amount equal to $350,000 plus salary remaining on the term of the Prior Agreement.
Addendum
to Prior Agreement
On
September 30, 2015, the Company and Ms. Hendrick entered into an Addendum to the Agreement (the “Addendum”) pursuant
to which in consideration for the issuance of 200,000 shares of the Company’s Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, Ms.
Hendrick granted the Company the first right to purchase or license any patents (the “Patent Option”) relating to
“Smartcards” which Ms. Hendrick (i) shall apply for with the relevant patent authorities during the term of the Agreement,
and (ii) are currently applied for with the relevant patent authorities or pending as of the date of the Prior Agreement (the
“Patent Rights”). In exchange for the Patent Option the Company agrees, during the term of the Prior Agreement, to
pay for any fees and/or expenses related to the application for the Ms. Hendrick’s Patent Rights with the relevant patent
authorities, including, but not limited to, legal or filing fees. If, upon the Company’s receipt of notice of any Patent
Rights of Ms. Hendrick’s in writing (“Patent Notification”) the parties fail to successfully negotiate and execute
a purchase or license agreement as it relates to the Patent Right that is the subject of such Patent Notification within 60 calendar
days of the receipt of such Patent Notification, the Ms. Hendrick shall be permitted to retain or transfer the Patent Rights to
a third party without any subsequent notice to the Company.
Amended
and Restated Employment Agreement
On
July 1, 2017, the Company and Ms. Hendrick entered into an amended and restated employment agreement (“Agreement”)
with a duration of sixty (60) months. Pursuant to the Agreement, Ms. Hendrick shall receive (i) an annual base salary of $190,000,
subject to adjustment at the end of each fiscal year at the discretion of the Board, with a minimum increase of 10% per annum
for the duration of the term, (ii) an incentive management fee equal to $50,000 upon the Company manufacturing its first product,
which shall increase by 25% per annum and based on the continued manufacturing and sales of products by our Company.
Additionally,
Ms. Hendrick shall maintain certain rights to initiate, write, invent and / or create inventions separate from SmartMetric, Inc.
and to retain the intellectual property rights of such patents, inventions or new products.
The
Agreement may be terminated on 30 days’ notice by Ms. Hendrick but may only be terminated by the Company for “cause.”
In the event that Ms. Hendrick’s employment is terminated by the Company for such “cause,” the Company is obligated
to pay to Ms. Hendrick an amount equal to $350,000 plus the remaining salary on the term of the Agreement.
Jay
Needelman Contract
We
currently have an oral agreement with Jay Needelman, our part-time Chief Financial Officer, whereby we pay Mr. Needelman an annual
fee of $15,000 for his services, payable in quarterly installments of $3,750.
Potential
Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control
SEC
regulations state that we must disclose information regarding agreements, plans or arrangements that provide for payments or benefits
to our executive officers in connection with any termination of employment or change in control of the Company. Such payments
are set forth above in the section entitled “Employment Agreements.”
None
of our executive officers or directors received, nor do we have any arrangements to pay out, any bonus, stock awards, option awards,
non-equity incentive plan compensation, or non-qualified deferred compensation.
Compensation of Directors
We have no standard arrangement to compensate
directors for their services in their capacity as directors. Directors are not paid for meetings attended. However, we intend to
review and consider future proposals regarding board compensation. All travel and lodging expenses associated with corporate matters
are reimbursed by us, if and when incurred.
Stock Option Plans - Outstanding Equity
Awards at Fiscal Year End
None.
Pension Table
None.
Retirement Plans
We do not offer any annuity, pension, or
retirement benefits to be paid to any of our officers, directors, or employees in the event of retirement. There are also no compensatory
plans or arrangements with respect to any individual named above which results or will result from the resignation, retirement,
or any other termination of employment with our company, or from a change in the control of our Company.
Compensation Committee
The Company does not have a separate Compensation
Committee. Instead, the Board reviews and approves executive compensation policies and practices, reviews salaries and bonuses
for other officers, administers the Company’s stock option plans and other benefit plans, if any, and considers other matters.
Risk Management Considerations
We believe that our compensation policies
and practices for our employees, including our executive officers, do not create risks that are reasonably likely to have a material
adverse effect on our Company.
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL
OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
As of July 30, 2020, we had outstanding
379,523,000 shares of common stock. Each share of common stock is currently entitled to one vote on all matters put to a vote of
our stockholders. The following table sets forth the number of common shares, and percentage of outstanding common shares, beneficially
owned as of the date hereof by:
|
|
●
|
each person known by us to be the beneficial owner of
more than five percent of our outstanding common stock;
|
|
|
●
|
each of our current directors;
|
|
|
●
|
each our current executive officers and any other persons
identified as a “named executive” in the Summary Compensation Table above; and
|
|
|
●
|
all our current executive officers and directors as a group.
|
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance
with the rules of the SEC and includes general voting power and/or investment power with respect to securities. Shares of common
stock issuable upon exercise of options or warrants that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of the record
date, and shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of other securities currently convertible or convertible within 60 days,
are deemed outstanding for computing the beneficial ownership percentage of the person holding such securities but are not deemed
outstanding for computing the beneficial ownership percentage of any other person. Under the applicable SEC rules, each person’s
beneficial ownership is calculated by dividing the total number of shares with respect to which they possess beneficial ownership
by the total number of outstanding shares. In any case where an individual has beneficial ownership over securities that are not
outstanding but are issuable upon the exercise of options or warrants or similar rights within the next 60 days, that same number
of shares is added to the denominator in the calculation described above. Because the calculation of each person’s beneficial
ownership set forth in the “Percentage Beneficially Owned” column of the table may include shares that are not presently
outstanding, the sum total of the percentages set forth in such column may exceed 100%. Unless otherwise indicated, the address
of each of the following persons is 3960 Howard Hughes Parkway, Suite 500, Las Vegas, NV 89169, and, based upon information available
or furnished to us, each such person has sole voting and investment power with respect to the shares set forth opposite his, her
or its name.
|
|
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner
|
|
Director/Officer
|
|
Number of
Shares
of Common
Stock (1)
|
|
|
Percentage
of Class (1)
|
|
|
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Chaya Hendrick (2)
145 East Harmon Avenue, Unit 19620
Las Vegas, NV 89109
|
|
Chief Executive Officer,
Chairman of the Board of Directors
|
|
|
89,127,778
|
(2)
|
|
|
23.5
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Jay Needelman, CPA
520 West 47th Street
Miami Beach, FL 33140
|
|
Director; Chief Financial Officer
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Elizabeth Ryba
73 Brown Road
Scarsdale, New York 10583
|
|
Director
|
|
|
40,000
|
|
|
|
*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Executive Officers and Directors as a Group (3 persons)
|
|
|
|
|
89,167,778
|
|
|
|
23.5
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5% Shareholders
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*
|
Less than one percent (1%)
|
|
|
(1)
|
In determining beneficial ownership of our common stock as of a
given date, the number of shares shown includes shares of common stock which may be acquired on exercise of warrants or options
or conversion of convertible securities within 60 days of that date. In determining the percent of common stock owned by a person
or entity on July 30, 2020, (a) the numerator is the number of shares of the class beneficially owned by such person or entity,
including shares which may be acquired within 60 days on exercise of warrants or options and conversion of convertible securities,
and (b) the denominator is the sum of (i) 379,523,000, the total shares of common stock outstanding on July 30, 2020, and
(ii) the total number of shares that the beneficial owner may acquire upon conversion of any preferred stock and on exercise of
the warrants and options. Unless otherwise stated, each beneficial owner has sole power to vote and dispose of its shares.
|
|
|
(2)
|
The 89,127,778 shares of
common stock include (i) 58,627,778 of Common Stock and; (ii) 610,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock convertible
into 30,500,000 shares of common stock held by Applied Cryptography, Inc. (“ACI”) and / or Chaya Hendrick. The outstanding
shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock are entitled to vote on any matter with the holders of Common Stock voting
together as one (1) class and shall have that number of votes (identical in every other respect to the voting rights of the holder
of common stock entitled to vote at any regular or special meeting of Stockholders) equal to that number of common shares which
is not less than 51% of the vote required to approve any action, which Nevada law provides may or must be approved by vote or
consent of the common shares or the holders of other securities entitled to vote, if any. Each share of Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock is convertible, at the option of the holder, into fifty (50) shares of Common Stock upon the satisfaction of certain
conditions and for purposes of determining a quorum of a shareholder meeting, the outstanding shares of Series B Convertible Preferred
Stock shall be deemed the equivalent of 51% of all shares of the Company’s Common Stock entitled to vote at such meetings. Our
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, has sole voting and dispositive power over all of the shares beneficially owned by ACI.
|
TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PERSONS
Except as set out below, as of July 30,
2020, there have been no transactions, or currently proposed transactions, in which we were or are to be a participant and the
amount involved exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or one percent of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed
fiscal years, and in which any of the following persons had or will have a direct or indirect material interest:
|
|
●
|
any director or executive officer of our company;
|
|
|
●
|
any person who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly,
shares carrying more than 5% of the voting rights attached to our outstanding shares of common stock;
|
|
|
●
|
any promoters and control persons; and
|
|
|
●
|
any member of the immediate family (including spouse, parents, children, siblings and in laws)
of any of the foregoing persons.
|
|
|
●
|
Chaya Hendrick, our CEO
has made cash advances to the Company periodically in exchange for promissory notes of such face values. As of the years ended
June 30, 2019 and 2018, we owed $3,759 and $15,000, respectively. These notes bear interest at 7.00% per annum. We have paid down
$11,241 of these cash advances during the year ended June 30, 2019.
|
|
|
●
|
During the years ended
June 30, 2019 and 2018, Chaya Hendrick, our CEO deferred $126,667 and $142,500 in annual salary, respectively. As of June 30,
2019 and 2018, respectively, the Company has accrued the amounts of $790,015 and $663,348 as deferred salary for the difference
between Chaya Hendrick’s contractual annual salary and the amounts actually paid. These amounts include previously deferred
salary prior to the years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018.
|
Director Independence
Our Board consists of Chaya Hendrick Jay
Needelman and Elizabeth Ryba. Our securities are quoted on the OTCQB, which does not have any director independence requirements.
