COMMVAULT SYSTEMS INC00011695612024FYfalseP3Y—P1YP1Y32218217382iso4217:USDxbrli:sharesiso4217:USDxbrli:sharesxbrli:purecvlt:tranchecvlt:segment00011695612023-04-012024-03-3100011695612023-09-3000011695612024-05-0900011695612024-03-3100011695612023-03-310001169561cvlt:SubscriptionMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:SubscriptionMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561cvlt:SubscriptionMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561cvlt:PerpetualLicenseMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:PerpetualLicenseMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561cvlt:PerpetualLicenseMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561cvlt:CustomerSupportServiceMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:CustomerSupportServiceMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561cvlt:CustomerSupportServiceMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:ServiceOtherMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ServiceOtherMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:ServiceOtherMember2021-04-012022-03-3100011695612022-04-012023-03-3100011695612021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-03-3100011695612021-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-03-3100011695612022-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMembercvlt:ArrowMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMembercvlt:ArrowMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMembercvlt:ArrowMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561cvlt:ArrowMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:ArrowMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2024-03-310001169561srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-03-310001169561srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-03-310001169561srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561srt:MinimumMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561srt:MaximumMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:TermBasedSoftwareLicensesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:PerpetualSoftwareLicensesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:ProfessionalServicesOtherMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:ProfessionalServicesEducationServicesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561srt:AmericasMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561srt:AmericasMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561srt:AmericasMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561cvlt:InternationalMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:InternationalMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561cvlt:InternationalMember2021-04-012022-03-3100011695612024-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:TradeAccountsReceivableMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:OtherAssetsMember2023-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueCurrentMember2023-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueNoncurrentMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:TradeAccountsReceivableMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:OtherAssetsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueCurrentMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueNoncurrentMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:TradeAccountsReceivableMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:OtherAssetsMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueCurrentMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:DeferredRevenueNoncurrentMember2024-03-3100011695612025-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember2023-03-310001169561cvlt:CorporateHeadquartersInTintonFallsNJMemberus-gaap:DisposalGroupHeldforsaleNotDiscontinuedOperationsMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:CorporateHeadquartersInTintonFallsNJMemberus-gaap:DisposalGroupHeldforsaleNotDiscontinuedOperationsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2023-03-3100011695612022-06-012022-06-3000011695612023-04-300001169561us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2024-04-180001169561cvlt:A2016IncentivePlanMember2023-08-290001169561cvlt:A2016IncentivePlanMember2023-08-292023-08-290001169561cvlt:A2016IncentivePlanMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestructuringChargesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestructuringChargesMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestructuringChargesMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561cvlt:PerformanceStockUnitsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:PerformanceStockUnitsMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:MaximumMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:CapitalLossCarryforwardMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:ForeignCountryMemberus-gaap:CapitalLossCarryforwardMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:DomesticCountryMemberus-gaap:ResearchMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMemberus-gaap:ResearchMember2024-03-310001169561stpr:NJus-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMemberus-gaap:ResearchMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMemberus-gaap:ResearchMemberstpr:CA2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:DomesticCountryMembercvlt:ForeignTaxCreditsMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:ForeignTaxCreditsMemberus-gaap:ForeignCountryMember2024-03-310001169561country:US2023-04-012024-03-310001169561country:US2022-04-012023-03-310001169561country:US2021-04-012022-03-310001169561us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:NonUsMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:NonUsMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561country:US2024-03-310001169561country:US2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:NonUsMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-03-310001169561cvlt:A2022RestructuringProgramMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-132021-12-130001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-130001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2021-12-132021-12-130001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-04-012023-03-310001169561us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembercvlt:SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-04-012022-03-310001169561cvlt:AppranixIncMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2024-04-152024-04-150001169561cvlt:NicholasAdamoMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:NicholasAdamoMember2024-01-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:NicholasAdamoMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:VivieLeeMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:VivieLeeMember2024-01-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:VivieLeeMember2024-03-310001169561cvlt:AllisonPickensMember2023-04-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:AllisonPickensMember2024-01-012024-03-310001169561cvlt:AllisonPickensMember2024-03-3100011695612024-01-012024-03-31
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☑ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission File Number: 1-33026
Commvault Systems, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 22-3447504 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
1 Commvault Way
Tinton Falls, New Jersey 07724
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code)
(732) 870-4000
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, $0.01 par value | CVLT | The Nasdaq Stock Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | þ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| Emerging growth company | ☐ | | | | | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No þ
As of September 30, 2023, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, the aggregate market value of voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant (based upon the closing price of the common stock as reported by The Nasdaq Stock Market) was approximately $2.9 billion.
As of May 9, 2024, there were 43,401,217 shares of the registrant’s common stock ($0.01 par value) outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Information required by Part III (Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14) is incorporated by reference to portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”), which is expected to be filed not later than 120 days after the registrant’s fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. Except as expressly incorporated by reference, the Proxy Statement shall not be deemed to be part of this report on Form 10-K.
COMMVAULT SYSTEMS, INC.
FORM 10-K
FISCAL YEAR ENDED MARCH 31, 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Page |
| PART I | |
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 1C. | | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| PART II | |
| Item 5. | | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| Item 9C. | | |
| PART III | |
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| PART IV | |
| Item 15. | | |
| Item 16. | | |
| |
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
The discussion throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify these statements by our use of forward-looking words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “expect,” “plan,” “believe,” “predict,” “potential,” “project,” “intend,” “could,” “feel” or similar expressions. In particular, statements regarding our plans, strategies, prospects and expectations regarding our business are forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"). You should be aware that these statements and any other forward-looking statements in this document reflect only our expectations and are not guarantees of performance. These statements involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Many of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions are beyond our control and may cause actual results and performance to differ materially from our expectations. Important factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from our expectations include the risks and uncertainties set forth under the heading “Risk Factors.” Accordingly, you should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date on which the statements were made. We undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
References in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "Commvault," the "Company", "we," "our" or "us" refer to Commvault Systems, Inc., including as the context requires, its direct and indirect subsidiaries.
PART I
Company Overview
Incorporated in Delaware in 1996, Commvault Systems, Inc. provides its customers with a scalable platform that enhances customers' cyber resiliency by protecting their data in a world of increasing threats. We provide these products and services for their data across many types of environments, including on-premises, hybrid and multi-cloud. Our offerings are delivered via self-managed software, software-as-a-service ("SaaS"), integrated appliances, or managed by partners. Customers use our Commvault Cloud platform to protect themselves from threats like ransomware and recover their data efficiently.
With Commvault Cloud, customers have access to business-critical capabilities such as layered defenses to detect and minimize the impact of bad actors; automation to verify clean recovery points; and cloud-native capabilities to dedupe, scale, and as necessary, recover business. We believe in solving hard problems for our customers by enabling them to protect their data in a difficult world. Our comprehensive solutions address the critical aspects of modern cyber resiliency, from data security to data recovery, data governance and compliance in a flexible and scalable platform.
Products
Commvault helps customers protect their data and be cyber resilient in a hybrid multi-cloud environment. Commvault delivers a portfolio of products and services to effectively secure, quickly capture intelligence, and rapidly recover from ransomware attacks or any other threats. Our solutions create an intuitive cyber resilience experience across customer-managed enterprise software and SaaS-delivered cloud native solutions that mitigate data sprawl, facilitate cloud adoption, and help customers modernize and transform their enterprise IT environment.
We do this by offering unified visibility and management across the entire hybrid enterprise so our customers can secure and recover data from any location to any location. Our Commvault Cloud offerings are organized in the following packages – Operational Recovery, Autonomous Recovery and Cyber Recovery.
Operational Recovery includes Commvault’s leading backup and recovery capabilities which can be utilized across hybrid enterprise workloads. It includes features like Zero Trust Architecture and immutable storage to ensure critical data is protected and recoverable. This solution can be delivered as customer-managed software, as SaaS, or a mix of the two to meet the requirements of hybrid enterprises worldwide. It is designed to meet the needs of any size business protecting workloads across all locations, including hybrid environments such as on-premises and multiple cloud providers; physical servers; virtual machines (“VMs”); applications and databases; endpoint devices; and cloud applications. Operational Recovery provides backup, verifiable recovery, and cost-optimized cloud workload mobility, helping to ensure data availability and granular recovery, even across multiple clouds all managed with Commvault’s Command Center.
Autonomous Recovery aims to reduce recovery time, downtime, and costs by bringing automation and validation to Operational Recovery. Designed for automated disaster and cyber recovery use cases, Autonomous Recovery can deliver backup, replication, and disaster recovery for all workloads, on-premises, in the cloud, across multiple clouds, and in hybrid environments. It provides trusted recovery of data and applications, VMs, and containers, along with verifiable recoverability of replicas, cost-optimized cloud data mobility and resilience. Organizations can automatically failover applications to the secondary site in the event of a data incident and continue running without interruption.
Cyber Recovery offers the most comprehensive set of Commvault Cloud capabilities. Building on Operational and Autonomous Recovery Solutions, Cyber Recovery adds data backup and data validation capabilities which help organizations scan for risks, remediate issues, identify compromises in the backup data, and recover clean data at scale. This includes threat scanning to hunt for threats within backup data and cyber deception and threat detection to provide early warning of attacks. This enables organizations to minimize the impact of attacks and aims towards a fast recovery after a cyber incident.
In addition, Commvault provides customers with a variety of industry-leading offerings, including Cleanroom Recovery, HyperScale X, Air Gap Protect and Compliance.
Commvault Cloud’s Cleanroom Recovery is a resilience offering. Traditional isolated on-premises cleanrooms can be expensive to build and maintain, and incident response plans often go untested, increasing an
organization’s risk and recovery time objectives. Our Cleanroom Recovery solution empowers organizations to be ready to recover by providing a clean, isolated, and on-demand recovery location in the cloud, as well as the ability to regularly and proactively test their response plans and recover quickly.
Commvault HyperScale X is an intuitive, easy-to-deploy and scale-out, integrated data protection solution to help enterprises transition from legacy scale-up infrastructures to the hybrid cloud, container and virtualized environments. Its flexible architecture allows customers to get up, run quickly and scale while delivering comprehensive data protection for all workloads, including containers, VMs and databases, from a single, extensible platform. With HyperScale X, customers can leverage the entire Commvault portfolio, giving them access to all the features, functions, and industry-leading integration with applications, databases, public cloud environments, hypervisors, operating systems, NAS systems, and primary storage arrays, wherever the data resides. It is available as a fully integrated appliance or as a reference architecture depending on an organization’s requirements.
Commvault Cloud Air Gap Protect is the “easy button” to adopt secure and scalable cloud storage in minutes, supporting an organization's hybrid cloud strategy without the need for additional cloud expertise. It is an integrated, air-gapped cloud storage target that enables IT organizations to efficiently adopt cloud storage for Operational Recovery, HyperScale X or SaaS to ease digital transformation, save costs, reduce risk and scale. This minimizes IT complexities and allows customers to easily store, isolate, and secure data while providing the foundation for predictable costs and reduced overhead.
Commvault's Compliance is an add-on product that facilitates efficient compliance and aids in ensuring relevant legal data remains unaltered. It provides built-in reporting, auditing, and logging to help ensure data is not modified or deleted for legal and compliance purposes. It reduces the time and costs spent between IT and legal departments to expedite discovery and review.
Professional & Customer Support Services
Commvault offers a wide range of professional and customer support services to complement its product portfolio. We offer multiple levels of service that can be tailored to our customers’ needs.
Our services consist of:
•Real-Time Support. Customers have 24/7 access to support with our support staff available by phone for first responses and to manage resolutions. Our customers also have access to an online support database for help with troubleshooting and operational questions. Innovative use of web-based diagnostic tools provides problem analysis and resolution. Our comprehensive customer support includes “summary of findings” problem analysis, intelligent alerting and troubleshooting assistance.
•Broad Expertise. Our support engineers have extensive knowledge of complex applications, servers and networks. We proactively take ownership of the customer’s problem. We have also developed and maintain a knowledge library of storage systems and software products to further enable our support organization to quickly and effectively resolve customer problems.
•Global Operations. We offer our global customer support from physical locations around the world, which allows us to provide 24/7 support. Our cloud-based support system creates a virtual global support center combining these locations to allow for the fastest possible resolution times for customer incidents. We have designed our support infrastructure to scale with the increasing globalization of our customers.
•Customer Success Options. We offer various enhanced Customer Success options, including Enterprise Success Program ("ESP") offerings, to our software and SaaS customers. Our Customer Success offerings provide resources focused on proactively helping our customers achieve their goals and are aligned to their business initiatives. Our ESP provides additional industry technical experts who provide strategic guidance and advice to ensure our enterprise customers achieve their cyber resiliency objectives. The entire Customer Success program is centered around driving customer adoption, customer satisfaction and quick time to value.
•Technology Consulting Services. Our technical consultants ensure that customers’ data protection environment is designed for optimal results, configured quickly, and is easy to maintain. We offer architecture design; implementation; automation and orchestration; data migration; and health assessment services. In addition, we offer customers staff-augmentation options via resident support engineers to assist with rapid expert deployment and operation of the Commvault portfolio.
•Recovery Services. Commvault Readiness Solutions provide the resources and expertise to quickly accelerate returning to normal business operations through the proper design, implementation, administration, and support of our customers' data protection and cyber resilience environment.
•Education Services. We offer training content for learners at all levels, with basic, intermediate, and expert certifications available. We also provide a selection of self-paced online content for our products in our On-Demand Learning Library.
•Remote Managed Services. Commvault Remote Managed Services provide results-oriented data protection and cyber resilience to customers worldwide. Commvault experts provide secure, reliable, and cost-effective remote monitoring and management of our customers' data protection environment.
Customers
Our current customer base spans thousands of organizations across a variety of sizes, including large global enterprise companies, and small or mid-sized businesses and government agencies. We support customers in a range of industries, including banking, insurance and financial services, government, healthcare, pharmaceuticals and medical services, technology, legal, manufacturing, utilities and energy.
Strategic Relationships
An important element of Commvault’s strategy is to establish partnerships that support development, marketing, selling and implementation of our solutions. We believe that strategic and technology-based relationships with industry leaders are fundamental to our success. We have forged numerous relationships with software, hardware, cloud and cybersecurity partners to enhance our combined capabilities and to create the optimal combination of data and information management applications. We believe this approach enhances our ability to expand our product offerings and customer base and to enter new markets. We have established the following types of strategic relationships:
Alliance and Technology Partners. We maintain strategic sales, marketing and technology relationships with industry leaders to ensure that our products are integrated with, supported by and add value to our partners’ portfolios. Collaboration with these market leaders allows us to provide solutions that enable our customers to improve data and information management efficiency. We also maintain relationships with a broad range of industry operating system, application and infrastructure vendors to verify and demonstrate the interoperability of our portfolio with their equipment and technologies. We believe these partnerships enhance our position in the market and serve as an accelerator to sales.
Distributors, Value-Added Reseller, Systems Integrator, Corporate Reseller and Original Equipment Manufacturer Relationships. These partners either bundle our solutions together with their own products or resell our solutions independently.
To broaden our market coverage, we work closely with our global original equipment manufacturer ("OEM") partners, investing significant time and resources to deliver joint solutions incorporating Commvault solutions. These partners team with our technical, engineering, marketing and sales force to enhance integration, tuning, operational management, implementation and vision for solutions that are designed to meet current and future data protection and cyber resilience needs. Our alliance managers work directly with global OEM partners to design, deliver and support field activities that make it easier for customers to locate, learn about, and purchase these differentiated solutions.
Additionally, we have a non-exclusive distribution agreement with Arrow Enterprise Computing Solutions, Inc. ("Arrow"), a subsidiary of Arrow Electronics, Inc. Arrow's primary role is to enable a more efficient and effective distribution channel for our products and services by managing our reseller partners and leveraging their own industry experience. Sales generated through our distribution agreement with Arrow accounted for 36% of our total revenue in fiscal 2024 and 37% in fiscal 2023.
Service Provider Partners. Our solutions are the cyber resilience platform for many service providers, which provide cloud-based solutions to customers worldwide. As companies of all sizes and markets rapidly adopt cloud infrastructures for cost efficiencies, speed and agility, we remain committed to these strategic relationships to address this growing trend. Customers looking to move IT operations to the cloud depend on service providers to migrate, manage and protect their data and cloud infrastructures. We partner with a broad ecosystem of managed service providers and cloud partners to effectively deliver data protection-as-a-service solutions based on Commvault solutions across geographies, vertical markets and offerings.
Marketplace. During fiscal year 2024, we began selling our solutions via marketplace offerings which enable customers to purchase our solutions through online platforms, such as Microsoft, AWS or Google. The marketplace allows us to publish an offer which an end user can then purchase directly, or through the assistance of a partner.
Competition
The data protection and cyber resilience market is intensely competitive and highly fragmented. The principal competitive factors in our industry include product functionality, performance, integration, platform coverage, scalability, price, global sales infrastructure, technical support, branding and reputation. The ability of major system vendors to bundle solutions is also a significant competitive factor in our industry.
Our primary competitors in the data protection software applications market, each of which has one or more products that compete with a part of or our entire product suite, include Avepoint, Cohesity, Dell-EMC, Druva, IBM, Rubrik, Veeam, and Veritas.
Some of our competitors have greater financial resources and may have the ability to offer their products at lower prices than ours. In addition, some have greater name recognition, longer operating histories, substantially larger technical, sales, marketing and other global resources, and larger installed customer base with broader product offerings. As a result, these competitors can devote greater resources to the development, promotion, sale and support of their products than we can. Refer to our "Risk Factors" below.
Sales and Marketing
We sell our cyber resilience solutions to businesses of all sizes and government agencies. We sell through our global direct sales force and partner channels.
We have a variety of marketing programs designed to create brand awareness and market recognition for our product offerings and sales lead generation. Our marketing efforts include sales campaigns, webinars, active participation at trade shows, technical conferences and seminars; advertising; content development and distribution; public relations; social media; industry analyst relations; publication of technical and educational articles in industry journals; sales training; and preparation of competitive analyses. In addition, our strategic partners augment our marketing and sales campaigns through seminars, trade shows, joint public relations and advertising campaigns. Our customers and strategic partners provide references and recommendations that we often feature in external marketing activities.
Research and Development
Our research and development organization is responsible for the design, development, testing and certification of our cyber resilience platform and solutions. Our engineering efforts support product development across all major operating systems, databases, applications, hyperscalers and network storage devices. A substantial amount of our development effort goes into certification, integration and support of our solutions to ensure interoperability with our strategic partners’ solutions. We have also made substantial investments in the automation of our product test and quality assurance laboratories.
Technology, Intellectual Property and Proprietary Rights
We believe our solutions are a major differentiator versus our competitors’ portfolios. Our Commvault Cloud platform powered by Metallic AI aims to deliver the highest security, most intelligence, and fastest recovery across on-premises, hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Our solutions’ unique features drive the performance, scale, TCO benefits and interoperability of our offerings. Such features include encryption, indexing and immutable recovery. Additional options enable content search and auditing features to support data discovery and compliance.
Our success and ability to compete depend on our continued development and protection of our solutions. We rely primarily on a combination of trade secret, patent, copyright and trademark laws, as well as contractual provisions, to establish and protect our intellectual property rights.
We patent our technical infrastructure and key usability and design concepts. Our software’s unique capabilities are covered by a robust portfolio of patents worldwide. Areas such as cyber resilience, data protection, security, transformation, insights, and compliance and governance, including our SaaS and HyperScale X solutions, are core to our competitive advantage. More than 1,400 patents have been issued to Commvault globally as a result of our strategic patenting. We also have established proprietary trademark rights in markets across the globe, and Commvault owns over 150 worldwide trademark registrations and pending registration applications. Refer to our “Risk Factors” below.
Government Regulations
The global legal environment of technology businesses is evolving rapidly and is often unclear. These topics include data privacy and security, pricing, advertising, taxation, economic sanctions, content regulation and intellectual property ownership and infringement.
We are subject to several local, state, federal and foreign laws and regulations regarding privacy and data protection. Regulators around the world have adopted or proposed limitations on, or requirements regarding, the collection, distribution, use, security and storage of personal information, payment card information or other confidential information of individuals, and the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and many state attorneys general are applying federal and state consumer protection laws to impose standards on the online collection, use and dissemination of data. In the event of a security breach, these laws may subject us to incident response, notice and remediation costs. Failure to safeguard data adequately or to destroy data securely could subject us to regulatory investigations or enforcement actions under applicable data security, unfair practices or consumer protection laws. The scope and interpretation of these laws could change, and the associated burdens and our compliance costs could increase in the future.
We are also subject to global laws and regulations that govern or restrict our business and activities in certain countries and with certain persons, including the U.S. Commerce Department’s Export Administration Regulations and economic and trade sanctions regulations maintained by OFAC, as well as anti-bribery and anti-corruption laws and regulations, including the FCPA and the U.K. Bribery Act.
People
Commvault aims to unlock potential in data, customers and our employees. To accomplish that, our employees are empowered to drive innovation and help our customers—by inspiring one another and working to make what’s already great, even greater—whether that’s product, process or team. As of March 31, 2024, we had 2,882 employees worldwide, of which approximately 40% were in the United States and 60% were located internationally.
We remain committed to providing employees with opportunities and resources that enable them to work successfully and creatively, while also investing in their professional and personal development. Throughout fiscal 2024, our employees participated in over 1,200 training programs, totaling more than 190,000 hours.
Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
At Commvault, we believe that diversity is a business imperative at the heart of our human capital management strategy. We not only drive the ability to be a best-in-class cyber resilience organization but also uphold our value in the marketplace by leading as an employer of choice.
We continue to elevate our employee engagement and belonging efforts which is the foundation of our approach. We have implemented an Employee Resource Group (“ERG”) operating model and have established five ERGs for cross-cultural learning, mentoring and relationship building across employees:
1.Women in Technology (WiT)
2.Multi-Culture
3.PRISM (LGBTQ+ & Allies)
4.VALOR (Veterans & Allies)
5.CapAbilities (Disability inclusion)
We also have two Employee Affinity Groups: Family Support Network and Environmental Group - VAST (Vaulters Advocating Sustainable Technology). Foundational to these engagement initiatives is our Courageous
Conversations program designed to foster difficult conversations in an open, safe and respectful manner. This program has become the hub for all diversity, equity and inclusion issues and related conversations, where employees and senior leaders share courageous life experiences related to bias and social injustice. Since its inception, we have hosted powerful sessions, each virtually, reaching our workforce around the globe.
We continue to be committed to securing the best talent with a concerted effort to expound on and build an inclusive and diverse pipeline of candidates. We are committed to providing an environment that fosters career growth, investing in the development, creativity and aspirational needs of all employees.
Employee Health, Safety and Wellness
Commvault values its people and their contribution to our company. In return for their contribution, we are committed to providing a corporate culture that is focused on the health, safety and well-being of our employees. We take a holistic approach to health and wellness to support the dynamic aspects of our employees’ lives, including their physical, social, emotional, family and financial well-being. We operate in accordance with applicable safety laws and procedures to ensure we provide a safe work environment for all.
Information about our Executive Officers
The following table presents information with respect to our executive officers as of May 9, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Sanjay Mirchandani | | 59 | | President and Chief Executive Officer |
| Gary Merrill | | 49 | | Chief Financial Officer |
Sanjay Mirchandani has served as our President and Chief Executive Officer ("CEO") since February 2019. Prior to joining Commvault, Mr. Mirchandani served from September 2016 to January 2019 as the Chief Executive Officer of Puppet, Inc. (“Puppet”), an Oregon-based IT automation company. Mr. Mirchandani joined Puppet in May 2016 as President and Chief Operating Officer. Mr. Mirchandani brings a wealth of international business experience through his diverse well-rounded career in technology. Before joining Puppet, from October 2013 to April 2016, Mr. Mirchandani served as Corporate Senior Vice President and General Manager of Asia Pacific and Japan at VMware, Inc. and, from June 2006 to October 2013, Mr. Mirchandani held various senior leadership positions at EMC Corporation, including Chief Information Officer and leader of the Global Centers of Excellence. Prior to that, Mr. Mirchandani held various positions at Microsoft Corporation and Arthur Andersen LLP. Mr. Mirchandani has a Master of Business Administration degree from the University of Pittsburgh and a bachelor’s degree in mathematics from Drew University.
Gary Merrill has served as our Chief Financial Officer ("CFO") since July 2022. Prior to his current role, Mr. Merrill served as our Chief of Business Operations from April 2021 until June 2022. He also held the position of Vice President of Operations from April 2019 through March 2021 and from December 2012 to March 2019, served as Chief Accounting Officer. Prior to joining Commvault, Mr. Merrill held accounting management positions with several publicly traded companies. Mr. Merrill began his career with Arthur Anderson LLP in its audit practice. Mr. Merrill obtained his bachelor’s degree in accounting from Elizabethtown College.
Available Information
Our website is located at: www.commvault.com. On the Investor Relations section of the website, we post filings as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with or furnished to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"), including: our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K, our proxy statements related to our annual stockholders’ meetings and any amendment to those reports or statements filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. All such filings are available on the Investor Relations portion of our website free of charge. The contents of our website are not incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K or in any other report, statement or document we file with the SEC.
You should consider each of the following factors as well as the other information in this Annual Report in evaluating our business and our prospects. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently consider immaterial may also impair our business operations. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business and financial results could be harmed. In that case, the trading price of our common stock could decline. You should also refer to the other information set forth in this Annual Report, including our financial statements and the related notes.
Risks Related to Our Business
Our industry is intensely competitive, and many of our competitors have greater financial, technical and sales and marketing resources and larger installed customer bases, which could enable them to compete more effectively than we do.
The cyber resiliency market is intensely competitive, highly fragmented and characterized by rapidly changing technology and evolving standards, changing customer requirements and frequent new product introductions. Competitors vary in size and in the scope and breadth of the products and services offered.
The principal competitive factors in our industry include product functionality and integration, platform coverage, ability to scale, price, worldwide sales infrastructure, global technical support, brand recognition and reputation. If we are unable to address these factors, our competitive position could weaken and we could experience a decline in revenues that could adversely affect our business.
It is also costly and time-consuming to change data management systems. Most of our new customers have installed data management systems, which gives an incumbent competitor an advantage in retaining a customer because the incumbent already understands the network infrastructure, user demands and information technology needs of the customer, and because some customers are reluctant to invest the time and money necessary to change vendors.
New competitors entering our markets can have a negative impact on our competitive positioning. In addition, we expect to encounter new competitors as we enter new markets. Furthermore, many of our existing competitors are broadening their operating systems platform coverage. We also expect increased competition from OEMs, including those we partner with, and from systems and network management companies, especially those that have historically focused on the mainframe computer market and have been making acquisitions and broadening their efforts to include data protection products. We expect that competition will increase as a result of future industry consolidation. Increased competition could harm our business by causing, among other things, price reductions of our products, reduced profitability and loss of market share.
We rely on indirect sales channels, such as value-added resellers, systems integrators, corporate resellers, distributors, OEMs, and marketplaces for the distribution of our solutions, and the failure of these channels to effectively sell our solutions could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
We rely significantly on our value-added resellers, systems integrators and corporate resellers, which we collectively refer to as resellers, for the marketing and distribution of our products and services. Resellers are our most significant distribution channel. However, our agreements with resellers are generally not exclusive, are generally renewable annually, typically do not contain minimum sales requirements and in many cases may be terminated by either party without cause. Many of our resellers carry data protection solutions that compete with ours. These resellers may give a higher priority to other software or SaaS applications, including those of our competitors, or may not continue to carry data protection solutions. If a number of resellers were to discontinue or reduce the sales of our products, or were to promote our competitors’ products in lieu of our own, it could have a material adverse effect on our future revenues. Events or occurrences of this nature could seriously harm our sales and results of operations. If we fail to manage our resellers successfully, there may be conflicts between resellers or they could fail to perform as we anticipate, including required compliance with the terms and obligations of our agreement, either of which could reduce our sales or impact our reputation in the market. In addition, we expect that a portion of our sales growth will depend upon our ability to identify and attract new resellers. Our competitors also use reseller arrangements and may be more successful in attracting reseller partners and could enter into exclusive relationships with resellers that make it difficult to expand our reseller network. Any failure on our part to maintain and/or expand our network of resellers could impair our ability to grow revenues in the future.
Some of our resellers may, either independently or jointly with our competitors, develop and market solutions that compete with our offerings. If this were to occur, these resellers might discontinue marketing and distributing our solutions. In addition, these resellers would have an advantage over us when marketing their competing products and related services because of their existing customer relationships. The occurrence of any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
In addition, we have a non-exclusive distribution agreement with Arrow pursuant to which Arrow’s primary role is to enable a more efficient and effective distribution channel for our solutions by managing our resellers and leveraging their own industry experience. Arrow accounted for approximately 36% of our total revenues for fiscal 2024 and 37% of our total revenues in both fiscal 2023 and fiscal 2022. If Arrow were to discontinue or reduce the sales of our solutions or if our agreement with Arrow was terminated, and if we were unable to take back the management of our reseller channel or find another distributor to replace Arrow, there could be a material adverse effect on our future business.
Our OEMs sell and integrate our solutions which represents a material portion of our revenues. We have no control over the shipping dates or volumes of systems these OEMs sell and they have no obligation to sell systems incorporating our solutions. They also have no obligation to recommend or offer our solutions exclusively or at all. They have no minimum sales requirements and can terminate our relationship at any time. These OEMs also could choose to develop their own data protection solutions. Our OEM partners compete with one another. If one of our OEM partners views our arrangement with another OEM as competing, it may decide to stop doing business with us. Any material decrease in the volume of sales generated by OEMs could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations in future periods.
We also sell our solutions via marketplace offerings which enable customers to purchase our solutions through online platforms, typically hosted by a cloud provider. The marketplace allows us to publish an offer which an end user can then purchase directly, or through the assistance of a partner. Similar to our resellers and OEMs, marketplace providers have no obligation to sell or recommend our solutions or offer our solutions exclusively or at all. Sales through the marketplace have not been material to date; however, we anticipate an increase in revenue through this channel. Failure to effectively compete in the marketplace could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations in future periods.
If the cost for maintenance and support agreements, or our term-based subscription licenses and SaaS arrangements, with our customers is not competitive in the market or if our customers do not renew their agreements either at all, or on terms that are less favorable to us, our business and financial performance might be adversely impacted.
Most of our support and maintenance agreements are for a one-year term and thereafter, we pursue renewal thereof. Historically, such renewals have represented a significant portion of our total revenue. If our customers do not renew their annual maintenance and support agreements either at all, or on terms that are less favorable to us, our business and financial performance might be adversely impacted.
Additionally, a significant amount of our revenues are from term-based software license and SaaS arrangements. The arrangements are typically one to three years in duration. If at the end of the initial term, customers elect to not renew, or they renew terms that are less favorable to us, our business and financial performance might be adversely impacted.
In periods of volatile economic conditions, our exposure to credit risk and payment delinquencies on our accounts receivable significantly increases.
Our outstanding accounts receivables are generally not secured. Our standard terms and conditions permit payment within a specified number of days following the receipt of our solution. Volatile economic conditions, including those related to the wars in Israel and Ukraine and the global response to the conflicts, the COVID-19 pandemic and its variants, or the financial instability of banking institutions could result in our customers and resellers facing liquidity concerns leading to them not being able to satisfy their payment obligations to us, which would have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, operating results and cash flows.
In addition, we have transitioned a more significant percentage of our revenue to subscription, or term-based, arrangements. In these arrangements, our customers may pay for solutions over a period of several years. Due to the potential for extended period of collection, we may be exposed to more significant credit risk.
We develop solutions that interoperate with certain products, operating systems and hardware developed by others, and if the developers of those operating systems and hardware do not cooperate with us or we are unable to devote the necessary resources so that our solutions interoperate with those systems, our development efforts may be delayed or foreclosed and our business and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Our solutions operate primarily on the Windows, UNIX, Linux and Novell Netware operating systems; used in conjunction with Microsoft SQL; and on hardware devices of numerous manufacturers. When new or updated versions of these operating systems, solution applications, and hardware devices are introduced, it is often necessary for us to develop updated versions of our solution applications so that they interoperate properly with these systems and devices. We may not accomplish these development efforts quickly or cost-effectively, and it is not clear what the relative growth rates of these operating systems and hardware will be.
We encounter long sales and implementation cycles, particularly for our larger customers, which could have an adverse effect on the size, timing and predictability of our revenues.
Potential or existing customers, particularly larger enterprise customers, generally commit significant resources to an evaluation of available solutions and require us to expend substantial time, effort and money educating them as to the value of our solutions. Sales often require an extensive education and marketing effort.
We could expend significant funds and resources during a sales cycle and ultimately fail to win the customer. Our sales cycle for all of our products and services is subject to significant risks and delays over which we have little or no control, including:
•our customers’ budgetary constraints;
•the timing of our customers’ budget cycles and approval processes;
•our customers’ willingness to replace their current solutions;
•our need to educate potential customers about the uses and benefits of our solutions; and
•the timing of the expiration of our customers’ current agreements for similar solutions.
If our sales cycles lengthen unexpectedly, they could adversely affect the timing of our revenues or increase costs, which may cause fluctuations in our quarterly revenues and results of operations. Finally, if we are unsuccessful in closing sales of our solutions after spending significant funds and management resources, our operating margins and results of operations could be adversely impacted, and the price of our common stock could decline.
We depend on growth in the data protection and cyber resiliency market, and lack of growth or contraction in this market could have a material adverse effect on our sales and financial condition.
Demand for data protection and cyber resilience solutions is linked to growth in the amount of data generated and stored, demand for data retention and management (whether as a result of regulatory requirements or otherwise) demand for and adoption of new backup devices and networking technologies, and ability to respond to and recover from data breaches in a secure environment. Because our solutions are concentrated within the data protection and cyber resiliency market, if the demand for backup and data protection solutions devices declines, our sales, profitability and financial condition would be materially adversely affected.
Furthermore, the data protection and cyber resiliency market is dynamic and evolving. Our future financial performance will depend in large part on continued growth in the number of organizations adopting data protection and cyber resilience solutions for their environments. The market for data protection and cyber resilience solutions may not continue to grow at historic rates, or at all. If this market fails to grow or grows more slowly than we currently anticipate, our sales and profitability could be adversely affected.
Our SaaS offerings require costly and continual infrastructure investments and if these investments do not yield the expected return, our business and financial performance might be adversely impacted.
In order to deliver our SaaS offerings via a cloud-based deployment, we have made and will continue to make capital investments and incur substantial costs to implement and maintain this business model. In addition, as we look to deliver new or different cloud-based services, we are making significant technology investments to deliver new capabilities and advance our software to deliver cloud-native customer experiences. Our revenues
related to SaaS offerings have increased in recent years. If there is a reduction in demand for these services caused by a lack of customer acceptance, technological challenges, weakening economic or political conditions, security or privacy concerns, inability to properly manage such services, competing technologies and products, decreases in corporate spending or otherwise, our financial results and competitive position could suffer. If these investments do not yield the expected return, or we are unable to decrease the cost of delivering our cloud services, our gross margins, overall financial results, business model and competitive position could suffer.
