Is China's Auto Market Invincible? - Analyst Blog
January 12 2012 - 10:54AM
Zacks
It seems that the Chinese auto market is invincible compared
with the U.S., the other biggest auto market in the world. Despite
posting the slowest growth in vehicle sales in more than decade,
the country saw the largest volume of sales in 2011 compared with
the U.S.
Total vehicle sales in China increased a tad 2.5% to 18.5
million units in 2011 while that in the U.S. rose 10% to 12.8
million units.
The expiration of tax incentives and subsidies, restrictions on
car purchases and higher prices are the main factors that kept auto
sales at bay during the year. However, rising disposable income,
growing domestic demand from lower-tier cities and much lower
vehicles to people ratio have kept the sales volumes in the country
intact.
Auto sales in China had grown at a double-digit pace since 1999,
except in 2008 when the global economic crisis crept in. In 2009,
China overtook the U.S. as the biggest auto market in the world by
sales volumes when the Beijing government introduced a stimulus
package, including tax incentives for small cars with engine sizes
of 1.6 liters or smaller.
However, the incentives were scrapped last year and the Beijing
government imposed quotas on new car registrations in order to
control the traffic gridlock. As a result, new car deliveries
plummeted 56% to 403,500 units in 2011.
According to China Passenger Car Association, the country’s
passenger car sales (excluding buses and heavy trucks) inched up
2.8% to 13.7 million units, sports utility vehicles (SUVs) sales
surged 25% to 1.5 million units and sedans rose 3.6% to 9.6 million
units in 2011. However, sales of vans and minivans fell sharply by
11% to 2.1 million units.
A Global Playground
China has become the playground for global automakers, which
outpaced the local automakers in terms of growth in sales mix.
Local brands in the country accounted for 29.1% of car sales in
2011, which is lower than 2010 by 1.78 percentage point, according
to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM).
However, share of German and U.S. brands in total sales rose 0.77
and 1.91 percentage points, respectively, in 2011 compared with
2010.
General Motors Co. (GM) took the No.1 spot
among the overseas automakers in China by outpacing Toyota
Motor Corp. (TM) in terms of sales volumes during 2011. GM
sold 2.55 million vehicles in its biggest international market
during the year, up 8.3% from 2010.
Meanwhile, Toyota sold 883,000 vehicles in the year, implying
the slowest increase (4%) since 2004, due to the backlash from the
twin disasters in Japan in early 2011 and severe flooding in
Thailand in the second half of the year.
In contrast, GM’s cross-town rival Ford Motor
Co. (F) sold 519,390 vehicles in 2011 through its
Chongqing Changan Automobile Co Ltd joint venture with Changan
Automobile and Japan’s Mazda Motor Corp, and Jiangling Motors Corp.
The sales were up 7% from 2010.
GM operates 11 joint ventures in China, including Shanghai GM
with Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation (SAIC) that occupies
a leading position in the Chinese auto market. Recently, GM
revealed its plan to increase its ownership stake in Shanghai GM by
1 percentage point to 50%.
The automaker employs more than 35,000 people in the country. It
has also expanded its dealership network to 2,700 covering all of
its mainland provinces.
GM expects its overseas sales to improve further in 2012, driven
mainly by China that accounted for 68% of the company’s
international division sales in 2011. The automaker’s market share
in China has increased from 12.7% in 2010 to 13.6% in 2011.
The Tailwinds
China’s automotive industry outlook is promising in 2012 and
beyond. According to CAAM, car sales in 2012 is expected to grow by
9.5%, which is much higher than 2011.
The recent statistical figures also indicate a pent-up demand in
the China’s lower tire cities. According to China’s State
Information Center (SIC), contribution of tier 1 cities to total
car sales declined to 30.7% in 2010 from 35.7% in 2007, while the
ratio in tier 3 cities escalated to 29.1% from 24.7% during the
same period.
Further, vehicles to people ratio in China is considerably
lower. According to World Bank data, there are about 37 vehicles
per 1000 people in China. This compared with 249 vehicles per 1000
people in Brazil and 828 vehicles per 1000 people in the U.S.
Although we are concerned about China’s decreasing GDP growth
(9.7% in the first quarter of 2011 to 9.1% in the third quarter of
the year), the recent monetary and fiscal policies adopted by the
government are likely to ease the fall.
China's inflation rate eased to a 15-month low in December last
year. The Beijing government has reduced banks’ cash reserve ratio
by 50 basis points to 21% in November 2011 for the first time in
three years in order to boost corporate credit lines and support
firms cushioning against both falling domestic and international
demands. Moreover, the government plans to cut interest rates in
March this year.
FORD MOTOR CO (F): Free Stock Analysis Report
GENERAL MOTORS (GM): Free Stock Analysis Report
TOYOTA MOTOR CP (TM): Free Stock Analysis Report
To read this article on Zacks.com click here.
Zacks Investment Research
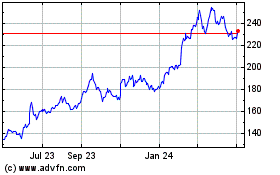
Toyota Motor (NYSE:TM)
Historical Stock Chart
From Sep 2024 to Oct 2024
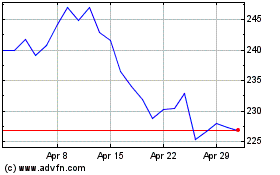
Toyota Motor (NYSE:TM)
Historical Stock Chart
From Oct 2023 to Oct 2024