At MWC 2023, Intel showcases support from
leading operators, OEMs and ISVs for new silicon and software as it
highlights that nearly all vRAN and virtualized network core
deployments run on Intel.
NEWS HIGHLIGHTS
- Intel launched the 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors
with Intel® vRAN Boost, delivering 2 times the capacity gains gen
over gen within the same power envelope1 and up to an additional
20% power savings2 with integrated acceleration, meeting critical
performance, scaling and energy efficiency requirements.
- Developed in collaboration with SK Telecom, Intel announced the
Intel® Infrastructure Power Manager for 5G core reference software,
which provides a 30% average run-time3 CPU power savings.
- Intel announced breakthrough performance by demonstrating the
industry’s first 1 terabit per second4 (Tbps) 5G user plane
function (UPF) workload performance on 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable
processors.
- To further help network operators deliver innovative services
on their platforms at the edge of their networks, Intel showcased
the Intel® Converged Edge Media Platform.
- For network and cloud programmable solutions, Intel continued
the expansion of its Intel Agilex® 7 family of FPGAs and eASIC
structured devices.
For more than a decade, Intel and its partners have been on a
mission to virtualize the world’s networks, from the core to the
RAN (radio access network) and out to the edge, moving them from
fixed-function hardware onto programmable, software-defined
platforms, making networks more agile while driving down their
complexity and cost.
This press release features multimedia. View
the full release here:
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230227005290/en/
At MWC 2023, Intel launched the 4th Gen
Intel Xeon Scalable processors with Intel vRAN Boost, a new
general-purpose chip that fully integrates Layer 1 acceleration
into the Xeon SoC and eliminates the need for external accelerator
cards. Intel vRAN Boost allows operators to consolidate all base
station layers on a common virtualized platform. (Credit: Intel
Corporation)
Now operators are looking to cross the next chasm in delivering
cloud-native functionality for automating, managing and responding
to an increasingly diverse mix of data and services, providing
organizations with the intelligence needed at the edge of their
operations.
More: Intel at 2023 MWC (Press kit) | The Future of RAN
is Virtualized and Open (Sachin Katti editorial)
Today, Intel announced a range of products and solutions driving
this transition and broad industry support from leading operators,
original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and independent software
vendors (ISVs).
“Intel powers the world’s clouds, networks and enterprises,
giving us unique insight on where to place compute and acceleration
along the entire cloud-to-edge continuum and helping our customers
scale to meet user demands,” said Sachin Katti, Intel senior vice
president and general manager of the Network and Edge Group. “The
advancements we’ve made in our 4th Gen Intel Xeon platforms to
double vRAN performance1 while staying within the same power
envelope, to nearly doubling the 5G core UPF throughput5, and to
speed the deployment of a wide range of network, security and
enterprise edge services, makes Intel the platform for our
customers to modernize and monetize their networks of the future,
today.”
vRAN is Here and Nearly All Deployments Run on Intel
The need for high-performance, scalable, flexible and
energy-efficient systems is driving the transformation of mobile
networks from fixed function, hardware-based silicon and
infrastructure to software-based, fully virtualized platforms
running on general-purpose processors. Accelerating the
virtualization of the RAN positions communications service
providers (CoSPs) to meet future requirements while improving RAN
energy efficiency and reducing their total cost of ownership
(TCO).
With expansive industry support from Advantech, Capgemini,
Canonical, Dell Technologies, Ericsson, Hewlett Packard Enterprise,
Mavenir, Quanta Cloud Technology, Rakuten Mobile, Red Hat,
SuperMicro, Telefonica, Verizon, VMware, Vodafone and Wind River,
among others, Intel launched 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors
with Intel vRAN Boost.
By fully integrating vRAN acceleration into the Intel Xeon
system-on-chip (SoC) and eliminating the need for an external
accelerator card, Intel is delivering 2x the capacity gains gen
over gen within the same power envelope1 and up to an additional
20% power savings2 with integrated acceleration, which is above and
beyond the 4th Gen Intel Xeon platform’s already outstanding
performance-per-watt gain. With this combination of processing
innovations and feature integration, Intel expects 4th Gen Xeon
Scalable processors with Intel vRAN Boost will match or better the
performance-per-watt of the best Layer 1 SoC accelerator cards in
the market today6, while delivering the benefits of
software-defined, virtualized networks.