We rely on third-party hosting providers to deliver our SaaS offerings. Therefore, any disruption or interference with our use of these services could adversely affect our business.
Our use of third-party hosting facilities requires us to rely on the functionality and availability of the third parties’ services, as well as their data security, which despite our due diligence, may be or become inadequate. Our continued growth depends in part on the ability of our existing and potential customers to use and access our cloud services or our website to download our software within an acceptable amount of time. Third-party service providers operate platforms that we access, and we are vulnerable to their service interruptions. We may experience interruptions, delays, and outages in service and availability due to problems with our third-party service providers’ infrastructure. This infrastructure’s lack of availability could be due to many potential causes, including technical failures, power shortages, natural disasters, fraud, terrorism, or security attacks that we cannot predict or prevent. Such outages could trigger our service level agreements and the issuance of credits to our customers, which may impact our business and consolidated financial statements.
If we are unable to renew our agreements with our cloud service providers on commercially reasonable terms, an agreement is prematurely terminated, or we need to add new cloud services providers to increase capacity and uptime, we could experience interruptions, downtime, delays, and additional expenses related to transferring to and providing support for these new platforms. Any of the above circumstances or events may harm our reputation and brand, reduce our platforms’ availability or usage, and impair our ability to attract new users, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We sell a backup appliance which integrates our solution with hardware. If we fail to accurately predict manufacturing requirements and manage our supply chain we could incur additional costs or experience manufacturing delays that could harm our business.
We generally provide forecasts of our requirements to our supply chain partners on a rolling basis. If our forecast exceeds our actual requirements, a supply chain partner may assess additional charges or we may incur costs for excess inventory they hold, each of which could negatively affect our gross margins. If our forecast is less than our actual requirements, the applicable supply chain partner may have insufficient time or components to produce or fulfill our solutions' requirements, which could delay or interrupt manufacturing of our products or fulfillment of orders for our solutions, and result in delays in shipments, customer dissatisfaction, and deferral or loss of revenue. If we fail to accurately predict our requirements, we may be unable to fulfill those orders or we may be required to record charges for excess inventory. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our complex solutions may contain undetected errors, which could adversely affect not only their performance but also our reputation and the acceptance of our solutions in the market.
Our complex solutions may contain undetected errors or failures, especially when they are made generally available or new versions are released. Despite extensive testing by us and customers, we have discovered errors in our solutions in the past and will do so in the future. As a result of past discovered errors, we experienced delays and lost revenues while we corrected those solutions. In addition, customers in the past have brought to our attention “bugs” in our software created by the customers’ unique operating environments, which are often characterized by a wide variety of both standard and non-standard configurations that make pre-release testing very difficult and time consuming. Although we have been able to fix these bugs in the past, we may not always be able to do so. Our solutions may also be subject to intentional attacks by viruses that seek to take advantage of these bugs, errors or other weaknesses. Any of these events may result in the loss of, or delay in, market acceptance of our solutions or damage to our reputation, which would seriously harm our sales, results of operations and financial condition.
Incorrect or improper implementation or use of our data security solutions could result in customer dissatisfaction and harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our products are deployed by our customers and partners in a wide variety of IT infrastructures, including large-scale, complex technology environments, and we believe our future success will depend, at least in part, on our ability to support such deployments. Implementations of our products may be technically complicated, and it may not be easy to maximize the value of our products without proper implementation, training, and support. Some of our customers have experienced difficulties implementing our products in the past and may experience implementation difficulties in the future. If our customers and partners are unable to implement our products successfully, perceptions of our products may be impaired, our reputation and brand may suffer, or customers may choose not to renew their subscriptions or purchase additional products from us.
Any failure by customers or partners to appropriately implement our products could result in customer dissatisfaction, impact the perceived reliability of our products, result in negative press coverage, negatively affect our reputation, and harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may not receive significant revenues from our current research and development efforts for several years, if at all.
Developing software and technology is expensive, and the investment in product development may involve a long payback cycle. Our research and development expenses were $132.3 million, or 16% of our total revenues in fiscal 2024, $141.8 million, or 18% of our total revenues in fiscal 2023 and $153.6 million, or 20% of our total revenues in fiscal 2022. We believe that we must continue to dedicate a significant amount of resources to our research and development efforts to maintain our competitive position. However, we may not recognize significant revenues from these investments for several years, if at all.
Our ability to sell our solutions is highly dependent on the quality of our customer support and professional services, and failure to offer high quality customer support and professional services would have a material adverse effect on our sales and results of operations.
Our services include the assessment and design of solutions to meet our customers’ storage management requirements and the efficient installation and deployment of our software applications based on specified business objectives. Further, once our software applications are deployed, our customers depend on us to resolve issues relating to our software applications. A high level of service is critical for the successful marketing and sale of our software. If we or our partners do not effectively install or deploy our applications, or succeed in helping our customers quickly resolve post-deployment issues, it would adversely affect our ability to sell software products to existing customers and could harm our reputation with prospective customers. As a result, our failure to maintain high quality support and professional services would have a material adverse effect on our sales of software applications and results of operations.
We implemented a restructuring plan in fiscal 2024, which we cannot guarantee will achieve its intended results.
In fiscal 2024, we initiated a restructuring plan to enhance customer satisfaction, optimize operational efficiency, and align our customer experience functions with our strategic goals. We cannot guarantee the restructuring plan will achieve its intended results. Risks associated with this restructuring plan also include additional unexpected costs, adverse effects on employee morale and the failure to meet operation and growth targets due to the loss of key employees, any of which may impair our ability to achieve anticipated results of operations or otherwise harm our business.
We are subject to several local, state, federal and foreign laws and regulations regarding privacy and data protection, and any actual or perceived failure by us to comply with such laws and regulations could adversely affect our business.
We are currently subject, and may become further subject, to local, state, federal and foreign laws and regulations regarding the privacy and protection of personal data or other potentially sensitive information. In the United States, federal, state, and local governments have enacted numerous data privacy security laws, including data breach notification laws, data privacy laws, consumer protection laws, and other similar laws. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018, as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act of 2020 (collectively, the "CCPA"), imposes obligations on certain businesses to provide specific disclosures in privacy notices and grants California residents certain rights related to their personal data. The CCPA imposes statutory fines for noncompliance (up to $7,500 per violation). Other states have enacted or proposed similar laws. These developments may increase legal risk and compliance costs for us and our customers.
Outside the United States, an increasing number of laws, regulations, and industry standards govern data privacy and security. For example, the European Union’s ("E.U.") General Data Protection Regulation ("E.U. GDPR"), and the United Kingdom’s ("U.K.") GDPR ("U.K. GDPR"), impose strict requirements for processing the personal data of individuals. Violations of these obligations carry significant potential consequences. For example, under the E.U. GDPR, government regulators may impose temporary or definitive bans on processing, as well as fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the annual global revenue, whichever is greater. Additionally, new and emerging data privacy regimes may be applicable in Asia, including India's Digital Personal Data Protection Act, China's Personal Information Protection Law, Japan's Act on the Protection of Personal Information, and Singapore's Personal Data Protection Act.
In addition, as a technology provider, our customers expect us to demonstrate compliance with current data privacy laws and further make contractual commitments and implement processes to enable the customer to comply with their own obligations under data privacy laws, and our actual or perceived inability to do so may adversely impact sales of our products and services, particularly to customers in highly regulated industries.
Our actual or perceived failure to comply with laws, regulations, contractual commitments, or other actual or asserted obligations, including certain industry standards, regarding personal information, or other confidential information of individuals could lead to costly legal action, brand and reputational damage, significant liability, inability to process data, and decreased demand for our services, which could adversely affect our business. In addition, any security breach that results in the release of, or unauthorized access to, personal information, or other confidential information of individuals could subject us to incident response, notice and remediation costs. Failure to safeguard data adequately or to destroy data securely could subject us to regulatory investigations or enforcement actions under applicable data security, unfair practices or consumer protection laws which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results. The scope and interpretation of these laws could change and the associated burdens and our compliance costs could increase in the future.
A portion of our revenue is generated by sales to government entities, which are subject to a number of challenges and risks.
Sales to global federal, state, and local governmental agencies account for a portion of our revenue, and we may in the future increase sales to government entities. This customer base experiences budgetary constraints or shifts in spending priorities regularly which may adversely affect sales of our solutions to government entities.
Selling to government entities can be highly competitive, expensive and time consuming, often requiring significant upfront time and expense without any assurance that we will successfully sell our solutions. Government entities may require contract terms that differ from our standard terms and conditions including termination rights favorable for the customer, audit rights, and maintenance of certain security clearances for facilities and employees which can entail administrative time and effort resulting in costs and delays. Government demand for our solutions may be more volatile as they are affected by stringent regulations, public sector budgetary cycles, funding authorizations, and the potential for funding reductions or delays, making the time to close such transactions more difficult to predict.
Changes in senior management or key personnel could cause disruption in the Company and have a material effect on our business.
We have had, and could have, changes in senior management which could be disruptive to management and operations of the Company and could have a material effect on our business, operating results and financial conditions. Turnover at the senior management level may create instability within the Company, which could impede the Company’s day-to-day operations. Such instability could impede our ability to fully implement our business plan and growth strategy, which would harm our business and prospects.
We rely on our key personnel to execute our existing business operations and identify and pursue new growth opportunities. The loss of key employees could result in significant disruptions to our business, and the integration and training of replacement personnel could be costly, time consuming, cause additional disruptions to our business and be unsuccessful.
We have engaged, and may continue to engage, in strategic acquisitions or transactions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Acquisitions involve a number of risks, including diversion of management’s attention, ability to finance the acquisition on attractive terms, failure to retain key personnel or valuable customers, legal liabilities, the need to amortize acquired intangible assets, and intellectual property ownership and infringement risks, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Any additional future acquisitions may also result in the incurrence of indebtedness or the issuance of additional equity securities.
We could also experience financial or other setbacks if transactions encounter unanticipated problems, including problems related to governmental approval, execution, integration or underperformance relative to prior expectations. Acquisitions may not result in long-term benefits to us or we may not be able to further develop the acquired business in the manner we anticipated.
Following the completion of acquisitions, we may have to rely on the seller to provide administrative and other support, including financial reporting and internal controls, and other transition services to the acquired business for a period of time. There can be no assurance that the seller will do so in a manner that is acceptable to us.
Actual or threatened public health crises could adversely affect our business in a material way.
As a global company, with employees and customers located around the world in a variety of industries, our performance may be impacted by public health crises, including the COVID-19 pandemic and its variants, which has caused global economic uncertainty. The emergence of a public health threat could pose the risk that our employees, partners, and customers may be prevented from conducting business activities at full capacity for an indefinite period, due to the spread of the disease or suggested or mandated by governmental authorities. Moreover, these conditions can affect the rate of information technology spending and may adversely affect our customers’ willingness to purchase our solutions, delay prospective customers’ purchasing decisions, reduce the value or duration of their contracts, cause our customers to request concessions including extended payment terms or better pricing, or affect attrition rates, all of which could adversely affect our future sales and operating results. The global spread of COVID-19 has created significant uncertainty, and economic disruption. We have undertaken measures to protect our employees, partners, and customers, including allowing our employees to work remotely; however, there can be no assurance that these measures will be sufficient or that we can implement them without adversely affecting our business operations.
Borrowing against our revolving credit facility could adversely affect our operations and financial results.
We have a $100 million revolving credit facility. As of March 31, 2024, there were no borrowings under the credit facility. If we were to borrow substantially against this facility the indebtedness could have adverse consequences, including:
•requiring us to devote a portion of our cash flow from operations to payments of indebtedness, which would reduce the availability of cash flow to fund working capital requirements, capital expenditures and other general purposes;
•limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, general adverse economic conditions or changes in our business and the industry in which we operate in;
•placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt; and
•limiting our ability to fund potential acquisitions.
The credit facility also contains financial maintenance covenants, including a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio, and customary events of defaults. Failure to comply with these covenants could result in an event of default, which, if not cured or waived, could accelerate our repayment obligations. For further discussion on our revolving credit facility, see Note 16 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Risks Related to our International Operations
If we are unable to effectively manage certain risks and challenges related to our India operations, our business could be harmed.
Our India operations are a key factor to our success. We believe that our significant presence in India provides certain important advantages for our business, such as direct access to a large pool of skilled professionals and assistance in growing our business internationally. However, it also creates certain risks that we must effectively manage. As of March 31, 2024, we had 1,037 employees located in India. Wage costs differentiate depending on regions throughout the world. Wages in India are increasing at a faster rate than in the many other countries, including the United States. These increases could result in us incurring increased costs for technical professionals and reduced margins. There is intense competition in India for skilled technical professionals, and we expect such competition to increase. As a result, we may be unable to cost-effectively retain our current employee base in India or hire additional new talent. In addition, India has experienced significant inflation, low growth in gross domestic product and shortages of foreign exchange. India also has experienced civil unrest and has been involved in conflicts with neighboring countries. The occurrence of any of these circumstances could result in disruptions to our India operations, which, if continued for an extended period of time, could have a material adverse effect on our business.
In recent years, India’s government has adopted policies that are designed to promote foreign investment, including significant tax incentives, relaxation of regulatory restrictions, liberalized import and export duties and preferential rules on foreign investment and repatriations. These policies may not continue. If we are unable to effectively manage any of the foregoing risks related to our India operations, our development efforts could be impaired, our growth could be slowed and our results of operations could be negatively impacted.
Volatility in the global economy could adversely impact our continued growth, results of operations and our ability to forecast future business.
As a global company, we have become increasingly subject to the risks arising from adverse changes in domestic and global economic and political conditions. Uncertainty in the macroeconomic environment and associated global economic conditions have resulted in volatility in credit, equity, debt and foreign currency markets.
These global economic conditions can result in slower economic activity, decreased consumer confidence, reduced corporate profits and capital spending, inflation, adverse business conditions and liquidity concerns. There has also been increased volatility in foreign exchange markets. These factors make it difficult for our customers, our vendors and us to accurately forecast and plan future business activities. These factors could cause customers to slow or defer spending on our solutions, which would delay and lengthen sales cycles and negatively affect our results of operations. If such conditions deteriorate or if the pace of economic recovery is slower or more uneven, our results of operations could be adversely affected, we may not be able to sustain the growth rates we have experienced recently, and we could fail to meet the expectations of stock analysts and investors, which could cause the price of our common stock to decline.
We continue to invest in our business internationally where there may be significant risks with overseas investments and growth prospects. Increased volatility or declines in the credit, equity, debt and foreign currency markets in these regions could cause delays in or cancellations of orders. Deterioration of economic conditions in the countries in which we do business could also cause slower or impaired collections on accounts receivable.
We may experience fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates that could adversely impact our results of operations.
Our international sales are generally denominated in foreign currencies, and this revenue could be materially affected by currency fluctuations. Our primary exposure is to fluctuations in exchange rates for the U.S. dollar versus the Euro and, to a lesser extent, the Australian dollar, British pound sterling, Canadian dollar, Chinese yuan, Indian rupee, Korean won and Singapore dollar. Changes in currency exchange rates could adversely affect our reported revenues and could require us to reduce our prices to remain competitive in foreign markets, which could also have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. An unfavorable change in the exchange rate of foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar would result in lower revenues when translated into U.S. dollars, although operating expenditures would be lower as well.
In recent fiscal years, we have selectively hedged our exposure to changes in foreign currency exchange rates on the balance sheet. In the future, we may enter into additional foreign currency-based hedging contracts to
reduce our exposure to significant fluctuations in currency exchange rates on the balance sheet, although there can be no assurances that we will do so. However, as our international operations grow, or if dramatic fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates continue or increase or if our hedging strategies become ineffective, the effect of changes in the foreign currency exchange rates could become material to revenue, operating expenses, and income.
Our international sales and operations are subject to factors that could have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
We have significant sales and services operations outside the United States and derive a substantial portion of our revenues from these operations. We generated approximately 48% and 47% of our revenues from outside the United States in fiscal 2024 and fiscal 2023, respectively. International revenue increased 9% in fiscal 2024 compared to fiscal 2023. Expansion of our international operations will require a significant amount of attention from our management and substantial financial resources and might require us to add qualified management in these markets.
In addition to facing risks similar to the risks faced by our domestic operations, our international operations are also subject to risks related to the differing legal, political, social and regulatory requirements and economic conditions of many countries, including:
•adverse effects in economic conditions in the countries in which we operate related specifically to the wars in Israel and Ukraine, the COVID-19 pandemic and the governmental regulations put in place as a result of the virus, and the financial instability of banking institutions;
•difficulties in staffing and managing our international operations;
•foreign countries may impose additional withholding taxes or otherwise tax our foreign income, impose tariffs or adopt other restrictions on foreign trade or investment, including currency exchange controls;
•difficulties in coordinating the activities of our geographically dispersed and culturally diverse operations;
•general economic conditions in the countries in which we operate, including seasonal reductions in business activity in the summer months in Europe and in other periods in other countries, could have an adverse effect on our earnings from operations in those countries;
•imposition of, or unexpected adverse changes in, foreign laws or regulatory requirements may occur, including those pertaining to sanctions, export restrictions, privacy and data protection, trade and employment restrictions and intellectual property protections;
•longer payment cycles for sales in foreign countries and difficulties in collecting accounts receivable;
•competition from local suppliers;
•greater risk of a failure of our employees and partners to comply with both U.S. and foreign laws, including antitrust regulations, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, the U.K. Bribery Act of 2010, and any trade regulations ensuring fair trade practices;
•costs and delays associated with developing solutions in multiple languages; and
•political unrest, war or acts of terrorism.
Our business in emerging markets requires us to respond to rapid changes in market conditions in those markets. Our overall success in international markets depends, in part, upon our ability to succeed in differing legal, regulatory, economic, social and political conditions. We may not continue to succeed in developing and implementing policies and strategies that will be effective in each location where we do business. The occurrence of any of the foregoing factors may have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Risks Related to Technology and Security
We may be subject to IT system failures, network disruptions, cybersecurity incidents and breaches in data security.
IT system failures, network disruptions, cybersecurity incidents and breaches of data security could disrupt our operations by causing delays or cancellation of customer orders, impeding the delivery of our solutions, negatively affecting customer support or professional services, preventing the processing of transactions and reporting of financial results, and disturbing our enterprise resource planning system. IT system failures, network disruptions, cybersecurity incidents and breaches of data security could also result in the unintentional disclosure of customer or our information as well as damage our reputation. There can be no assurance that a system failure, network disruption, cybersecurity incident or data security breach will not have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and operating results. Cybersecurity breaches or incidents and other exploited security vulnerabilities could subject us to significant costs and third-party liabilities, result in improper disclosure of data and violations of applicable privacy and other laws, require us to change our business practices, cause us to incur significant remediation costs, lead to loss of customer confidence in, or decreased use of our products and services, damage our reputation, divert the attention of management from the operation of our business, result in significant compensation or contractual penalties from us to our customers and their business partners as a result of losses to or claims by them, or expose us to litigation, regulatory investigations, and significant fines and penalties.
Bad actors regularly attempt to gain unauthorized access to our IT systems, and many such attempts are increasingly sophisticated. These attempts, which might be related to industrial, corporate or other espionage, criminal hackers or state-sponsored intrusions, include trying to covertly introduce malware or ransomware to our environments and impersonating authorized users.
Third-party service providers that we may rely on to back up and process our confidential information may also be subject to similar threats. Such threats could result in the misappropriation, theft, misuse, disclosure, loss or destruction of the technology, intellectual property, or the proprietary, confidential or personal information, of us or our employees, customers, licensees, suppliers or partners, as well as damage to or disruptions in our IT systems. These threats are constantly evolving, increasing the difficulty of successfully defending against them or implementing adequate preventative measures. We seek to detect and investigate all cybersecurity incidents and to prevent their recurrence, but attempts to gain unauthorized access to our IT systems or other attacks may be successful, and in some cases, we might be unaware of an incident or its magnitude and effects.
In addition, any failure to successfully implement new information systems and technologies, or improvements or upgrades to existing information systems and technologies in a timely manner could adversely impact our business, internal controls, results of operations, and financial condition.
We may not be successful in our initiatives that utilize AI, which could adversely affect our business, reputation, or financial results.
There are significant risks involved in utilizing AI and no assurance can be provided that such usage will enhance our business or assist our business in being more efficient or profitable. Known risks currently include accuracy, bias, toxicity, intellectual property infringement or misappropriation, data privacy, and cybersecurity and data provenance. In addition, AI may have errors or inadequacies that are not easily detectable. For example, certain AI may utilize historical data in its analytics. To the extent that such historical data is not indicative of the current or future conditions, or models fail to filter biases in the underlying data or collection methods, such AI usage may lead us to make determinations on behalf of our business, recommendations to our clients, or developments to our products and services, in each case, that may have an adverse effect on our business and financial results. If AI models are incorrectly designed or the data used to train them is overbroad, incomplete, inadequate or biased in some way, our use may inadvertently reduce our efficiency or cause unintentional or unexpected outputs that are incorrect, do not match our business goals, do not comply with our policies or interfere with the performance of our products and services, business and reputation.
AI is a complex and rapidly evolving regulatory landscape. The use of AI may increase intellectual property, cybersecurity and data protection, operational and technological risks, and our related efforts may result in new or enhanced governmental or regulatory scrutiny, litigation, ethical concerns, or other complications that could adversely affect our business, reputation, or financial results or subject us to legal liability. In particular, technologies underlying AI and their use cases are subject to a variety of laws, including intellectual property, cybersecurity and data protection, consumer protection and equal opportunity laws. If we do not have sufficient rights to use the data on which these models rely, we may incur liability through the violation of such laws, third-party privacy or other
rights or contracts to which we are a party. Changes in laws, rules, directives and regulations may adversely affect the ability of our business to develop and use AI.
We may also market our own products as containing AI features. Some of our customers, especially those in highly regulated industries, may be reluctant or unwilling to adopt such AI features which could reduce or delay customer adoption.
Any of these factors could adversely affect our business, reputation, or financial results or subject us to legal liability.
If we fail to adapt and respond effectively to rapidly changing technology, evolving industry standards, changing regulations, or to changing customer needs, requirements, or preferences, our products may become less competitive.
Our ability to attract new users and customers and increase revenue from existing customers depends in large part on our ability to enhance, improve, and differentiate our products, increase adoption and usage of our products, and introduce new products and capabilities. The market in which we compete is subject to rapid technological change, evolving industry standards, and changing regulations, as well as changing customer needs, requirements, and preferences. The success of our business will depend, in part, on our ability to adapt and respond effectively to these changes on a timely basis. If we are unable to enhance our products and keep pace with rapid technological change, or if new technologies emerge that are able to deliver competitive products at lower prices, more efficiently, more conveniently, or more securely than our products, our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Legal Matters
We have been, and may in the future become, involved in litigation that may have a material adverse effect on our business.
From time to time, we may become involved in various other legal proceedings relating to matters incidental to the ordinary course of our business, including intellectual property, commercial, product liability, employment, class action, whistleblower and other litigation and claims, and governmental and other regulatory investigations and proceedings. Such matters can be time-consuming, divert management’s attention and resources and cause us to incur significant expenses. Furthermore, because litigation is inherently uncertain, there can be no assurance that the results of any of these actions will not have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Risks Related to Tax and Accounting
Our effective tax rate is difficult to project, and changes in such tax rate or adverse results of tax examinations could adversely affect our operating results.
We are a U.S.-based multinational company subject to tax in multiple U.S. and foreign tax jurisdictions. Our results of operations would be adversely affected to the extent that our geographical mix of income becomes more weighted toward jurisdictions with higher tax rates and would be favorably affected to the extent the relative geographic mix shifts to lower tax jurisdictions. Any change in our mix of earnings is dependent upon many factors and is therefore difficult to predict.
The process of determining our anticipated tax liabilities involves many calculations and estimates that are inherently complex and make the ultimate tax obligation determination uncertain. As part of the process of preparing our consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate our income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate prior to the completion and filing of tax returns for such periods. These estimates involve complex issues, require extended periods of time to resolve, and require us to make judgments, such as anticipating the outcomes of audits with tax authorities and the positions that we will take on tax returns prior to our actually preparing the returns. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. The final determination of tax audits and any related litigation could be materially different from our historical tax provisions and accruals. For further discussion on income taxes, see Note 11 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Furthermore, our overall effective income tax rate and tax expenses may be affected by various factors in our business, including changes in our entity structure, geographic mix of income and expenses, tax laws, and variations in the estimated and actual level of annual profits before income tax.
Our reported financial results may be adversely affected by changes in accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
Generally accepted accounting principles in the United States are subject to interpretation by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, the SEC, and various bodies formed to promulgate and interpret appropriate accounting principles. A change in these principles or interpretations could have a significant effect on our reported financial results, and may even affect the reporting of transactions completed before the announcement or effectiveness of a change.
Risks Related to our Common Stock
Goodwill represents a portion of our assets and any impairment of these assets could negatively impact our results of operations.
At March 31, 2024, our goodwill was approximately $127.8 million, which represented approximately 14% of our total assets. We test goodwill for impairment at least annually at the reporting unit level, or more often if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of its carrying amount. This qualitative assessment requires us to assess and make judgments regarding a variety of factors which impact the fair value of the reporting unit or asset being tested, including business plans, anticipated future cash flows, economic projections and other market data. Because there are inherent uncertainties involved in these factors, significant differences between these estimates and actual results could result in future impairment charges and could materially impact our future financial results. For additional information on our goodwill impairment testing, see Note 2 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements. Any future impairment of this asset could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, which may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Impairment charges of long-lived assets, including assets held for sale, could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. In January 2023, we entered into an exclusive agreement to sell our owned corporate headquarters and reclassified the assets as held for sale. As a result, we evaluated the carrying value of our long-lived assets related to the property and determined that the carrying value of those assets may not be fully recoverable, and as such, recorded an impairment charge of $53.5 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023. As of March 31, 2024, the sale has not yet been finalized and the exclusivity of the agreement has expired. We are continuing to market the building for sale and expect the transaction to be completed within calendar year 2024. While classified as held for sale, we may need to reassess the fair value of the building at each of our reporting periods and determine whether the carrying value is recoverable. If the carrying value is not deemed to be recoverable based on current market conditions, we may be required to record additional impairment charges in the future. In addition, if certain events or changes in circumstances arise, such as being unable to sell the building within a reasonable timeframe or if selling the building would result in a negative economic future state, we may need to reclassify the building from “assets held for sale” to “assets held and used,” and record a cumulative catch-up on the depreciable assets, which may have a material impact on our operating results and could impact the market price of our common stock. See Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements for additional information on our assets held for sale.
We may experience a decline in revenues or volatility in our quarterly operating results, which may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
We cannot predict our future quarterly revenues or operating results with certainty because of many factors outside of our control. A significant revenue or profit decline, lowered forecasts or volatility in our operating results could cause the market price of our common stock to decline substantially. Factors that could affect our revenues and operating results include the following:
•the unpredictability of the timing and magnitude of orders for our solutions, particularly transactions greater than $100,000, as a majority of our quarterly revenues were earned and recorded near the end of each quarter;
•failure to develop substantial sales pipeline for our products;
•failure to attract new customers and expand sales to our existing customers, including by effectively marketing and pricing our products;
•the possibility that our customers may cancel, defer or limit purchases as a result of reduced information technology budgets;
•the possibility that our customers may defer purchases of our solutions in anticipation of new solutions or updates from us or our competitors;
•the ability of our OEMs and resellers to meet their sales objectives;
•market acceptance of our new solutions and enhancements;
•our ability to control expenses;
•changes in our pricing, packaging and distribution terms or those of our competitors; and
•the demands on our management, sales force and customer services infrastructure as a result of the introduction of new solutions or updates.
Our expense levels are relatively fixed and are based, in part, on our expectations of future revenues. If revenue levels fall below our expectations and we are profitable at the time, our net income would decrease because only a small portion of our expenses varies with our revenues. Therefore, any significant decline in revenues for any period could have an immediate adverse impact on our results of operations for that period. We believe that period-to-period comparisons of our results of operations should not be relied upon as an indication of future performance. Our results of operations could be below expectations of public market analysts and investors in future periods which would likely cause the market price of our common stock to decline.
The price of our common stock may be highly volatile and may decline regardless of our operating performance.
The market price of our common stock could be subject to significant fluctuations in response to:
•variations in our quarterly or annual operating results;
•changes in financial estimates, treatment of our tax assets or liabilities or investment recommendations by securities analysts following our business or our competitors;
•the public’s response to our press releases, rumors, our other public announcements and our filings with the SEC;
•changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance or interpretations or principles;
•sales of common stock by our directors, officers and significant stockholders;
•announcements of technological innovations or enhanced or new products by us or our competitors;
•our failure to achieve operating results consistent with securities analysts’ projections;
•the operating and stock price performance of other companies that investors may deem comparable to us;
•broad market and industry factors, including financial instability of banking institutions; and
•other events or factors, including those resulting from war, incidents of terrorism or responses to such events.
The market prices of data protection solutions companies have been extremely volatile. Stock prices of many of those companies have often fluctuated in a manner unrelated or disproportionate to their operating performance. In the past, following periods of market volatility, stockholders have often instituted securities class
action litigation. Securities litigation could have a substantial cost and divert resources and the attention of management from our business.
Although we believe we currently have adequate internal control over financial reporting, we are required to assess our internal control over financial reporting on an annual basis, and any future adverse results from such assessment could result in a loss of investor confidence in our financial reports and have an adverse effect on our stock price.
Management has assessed that our internal control over financial reporting is effective and lacks any material weaknesses. Such assessment is made through subjective judgment of our management that may be open to interpretation. The effectiveness of our internal control in the future is subject to the risk that such internal controls may become inadequate. In the future, if we fail to timely complete this assessment, or if our independent auditors are unable to express an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal controls, there may be a loss of public confidence in our financial reporting, the market price of our stock could decline and we could be subject to regulatory sanctions or investigations by the Nasdaq Stock Market, the SEC or other regulatory authorities, which would require additional financial and management resources. Any failure to implement required new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in their implementation, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to timely meet our regulatory reporting obligations.
Certain provisions of our certificate of formation and our amended and restated bylaws or Delaware law could prevent or delay a potential acquisition of control of our Company, which could decrease the trading price of our common stock.
Our certificate of formation, amended and restated bylaws and the laws in the State of Delaware contain provisions that are intended to deter coercive takeover practices and inadequate takeover bids by making such practices or bids unacceptably expensive to the prospective acquirer and to encourage prospective acquirers to negotiate with our Board of Directors rather than to attempt a hostile takeover. Delaware law also imposes restrictions on mergers and other business combinations between us and any holder of 15% or more of our outstanding common stock.
We believe that these provisions protect our shareholders from coercive or otherwise unfair takeover tactics by effectively requiring those who seek to obtain control of the Company to negotiate with our Board of Directors and by providing our Board of Directors with more time to assess any acquisition of control. However, these provisions could apply even if an acquisition of control of the Company may be considered beneficial by some shareholders and could delay or prevent an acquisition of control that our Board of Directors determines is not in the best interests of our Company and our shareholders.
General Risks
Our business could be materially and adversely affected as a result of natural disasters, terrorism or other catastrophic events.
Any economic failure or other material disruption caused by war, climate change or natural disasters, including fires, floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, and tornadoes; power loss or shortages; environmental disasters; telecommunications or business information systems failures or similar events could also adversely affect our ability to conduct business. If such disruptions result in cancellations of customer orders or contribute to a general decrease in economic activity or corporate spending on IT, or impair our ability to meet our customer demands, our operating results and financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
There is also an increasing concern over the risks of climate change and related environmental sustainability matters. In addition to physical risks, climate change risk includes longer-term shifts in climate patterns, such as extreme heat, sea level rise, and more frequent and prolonged drought. Such events could disrupt our operations or those of our customers or third parties on which we rely, including through direct damage to assets and indirect impacts from supply chain disruption and market volatility.
Our business may be adversely affected by the impact of the wars in Israel and Ukraine and a widespread outbreak of contagious diseases, including the COVID-19 pandemic and its variants. These events may cause us or our customers to temporarily suspend operations and could adversely affect the economies and financial markets of many countries, resulting in an economic downturn that could affect demand for our solutions, our ability to collect against existing trade receivables and our operating results.
We currently, and may in the future, have assets held at financial institutions that may exceed the insurance coverage offered by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”), the loss of which would have a severe negative affect on our operations and liquidity.
We may maintain our cash assets at financial institutions in the U.S. in amounts that may be in excess of the FDIC insurance limit of $250,000. Actual events involving limited liquidity, defaults, non-performance or other adverse developments that affect financial institutions, transactional counterparties or other companies in the financial services industry or the financial services industry generally, or concerns or rumors about any events of these kinds or other similar risks, have in the past and may in the future lead to market-wide liquidity problems. In the event of a failure or liquidity issues of or at any of the financial institutions where we maintain our deposits or other assets, we may incur a loss to the extent such loss exceeds the FDIC insurance limitation, which could have a material adverse effect upon our liquidity, financial condition and our results of operations.
Similarly, if our customers or partners experience liquidity issues as a result of financial institution defaults or non-performance where they hold cash assets, their ability to pay us may become impaired and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, including the collection of accounts receivable and cash flows.
| | | | | |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
Risk Management and Strategy
Commvault has established a cybersecurity program for the benefit of the company, our customers, partners and stockholders. The cybersecurity program includes policies, processes and practices that are designed to assess, identify and manage material risks from cybersecurity threats and is integrated into our enterprise risk management program. Led by the Chief Information Security Officer (“CISO”), Commvault’s cybersecurity program leverages the National Institute of Standards and Technology ("NIST") Cybersecurity Framework, with the primary objective of securing systems and data from cyber threats. We procure security technologies, consistently work to mature our cybersecurity program, and partner with security service providers. We have established a Security Incident Response Plan ("SIRP") which outlines our processes for incident preparation, detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and post-incident analysis. In addition to the SIRP, we maintain a Crisis Management Plan to organize roles and responsibilities in the event of a crisis, a Disaster Recovery Plan to provide guidance in the recovery of systems following an outage, and a Business Continuity Plan to identify alternative means of conducting business in the event of business disruption. We partner with third parties to enhance monitoring and response capabilities and facilitate readiness activities including tabletop exercises and penetration testing. All employees are required to undergo annual security awareness training on current and potential cybersecurity threats and report suspicious activity. We also assess third-party service provider cybersecurity controls through a risk assessment questionnaire and include security and privacy terms in contracts as appropriate.