We evaluate independence by the standards for director independence established by applicable laws, rules, and listing standards
including, without limitation, the standards for independent directors established by The New York Stock Exchange, Inc., the NASDAQ
National Market, and the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Subject to some exceptions, these standards
generally provide that a director will not be independent if (a) the director is, or in the past three years has been, an employee
of ours; (b) a member of the director’s immediate family is, or in the past three years has been, an executive officer of
ours; (c) the director or a member of the director’s immediate family has received more than $120,000 per year in direct
compensation from us other than for service as a director (or for a family member, as a non-executive employee); (d) the director
or a member of the director’s immediate family is, or in the past three years has been, employed in a professional capacity
by our independent public accountants, or has worked for such firm in any capacity on our audit; (e) the director or a member of
the director’s immediate family is, or in the past three years has been, employed as an executive officer of a company where
one of our executive officers serves on the compensation committee; or (f) the director or a member of the director’s immediate
family is an executive officer of a company that makes payments to, or receives payments from, us in an amount which, in any twelve-month
period during the past three years, exceeds the greater of $1,000,000 or two percent of that other company’s consolidated
gross revenues. Based on these standards, we have determined that Elizabeth Ryba is our only independent director.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Audited Consolidated Financial Statements
Unaudited Consolidated Financial Statements
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC
ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
of
Smartmetric, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance
sheet of Smartmetric, Inc. (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2019 and the related statements of operations, stockholders’
(deficit), and cash flows for the year ended June 30, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial
statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of
the Company as of June 30, 2019, and the result of its operations and its cash flow for the year ended June 30, 2019, in conformity
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Emphasis of Matter
The accompanying financial statements have
been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the
Company has incurred recurring losses which raises substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s
plans concerning these matters are also described in Note 1. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might
result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility
of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based
on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”)
and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable
rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with
the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether
the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The company is not required to have,
nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required
to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the
effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures
to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures
that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures
in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made
by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a
reasonable basis for our opinion.
|
/s/ Prager Metis CPAs, LLC
|
|
|
|
|
|
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019
|
|
|
Basking Ridge, New Jersey
|
|
|
September 30, 2019
|
|
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC
ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
of
Smartmetric, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance
sheets of Smartmetric, Inc. (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2018 and June 30, 2017 and the related statements of operations,
stockholders’ (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended June 30, 2018, and the related
notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly,
in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of June 30, 2018 and June 30, 2017, and the results of its operations
and its cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended June 30, 2018 in conformity with accounting principles generally
accepted in the United States of America.
Emphasis of Matter
The accompanying financial statements have
been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the
Company has no revenues, has negative working capital at June 30, 2018, has incurred recurring losses and recurring negative cash
flow from operating activities, and has an accumulated deficit which raises substantial doubt about its ability to continue as
a going concern. Management’s plans concerning these matters are also described in Note 1. The financial statements do not
include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility
of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based
on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”)
and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable
rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with
the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether
the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The company is not required to have,
nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required
to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the
effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures
to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures
that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures
in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made
by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a
reasonable basis for our opinion.
|
/s/ AMC Auditing
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMC Auditing
|
|
|
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017
|
|
|
Las Vegas, Nevada
|
|
|
October 5, 2018
|
|
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
$
|
4,427
|
|
|
Receivables
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
10,400
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
6,450
|
|
|
|
8,767
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
16,611
|
|
|
|
23,594
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
|
$
|
23,594
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
$
|
880,390
|
|
|
$
|
730,794
|
|
|
Liability for stock to be issued
|
|
|
147,484
|
|
|
|
103,718
|
|
|
Deferred Officer’s salary
|
|
|
790,015
|
|
|
|
663,348
|
|
|
Related party interest payable
|
|
|
93,488
|
|
|
|
40,055
|
|
|
Dividends payable
|
|
|
3,123
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Credit card payable
|
|
|
3,750
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Shareholder loan
|
|
|
3,759
|
|
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,922,009
|
|
|
|
1,552,915
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 4 and 8)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of discount, authorized 1,000,000 shares 121,700 and 0 shares issued and outstanding, respectively
|
|
|
99,278
|
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ deficit:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock, $.001 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized, 610,000 and 610,000 shares issued and outstanding
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
Common stock, $.001 par value; 300,000,000 shares authorized, 264,648,821 and 249,147,547 shares issued and outstanding , respectively
|
|
|
264,649
|
|
|
|
249,148
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
24,663,528
|
|
|
|
24,217,831
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(26,933,463
|
)
|
|
|
(25,996,910
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(2,004,676
|
)
|
|
|
(1,529,321
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
|
$
|
23,594
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements Of Operations
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer’s salary
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
|
190,000
|
|
|
Other general and administrative
|
|
|
577,756
|
|
|
|
683,329
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
107,962
|
|
|
|
129,375
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
875,718
|
|
|
|
1,002,704
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations before other expense
|
|
|
(875,718
|
)
|
|
|
(1,002,704
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other expense:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(53,432
|
)
|
|
|
(39,084
|
)
|
|
Loss on patent impairment
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(600,000
|
)
|
|
Total other expense
|
|
|
(53,432
|
)
|
|
|
(639,084
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
Preferred stock dividends
|
|
|
(7,401
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Net loss available for common stockholders
|
|
$
|
(936,551
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.01
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
|
240,133,406
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements Of Cash Flows
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(936,551
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Asset impairment
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
600,000
|
|
|
Common stock issued and issuable for services
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
66,824
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in assets and liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
2,317
|
|
|
|
50,560
|
|
|
(Decrease) increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
149,596
|
|
|
|
104,822
|
|
|
Increase in deferred officer salary
|
|
|
126,667
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
Increase (decrease) in credit card debt
|
|
|
3,750
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Increase (decrease) in allowance for bad debt
|
|
|
10,400
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Increase (decrease) in dividends payable
|
|
|
1,458
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Increase in accrued interest payable
|
|
|
53,433
|
|
|
|
39,084
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
|
(588,930
|
)
|
|
|
(637,998
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loans from related parties
|
|
|
(11,241
|
)
|
|
|
10,200
|
|
|
Proceeds from sale of common stock
|
|
|
507,782
|
|
|
|
580,530
|
|
|
Proceeds from sale of Series C Preferred stock
|
|
|
95,000
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Dividends payable
|
|
|
3,123
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
|
|
594,664
|
|
|
|
590,730
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH
|
|
|
5,734
|
|
|
|
(47,268
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT BEGINNING OF YEAR
|
|
|
4,427
|
|
|
|
51,695
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT END OF YEAR
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
$
|
4,427
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH PAID DURING THE YEAR FOR:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income taxes
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
Interest
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
SMARTMETRIC, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Stock
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
Paid-In
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
Balance June 30, 2017
|
|
|
410,000
|
|
|
$
|
410
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
226,172,799
|
|
|
$
|
226,173
|
|
|
$
|
22,778,252
|
|
|
$
|
(24,346,047
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,341,212
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series B Preferred
|
|
|
200,000
|
|
|
|
200
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
599,800
|
|
|
|
200
|
|
|
|
600,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for services rendered
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
1,083,948
|
|
|
|
1,083
|
|
|
|
65,742
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
66,825
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
21,891,800
|
|
|
|
21,892
|
|
|
|
774,037
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
795,929
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To adjust for prior period expense
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(9,075
|
)
|
|
|
(9,075
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for period
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
(1,641,788
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance June 30, 2018
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
249,147,547
|
|
|
|
249,148
|
|
|
|
24,217,831
|
|
|
|
(25,996,910
|
)
|
|
|
(1,529,321
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
15,501,274
|
|
|
|
15,501
|
|
|
|
445,697
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
461,198
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7,401
|
)
|
|
|
(7,401
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the period
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
(929,150
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance June 30, 2019
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
264,648,821
|
|
|
$
|
264,649
|
|
|
$
|
24,663,528
|
|
|
$
|
(26,933,461
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,004,674
|
)
|
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 1 -
|
ORGANIZATION AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
|
SmartMetric, Inc. (the “Company”
or “SmartMetric”) was incorporated in the State of Nevada on December 18, 2002. SmartMetric’s main product is
a fingerprint sensor-activated card with a finger sensor onboard the card and a built-in rechargeable battery for portable biometric
identification. This card may be referred to as a biometric card or the SmartMetric Biometric Datacard. SmartMetric
has completed development of its card along with pre-mass manufacturing cards but has not yet begun to mass manufacture the biometric
fingerprint activated cards.
Basis of Presentation
The financial statements present
the balance sheets, statements of operations, stockholder’s equity (deficit) and cash flows of the Company. The financial
statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of
America.
The Company has adopted June
30 as its fiscal year end.
Going Concern
As shown in the accompanying
consolidated financial statements the Company has incurred recurring losses of $936,551 and $1,641,788 for the years ended June
30, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and has incurred a cumulative loss of $26,933,463 since inception (December 18, 2002).
The Company is currently in the development stage and has spent a substantial portion of its time in the development of its technology.
There are no assurances that
the Company will be able to achieve the level of revenues adequate to generate a sufficient cash flow from operations to support
the Company’s working capital requirements. To the extent that funds generated are insufficient, the Company will have to
raise additional working capital. No assurance can be given that additional financing will be available, or if available, will
be on terms acceptable to the Company. If adequate working capital is not available, the Company may not continue its operations.