5G Core Networks Run on Software, Delivering Cloud-Native
Agility
At the core of the network, Intel is leading the evolution to
cloud-native, service-based architectures with open solutions for
addressing challenges like performance, TCO, power efficiency,
security and lack of visibility across the network stack. Intel’s
hardware and software solutions will enable 5G core networks to
work harder and smarter at achieving a balance between critical
business and customer requirements for power efficiency,
performance and latency.
To further assist network operators in modernizing their
networks, reducing their total cost of ownership (TCO) at the 5G
core, Intel demonstrated 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors now
enable the industry’s first 1 Tbps of performance for the 5G UPF
workload within a single dual-socket server4, further validated by
Samsung.
Additionally, the new Intel Infrastructure Power Manager for 5G
Core reference software dynamically matches run-time server power
consumption with data traffic without compromising key performance
indicators such as throughput, latency and packet drop.
The software, in tests with Casa Systems, NEC and Nokia,
significantly reduces time-to-market for ISVs and operators by
simplifying access to key capabilities in Intel’s 3rd and 4th Gen
Xeon Scalable processors, including power telemetry, granular power
control states and low-latency frequency change. Operators can use
the reference software to reduce network TCO and accelerate
progress toward net zero emissions goals, realizing millions of
dollars in potential savings and a significant amount of CO2
emissions offset7.
Intel is Setting the Pace at the Edge
Massive growth at the network edge, largely in video services,
will define much of this decade’s competitive landscape for service
providers. The operators’ network edge facilities position them for
a competitive advantage to deliver to this growth, yet it’s
challenging to predict which specific video services will take
off.
Alongside partners Broadpeak, China Mobile, Cloudsky,
Thundersoft and ZTE, Intel showcased the Intel Converged Edge Media
Platform, which delivers multiple video services from a shared,
multitenant architecture and leverages cloud-native scalability to
intelligently respond to shifting requirements.
Video services – such as CDNs (content delivery networks), cloud
gaming, mixed reality and 3D rendering – can be delivered in a
single cloud-native environment supported by both CPU and
GPU-accelerated applications. Operators no longer need to invest in
dedicated resources for services that may not take off. Instead,
they can build on a general-purpose architecture where services
reside together and can leverage cloud-native scalability to
automatically change or resize services to changing needs.
Delivering Customer Choice in Acceleration
Alongside the integrated network acceleration built into 4th Gen
Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Intel is expanding its Agilex 7
FPGAs and eASIC N5X structure ASIC devices for cloud,
communications and embedded applications.
As cloud service providers (CSPs) begin transitioning from 200G
to 400G networks in 2023, with CoSPs to follow suit in 2024, Intel
Agilex 7 FPGA AGI 041 devices will enable next-generation 400G
infrastructure acceleration solutions. AGI 041 devices deliver the
right balance of capacity, power efficiency and performance for the
400G Infrastructure Processing Unit (IPU) and networking
solutions.
Additionally, Intel provides the unique ability to further
optimize cost and power across customers’ 400G infrastructure
solutions through Intel eASIC structured ASICs. For networking
workloads, N5X080 devices are capable of reducing core power by up
to 60% versus an FPGA, while reducing prototyping time by 50%
compared to a traditional ASIC8.
Visit the Intel Booth at MWC 2023 and don’t miss
its technology demo showcases on building 5G networks and
delivering 5G services, featuring voices from industry partners
including Dell, Ericsson, Microsoft and Verizon, among others.
About Intel
Intel (Nasdaq: INTC) is an industry leader, creating
world-changing technology that enables global progress and enriches
lives. Inspired by Moore’s Law, we continuously work to advance the
design and manufacturing of semiconductors to help address our
customers’ greatest challenges. By embedding intelligence in the
cloud, network, edge and every kind of computing device, we unleash
the potential of data to transform business and society for the
better. To learn more about Intel’s innovations, go to
newsroom.intel.com and intel.com.
1 (2x capacity): Estimated as of 12/06/2022 based on 4th Gen
Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor as compared to 3rd generation Intel
Xeon Scalable at similar core count, socket power, and frequency,
using a FlexRAN test scenario. Results may vary. Performance varies
by use, configuration and other factors. … (double PPW): Estimated
as of 12/06/2022 based on 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor
as compared to 3rd generation Intel Xeon Scalable at similar core
count, socket power, and frequency, using a FlexRAN test scenario.
Results may vary. Performance varies by use, configuration and
other factors.
2 Estimated as of 12/06/2022 based on scenario design power
(SDP) analysis on pre-production 4th Generation Intel® Xeon®
Scalable processor with Intel® vRAN Boost and pre-production 4th
Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor with external 5G
accelerator card, at same core count and frequency. Performance and
power varies by use, configuration and other factors.