Commvault maintains a variety of third-party certifications and undergoes annual assessments for SOC 2 Type 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, CJIS, and PCI DSS. In support of these certifications and assessments, our products also undergo security testing. Annually, internal auditors complete a risk assessment of specific business operations like privacy and sanctions compliance or travel & expense policy compliance, identify areas of heightened risk, and conduct dedicated audit engagements at the direction of Management. The findings, observations, and recommendations from these engagements are shared with Management and the Audit Committee, as appropriate.
To date, Commvault is not aware of any cybersecurity incidents that have materially affected Commvault’s financial condition or business operations. Given the increasingly complex and sophisticated cyber threat landscape, we try to be vigilant to predict and prevent attacks. Commvault has prioritized cyber resilience measures and leverages governance processes and procedures to mitigate potential business impacts if and when an adverse event occurs. Although no material impacts have been recorded to date, IT system failures, network disruptions, cybersecurity incidents, and data breaches could adversely impact our business, internal controls, results of operations, and financial condition.
For additional description of cybersecurity risks and potential related impacts on Commvault, refer to the risk factor captioned “Risks Related to Technology and Security – We may be subject to IT system failures, network disruptions, cybersecurity incidents and breaches in data security” in Part 1, Item 1A. “Risk Factors.”
Governance
Commvault’s Board of Directors (the "Board") provides oversight of Commvault’s enterprise risk management strategy, which includes risks from cybersecurity threats. The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors receives quarterly briefings on the cybersecurity program from the CISO and briefings on the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (“ERMC”) and Cybersecurity Oversight Team (“CSOT”) from the Chief Legal and Compliance Officer (“CLCO”). The Board is kept apprised of cybersecurity updates through quarterly, or as needed, reporting from the Audit Committee Chair and annual, or as needed, reporting directly to the Board from the CISO.
Commvault’s Management, including the CEO, CFO, CLCO, CISO, Chief Information Officer (“CIO”), and Senior Vice President of Engineering, is responsible for our cybersecurity risk management strategy, operational decision-making, and incident preparedness and response. The current CISO holds a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology, industry certifications such as CISSP, CISA, CISM, is affiliated with various CISO professional working groups, and has over twenty-five years of experience in information security, compliance, technology, and program management across financial, telecommunications, audit, healthcare, retail, and professional services organizations. Management ensures cybersecurity risks are communicated through the establishment of the ERMC and the CSOT and regular, or as needed, reporting to the Audit Committee and the Board. The ERMC is responsible for the implementation, maintenance, and execution of our enterprise risk management program. The ERMC meets quarterly, or as needed, to assess, consider, and manage material risks including cybersecurity threats across the business. The CSOT is responsible for the significant operational decisions in the event of an active cybersecurity incident. The CSOT meets as needed, with the Audit Committee Chair as an optional attendee, to provide counsel and foster productive communication between Management and the Board.
Our principal administrative, sales, marketing, customer support and research and development facility is located at our owned corporate headquarters in Tinton Falls, New Jersey. In January 2023, we entered into an exclusive agreement to sell the property. The exclusivity expired in January 2024 and we are currently marketing the corporate headquarters for sale. We believe the sale will be completed in calendar year 2024. Upon closing of the transaction, we intend to enter into a lease for a portion of the premises.
In addition, we have offices in the United States in Florida and Texas; and outside the United States in Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, France, Germany, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Netherlands, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, Taiwan, United Arab Emirates, and United Kingdom.
From time to time, we are subject to claims in legal proceedings arising in the normal course of business. We do not believe that we are currently party to any pending legal action that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on our business or operating results.
| | | | | |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not Applicable.
PART II
| | | | | |
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market for our Common Stock
Our common stock is listed and traded on The Nasdaq Stock Market under the symbol “CVLT”.
Stockholders
As of May 9, 2024, there were approximately 41 holders of our common stock. The number of record holders does not represent the actual number of beneficial owners of shares of our common stock because shares are frequently held in street name by securities dealers and others for the benefit of individual owners who have the right to vote their shares.
Dividend Policy
We have never paid cash dividends on our common stock, and we intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to fund the growth of our business. We therefore do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Our future decisions concerning the payment of dividends on our common stock will depend upon our results of operations, financial condition and capital expenditure plans, as well as any other factors that the Board of Directors, in its sole discretion, may consider relevant.
Stock Performance Graph
The graph set forth below compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock between March 31, 2019 and March 31, 2024, with the cumulative total return of (i) The Nasdaq Composite Index and (ii) The Nasdaq Computer Index, over the same period. This graph assumes the investment of $100,000 on March 31, 2019 in our common stock, The Nasdaq Composite Index and The Nasdaq Computer Index, and assumes the reinvestment of dividends, if any. The graph assumes the initial value of our common stock on March 31, 2019 was the closing sales price of $64.74 per share.
The comparisons shown in the graph below are based upon historical data. The stock price performance shown in the graph below is not necessarily indicative of, nor is it intended to forecast, the future performance of our common stock. Information used in the graph was obtained from Nasdaq, a source we believe to be reliable, but we are not responsible for any errors or omissions in such information.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 3/31/2019 | 3/31/2020 | 3/31/2021 | 3/31/2022 | 3/31/2023 | 3/31/2024 |
| Commvault | 100.00 | | 62.53 | | 99.63 | | 102.49 | | 87.64 | | 156.67 | |
| Nasdaq Composite Index | 100.00 | | 99.62 | | 171.38 | | 183.98 | | 158.12 | | 211.91 | |
| Nasdaq Computer Index | 100.00 | | 112.16 | | 196.63 | | 236.26 | | 211.45 | | 316.72 | |
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
During the three months ended March 31, 2024, we repurchased $50.4 million of common stock, or approximately 0.5 million shares, under our repurchase program. As a result, $71.9 million remained available under the current authorization. A summary of our repurchases of common stock is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Total number of shares purchased | | Average price paid per share | | Total number of shares purchased as part of publicly announced programs | | Approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the program
(in thousands) |
| January 1-31, 2024 | | 132,303 | | | $ | 78.88 | | | 132,303 | | | $ | 111,875 | | |
| February 1-29, 2024 | | 210,163 | | | 93.78 | | | 210,163 | | | 92,166 | | |
| March 1-31, 2024 | | 204,571 | | | 98.85 | | | 204,571 | | | 71,944 | | * |
| Three months ended March 31, 2024 | | 547,037 | | | $ | 92.07 | | | 547,037 | | | | |
*On April 18, 2024, the Board of Directors approved an increase in our share repurchase program so that $250.0 million was available. The Board's authorization has no expiration date.
| | | | | |
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
You should read the following discussion and analysis along with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The statements in this discussion regarding our expectations of our future performance, liquidity and capital resources, and other non-historical statements are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties described under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our actual results may differ materially from those contained in or implied by any forward-looking statements. For discussion comparing the period ended March 31, 2023 to March 31, 2022, please refer to our Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed with the SEC on May 5, 2023.
Overview
Incorporated in Delaware in 1996, Commvault Systems, Inc. provides its customers with a scalable platform that enhances customers' cyber resiliency by protecting their data in a world of increasing threats. We provide these products and services for their data across many types of environments, including on-premises, hybrid and multi-cloud. Our offerings are delivered via self-managed software, software-as-a-service ("SaaS"), integrated appliances, or managed by partners. Customers use our Commvault Cloud platform to protect themselves from threats like ransomware and recover their data efficiently.
Industry
Our industry continues to go through accelerating changes as the result of compounding data growth, increasing security threats, and the introduction of new technologies. These changes are shifting the demands on the importance of resilience for the modern enterprise. Companies now require a comprehensive cyber resilience platform that simplifies and manages these forces holistically. Commvault Cloud is designed to secure and accelerate the recovery so that data can be restored from anywhere to anywhere, rapidly, reliably, and at scale.
Sources of Revenues
We generate revenues through subscription arrangements, perpetual software licenses, customer support contracts and other services. A significant portion of our total revenues comes from subscription arrangements, which include both sales of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. We are focused on these types of recurring revenue arrangements.
We expect our subscription arrangements will continue to generate revenues from the renewals of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings sold in prior years. Any of our pricing models (capacity, instance based, etc.) can be sold via a subscription arrangement, either through term-based licensing or hosted services. In term-based license arrangements, the customer has the right to use the software over a designated period of time. The capacity of the license is fixed and the customer has made an unconditional commitment to pay. Software revenue in these arrangements is generally recognized when the software is delivered. In SaaS offerings, customers use hosted software over the contract period without taking possession of the software. Revenue related to SaaS is recognized ratably over the contract period.
We sell to end-user customers both directly through our sales force and indirectly through our global network of value-added reseller partners, systems integrators, corporate resellers, OEMs and marketplaces. Subscription revenue generated through indirect distribution channels accounted for approximately 90% of total subscription revenue in recent fiscal years. Subscription revenue generated through direct distribution channels accounted for approximately 10% of total subscription revenue in recent fiscal years. Deals initiated by our direct sales force are sometimes transacted through indirect channels based on end-user customer requirements, which are not always in our control and can cause this overall percentage split to vary from period-to-period. As such, there may be fluctuations in the dollars and percentage of subscription revenue generated through our direct distribution channels from time-to-time. We believe that the growth of our subscription revenue, derived from both our indirect channel partners and direct sales force, are key attributes to our long-term growth strategy. We intend to continue to invest in both our channel relationships and direct sales force in the future, but we continue to expect more revenue to be generated through indirect distribution channels over the long term. The failure of our indirect distribution channels or our direct sales force to effectively sell our products and services could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
We have a non-exclusive distribution agreement with Arrow pursuant to which Arrow's primary role is to enable a more efficient and effective distribution channel for our solutions by managing our resellers and leveraging their own industry experience. We generated 36% of our total revenues through Arrow in fiscal 2024, and 37% of our total revenues in both fiscal 2023 and fiscal 2022. If Arrow were to discontinue or reduce the sales of our solutions or if our agreement with Arrow was terminated, and if we were unable to take back the management of our reseller channel or find another distributor to replace Arrow, there could be a material adverse effect on our future business.
Our customer support revenue includes support contracts tied to our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both term-based software license and perpetual software license arrangements. We sell our customer support contracts as a percentage of net software. Customer support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement, which is typically one year on our perpetual licenses. The term of our subscription arrangements is typically one to three years, but can range between one and five years.
Our other services revenue consists primarily of professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues from other services can vary period over period based on the timing services are delivered and are typically recognized as the services are performed.
Description of Costs and Expenses
Our cost of revenues is as follows:
•Cost of Subscription Revenue, consists primarily of the cost of third-party royalties and other costs such as media, manuals, translation and distribution costs, and hardware associated with our appliances as well as third-party hosting fees related to our SaaS offerings;
•Cost of Perpetual License Revenue, consists primarily of the cost of third-party royalties and other costs such as media, manuals, translation and distribution costs;
•Cost of Customer Support Revenue, consists of salary and employee benefit costs in providing customer support services; and
•Cost of Other Services Revenue, consists of salary and employee benefit costs in providing professional services.
Our operating expenses are as follows:
•Sales and Marketing, consists primarily of salaries, commissions, employee benefits, stock-based compensation and other direct and indirect business expenses, including travel and related expenses, sales promotion expenses, public relations expenses and costs for marketing materials and other marketing events (such as trade shows and advertising);
•Research and Development, which is primarily the expense of developing new software applications and modifying existing software applications, consists principally of salaries, stock-based compensation and benefits for research and development personnel and related expenses; contract labor expense and consulting fees as well as other expenses associated with the design, certification and testing of our software applications; and legal costs associated with the patent registration of such software applications;
•General and Administrative, consists primarily of salaries, stock-based compensation and benefits for our executive, accounting, human resources, legal, information systems and other administrative personnel. Also included in this category are other general corporate expenses, such as outside legal and accounting services, compliance costs and insurance; and
•Depreciation and Amortization, consists of depreciation expense for computer equipment we use for information services and in our development and test labs, amortization of intangible assets, and in fiscal years 2023 and 2022, depreciation for our owned corporate headquarters.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates’ Impact on Results of Operations
Sales outside the United States were 48% of our total revenue for fiscal 2024, 47% for fiscal 2023 and 48% for fiscal 2022. The income statements of our non-U.S. operations are translated into U.S. dollars at the average exchange rates for each applicable month in a period. To the extent the U.S. dollar weakens against foreign currencies, the translation of these foreign currency denominated transactions generally results in increased revenue, operating expenses and income from operations for our non-U.S. operations. Similarly, our revenue, operating expenses and net income will generally decrease for our non-U.S. operations if the U.S. dollar strengthens against foreign currencies.
Using the average foreign currency exchange rates from fiscal 2023, our total revenues would have been lower by $4.1 million, our cost of revenues would have been higher by $0.1 million, and our operating expenses would have been lower by $1.4 million from non-U.S. operations for fiscal 2024.
In addition, we are exposed to risks of foreign currency fluctuation primarily from cash balances, accounts receivables and intercompany accounts denominated in foreign currencies and are subject to the resulting transaction gains and losses, which are recorded as a component of general and administrative expenses. We recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $2.4 million and $1.2 million in fiscal 2024 and fiscal 2023, respectively, and insignificant losses in fiscal 2022.
Critical Accounting Policies
In presenting our consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP"), we are required to make estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported therein. Some of the estimates and assumptions we are required to make relate to matters that are inherently uncertain as they pertain to future events. We base these estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable and appropriate. Actual results may differ significantly from these estimates. To the extent that there are material differences between these estimates and actual results, our future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows may be affected.
In many cases, the accounting treatment of a particular transaction is specifically dictated by GAAP and does not require management’s judgment in its application, while in other cases, significant judgment is required in selecting among available alternative accounting standards that allow different accounting treatment for similar transactions. We consider these policies requiring significant management judgment to be critical accounting policies. The following is a description of these critical accounting policies.
Revenue Recognition
We account for revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. Our revenue recognition policies require us to make significant judgments and estimates. In applying our revenue recognition policy, we must determine which portions of our revenue are recognized currently (generally software related revenue) and which portions must be deferred and recognized in future periods (generally SaaS, customer support, and other services revenue). We analyze various factors including, but not limited to, the selling price of undelivered services when sold on a stand-alone basis, our pricing policies, the credit-worthiness of our customers, and contractual terms and conditions in helping us to make such judgments about revenue recognition. Changes in judgment on any of these factors could materially impact the timing and amount of revenue recognized in a given period. We recognize revenue net of sales tax.
We generate revenues through subscription arrangements, perpetual software licenses, customer support contracts and other services. A significant portion of our total revenues comes from subscription arrangements, which include both sales of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. We are focused on these types of recurring revenue arrangements.
We expect our subscription arrangements will continue to generate revenues from the renewals of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings sold in prior years. Any of our pricing models (capacity, instance based, etc.) can be sold via a subscription arrangement, either through term-based licensing or hosted services. In term-based license arrangements, the customer has the right to use the software over a designated period of time. The capacity of the license is fixed and the customer has made an unconditional commitment to pay. Software revenue in these arrangements is generally recognized when the software is delivered. In SaaS offerings, customers use hosted software over the contract period without taking possession of the software. Revenue related to SaaS is recognized ratably over the contract period.
We sell both perpetual and term-based licenses of our software. We refer to our term-based software licenses as subscription arrangements. We do not customize our software and installation services are not required. The software is delivered before related services are provided and is functional without professional services, updates and technical support. We have concluded that our software licenses (both perpetual and subscription) are functional intellectual property that is distinct, as the user can benefit from the software on its own. Revenues for both perpetual and term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered and/or made available for download as this is the point the user of the software can direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the remaining benefits from, the functional intellectual property. We do not recognize software revenue related to the renewal of subscription software licenses earlier than the beginning of the new subscription period.
We also offer appliances that integrate our software with hardware and address a wide-range of business needs and use cases, ranging from support for remote or branch offices with limited IT staff up to large corporate data centers. Our appliances are almost exclusively sold via a software only model in which we sell software to a third party, which assembles an integrated appliance that is sold to end user customers. As a result, the revenues and costs associated with hardware are usually not included in our financial statements.
Our customer support revenue includes support contracts tied to our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both term-based software license and perpetual software license arrangements. We sell our customer support contracts as a percentage of net software. Customer support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement, which is typically one year on our perpetual licenses. The term of our subscription arrangements is typically one to three years, but can range between one and five years.
Our other services revenue consists primarily of professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues from other services can vary period over period based on the timing services are delivered and are typically recognized as the services are performed.
Most of our contracts with customers contain multiple performance obligations. For these contracts, we evaluate and account for individual performance obligations separately if they are determined to be distinct. The transaction price is allocated to the separate performance obligations on a relative standalone selling price basis. Standalone selling prices of software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are typically estimated using the residual approach. Standalone selling prices for SaaS, customer support contracts, and other services are typically estimated based on observable transactions when these services are sold on a standalone basis.
Our typical performance obligations include the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Performance Obligation | When Performance Obligation
is Typically Satisfied | When Payment is
Typically Due | How Standalone Selling Price is
Typically Estimated |
| Subscription |
| Term-based software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment except for certain subscription licenses which are paid for over time | Residual approach |
| Software-as-a-service (SaaS) | Ratably over the course of the contract (over time) | Annually or at the beginning of the contract period | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
| Perpetual License |
| Perpetual software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment | Residual approach |
| Customer Support |
| Software updates | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions |
| Customer support | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions |
| Other Services |
| Other professional services (except for education services) | As work is performed (over time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
| Education services | When the class is taught (point in time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
Accounting for Income Taxes
Under ASC 740, deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts. Valuation allowances are established when, in our judgment, it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we considered all available objective and verifiable evidence both positive and negative, including historical levels of pre-tax income (loss) both on a consolidated basis and tax reporting entity basis, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies. In prior years, we believed that it was more likely than not that we would not realize the benefits of our gross deferred tax assets and therefore had recorded a valuation allowance to reduce the carrying value of those deferred tax assets, net of the impact of the reversals of taxable temporary differences, to zero. As and for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024, we believe that it is more likely than not that we will realize the benefits of our gross deferred tax assets and therefore we have released the previously recorded valuation allowance, resulting in an income tax benefit in the current period. In the future, changes to our estimates regarding the realizability of our gross deferred tax assets could materially impact our results of operations.
We conduct business globally and as a result, file income tax returns in the United States and in various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world, including such major jurisdictions as the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Netherlands and United Kingdom.
Goodwill
We test goodwill for impairment at least annually, on January 1, by performing a qualitative assessment of whether the fair value of each reporting unit or asset exceeds its carrying amount. We have one reporting unit. Goodwill is tested at this reporting unit level. This requires us to assess and make judgments regarding a variety of factors which impact the fair value of the reporting unit or asset being tested, including business plans, anticipated future cash flows, economic projections and other market data. Because there are inherent uncertainties involved in these factors, significant differences between these estimates and actual results could result in future impairment charges and could materially impact our future financial results. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2024, we performed a qualitative impairment test for goodwill and concluded that the carrying amount of the reporting unit does not exceed the fair value. No goodwill impairment charges were recorded for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Results of Operations
Amounts reported in millions are rounded based on the amounts in thousands. As a result, the sum of the components reported in millions may not equal the total amount reported in millions due to rounding.
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2024 compared to fiscal year ended March 31, 2023
Revenues (in millions)
–Total revenues increased $54.7 million, or 7% year over year, driven primarily by an increase in subscription revenue, offset by decreases in perpetual license and customer support revenues. We remain focused on selling subscription arrangements through both term-based software licenses and SaaS offerings.
–Subscription revenue increased $81.4 million, or 23% year over year, driven primarily by an 87% increase in our SaaS revenue compared to the same period in the prior year. Term-based license revenue increased 8% year over year, due to an increase in the number of larger term-based license transactions (deals greater than $0.1 million) period over period. Subscription revenue accounted for 51% of total revenues in fiscal 2024 compared to 44% in fiscal 2023.
–Perpetual license revenue decreased $17.3 million, or 23% year over year. This decrease is primarily a result of our preferred route to market which is led by the sale of term-based licenses. Perpetual licenses are generally only sold in certain verticals and geographies. Perpetual license revenue accounted for 7% of total revenues in fiscal 2024 compared to 10% in fiscal 2023.
–Customer support revenue decreased $6.5 million, or 2% year over year, driven by a $32.4 million decrease in customer support revenue attached to perpetual license support renewals, partially offset by a $25.9 million increase in customer support allocated to term-based license arrangements.
–Other services revenue decreased $2.9 million, or 6% year over year. Changes in other services revenue can vary period over period primarily due to the timing professional services are delivered.
We track total revenues on a geographic basis. Our Americas region includes the United States, Canada, and Latin America. Our International region primarily includes Europe, Middle East, Africa, Australia, India, Southeast Asia and China. Americas and International represented 59% and 41% of total revenues, respectively, for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. Total revenues increased 6% and 8% in the Americas and International, respectively.
▪Total revenues in the Americas was impacted by a 24% increase in subscription revenue, offset by a 45% decrease in perpetual license revenue, driven by the shift from selling perpetual licenses to subscription arrangements. Customer support and other services revenues declined 5% and 9%, respectively.
▪The increase in International total revenues was primarily due to a 21% increase in subscription revenue, offset by an 8% decrease in perpetual license revenue. Customer support revenue increased 2% year over year. Other services revenue was flat year over year.
Our total revenues in International is subject to changes in foreign exchange rates as further discussed above in the “Foreign Currency Exchange Rates’ Impact on Results of Operations” section.
Cost of Revenues and Gross Margin ($ in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | Cost of Revenues | Gross
Margin | | Cost of Revenues | Gross
Margin |
| Subscription | | $ | 58.4 | | 86 | % | | $ | 44.5 | | 87 | % |
| Perpetual license | | 2.2 | | 96 | % | | 2.4 | | 97 | % |
| Customer support | | 60.8 | | 80 | % | | 58.3 | | 81 | % |
| Other services | | 30.3 | | 32 | % | | 30.2 | | 37 | % |
| Total | | $ | 151.6 | | 82 | % | | $ | 135.4 | | 83 | % |
–Total cost of revenues increased $16.2 million and represented 18% and 17% of our total revenues in fiscal 2024 and fiscal 2023, respectively.
–Cost of subscription revenue increased $13.9 million, representing 14% of our total subscription revenue in fiscal 2024 compared to 13% in fiscal 2023. The year over year increase is primarily the result of an increase in the cost of infrastructure related to growth in our SaaS offerings.
–Cost of perpetual license revenue decreased $0.3 million and represented 4% of our total perpetual revenue in fiscal 2024 compared to 3% in fiscal 2023.
–Cost of customer support revenue increased $2.5 million and represented 20% of our total customer support revenue in fiscal 2024 compared to 19% in fiscal 2023.
–Cost of other services revenue increased $0.1 million, representing 68% of our total other services revenue in fiscal 2024 compared to 63% in fiscal 2023. The increase in cost of other services revenue was driven by timing of the delivery of certain professional services.
Operating Expenses ($ in millions)
–Sales and marketing expenses increased $14.2 million, or 4%, driven by increases in employee compensation and sales commissions associated with increased revenues relative to the same period in the prior year as well as increases in marketing spend related to Commvault's SHIFT event in New York City. These increases were partially offset by a $6.5 million decrease in stock-based compensation.
–Research and development expenses decreased $9.5 million, or 7%, driven by decreases in employee compensation and related expenses, including a $7.0 million decrease in stock-based compensation. Investing in research and development remains a priority for Commvault and we anticipate continued responsible spending related to the development of our software applications and hosted services.
–General and administrative expenses increased $9.8 million, or 9%, primarily driven by a $4.4 million increase in employee compensation and related expenses including a $1.3 million increase in stock-based compensation year over year. In addition, we recorded $2.4 million in foreign currency transaction losses compared to $1.2 million in foreign currency transaction losses recorded in the prior fiscal year.
–Restructuring: Our restructuring plan, initiated in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2024, is intended to enhance customer satisfaction through the reorganization and redesign of our customer success functions. The realignment of the customer success structure aims to optimize operational efficiency and improve continuity for our customers through the pre-sales and post-sales experience. Restructuring expenses were $4.5 million for the year ended March 31, 2024. These charges relate primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions as well as costs related to office termination and exit charges. These expenses included $1.5 million in fiscal 2024 of stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan. We anticipate the restructuring plan will be completed in the second half of fiscal 2025.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2022 we initiated a restructuring plan which was completed in fiscal 2023. It was aimed to increase efficiency in our sales, marketing and distribution functions as well as reduce costs across all functional areas. Restructuring expenses were $15.5 million for the year ended March 31, 2023. These restructuring charges relate primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions. These expenses included $2.6 million in fiscal 2023 of stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan.
Risks associated with our restructuring plans include additional unexpected costs, adverse effects on employee morale and the failure to meet operational and growth targets due to the loss of key employees, any of which may impair our ability to achieve anticipated results of operations or otherwise harm our business.
–Depreciation and amortization expense decreased $2.9 million, from $9.3 million in fiscal 2023 to $6.4 million in fiscal 2024, driven by the reclassification of our owned corporate headquarters as assets held for sale in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023.
–Impairment charges: During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, we entered into an exclusive agreement to sell our owned corporate headquarters in Tinton Falls, New Jersey. The property was reclassified as assets held for sale and the previous carrying amount was written down to its estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell, resulting in a noncash impairment charge of $53.5 million.
Interest Income
Interest income increased $4.1 million, from $1.3 million in fiscal 2023 to $5.4 million in fiscal 2024 primarily as a result of increases in interest rates and the amount of invested funds subject to interest income.
Interest Expense
Interest expense was $0.4 million in fiscal 2024 compared to $0.5 million in fiscal 2023. These charges relate primarily to our revolving credit facility. Refer to Note 16 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion on the revolving credit facility.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income was $3.3 million in fiscal 2024 compared to expense of $0.3 million in fiscal 2023. Other income for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024 includes a $1.7 million gain on a non-refundable escrow payment, $1.6 million related to U.S. business incentive programs and insignificant changes in fair value related to our investments in equity securities.
Income Tax Expense (Benefit)
Income tax benefit was $85.3 million in fiscal 2024 compared to expense of $20.4 million in fiscal 2023. The income tax benefit for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024 relates primarily to the release of the previously recorded valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets in the U.S. and foreign jurisdictions.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
In recent fiscal years, our principal source of liquidity has been cash provided by operations. As of March 31, 2024, our cash and cash equivalents balance was $312.8 million, of which approximately $214.2 million was held outside of the United States by our foreign legal entities. These balances are dispersed across approximately 35 international locations around the world. We believe that such dispersion meets the current and anticipated future liquidity needs of our foreign legal entities. In the event we need to repatriate funds from outside of the United States, such repatriation would likely be subject to restrictions by local laws and/or tax consequences, including foreign withholding taxes.
On December 13, 2021, we entered into a five-year $100 million senior secured revolving credit facility (the “Credit Facility”) with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. The Credit Facility is available for share repurchases, general corporate purposes, and letters of credit. The Credit Facility contains financial maintenance covenants including a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio. The Credit Facility also contains certain customary events of default
which would permit the lender to, among other things, declare all loans then outstanding to be immediately due and payable if such default is not cured within applicable grace periods. The Credit Facility also limits our ability to incur certain additional indebtedness, create or permit liens on assets, make acquisitions, make investments, loans or advances, sell or transfer assets, pay dividends or distributions, and engage in certain transactions with foreign affiliates. Outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility accrue interest at an annual rate equal to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate plus 1.25% subject to increases based on our actual leverage. The unused balance on the Credit Facility is also subject to a 0.25% annual interest charge subject to increases based on our actual leverage. As of March 31, 2024, there were no borrowings under the Credit Facility and we were in compliance with all covenants.
During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024, we repurchased $184.0 million of common stock, or approximately 2.5 million shares. On April 18, 2024, the Board of Directors approved an increase in our share repurchase program so that $250.0 million was available. The Board's authorization has no expiration date.
A summary of the cash used for the stock repurchase program consists of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Cash used for repurchases (in thousands) | | $ | 184,021 | | | $ | 150,921 | | | $ | 305,239 | | | $ | 95,259 | | | $ | 77,198 | |
| Shares repurchased (in thousands) | | 2,479 | | | 2,521 | | | 4,307 | | | 1,643 | | | 1,701 | |
| Average price per share | | $ | 74.24 | | | $ | 59.90 | | | $ | 70.87 | | | $ | 57.97 | | | $ | 45.37 | |
Our summarized cash flow information is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | 203,798 | | | $ | 170,288 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | (5,521) | | | (5,286) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | | (170,581) | | | (135,579) | |
| Effects of exchange rate — changes in cash | | (2,720) | | | (9,152) | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 24,976 | | | $ | 20,271 | |
- Net cash provided by operating activities was impacted by:
•Fiscal 2024: net income adjusted for the impact of non-cash charges and increases in deferred revenue, partially offset by increases in accounts receivable.
•Fiscal 2023: net loss adjusted for the impact of non-cash charges, including the impairment of our owned corporate headquarters and increases in deferred revenue partially offset by decreases in accrued expenses.
- Net cash used in investing activities was impacted by:
•Fiscal 2024: $4.1 million of capital expenditures and $1.4 million for the purchase of equity securities.
•Fiscal 2023: $3.2 million of capital expenditures and $2.1 million for the purchase of equity securities.
- Net cash used in financing activities was impacted by:
•Fiscal 2024: $184.0 million used to repurchase shares of our common stock under our repurchase program, partially offset by $13.4 million of proceeds from the exercise of stock options and the Employee Stock Purchase Plan.
•Fiscal 2023: $150.9 million used to repurchase shares of our common stock under our repurchase program and $0.1 million of debt issuance costs paid, partially offset by $15.4 million of proceeds from the exercise of stock options and the Employee Stock Purchase Plan.
Working capital decreased $30.6 million from $140.8 million as of March 31, 2023 to $110.2 million as of March 31, 2024. The decrease in working capital is primarily due to increases in accrued liabilities and the current portion of deferred revenue, partially offset by increases in cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable.
We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and our cash from operations will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash needs for working capital, income taxes, capital expenditures and potential stock repurchases for at least the next twelve months. We may seek additional funding through public or private financings or other arrangements during this period. Adequate funds may not be available when needed or may not be available on terms favorable to us, or at all. If additional funds are raised by issuing equity securities, dilution to existing stockholders will result. If we raise additional funds by obtaining loans from third parties, the terms of those financing arrangements may include negative covenants or other restrictions on our business that could impair our operational flexibility, and would also require us to fund additional interest expense. If funding is insufficient at any time in the future, we may be unable to develop or enhance our products or services, take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Summary Disclosures about Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
Our material capital commitments consist of obligations under facilities and operating leases. Some of these leases have free or escalating rent payment provisions. Refer to Note 15 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion on operating leases.
We have certain software royalty commitments associated with the shipment and licensing of certain products. Royalty expense is generally based on a fixed cost per unit shipped or a fixed fee for unlimited units shipped over a designated period. Royalty expense, included in cost of subscription and perpetual license revenues, was $9.7 million in fiscal 2024 and $9.3 million in fiscal 2023.
We offer a 90-day limited product warranty for our software. To date, costs relating to this product warranty have not been material.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of March 31, 2024, we did not have off-balance sheet financing arrangements, including any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities.
Indemnifications
Certain of our software licensing agreements contain certain provisions that indemnify our customers from any claim, suit or proceeding arising from alleged or actual intellectual property infringement. These provisions continue in perpetuity along with our software licensing and SaaS agreements. We have never incurred a liability relating to one of these indemnification provisions in the past and we believe that the likelihood of any future payout relating to these provisions is remote. Therefore, we have not recorded a liability during any period related to these indemnification provisions.
Impact of Recently Issued Accounting Standards
See Note 2 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of the impact of recently issued accounting standards.
| | | | | |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
Interest Rate Risk
None.
Foreign Currency Risk
Economic Exposure
As a global company, we face exposure to adverse movements in foreign currency exchange rates. Our international sales are generally denominated in foreign currencies and this revenue could be materially affected by currency fluctuations. Approximately 48% of our sales were outside the United States in fiscal 2024 and 47% in fiscal 2023. Our primary exposures are to fluctuations in exchange rates for the U.S. dollar versus the Euro, and to a lesser extent, the Australian dollar, British pound sterling, Canadian dollar, Chinese yuan, Indian rupee, Korean won and Singapore dollar. Changes in currency exchange rates could adversely affect our reported revenues and require us to reduce our prices to remain competitive in foreign markets, which could also have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. Historically, we have periodically reviewed and revised the pricing of our products available to our customers in foreign countries and we have not maintained excess cash balances in foreign accounts.
We estimate that a 10% change in all foreign exchange rates would impact our reported operating profit by approximately $13.4 million annually. This sensitivity analysis disregards the possibilities that rates can move in opposite directions and that losses from one geographic area may be offset by gains from another geographic area.
Transaction Exposure
Our exposure to foreign currency transaction gains and losses is primarily the result of certain net receivables due from our foreign subsidiaries and customers being denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of the subsidiary. Our foreign subsidiaries conduct their businesses in local currency and we generally do not maintain excess U.S. dollar cash balances in foreign accounts.
Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are recorded in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. We recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $2.4 million and $1.2 million in fiscal 2024 and fiscal 2023, respectively, and insignificant losses in fiscal 2022.
| | | | | |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Financial Statements
Fiscal Years Ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of Commvault Systems, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Commvault Systems, Inc. (the Company) as of March 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at March 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated May 13, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Accounting for Revenue Recognition |
Description of the Matter
| | As described in Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company derives revenues from two primary sources: software and products, and services. Most of the Company’s contracts with customers contain multiple performance obligations which are accounted for separately if they are distinct. The transaction price is allocated to separate performance obligations on a relative standalone selling price basis. Auditing the identification of performance obligations in a software contract requires significant judgment as it relates to the evaluation of the contractual terms of the arrangement. |
How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit
| | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s revenue recognition process, including the evaluation of the contractual terms of the revenue arrangements.
To test the amount of revenue recognized, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, testing a sample of revenue transactions during the year and evaluating the identification of performance obligations based on an analysis of the contractual terms and independent confirmations of the terms and conditions of the contract directly with customers. |
| | Realizability of Deferred Tax Assets |
| Description of the Matter | | As described in Note 11 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company reduced its valuation allowance by approximately $105 million as it determined that certain deferred tax assets were now more likely than not to be realized. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if, based on the weight of all available evidence, in management’s judgment it is more likely than not that some portion, or all, of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Once established, the valuation allowance is released when, based on the weight of all available evidence, management concludes that related deferred tax assets are more likely than not to be realized. As of March 31, 2024, the Company was in a three-year cumulative income position. As a result of the removal of this negative evidence and the existence of other positive evidence, including projected future taxable income, the Company has determined that the majority of deferred tax assets are now more likely than not to be realized, and the valuation allowance on those deferred tax assets should be released.
Auditing management’s assessment of the realizability of the Company’s deferred tax assets involved complex judgments due to the significant estimation involved regarding projected future taxable income. |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over management’s process for assessing the realization of the Company’s deferred tax assets, including controls over management’s review of its projected future taxable income.