These conditions raise substantial
doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The financial statements do not include any adjustments
relating to the recoverability and classification of asset carrying amounts or the amount and classification of liabilities that
might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
Management believes that the
Company’s capital requirements will depend on many factors. These factors include product marketing and distribution. The
management plans include equity sales and borrowing in order to fund the operations.
|
NOTE 2 -
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
|
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, the FASB
or other standards setting bodies issue new accounting pronouncements. Updates to the FASB ASCs are communicated through issuance
of an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”). Unless otherwise discussed, we believe that the impact of recently issued
guidance, whether adopted or to be adopted in the future, is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial
statements upon adoption.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements
include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary, SmartMetric Australia Pty. Ltd. All significant
intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 2 -
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
|
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts reflected
in the balance sheets for cash, accounts payable and related party payables approximate the respective fair values due to the short
maturities of these items. The Company does not hold any investments that are available-for-sale.
As required by the Fair Value
Measurements and Disclosures Topic of the FASB ASC, fair value is measured based on a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes
the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows: (Level 1) observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets; (Level
2) inputs, other than the quoted prices in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly; and (Level 3) unobservable
inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions.
The three levels of the fair
value hierarchy are described below:
Level 1: Unadjusted quoted prices
in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities;
Level 2: Quoted prices in markets
that are not active, or inputs that are observable, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the asset
or liability;
Level 3: Prices or valuation
techniques that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable (supported by little or
no market activity).
The Company at present does
not have any Level 2 or Level 3 fair value instruments.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make
estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities
at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. On
an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates, including, but not limited to, those related to income taxes and contingencies. The
Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under
the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities
that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash
The Company considers all highly
liquid debt instruments and other short-term investments with an initial maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Any amounts of cash in financial institutions which exceed FDIC insured limits exposes the Company to cash concentration risk.
The Company had no cash equivalents at June 30, 2019 and 2018.
Research and Development
The Company annually incurs
costs on activities that relate to research and development of new technology and products. Research and development
costs are expensed as incurred.
Revenue Recognition
The Company has not recognized
revenues to date. Therefore, the Company has not yet adopted a revenue recognition policy.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 2 -
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
|
Accounts Receivable
The Company will extend credit
based on its evaluation of the customers’ financial condition, generally without requiring collateral. Exposure
to losses on receivables is expected to vary by customer due to the financial condition of each customer. The Company
will monitor exposure to credit losses and maintains allowances for anticipated losses considered necessary under the circumstances. The
Company has not recorded any receivables, and therefore no allowance for doubtful accounts.
Uncertainty in Income
Taxes
GAAP requires the recognition
and measurement of uncertain income tax positions using a “more-likely-than-not” approach. Management
evaluates Company tax positions on an annual basis and has determined that as of June 30, 2019 and 2018, no accrual for uncertain
income tax positions is necessary.
Loss Per Share of Common
Stock
In accordance with FASB ASC
260, “Earnings Per Share,” the basic loss per share is computed by dividing the loss attributable to common stockholders
by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Basic net loss per share excludes the dilutive effect
of stock options or warrants and convertible notes. Diluted net earnings (loss) per common share is determined using the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding during the period, adjusted for the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents, consisting
of shares that might be issued upon exercise of common stock options and warrants. In periods where losses are reported, the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding excludes common stock equivalents, because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive. As of June
30, 2019, and 2018, respectively, 26,526,234 and 14,842,583 dilutive shares were excluded from the calculation of diluted loss
per common share.
Patent Impairment
When the carrying balance of
the Company’s patent is more than what it could be sold for on the open market and/or is not recoverable through future use,
the Company decreases its value. In determining whether the carrying value is not recoverable, the Company estimates the sum of
the expected cash flows from the use of the patent or its possible sale. If the results in an amount less that the patent’s
value on the financial statements, the Company will deem the patent’s carrying value on the balance sheet to be impaired
by the amount that the carrying value exceeds the fair market value of the asset. The decrease in the patent’s value will
then be included as a loss in the Company’s profit and loss statement. The Company recorded no loss from patent impairment
during the year ended June 30, 2019. During the year ended June 30, 2018, the Company recorded a loss of $600,000 related to the
patent impairment.
|
NOTE 3 -
|
PREPAID EXPENSES
|
Prepaid expenses represent the
unexpired terms of any consulting agreements, as well as advance rental payments. All consulting agreements are entered
into for the issuance of common stock and warrants and are valued based on the stock price or computed warrant value at the time
of the respective agreement.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Lease Agreement
The Company utilizes office
in Las Vegas, NV on a short-term lease basis. The Company’s main office is located in Las Vegas, NV. Rent expense for the
years ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 was $12,522 and $30,947, respectively.
The Company adopted ASC 842
on January 1, 2019 and evaluated to conclude that it has no impact on the financial statements, as under the practical expedient,
the lease consists of terms less than one year, and therefore is not required to be capitalized.
Related Party
Transactions
The Company’s Chief Executive
Officer has made cash advances to the Company with an aggregate amount due of $3,759 and $15,000 as of June 30, 2019 and 2018,
respectively. These advances bear interest at 7.00% per annum.
As of June 30, 2019 and June
30, 2018, the Company has accrued the amounts of $790,015 and $663,348, respectively, as deferred Officer’s salary for the
difference between the president’s annual salary and the amounts paid.
|
NOTE 5 -
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
Preferred Stock
As of June 30, 2019, the Company
has 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001, authorized and 610,000 shares issued and outstanding.
On December 11, 2009, the Company
filed a Certificate of Designation with the State of Nevada, to designate 500,000 shares of the preferred stock to be designated
as Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series B Convertible Preferred Stock”).
Each share of Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock has a par value of $0.001, and a stated value equal to $5.00 (“Stated Value”). Holders of the Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock are entitled to receive dividends or other distributions with the holders of the common stock of
the Company on an as converted basis when, as, and if declared by the directors of the Company. Holders of the Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock are entitled to convert all or any one (1) share of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock into fifty (50) shares
of common stock.
Upon any liquidation, dissolution
or winding-up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary (“liquidation”), holders of the Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock are entitled to receive out of the assets, whether capital or surplus, of the Company an amount equal to the Stated
Value, pro rata with the holders of the common stock.
On September 11, 2017, the Company
issued 200,000 shares of Series B preferred shares to its CEO, Chaya Hendrick, in consideration for grant of exclusive rights to
the licensed patent.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 5 -
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (CONTINUED)
|
Class A Common Stock
As of June 30, 2019, the Company
has 50,000,000 shares of Class A common stock, par value $0.001, authorized and no shares issued and outstanding.
Common Stock and Warrants
During the three months ended
to September 30, 2017, the Company sold for cash 2,500,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase (i) 1,437,500 shares
at $0.70 and $0.20 per share and (ii) 724,500 shares at $1.00 and $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $114,625.
During the three months ended
September 30, 2017, the Company issued 362,864 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $21,825, based on the stock
price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided.
During the three months ended
December 31, 2017, the Company sold for cash 8,319,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,250,000 shares at
$0.20 per share and (ii) 1,638,000 shares at $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $259,362.
The warrants expire at various times through December
29, 2019.
During the three months ended
December 31, 2017, the Company issued 212,164 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $15,000 based on the stock
price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided.
During the three months ended
March 31, 2018, the Company sold for cash 2,850,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 2,051,250 shares at $0.70
per share and (ii) 929,250 shares at $1.00 per share, for net proceeds of $142,305. The warrants expire at various times through
February 21, 2020. None of the 2,850,000 shares were issued as of March 31, 2018.
During the three months ended
March 31, 2018, the Company issued 508,620 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $30,000, based on the stock
price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided. These shares were issued on February 26, 2018.
During the three months ended
June 30, 2018, the Company sold for cash 2,646,100 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 1,536,625 shares at $0.70
per share and (ii) 774,459 shares at $1.00 per share, for net proceeds of $119,738. The warrants expire at various times through
June 15, 2020.
During the three months ended
June 30, 2018, the Company issued zero shares of common stock for consulting services.
During the three months ended
September 30, 2018, the Company sold for cash 4,624,153 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $145,770 and warrants to purchase
(i) 3,699,988 shares at $0.25, (ii) 60,000 shares at $0.30, (iii) 30,000 shares at $0.50, (iv) 301,875 shares at $0.70 and (v)
152,210 shares at $1.00.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 5 -
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (CONTINUED)
|
During the three months ended
December 31, 2018, the Company sold for cash 5,212,499 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,712,499 shares at
$0.25 per share and (ii) 1,500,000 shares at $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $106,060. The warrants expire at various times
through December 4, 2020.
During the three months ended
March 31, 2019, the Company sold for cash 7,541,663 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 7,541,663 shares at prices
ranging from $0.05 per share to $0.50 per share for net proceeds of $165,749. The warrants expire at various times through March
21, 2021.
During the three months ended
June 30, 2019, the Company sold for cash 1,740,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 1,740,000 shares at a price
of $0.05 per share for net proceeds of $86,934. The warrants expire at various times through June 10, 2021.
During the year ended June 30,
2018, the Company issued a total of 21,891,800 shares of common stock for cash totaling $759,929. In addition, the Company sold
common shares, which have not yet been issued as June 30, 2018 and are considered stock payable in the amount of $103,718.
During the year ended June 30,
2019, the Company issued a total of 15,501,274 shares of common stock for cash totaling $461,198. In addition, the Company sold
common shares, which have not yet been issued as June 30, 2019 and are considered stock payable in the amount of $147,484.
The common shares issued for
services was 0, and 1,083,948, as of June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The following information summarizes the warrants outstanding
and exercisable.