3 Tested by Intel as of 01/26/23. 1-node, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R)
Gold 6438N CPU, 32 cores, HT On, Turbo Off, Total Memory 512GB
(16x32GB DDR5 4800 MT/s [4000 MT/s]), BIOS
EGSDCRB1.SYS.0090.D03.2210040200, microcode 0x2b0000c0, 2x Intel
E810-2CQDA2 (CVL, Chapman Beach, Total – 4x100G ports), 1x 223.6G
INTEL SSDSC2KB240G8, 1x 745.2G INTEL SSDSC2BA800G3, Ubuntu 22.04
LTS, 5.15.0-27-generic, GCC 7.5.0, DPDK 22.11
4 Tested by Intel as of 01/27/23. 1-node, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R)
Platinum 8470N CPU, 52 cores(104 Total), HT On, Turbo Off, Total
Memory 1024GB (16x64GB DDR5 4800 MT/s [4800 MT/s]), BIOS
EGSDCRB1.SYS.0093.D22.2211170057, microcode 0x2b000130, 6x Intel
E810-2CQDA2 (CVL, Chapman Beach, Total – 6x100G ports), 1x Intel
E810-CQDA2 (CVL, Tacoma Rapids, Total – 2x100G ports) 1x 447.1G
INTEL SSDSCKKB8 , 1x 931.5G CT1000MX500SSD1, Ubuntu 22.04 LTS,
5.15.0-53-generic, UPF(GCC 9.4.0/Clang9.0.0,DPDK 22.07,VPP
20.09)
5 Tested by Intel as of 01/26/23. 1-node, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R)
Gold 6438N CPU, 32 cores, HT On, Turbo Off, Total Memory 512GB
(16x32GB DDR5 4800 MT/s [4000 MT/s]), BIOS
EGSDCRB1.SYS.0090.D03.2210040200, microcode 0x2b0000c0, 2x Intel
E810-2CQDA2 (CVL, Chapman Beach, Total – 4x100G ports), 1x 223.6G
INTEL SSDSC2KB240G8, 1x 745.2G INTEL SSDSC2BA800G3, Ubuntu 22.04
LTS, 5.15.0-27-generic, GCC 7.5.0, DPDK 22.11
6 Performance/power projections are based on Intel estimates and
simulations as of October 2022.
7 Estimated by Intel as of 02/21/23. Calculations: OPEX power
energy cost savings per year: Total number of CPUs X (CPU TDP in KW
x POWER SAVINGS) X PUE X (COST/KWH) X (24x365); CO2 emission
offset:((CPU TDP in KW x POWER SAVINGS) X PUE) / (1 Metric Ton to
KWH conversion); Source of energy prices – US and EU: $0.155/KWH:
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1267500/eu-monthly-wholesale-electricity-price-country/;
Source of Euro to $$ conversion rate: 1 Euro = US $1.06;
https://www.xe.com/currencyconverter/convert/?Amount=1&From=EUR&To=USD;
Source of KWH to Metric Tons of CO2 emission conversion: 1450 KWH =
1 Metric Ton of CO2 emission;
https://www.epa.gov/energy/greenhouse-gasequivalencies-calculator#results;
PUE Source: 1.5 -
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1229367/data-center-average-annual-pueworldwide/
8 Up to 50% lower power at same performance compared to FPGA –
Power estimation completed by Intel July 28, 2020. Power estimated
using Quartus 20.3 for Agilex FPGAs and pre-silicon projections for
N5X devices. FPGA device is Agilex AGF014 and N5X device is N5X047.
Logic and memory clock rates used are 500MHz and toggle rates are
33% for logic and 50% for memory for both devices.
© Intel Corporation. Intel, the Intel logo and other Intel marks
are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other
names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
View source
version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230227005290/en/
Tracy Brawley 1-503-780-2835 tracy.brawley@intel.com
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC)
Historical Stock Chart
From Jun 2024 to Jul 2024
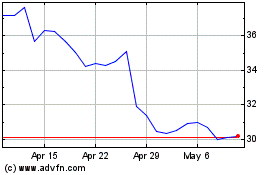
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC)
Historical Stock Chart
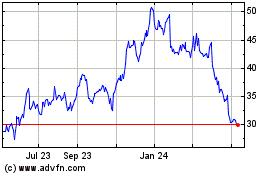
From Jul 2023 to Jul 2024