To test the realizability of deferred tax assets, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, testing the Company’s scheduling of the reversal of existing temporary differences, performing sensitivity analyses on and testing significant assumptions used by the Company in determining its projected future taxable income, and testing the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data used in its projections. We compared the projections of future taxable income with the actual results of the current period and that of industry peers. We involved our tax professionals to evaluate the application of tax law in the Company’s projected future taxable income, the scheduling of the reversal of existing temporary differences, and the evaluation of the realizability of the deferred tax assets. |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1998.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Iselin, New Jersey
May 13, 2024
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| ASSETS |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 312,754 | | | $ | 287,778 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Trade accounts receivable, net | | 222,683 | | | 210,441 | |
| Assets held for sale | | 38,680 | | | 38,680 | |
| Other current assets | | 21,009 | | | 14,015 | |
| Total current assets | | 595,126 | | | 550,914 | |
| Deferred tax assets, net | | 111,181 | | | — | |
| Property and equipment, net | | 7,961 | | | 8,287 | |
| Operating lease assets | | 10,545 | | | 11,784 | |
| Deferred commissions cost | | 62,837 | | | 59,612 | |
| Intangible assets, net | | 1,042 | | | 2,292 | |
| Goodwill | | 127,780 | | | 127,780 | |
| Other assets | | 27,441 | | | 21,905 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 943,913 | | | $ | 782,574 | |
| | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
| Current liabilities: | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 108 | |
| Accrued liabilities | | 117,244 | | | 97,888 | |
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities | | 4,935 | | | 4,518 | |
| Deferred revenue | | 362,450 | | | 307,562 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 484,928 | | | 410,076 | |
| Deferred revenue, less current portion | | 168,472 | | | 174,393 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | 1,717 | | | 134 | |
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | | 7,155 | | | 8,260 | |
| Other liabilities | | 3,556 | | | 3,613 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) | | | | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value: 50,000 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding | | — | | | — | |
Common stock, $0.01 par value, 250,000 shares authorized, 43,548 shares and 44,140 shares issued and outstanding at March 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively | | 435 | | | 440 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | 1,349,603 | | | 1,264,608 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | (1,056,011) | | | (1,062,900) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | (15,942) | | | (16,050) | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | 278,085 | | | 186,098 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 943,913 | | | $ | 782,574 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenues: | | | | | | |
| Subscription | | $ | 429,167 | | | $ | 347,784 | | | $ | 268,359 | |
| Perpetual license | | 57,613 | | | 74,918 | | | 111,857 | |
| Customer support | | 307,771 | | | 314,313 | | | 347,115 | |
| Other services | | 44,696 | | | 47,575 | | | 42,260 | |
| Total revenues | | 839,247 | | | 784,590 | | | 769,591 | |
| Cost of revenues: | | | | | | |
| Subscription | | 58,406 | | | 44,482 | | | 24,578 | |
| Perpetual license | | 2,168 | | | 2,439 | | | 4,563 | |
| Customer support | | 60,752 | | | 58,273 | | | 54,719 | |
| Other services | | 30,284 | | | 30,208 | | | 29,999 | |
| Total cost of revenues | | 151,610 | | | 135,402 | | | 113,859 | |
| Gross margin | | 687,637 | | | 649,188 | | | 655,732 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | 354,994 | | | 340,783 | | | 341,644 | |
| Research and development | | 132,328 | | | 141,847 | | | 153,615 | |
| General and administrative | | 113,997 | | | 104,240 | | | 103,049 | |
| Restructuring | | 4,548 | | | 15,452 | | | 6,192 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 6,415 | | | 9,270 | | | 9,666 | |
| Headquarters impairment | | — | | | 53,481 | | | — | |
| Total operating expenses | | 612,282 | | | 665,073 | | | 614,166 | |
| Income (loss) from operations | | 75,355 | | | (15,885) | | | 41,566 | |
| Interest income | | 5,423 | | | 1,300 | | | 656 | |
| Interest expense | | (415) | | | (472) | | | (109) | |
| Other income (expense), net | | 3,250 | | | (305) | | | 1,301 | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | | 83,613 | | | (15,362) | | | 43,414 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | | (85,293) | | | 20,412 | | | 9,790 | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | |
| Net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | 3.85 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | 0.74 | |
| Diluted | | $ | 3.75 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | 0.71 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | |
| Diluted | | 45,100 | | | 44,664 | | | 47,220 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | 108 | | | (4,187) | | | (1,513) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | | $ | 169,014 | | | $ | (39,961) | | | 32,111 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In
Capital | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Loss | | Total |
| | | Shares | | Amount | |
| Balance at March 31, 2021 | | 46,482 | | | $ | 463 | | | $ | 1,069,695 | | | $ | (665,774) | | | $ | (10,350) | | | $ | 394,034 | |
| Stock-based compensation | | | | | | 105,163 | | | | | | | 105,163 | |
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation | | 2,336 | | | 23 | | | 29,737 | | | | | | | 29,760 | |
| Repurchase of common stock | | (4,307) | | | (43) | | | (38,647) | | | (266,549) | | | | | (305,239) | |
| Net income | | | | | | | | 33,624 | | | | | 33,624 | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | (1,513) | | | (1,513) | |
| Balance at March 31, 2022 | | 44,511 | | | 443 | | | 1,165,948 | | | (898,699) | | | (11,863) | | | 255,829 | |
| Stock-based compensation | | | | | | 105,746 | | | | | | | 105,746 | |
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation | | 2,150 | | | 22 | | | 15,383 | | | | | | | 15,405 | |
| Repurchase of common stock | | (2,521) | | | (25) | | | (22,469) | | | (128,427) | | | | | (150,921) | |
| Net loss | | | | | | | | (35,774) | | | | | (35,774) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | (4,187) | | | (4,187) | |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | | 44,140 | | | 440 | | | 1,264,608 | | | (1,062,900) | | | (16,050) | | | 186,098 | |
| Stock-based compensation | | | | | | 94,551 | | | | | | | 94,551 | |
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation | | 1,887 | | | 19 | | | 13,421 | | | | | | | 13,440 | |
| Repurchase of common stock | | (2,479) | | | (24) | | | (22,977) | | | (162,017) | | | | | (185,018) | |
| Net income | | | | | | | | 168,906 | | | | | 168,906 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | 108 | | | 108 | |
| Balance at March 31, 2024 | | 43,548 | | | $ | 435 | | | $ | 1,349,603 | | | $ | (1,056,011) | | | $ | (15,942) | | | $ | 278,085 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 6,530 | | | 10,323 | | | 10,950 | |
| Noncash stock-based compensation | | 94,551 | | | 105,746 | | | 105,163 | |
| Noncash change in fair value of equity securities | | 17 | | | 305 | | | (301) | |
| | | | | | |
| Noncash headquarters impairment | | — | | | 53,481 | | | — | |
| | | | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | | (109,598) | | | (674) | | | 49 | |
| | | | | | |
| Amortization of deferred commissions cost | | 26,531 | | | 22,626 | | | 18,339 | |
| | | | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts receivable, net | | (21,725) | | | (11,596) | | | (20,371) | |
| Operating lease assets and liabilities, net | | 550 | | | (56) | | | (925) | |
| Other current assets and Other assets | | 336 | | | 6,179 | | | 3,732 | |
| Deferred commissions cost | | (29,952) | | | (30,529) | | | (33,512) | |
| Accounts payable | | 195 | | | (297) | | | 60 | |
| Accrued liabilities | | 16,998 | | | (24,213) | | | 10,400 | |
| Deferred revenue | | 50,394 | | | 73,756 | | | 48,295 | |
| Other liabilities | | 65 | | | 1,011 | | | 1,677 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | 203,798 | | | 170,288 | | | 177,180 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | (4,086) | | | (3,241) | | | (3,911) | |
| Purchase of equity securities | | (1,435) | | | (2,045) | | | (4,139) | |
| Business combination, net of cash acquired | | — | | | — | | | (16,894) | |
| Other | | — | | | — | | | 500 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | (5,521) | | | (5,286) | | | (24,444) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | |
| Repurchase of common stock | | (184,021) | | | (150,921) | | | (305,239) | |
| Proceeds from stock-based compensation plans | | 13,440 | | | 15,405 | | | 29,760 | |
| Debt issuance costs | | — | | | (63) | | | (609) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | | (170,581) | | | (135,579) | | | (276,088) | |
| Effects of exchange rate — changes in cash | | (2,720) | | | (9,152) | | | (6,378) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | 24,976 | | | 20,271 | | | (129,730) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | 287,778 | | | 267,507 | | | 397,237 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | $ | 312,754 | | | $ | 287,778 | | | $ | 267,507 | |
| | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information | | | | | | |
| Interest paid | | $ | 253 | | | $ | 253 | | | $ | 13 | |
| Income taxes paid | | $ | 19,970 | | | $ | 15,175 | | | $ | (1,493) | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(In thousands, except per share data)
1. Nature of Business
Commvault Systems, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Commvault," "we," "us," or "our") provides its customers with a scalable platform that enhances customers' cyber resiliency by protecting their data in a world of increasing threats. We provide these products and services across many types of environments, including on-premises, hybrid and multi-cloud. Our offerings are delivered via self-managed software, software-as-a-service ("SaaS"), integrated appliances, or managed by partners. Customers use our Commvault Cloud platform to protect themselves from threats like ransomware and recover their data efficiently.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Reclassification of Prior Year Balances
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified for consistency with the current year presentation. These reclassifications have no impact on the amount of total revenues or net income. Beginning in fiscal 2024, the software and services line items on the consolidated statements of operations, related to revenues and cost of revenues, are being presented in the following categories:
Subscription - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs of recurring time-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer.
Perpetual license - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download.
Customer support - The amounts on this line include customer support revenues and costs associated with our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. Customer support revenue is typically recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement.
Other services - The amounts included on this line consist primarily of revenues and costs related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other professional services are typically recognized as the services are performed.
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Commvault. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") requires management to make judgments and estimates that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. The amounts of assets and liabilities reported in our balance sheets and the amounts of revenues and expenses reported for each of the periods presented are affected by estimates and assumptions, which are used for, but not limited to, the accounting for revenue recognition, income taxes and related reserves, deferred commissions, purchased intangible assets and goodwill. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Revenue
We account for revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("ASC 606"). We record revenue net of sales tax. For a further discussion of our accounting policies related to revenue, see Note 3 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation
Restricted stock units without a market condition are measured based on the fair market values of the underlying stock on the date of grant. We recognize stock-based compensation expense using the straight-line method for all stock awards that do not include a market or performance condition. Awards that include a market or performance condition are expensed using the accelerated method.
Software Development Costs
The costs for the development of new products and substantial enhancements to existing products are expensed as incurred until technological feasibility has been established, at which time any additional costs would be capitalized in accordance with the accounting guidance for software. Because our current process for developing software is essentially completed concurrently with the establishment of technological feasibility, which occurs upon the completion of a working model, no costs have been capitalized for any of the periods presented.
Advertising Costs
We expense advertising costs as incurred. Advertising expenses were $8,514, $8,663, and $9,572 for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Accounting for Income Taxes
We account for income taxes in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes ("ASC 740"). The provision for income taxes and effective tax rates are calculated by legal entity and jurisdiction and are based on a number of factors, including the level of pre-tax earnings, income tax planning strategies, differences between tax laws and accounting rules, statutory tax rates and credits, uncertain tax positions and valuation allowances. We provide for global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) earned by certain foreign subsidiaries in the year the tax is incurred and record an estimate of GILTI as a component of the tax provision. We use significant judgment and estimates in evaluating tax positions. The effective tax rate in a given financial statement period may be materially impacted by changes in the mix and level of earnings by taxing jurisdiction.
Under ASC 740, deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts. Valuation allowances are established when, in our judgment, it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we weigh the available positive and negative evidence, including historical levels of pre-tax income, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies.
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currencies of our foreign operations are deemed to be the local country’s currency. Assets and liabilities of our international subsidiaries are translated at their respective period-end exchange rates, and revenues and expenses are translated at average currency exchange rates for the period. The resulting balance sheet translation adjustments are included in other comprehensive income (loss) and are reflected as a separate component of stockholders’ equity.
Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are recorded in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. These gains and losses relate primarily to receivables and payables that are not denominated in the functional currency of the subsidiary they relate to. We recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $2,388 and $1,163 in the years ended March 31, 2024, and 2023, respectively, and insignificant losses in the year ended March 31, 2022.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Net Income (Loss) per Common Share
Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of common shares during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares consist of the incremental common shares issuable upon the vesting of restricted stock units, shares to be purchased under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan ("ESPP"), and the exercise of stock options. The dilutive effect of such potential common shares is reflected in diluted earnings (loss) per share by application of the treasury stock method.
The following table sets forth the reconciliation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per common share:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | |
| Basic net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | |
| Basic net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 3.85 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | 0.74 | |
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted-average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | |
Dilutive effect of stock options and restricted stock units (1) | | 1,215 | | | — | | | 1,777 | |
| Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding | | 45,100 | | | 44,664 | | | 47,220 | |
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share | | 3.75 | | | (0.80) | | | 0.71 | |
(1) In fiscal 2023 dilutive shares have been excluded because we were in a net loss position.
The diluted weighted-average shares outstanding exclude restricted stock units, performance restricted stock units, shares to be purchased under the ESPP and outstanding stock options totaling 271, 3,939 and 505 for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, because the effect would have been anti-dilutive.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid investments purchased with maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Trade and Other Receivables
Trade and other receivables are primarily comprised of trade receivables that are recorded at the invoice amount, net of an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is not material. Unbilled receivables represent amounts for which revenue has been recognized but which have not yet been invoiced to the customer. The current portion of unbilled receivables is included in trade accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets. The allowance for doubtful accounts was $173 as of March 31, 2024 and $197 as of March 31, 2023. For the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, bad debt expense was immaterial.
Historically, we have not experienced material losses related to the inability to collect receivables from our customers. There is presently no indication that we will not collect material amounts of accounts receivable as of March 31, 2024. The inability to collect receivables could have a material impact on our results of operations.
Concentration of Credit Risk
We grant credit to customers in a wide variety of industries worldwide and generally do not require collateral. Credit losses relating to these customers have been minimal.
Sales through our distribution agreement with Arrow Enterprise Computing Solutions, Inc. ("Arrow") totaled approximately 36% of total revenues for the year ended March 31, 2024, and 37% of total revenues for the years
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. Arrow accounted for approximately 29% and 34% of total accounts receivable as of March 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for such asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value should maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. To measure fair value, we use the following fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable:
Level 1 — Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
Level 2 — Inputs other than Level 1, that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly; and
Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions.
The carrying amounts of our cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to the short-term maturity of these instruments. Our cash equivalents balance consists primarily of U.S. Treasury Bills with maturities of one month or less.
The following table summarizes the composition of our financial assets measured at fair value at March 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| Cash equivalents | $ | 24,902 | | | — | | | — | | | $ | 24,902 | |
There were no financial assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the year ended March 31, 2023.
Equity Securities Accounted for at Net Asset Value
We held equity interests in private equity funds of $7,318 as of March 31, 2024, which are accounted for under the net asset value practical expedient as permitted under ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement. These investments are included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The net asset values of these investments are determined using quarterly capital statements from the funds, which are based on our contributions to the funds, allocation of profit and loss and changes in fair value of the underlying fund investments. Changes in fair value as reported on the capital statements are recorded through the consolidated statements of operations as non-operating income or expense. These private equity funds focus on making investments in key technology sectors, principally by investing in companies at expansion capital and growth equity stages. We have total unfunded commitments in private equity funds of $2,645 as of March 31, 2024.
Leases
We account for leases in accordance with ASC 842, Leases. For a further discussion of our accounting policies related to leases, see Note 15 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Land is not depreciated. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Computer and related equipment is generally depreciated over eighteen months to three years and furniture and fixtures are generally depreciated over three to twelve years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the useful life of the improvement or the term of the related lease. Expenditures for routine maintenance and repairs are charged against operations. Major replacements, improvements and additions are capitalized.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
In January 2023, the assets that previously comprised our owned corporate headquarters met the held for sale criteria in accordance with ASC 360, Property, Plant and Equipment ("ASC 360"), and were reclassified as such. These assets are no longer being depreciated. For further discussion on assets held for sale, see Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill is recorded when the consideration paid for an acquisition exceeds the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired. The carrying value of goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis on January 1, or more often if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of its carrying amount. For the purpose of impairment testing, we have a single reporting unit. The impairment test consists of comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount that includes goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, an impairment loss would be recognized to reduce the carrying amount to its fair value.
Our finite lived purchased intangible asset, developed technology, was valued using the replacement cost method and is being amortized on a straight-line basis over its economic life of three years as we believed this method most closely reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the assets will be consumed. Impairment losses are recognized if the carrying amount of an intangible asset is both not recoverable and exceeds its fair value.
Long-Lived Assets
We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. To determine the recoverability of our long-lived assets, we evaluate the estimated future undiscounted cash flows that are directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the long-lived asset. If the estimated future undiscounted cash flows demonstrate that recoverability is not probable, an impairment loss would be recognized. An impairment loss would be calculated based on the excess carrying amount of the long-lived asset over the long-lived asset’s fair value. The fair value would be determined based on valuation techniques such as a comparison to fair values of similar assets.
Deferred Commissions Cost
Sales commissions, bonuses, and related payroll taxes earned by our employees are considered incremental and recoverable costs of obtaining a contract with a customer. Our typical contracts include performance obligations related to term-based software licenses, SaaS offerings, perpetual software licenses, software updates, and customer support. In these contracts, incremental costs of obtaining a contract are allocated to the performance obligations based on the relative estimated standalone selling prices and then recognized on a systematic basis that is consistent with the transfer of the goods or services to which the asset relates. We do not pay commissions on annual renewals of customer support contracts for perpetual licenses. The costs allocated to software and products are expensed at the time of sale, when revenue for the functional software license or appliance is recognized. The costs allocated to software updates and customer support for perpetual licenses are amortized ratably over a period of approximately five years, the expected period of benefit of the asset capitalized. We currently estimate a period of five years is appropriate based on consideration of historical average customer life and the estimated useful life of the underlying software sold as part of the transaction. The commission paid on the renewal of subscription arrangements is not commensurate with the commission paid on the initial purchase. As a result, the cost of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and customer support on the initial term-based software license transactions are amortized over a period of approximately five years, consistent with the accounting for these costs associated with perpetual licenses. The costs of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and support for the renewal of term-based software licenses is limited to the contractual period of the arrangement, as we pay a commensurate renewal commission upon the next renewal of the subscription software license and related updates and support.
The incremental costs attributable to professional services are generally amortized over the period the related services are provided and revenue is recognized. Amortization expense related to these costs is included in sales and marketing expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenues represent amounts collected from, or invoiced to, customers in excess of revenues recognized. This results primarily from the billing of annual customer support agreements, the billing of SaaS subscription arrangements and billings for other services that have not yet been performed by us. The value of deferred revenues will increase or decrease based on the timing of invoices and recognition of revenue.
Share Repurchases
We consider all shares repurchased as canceled shares restored to the status of authorized but unissued shares on the trade date. The aggregate purchase price of the shares of our common stock repurchased is reflected as a reduction to stockholders’ equity. We account for shares repurchased as an adjustment to common stock (at par value) with the excess repurchase price allocated between additional paid-in capital and accumulated deficit.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is defined to include all changes in equity, except those resulting from investments by stockholders and distribution to stockholders.
Recently Adopted and Recently Issued Accounting Standards
There were no recently adopted accounting standards that had a material effect on our condensed consolidated financial statements and accompanying disclosures. The table below outlines recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Standard | Description | Effective Date | Effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements (or Other Significant Matters) |
| Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-07 (Topic 280): Segment Reporting | In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued a new standard to improve reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. In addition, the amendments enhance interim disclosure requirements, clarify circumstances in which an entity can disclose multiple segment measures of profit or loss, provide new segment disclosure requirements for entities with a single reportable segment, and contain other disclosure requirements. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2024, and interim periods within our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We will adopt this standard using a retrospective approach on April 1, 2024. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. |
| ASU No. 2023-09 (Topic 740): Income Taxes | In December 2023, the FASB issued a new standard to improve income tax disclosures. The standard requires greater disaggregated information about a reporting entity’s effective tax rate reconciliation as well as information on income taxes paid. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. |
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
3. Revenue
We derive revenues from various sources, including subscriptions, perpetual software licenses, customer support contracts and other services.
Subscription
Subscription includes the revenues derived from term-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. The term of our subscription arrangements is typically one to three years, but can range between one and five years. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer.
Perpetual License
Perpetual license includes the revenues from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download.
Customer Support
Customer support includes revenues associated with support contracts tied to our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. We sell our customer support contracts as a percentage of net software purchases. Customer support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement, which is typically one year on our perpetual licenses and over the term on our term-based licenses.
Other Services
Other services consist primarily of revenues related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other services can vary period over period based on the timing services are delivered and are typically recognized as the services are performed.
We do not customize our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) and installation services are not required. Software licenses are delivered before related services are provided and are functional without professional services, updates and technical support. We have concluded that our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are functional intellectual property that is distinct, as the user can benefit from the software on its own. Revenues for both perpetual and term-based licenses are typically recognized when the software is delivered and/or made available for download as this is the point the user of the software can direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the remaining benefits from, the functional intellectual property. We do not recognize software revenue related to the renewal of subscription software licenses earlier than the beginning of the new subscription period.
We also offer appliances that integrate our software with hardware and address a wide-range of business needs and use cases, ranging from support for remote or branch offices with limited IT staff up to large corporate data centers. Our appliances are almost exclusively sold via a software only model in which we sell software to a third party, which assembles an integrated appliance that is sold to end user customers. As a result, the revenues and costs associated with hardware are usually not included in our financial statements.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Our typical performance obligations include the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Performance Obligation | When Performance Obligation
is Typically Satisfied | When Payment is
Typically Due | How Standalone Selling Price is
Typically Estimated |
| Subscription |
| Term-based software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment except for certain subscription licenses which are paid for over time | Residual approach |
| Software-as-a-service (SaaS) | Ratably over the course of the contract (over time) | Annually or at the beginning of the contract period | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
| Perpetual License |
| Perpetual software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment | Residual approach |
| Customer Support |
| Software updates | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions |
| Customer support | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions |
| Other Services |
| Other professional services (except for education services) | As work is performed (over time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
| Education services | When the class is taught (point in time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
Judgments related to revenue recognition
Most of our contracts with customers contain multiple performance obligations. For these contracts, we evaluate and account for individual performance obligations separately if they are determined to be distinct. The transaction price is allocated to the separate performance obligations on a relative standalone selling price basis. Standalone selling prices of software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are typically estimated using the residual approach. Standalone selling prices for SaaS, customer support contracts, and other services are typically estimated based on observable transactions when these services are sold on a standalone basis. We recognize revenue net of sales tax.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Disaggregation of Revenue
We disaggregate revenues from contracts with customers into geographical regions. Our Americas region includes the United States, Canada, and Latin America. Our International region primarily includes Europe, Middle East, Africa, Australia, India, Southeast Asia, and China.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended March 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Americas | $ | 498,545 | | | $ | 469,244 | | | $ | 457,895 | |
| International | 340,702 | | | 315,346 | | | 311,696 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
Remaining Performance Obligations
Remaining performance obligations represent expected future revenue from existing contracts where performance obligations are unsatisfied or partially unsatisfied at the end of the reporting period. As of March 31, 2024, our remaining performance obligations (inclusive of deferred revenues) were $618,907, of which approximately 68% is expected to be recognized as revenue over the next 12 months and the remainder recognized thereafter. The vast majority of these revenues consist of SaaS arrangements, customer support, and other services. Other services consists primarily of professional services revenue which is contingent upon a number of factors, including customers' needs and scheduling.
Information about Contract Balances
Amounts collected in advance of services being provided are accounted for as deferred revenue. Nearly all of our deferred revenue balance is related to SaaS arrangements, customer support, and other services.
In some arrangements we allow customers to pay for term-based licenses over the term of the software license. Amounts recognized as revenue in excess of amounts billed are recorded as unbilled receivables. Unbilled receivables which are anticipated to be invoiced in the next twelve months are included in accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets. The opening and closing balances of our accounts receivable, unbilled receivables and deferred revenues are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts Receivable | Unbilled Receivable
(current) | Unbilled Receivable
(long-term) | Deferred Revenue
(current) | Deferred Revenue
(long-term) |
Opening balance as of March 31, 2023 | $ | 188,736 | | $ | 21,705 | | $ | 9,867 | | $ | 307,562 | | $ | 174,393 | |
| Increase/(decrease), net | 8,215 | | 4,027 | | 4,604 | | 54,888 | | (5,921) | |
Ending balance as of March 31, 2024 | $ | 196,951 | | $ | 25,732 | | $ | 14,471 | | $ | 362,450 | | $ | 168,472 | |
The net increase in accounts receivable (inclusive of unbilled receivables) is primarily a result of an increase in revenue relative to the prior year period. The net increase in deferred revenue is a result of an increase in SaaS contracts which are billed upfront but recognized ratably over the contract period and an increase in deferred customer support revenue.
The amount of revenue recognized in the period that was included in the opening deferred revenue balance was approximately $313,766 for the year ended March 31, 2024. The vast majority of this revenue consists of customer support and SaaS arrangements. The amount of revenue recognized from performance obligations satisfied in prior periods was not significant.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
4. Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the residual purchase price paid in a business combination after the fair value of all identified assets and liabilities have been recorded. It includes the estimated value of potential expansion with new customers, the opportunity to further develop sales relationships with new customers and intangible assets that do not qualify for separate recognition. Goodwill is not amortized. None of the goodwill recorded is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
There were no impairments to the carrying amount of goodwill during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 or 2022.
Goodwill balances are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Opening balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | |
| Additions/(Impairments) | | — | | | — | |
| Ending balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | |
Intangible assets, net
Intangible assets are recorded at cost and amortized over useful lives of three years.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2024 | | March 31, 2023 |
| Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value |
| Developed technology | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (2,708) | | | $ | 1,042 | | | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (1,458) | | | $ | 2,292 | |
Amortization expense from acquired intangible assets was $1,250 for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024 and 2023 and $208 for fiscal year ended 2022.
As of March 31, 2024, the estimated future amortization expense of intangible assets with finite lives is $1,042, which will be fully recognized in fiscal year 2025.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
5. Assets Held for Sale
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, we entered into an exclusive agreement to sell our owned corporate headquarters in Tinton Falls, New Jersey for $40,000 in cash consideration and determined the assets and land related to headquarters met the criteria for classification as assets held for sale in accordance with ASC 360, Impairment and Disposal of Long-Lived Assets ("ASC 360"). The property's previous carrying amount of $92,161 was written down to its estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell, of $38,680, resulting in a non-cash impairment charge of $53,481 on our consolidated statements of operations for the period ended March 31, 2023. Upon closing of the transaction, we intend to enter into a lease for a portion of the premises.
As of March 31, 2024, the sale has not yet been finalized and the exclusivity of the agreement has expired. As a result of the expiration of the exclusivity, we received a payment for $1,670 related to non-refundable escrow, which is recorded in other income (loss) on our consolidated statements of operations for the period ended March 31, 2024.
The assets have been classified as held for sale for more than one year. In accordance with ASC 360, assets not sold by the end of the one-year period may still qualify as held for sale, if certain conditions are met. The Board of Directors reconfirmed their approval of the sale at the January 2024 meeting and we believe the sale will be completed in calendar year 2024. As of March 31, 2024, we concluded all of the held for sale criteria is still met, and the assets are properly classified on the consolidated balance sheets. In addition, we have assessed whether there are any indicators of impairment and have concluded that the current carrying amount represents the estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell, and no additional remeasurement should be recorded.
6. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Computers, servers and other equipment | | $ | 45,620 | | | $ | 43,135 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | 2,965 | | | 3,264 | |
| Leasehold improvements | | 8,180 | | | 8,433 | |
| Purchased software | | 2,586 | | | 1,862 | |
| Construction in process | | 189 | | | 111 | |
| | 59,540 | | | 56,805 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (51,579) | | | (48,518) | |
| | $ | 7,961 | | | $ | 8,287 | |
We recorded depreciation and amortization expense of $5,165, $8,958, and $10,708 for the years ended 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Depreciation expense allocated to our cost of goods sold was approximately $938 for the year ended 2023, and $1,250 for the year ended 2022. There was no depreciation expense allocated to our cost of goods sold for the year ended 2024.
As discussed in Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements, assets related to the sale of the Tinton Falls, New Jersey headquarters were reclassified to assets held for sale in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, at which time depreciation ended.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
7. Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Compensation and related payroll taxes | | $ | 70,961 | | | $ | 58,112 | |
| Other | | 46,283 | | | 39,776 | |
| | $ | 117,244 | | | $ | 97,888 | |
8. Commitments and Contingencies
Purchase Commitments
We, in the normal course of business, enter into various purchase commitments for goods or services. Our outstanding commitments primarily relate to marketing and IT services and also include the remaining purchase commitments for our use of certain cloud services with third-party providers. Total non-cancellable purchase commitments as of March 31, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended March 31, |
| | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 and beyond | | Total |
| Purchase commitments | | $ | 42,011 | | | $ | 9,652 | | | $ | 1,532 | | | $ | 111,527 | | | $ | 164,722 | |
In June 2022, we entered into an amended agreement with a third-party provider, in the ordinary course of business, for the use of certain cloud services through June 2027. Under the amended agreement, we committed to a purchase of $200,000 throughout the term of the agreement. As of March 31, 2024, we had $111,500 of remaining obligations under the purchase agreement.
We have certain software royalty commitments associated with the shipment and licensing of certain products. Royalty expense is generally based on a fixed cost per unit shipped or a fixed fee for unlimited units shipped over a designated period. Royalty expense, included in cost of subscription and perpetual license revenues, was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended March 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Royalty expense | | $ | 9,717 | | | $ | 9,339 | | | $ | 11,188 | |
Warranties and Indemnifications
We typically offer a 90-day limited product warranty for our software. To date, costs related to this product warranty have not been significant.
We provide certain provisions within our software licensing agreements to indemnify our customers from any claim, suit or proceeding arising from alleged or actual intellectual property infringement. These provisions continue in perpetuity, along with our software licensing agreements. We have never incurred a liability relating to one of these indemnification provisions, and management believes that the likelihood of any future payout relating to these provisions is remote. Therefore, we have not recorded a liability during any period for these indemnification provisions.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Lease Obligations
Please refer to Note 15 of the notes to the financial statements for more detail on our minimum lease commitments.
Legal Proceedings
We do not believe that we are currently party to any pending legal action that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on our business or operating results.
During fiscal 2022, we entered into settlement agreements resulting in a $7,900 gain which resolved certain legal matters. The settlement amounts are recorded in general and administrative expenses net against related legal expenses.
9. Capitalization
Common Stock
We have 43,548 and 44,140 shares of common stock, par value $0.01, outstanding at March 31, 2024 and March 31, 2023, respectively.
Our share repurchase program has been funded by our existing cash and cash equivalent balances, as well as cash flows provided by our operations.
The Board of Directors (the "Board") had previously approved a share repurchase program of $250,000 in April 2023. The Board's authorization has no expiration date. During fiscal 2024, we repurchased $184,021 of our common stock, or approximately 2,479 shares. As a result, $71,944 remained available under the current authorization as of March 31, 2024.
Subsequent Event
On April 18, 2024, the Board of Directors approved an increase in our share repurchase program so that $250,000 was available. The Board's authorization has no expiration date.
Shares Reserved for Issuance
At March 31, 2024, we have reserved 6,149 shares in connection with our Stock Plans discussed in Note 10 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
10. Stock Plans
We maintain the Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2016 Incentive Plan”) for granting awards to employees. On August 29, 2023, our shareholders approved an amendment to the 2016 Incentive Plan to increase the maximum number of shares of common stock that may be delivered under the plan to 14,250, an increase of 3,200 shares. The 2016 Incentive Plan authorizes a broad range of awards including stock options, stock appreciation rights, full value awards (including restricted stock, restricted stock units, performance shares or units and other stock-based awards) and cash-based awards. As of March 31, 2024, approximately 3,754 shares were available for future grant under the 2016 Incentive Plan.
As of March 31, 2024, we have granted non-qualified stock options, restricted stock units and performance stock awards under our stock incentive plans. Historically, most equity awards granted by us under our stock incentive plans generally vest quarterly over a three-year period, except that the shares that would otherwise vest quarterly over the first twelve months do not vest until the first anniversary of the grant. We anticipate that future grants under our stock incentive plans will be restricted stock units and performance stock awards and do not anticipate that we will grant stock options.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
The following table presents the stock-based compensation expense included in cost of revenues, sales and marketing, research and development, general and administrative and restructuring expenses for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022. Stock-based compensation is attributable to restricted stock units, performance-based awards and the ESPP.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cost of revenues | | $ | 6,832 | | | $ | 4,787 | | | $ | 4,474 | |
| Sales and marketing | | 36,630 | | | 43,081 | | | 37,431 | |
| Research and development | | 21,585 | | | 28,540 | | | 33,870 | |
| General and administrative | | 27,987 | | | 26,731 | | | 27,679 | |
| Restructuring | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | $ | 94,551 | | | $ | 105,746 | | | $ | 105,163 | |
As of March 31, 2024, there was approximately $125,213 of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to all of our employee stock plans that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.76 years. We account for forfeitures as they occur. To the extent that awards are forfeited, stock-based compensation will be different from our current estimate.
Stock option activity is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options | | Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | | 553 | | | $ | 73.58 | | | | | |
| Granted | | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Exercised | | (58) | | | 48.88 | | | | | |
| Forfeited | | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Expired | | (371) | | | 86.95 | | | | | |
Outstanding at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Exercisable at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | |
The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $1,378, $1,176, and $12,704 in the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Restricted stock unit activity is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-Vested Restricted Stock Units | | Number
of
Awards | | Weighted-
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value |
| Non-vested as of March 31, 2023 | | 2,953 | | | $ | 62.52 | |
| Granted | | 1,483 | | | 70.42 | |
| Vested | | (1,641) | | | 60.08 | |
| Forfeited | | (378) | | | 65.74 | |
| Non-vested as of March 31, 2024 | | 2,417 | | | $ | 68.52 | |
The total fair value of the restricted stock units that vested during the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $118,047, $114,422 and $122,259, respectively. The fair value of awards includes the awards with a market condition described below.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Performance Based Awards
In fiscal 2024, we granted 120 performance stock units ("PSUs") to certain executives. Vesting of these awards is contingent upon i) us meeting certain non-GAAP performance goals (performance-based) in fiscal 2024 and ii) our customary service periods. The awards vest over three years. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized over the vesting term using the accelerated method. During each financial period, management estimates the probable number of PSUs that would vest until the ultimate achievement of the performance goals is known. Based on our results, the PSUs achieved at 108%. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table.