Warrants Outstanding and Exercisable at June 30, 2019:
|
Range of Exercise Prices
|
|
Number of Warrants Outstanding
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Contractual Life Remining in Years
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Exercise Price
|
|
|
Number Exercisable
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Exercise Price
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$0.05 - $1.00
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
|
|
1.120
|
|
|
$
|
0.33
|
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
|
$
|
0.33
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants Outstanding and Exercisable at September 30, 2018:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$0.20 - $1.00
|
|
|
14,842,583
|
|
|
|
0.527
|
|
|
$
|
0.53
|
|
|
|
14,842,583
|
|
|
$
|
0.53
|
|
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 5 -
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (CONTINUED)
|
Warrant Activity:
As of June 30, 2019 and 2018,
the following is a breakdown of the activity:
June 30, 2019:
|
Outstanding - beginning of year
|
|
|
14,842,583
|
|
|
Issued
|
|
|
18,738,235
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
|
|
|
(7,054,584
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding - end of year
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
June 30, 2018:
|
Outstanding - beginning of year
|
|
|
20,276,399
|
|
|
Issued
|
|
|
12,341,584
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
|
|
|
(17,775,400
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding - end of year
|
|
|
14,842,583
|
|
At June 30, 2019, all of the
26,526,234 warrants are vested, 23,226,234 warrants expire at various times through July 2020, 3,000,000 warrants expire in September
2019, and 300,000 warrants expire in July 2020.
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 6 -
|
MANDATORY REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK
|
Issuances of Series C Mandatory Redeemable
Convertible Preferred Stock
On January 10, 2019, the Board of Directors
of the Company adopted a resolution pursuant to the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, providing for the
designations, preferences and relative, participating, optional and other rights, and the qualifications, limitations and restrictions,
of the Series C Convertible Preferred Stock.
On January 14, 2019, the Company filed
a Certificate of Designations for a Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. The authorized number of Series C Convertible Preferred
Stock is 1,000,000 shares, par value 0.001. The Series C Preferred Stock will, with respect to dividend
rights and rights upon liquidation, winding-up or dissolution, rank: (a) senior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation with the Company’s
common stock, , (b) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation with respect to the
Company’s Series B Preferred Stock; and (c) junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation
to all existing indebtedness of the Company. Series C Preferred Stock will carry an annual ten percent (10%)
cumulative dividend, compounded daily, payable solely upon redemption, liquidation or conversion. The Company
will have a right, at any time in the period of 180 days from the date of the issuance, at the Company’s option, to redeem
all or any portion of the Series C Preferred Stock at prices ranging from 105% to 130%, based on the passage of time.
The Holder shall have the right at any
time during the period beginning on the date which is six (6) months following the Issuance Date, to convert all or any part
of the outstanding Series C Preferred Stock into fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common Stock at the Variable Conversion
Price. The “Variable Conversion Price” shall mean 71% multiplied by the Market Price (representing a discount rate
of 29%). “Market Price” means the average of the two (2) lowest Trading Prices (as defined here) for the Common Stock
during the fifteen (15) Trading Day period ending on the latest complete Trading Day prior to the Conversion Date.
On the date which is eighteen (18) months
following the Issuance Date or upon the occurrence of an Event of Default (the “Mandatory Redemption Date”), the Company
shall redeem all of the shares of Series C Preferred Stock of the Holder (which have not been previously redeemed or converted).
With five (5) days of the Mandatory Redemption Date, the Company shall make payment to each Holder of an amount in cash equal to
the total number of shares of Series C Preferred Stock held by such Holder multiplied by the then current Stated Value.
All shares of mandatorily redeemable convertible
preferred stock have been presented outside of permanent equity in accordance with ASC 480, Classification and Measurement
of Redeemable Securities. The Company accretes the carrying value of its Series C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred
stock to its estimate of fair value (i.e. redemption value) at period end.
The estimated fair value of the Series
C, mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock at June 30, 2019 and 2018 was $110,000 and $0, respectively.
The Company recorded preferred stock dividends
of $7,401 during fiscal year 2019, and accrued dividends payable of $3,123.
Deferred income taxes are determined using
the liability method for the temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and income tax basis of the Company’s
assets and liabilities. Deferred income taxes are measured based on the tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences
are included in the Company’s tax return. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized based on anticipated future
tax consequences attributable to differences between financial statement carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective
tax bases. The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to income tax matters as a component of income tax
expense.
At June 30, 2019 and 2018, deferred tax assets consist of the
following:
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
Net operating loss carryforward
|
|
$
|
7,972,161
|
|
|
$
|
6,958,336
|
|
|
Warrant issuances
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Deferred officer compensation
|
|
|
790,015
|
|
|
|
225,538
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
371
|
|
|
|
644
|
|
|
Valuation allowance
|
|
|
(8,762,547
|
)
|
|
|
(7,184,518
|
)
|
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
SMARTMETRIC INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
NOTE 7 -
|
INCOME TAXES (CONTINUED)
|
At June 30, 2019, the Company had a net
operating loss carry-forwards in the amount of approximately $21.0 million available to offset future taxable income through 2036,
which will begin to expire in 2021. The Company established valuation allowances equal to the full amount of the deferred
tax assets due to the uncertainty of the utilization of the operating losses in future periods. A reconciliation of the Company’s
effective tax rate as a percentage of income before taxes and federal statutory rate for the period ended June 30, 2019 and 2018
is summarized as follows:
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
Tax on income before income tax
|
|
|
21.00
|
%
|
|
|
34.00
|
%
|
|
Effect of non-temporary differences
|
|
|
(0.01
|
)%
|
|
|
(0.07
|
)%
|
|
Effect of prior year items
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
Effect of temporary differences
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
Change in valuation allowance
|
|
|
(20.99
|
)%
|
|
|
(33.90
|
)%
|
|
|
|
|
0.00
|
%
|
|
|
0.00
|
%
|
The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits
can change due to tax examination activities, lapse of applicable statutes of limitations and the recognition and measurement criteria
under the guidance related to accounting for uncertainty in income taxes. The Company does not believe any significant
increases or decreases will occur within the next twelve months.
The Company files income tax returns in
the United States (“U.S.”) federal jurisdiction. Generally, the Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal
examinations by tax authorities for fiscal years prior to 2015. The Company does not file in any other jurisdiction
and remains open for audit for all tax years as the statute of limitations does not begin until the returns are filed.
From time to time we may be a defendant
or plaintiff in various legal proceedings arising in the normal course of our business. We know of no material, active,
pending or threatened proceeding against us or our subsidiaries, nor are we, or any subsidiary, involved as a plaintiff or defendant
in any material proceeding or pending litigation.
|
NOTE 9 -
|
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
|
In accordance with ASC 855-10, the Company
has analyzed its operations subsequent to June 30, 2019 to the date these financial statements were issued.
Subsequent to June 30, 2019, the Company
sold 52,800 shares of Series C Preferred Stock on August 26, 2019 for gross proceeds of $48,000.
Subsequent to June 30, 2019, the Company
issued 11,216,305 common shares, all of which were for stock payable existing as of year end. These shares had a cash value of
$226,000.
SMARTMETRIC,
INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Condensed
Consolidated Balance Sheet
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
10,161
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
10,017
|
|
|
|
6,450
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
10,017
|
|
|
|
16,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
10,017
|
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
$
|
898,380
|
|
|
$
|
884,140
|
|
|
Liability for stock to be issued
|
|
|
69,183
|
|
|
|
147,484
|
|
|
Deferred Officer’s salary
|
|
|
821,682
|
|
|
|
790,015
|
|
|
Related party interest payable
|
|
|
135,240
|
|
|
|
93,488
|
|
|
Dividends payable
|
|
|
2,489
|
|
|
|
3,123
|
|
|
Due to shareholders
|
|
|
41,343
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Shareholder loan
|
|
|
6,571
|
|
|
|
3,759
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
1,974,888
|
|
|
|
1,922,009
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
1,974,888
|
|
|
|
1,922,009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 4)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of discount, authorized 1,000,000 shares 128,500 and 121,700 shares issued and outstanding, respectively
|
|
|
106,580
|
|
|
|
99,278
|
|
|
Preferred Series C stock subscriptions receivable
|
|
|
(30,000
|
)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ deficit:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred B stock, $.001 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized, 610,000 and 610,000 shares issued and outstanding
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
|
610
|
|
|
Common stock, $.001 par value; 600,000,000 and 300,000,000 shares authorized, 316,875,686 and 264,648,821 shares issued and outstanding , respectively
|
|
|
316,876
|
|
|
|
264,649
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
25,215,910
|
|
|
|
24,663,528
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(27,574,847
|
)
|
|
|
(26,933,463
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit
|
|
|
(2,041,451
|
)
|
|
|
(2,004,676
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and equity
|
|
$
|
10,017
|
|
|
$
|
16,611
|
|
The
accompanying unaudited notes are an integral part of these unaudited consolidated financial statements
SMARTMETRIC,
INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Condensed
Consolidated Statement of Operations
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Three
Months
|
|
|
Three
Months
|
|
|
Nine
Months
|
|
|
Nine
Months
|
|
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Officer’s salary
|
|
|
47,500
|
|
|
|
47,500
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
Other general and administrative
|
|
|
93,200
|
|
|
|
121,200
|
|
|
|
375,779
|
|
|
|
369,361
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
14,090
|
|
|
|
38,949
|
|
|
|
60,796
|
|
|
|
90,084
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
154,790
|
|
|
|
207,649
|
|
|
|
579,075
|
|
|
|
601,945
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations before other expense
|
|
|
(154,790
|
)
|
|
|
(207,649
|
)
|
|
|
(579,075
|
)
|
|
|
(601,945
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other expense
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(14,081
|
)
|
|
|
(13,647
|
)
|
|
|
(41,731
|
)
|
|
|
(39,468
|
)
|
|
Total Other expense
|
|
|
(14,081
|
)
|
|
|
(13,647
|
)
|
|
|
(41,731
|
)
|
|
|
(39,468
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
(620,806
|
)
|
|
|
(641,413
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
(620,806
|
)
|
|
|
(641,413
|
)
|
|
Preferred C stock dividends
|
|
|
(4,614
|
)
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
|
(20,577
|
)
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
Net loss available for common stockholders
|
|
$
|
(173,485
|
)
|
|
$
|
(225,569
|
)
|
|
$
|
(641,383
|
)
|
|
$
|
(645,686
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
|
|
307,327,958
|
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
|
285,940,273
|
|
|
|
253,891,612
|
|
The
accompanying unaudited notes are an integral part of these unaudited consolidated financial statements
SMARTMETRIC,
INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated
Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ (Deficit)
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Preferred Series B
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Paid In
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance June 30, 2019
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
264,648,821
|
|
|
|
264,649
|
|
|
$
|
24,663,528
|
|
|
$
|
(26,933,461
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,004,674
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
7,991,662
|
|
|
|
7,992
|
|
|
|
218,008
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
226,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares converted from Preferred Series C shares
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
3,224,643
|
|
|
|
3,224
|
|
|
|
63,289
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
66,513
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Series C dividends
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(11,725
|
)
|
|
|
(11,725
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss available for common shareholders
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(215,296
|
)
|
|
|
(215,296
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance September 30, 2019
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
275,865,126
|
|
|
$
|
275,865
|
|
|
$
|
24,944,825
|
|
|
$
|
(27,160,482
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,939,182
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
3,730,000
|
|
|
|
3,730
|
|
|
|
77,720
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
81,450
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares converted from Preferred Series C shares
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
2,370,696
|
|
|
|
2,371
|
|
|
|
28,538
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
30,909
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Series C dividends
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4,238
|
)
|
|
|
(4,238
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss available for common shareholders
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(236,638
|
)
|
|
|
(236,638
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2019
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
281,965,822
|
|
|
$
|
281,966
|
|
|
$
|
25,051,083
|
|
|
$
|
(27,401,358
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,067,699
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock for services
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
|
1,450
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,500
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
28,475,000
|
|
|
|
28,475
|
|
|
|
118,275
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
146,750
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares converted from Preferred Series C shares
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
6,384,864
|
|
|
|
6,385
|
|
|
|
45,102
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
51,487
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Series C dividends
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4,614
|
)
|
|
|
(4,614
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss available for common shareholders
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
(168,871
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance March 31, 2020
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
316,875,686
|
|
|
$
|
316,876
|
|
|
$
|
25,215,910
|
|
|
$
|
(27,574,847
|
)
|
|
$
|
(2,041,451
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance June 30, 2018
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
249,147,547
|
|
|
$
|
249,148
|
|
|
$
|
24,217,831
|
|
|
$
|
(25,996,910
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,529,321
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
5,502,538
|
|
|
|
5,503
|
|
|
|
201,196
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
206,699
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the period
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(213,827
|
)
|
|
|
(213,827
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance September 30, 2018
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
254,650,085
|
|
|
$
|
254,651
|
|
|
$
|
24,419,027
|
|
|
$
|
(26,210,237
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,526,479
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued of common stock and warrants for cash
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
2,026,660
|
|
|
|
2,027
|
|
|
|
59,973
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
62,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the period
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(206,790
|
)
|
|
|
(206,790
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2018
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
$
|
256,678
|
|
|
$
|
24,479,000
|
|
|
$
|
(26,417,027
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,671,269
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Series C dividends
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
|
(4,273
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the period
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
(221,296
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance March 31, 2019
|
|
|
610,000
|
|
|
$
|
610
|
|
|
|
256,676,745
|
|
|
$
|
256,678
|
|
|
$
|
24,479,000
|
|
|
$
|
(26,642,596
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,896,838
|
)
|
The accompanying unaudited notes are an
integral part of these unaudited consolidated financial statements
SMARTMETRIC,
INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Condensed
Consolidated Statements Of Cash Flows
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Nine Months
|
|
|
Nine Months
|
|
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
Ended
|
|
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
March 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(620,806
|
)
|
|
$
|
(641,413
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in assets and liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
(3,567
|
)
|
|
|
(2,250
|
)
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
14,240
|
|
|
|
58,414
|
|
|
Deferred officer salary
|
|
|
31,667
|
|
|
|
142,500
|
|
|
Credit card debt
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(536
|
)
|
|
Due to shareholder
|
|
|
41,343
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued interest payable
|
|
|
41,752
|
|
|
|
39,469
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
|
(495,371
|
)
|
|
|
(403,816
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loans from related parties
|
|
|
2,812
|
|
|
|
(7,261
|
)
|
|
Proceeds from sale of common stock
|
|
|
377,398
|
|
|
|
417,579
|
|
|
Proceeds from sale of Series C Preferred stock
|
|
|
105,000
|
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
|
|
485,210
|
|
|
|
460,318
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET DECREASE IN CASH
|
|
|
(10,161
|
)
|
|
|
56,502
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
|
|
10,161
|
|
|
|
4,427
|
|
|
CASH, END OF PERIOD
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
60,929
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH PAID DURING THE PERIOD FOR:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income taxes
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
Interest
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-cash investing and financing activity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conversion of 157,700 Preferred C shares into 11,980,203 shares of Common stock
|
|
$
|
142,722
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
The
accompanying unaudited notes are an integral part of these unaudited consolidated financial statements
SMARTMETRIC
INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES
TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(UNAUDITED)
NOTE
1 - ORGANIZATION AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
SmartMetric,
Inc. (“SmartMetric” or the “Company”) was incorporated pursuant to the laws of Nevada on December 18,
2002. SmartMetric is a company engaged in the technology industry. SmartMetric’s main products are a fingerprint sensor
activated payments card and a security card with a finger sensor and fully functional fingerprint reader embedded inside the card.
The SmartMetric biometric cards have a rechargeable battery allowing for portable biometric identification and card activation.
This card is referred to as a biometric card or the SmartMetric Biometric Card.
The
accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting
principles for interim financial information and with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Regulation S-X. Accordingly, they do not
include all the information and footnotes required by generally accepted accounting principles for complete financial statements.
In the opinion of management of the Company, the accompanying unaudited financial statements contain all the adjustments (which
are of a normal recurring nature) necessary for a fair presentation. Operating results for the nine months ended March 31, 2020
are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the year ending June 30, 2020. For further information,
refer to the financial statements and the footnotes thereto contained in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the
year ended June 30, 2019, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 30, 2019. The condensed consolidated
balance sheet as of June 30, 2019, has been derived from the audited financial statements at that date, but does not include all
the information and footnotes required by US GAAP for complete financial statements.
Going
Concern
As
shown in the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements the Company has sustained recurring losses of $641,383 and
$645,686 for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and has an accumulated deficit of $27,574,847 at March
31, 2020.
These
conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the date
of this filing. The financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability and classification of asset
carrying amounts or the amount and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue
as a going concern.
Management
believes that the Company’s capital requirements will depend on many factors. These factors include product marketing and
distribution. The management plans include equity sales and borrowing in order to fund the operations.
There
are no assurances that the Company will be able to achieve the level of revenues adequate to generate sufficient cash flow from
operations to support the Company’s working capital requirements. To the extent that funds generated are insufficient, the
Company will have to raise additional working capital. No assurance can be given that additional financing will be available,
or if available, will be on terms acceptable to the Company. If adequate working capital is not available, the Company may not
continue its operations.
In
December 2019, an outbreak of a novel strain of coronavirus originated in Wuhan, China (“COVID-19”) and has since
spread worldwide, including to the Unites States, posing public health risks that have reached pandemic proportions (the “COVID-19
Pandemic”). The COVID-19 Pandemic poses a threat to the health and economic wellbeing of our employees, customers and vendors.
Like most businesses world-wide, the COVID-19 Pandemic has impacted the Company financially; however, management cannot presently
predict the scope and severity with which COVID-19 will impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash
flows.
Principles
of Consolidation
The
condensed consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary, SmartMetric Australia
Pty. Ltd. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
NOTE
2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Use
of Estimates
The
preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying disclosures. Actual results may
differ from those estimates.
Research
and Development
Research
and development costs are charged to expense as incurred. Our research and development expenses consist primarily of expenditures
for electronics design and engineering, software design and engineering, component sourcing, component engineering, manufacturing,
product trials, compensation and consulting costs.
Recent
Accounting Pronouncements
The
Company does not expect the adoption of recently issued accounting pronouncements to have a significant impact on the Company’s
results of operations, financial position or cash flow except as noted below.
In
February 2016, the FASB issued authoritative guidance, which is included in ASC 842, “Leases.” This guidance requires
lessees to recognize most leases on the balance sheet by recording a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. The Company has
made the decision to adopt this guidance early, and it was adopted by the Company as of March 1, 2019. Based on the completed
analysis, the Company has determined that the adjustment did not have a material impact on the financial statements.
In
June 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-07, Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based
Payment Accounting, which aligns accounting for share-based payments issued to nonemployees to that of employees under the existing
guidance of Topic 718, with certain exceptions. This update supersedes previous guidance for equity-based payments to nonemployees
under Subtopic 505-50, Equity—Equity-Based Payments to Non-Employees. This guidance was adopted by the Company as of March
1, 2019. Based on the completed analysis, the Company has determined the adjustment did not have a material impact on the financial
statements.
Loss
Per Share of Common Stock
In
accordance with FASB ASC 260, “Earnings Per Share,” the basic loss per share is computed by dividing the loss attributable
to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Basic net loss per share
excludes the dilutive effect of stock options or warrants and convertible notes. Diluted net earnings (loss) per common share
is determined using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period, adjusted for the dilutive effect
of common stock equivalents, consisting of shares that might be issued upon exercise of common stock options and warrants. In
periods where losses are reported, the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding excludes common stock equivalents,
because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive. As of March 31, 2020 and 2019, 30,079,406 and 26,392,318 dilutive shares were
excluded from the calculation of diluted loss per common share, with all dilutive shares being Common stock warrants at March
31, 2020 and 2019.