In fiscal 2023, we granted 126 PSUs to certain executives. Vesting of these awards is contingent upon i) us meeting certain non-GAAP performance goals (performance-based) in fiscal 2023 and ii) our customary service periods. The awards vest over three years. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized over the vesting term using the accelerated method. Based on our results, the PSUs achieved at 128%. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table.
Awards with a Market Condition
In fiscal 2024, we granted 120 market PSUs to certain executives. The vesting of these awards is contingent upon us meeting certain total shareholder return ("TSR") levels as compared to the Russell 3000 market index over the next three years. The awards vest in three annual tranches and have a maximum potential to vest at 200% (240 shares) based on TSR performance. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the estimated fair value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized using the accelerated method over the vesting term. The estimated fair value was calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the awards granted during the year was $87.90 per unit. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table above.
In fiscal 2023, we granted 126 market PSUs to certain executives. The vesting of these awards is contingent upon us meeting certain TSR levels as compared to the Russell 3000 market index over the next three years. The awards vest in three annual tranches and have a maximum potential to vest at 200% (252 shares) based on TSR performance. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the estimated fair value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized using the accelerated method over the vesting term. The estimated fair value was calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the awards granted during the year was $76.48 per unit. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table above.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The ESPP is a shareholder approved plan under which substantially all employees may purchase our common stock through payroll deductions at a price equal to 85% of the lower of the fair market values of the stock as of the beginning or the end of six-month offering periods. An employee’s payroll deductions under the ESPP are limited to 10% of the employee’s salary and employees may not purchase more than $25 of stock during any calendar year. Employees purchased 188 shares in exchange for $10,578 of proceeds in fiscal 2024 and 213 shares in exchange for $10,873 of proceeds in fiscal 2023. The ESPP is considered compensatory and the fair value of the discount and look back provision are estimated using the Black-Scholes formula and recognized over the six-month withholding period prior to purchase. The total expense associated with the ESPP for fiscal 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $3,146, $3,740 and $3,341, respectively. As of March 31, 2024, there was approximately $1,177 of unrecognized cost related to the current purchase period of our ESPP.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
11. Income Taxes
The components of income (loss) before income taxes were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Domestic | | $ | 62,082 | | | $ | (35,288) | | | $ | 25,905 | |
| Foreign | | 21,531 | | | 19,926 | | | 17,509 | |
| | $ | 83,613 | | | $ | (15,362) | | | $ | 43,414 | |
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
The components of income tax expense (benefit) were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Current: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | 7,845 | | | $ | 6,986 | | | $ | 284 | |
| State | | 4,242 | | | 3,375 | | | 361 | |
| Foreign | | 12,220 | | | 10,725 | | | 9,096 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | (82,773) | | | (607) | | | 28 | |
| State | | (19,740) | | | — | | | — | |
| Foreign | | (7,087) | | | (67) | | | 21 | |
| | $ | (85,293) | | | $ | 20,412 | | | $ | 9,790 | |
A reconciliation of the statutory tax rates and the effective tax rates for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Statutory federal income tax expense (benefit) rate | | 21.0 | % | | (21.0) | % | | 21.0 | % |
| State and local income tax expense, net of federal income tax effect | | 2.4 | % | | (11.8) | % | | 0.8 | % |
| Foreign earnings taxed at different rates | | 5.7 | % | | 28.0 | % | | 6.2 | % |
| U.S. tax on GILTI & FDII | | (3.3) | % | | (17.1) | % | | 0.5 | % |
| Domestic permanent differences including acquisition items | | 1.1 | % | | 4.7 | % | | 3.6 | % |
| Foreign tax credits | | (2.5) | % | | (35.5) | % | | (5.3) | % |
| Research credits | | (9.3) | % | | (74.6) | % | | (28.3) | % |
| Tax reserves | | — | % | | (1.2) | % | | 2.6 | % |
| Valuation allowance | | (125.3) | % | | 219.9 | % | | 18.3 | % |
| Enacted tax law changes | | (0.4) | % | | 3.6 | % | | 0.3 | % |
| Stock-based compensation | | 6.7 | % | | 41.6 | % | | (1.6) | % |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Other differences, net | | 1.9 | % | | (3.7) | % | | 4.5 | % |
| Effective income tax expense (benefit) | | (102.0) | % | | 132.9 | % | | 22.6 | % |
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
The significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | |
| Net operating losses | | $ | 6,533 | | | $ | 9,106 | |
| Equity investment/Capital losses | | 952 | | | 889 | |
| Stock-based compensation | | 5,338 | | | 11,912 | |
| Deferred revenue | | 29,748 | | | 24,025 | |
| Tax credits | | 28,020 | | | 42,986 | |
| Accrued expenses | | 1,775 | | | 1,816 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts and other reserves | | 928 | | | 572 | |
| R&D Capitalization under IRC § 174 | | 58,867 | | | 32,091 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 9,305 | | | 9,449 | |
| Other, DTA | | 2,228 | | | 98 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | | (18,140) | | | (122,921) | |
| Total deferred tax assets | | 125,554 | | | 10,023 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
| | | | |
| Withholding taxes | | (1,091) | | | (393) | |
| Deferred commissions | | (12,573) | | | (9,764) | |
| Other, DTL | | (2,426) | | | — | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | | (16,090) | | | (10,157) | |
| Net deferred tax asset (liability) | | $ | 109,464 | | | $ | (134) | |
Net deferred tax assets arise due to the recognition of income and expense items for tax purposes, which differ from those used for financial statement purposes. ASC 740, Income Taxes, provides for the recognition of deferred tax assets if realization of such assets is more likely than not. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we considered all available objective and verifiable evidence both positive and negative, including historical levels of pre-tax income (loss) both on a consolidated basis and tax reporting entity basis, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies. As a result of this analysis, we determined that it is more likely than not that we will realize the benefits of the majority of our gross deferred tax assets and therefore recorded the release of the previously established valuation allowance as an income tax benefit in the current period. At March 31, 2024 and 2023, we recorded valuation allowances of $18,140 and $122,921, respectively, representing an increase in deferred tax benefit of $104,781 for the period ended March 31, 2024.
At March 31, 2024, we had federal net operating loss ("NOL") carryforwards of $5,981, all of which will not expire. As of March 31, 2024, we had deferred tax assets related to state NOL carryforwards of $1,013 which expire over various years beginning in March 2033 depending on the jurisdiction. As of March 31, 2024, we had foreign NOL carryforwards of $3,064 that will expire over various years beginning in March 2028 depending on the jurisdiction and $34,035 that will not expire. As of March 31, 2024, we had federal capital loss carryforwards of $3,988 that will expire in March 2027. At March 31, 2024, we had foreign capital loss carryforwards of $310 that will not expire.
We also had federal and state research tax credits ("R&D credit") carryforwards of approximately $5,177 and $26,467, respectively. The federal R&D credit carryforwards expire from March 2039 through March 2044, and the New Jersey R&D credit carryforwards of $16,857 expire over various years beginning from March 2025 through March 2038. The California R&D credits of $9,610 do not expire. We also had federal foreign tax credits (“FTC”) carryforwards of approximately $3,999. The federal FTC carryforwards expire from March 2030 through March 2034. We also had $215 in foreign FTC carryforwards that will expire over various years beginning in March 2025.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
We conduct business globally and as a result, file income tax returns in the United States and in various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. The following table summarizes the tax years subject to income tax examinations by tax authorities as of March 31, 2024. The years subject to income tax examination in our foreign jurisdictions cover the maximum time period with respect to these jurisdictions. Due to NOLs, in some cases the tax years continue to remain subject to examination with respect to such NOLs.
| | | | | |
| Tax Jurisdiction | Years Subject to Income
Tax Examination |
| U.S. Federal | 2020 - Present |
| Foreign jurisdictions | 2013 - Present |
The calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax regulations in each of our tax jurisdictions. The number of years with open tax audits varies depending on the tax jurisdiction. A number of years may lapse before a particular matter is audited and finally resolved. A reconciliation of the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| | | | | |
| Balance at March 31, 2021 | $ | 2,211 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2022 | 2,808 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 90 | |
| Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | |
| Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (117) | |
| Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | 4,232 | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | |
| Balance at March 31, 2022 | 9,224 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2023 | 394 | |
| Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | (90) | |
| Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | |
| Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (140) | |
| Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | |
| Balance at March 31, 2023 | 9,388 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2024 | 502 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 3 | |
| Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | |
| Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (220) | |
| Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | |
| Balance at March 31, 2024 | $ | 9,673 | |
We estimate that no significant remaining unrecognized tax benefits will be realized during the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025. Interest income, expense and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recorded in income tax expense in the consolidated statements of operations. In the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, the impact related to interest expense, interest income and penalties was not significant.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
12. Employee Benefit Plan
We have a defined contribution plan, as allowed under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code, covering substantially all US employees. Effective January 1, 2012, we make contributions equal to a discretionary percentage of the employee’s contributions determined by us. During the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we made contributions of $2,889, $2,525, and $2,923, respectively.
13. Segment Information
We operate in one segment. Our products and services are sold throughout the world, through direct and indirect sales channels. Our chief operating decision maker (the “CODM”) is the Chief Executive Officer. The CODM makes operating performance assessment and resource allocation decisions on a global basis. The CODM does not receive discrete financial information about asset allocation, expense allocation or profitability by product or geography.
Revenues by geography are based upon the billing address of the customer. All transfers between geographic regions have been eliminated from consolidated revenues. The following table sets forth revenue and long-lived assets by geographic area:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenue: | | | | | | |
| United States | | $ | 437,560 | | | $ | 416,347 | | | $ | 398,632 | |
| Other | | 401,687 | | | 368,243 | | | 370,959 | |
| | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
No individual country other than the United States accounts for 10% or more of revenues in the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022. Revenue included in the “Other” caption above primarily relates to our operations in Europe, Australia, Canada and Asia.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Long-lived assets: | | | | |
| United States | | $ | 192,485 | | | $ | 184,356 | |
| Other | | 45,121 | | | 47,304 | |
| | $ | 237,606 | | | $ | 231,660 | |
At March 31, 2024 and 2023 no individual country, other than the United States, accounts for 10% or more of long-lived assets.
14. Restructuring
Beginning in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2024, we initiated a restructuring plan intended to enhance customer satisfaction through the reorganization and redesign of our customer success functions. The realignment of the customer success structure aims to optimize operational efficiency and improve continuity for our customers through the pre-sales and post-sales experience. These charges relate primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions, stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan and office termination and exit charges. We anticipate the restructuring plan will be completed in the second half of fiscal 2025. The total costs to be incurred related to the restructuring plan cannot be estimated at this time.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2022 we initiated a restructuring program which was completed in fiscal 2023. It was aimed to increase efficiency in our sales, marketing and distribution functions as well as reduce costs across all functional areas. The plan included a reorganization to combine our EMEA and APJ field organizations into our
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
International region. These restructuring charges related primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions and stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan.
For the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, restructuring charges were comprised of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Employee severance and related costs | | $ | 2,811 | | | $ | 12,845 | | | $ | 4,483 | |
Lease exit costs (1) | | 220 | | | — | | | — | |
| Stock-based compensation | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | |
| Total restructuring charges | | $ | 4,548 | | | $ | 15,452 | | | $ | 6,192 | |
(1) Lease exit costs relate to one office for the year ended March 31, 2024. There were no lease exit charges for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022.
Restructuring accrual
The accrual activity related to our restructuring plans for the years ended March 31, 2024 and 2023 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended March 31, |
| | | 2024 (1) | | 2023 |
| Beginning balance | | $ | 3,211 | | | $ | 2,261 | |
| Employee severance and related costs | | 2,811 | | | 12,845 | |
| Payments | | (3,276) | | | (11,895) | |
| Ending balance | | $ | 2,746 | | | $ | 3,211 | |
(1) During fiscal 2024, there were no new charges incurred related to the completed restructuring plan. Payments made related to the completed plan were $3,149, resulting in an insignificant remaining accrual at March 31, 2024.
15. Leases
We determine if an arrangement contains a lease at inception. We generally lease our facilities under operating leases. Operating lease right-of-use ("ROU") assets are included in operating lease assets on our consolidated balance sheets. Current portion of operating lease liabilities and long-term operating lease liabilities are included on our consolidated balance sheets.
ROU assets represent our right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent our obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of our leases do not provide an implicit rate, we generally use our incremental borrowing rate based on the estimated rate of interest for collateralized borrowing over a similar term of the lease payments at the commencement date.
We recognize operating lease costs over the estimated term of the lease, which includes options to extend lease terms that are reasonably certain of being exercised, starting when possession of the property is taken from the landlord. When a lease contains a predetermined fixed escalation of the minimum rent, we recognize the related
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
operating lease cost on a straight-line basis over the lease term. In addition, certain of our lease agreements include variable lease payments, such as estimated tax and maintenance charges. These variable lease payments are excluded from minimum lease payments and are included in the determination of lease cost when it is probable that the expense has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated.
Our lease liabilities relate primarily to operating leases for our global office infrastructure. These operating leases expire at various dates through fiscal 2031. We did not have any finance leases for the years ended March 31, 2024 or 2023.
Net lease cost recognized in our consolidated statements of operations is summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended March 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Operating lease cost | $ | 5,770 | | | $ | 5,449 | | | $ | 7,129 | |
| Short-term lease cost | 272 | | | 631 | | | 123 | |
| Variable lease cost | 1,333 | | | 1,360 | | | 1,608 | |
| Net lease cost | $ | 7,375 | | | $ | 7,440 | | | $ | 8,860 | |
Cash flow information
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended March 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash paid for operating lease liabilities | $ | 5,033 | | | $ | 5,421 | | | $ | 8,277 | |
| Additions of operating lease assets (non-cash) | $ | 5,528 | | | $ | 3,023 | | | $ | 1,827 | |
As of March 31, 2024, the maturities of lease liabilities based on the total minimum lease commitment amount including options to extend lease terms that are reasonably certain of being exercised are as follows:
| | | | | |
| 2025 | $ | 4,624 | |
| 2026 | 2,973 | |
| 2027 | 1,740 | |
| 2028 | 1,601 | |
| 2029 | 932 | |
| Thereafter | 683 | |
| Total minimum lease payments | 12,553 | |
| Less: Imputed interest | 463 | |
| Present value of operating lease liabilities | 12,090 | |
| Less: Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 4,935 | |
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | $ | 7,155 | |
As of March 31, 2024, the minimum lease commitment amount for operating leases signed but not yet commenced was $743. These commitments are related to office lease renewals that expire at various dates through fiscal 2030.
Commvault Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(In thousands, except per share data)
Lease term and Discount rate
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended March 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Weighted-average remaining term (in years) | 3.60 | | 3.72 |
| Weighted-average discount rate | 4 | % | | 4 | % |
16. Revolving Credit Facility
On December 13, 2021, we entered into a five-year $100,000 senior secured revolving credit facility (the “Credit Facility”) with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. The Credit Facility is available for share repurchases, general corporate purposes, and letters of credit. The Credit Facility contains financial maintenance covenants, including a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio. The Credit Facility also contains certain customary events of default which would permit the lender to, among other things, declare all loans then outstanding to be immediately due and payable if such default is not cured within applicable grace periods. The Credit Facility also limits our ability to incur certain additional indebtedness, create or permit liens on assets, make acquisitions, make investments, loans or advances, sell or transfer assets, pay dividends or distributions, and engage in certain transactions with foreign affiliates. Outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility accrue interest at an annual rate equal to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate plus 1.25% subject to increases based on our actual leverage. The unused balance on the Credit Facility is also subject to a 0.25% annual interest charge subject to increases based on our actual leverage. As of March 31, 2024, there were no borrowings under the Credit Facility and we were in compliance with all covenants.
We have deferred the expense related to debt issuance costs, which are classified as other assets, and will amortize the costs into interest expense over the term of the Credit Facility. Unamortized amounts at March 31, 2024 and 2023 were $313 and $428, respectively. The amortization of debt issuance costs and interest expense incurred for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended March 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | $ | 115 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 34 | |
| Interest expense | 253 | | | 253 | | | 75 | |
| Total charges | $ | 368 | | | $ | 368 | | | $ | 109 | |
17. Subsequent Event
On April 15, 2024, we signed an agreement to acquire all of the shares of Appranix, Inc., a Boston based cloud cyber resilience company, for total consideration of approximately $26,000, subject to customary transaction adjustments. There is an additional potential earn out if certain financial metrics are met through the initial fourteen-month period after the closing date. The primary reason for the business combination is to extend our product offerings in our existing cyber resiliency market opportunity. As the transaction occurred subsequent to year-end, we are still evaluating the purchase price allocation of the transaction but expect the primary assets acquired to be intangible assets and goodwill. Acquired tangible assets and assumed liabilities are expected to be immaterial. The allocation is expected to be finalized during fiscal 2025.
| | | | | |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| | | | | |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
(a)Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as of March 31, 2024. Based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of March 31, 2024.
(b)Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. There are inherent limitations in the effectiveness of any internal control, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of controls. Accordingly, even an effective internal control can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation. Further, because of changes in conditions, the effectiveness of any internal control may vary over time.
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2024. In making this assessment, management used the framework set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") in the 2013 Internal Control—Integrated Framework.
Based on our assessment, using those criteria, our management concluded that, as of March 31, 2024, our internal control over financial reporting was effective. The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2024 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report, which is included below in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(c)Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2024 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of Commvault Systems, Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Commvault Systems, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Commvault Systems, Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2024, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of March 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2024, and the related notes and our report dated May 13, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Iselin, New Jersey
May 13, 2024
| | | | | |
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
On February 1, 2024, Nicholas Adamo, Chairman of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 2,450 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until September 6, 2024.
On February 2, 2024, Vivie Lee, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 4,100 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until September 6, 2024.
On February 16, 2024, Allison Pickens, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 4,100 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until March 4, 2025.
During the three months ended March 31, 2024, no other directors or officers of the Company adopted or terminated any Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement or “Non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” as each term is defined in Item 408 of Regulation S-K.
| | | | | |
| Item 9C. | Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
Not applicable.
PART III
| | | | | |
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
We will furnish to the SEC a definitive Proxy Statement not later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. Information with respect to this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the sections of our 2024 Proxy Statement captioned, “Board of Directors” and “Corporate Governance”.
Our Board of Directors has adopted a code of business ethics and conduct, which applies to all of our employees. The code of business ethics and conduct is in addition to our code of ethics for senior financial officers. The full texts of our code of business ethics and conduct and our code of ethics for senior financial officers can be found on our website, www.commvault.com.
| | | | | |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
Information with respect to this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the sections of our 2024 Proxy Statement captioned “Executive Compensation” (excluding the information under the subheading "Pay Versus Performance").
| | | | | |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
Information with respect to this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the section of our 2024 Proxy Statement captioned "Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" and "Fiscal 2024 Equity Compensation Plan Information".
| | | | | |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
Information with respect to this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the sections of our 2024 Proxy Statement captioned “Transactions with Related Persons” and "Corporate Governance - Independence and Composition of our Board of Directors".
| | | | | |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
Information with respect to this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the section of our 2024 Proxy Statement captioned “Ratification of the Appointment of Independent Auditors - Audit, Audit-related, Tax and All Other Fees”.
PART IV
| | | | | |
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
Financial Statements
See “Index to Consolidated Financial Statements” set forth in Item 8 for a list of financial statements filed as part of this report.
Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules are omitted because they are not required or because the required information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto.
Exhibits
The following exhibits are incorporated by reference or filed herewith.
| | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | Description |
| Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Commvault Systems, Inc., as amended (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2019). |
| Certificate of Amendment of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Commvault Systems, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant's Form 8-K dated August 28, 2020). |
| Certificate of Amendment of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Commvault Systems, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant's Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2023). |
| Amended and Restated Bylaws of Commvault Systems, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2022). |
| Certification of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock of Commvault Systems, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated November 14, 2008). |
| Form of Common Stock Certificate (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Commission File No. 333-132550). |
| Description of Securities. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2023). |
| Form of Voting Trust Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 9.1 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Commission File No. 333-132550). |
| Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Commission File No. 333-132550). |
| Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2007). |
| Form of Indemnity Agreement between Commvault Systems, Inc. and each of its current officers and directors (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2022). |
| Commvault Systems, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan dated December 9, 2013 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2014). |
| Employment Agreement, dated January 8, 2019, between the Company and Sanjay Mirchandani. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 5, 2019). |
| Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan (as amended by the Sixth Amendment thereof) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2022). |
| Credit Agreement, dated December 13, 2021, by and among Commvault Systems, Inc., the Lenders from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Form 10-Q for the quarter ended December 31, 2021). |
| Offer Letter with Gary Merrill, dated April 28, 2022 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K dated April 28, 2022). |
| Executive Retention Agreement with Gary Merrill dated July 27, 2022 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2022). |
| List of Subsidiaries of Commvault Systems, Inc. |
| Consent of Ernst & Young LLP |
| Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| Commvault Systems, Inc. Clawback Policy dated October 16, 2023. |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
| | | | | |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| ** | Furnished herewith. |
| | | | | |
| Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary |
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of Tinton Falls, State of New Jersey, on May 13, 2024.
| | | | | |
| COMMVAULT SYSTEMS, INC. |
| |
| By: | /s/ SANJAY MIRCHANDANI |
| Sanjay Mirchandani |
| Director, President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on May 13, 2024.
| | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title |
| |
| /s/ SANJAY MIRCHANDANI | | Director, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
| Sanjay Mirchandani | |
| /s/ GARY MERRILL | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
| Gary Merrill | |
| /s/ NICHOLAS ADAMO | | Chairman of the Board |
| Nicholas Adamo | |
| /s/ MARTHA H. BEJAR | | Director |
| Martha H. Bejar | | |
| /s/ KEITH GEESLIN | | Director |
| Keith Geeslin | |
| /s/ VIVIE LEE | | Director |
| Vivie Lee | |
| /s/ CHARLES E. MORAN | | Director |
| Charles E. Moran | |
| /s/ ALLISON PICKENS | | Director |
| Allison Pickens | |
| /s/ A. SHANE SANDERS | | Director |
| A. Shane Sanders | | |
| /s/ ARLEN SHENKMAN | | Director |
| Arlen Shenkman | |
Exhibit 21.1
Subsidiaries of Commvault Systems, Inc.
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| Subsidiary | | Jurisdiction of Organization |
| | |
| Advanced Data Life Cycle Management Inc. | | Delaware |
| Commvault Tinton Falls Urban Renewal LLC | | Delaware |
| Hedvig, Inc. | | Delaware |
| Commvault Systems (Canada) Inc. | | Ontario, Canada |
| Commvault Systems Mexico S. de R.L. de C.V. | | Mexico |
| Commvault Systems Mexico Administracion, S. de R.L. de C.V. | | Mexico |
| Commvault Systems International B.V. | | The Netherlands |
| Commvault Systems (India) Private Limited | | India |
| Commvault Systems (Australia) Pty. Ltd. | | Australia |
| Commvault Systems (New Zealand) Limited | | New Zealand |
| Commvault Systems (Singapore) Private Limited | | Singapore |
| Commvault Systems Limited | | England |
| Commvault Systems GmbH | | Germany |
| Commvault Systems (Japan) KK | | Japan |
| Commvault Systems Ireland Limited | | Ireland |
| Commvault Systems Italia Srl | | Italy |
| Commvault Systems AB Srl | | Sweden |
| Commvault Systems (Hong Kong) Limited | | Hong Kong |
| Commvault Software Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd | | China |
| Commvault Systems (South Africa) (Pty) Ltd | | South Africa |
| Commvault Systems (Israel) Ltd. | | Israel |
Commvault Systems Belgium BVBA | | Belgium |
Commvault Systems (Thailand) Ltd. | | Thailand |
| CommVault Istanbul Yazýlým Hizmetleri Limited Sirketi (Commvault Software Services Ltd.) | | Turkey |
Commvault Systems (Austria) GmbH | | Austria |
| Commvault Systems (Switzerland) GmbH | | Switzerland |
| Commvault Systems (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. | | Malaysia |
| Commvault Systems (Poland) sp. zo.o. | | Poland |
| Commvault System, S.L.U. | | Spain |
Exhibit 23.1
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
We consent to the incorporation by reference in the following Registration Statements:
(1)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-138578) pertaining to the 1996 Stock Option Plan and the 2006 Long-Term Stock Incentive Plan of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(2)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-192014) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(3)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-213211) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(4)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-221163) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the First Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(5)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-228076) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Second Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(6)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-234384) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Third Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(7)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-249710) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Fourth Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(8)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-260526) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Fifth Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.,
(9)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-268097) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Sixth Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc., and
(10)Registration Statement (Form S-8 No. 333-275247) pertaining to the Commvault Systems, Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended through the Seventh Amendment, of Commvault Systems, Inc.
of our reports dated May 13, 2024, with respect to the consolidated financial statements of Commvault Systems, Inc. and the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting of Commvault Systems, Inc. included in this Annual Report (Form 10-K) of Commvault Systems, Inc. for the year ended March 31, 2024.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Iselin, New Jersey
May 13, 2024
Exhibit 31.1
Certification of Chief Executive Officer
Required by Rule 13a-14(a) (17 CFR 240.13a-14(a))
I, Sanjay Mirchandani, certify that:
1.I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Commvault Systems, Inc.;
2.Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3.Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4.The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a)Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b)Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c)Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d)Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5.The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing equivalent functions):
(a)All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b)Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
| | |
| /s/ SANJAY MIRCHANDANI |
| Sanjay Mirchandani |
| Director, President and Chief Executive Officer |
| (Principal Executive Officer) |
Date: May 13, 2024
Exhibit 31.2
Certification of Chief Financial Officer
Required by Rule 13a-14(a) (17 CFR 240.13a-14(a))
I, Gary Merrill, certify that:
1.I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Commvault Systems, Inc.;
2.Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3.Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4.The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a)Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b)Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c)Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d)Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5.The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing equivalent functions):
(a)All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b)Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
| | |
| /s/ GARY MERRILL |
| Gary Merrill |
| Chief Financial Officer |
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
Date: May 13, 2024
Exhibit 32.1
Certification Pursuant To
18 U.S.C. Section 1350
As Adopted Pursuant To
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Commvault Systems, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the period ended March 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Report”), I, Sanjay Mirchandani, Director, President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. § 1350, as adopted pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1)The Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2)The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| | |
| /s/ SANJAY MIRCHANDANI |
| Sanjay Mirchandani |
| Director, President and Chief Executive Officer |
| (Principal Executive Officer) |
May 13, 2024
Exhibit 32.2
Certification Pursuant To
18 U.S.C. Section 1350
As Adopted Pursuant To
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Commvault Systems, Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the period ended March 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Report”), I, Gary Merrill, Chief Financial Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. § 1350, as adopted pursuant to § 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1)The Report fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2)The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| | |
| /s/ GARY MERRILL |
| Gary Merrill |
| Chief Financial Officer |
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
May 13, 2024
COMMVAULT SYSTEMS, INC.
Clawback Policy
(as of October 16, 2023)
The Board of Directors (the “Board”) of Commvault Systems, Inc. (the “Company”) believes it is appropriate for the Company to adopt the following clawback policy (the “Policy”) to be applied to Executive Officers of the Company. This Policy is in addition to, and not in substitution of, any clawback policy maintained by the Company as of the date hereof.
1. Definitions
a) “Committee” means the Talent Management and Compensation Committee of the Board.
b) “Company Group” means the Company and each of its Subsidiaries, as applicable.
c) “Covered Compensation” means any Incentive-Based Compensation granted, vested or paid to a person who served as an Executive Officer at any time during the performance period for the Incentive-Based Compensation and that was Received (i) on or after the effective date of the applicable Nasdaq listing standards, (ii) after the person became an Executive Officer, and (iii) at a time that the Company had a class of securities listed on a national securities exchange or a national securities association.
d) “Effective Date” means October 16, 2023, the date such Policy was adopted by the Board.
e) “Erroneously Awarded Compensation” means the amount of Covered Compensation granted, vested or paid to a person during the fiscal period when the applicable Financial Reporting Measure relating to such Covered Compensation was attained that exceeds the amount of Covered Compensation that otherwise would have been granted, vested or paid to the person had such amount been determined based on the applicable Restatement, computed without regard to any taxes paid (i.e., on a pre-tax basis). For Covered Compensation based on stock price or total stockholder return, where the amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation is not subject to mathematical recalculation directly from the information in a Restatement, the Committee will determine the amount of such Covered Compensation that constitutes Erroneously Awarded Compensation, if any, based on a reasonable estimate of the effect of the Restatement on the stock price or total stockholder return upon which the Covered Compensation was granted, vested or paid and the Committee shall maintain documentation of such determination and provide such documentation to the Nasdaq.
f) “Exchange Act” means the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
g) “Executive Officer” means each “officer” of the Company as defined under Rule 16a-1(f) under Section 16 of the Exchange Act, which shall be deemed to include any individuals identified by the Company as executive officers pursuant to Item 401(b) of Regulation S-K under the Exchange Act. Both current and former Executive Officers are subject to the Policy in accordance with its terms.
h) “Financial Reporting Measure” means (i) any measure that is determined and presented in accordance with the accounting principles used in preparing the Company’s financial statements, and any measures derived wholly or in part from such measures and may consist of GAAP or non-GAAP financial measures (as defined under Regulation G of the Exchange Act and Item 10 of Regulation S-K under the Exchange Act), (ii) stock price, or (iii) total stockholder return. Financial Reporting Measures may or may not be filed with the SEC and may be presented outside the Company’s financial statements, such as in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Result of Operations or in the performance graph required under Item 201(e) of Regulation S-K under the Exchange Act.
i) “Home Country” means the Company’s jurisdiction of incorporation.
j) “Incentive-Based Compensation” means any compensation that is granted, earned or vested based wholly or in part upon the attainment of a Financial Reporting Measure.
k) “Lookback Period” means the three completed fiscal years (plus any transition period of less than nine months that is within or immediately following the three completed fiscal years and that results from a change in the Company’s fiscal year) immediately preceding the date on which the Company is required to prepare a Restatement for a given reporting period, with such date being the earlier of: (i) the date the Board, a committee of the Board, or the officer or officers of the Company authorized to take such action if Board action is not required, concludes, or reasonably should have concluded, that the Company is required to prepare a Restatement, or (ii) the date a court, regulator or other legally authorized body directs the Company to prepare a Restatement. Recovery of any Erroneously Awarded Compensation under the Policy is not dependent on if or when the Restatement is actually filed.
l) “Nasdaq” means the Nasdaq Stock Market.
m) “Received”: Incentive-Based Compensation is deemed “Received” in the Company’s fiscal period during which the Financial Reporting Measure specified in or otherwise relating to the Incentive-Based Compensation award is attained, even if the grant, vesting or payment of the Incentive-Based Compensation occurs after the end of that period.
n) “Restatement” means a required accounting restatement of any Company financial statement due to the material noncompliance of the Company with any financial reporting requirement under the securities laws, including (i) to correct an error in previously issued financial statements that is material to the previously issued financial statements (commonly referred to as a “Big R” restatement) or (ii) to correct an error in previously issued financial statements that is not material to the previously issued financial statements but that would result in a material misstatement if the error was corrected in the current period or left uncorrected in the current period (commonly referred to as a “little r” restatement). Changes to the Company’s financial statements that do not represent error corrections under the then-current relevant accounting standards will not constitute Restatements. Recovery of any Erroneously Awarded Compensation under the Policy is not dependent on fraud or misconduct by any person in connection with the Restatement.
o) “SEC” means the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
p) “Subsidiary” means any domestic or foreign corporation, partnership, association, joint stock company, joint venture, trust or unincorporated organization “affiliated” with the Company, that is, directly or indirectly, through one or more intermediaries, “controlling”, “controlled by” or “under common control with”, the Company. “Control” for this purpose means the possession, direct or indirect, of the power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of such person, whether through the ownership of voting securities, contract or otherwise.
2. Recovery and Forfeiture of Erroneously Awarded Compensation
In the event of a Restatement, any Erroneously Awarded Compensation Received during the Lookback Period prior to the Restatement (a) that is then-outstanding but has not yet been paid shall be automatically and immediately forfeited and (b) that has been paid to any person shall be subject to reasonably prompt recovery to the applicable member of the Company Group in accordance with Section 3 of this Policy. The Committee must pursue (and shall not have the discretion to waive) the forfeiture and/or recovery of such Erroneously Awarded Compensation in accordance with Section 3 of this Policy, except as provided below.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Committee (or, if at any time the Committee is not a committee of the Board responsible for the Company’s executive compensation decisions and composed entirely of independent directors, a majority of the independent directors serving on the Board) may determine not to pursue the forfeiture and/or recovery of Erroneously Awarded Compensation from any person if the Committee determines that such forfeiture and/or recovery would be impracticable due to any of the
following circumstances: (i) the direct expense paid to a third party (for example, reasonable legal expenses and consulting fees) to assist in enforcing the Policy would exceed the amount to be recovered (following reasonable attempts by one or more members of the Company Group to recover such Erroneously Awarded Compensation, the documentation of such attempts, and the provision of such documentation to the Nasdaq), (ii) pursuing such recovery would violate the Company’s Home Country laws adopted prior to November 28, 2022 (provided that the Company obtains an opinion of Home Country counsel acceptable to the Nasdaq that recovery would result in such a violation and provides such opinion to the Nasdaq), or (iii) recovery would likely cause any otherwise tax-qualified retirement plan, under which benefits are broadly available to employees of the Company Group, to fail to meet the requirements of 26 U.S.C. 401(a)(13) or 26 U.S.C. 411(a) and regulations thereunder.
3. Means of Recovery
In the event that the Committee determines that any person shall repay any Erroneously Awarded Compensation, the Committee shall provide written notice to such person by email or certified mail to the physical address on file with the Company Group for such person, and the person shall satisfy such repayment in a manner and on such terms as required by the Committee, and any member of the Company Group shall be entitled to set off the repayment amount against any amount owed to the person by the applicable member of the Company Group, to require the forfeiture of any award granted by any member of the Company Group to the person, or to take any and all necessary actions to reasonably promptly recoup the repayment amount from the person, in each case, to the fullest extent permitted under applicable law, including without limitation, Section 409A of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and the regulations and guidance thereunder. If the Committee does not specify a repayment timing in the written notice described above, the applicable person shall be required to repay the Erroneously Awarded Compensation to the Company by wire, cash or cashier’s check no later than thirty (30) days after receipt of such notice.
4. No Indemnification
No person shall be indemnified, insured or reimbursed by any member of the Company Group in respect of any loss of compensation by such person in accordance with this Policy, nor shall any person receive any advancement of expenses for disputes related to any loss of compensation by such person in accordance with this Policy, and no person shall be paid or reimbursed by any member of the Company Group for any premiums paid by such person for any third-party insurance policy covering potential recovery obligations under this Policy. For this purpose, “indemnification” includes any modification to current compensation arrangements or other means that would amount to de facto indemnification (for example, providing the person a new cash award which would be cancelled to effect the recovery of any Erroneously Awarded Compensation). In no event shall any member of the Company Group be required to award any person an additional payment if any Restatement would result in a higher incentive compensation payment.
5. Authority and Interpretations
This Policy generally will be administered and interpreted by the Committee, provided that the Board may, from time to time, exercise discretion to administer and interpret this Policy, in which case, all references herein to “Committee” shall be deemed to refer to the Board. Any determination by the Committee with respect to this Policy shall be final, conclusive and binding on all interested parties. Any discretionary determinations of the Committee under this Policy, if any, need not be uniform with respect to all persons, and may be made selectively amongst persons, whether or not such persons are similarly situated.
This Policy is intended to satisfy the requirements of Section 954 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, as it may be amended from time to time, and any related rules or regulations promulgated by the SEC or the Nasdaq, including any additional or new requirements that
become effective after the Effective Date which upon effectiveness shall be deemed to automatically amend this Policy to the extent necessary to comply with such additional or new requirements.
The provisions in this Policy are intended to be applied to the fullest extent of the law. To the extent that any provision of this Policy is found to be unenforceable or invalid under any applicable law, such provision will be applied to the maximum extent permitted and shall automatically be deemed amended in a manner consistent with its objectives to the extent necessary to conform to applicable law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any provision of this Policy shall not affect the validity or enforceability of any other provision of this Policy. Recovery of Erroneously Awarded Compensation under this Policy is not dependent upon the Company Group satisfying any conditions in this Policy, including any requirements to provide applicable documentation to the Nasdaq.
The rights of the members of the Company Group under this Policy to seek forfeiture or recovery are in addition to, and not in lieu of, any rights of recoupment, or remedies or rights other than recoupment, that may be available to any member of the Company Group pursuant to the terms of any law, government regulation or stock exchange listing requirement or any other policy, code of conduct, employee handbook, employment agreement, offer letter, equity award agreement, or other plan or agreement of any member of the Company Group.
6. Amendment and Termination
To the extent permitted by, and in a manner consistent with applicable law, including SEC and Nasdaq rules, the Committee may terminate, suspend or amend this Policy at any time in its discretion.
7. Successors
This Policy shall be binding and enforceable against all persons and their respective beneficiaries, heirs, executors, administrators or other legal representatives with respect to any Covered Compensation granted, vested or paid to or administered by such persons or entities.
8. Governing Law
This Policy and all rights and obligations hereunder are governed by and construed in accordance with the internal laws of the State of Delaware, excluding any choice of law rules or principles that may direct the application of the laws of another jurisdiction.
v3.24.1.1.u2
Cover page - USD ($)
$ in Billions |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Mar. 31, 2024 |
May 09, 2024 |
Sep. 30, 2023 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Mar. 31, 2024
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--03-31
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
1-33026
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
DE
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
22-3447504
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
1 Commvault Way
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
Tinton Falls
|
|
|
| Entity Address, State or Province |
NJ
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
07724
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
732
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
870-4000
|
|
|
| Title of 12(b) Security |
Common Stock, $0.01 par value
|
|
|
| Trading Symbol |
CVLT
|
|
|
| Security Exchange Name |
NASDAQ
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Large Accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| ICFR Auditor Attestation Flag |
true
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 2.9
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding |
|
43,401,217
|
|
| Documents Incorporated by Reference |
Information required by Part III (Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14) is incorporated by reference to portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”), which is expected to be filed not later than 120 days after the registrant’s fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. Except as expressly incorporated by reference, the Proxy Statement shall not be deemed to be part of this report on Form 10-K.
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
COMMVAULT SYSTEMS INC
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0001169561
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2024
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDocuments incorporated by reference. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-23
| Name: |
dei_DocumentsIncorporatedByReferenceTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the state or province.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressStateOrProvince |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:stateOrProvinceItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(b) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b
| Name: |
dei_Security12bTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionName of the Exchange on which a security is registered. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection d1-1
| Name: |
dei_SecurityExchangeName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarExchangeCodeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTrading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.
| Name: |
dei_TradingSymbol |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:tradingSymbolItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Balance Sheets - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Current assets: |
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 312,754
|
$ 287,778
|
| Trade accounts receivable, net |
222,683
|
210,441
|
| Assets held for sale |
38,680
|
38,680
|
| Other current assets |
21,009
|
14,015
|
| Total current assets |
595,126
|
550,914
|
| Deferred tax assets, net |
111,181
|
0
|
| Property and equipment, net |
7,961
|
8,287
|
| Operating lease assets |
10,545
|
11,784
|
| Deferred commissions cost |
62,837
|
59,612
|
| Intangible assets, net |
1,042
|
2,292
|
| Goodwill |
127,780
|
127,780
|
| Other assets |
27,441
|
21,905
|
| Total assets |
943,913
|
782,574
|
| Current liabilities: |
|
|
| Accounts payable |
299
|
108
|
| Accrued liabilities |
117,244
|
97,888
|
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities |
4,935
|
4,518
|
| Deferred revenue |
362,450
|
307,562
|
| Total current liabilities |
484,928
|
410,076
|
| Deferred revenue, less current portion |
168,472
|
174,393
|
| Deferred tax liabilities |
1,717
|
134
|
| Long-term operating lease liabilities |
7,155
|
8,260
|
| Other liabilities |
3,556
|
3,613
|
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) |
|
|
| Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, $0.01 par value: 50,000 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding |
0
|
0
|
| Common stock, $0.01 par value, 250,000 shares authorized, 43,548 shares and 44,140 shares issued and outstanding at March 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively |
435
|
440
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
1,349,603
|
1,264,608
|
| Accumulated deficit |
(1,056,011)
|
(1,062,900)
|
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(15,942)
|
(16,050)
|
| Total stockholders’ equity |
278,085
|
186,098
|
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ 943,913
|
$ 782,574
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481990/310-10-45-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after tax, of accumulated increase (decrease) in equity from transaction and other event and circumstance from nonowner source. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14A
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue received from shareholders in common stock-related transactions that are in excess of par value or stated value and amounts received from other stock-related transactions. Includes only common stock transactions (excludes preferred stock transactions). May be called contributed capital, capital in excess of par, capital surplus, or paid-in capital. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapitalCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are recognized. Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 26: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed within one year (or the normal operating cycle, if longer). Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount classified as assets attributable to disposal group held for sale or disposed of, expected to be disposed of within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 205
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483475/205-20-45-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5C
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-5C
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-9
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-5B
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-3
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483475/205-20-45-11
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsOfDisposalGroupIncludingDiscontinuedOperationCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after accumulated amortization and accumulated impairment loss, of asset recognized from cost incurred to obtain or fulfill contract with customer; classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 340
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479483/340-40-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalizedContractCostNetNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the caption on the face of the balance sheet to indicate that the entity has entered into (1) purchase or supply arrangements that will require expending a portion of its resources to meet the terms thereof, and (2) is exposed to potential losses or, less frequently, gains, arising from (a) possible claims against a company's resources due to future performance under contract terms, and (b) possible losses or likely gains from uncertainties that will ultimately be resolved when one or more future events that are deemed likely to occur do occur or fail to occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.17)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.25)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingencies |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated impairment loss of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Goodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts of all intangible assets, excluding goodwill, as of the balance sheet date, net of accumulated amortization and impairment charges. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ((a)(1),(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntangibleAssetsNetExcludingGoodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.21)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's right to use underlying asset under operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncurrent assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities classified as other, due after one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.24)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable preferred shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480842/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Balance Sheets (Parenthetical) - $ / shares
|
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Statement of Financial Position [Abstract] |
|
|
| Preferred stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.01
|
$ 0.01
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
50,000,000
|
50,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
0
|
0
|
| Common stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.01
|
$ 0.01
|
| Common stock, shares authorized (in shares) |
250,000,000
|
250,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued (in shares) |
43,548,000
|
44,140,000
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
43,548,000
|
44,140,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of preferred stock nonredeemable or redeemable solely at the option of the issuer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) issued to shareholders (includes related preferred shares that were issued, repurchased, and remain in the treasury). May be all or portion of the number of preferred shares authorized. Excludes preferred shares that are classified as debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate share number for all nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) held by stockholders. Does not include preferred shares that have been repurchased. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfFinancialPositionAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Statements of Operations - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 839,247
|
$ 784,590
|
$ 769,591
|
| Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenues |
151,610
|
135,402
|
113,859
|
| Gross margin |
687,637
|
649,188
|
655,732
|
| Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
| Sales and marketing |
354,994
|
340,783
|
341,644
|
| Research and development |
132,328
|
141,847
|
153,615
|
| General and administrative |
113,997
|
104,240
|
103,049
|
| Restructuring |
4,548
|
15,452
|
6,192
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
6,415
|
9,270
|
9,666
|
| Headquarters impairment |
0
|
53,481
|
0
|
| Total operating expenses |
612,282
|
665,073
|
614,166
|
| Income (loss) from operations |
75,355
|
(15,885)
|
41,566
|
| Interest income |
5,423
|
1,300
|
656
|
| Interest expense |
(415)
|
(472)
|
(109)
|
| Other income (expense), net |
3,250
|
(305)
|
1,301
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
83,613
|
(15,362)
|
43,414
|
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
(85,293)
|
20,412
|
9,790
|
| Net income (loss) |
$ 168,906
|
$ (35,774)
|
$ 33,624
|
| Net income (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
| Basic (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.85
|
$ (0.80)
|
$ 0.74
|
| Diluted (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.75
|
$ (0.80)
|
$ 0.71
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
| Basic (in shares) |
43,885
|
44,664
|
45,443
|
| Diluted (in shares) |
45,100
|
44,664
|
47,220
|
| Subscription |
|
|
|
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 429,167
|
$ 347,784
|
$ 268,359
|
| Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenues |
58,406
|
44,482
|
24,578
|
| Perpetual license |
|
|
|
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
57,613
|
74,918
|
111,857
|
| Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenues |
2,168
|
2,439
|
4,563
|
| Customer support |
|
|
|
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
307,771
|
314,313
|
347,115
|
| Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenues |
60,752
|
58,273
|
54,719
|
| Other services |
|
|
|
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
44,696
|
47,575
|
42,260
|
| Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
| Total cost of revenues |
$ 30,284
|
$ 30,208
|
$ 29,999
|
| X |
- DefinitionAsset Impairment Charges, Excluding Impairment Of Operating Lease Assets
| Name: |
cvlt_AssetImpairmentChargesExcludingImpairmentOfOperatingLeaseAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs related to goods produced and sold and services rendered by an entity during the reporting period. This excludes costs incurred during the reporting period related to financial services rendered and other revenue generating activities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.2(a),(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfGoodsAndServicesSold |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfGoodsAndServicesSoldAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe current period expense charged against earnings on long-lived, physical assets not used in production, and which are not intended for resale, to allocate or recognize the cost of such assets over their useful lives; or to record the reduction in book value of an intangible asset over the benefit period of such asset; or to reflect consumption during the period of an asset that is not used in production. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total of expenses of managing and administering the affairs of an entity, including affiliates of the reporting entity, which are not directly or indirectly associated with the manufacture, sale or creation of a product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1,2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the cost of borrowed funds accounted for as interest expense. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (210.5-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accretion (amortization) of purchase discount (premium) of interest income on nonoperating securities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InvestmentIncomeInterest |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Includes selling, general and administrative expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpensesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income (expense) related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate costs incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process whether intended for sale or the entity's use, during the reporting period charged to research and development projects, including the costs of developing computer software up to the point in time of achieving technological feasibility, and costs allocated in accounting for a business combination to in-process projects deemed to have no alternative future use. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482916/730-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 730
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482517/912-730-25-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482047/420-10-45-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total amount of expenses directly related to the marketing or selling of products or services.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingAndMarketingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_SubscriptionMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_PerpetualLicenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_CustomerSupportServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_ServiceOtherMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Statement of Comprehensive Income [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
$ 168,906
|
$ (35,774)
|
$ 33,624
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss): |
|
|
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
108
|
(4,187)
|
(1,513)
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ 169,014
|
$ (39,961)
|
$ 32,111
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income and other comprehensive income, attributable to parent entity. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax and reclassification adjustments of gain (loss) on foreign currency translation adjustments, foreign currency transactions designated and effective as economic hedges of a net investment in a foreign entity and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term-investment nature, attributable to parent entity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-20
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(3)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeForeignCurrencyTransactionAndTranslationAdjustmentNetOfTaxPortionAttributableToParent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTaxPeriodIncreaseDecreaseAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementOfIncomeAndComprehensiveIncomeAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
Total |
Common Stock |
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
| Beginning Balance (in shares) at Mar. 31, 2021 |
|
46,482
|
|
|
|
| Beginning balance at Mar. 31, 2021 |
$ 394,034
|
$ 463
|
$ 1,069,695
|
$ (665,774)
|
$ (10,350)
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation |
105,163
|
|
105,163
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation (in shares) |
|
2,336
|
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation |
29,760
|
$ 23
|
29,737
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock (in shares) |
|
(4,307)
|
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
(305,239)
|
$ (43)
|
(38,647)
|
(266,549)
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
33,624
|
|
|
33,624
|
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
(1,513)
|
|
|
|
(1,513)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Mar. 31, 2022 |
|
44,511
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Mar. 31, 2022 |
255,829
|
$ 443
|
1,165,948
|
(898,699)
|
(11,863)
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation |
105,746
|
|
105,746
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation (in shares) |
|
2,150
|
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation |
15,405
|
$ 22
|
15,383
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock (in shares) |
|
(2,521)
|
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
(150,921)
|
$ (25)
|
(22,469)
|
(128,427)
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
(35,774)
|
|
|
(35,774)
|
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ (4,187)
|
|
|
|
(4,187)
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Mar. 31, 2023 |
44,140
|
44,140
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Mar. 31, 2023 |
$ 186,098
|
$ 440
|
1,264,608
|
(1,062,900)
|
(16,050)
|
| Increase (Decrease) in Stockholders' Equity [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation |
94,551
|
|
94,551
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation (in shares) |
|
1,887
|
|
|
|
| Share issuance related to stock-based compensation |
$ 13,440
|
$ 19
|
13,421
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock (in shares) |
(2,479)
|
(2,479)
|
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
$ (185,018)
|
$ (24)
|
(22,977)
|
(162,017)
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
168,906
|
|
|
168,906
|
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ 108
|
|
|
|
108
|
| Ending balance (in shares) at Mar. 31, 2024 |
43,548
|
43,548
|
|
|
|
| Ending balance at Mar. 31, 2024 |
$ 278,085
|
$ 435
|
$ 1,349,603
|
$ (1,056,011)
|
$ (15,942)
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase to additional paid-in capital (APIC) for recognition of cost for award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-13
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 20
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481089/718-20-55-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToAdditionalPaidInCapitalSharebasedCompensationRequisiteServicePeriodRecognitionValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInStockholdersEquityRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax and reclassification adjustments of other comprehensive income (loss). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-17
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-4
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-5
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 220
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482739/220-10-55-15
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber, after forfeiture, of shares or units issued under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes shares or units issued under employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue, after forfeiture, of shares issued under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares that have been repurchased during the period and have not been retired and are not held in treasury. Some state laws may govern the circumstances under which an entity may acquire its own stock and prescribe the accounting treatment therefore. This element is used when state law does not recognize treasury stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchasedDuringPeriodShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the value of stock that has been repurchased during the period and has not been retired and is not held in treasury. Some state laws may mandate the circumstances under which an entity may acquire its own stock and prescribe the accounting treatment therefore. This element is used when state law does not recognize treasury stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchasedDuringPeriodValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
$ 168,906
|
$ (35,774)
|
$ 33,624
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
6,530
|
10,323
|
10,950
|
| Noncash stock-based compensation |
94,551
|
105,746
|
105,163
|
| Noncash change in fair value of equity securities |
17
|
305
|
(301)
|
| Noncash headquarters impairment |
0
|
53,481
|
0
|
| Deferred income taxes |
(109,598)
|
(674)
|
49
|
| Amortization of deferred commissions cost |
26,531
|
22,626
|
18,339
|
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
| Trade accounts receivable, net |
(21,725)
|
(11,596)
|
(20,371)
|
| Operating lease assets and liabilities, net |
550
|
(56)
|
(925)
|
| Other current assets and Other assets |
336
|
6,179
|
3,732
|
| Deferred commissions cost |
(29,952)
|
(30,529)
|
(33,512)
|
| Accounts payable |
195
|
(297)
|
60
|
| Accrued liabilities |
16,998
|
(24,213)
|
10,400
|
| Deferred revenue |
50,394
|
73,756
|
48,295
|
| Other liabilities |
65
|
1,011
|
1,677
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
203,798
|
170,288
|
177,180
|
| Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
|
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(4,086)
|
(3,241)
|
(3,911)
|
| Purchase of equity securities |
(1,435)
|
(2,045)
|
(4,139)
|
| Business combination, net of cash acquired |
0
|
0
|
(16,894)
|
| Other |
0
|
0
|
500
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(5,521)
|
(5,286)
|
(24,444)
|
| Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
(184,021)
|
(150,921)
|
(305,239)
|
| Proceeds from stock-based compensation plans |
13,440
|
15,405
|
29,760
|
| Debt issuance costs |
0
|
(63)
|
(609)
|
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(170,581)
|
(135,579)
|
(276,088)
|
| Effects of exchange rate — changes in cash |
(2,720)
|
(9,152)
|
(6,378)
|
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
24,976
|
20,271
|
(129,730)
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
287,778
|
267,507
|
397,237
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
312,754
|
287,778
|
267,507
|
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information |
|
|
|
| Interest paid |
253
|
253
|
13
|
| Income taxes paid |
$ 19,970
|
$ 15,175
|
$ (1,493)
|
| X |
- DefinitionAsset Impairment Charges, Excluding Impairment Of Operating Lease Assets
| Name: |
cvlt_AssetImpairmentChargesExcludingImpairmentOfOperatingLeaseAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncrease (Decrease) in Deferred Sales Commissions
| Name: |
cvlt_IncreaseDecreaseInDeferredSalesCommissions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIncrease (Decrease) In Operating Lease, Right-Of-Use Asset And Liability, Net
| Name: |
cvlt_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseRightOfUseAssetAndLiabilityNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNoncash Change In Fair Value Of Equity Securities
| Name: |
cvlt_NoncashChangeInFairValueOfEquitySecurities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period for the periodic realization of capitalized fees that were paid to salespeople, distributors, brokers, and agents at the time of the conclusion of the sale. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfDeferredSalesCommissions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense recognized in the current period that allocates the cost of tangible assets, intangible assets, or depleting assets to periods that benefit from use of the assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
| Name: |
us-gaap_DepreciationDepletionAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) from effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; held in foreign currencies. Excludes amounts for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 230
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_EffectOfExchangeRateOnCashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate amount of liabilities incurred (and for which invoices have typically been received) and payable to vendors for goods and services received that are used in an entity's business. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate amount of expenses incurred but not yet paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482312/912-310-45-11
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInContractWithCustomerLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingCapitalAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in operating assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherOperatingAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in operating liabilities classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOtherOperatingLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the total amount due within one year (or one operating cycle) from all parties, associated with underlying transactions that are classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInReceivables |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash paid for interest, excluding capitalized interest, classified as operating activity. Includes, but is not limited to, payment to settle zero-coupon bond for accreted interest of debt discount and debt instrument with insignificant coupon interest rate in relation to effective interest rate of borrowing attributable to accreted interest of debt discount. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPaidNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash (inflow) outflow from investing activities classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForProceedsFromOtherInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow to reacquire common stock during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRepurchaseOfCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow paid to third parties in connection with debt origination, which will be amortized over the remaining maturity period of the associated long-term debt. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsOfDebtIssuanceCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of a business, net of the cash acquired from the purchase. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquireBusinessesNetOfCashAcquired |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow to acquire investment in equity security measured at fair value with change in fair value recognized in net income (FV-NI), classified as investing activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 321
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479567/321-10-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquireEquitySecuritiesFvNi |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow associated with the acquisition of long-lived, physical assets that are used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale; includes cash outflows to pay for construction of self-constructed assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquirePropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow from issuance of shares under share-based payment arrangement. Includes, but is not limited to, option exercised. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2A
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2A
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromIssuanceOfSharesUnderIncentiveAndShareBasedCompensationPlansIncludingStockOptions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of noncash expense for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Nature of Business
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
| Nature of Business |
Nature of Business Commvault Systems, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Commvault," "we," "us," or "our") provides its customers with a scalable platform that enhances customers' cyber resiliency by protecting their data in a world of increasing threats. We provide these products and services across many types of environments, including on-premises, hybrid and multi-cloud. Our offerings are delivered via self-managed software, software-as-a-service ("SaaS"), integrated appliances, or managed by partners. Customers use our Commvault Cloud platform to protect themselves from threats like ransomware and recover their data efficiently.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for the nature of an entity's business, major products or services, principal markets including location, and the relative importance of its operations in each business and the basis for the determination, including but not limited to, assets, revenues, or earnings. For an entity that has not commenced principal operations, disclosures about the risks and uncertainties related to the activities in which the entity is currently engaged and an understanding of what those activities are being directed toward. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//275/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NatureOfOperations |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies Reclassification of Prior Year Balances Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified for consistency with the current year presentation. These reclassifications have no impact on the amount of total revenues or net income. Beginning in fiscal 2024, the software and services line items on the consolidated statements of operations, related to revenues and cost of revenues, are being presented in the following categories:
Subscription - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs of recurring time-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer.
Perpetual license - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download.
Customer support - The amounts on this line include customer support revenues and costs associated with our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. Customer support revenue is typically recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement.
Other services - The amounts included on this line consist primarily of revenues and costs related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other professional services are typically recognized as the services are performed. Basis of Presentation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Commvault. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") requires management to make judgments and estimates that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. The amounts of assets and liabilities reported in our balance sheets and the amounts of revenues and expenses reported for each of the periods presented are affected by estimates and assumptions, which are used for, but not limited to, the accounting for revenue recognition, income taxes and related reserves, deferred commissions, purchased intangible assets and goodwill. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Revenue We account for revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("ASC 606"). We record revenue net of sales tax. For a further discussion of our accounting policies related to revenue, see Note 3 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements. Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation Restricted stock units without a market condition are measured based on the fair market values of the underlying stock on the date of grant. We recognize stock-based compensation expense using the straight-line method for all stock awards that do not include a market or performance condition. Awards that include a market or performance condition are expensed using the accelerated method. Software Development Costs The costs for the development of new products and substantial enhancements to existing products are expensed as incurred until technological feasibility has been established, at which time any additional costs would be capitalized in accordance with the accounting guidance for software. Because our current process for developing software is essentially completed concurrently with the establishment of technological feasibility, which occurs upon the completion of a working model, no costs have been capitalized for any of the periods presented. Advertising Costs We expense advertising costs as incurred. Advertising expenses were $8,514, $8,663, and $9,572 for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Accounting for Income Taxes We account for income taxes in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes ("ASC 740"). The provision for income taxes and effective tax rates are calculated by legal entity and jurisdiction and are based on a number of factors, including the level of pre-tax earnings, income tax planning strategies, differences between tax laws and accounting rules, statutory tax rates and credits, uncertain tax positions and valuation allowances. We provide for global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) earned by certain foreign subsidiaries in the year the tax is incurred and record an estimate of GILTI as a component of the tax provision. We use significant judgment and estimates in evaluating tax positions. The effective tax rate in a given financial statement period may be materially impacted by changes in the mix and level of earnings by taxing jurisdiction. Under ASC 740, deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts. Valuation allowances are established when, in our judgment, it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we weigh the available positive and negative evidence, including historical levels of pre-tax income, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies. Foreign Currency Translation The functional currencies of our foreign operations are deemed to be the local country’s currency. Assets and liabilities of our international subsidiaries are translated at their respective period-end exchange rates, and revenues and expenses are translated at average currency exchange rates for the period. The resulting balance sheet translation adjustments are included in other comprehensive income (loss) and are reflected as a separate component of stockholders’ equity. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are recorded in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. These gains and losses relate primarily to receivables and payables that are not denominated in the functional currency of the subsidiary they relate to. We recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $2,388 and $1,163 in the years ended March 31, 2024, and 2023, respectively, and insignificant losses in the year ended March 31, 2022. Net Income (Loss) per Common Share Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of common shares during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares consist of the incremental common shares issuable upon the vesting of restricted stock units, shares to be purchased under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan ("ESPP"), and the exercise of stock options. The dilutive effect of such potential common shares is reflected in diluted earnings (loss) per share by application of the treasury stock method. The following table sets forth the reconciliation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | | | Basic net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | | | Basic net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 3.85 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | 0.74 | | | Diluted net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | Basic weighted-average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | | Dilutive effect of stock options and restricted stock units (1) | | 1,215 | | | — | | | 1,777 | | | Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding | | 45,100 | | | 44,664 | | | 47,220 | | | Diluted net income (loss) per common share | | 3.75 | | | (0.80) | | | 0.71 | |
(1) In fiscal 2023 dilutive shares have been excluded because we were in a net loss position.
The diluted weighted-average shares outstanding exclude restricted stock units, performance restricted stock units, shares to be purchased under the ESPP and outstanding stock options totaling 271, 3,939 and 505 for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, because the effect would have been anti-dilutive. Cash and Cash Equivalents We consider all highly liquid investments purchased with maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents. Trade and Other Receivables Trade and other receivables are primarily comprised of trade receivables that are recorded at the invoice amount, net of an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is not material. Unbilled receivables represent amounts for which revenue has been recognized but which have not yet been invoiced to the customer. The current portion of unbilled receivables is included in trade accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets. The allowance for doubtful accounts was $173 as of March 31, 2024 and $197 as of March 31, 2023. For the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, bad debt expense was immaterial. Historically, we have not experienced material losses related to the inability to collect receivables from our customers. There is presently no indication that we will not collect material amounts of accounts receivable as of March 31, 2024. The inability to collect receivables could have a material impact on our results of operations. Concentration of Credit Risk We grant credit to customers in a wide variety of industries worldwide and generally do not require collateral. Credit losses relating to these customers have been minimal. Sales through our distribution agreement with Arrow Enterprise Computing Solutions, Inc. ("Arrow") totaled approximately 36% of total revenues for the year ended March 31, 2024, and 37% of total revenues for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. Arrow accounted for approximately 29% and 34% of total accounts receivable as of March 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Fair Value of Financial Instruments Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for such asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value should maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. To measure fair value, we use the following fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable: Level 1 — Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; Level 2 — Inputs other than Level 1, that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly; and Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions.
The carrying amounts of our cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to the short-term maturity of these instruments. Our cash equivalents balance consists primarily of U.S. Treasury Bills with maturities of one month or less. The following table summarizes the composition of our financial assets measured at fair value at March 31, 2024: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | Cash equivalents | $ | 24,902 | | | — | | | — | | | $ | 24,902 | |
There were no financial assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the year ended March 31, 2023. Equity Securities Accounted for at Net Asset Value We held equity interests in private equity funds of $7,318 as of March 31, 2024, which are accounted for under the net asset value practical expedient as permitted under ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement. These investments are included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The net asset values of these investments are determined using quarterly capital statements from the funds, which are based on our contributions to the funds, allocation of profit and loss and changes in fair value of the underlying fund investments. Changes in fair value as reported on the capital statements are recorded through the consolidated statements of operations as non-operating income or expense. These private equity funds focus on making investments in key technology sectors, principally by investing in companies at expansion capital and growth equity stages. We have total unfunded commitments in private equity funds of $2,645 as of March 31, 2024. Leases We account for leases in accordance with ASC 842, Leases. For a further discussion of our accounting policies related to leases, see Note 15 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements. Property and Equipment Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Land is not depreciated. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Computer and related equipment is generally depreciated over eighteen months to three years and furniture and fixtures are generally depreciated over three to twelve years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the useful life of the improvement or the term of the related lease. Expenditures for routine maintenance and repairs are charged against operations. Major replacements, improvements and additions are capitalized. In January 2023, the assets that previously comprised our owned corporate headquarters met the held for sale criteria in accordance with ASC 360, Property, Plant and Equipment ("ASC 360"), and were reclassified as such. These assets are no longer being depreciated. For further discussion on assets held for sale, see Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements. Goodwill and Intangible Assets Goodwill is recorded when the consideration paid for an acquisition exceeds the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired. The carrying value of goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis on January 1, or more often if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of its carrying amount. For the purpose of impairment testing, we have a single reporting unit. The impairment test consists of comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount that includes goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, an impairment loss would be recognized to reduce the carrying amount to its fair value.
Our finite lived purchased intangible asset, developed technology, was valued using the replacement cost method and is being amortized on a straight-line basis over its economic life of three years as we believed this method most closely reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the assets will be consumed. Impairment losses are recognized if the carrying amount of an intangible asset is both not recoverable and exceeds its fair value. Long-Lived Assets We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. To determine the recoverability of our long-lived assets, we evaluate the estimated future undiscounted cash flows that are directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the long-lived asset. If the estimated future undiscounted cash flows demonstrate that recoverability is not probable, an impairment loss would be recognized. An impairment loss would be calculated based on the excess carrying amount of the long-lived asset over the long-lived asset’s fair value. The fair value would be determined based on valuation techniques such as a comparison to fair values of similar assets. Deferred Commissions Cost Sales commissions, bonuses, and related payroll taxes earned by our employees are considered incremental and recoverable costs of obtaining a contract with a customer. Our typical contracts include performance obligations related to term-based software licenses, SaaS offerings, perpetual software licenses, software updates, and customer support. In these contracts, incremental costs of obtaining a contract are allocated to the performance obligations based on the relative estimated standalone selling prices and then recognized on a systematic basis that is consistent with the transfer of the goods or services to which the asset relates. We do not pay commissions on annual renewals of customer support contracts for perpetual licenses. The costs allocated to software and products are expensed at the time of sale, when revenue for the functional software license or appliance is recognized. The costs allocated to software updates and customer support for perpetual licenses are amortized ratably over a period of approximately five years, the expected period of benefit of the asset capitalized. We currently estimate a period of five years is appropriate based on consideration of historical average customer life and the estimated useful life of the underlying software sold as part of the transaction. The commission paid on the renewal of subscription arrangements is not commensurate with the commission paid on the initial purchase. As a result, the cost of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and customer support on the initial term-based software license transactions are amortized over a period of approximately five years, consistent with the accounting for these costs associated with perpetual licenses. The costs of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and support for the renewal of term-based software licenses is limited to the contractual period of the arrangement, as we pay a commensurate renewal commission upon the next renewal of the subscription software license and related updates and support.
The incremental costs attributable to professional services are generally amortized over the period the related services are provided and revenue is recognized. Amortization expense related to these costs is included in sales and marketing expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Deferred Revenue Deferred revenues represent amounts collected from, or invoiced to, customers in excess of revenues recognized. This results primarily from the billing of annual customer support agreements, the billing of SaaS subscription arrangements and billings for other services that have not yet been performed by us. The value of deferred revenues will increase or decrease based on the timing of invoices and recognition of revenue. Share Repurchases We consider all shares repurchased as canceled shares restored to the status of authorized but unissued shares on the trade date. The aggregate purchase price of the shares of our common stock repurchased is reflected as a reduction to stockholders’ equity. We account for shares repurchased as an adjustment to common stock (at par value) with the excess repurchase price allocated between additional paid-in capital and accumulated deficit. Comprehensive Income Comprehensive income is defined to include all changes in equity, except those resulting from investments by stockholders and distribution to stockholders. Recently Adopted and Recently Issued Accounting Standards There were no recently adopted accounting standards that had a material effect on our condensed consolidated financial statements and accompanying disclosures. The table below outlines recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Standard | Description | Effective Date | Effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements (or Other Significant Matters) | | Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-07 (Topic 280): Segment Reporting | In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued a new standard to improve reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. In addition, the amendments enhance interim disclosure requirements, clarify circumstances in which an entity can disclose multiple segment measures of profit or loss, provide new segment disclosure requirements for entities with a single reportable segment, and contain other disclosure requirements. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2024, and interim periods within our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We will adopt this standard using a retrospective approach on April 1, 2024. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. | | ASU No. 2023-09 (Topic 740): Income Taxes | In December 2023, the FASB issued a new standard to improve income tax disclosures. The standard requires greater disaggregated information about a reporting entity’s effective tax rate reconciliation as well as information on income taxes paid. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| Revenue |
Revenue We derive revenues from various sources, including subscriptions, perpetual software licenses, customer support contracts and other services. Subscription Subscription includes the revenues derived from term-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. The term of our subscription arrangements is typically one to three years, but can range between one and five years. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer. Perpetual License Perpetual license includes the revenues from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. Customer Support Customer support includes revenues associated with support contracts tied to our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. We sell our customer support contracts as a percentage of net software purchases. Customer support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement, which is typically one year on our perpetual licenses and over the term on our term-based licenses. Other Services Other services consist primarily of revenues related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other services can vary period over period based on the timing services are delivered and are typically recognized as the services are performed. We do not customize our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) and installation services are not required. Software licenses are delivered before related services are provided and are functional without professional services, updates and technical support. We have concluded that our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are functional intellectual property that is distinct, as the user can benefit from the software on its own. Revenues for both perpetual and term-based licenses are typically recognized when the software is delivered and/or made available for download as this is the point the user of the software can direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the remaining benefits from, the functional intellectual property. We do not recognize software revenue related to the renewal of subscription software licenses earlier than the beginning of the new subscription period. We also offer appliances that integrate our software with hardware and address a wide-range of business needs and use cases, ranging from support for remote or branch offices with limited IT staff up to large corporate data centers. Our appliances are almost exclusively sold via a software only model in which we sell software to a third party, which assembles an integrated appliance that is sold to end user customers. As a result, the revenues and costs associated with hardware are usually not included in our financial statements. Our typical performance obligations include the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | Performance Obligation | When Performance Obligation
is Typically Satisfied | When Payment is
Typically Due | How Standalone Selling Price is
Typically Estimated | | Subscription | | Term-based software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment except for certain subscription licenses which are paid for over time | Residual approach | | Software-as-a-service (SaaS) | Ratably over the course of the contract (over time) | Annually or at the beginning of the contract period | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Perpetual License | | Perpetual software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment | Residual approach | | Customer Support | | Software updates | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Customer support | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Other Services | | Other professional services (except for education services) | As work is performed (over time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Education services | When the class is taught (point in time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
Judgments related to revenue recognition Most of our contracts with customers contain multiple performance obligations. For these contracts, we evaluate and account for individual performance obligations separately if they are determined to be distinct. The transaction price is allocated to the separate performance obligations on a relative standalone selling price basis. Standalone selling prices of software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are typically estimated using the residual approach. Standalone selling prices for SaaS, customer support contracts, and other services are typically estimated based on observable transactions when these services are sold on a standalone basis. We recognize revenue net of sales tax. Disaggregation of Revenue
We disaggregate revenues from contracts with customers into geographical regions. Our Americas region includes the United States, Canada, and Latin America. Our International region primarily includes Europe, Middle East, Africa, Australia, India, Southeast Asia, and China.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Americas | $ | 498,545 | | | $ | 469,244 | | | $ | 457,895 | | | International | 340,702 | | | 315,346 | | | 311,696 | | | Total revenues | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
Remaining Performance Obligations
Remaining performance obligations represent expected future revenue from existing contracts where performance obligations are unsatisfied or partially unsatisfied at the end of the reporting period. As of March 31, 2024, our remaining performance obligations (inclusive of deferred revenues) were $618,907, of which approximately 68% is expected to be recognized as revenue over the next 12 months and the remainder recognized thereafter. The vast majority of these revenues consist of SaaS arrangements, customer support, and other services. Other services consists primarily of professional services revenue which is contingent upon a number of factors, including customers' needs and scheduling.