Stock-Based
Compensation
The
Company measures expense for issuances of stock-based compensation to employees and others at fair value of the stock and warrants
issued, as this is more reliable than the fair value of the services received complete. The fair value of the equity instrument
is charged directly to compensation expense and additional paid-in capital.
Reclassifications
Certain
prior year amounts have been reclassified for consistency with the current period presentation. These reclassifications had no
effect on the reported results of operations.
NOTE
3 - PREPAID EXPENSES
Prepaid
expenses represent the unexpired terms of various consulting agreements as well as advance rental payments. The Company does not
currently have any prepaid items related to shares issued for services.
NOTE
4 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Lease
Agreement
The
Company’s main office is in Las Vegas, Nevada. Rent expense under all leases for the nine months ended March 31, 2020 and
2019 was $3,600 and $10,545 respectively. The Company maintains only one office. This office is in Las Vegas, NV and is a month-to-month
lease.
Related
Party Transactions
The
Company’s Chief Executive Officer has made cash advances to the Company with an aggregate amount due of $6,571 and $3,759
at March 31, 2020 and June 30, 2019, respectively. These advances bear interest at the rate of five percent (5%) per annum.
The
Company has accrued the amounts of $821,682 and $790,015 at March 31, 2020 and June 30, 2019, respectively, as deferred officer’s
salary, for the difference between the Chief Executive Officer’s annual salary and the amounts paid.
On
September 11, 2017, we received a license to certain patents from Chaya Hendrick, our founder and CEO, related to our technologies
until the expiration of the patents. As consideration, we issued Chaya Hendrick, or her assigns, (i) 200,000 shares of Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock, (ii) a royalty equal to 5% of gross revenues derived from products sold related to the patents,
and (iii) certain minimum required payments beginning at $50,000 and doubling each year thereafter. The Series B Preferred Shares
may be converted at the election of holder on a basis for 50 common shares for each preferred share at any time or an aggregate
of 10,000,000 common shares in exchange for all 200,000 preferred shares.
Litigation
From
time to time we may be a defendant or plaintiff in various legal proceedings arising in the normal course of our business. As
of the date of this Quarterly Report, there are no material pending legal or governmental proceedings relating to us or properties
to which we are a party, and, to our knowledge, there are no material proceedings to which any of our directors, executive officers
or affiliates are a party adverse to us or which have a material interest adverse to us.
NOTE
5 - STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Preferred
Stock
As
of March 31, 2020, the Company has 5,000,000 shares of Class B preferred stock, par value $0.001, authorized and 610,000 shares
issued and outstanding.
On
December 11, 2009, the Company filed a Certificate of Designation with the State of Nevada, to designate 500,000 shares of preferred
stock as Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series B Convertible Preferred Stock”). Effective November 5, 2014,
the number of shares designated as Series B Convertible Preferred Stock was increased to 5,000,000 shares.
Each
share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock has a par value of $0.001, and a stated value equal to $5.00 (“Stated Value”).
Holders of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock are entitled to receive dividends or other distributions with the holders
of the common stock of the Company on an as converted basis when, as, and if declared by the directors of the Company. Holders
of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock are entitled to convert each share of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock into
fifty (50) shares of common stock.
Upon
any liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, holders of the Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock are entitled to receive out of the assets, whether capital or surplus, of the Company an amount equal to the Stated
Value, pro rata with the holders of the common stock.
NOTE
5 - STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (CONTINUED)
Class
A Common Stock
As
of March 31, 2020, the Company has 50,000,000 shares of Class A common stock, par value $0.001, authorized and no shares issued
and outstanding.
Common
Stock
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended September 30, 2019, the Company sold for cash 6,337,500 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i)
6,337,500 shares at prices ranging from $0.10 per share to $0.25 per share for net proceeds of $133,495. The warrants expire
at various times through September 17, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended September 30, 2019,
with all 6,337,500 shares being recorded as stock payable. There were 52,800 Preferred C shares issued for net proceeds of
$45,000 and 70,000 Preferred C shares converted to 3,224,643 Common shares for the three month period ending September 30,
2019, see Note 6.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
month period ending December 31, 2019, the Company increased its total number of shares of authorized capital stock to 600,000,000
shares, par value $0.001 per share.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended December 31, 2019, the Company sold for cash 40,675,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i)
825,000 shares at prices ranging from $0.20 per share to $0.25 per share for net proceeds of $214,510. The warrants expire
at various times through November 1, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended December 31, 2019, with
all 40,675,000 shares being recorded as stock payable. There were 36,300 Preferred C shares converted to 2,370,696 Common
shares for the three month period ending December 31, 2019, see Note 6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2020, the Company sold for cash 9,550,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,500,000
shares at prices ranging from $0.05 per share to $1.00 per share for net proceeds of $66,500. The warrants expire at various
times through March 12, 2022. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended March 31, 2020, with all 9,550,000
shares being recorded as stock payable. There were 53,700 Preferred C shares converted to 6,384,864 Common shares
for the three month period ending March 31, 2020. The Company issued 41,800 preferred shares for net proceeds of $35,000 and
another 33,600 preferred shares for which the net proceeds of $30,000 had not been received as of March 31, 2020.
|
|
|
●
|
As of March 31,
2020, the Company had 316,875,686 shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended September 30, 2018, the Company sold for cash 4,624,153 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $145,770 and
warrants to purchase (i) 3,699,988 shares at $0.25, (ii) 60,000 shares at $0.30, (iii) 30,000 shares at $0.50, (iv) 301,875
shares at $0.70 and (v) 151,970 shares at $1.00. During the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company issued
a total of 5,502,538 shares of common stock. Of the total number of shares issued, 3,061,659 shares were for proceeds
received during the quarter and 2,440,879 shares to reduce the liability for stock to be issued.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended December 31, 2018, the Company sold for cash 5,212,499 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,712,499
shares at $0.25 per share and (ii) 1,500,000 shares at $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $106,060. The warrants expire
at various times through December 4, 2020. During the quarter ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued a total of 2,026,660
shares of common stock. Of the total number of shares issued, 250,000 shares were for proceeds received during the quarter
and 4,962,499 shares to reduce the liability for stock to be issued.
|
|
|
●
|
As of March 31,
2019, the Company had 256,676,745 shares of common stock issued and outstanding
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2019, the Company sold for cash 7,541,663 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 7,541,663
shares at prices ranging from $0.05 per share to $0.50 per share for net proceeds of $165,749. The warrants expire at various
times through March 21, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended March 31, 2019.
|
Equity
Financing Agreement
On
March 5, 2020, the Company entered into an equity financing agreement with GHS Investments, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company
(“Investor”). Pursuant to the agreement, the Company agrees the sell to the investor an indeterminate amount of shares
of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, up to an aggregate price of four million dollars ($4,000,000).
Pursuant
to the agreement, the Company is required, to within sixty (60) calendar days upon the date of execution of this agreement, use
its best efforts to file with the SEC a registration statement or registration statements (as is necessary) on Form S-1, covering
the resale of all of the registrable securities, which registration statement(s) shall state that, in accordance with Rule 416
promulgated under the 1933 Act, such registration statement also covers such indeterminate number of additional shares of Common
Stock as may become issuable upon stock splits, stock dividends or similar transactions. The Company failed to file the Registration
S-1 within 60 days of the execution of the Equity Financing Agreement, and has not been able to comply with that requirement as
of the date of this filing.
Concurrently
with the execution of the equity financing agreement, the company entered into a convertible promissory note, for the principal
balance of $35,000. Per the terms of the convertible note agreement, the Company agrees to pay the investor interest at the rate
of ten percent (10%) until it is due on December 5, 2020. The holder shall have the right at any time to convert all or any part
of the outstanding and unpaid principal and interest at a fixed conversion price of $0.0175. As of the date of this filing, the
Company has not yet received this money.
NOTE
5 - STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (CONTINUED)
Warrants
From
time to time the Company granted warrants in connection with private placements of securities, as described herein.
As
of March 31, 2020, and June 30, 2019, the following is a breakdown of the warrant activity:
|
Range of Exercise Prices
|
|
Number of
Warrants
Outstanding
|
|
|
Weighted-Average
Contractual Life
Remaining in Years
|
|
|
Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price
|
|
|
Number
Exercisable
|
|
|
Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price
|
|
|
Warrants Outstanding and Exercisable at March 31, 2020:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$0.05 - $1.00
|
|
|
30,079,406
|
|
|
|
1.27
|
|
|
$
|
0.28
|
|
|
|
30,079,406
|
|
|
$
|
0.28
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrants Outstanding and Exercisable at June 30, 2019:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$0.20 - $1.00
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
|
|
1.12
|
|
|
$
|
0.34
|
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
|
$
|
0.34
|
|
Warrant
Activity:
March
31, 2020:
|
Outstanding - June 30, 2019
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
|
Issued
|
|
|
10,662,500
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
|
|
|
(7,109,328
|
)
|
|
Outstanding - March 31, 2020
|
|
|
30,079,406
|
|
June
30, 2019:
|
Outstanding - June 30, 2018
|
|
|
14,842,583
|
|
|
Issued
|
|
|
18,738,235
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
|
|
|
(7,054,584
|
)
|
|
Outstanding - June 30, 2019
|
|
|
26,526,234
|
|
At
March 31, 2020, all 30,079,406 warrants are vested and (i) 29,779,406 warrants expire at various times prior to March 12, 2022,
(ii) 300,000 warrants expire in July 2020,
NOTE
6 - MANDATORY REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK
Issuances
of Series C Mandatory Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock
On
January 10, 2019, the Board of Directors of the Company adopted a resolution pursuant to the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation,
as amended, providing for the designations, preferences and relative, participating, optional and other rights, and the qualifications,
limitations and restrictions, of the Series C Convertible Preferred Stock.