Information about Contract Balances
Amounts collected in advance of services being provided are accounted for as deferred revenue. Nearly all of our deferred revenue balance is related to SaaS arrangements, customer support, and other services.
In some arrangements we allow customers to pay for term-based licenses over the term of the software license. Amounts recognized as revenue in excess of amounts billed are recorded as unbilled receivables. Unbilled receivables which are anticipated to be invoiced in the next twelve months are included in accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets. The opening and closing balances of our accounts receivable, unbilled receivables and deferred revenues are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Accounts Receivable | Unbilled Receivable
(current) | Unbilled Receivable
(long-term) | Deferred Revenue
(current) | Deferred Revenue
(long-term) | Opening balance as of March 31, 2023 | $ | 188,736 | | $ | 21,705 | | $ | 9,867 | | $ | 307,562 | | $ | 174,393 | | | Increase/(decrease), net | 8,215 | | 4,027 | | 4,604 | | 54,888 | | (5,921) | | Ending balance as of March 31, 2024 | $ | 196,951 | | $ | 25,732 | | $ | 14,471 | | $ | 362,450 | | $ | 168,472 | |
The net increase in accounts receivable (inclusive of unbilled receivables) is primarily a result of an increase in revenue relative to the prior year period. The net increase in deferred revenue is a result of an increase in SaaS contracts which are billed upfront but recognized ratably over the contract period and an increase in deferred customer support revenue. The amount of revenue recognized in the period that was included in the opening deferred revenue balance was approximately $313,766 for the year ended March 31, 2024. The vast majority of this revenue consists of customer support and SaaS arrangements. The amount of revenue recognized from performance obligations satisfied in prior periods was not significant.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure of revenue from contract with customer to transfer good or service and to transfer nonfinancial asset. Includes, but is not limited to, disaggregation of revenue, credit loss recognized from contract with customer, judgment and change in judgment related to contract with customer, and asset recognized from cost incurred to obtain or fulfill contract with customer. Excludes insurance and lease contracts. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-15
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net |
Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net Goodwill Goodwill represents the residual purchase price paid in a business combination after the fair value of all identified assets and liabilities have been recorded. It includes the estimated value of potential expansion with new customers, the opportunity to further develop sales relationships with new customers and intangible assets that do not qualify for separate recognition. Goodwill is not amortized. None of the goodwill recorded is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes. There were no impairments to the carrying amount of goodwill during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 or 2022. Goodwill balances are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Opening balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | | | Additions/(Impairments) | | — | | | — | | | Ending balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | |
Intangible assets, net Intangible assets are recorded at cost and amortized over useful lives of three years. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, 2024 | | March 31, 2023 | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value | | Developed technology | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (2,708) | | | $ | 1,042 | | | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (1,458) | | | $ | 2,292 | |
Amortization expense from acquired intangible assets was $1,250 for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2024 and 2023 and $208 for fiscal year ended 2022. As of March 31, 2024, the estimated future amortization expense of intangible assets with finite lives is $1,042, which will be fully recognized in fiscal year 2025.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//350/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Assets Held for Sale
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Discontinued Operations and Disposal Groups [Abstract] |
|
| Assets Held for Sale |
Assets Held for Sale During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, we entered into an exclusive agreement to sell our owned corporate headquarters in Tinton Falls, New Jersey for $40,000 in cash consideration and determined the assets and land related to headquarters met the criteria for classification as assets held for sale in accordance with ASC 360, Impairment and Disposal of Long-Lived Assets ("ASC 360"). The property's previous carrying amount of $92,161 was written down to its estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell, of $38,680, resulting in a non-cash impairment charge of $53,481 on our consolidated statements of operations for the period ended March 31, 2023. Upon closing of the transaction, we intend to enter into a lease for a portion of the premises. As of March 31, 2024, the sale has not yet been finalized and the exclusivity of the agreement has expired. As a result of the expiration of the exclusivity, we received a payment for $1,670 related to non-refundable escrow, which is recorded in other income (loss) on our consolidated statements of operations for the period ended March 31, 2024. The assets have been classified as held for sale for more than one year. In accordance with ASC 360, assets not sold by the end of the one-year period may still qualify as held for sale, if certain conditions are met. The Board of Directors reconfirmed their approval of the sale at the January 2024 meeting and we believe the sale will be completed in calendar year 2024. As of March 31, 2024, we concluded all of the held for sale criteria is still met, and the assets are properly classified on the consolidated balance sheets. In addition, we have assessed whether there are any indicators of impairment and have concluded that the current carrying amount represents the estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell, and no additional remeasurement should be recorded.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DiscontinuedOperationsAndDisposalGroupsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure related to a disposal group. Includes, but is not limited to, a discontinued operation, disposal classified as held-for-sale or disposed of by means other than sale or disposal of an individually significant component. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//205-20/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//360/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisposalGroupsIncludingDiscontinuedOperationsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Property and Equipment
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| Property and Equipment |
Property and Equipment Property and equipment consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | Computers, servers and other equipment | | $ | 45,620 | | | $ | 43,135 | | | Furniture and fixtures | | 2,965 | | | 3,264 | | | Leasehold improvements | | 8,180 | | | 8,433 | | | Purchased software | | 2,586 | | | 1,862 | | | Construction in process | | 189 | | | 111 | | | | 59,540 | | | 56,805 | | | Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (51,579) | | | (48,518) | | | | $ | 7,961 | | | $ | 8,287 | |
We recorded depreciation and amortization expense of $5,165, $8,958, and $10,708 for the years ended 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Depreciation expense allocated to our cost of goods sold was approximately $938 for the year ended 2023, and $1,250 for the year ended 2022. There was no depreciation expense allocated to our cost of goods sold for the year ended 2024. As discussed in Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements, assets related to the sale of the Tinton Falls, New Jersey headquarters were reclassified to assets held for sale in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2023, at which time depreciation ended.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//360/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-6
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Accrued Liabilities
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Payables and Accruals [Abstract] |
|
| Accrued Liabilities |
Accrued Liabilities Accrued liabilities consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Compensation and related payroll taxes | | $ | 70,961 | | | $ | 58,112 | | | Other | | 46,283 | | | 39,776 | | | | $ | 117,244 | | | $ | 97,888 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for accounts payable and accrued liabilities at the end of the reporting period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(a),20,24)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Commitments and Contingencies
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Commitments and Contingencies |
Commitments and Contingencies Purchase Commitments
We, in the normal course of business, enter into various purchase commitments for goods or services. Our outstanding commitments primarily relate to marketing and IT services and also include the remaining purchase commitments for our use of certain cloud services with third-party providers. Total non-cancellable purchase commitments as of March 31, 2024 are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 and beyond | | Total | | Purchase commitments | | $ | 42,011 | | | $ | 9,652 | | | $ | 1,532 | | | $ | 111,527 | | | $ | 164,722 | |
In June 2022, we entered into an amended agreement with a third-party provider, in the ordinary course of business, for the use of certain cloud services through June 2027. Under the amended agreement, we committed to a purchase of $200,000 throughout the term of the agreement. As of March 31, 2024, we had $111,500 of remaining obligations under the purchase agreement. We have certain software royalty commitments associated with the shipment and licensing of certain products. Royalty expense is generally based on a fixed cost per unit shipped or a fixed fee for unlimited units shipped over a designated period. Royalty expense, included in cost of subscription and perpetual license revenues, was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Royalty expense | | $ | 9,717 | | | $ | 9,339 | | | $ | 11,188 | |
Warranties and Indemnifications
We typically offer a 90-day limited product warranty for our software. To date, costs related to this product warranty have not been significant. We provide certain provisions within our software licensing agreements to indemnify our customers from any claim, suit or proceeding arising from alleged or actual intellectual property infringement. These provisions continue in perpetuity, along with our software licensing agreements. We have never incurred a liability relating to one of these indemnification provisions, and management believes that the likelihood of any future payout relating to these provisions is remote. Therefore, we have not recorded a liability during any period for these indemnification provisions. Lease Obligations
Please refer to Note 15 of the notes to the financial statements for more detail on our minimum lease commitments.
Legal Proceedings We do not believe that we are currently party to any pending legal action that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on our business or operating results. During fiscal 2022, we entered into settlement agreements resulting in a $7,900 gain which resolved certain legal matters. The settlement amounts are recorded in general and administrative expenses net against related legal expenses.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//450/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480327/954-440-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Capitalization
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Equity [Abstract] |
|
| Capitalization |
Capitalization Common Stock We have 43,548 and 44,140 shares of common stock, par value $0.01, outstanding at March 31, 2024 and March 31, 2023, respectively. Our share repurchase program has been funded by our existing cash and cash equivalent balances, as well as cash flows provided by our operations. The Board of Directors (the "Board") had previously approved a share repurchase program of $250,000 in April 2023. The Board's authorization has no expiration date. During fiscal 2024, we repurchased $184,021 of our common stock, or approximately 2,479 shares. As a result, $71,944 remained available under the current authorization as of March 31, 2024. Subsequent Event On April 18, 2024, the Board of Directors approved an increase in our share repurchase program so that $250,000 was available. The Board's authorization has no expiration date. Shares Reserved for Issuance At March 31, 2024, we have reserved 6,149 shares in connection with our Stock Plans discussed in Note 10 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-6
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480237/815-40-50-6
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(e)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//505/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 16
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-16
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityNoteDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Stock Plans |
Stock Plans We maintain the Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2016 Incentive Plan”) for granting awards to employees. On August 29, 2023, our shareholders approved an amendment to the 2016 Incentive Plan to increase the maximum number of shares of common stock that may be delivered under the plan to 14,250, an increase of 3,200 shares. The 2016 Incentive Plan authorizes a broad range of awards including stock options, stock appreciation rights, full value awards (including restricted stock, restricted stock units, performance shares or units and other stock-based awards) and cash-based awards. As of March 31, 2024, approximately 3,754 shares were available for future grant under the 2016 Incentive Plan. As of March 31, 2024, we have granted non-qualified stock options, restricted stock units and performance stock awards under our stock incentive plans. Historically, most equity awards granted by us under our stock incentive plans generally vest quarterly over a three-year period, except that the shares that would otherwise vest quarterly over the first twelve months do not vest until the first anniversary of the grant. We anticipate that future grants under our stock incentive plans will be restricted stock units and performance stock awards and do not anticipate that we will grant stock options. The following table presents the stock-based compensation expense included in cost of revenues, sales and marketing, research and development, general and administrative and restructuring expenses for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022. Stock-based compensation is attributable to restricted stock units, performance-based awards and the ESPP. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Cost of revenues | | $ | 6,832 | | | $ | 4,787 | | | $ | 4,474 | | | Sales and marketing | | 36,630 | | | 43,081 | | | 37,431 | | | Research and development | | 21,585 | | | 28,540 | | | 33,870 | | | General and administrative | | 27,987 | | | 26,731 | | | 27,679 | | | Restructuring | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | | | Stock-based compensation expense | | $ | 94,551 | | | $ | 105,746 | | | $ | 105,163 | |
As of March 31, 2024, there was approximately $125,213 of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to all of our employee stock plans that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.76 years. We account for forfeitures as they occur. To the extent that awards are forfeited, stock-based compensation will be different from our current estimate. Stock option activity is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Options | | Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | | 553 | | | $ | 73.58 | | | | | | | Granted | | — | | | — | | | | | | | Exercised | | (58) | | | 48.88 | | | | | | | Forfeited | | — | | | — | | | | | | | Expired | | (371) | | | 86.95 | | | | | | Outstanding at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | |
The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $1,378, $1,176, and $12,704 in the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Restricted stock unit activity is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Non-Vested Restricted Stock Units | | Number
of
Awards | | Weighted-
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | | Non-vested as of March 31, 2023 | | 2,953 | | | $ | 62.52 | | | Granted | | 1,483 | | | 70.42 | | | Vested | | (1,641) | | | 60.08 | | | Forfeited | | (378) | | | 65.74 | | | Non-vested as of March 31, 2024 | | 2,417 | | | $ | 68.52 | |
The total fair value of the restricted stock units that vested during the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $118,047, $114,422 and $122,259, respectively. The fair value of awards includes the awards with a market condition described below. Performance Based Awards In fiscal 2024, we granted 120 performance stock units ("PSUs") to certain executives. Vesting of these awards is contingent upon i) us meeting certain non-GAAP performance goals (performance-based) in fiscal 2024 and ii) our customary service periods. The awards vest over three years. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized over the vesting term using the accelerated method. During each financial period, management estimates the probable number of PSUs that would vest until the ultimate achievement of the performance goals is known. Based on our results, the PSUs achieved at 108%. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table.
In fiscal 2023, we granted 126 PSUs to certain executives. Vesting of these awards is contingent upon i) us meeting certain non-GAAP performance goals (performance-based) in fiscal 2023 and ii) our customary service periods. The awards vest over three years. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized over the vesting term using the accelerated method. Based on our results, the PSUs achieved at 128%. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table. Awards with a Market Condition
In fiscal 2024, we granted 120 market PSUs to certain executives. The vesting of these awards is contingent upon us meeting certain total shareholder return ("TSR") levels as compared to the Russell 3000 market index over the next three years. The awards vest in three annual tranches and have a maximum potential to vest at 200% (240 shares) based on TSR performance. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the estimated fair value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized using the accelerated method over the vesting term. The estimated fair value was calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the awards granted during the year was $87.90 per unit. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table above.
In fiscal 2023, we granted 126 market PSUs to certain executives. The vesting of these awards is contingent upon us meeting certain TSR levels as compared to the Russell 3000 market index over the next three years. The awards vest in three annual tranches and have a maximum potential to vest at 200% (252 shares) based on TSR performance. The related stock-based compensation expense is determined based on the estimated fair value of the underlying shares on the date of grant and is recognized using the accelerated method over the vesting term. The estimated fair value was calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of the awards granted during the year was $76.48 per unit. The awards are included in the restricted stock unit table above. Employee Stock Purchase Plan The ESPP is a shareholder approved plan under which substantially all employees may purchase our common stock through payroll deductions at a price equal to 85% of the lower of the fair market values of the stock as of the beginning or the end of six-month offering periods. An employee’s payroll deductions under the ESPP are limited to 10% of the employee’s salary and employees may not purchase more than $25 of stock during any calendar year. Employees purchased 188 shares in exchange for $10,578 of proceeds in fiscal 2024 and 213 shares in exchange for $10,873 of proceeds in fiscal 2023. The ESPP is considered compensatory and the fair value of the discount and look back provision are estimated using the Black-Scholes formula and recognized over the six-month withholding period prior to purchase. The total expense associated with the ESPP for fiscal 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $3,146, $3,740 and $3,341, respectively. As of March 31, 2024, there was approximately $1,177 of unrecognized cost related to the current purchase period of our ESPP.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//718/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisclosureOfCompensationRelatedCostsShareBasedPaymentsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Income Taxes |
Income Taxes The components of income (loss) before income taxes were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Domestic | | $ | 62,082 | | | $ | (35,288) | | | $ | 25,905 | | | Foreign | | 21,531 | | | 19,926 | | | 17,509 | | | | $ | 83,613 | | | $ | (15,362) | | | $ | 43,414 | |
The components of income tax expense (benefit) were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Current: | | | | | | | | Federal | | $ | 7,845 | | | $ | 6,986 | | | $ | 284 | | | State | | 4,242 | | | 3,375 | | | 361 | | | Foreign | | 12,220 | | | 10,725 | | | 9,096 | | | Deferred: | | | | | | | | Federal | | (82,773) | | | (607) | | | 28 | | | State | | (19,740) | | | — | | | — | | | Foreign | | (7,087) | | | (67) | | | 21 | | | | $ | (85,293) | | | $ | 20,412 | | | $ | 9,790 | |
A reconciliation of the statutory tax rates and the effective tax rates for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Statutory federal income tax expense (benefit) rate | | 21.0 | % | | (21.0) | % | | 21.0 | % | | State and local income tax expense, net of federal income tax effect | | 2.4 | % | | (11.8) | % | | 0.8 | % | | Foreign earnings taxed at different rates | | 5.7 | % | | 28.0 | % | | 6.2 | % | | U.S. tax on GILTI & FDII | | (3.3) | % | | (17.1) | % | | 0.5 | % | | Domestic permanent differences including acquisition items | | 1.1 | % | | 4.7 | % | | 3.6 | % | | Foreign tax credits | | (2.5) | % | | (35.5) | % | | (5.3) | % | | Research credits | | (9.3) | % | | (74.6) | % | | (28.3) | % | | Tax reserves | | — | % | | (1.2) | % | | 2.6 | % | | Valuation allowance | | (125.3) | % | | 219.9 | % | | 18.3 | % | | Enacted tax law changes | | (0.4) | % | | 3.6 | % | | 0.3 | % | | Stock-based compensation | | 6.7 | % | | 41.6 | % | | (1.6) | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other differences, net | | 1.9 | % | | (3.7) | % | | 4.5 | % | | Effective income tax expense (benefit) | | (102.0) | % | | 132.9 | % | | 22.6 | % |
The significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | Net operating losses | | $ | 6,533 | | | $ | 9,106 | | | Equity investment/Capital losses | | 952 | | | 889 | | | Stock-based compensation | | 5,338 | | | 11,912 | | | Deferred revenue | | 29,748 | | | 24,025 | | | Tax credits | | 28,020 | | | 42,986 | | | Accrued expenses | | 1,775 | | | 1,816 | | | Allowance for doubtful accounts and other reserves | | 928 | | | 572 | | | R&D Capitalization under IRC § 174 | | 58,867 | | | 32,091 | | | Depreciation and amortization | | 9,305 | | | 9,449 | | | Other, DTA | | 2,228 | | | 98 | | | Less: valuation allowance | | (18,140) | | | (122,921) | | | Total deferred tax assets | | 125,554 | | | 10,023 | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | Withholding taxes | | (1,091) | | | (393) | | | Deferred commissions | | (12,573) | | | (9,764) | | | Other, DTL | | (2,426) | | | — | | | Total deferred tax liabilities | | (16,090) | | | (10,157) | | | Net deferred tax asset (liability) | | $ | 109,464 | | | $ | (134) | |
Net deferred tax assets arise due to the recognition of income and expense items for tax purposes, which differ from those used for financial statement purposes. ASC 740, Income Taxes, provides for the recognition of deferred tax assets if realization of such assets is more likely than not. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we considered all available objective and verifiable evidence both positive and negative, including historical levels of pre-tax income (loss) both on a consolidated basis and tax reporting entity basis, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies. As a result of this analysis, we determined that it is more likely than not that we will realize the benefits of the majority of our gross deferred tax assets and therefore recorded the release of the previously established valuation allowance as an income tax benefit in the current period. At March 31, 2024 and 2023, we recorded valuation allowances of $18,140 and $122,921, respectively, representing an increase in deferred tax benefit of $104,781 for the period ended March 31, 2024.
At March 31, 2024, we had federal net operating loss ("NOL") carryforwards of $5,981, all of which will not expire. As of March 31, 2024, we had deferred tax assets related to state NOL carryforwards of $1,013 which expire over various years beginning in March 2033 depending on the jurisdiction. As of March 31, 2024, we had foreign NOL carryforwards of $3,064 that will expire over various years beginning in March 2028 depending on the jurisdiction and $34,035 that will not expire. As of March 31, 2024, we had federal capital loss carryforwards of $3,988 that will expire in March 2027. At March 31, 2024, we had foreign capital loss carryforwards of $310 that will not expire.
We also had federal and state research tax credits ("R&D credit") carryforwards of approximately $5,177 and $26,467, respectively. The federal R&D credit carryforwards expire from March 2039 through March 2044, and the New Jersey R&D credit carryforwards of $16,857 expire over various years beginning from March 2025 through March 2038. The California R&D credits of $9,610 do not expire. We also had federal foreign tax credits (“FTC”) carryforwards of approximately $3,999. The federal FTC carryforwards expire from March 2030 through March 2034. We also had $215 in foreign FTC carryforwards that will expire over various years beginning in March 2025. We conduct business globally and as a result, file income tax returns in the United States and in various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. The following table summarizes the tax years subject to income tax examinations by tax authorities as of March 31, 2024. The years subject to income tax examination in our foreign jurisdictions cover the maximum time period with respect to these jurisdictions. Due to NOLs, in some cases the tax years continue to remain subject to examination with respect to such NOLs. | | | | | | | Tax Jurisdiction | Years Subject to Income
Tax Examination | | U.S. Federal | 2020 - Present | | Foreign jurisdictions | 2013 - Present |
The calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax regulations in each of our tax jurisdictions. The number of years with open tax audits varies depending on the tax jurisdiction. A number of years may lapse before a particular matter is audited and finally resolved. A reconciliation of the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| | | | | | | Balance at March 31, 2021 | $ | 2,211 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2022 | 2,808 | | | Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 90 | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (117) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | 4,232 | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2022 | 9,224 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2023 | 394 | | | Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | (90) | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (140) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2023 | 9,388 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2024 | 502 | | | Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 3 | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (220) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2024 | $ | 9,673 | |
We estimate that no significant remaining unrecognized tax benefits will be realized during the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025. Interest income, expense and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recorded in income tax expense in the consolidated statements of operations. In the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, the impact related to interest expense, interest income and penalties was not significant.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income taxes. Disclosures may include net deferred tax liability or asset recognized in an enterprise's statement of financial position, net change during the year in the total valuation allowance, approximate tax effect of each type of temporary difference and carryforward that gives rise to a significant portion of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets, utilization of a tax carryback, and tax uncertainties information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//740/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482526/740-270-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Employee Benefit Plan
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Retirement Benefits [Abstract] |
|
| Employee Benefit Plan |
Employee Benefit Plan We have a defined contribution plan, as allowed under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code, covering substantially all US employees. Effective January 1, 2012, we make contributions equal to a discretionary percentage of the employee’s contributions determined by us. During the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we made contributions of $2,889, $2,525, and $2,923, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationAndRetirementDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for retirement benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 70
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480794/715-70-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480482/715-20-55-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (q)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (l)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//715/tableOfContent
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (o)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (p)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (r)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480126/715-20-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 60
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480266/715-60-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_PensionAndOtherPostretirementBenefitsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Segment Information
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| Segment Information |
Segment Information We operate in one segment. Our products and services are sold throughout the world, through direct and indirect sales channels. Our chief operating decision maker (the “CODM”) is the Chief Executive Officer. The CODM makes operating performance assessment and resource allocation decisions on a global basis. The CODM does not receive discrete financial information about asset allocation, expense allocation or profitability by product or geography. Revenues by geography are based upon the billing address of the customer. All transfers between geographic regions have been eliminated from consolidated revenues. The following table sets forth revenue and long-lived assets by geographic area: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Revenue: | | | | | | | | United States | | $ | 437,560 | | | $ | 416,347 | | | $ | 398,632 | | | Other | | 401,687 | | | 368,243 | | | 370,959 | | | | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
No individual country other than the United States accounts for 10% or more of revenues in the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022. Revenue included in the “Other” caption above primarily relates to our operations in Europe, Australia, Canada and Asia. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Long-lived assets: | | | | | | United States | | $ | 192,485 | | | $ | 184,356 | | | Other | | 45,121 | | | 47,304 | | | | $ | 237,606 | | | $ | 231,660 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for reporting segments including data and tables. Reportable segments include those that meet any of the following quantitative thresholds a) it's reported revenue, including sales to external customers and intersegment sales or transfers is 10 percent or more of the combined revenue, internal and external, of all operating segments b) the absolute amount of its reported profit or loss is 10 percent or more of the greater, in absolute amount of 1) the combined reported profit of all operating segments that did not report a loss or 2) the combined reported loss of all operating segments that did report a loss c) its assets are 10 percent or more of the combined assets of all operating segments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//280/tableOfContent
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 26
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-26
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 34
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-34
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-21
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Restructuring
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Restructuring and Related Activities [Abstract] |
|
| Restructuring |
Restructuring Beginning in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2024, we initiated a restructuring plan intended to enhance customer satisfaction through the reorganization and redesign of our customer success functions. The realignment of the customer success structure aims to optimize operational efficiency and improve continuity for our customers through the pre-sales and post-sales experience. These charges relate primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions, stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan and office termination and exit charges. We anticipate the restructuring plan will be completed in the second half of fiscal 2025. The total costs to be incurred related to the restructuring plan cannot be estimated at this time. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2022 we initiated a restructuring program which was completed in fiscal 2023. It was aimed to increase efficiency in our sales, marketing and distribution functions as well as reduce costs across all functional areas. The plan included a reorganization to combine our EMEA and APJ field organizations into our International region. These restructuring charges related primarily to severance and related costs associated with headcount reductions and stock-based compensation related to modifications of existing awards granted to certain employees impacted by the plan. For the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, restructuring charges were comprised of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Employee severance and related costs | | $ | 2,811 | | | $ | 12,845 | | | $ | 4,483 | | Lease exit costs (1) | | 220 | | | — | | | — | | | Stock-based compensation | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | | | Total restructuring charges | | $ | 4,548 | | | $ | 15,452 | | | $ | 6,192 | |
(1) Lease exit costs relate to one office for the year ended March 31, 2024. There were no lease exit charges for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. Restructuring accrual The accrual activity related to our restructuring plans for the years ended March 31, 2024 and 2023 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 (1) | | 2023 | | Beginning balance | | $ | 3,211 | | | $ | 2,261 | | | Employee severance and related costs | | 2,811 | | | 12,845 | | | Payments | | (3,276) | | | (11,895) | | | Ending balance | | $ | 2,746 | | | $ | 3,211 | |
(1) During fiscal 2024, there were no new charges incurred related to the completed restructuring plan. Payments made related to the completed plan were $3,149, resulting in an insignificant remaining accrual at March 31, 2024.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for restructuring and related activities. Description of restructuring activities such as exit and disposal activities, include facts and circumstances leading to the plan, the expected plan completion date, the major types of costs associated with the plan activities, total expected costs, the accrual balance at the end of the period, and the periods over which the remaining accrual will be settled. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//420/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(e))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringAndRelatedActivitiesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Leases
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Leases |
Leases We determine if an arrangement contains a lease at inception. We generally lease our facilities under operating leases. Operating lease right-of-use ("ROU") assets are included in operating lease assets on our consolidated balance sheets. Current portion of operating lease liabilities and long-term operating lease liabilities are included on our consolidated balance sheets. ROU assets represent our right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent our obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of our leases do not provide an implicit rate, we generally use our incremental borrowing rate based on the estimated rate of interest for collateralized borrowing over a similar term of the lease payments at the commencement date. We recognize operating lease costs over the estimated term of the lease, which includes options to extend lease terms that are reasonably certain of being exercised, starting when possession of the property is taken from the landlord. When a lease contains a predetermined fixed escalation of the minimum rent, we recognize the related operating lease cost on a straight-line basis over the lease term. In addition, certain of our lease agreements include variable lease payments, such as estimated tax and maintenance charges. These variable lease payments are excluded from minimum lease payments and are included in the determination of lease cost when it is probable that the expense has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated. Our lease liabilities relate primarily to operating leases for our global office infrastructure. These operating leases expire at various dates through fiscal 2031. We did not have any finance leases for the years ended March 31, 2024 or 2023.
Net lease cost recognized in our consolidated statements of operations is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Operating lease cost | $ | 5,770 | | | $ | 5,449 | | | $ | 7,129 | | | Short-term lease cost | 272 | | | 631 | | | 123 | | | Variable lease cost | 1,333 | | | 1,360 | | | 1,608 | | | Net lease cost | $ | 7,375 | | | $ | 7,440 | | | $ | 8,860 | |
Cash flow information | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Cash paid for operating lease liabilities | $ | 5,033 | | | $ | 5,421 | | | $ | 8,277 | | | Additions of operating lease assets (non-cash) | $ | 5,528 | | | $ | 3,023 | | | $ | 1,827 | |
As of March 31, 2024, the maturities of lease liabilities based on the total minimum lease commitment amount including options to extend lease terms that are reasonably certain of being exercised are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 4,624 | | | 2026 | 2,973 | | | 2027 | 1,740 | | | 2028 | 1,601 | | | 2029 | 932 | | | Thereafter | 683 | | | Total minimum lease payments | 12,553 | | | Less: Imputed interest | 463 | | | Present value of operating lease liabilities | 12,090 | | | Less: Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 4,935 | | | Long-term operating lease liabilities | $ | 7,155 | |
As of March 31, 2024, the minimum lease commitment amount for operating leases signed but not yet commenced was $743. These commitments are related to office lease renewals that expire at various dates through fiscal 2030. Lease term and Discount rate | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Weighted-average remaining term (in years) | 3.60 | | 3.72 | | Weighted-average discount rate | 4 | % | | 4 | % |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for operating leases of lessee. Includes, but is not limited to, description of operating lease and maturity analysis of operating lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//842-20/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeasesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revolving Credit Facility
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Revolving Credit Facility |
Revolving Credit Facility On December 13, 2021, we entered into a five-year $100,000 senior secured revolving credit facility (the “Credit Facility”) with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. The Credit Facility is available for share repurchases, general corporate purposes, and letters of credit. The Credit Facility contains financial maintenance covenants, including a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio. The Credit Facility also contains certain customary events of default which would permit the lender to, among other things, declare all loans then outstanding to be immediately due and payable if such default is not cured within applicable grace periods. The Credit Facility also limits our ability to incur certain additional indebtedness, create or permit liens on assets, make acquisitions, make investments, loans or advances, sell or transfer assets, pay dividends or distributions, and engage in certain transactions with foreign affiliates. Outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility accrue interest at an annual rate equal to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate plus 1.25% subject to increases based on our actual leverage. The unused balance on the Credit Facility is also subject to a 0.25% annual interest charge subject to increases based on our actual leverage. As of March 31, 2024, there were no borrowings under the Credit Facility and we were in compliance with all covenants. We have deferred the expense related to debt issuance costs, which are classified as other assets, and will amortize the costs into interest expense over the term of the Credit Facility. Unamortized amounts at March 31, 2024 and 2023 were $313 and $428, respectively. The amortization of debt issuance costs and interest expense incurred for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | $ | 115 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 34 | | | Interest expense | 253 | | | 253 | | | 75 | | | Total charges | $ | 368 | | | $ | 368 | | | $ | 109 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for information about short-term and long-term debt arrangements, which includes amounts of borrowings under each line of credit, note payable, commercial paper issue, bonds indenture, debenture issue, own-share lending arrangements and any other contractual agreement to repay funds, and about the underlying arrangements, rationale for a classification as long-term, including repayment terms, interest rates, collateral provided, restrictions on use of assets and activities, whether or not in compliance with debt covenants, and other matters important to users of the financial statements, such as the effects of refinancing and noncompliance with debt covenants. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 470
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//470/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1B
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1C
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1C
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1E
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1E
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1I
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1I
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Subsequent Event
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Subsequent Events [Abstract] |
|
| Subsequent Event |
Subsequent Event On April 15, 2024, we signed an agreement to acquire all of the shares of Appranix, Inc., a Boston based cloud cyber resilience company, for total consideration of approximately $26,000, subject to customary transaction adjustments. There is an additional potential earn out if certain financial metrics are met through the initial fourteen-month period after the closing date. The primary reason for the business combination is to extend our product offerings in our existing cyber resiliency market opportunity. As the transaction occurred subsequent to year-end, we are still evaluating the purchase price allocation of the transaction but expect the primary assets acquired to be intangible assets and goodwill. Acquired tangible assets and assumed liabilities are expected to be immaterial. The allocation is expected to be finalized during fiscal 2025.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for significant events or transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date the financial statements were issued or the date the financial statements were available to be issued. Examples include: the sale of a capital stock issue, purchase of a business, settlement of litigation, catastrophic loss, significant foreign exchange rate changes, loans to insiders or affiliates, and transactions not in the ordinary course of business. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//855/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483399/855-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection v
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_PvpTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Insider Trading Arrangements
|
3 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024
shares
|
Mar. 31, 2024
shares
|
| Trading Arrangements, by Individual |
|
|
| Non-Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Adopted |
false
|
|
| Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Terminated |
false
|
|
| Non-Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Terminated |
false
|
|
| Nicholas Adamo [Member] |
|
|
| Trading Arrangements, by Individual |
|
|
| Material Terms of Trading Arrangement |
|
On February 1, 2024, Nicholas Adamo, Chairman of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 2,450 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until September 6, 2024.
|
| Name |
Nicholas Adamo
|
|
| Title |
Chairman of our Board of Directors
|
|
| Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Adopted |
true
|
|
| Adoption Date |
February 1, 2024
|
|
| Arrangement Duration |
218 days
|
|
| Aggregate Available |
2,450
|
2,450
|
| Vivie Lee [Member] |
|
|
| Trading Arrangements, by Individual |
|
|
| Material Terms of Trading Arrangement |
|
On February 2, 2024, Vivie Lee, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 4,100 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until September 6, 2024.
|
| Name |
Vivie Lee
|
|
| Title |
member of our Board of Directors
|
|
| Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Adopted |
true
|
|
| Adoption Date |
February 2, 2024
|
|
| Arrangement Duration |
217 days
|
|
| Aggregate Available |
4,100
|
4,100
|
| Allison Pickens [Member] |
|
|
| Trading Arrangements, by Individual |
|
|
| Material Terms of Trading Arrangement |
|
On February 16, 2024, Allison Pickens, a member of our Board of Directors, adopted a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) for the sale of up to approximately 4,100 shares of the Company’s common stock. The plan is in effect until March 4, 2025.
|
| Name |
Allison Pickens
|
|
| Title |
member of our Board of Directors
|
|
| Rule 10b5-1 Arrangement Adopted |
true
|
|
| Adoption Date |
February 16, 2024
|
|
| Arrangement Duration |
382 days
|
|
| Aggregate Available |
4,100
|
4,100
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_MtrlTermsOfTrdArrTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph A
| Name: |
ecd_TradingArrByIndTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph B
| Name: |
ecd_TrdArrAdoptionDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph C
| Name: |
ecd_TrdArrDuration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph A
| Name: |
ecd_TrdArrIndName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph A
| Name: |
ecd_TrdArrIndTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph D
| Name: |
ecd_TrdArrSecuritiesAggAvailAmt |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
ecd_IndividualAxis=cvlt_NicholasAdamoMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
ecd_IndividualAxis=cvlt_VivieLeeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
ecd_IndividualAxis=cvlt_AllisonPickensMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Reclassification of Prior Year Balances |
Reclassification of Prior Year Balances Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified for consistency with the current year presentation. These reclassifications have no impact on the amount of total revenues or net income. Beginning in fiscal 2024, the software and services line items on the consolidated statements of operations, related to revenues and cost of revenues, are being presented in the following categories:
Subscription - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs of recurring time-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer.