On
January 14, 2019, the Company filed a Certificate of Designations for a Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. The authorized number
of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock is 1,000,000 shares, par value 0.001. The Series C Preferred Stock will, with respect to
dividend rights and rights upon liquidation, winding-up or dissolution, rank: (a) senior with respect to dividends
and right of liquidation with the Company’s common stock, (b) junior with respect to
dividends and right of liquidation with respect to the Company’s Series B Preferred Stock; and (c)
junior with respect to dividends and right of liquidation to all existing indebtedness of the Company.
Series C Preferred Stock will carry an annual ten percent (10%) cumulative dividend, compounded daily, payable solely
upon redemption, liquidation or conversion. The Company will have a right, at any time in the period of 180 days from
the date of the issuance, at the Company’s option, to redeem all or any portion of the Series C Preferred Stock at prices
ranging from 105% to 130%, based on the passage of time.
NOTE
6 - MANDATORY REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK (CONTINUED)
The
number of Series C, mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock shares issued and outstanding were 128,500 and 121,700, respectively,
for March 31, 2020 and June 30, 2019.
The
Holder shall have the right at any time during the period beginning on the date which is six (6) months following the Issuance
Date, to convert all or any part of the outstanding Series C Preferred Stock into fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common
Stock at the Variable Conversion Price. The “Variable Conversion Price” shall mean 71% multiplied by the Market Price
(representing a discount rate of 29%). “Market Price” means the average of the two (2) lowest Trading Prices (as defined
here) for the Common Stock during the fifteen (15) Trading Day period ending on the latest complete Trading Day prior to the Conversion
Date.
On
the date which is eighteen (18) months following the Issuance Date or upon the occurrence of an Event of Default (the “Mandatory
Redemption Date”), the Company shall redeem all of the shares of Series C Preferred Stock of the Holder (which have not
been previously redeemed or converted). With five (5) days of the Mandatory Redemption Date, the Company shall make payment to
each Holder of an amount in cash equal to the total number of shares of Series C Preferred Stock held by such Holder multiplied
by the then current Stated Value.
All
shares of mandatorily redeemable convertible preferred stock have been presented outside of permanent equity in accordance with
ASC 480, Classification and Measurement of Redeemable Securities. The Company accretes the carrying value of its Series
C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock to its estimate of fair value (i.e. redemption value) at period end.
The
carrying value of the Series C mandatory redeemable convertible preferred stock at March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $106,580 and $52,815,
respectively. There were 75,400 Preferred C shares issued for net proceeds of $65,000 and 75,400 Preferred C shares converted
to 6,384,864 Common shares for the three month period ended March 31, 2020. For the nine month period ended March 31, 2020, there
were 164,500 Preferred C shares issued for net proceeds of $135,000 and 157,700 Preferred C shares converted to 11,980,203 Common
shares.
|
|
|
Preferred C Stock
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2019
|
|
$
|
121,700
|
|
|
$
|
99,278
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
52,800
|
|
|
|
45,000
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
9,473
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
(70,000
|
)
|
|
|
(63,000
|
)
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2019
|
|
$
|
104,500
|
|
|
$
|
90,751
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
36,300
|
|
|
|
25,000
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
1,722
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
(34,000
|
)
|
|
|
(30,909
|
)
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019
|
|
$
|
106,800
|
|
|
$
|
86,564
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
75,400
|
|
|
|
65,000
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
3,825
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
(53,700
|
)
|
|
|
(48,813
|
)
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2020
|
|
$
|
128,500
|
|
|
$
|
106,580
|
|
NOTE
6 - MANDATORY REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK (CONTINUED)
|
|
|
Preferred C Stock
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2018
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2018
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2018
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash - Preferred Stock C
|
|
|
70,000
|
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
Preferred C accretion
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
2,815
|
|
|
Preferred shares converted into common stock
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
|
-0-
|
|
|
Balance, March 31, 2019
|
|
$
|
70,000
|
|
|
$
|
52,815
|
|
NOTE
7 - INCOME TAXES
The
Company provides for income taxes at the end of each interim period based on the estimated effective tax rate for the full fiscal
year. Cumulative adjustments to the Company’s estimate are recorded in the interim period in which a change in the estimated
annual effective rate is determined.
The
Company has estimated its effective tax rate to be 0%, based primarily on losses incurred and the uncertainty of realization of
the tax benefit of such losses.
NOTE
8 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In
accordance with ASC 855-10, the Company has analyzed its operations subsequent to March 31, 2020 to the date these financial statements
were issued. On April 2, 2020, the Company converted 12,000 preferred C shares into 1,909,091 common shares and on April 24, 2020
the Company converted 4,800 preferred shares into 775,385 common shares. On April 8, 2020 9,287,500 common shares were issued
and on April 22, 2020, 12,000,000 common shares were issued. On May 1, 2020, 41,800 preferred shares were issued for net proceeds
of $35,000.
PART
II
INFORMATION
NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Other
Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The
following table sets forth the costs and expenses to be paid by the Registrant in connection with the issuance and distribution
of the securities being registered. All amounts other than the SEC registration fee are estimates.
|
Securities and Exchange Commission registration fee
|
|
$
|
181.72
|
|
|
Accounting fees and expenses
|
|
$
|
|
*
|
|
Legal fees and expenses
|
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
Miscellaneous
|
|
$
|
|
*
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
15,181.72
|
*
|
|
*
|
To be provided by
amendment.
|
Indemnification
of Officers and Directors
Nevada
Law
The
Nevada Revised Statutes limits or eliminates the personal liability of directors to corporations and their stockholders for monetary
damages for breaches of directors’ fiduciary duties as directors. Our bylaws include provisions that require the company
to indemnify our directors or officers against monetary damages for actions taken as a director or officer of our Company. We
are also expressly authorized to carry directors’ and officers’ insurance to protect our directors, officers, employees
and agents for certain liabilities. Our articles of incorporation do not contain any limiting language regarding director immunity
from liability.
The
limitation of liability and indemnification provisions under the Nevada Revise Statutes and our bylaws may discourage stockholders
from bringing a lawsuit against directors for breach of their fiduciary duties. These provisions may also have the effect of reducing
the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise
benefit us and our stockholders. However, these provisions do not limit or eliminate our rights, or those of any stockholder,
to seek non-monetary relief such as injunction or rescission in the event of a breach of a director’s fiduciary duties.
Moreover, the provisions do not alter the liability of directors under the federal securities laws. In addition, your investment
may be adversely affected to the extent that, in a class action or direct suit, we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards
against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
RECENT
SALES OF UNREGISTERED SECURITIES
The
following sets forth information regarding all unregistered securities sold by us in transactions that were exempt from the requirements
of the Securities Act in the last three years. Except where noted, all of the securities discussed in this Item 15 were all issued
in reliance on the exemption under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. Unless otherwise indicated, all of the share issuances
described below were made in reliance on the exemption from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act.
Except
where noted, all of the securities discussed in this section were issued in reliance on the exemption under Section 4(a)(2) of
the Securities Act.
|
|
●
|
On September 11,
2017, we received a license to certain patents from Chaya Hendrick, our founder and CEO, related to our technologies until
the expiration of the patents. As consideration, we issued Chaya Hendrick, or her assigns, (i) 200,000 shares of Series B
Convertible Preferred Stock, (ii) a royalty equal to 5% of gross revenues derived from products sold related to the patents,
and (iii) certain minimum required payments beginning at $50,000 and doubling each year thereafter. The Series B Convertible
Preferred Shares may be converted at the election of holder on a basis for 50 common shares for each preferred share at any
time or an aggregate of 10,000,000 common shares in exchange for all 200,000 preferred shares.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended June 30, 2017, the Company sold, for net proceeds of $242,157, units consisting of an aggregate of (i) 7,450,000
shares, (ii) warrants to purchase 3,031,250 shares at $0.70 per share, and (iii) warrants to purchase 1,527,750 shares at
$1.00 per share. The warrants expire at various times through October 20, 2018.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2017, the Company issued an aggregate of 2,423,000 shares of common stock for consulting services valued
at $283,955, based on the stock price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2017, the Company sold, for net proceeds of $127,247.50, units consisting of an aggregate of (i) 2,550,000
shares, (ii) warrants to purchase 1,593,750 shares at $0.70 per share, and (iii) warrants to purchase 803,250 shares at $1.00
per share. The warrants have all expired and no warrants were exercised.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended September 30, 2017, the Company sold for cash 2,500,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i)
1,437,500 shares at $0.70 and $0.20 per share and (ii) 724,500 shares at $1.00 and $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $114,625.
The warrants expire at various times through September 28, 2019. During the three months ended September 30, 2017, 300,000
shares were issued and 2,200,000 shares were accrued as stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended September 30, 2017, the Company issued 362,864 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $21,825,
based on the stock price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided. All 362,864 shares were
accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended December 31, 2017, the Company sold for cash 8,319,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,250,000
shares at $0.20 per share and (ii) 1,638,000 shares at $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $259,362. The warrants expire
at various times through December 29, 2019. During the three months ended December 31, 2017, 5,120,000 were issued and 3,199,000
shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended December 31, 2017, the Company issued 212,164 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $15,000,
based on the stock price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided. These shares were issued
on November 8, 2017.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2018, the Company sold for cash 2,850,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 2,051,250
shares at $0.70 per share and (ii) 929,250 shares at $1.00 per share, for net proceeds of $142,305. The warrants expire at
various times through February 21, 2020. None of the 2,850,000 shares were issued as of March 31, 2018.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2018, the Company issued 508,620 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $30,000,
based on the stock price at the time of the respective agreements underlying the services provided. These shares were issued
on February 26, 2018.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended June 30, 2018, the Company sold for cash 2,646,100 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 1,536,625
shares at $0.70 per share and (ii) 774,459 shares at $1.00 per share, for net proceeds of $119,738. The warrants expire at
various times through June 15, 2020. During the three months ended June 30, 2018, 1,937,500 of these shares were issued and
708,600 shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended September 30, 2018, the Company sold for cash 4,624,153 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $145,770 and
warrants to purchase (i) 3,699,988 shares at $0.25, (ii) 60,000 shares at $0.30, (iii) 30,000 shares at $0.50, (iv) 301,875
shares at $0.70 and (v) 151,970 shares at $1.00. During the quarter ended September 30, 2018, the Company issued
a total of 5,502,538 shares of common stock. Of the total number of shares issued, 3,061,659 shares were for proceeds
received during the quarter and 2,440,879 shares to reduce the liability for stock to be issued. During the three months ended
September 30, 2018, 3,061,659 of these shares were issued and 1,562,494 shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended December 31, 2018, the Company sold for cash 5,212,499 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 3,712,499
shares at $0.25 per share and (ii) 1,500,000 shares at $0.50 per share, for net proceeds of $106,060. The warrants expire
at various times through December 4, 2020. During the quarter ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued a total of 2,026,660
shares of common stock. Of the total number of shares issued, 250,000 shares were for proceeds received during the quarter
and 4,962,499 shares to reduce the liability for stock to be issued. During the three months ended December 31, 2018, 250,000
shares were issued and 4,962,499 shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three
months ended March 31, 2019, the Company sold for cash 7,541,663 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 7,541,663
shares at prices ranging from $0.05 per share to $0.50 per share for net proceeds of $165,749. The warrants expire at various
times through March 21, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended March 31, 2019. During the three months
ended March 31, 2019, none of the 7,541,663 were issued and all 7,541,663 shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During
the three months ended June 30, 2019, the Company sold for cash 1,740,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i)
1,740,000 shares at a price of $0.25 per share for net proceeds of $86,934. The warrants expire at various times through June
10, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended June 30, 2019. During the three months ended June 30, 2019,
none of the 1,740,000 shares were issued and all 1,740,000 shares were accrued to stock payable.
|
|
|
●
|
During the three months ended September 30, 2019, the
Company sold for cash 6,337,500 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i) 6,337,500 shares at prices ranging from $0.10
per share to $0.25 per share for net proceeds of $133,495. The warrants expire at various times through September 17, 2021. None
of these shares were issued during the quarter ended September 30, 2019, with all 6,337,500 shares being recorded as stock payable.
There were 52,800 Preferred C shares issued for net proceeds of $45,000 and 70,000 Preferred C shares converted to 3,224,643 Common
shares for the three month period ending September 30, 2019, see Note 6.
|
|
|
●
|
During
the three months ended December 31, 2019, the Company sold for cash 40,675,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase:
(i) 825,000 shares at prices ranging from $0.20 per share to $0.25 per share for net proceeds of $214,510. The warrants expire
at various times through November 1, 2021. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended December 31, 2019, with all
40,675,000 shares being recorded as stock payable. There were 36,300 Preferred C shares converted to 2,370,696 Common shares for
the three month period ending December 31, 2019, see Note 6.
|
|
|
●
|
During
the three months ended March 31, 2020, the Company sold for cash 9,550,000 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase: (i)
3,500,000 shares at prices ranging from $0.05 per share to $1.00 per share for net proceeds of $66,500. The warrants expire at
various times through March 12, 2022. None of these shares were issued during the quarter ended March 31, 2020, with all 9,550,000
shares being recorded as stock payable. There were 53,700 Preferred C shares converted to 6,384,864 Common shares for the three
month period ending March 31, 2020. The Company issued 41,800 preferred shares for net proceeds of $35,000 and another 33,600
preferred shares for which the net proceeds of $30,000 had not been received as of March 31, 2020.
|
The
preceding securities were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), but
qualified for exemption under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. The securities were exempt from registration under Section
4(a)(2) of the Securities Act because the issuance of such securities by the Company did not involve a “public offering,”
as defined in Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act, due to the insubstantial number of persons involved in the transaction, size
of the offering, and manner of the offering and number of securities offered. The Company did not undertake an offering in which
it sold a high number of securities to a high number of investors. In addition, the Investor had the necessary investment intent
as required by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act since they agreed to, and received, the securities bearing a legend stating
that such securities are restricted pursuant to Rule 144 of the Securities Act. This restriction ensures that these securities
would not be immediately redistributed into the market and therefore not be part of a “public offering.” Based on
an analysis of the above factors, the Company has met the requirements to qualify for exemption under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities
Act.
EXHIBIT
INDEX
|
10.6*
|
|
Employment Agreement with Chaya Hendrick dated July 1, 2017
|
|
10-K
|
|
10.06
|
|
10/13/17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.7*
|
|
Issued Patent License and Royalty Agreement dated 9/11/17 with Chaya Hendrick
|
|
10-K
|
|
10.07
|
|
10/13/17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.8*
|
|
Jay Needelman Services Agreement
|
|
10-K/A
|
|
10.01
|
|
10/27/17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9
|
|
Manufacturer’s Representative Agreement
|
|
8-K
|
|
10.01
|
|
12/26/17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.10
|
|
Agreement by and between the Company and Hogier Gartner CIA S.A. dated February 16, 2018
|
|
8-K
|
|
10.1
|
|
2/23/18
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.11*
|
|
2018 Professional/Consultant Stock Compensation Plan
|
|
S-8
|
|
10.1
|
|
7/18/18
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.12
|
|
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between the Company and Geneva Roth Remark Holdings, Inc., dated January 9, 2019
|
|
8-K
|
|
10.1
|
|
1/18/19
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.13
|
|
Equity Financing Agreement dated March 5, 2020 by and between SmartMetric, Inc. and GHS Investments LLC
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.14
|
|
Registration Rights Agreement by and between the Company and GHS Investments LLC, dated March 5, 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.1
|
|
SmartMetric Code of Ethics
|
|
SB-2
|
|
16.1
|
|
9/3/04
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.1
|
|
Subsidiaries of the Registrant
|
|
S-B/A
|
|
21.1
|
|
2/3/05
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.1
|
|
Consent of AMC Auditing, LLC
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.2
|
|
Consent of Prager Metis CPAs LLC
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.3**
|
|
Consent
of Lucosky Brookman LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*
|
Management
contracts or compensation plans or arrangements in which directors or executive officers
are eligible to participate.
|
|
|
**
|
To
be filed by amendment
|
UNDERTAKINGS
The
undersigned registrant hereby undertakes
|
|
1.
|
To
file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment
to this registration statement:
|
|
|
i.
|
To
include any Prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
|
|
|
ii.
|
To
reflect in the Prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the
registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually
or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the
registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume
of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed
that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated
maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of Prospectus filed with the Commission
pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent
no more than 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation
of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement.
|
|
|
iii.
|
To
include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously
disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in
the registration statement;
|
|
|
2.
|
That,
for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such
post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating
to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall
be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
|
|
|
3.
|
To
remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities
being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
|
|
|
4.
|
That,
for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of
1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities: The undersigned
registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant
pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to
sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser
by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a
seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such
purchaser:
|
|
|
i.
|
Any
Preliminary Prospectus or Prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering
required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
|
|
|
ii.
|
Any
free writing Prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned
registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
|
|
|
iii.
|
The
portion of any other free writing Prospectus relating to the offering containing material
information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf
of the undersigned registrant; and
|
|
|
iv.
|
Any
other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant
to the purchaser.
|
|
|
5.
|
That,
for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser:
Each Prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating
to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than
Prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included
in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided,
however, that no statement made in a registration statement or Prospectus that is part
of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated
by reference into the registration statement or Prospectus that is part of the registration
statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first
use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or
Prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately
prior to such date of first use.
|
Insofar
as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to our directors, officers and controlling
persons, we have been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission, such indemnification is against public
policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933 and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification
against such liabilities (other than the payment by us of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person
of the corporation in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling
person in connection with the securities being registered, we will, unless in the opinion of our counsel the matter has been settled
by a controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question of whether such indemnification by us is
against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and will be governed by the final adjudication of
such case.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities
Act of 1933, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto
duly authorized on August 5, 2020.
|
SIGNATURE
|
|
TITLE
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Chaya Hendrick
|
|
President, Chief Executive Officer,
and Chairman of the Board
|
|
Chaya Hendrick
|
|
|
In
accordance with the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement was signed by the following persons
in the capacities and on the dates stated:
|
DATE
|
|
SIGNATURE
|
|
TITLE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 5, 2020
|
|
/s/ Chaya Hendrick
|
|
President, Chief Executive Officer,
and Chairman of the Board
|
|
|
|
Chaya Hendrick
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 5, 2020
|
|
/s/ Jay Needelman
|
|
Chief Financial Officer and Director
|
|
|
|
Jay Needelman
|
|
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 5, 2020
|
|
/s/ Elizabeth Ryba
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
Elizabeth Ryba
|
|
|
II-7
SmartMetric (PK) (USOTC:SMME)
Historical Stock Chart
From Mar 2024 to Apr 2024
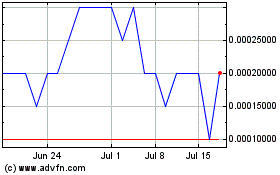
SmartMetric (PK) (USOTC:SMME)
Historical Stock Chart
From Apr 2023 to Apr 2024