Perpetual license - The amounts on this line include the revenues and costs from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download.
Customer support - The amounts on this line include customer support revenues and costs associated with our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. Customer support revenue is typically recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement.
Other services - The amounts included on this line consist primarily of revenues and costs related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other professional services are typically recognized as the services are performed.
|
| Basis of Presentation |
Basis of Presentation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Commvault. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
|
| Use of Estimates |
Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") requires management to make judgments and estimates that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. The amounts of assets and liabilities reported in our balance sheets and the amounts of revenues and expenses reported for each of the periods presented are affected by estimates and assumptions, which are used for, but not limited to, the accounting for revenue recognition, income taxes and related reserves, deferred commissions, purchased intangible assets and goodwill. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
|
| Revenue, Deferred Commissions Cost and Deferred Revenue |
Revenue We account for revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("ASC 606"). We record revenue net of sales tax. For a further discussion of our accounting policies related to revenue,Deferred Commissions Cost Sales commissions, bonuses, and related payroll taxes earned by our employees are considered incremental and recoverable costs of obtaining a contract with a customer. Our typical contracts include performance obligations related to term-based software licenses, SaaS offerings, perpetual software licenses, software updates, and customer support. In these contracts, incremental costs of obtaining a contract are allocated to the performance obligations based on the relative estimated standalone selling prices and then recognized on a systematic basis that is consistent with the transfer of the goods or services to which the asset relates. We do not pay commissions on annual renewals of customer support contracts for perpetual licenses. The costs allocated to software and products are expensed at the time of sale, when revenue for the functional software license or appliance is recognized. The costs allocated to software updates and customer support for perpetual licenses are amortized ratably over a period of approximately five years, the expected period of benefit of the asset capitalized. We currently estimate a period of five years is appropriate based on consideration of historical average customer life and the estimated useful life of the underlying software sold as part of the transaction. The commission paid on the renewal of subscription arrangements is not commensurate with the commission paid on the initial purchase. As a result, the cost of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and customer support on the initial term-based software license transactions are amortized over a period of approximately five years, consistent with the accounting for these costs associated with perpetual licenses. The costs of commissions allocated to SaaS offerings, software updates and support for the renewal of term-based software licenses is limited to the contractual period of the arrangement, as we pay a commensurate renewal commission upon the next renewal of the subscription software license and related updates and support.
The incremental costs attributable to professional services are generally amortized over the period the related services are provided and revenue is recognized. Amortization expense related to these costs is included in sales and marketing expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Deferred Revenue Deferred revenues represent amounts collected from, or invoiced to, customers in excess of revenues recognized. This results primarily from the billing of annual customer support agreements, the billing of SaaS subscription arrangements and billings for other services that have not yet been performed by us. The value of deferred revenues will increase or decrease based on the timing of invoices and recognition of revenue. RevenueWe derive revenues from various sources, including subscriptions, perpetual software licenses, customer support contracts and other services. Subscription Subscription includes the revenues derived from term-based arrangements, including the software portion of term-based licenses and SaaS offerings. The software component of term-based licenses is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. The term of our subscription arrangements is typically one to three years, but can range between one and five years. For SaaS offerings, revenue is generally recognized ratably over the contract term beginning on the date that the service is made available to the customer. Perpetual License Perpetual license includes the revenues from the sale of perpetual software licenses. Perpetual software license revenue is typically recognized when the software is delivered or made available for download. Customer Support Customer support includes revenues associated with support contracts tied to our software products. Customer support includes software updates on a when-and-if-available basis, telephone support, integrated web-based support, and other premium support offerings, for both subscription software and perpetual software license arrangements. We sell our customer support contracts as a percentage of net software purchases. Customer support revenue is recognized ratably over the term of the customer support agreement, which is typically one year on our perpetual licenses and over the term on our term-based licenses. Other Services Other services consist primarily of revenues related to professional service offerings, including consultation, assessment and design, installation services, and customer education. Revenues related to other services can vary period over period based on the timing services are delivered and are typically recognized as the services are performed. We do not customize our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) and installation services are not required. Software licenses are delivered before related services are provided and are functional without professional services, updates and technical support. We have concluded that our software licenses (both perpetual and term-based) are functional intellectual property that is distinct, as the user can benefit from the software on its own. Revenues for both perpetual and term-based licenses are typically recognized when the software is delivered and/or made available for download as this is the point the user of the software can direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the remaining benefits from, the functional intellectual property. We do not recognize software revenue related to the renewal of subscription software licenses earlier than the beginning of the new subscription period. We also offer appliances that integrate our software with hardware and address a wide-range of business needs and use cases, ranging from support for remote or branch offices with limited IT staff up to large corporate data centers. Our appliances are almost exclusively sold via a software only model in which we sell software to a third party, which assembles an integrated appliance that is sold to end user customers. As a result, the revenues and costs associated with hardware are usually not included in our financial statements. Our typical performance obligations include the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | Performance Obligation | When Performance Obligation
is Typically Satisfied | When Payment is
Typically Due | How Standalone Selling Price is
Typically Estimated | | Subscription | | Term-based software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment except for certain subscription licenses which are paid for over time | Residual approach | | Software-as-a-service (SaaS) | Ratably over the course of the contract (over time) | Annually or at the beginning of the contract period | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Perpetual License | | Perpetual software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment | Residual approach | | Customer Support | | Software updates | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Customer support | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Other Services | | Other professional services (except for education services) | As work is performed (over time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Education services | When the class is taught (point in time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
Information about Contract Balances
Amounts collected in advance of services being provided are accounted for as deferred revenue. Nearly all of our deferred revenue balance is related to SaaS arrangements, customer support, and other services. In some arrangements we allow customers to pay for term-based licenses over the term of the software license. Amounts recognized as revenue in excess of amounts billed are recorded as unbilled receivables. Unbilled receivables which are anticipated to be invoiced in the next twelve months are included in accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets.
|
| Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation |
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation Restricted stock units without a market condition are measured based on the fair market values of the underlying stock on the date of grant. We recognize stock-based compensation expense using the straight-line method for all stock awards that do not include a market or performance condition. Awards that include a market or performance condition are expensed using the accelerated method.
|
| Software Development Costs |
Software Development Costs The costs for the development of new products and substantial enhancements to existing products are expensed as incurred until technological feasibility has been established, at which time any additional costs would be capitalized in accordance with the accounting guidance for software. Because our current process for developing software is essentially completed concurrently with the establishment of technological feasibility, which occurs upon the completion of a working model, no costs have been capitalized for any of the periods presented.
|
| Advertising Costs |
Advertising Costs We expense advertising costs as incurred.
|
| Accounting for Income Taxes |
Accounting for Income Taxes We account for income taxes in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes ("ASC 740"). The provision for income taxes and effective tax rates are calculated by legal entity and jurisdiction and are based on a number of factors, including the level of pre-tax earnings, income tax planning strategies, differences between tax laws and accounting rules, statutory tax rates and credits, uncertain tax positions and valuation allowances. We provide for global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) earned by certain foreign subsidiaries in the year the tax is incurred and record an estimate of GILTI as a component of the tax provision. We use significant judgment and estimates in evaluating tax positions. The effective tax rate in a given financial statement period may be materially impacted by changes in the mix and level of earnings by taxing jurisdiction. Under ASC 740, deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts. Valuation allowances are established when, in our judgment, it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized. In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we weigh the available positive and negative evidence, including historical levels of pre-tax income, legislative developments, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future pre-tax income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies.
|
| Foreign Currency Translation |
Foreign Currency Translation The functional currencies of our foreign operations are deemed to be the local country’s currency. Assets and liabilities of our international subsidiaries are translated at their respective period-end exchange rates, and revenues and expenses are translated at average currency exchange rates for the period. The resulting balance sheet translation adjustments are included in other comprehensive income (loss) and are reflected as a separate component of stockholders’ equity. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are recorded in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. These gains and losses relate primarily to receivables and payables that are not denominated in the functional currency of the subsidiary they relate to.
|
| Net Income (Loss) per Common Share |
Net Income (Loss) per Common Share Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of common shares during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares consist of the incremental common shares issuable upon the vesting of restricted stock units, shares to be purchased under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan ("ESPP"), and the exercise of stock options. The dilutive effect of such potential common shares is reflected in diluted earnings (loss) per share by application of the treasury stock method.
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and Cash Equivalents We consider all highly liquid investments purchased with maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents.
|
| Trade and Other Receivables |
Trade and Other Receivables Trade and other receivables are primarily comprised of trade receivables that are recorded at the invoice amount, net of an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is not material. Unbilled receivables represent amounts for which revenue has been recognized but which have not yet been invoiced to the customer. The current portion of unbilled receivables is included in trade accounts receivable on the consolidated balance sheets. Long-term unbilled receivables are included in other assets.
|
| Concentration of Credit Risk |
Concentration of Credit Risk We grant credit to customers in a wide variety of industries worldwide and generally do not require collateral. Credit losses relating to these customers have been minimal.
|
| Fair Value of Financial Instruments |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for such asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value should maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. To measure fair value, we use the following fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable: Level 1 — Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; Level 2 — Inputs other than Level 1, that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly; and Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions.
The carrying amounts of our cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to the short-term maturity of these instruments. Our cash equivalents balance consists primarily of U.S. Treasury Bills with maturities of one month or less.
|
| Equity Securities Accounted for at Net Asset Value |
Equity Securities Accounted for at Net Asset Value We held equity interests in private equity funds of $7,318 as of March 31, 2024, which are accounted for under the net asset value practical expedient as permitted under ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement. These investments are included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The net asset values of these investments are determined using quarterly capital statements from the funds, which are based on our contributions to the funds, allocation of profit and loss and changes in fair value of the underlying fund investments. Changes in fair value as reported on the capital statements are recorded through the consolidated statements of operations as non-operating income or expense. These private equity funds focus on making investments in key technology sectors, principally by investing in companies at expansion capital and growth equity stages. We have total unfunded commitments in private equity funds of $2,645 as of March 31, 2024.
|
| Leases |
Leases We account for leases in accordance with ASC 842, Leases.
|
| Property and Equipment |
Property and Equipment Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Land is not depreciated. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Computer and related equipment is generally depreciated over eighteen months to three years and furniture and fixtures are generally depreciated over three to twelve years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the useful life of the improvement or the term of the related lease. Expenditures for routine maintenance and repairs are charged against operations. Major replacements, improvements and additions are capitalized. In January 2023, the assets that previously comprised our owned corporate headquarters met the held for sale criteria in accordance with ASC 360, Property, Plant and Equipment ("ASC 360"), and were reclassified as such. These assets are no longer being depreciated. For further discussion on assets held for sale, see Note 5 of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets |
Goodwill and Intangible Assets Goodwill is recorded when the consideration paid for an acquisition exceeds the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired. The carrying value of goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis on January 1, or more often if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of its carrying amount. For the purpose of impairment testing, we have a single reporting unit. The impairment test consists of comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount that includes goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, an impairment loss would be recognized to reduce the carrying amount to its fair value. Our finite lived purchased intangible asset, developed technology, was valued using the replacement cost method and is being amortized on a straight-line basis over its economic life of three years as we believed this method most closely reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the assets will be consumed. Impairment losses are recognized if the carrying amount of an intangible asset is both not recoverable and exceeds its fair value.
|
| Long-Lived Assets |
Long-Lived Assets We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. To determine the recoverability of our long-lived assets, we evaluate the estimated future undiscounted cash flows that are directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of, the use and eventual disposition of the long-lived asset. If the estimated future undiscounted cash flows demonstrate that recoverability is not probable, an impairment loss would be recognized. An impairment loss would be calculated based on the excess carrying amount of the long-lived asset over the long-lived asset’s fair value. The fair value would be determined based on valuation techniques such as a comparison to fair values of similar assets.
|
| Share Repurchases |
Share Repurchases We consider all shares repurchased as canceled shares restored to the status of authorized but unissued shares on the trade date. The aggregate purchase price of the shares of our common stock repurchased is reflected as a reduction to stockholders’ equity. We account for shares repurchased as an adjustment to common stock (at par value) with the excess repurchase price allocated between additional paid-in capital and accumulated deficit.
|
| Comprehensive Income |
Comprehensive Income Comprehensive income is defined to include all changes in equity, except those resulting from investments by stockholders and distribution to stockholders.
|
| Recently Adopted and Recently Issued Accounting Standards |
Recently Adopted and Recently Issued Accounting Standards There were no recently adopted accounting standards that had a material effect on our condensed consolidated financial statements and accompanying disclosures. The table below outlines recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Standard | Description | Effective Date | Effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements (or Other Significant Matters) | | Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-07 (Topic 280): Segment Reporting | In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued a new standard to improve reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. In addition, the amendments enhance interim disclosure requirements, clarify circumstances in which an entity can disclose multiple segment measures of profit or loss, provide new segment disclosure requirements for entities with a single reportable segment, and contain other disclosure requirements. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2024, and interim periods within our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We will adopt this standard using a retrospective approach on April 1, 2024. We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. | | ASU No. 2023-09 (Topic 740): Income Taxes | In December 2023, the FASB issued a new standard to improve income tax disclosures. The standard requires greater disaggregated information about a reporting entity’s effective tax rate reconciliation as well as information on income taxes paid. | This standard will be effective for our fiscal year beginning April 1, 2025. | We are currently evaluating the impact of this standard in our consolidated financial statements, including accounting policies, processes, and systems. |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDescribes an entities policy for shares repurchased under its stock plan.
| Name: |
cvlt_StockRepurchasesPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for advertising cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 35
-Topic 720
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483406/720-35-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdvertisingCostsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for basis of accounting, or basis of presentation, used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS).
| Name: |
us-gaap_BasisOfAccountingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cash and cash equivalents, including the policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Other information that may be disclosed includes (1) the nature of any restrictions on the entity's use of its cash and cash equivalents, (2) whether the entity's cash and cash equivalents are insured or expose the entity to credit risk, (3) the classification of any negative balance accounts (overdrafts), and (4) the carrying basis of cash equivalents (for example, at cost) and whether the carrying amount of cash equivalents approximates fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for salaries, bonuses, incentive awards, postretirement and postemployment benefits granted to employees, including equity-based arrangements; discloses methodologies for measurement, and the bases for recognizing related assets and liabilities and recognizing and reporting compensation expense. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b),(f(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationRelatedCostsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for comprehensive income.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomePolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for credit risk. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 825
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480981/942-825-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskCreditRisk |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for determining the fair value of financial instruments. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 60
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 820
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482053/820-10-60-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 825
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueOfFinancialInstrumentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for (1) transactions denominated in a currency other than the reporting enterprise's functional currency, (2) translating foreign currency financial statements that are incorporated into the financial statements of the reporting enterprise by consolidation, combination, or the equity method of accounting, and (3) remeasurement of the financial statements of a foreign reporting enterprise in a hyperinflationary economy. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//830/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ForeignCurrencyTransactionsAndTranslationsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for goodwill and intangible assets. This accounting policy also may address how an entity assesses and measures impairment of goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for leasing arrangement entered into by lessee. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeLeasesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for investment classified as marketable security. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 320
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480832/942-320-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_MarketableSecuritiesPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for reclassification affecting comparability of financial statement. Excludes amendment to accounting standards, other change in accounting principle, and correction of error. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483504/205-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PriorPeriodReclassificationAdjustmentDescription |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for long-lived, physical asset used in normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, work of art, historical treasure, and similar asset classified as collections. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 360
-Topic 958
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480321/958-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for receivable. Includes, but is not limited to, accounts receivable and financing receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481569/310-20-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReceivablesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for its research and development and computer software activities including the accounting treatment for costs incurred for (1) research and development activities, (2) development of computer software for internal use, (3) computer software to be sold, leased or otherwise marketed as a separate product or as part of a product or process and (4) in-process research and development acquired in a purchase business combination. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 985
-SubTopic 20
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481283/985-20-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 50
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482610/350-50-25-4
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 30
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 40
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482633/350-40-30-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchDevelopmentAndComputerSoftwarePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue from contract with customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-19
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-20
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for the use of estimates in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_UseOfEstimates |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Computation of Basic and Diluted Net Income (loss) Per Common Share |
The following table sets forth the reconciliation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Net income (loss) | | $ | 168,906 | | | $ | (35,774) | | | $ | 33,624 | | | Basic net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | | | Basic net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 3.85 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | 0.74 | | | Diluted net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | Basic weighted-average shares outstanding | | 43,885 | | | 44,664 | | | 45,443 | | Dilutive effect of stock options and restricted stock units (1) | | 1,215 | | | — | | | 1,777 | | | Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding | | 45,100 | | | 44,664 | | | 47,220 | | | Diluted net income (loss) per common share | | 3.75 | | | (0.80) | | | 0.71 | |
(1) In fiscal 2023 dilutive shares have been excluded because we were in a net loss position.
|
| Schedule of Composition of Financial Assets Measured at Fair value |
The following table summarizes the composition of our financial assets measured at fair value at March 31, 2024: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | Cash equivalents | $ | 24,902 | | | — | | | — | | | $ | 24,902 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the fair value of financial instruments, including financial assets and financial liabilities, and the measurements of those instruments, assets, and liabilities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-11
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByBalanceSheetGroupingTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction |
Our typical performance obligations include the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | Performance Obligation | When Performance Obligation
is Typically Satisfied | When Payment is
Typically Due | How Standalone Selling Price is
Typically Estimated | | Subscription | | Term-based software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment except for certain subscription licenses which are paid for over time | Residual approach | | Software-as-a-service (SaaS) | Ratably over the course of the contract (over time) | Annually or at the beginning of the contract period | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Perpetual License | | Perpetual software licenses | Upon shipment or made available for download (point in time) | Within 90 days of shipment | Residual approach | | Customer Support | | Software updates | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Customer support | Ratably over the course of the support contract (over time) | At the beginning of the contract period | Observable in renewal transactions | | Other Services | | Other professional services (except for education services) | As work is performed (over time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations | | Education services | When the class is taught (point in time) | Within 90 days of services being performed | Observable in transactions without multiple performance obligations |
|
| Schedule of Disaggregation of Revenue |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Americas | $ | 498,545 | | | $ | 469,244 | | | $ | 457,895 | | | International | 340,702 | | | 315,346 | | | 311,696 | | | Total revenues | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
|
| Schedule of Contract with Customer, Asset and Liability |
The opening and closing balances of our accounts receivable, unbilled receivables and deferred revenues are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Accounts Receivable | Unbilled Receivable
(current) | Unbilled Receivable
(long-term) | Deferred Revenue
(current) | Deferred Revenue
(long-term) | Opening balance as of March 31, 2023 | $ | 188,736 | | $ | 21,705 | | $ | 9,867 | | $ | 307,562 | | $ | 174,393 | | | Increase/(decrease), net | 8,215 | | 4,027 | | 4,604 | | 54,888 | | (5,921) | | Ending balance as of March 31, 2024 | $ | 196,951 | | $ | 25,732 | | $ | 14,471 | | $ | 362,450 | | $ | 168,472 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of receivable, contract asset, and contract liability from contract with customer. Includes, but is not limited to, change in contract asset and contract liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerAssetAndLiabilityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of disaggregation of revenue into categories depicting how nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of expected timing for satisfying remaining performance obligation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Goodwill |
Goodwill balances are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Opening balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | | | Additions/(Impairments) | | — | | | — | | | Ending balance | | $ | 127,780 | | | $ | 127,780 | |
|
| Schedule of Purchased Intangible Assets, Net of Amortization |
Intangible assets are recorded at cost and amortized over useful lives of three years. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, 2024 | | March 31, 2023 | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value | | Developed technology | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (2,708) | | | $ | 1,042 | | | $ | 3,750 | | | $ | (1,458) | | | $ | 2,292 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of finite-lived intangible assets acquired as part of a business combination or through an asset purchase, by major class and in total, including the value of the asset acquired, any significant residual value (the expected value of the asset at the end of its useful life) and the weighted-average amortization period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAcquiredAsPartOfBusinessCombinationTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of goodwill by reportable segment and in total which includes a rollforward schedule. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfGoodwillTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Property and Equipment (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | Computers, servers and other equipment | | $ | 45,620 | | | $ | 43,135 | | | Furniture and fixtures | | 2,965 | | | 3,264 | | | Leasehold improvements | | 8,180 | | | 8,433 | | | Purchased software | | 2,586 | | | 1,862 | | | Construction in process | | 189 | | | 111 | | | | 59,540 | | | 56,805 | | | Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (51,579) | | | (48,518) | | | | $ | 7,961 | | | $ | 8,287 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Includes, but is not limited to, balances by class of assets, depreciation and depletion expense and method used, including composite depreciation, and accumulated deprecation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of accrued liabilities.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfAccruedLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Commitments and Contingencies (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Long-term Purchase Commitment |
Total non-cancellable purchase commitments as of March 31, 2024 are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 and beyond | | Total | | Purchase commitments | | $ | 42,011 | | | $ | 9,652 | | | $ | 1,532 | | | $ | 111,527 | | | $ | 164,722 | |
|
| Schedule of Royalty Expense |
Royalty expense, included in cost of subscription and perpetual license revenues, was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Royalty expense | | $ | 9,717 | | | $ | 9,339 | | | $ | 11,188 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule Of Royalty Expense [Table Text Block]
| Name: |
cvlt_ScheduleOfRoyaltyExpenseTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of key provisions of an arrangement under which the entity has agreed to purchase goods or services over a period of time greater than one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer, including the item for which expenditures will be made, minimum quantities, milestones, time period and committed amount.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermPurchaseCommitmentTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Share-Based Payment Arrangement [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Stock-Based Compensation Expense |
The following table presents the stock-based compensation expense included in cost of revenues, sales and marketing, research and development, general and administrative and restructuring expenses for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022. Stock-based compensation is attributable to restricted stock units, performance-based awards and the ESPP. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Cost of revenues | | $ | 6,832 | | | $ | 4,787 | | | $ | 4,474 | | | Sales and marketing | | 36,630 | | | 43,081 | | | 37,431 | | | Research and development | | 21,585 | | | 28,540 | | | 33,870 | | | General and administrative | | 27,987 | | | 26,731 | | | 27,679 | | | Restructuring | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | | | Stock-based compensation expense | | $ | 94,551 | | | $ | 105,746 | | | $ | 105,163 | |
|
| Schedule of Stock Option Activity |
Stock option activity is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Options | | Number of
Options | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value | Outstanding at March 31, 2023 | | 553 | | | $ | 73.58 | | | | | | | Granted | | — | | | — | | | | | | | Exercised | | (58) | | | 48.88 | | | | | | | Forfeited | | — | | | — | | | | | | | Expired | | (371) | | | 86.95 | | | | | | Outstanding at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | | | | | | | | | | | Exercisable at March 31, 2024 | | 124 | | | $ | 45.25 | | | 0.63 | | $ | 6,969 | |
|
| Schedule of Restricted Stock Unit Activity |
Restricted stock unit activity is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Non-Vested Restricted Stock Units | | Number
of
Awards | | Weighted-
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | | Non-vested as of March 31, 2023 | | 2,953 | | | $ | 62.52 | | | Granted | | 1,483 | | | 70.42 | | | Vested | | (1,641) | | | 60.08 | | | Forfeited | | (378) | | | 65.74 | | | Non-vested as of March 31, 2024 | | 2,417 | | | $ | 68.52 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of allocation of amount expensed and capitalized for award under share-based payment arrangement to statement of income or comprehensive income and statement of financial position. Includes, but is not limited to, corresponding line item in financial statement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the changes in outstanding nonvested restricted stock units. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfNonvestedRestrictedStockUnitsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure for stock option plans. Includes, but is not limited to, outstanding awards at beginning and end of year, grants, exercises, forfeitures, and weighted-average grant date fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 718
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfShareBasedCompensationStockOptionsActivityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Components of Income (Loss) Before Income Taxes |
The components of income (loss) before income taxes were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Domestic | | $ | 62,082 | | | $ | (35,288) | | | $ | 25,905 | | | Foreign | | 21,531 | | | 19,926 | | | 17,509 | | | | $ | 83,613 | | | $ | (15,362) | | | $ | 43,414 | |
|
| Schedule of Components of Income Tax Expense (Benefit) |
The components of income tax expense (benefit) were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Current: | | | | | | | | Federal | | $ | 7,845 | | | $ | 6,986 | | | $ | 284 | | | State | | 4,242 | | | 3,375 | | | 361 | | | Foreign | | 12,220 | | | 10,725 | | | 9,096 | | | Deferred: | | | | | | | | Federal | | (82,773) | | | (607) | | | 28 | | | State | | (19,740) | | | — | | | — | | | Foreign | | (7,087) | | | (67) | | | 21 | | | | $ | (85,293) | | | $ | 20,412 | | | $ | 9,790 | |
|
| Schedule of Reconciliation of Statutory Tax Rates and Effective Tax Rates |
A reconciliation of the statutory tax rates and the effective tax rates for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Statutory federal income tax expense (benefit) rate | | 21.0 | % | | (21.0) | % | | 21.0 | % | | State and local income tax expense, net of federal income tax effect | | 2.4 | % | | (11.8) | % | | 0.8 | % | | Foreign earnings taxed at different rates | | 5.7 | % | | 28.0 | % | | 6.2 | % | | U.S. tax on GILTI & FDII | | (3.3) | % | | (17.1) | % | | 0.5 | % | | Domestic permanent differences including acquisition items | | 1.1 | % | | 4.7 | % | | 3.6 | % | | Foreign tax credits | | (2.5) | % | | (35.5) | % | | (5.3) | % | | Research credits | | (9.3) | % | | (74.6) | % | | (28.3) | % | | Tax reserves | | — | % | | (1.2) | % | | 2.6 | % | | Valuation allowance | | (125.3) | % | | 219.9 | % | | 18.3 | % | | Enacted tax law changes | | (0.4) | % | | 3.6 | % | | 0.3 | % | | Stock-based compensation | | 6.7 | % | | 41.6 | % | | (1.6) | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Other differences, net | | 1.9 | % | | (3.7) | % | | 4.5 | % | | Effective income tax expense (benefit) | | (102.0) | % | | 132.9 | % | | 22.6 | % |
|
| Schedule of Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities |
The significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | Net operating losses | | $ | 6,533 | | | $ | 9,106 | | | Equity investment/Capital losses | | 952 | | | 889 | | | Stock-based compensation | | 5,338 | | | 11,912 | | | Deferred revenue | | 29,748 | | | 24,025 | | | Tax credits | | 28,020 | | | 42,986 | | | Accrued expenses | | 1,775 | | | 1,816 | | | Allowance for doubtful accounts and other reserves | | 928 | | | 572 | | | R&D Capitalization under IRC § 174 | | 58,867 | | | 32,091 | | | Depreciation and amortization | | 9,305 | | | 9,449 | | | Other, DTA | | 2,228 | | | 98 | | | Less: valuation allowance | | (18,140) | | | (122,921) | | | Total deferred tax assets | | 125,554 | | | 10,023 | | | Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | Withholding taxes | | (1,091) | | | (393) | | | Deferred commissions | | (12,573) | | | (9,764) | | | Other, DTL | | (2,426) | | | — | | | Total deferred tax liabilities | | (16,090) | | | (10,157) | | | Net deferred tax asset (liability) | | $ | 109,464 | | | $ | (134) | |
|
| Schedule of Tax Years Subject to Income Tax Examination |
The following table summarizes the tax years subject to income tax examinations by tax authorities as of March 31, 2024. The years subject to income tax examination in our foreign jurisdictions cover the maximum time period with respect to these jurisdictions. Due to NOLs, in some cases the tax years continue to remain subject to examination with respect to such NOLs. | | | | | | | Tax Jurisdiction | Years Subject to Income
Tax Examination | | U.S. Federal | 2020 - Present | | Foreign jurisdictions | 2013 - Present |
|
| Schedule of Reconciliation of Amounts of Unrecognized Tax Benefits |
A reconciliation of the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows: | | | | | | | Balance at March 31, 2021 | $ | 2,211 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2022 | 2,808 | | | Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 90 | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (117) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | 4,232 | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2022 | 9,224 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2023 | 394 | | | Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | (90) | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (140) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2023 | 9,388 | | | Additions for tax positions related to fiscal 2024 | 502 | | | Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 3 | | | Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements | — | | | Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations | (220) | | | Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting | — | | | Foreign currency translation adjustment | — | | | Balance at March 31, 2024 | $ | 9,673 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 9
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the reconciliation using percentage or dollar amounts of the reported amount of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for the year to the amount of income tax expense that would result from applying domestic federal statutory tax rates to pretax income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 12
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEffectiveIncomeTaxRateReconciliationTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of income before income tax between domestic and foreign jurisdictions. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfIncomeBeforeIncomeTaxDomesticAndForeignTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure for tax positions taken in the tax returns filed or to be filed for which it is more likely than not that the tax position will not be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities and other income tax contingencies. Includes, but is not limited to, interest and penalties, reconciliation of unrecognized tax benefits, unrecognized tax benefits that would affect the effective tax rate, tax years that remain subject to examination by tax jurisdictions, and information about positions for which it is reasonably possible that amounts unrecognized will significantly change within 12 months. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
| Name: |
us-gaap_SummaryOfIncomeTaxContingenciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Segment Information (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Segment Reporting [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Revenue by Geographic Area |
The following table sets forth revenue and long-lived assets by geographic area: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Revenue: | | | | | | | | United States | | $ | 437,560 | | | $ | 416,347 | | | $ | 398,632 | | | Other | | 401,687 | | | 368,243 | | | 370,959 | | | | $ | 839,247 | | | $ | 784,590 | | | $ | 769,591 | |
|
| Schedule of Long-Lived Assets by Geographic Area |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Long-lived assets: | | | | | | United States | | $ | 192,485 | | | $ | 184,356 | | | Other | | 45,121 | | | 47,304 | | | | $ | 237,606 | | | $ | 231,660 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the names of foreign countries in which material long-lived assets other than financial instruments, long-term customer relationships of a financial institution, mortgage and other servicing rights, deferred policy acquisition costs, and deferred tax assets are located, and amount of such long-lived assets located in that country or foreign geographic area. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEntityWideDisclosureOnGeographicAreasLongLivedAssetsInIndividualForeignCountriesByCountryTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the names of foreign countries from which revenue is material and the amount of revenue from external customers attributed to those countries. An entity may also provide subtotals of geographic information about groups of countries. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfRevenueFromExternalCustomersAttributedToForeignCountriesByGeographicAreaTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Restructuring (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Restructuring and Related Activities [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Restructuring Accruals |
For the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, restructuring charges were comprised of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Employee severance and related costs | | $ | 2,811 | | | $ | 12,845 | | | $ | 4,483 | | Lease exit costs (1) | | 220 | | | — | | | — | | | Stock-based compensation | | 1,517 | | | 2,607 | | | 1,709 | | | Total restructuring charges | | $ | 4,548 | | | $ | 15,452 | | | $ | 6,192 | |
(1) Lease exit costs relate to one office for the year ended March 31, 2024. There were no lease exit charges for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022.
|
| Schedule of Activity in Restructuring Accrual |
The accrual activity related to our restructuring plans for the years ended March 31, 2024 and 2023 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | | | 2024 (1) | | 2023 | | Beginning balance | | $ | 3,211 | | | $ | 2,261 | | | Employee severance and related costs | | 2,811 | | | 12,845 | | | Payments | | (3,276) | | | (11,895) | | | Ending balance | | $ | 2,746 | | | $ | 3,211 | |
(1) During fiscal 2024, there were no new charges incurred related to the completed restructuring plan. Payments made related to the completed plan were $3,149, resulting in an insignificant remaining accrual at March 31, 2024.
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of costs incurred for restructuring including, but not limited to, exit and disposal activities, remediation, implementation, integration, asset impairment, and charges against earnings from the write-down of assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 5.P.4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfRestructuringAndRelatedCostsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's restructuring reserve that occurred during the period associated with the exit from or disposal of business activities or restructurings for each major type of cost. This element may also include a description of any reversal and other adjustment made during the period to the amount of an accrued liability for restructuring activities. This element may be used to encapsulate the roll forward presentations of an entity's restructuring reserve by type of cost and in total, and explanation of changes that occurred in the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfRestructuringReserveByTypeOfCostTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Leases (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Net Lease Cost Recognized on Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations and Cash Flow Information |
Net lease cost recognized in our consolidated statements of operations is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Operating lease cost | $ | 5,770 | | | $ | 5,449 | | | $ | 7,129 | | | Short-term lease cost | 272 | | | 631 | | | 123 | | | Variable lease cost | 1,333 | | | 1,360 | | | 1,608 | | | Net lease cost | $ | 7,375 | | | $ | 7,440 | | | $ | 8,860 | |
Cash flow information | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Cash paid for operating lease liabilities | $ | 5,033 | | | $ | 5,421 | | | $ | 8,277 | | | Additions of operating lease assets (non-cash) | $ | 5,528 | | | $ | 3,023 | | | $ | 1,827 | |
|
| Schedule of Maturities of Lease Liabilities |
As of March 31, 2024, the maturities of lease liabilities based on the total minimum lease commitment amount including options to extend lease terms that are reasonably certain of being exercised are as follows:
| | | | | | | 2025 | $ | 4,624 | | | 2026 | 2,973 | | | 2027 | 1,740 | | | 2028 | 1,601 | | | 2029 | 932 | | | Thereafter | 683 | | | Total minimum lease payments | 12,553 | | | Less: Imputed interest | 463 | | | Present value of operating lease liabilities | 12,090 | | | Less: Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 4,935 | | | Long-term operating lease liabilities | $ | 7,155 | |
|
| Schedule of Lease Term and Discount Rate |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | Weighted-average remaining term (in years) | 3.60 | | 3.72 | | Weighted-average discount rate | 4 | % | | 4 | % |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSchedule of Lease Term and Discount Rate
| Name: |
cvlt_ScheduleOfLeaseTermAndDiscountRateTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of lessee's lease cost. Includes, but is not limited to, interest expense for finance lease, amortization of right-of-use asset for finance lease, operating lease cost, short-term lease cost, variable lease cost and sublease income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCostTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of undiscounted cash flows of lessee's operating lease liability. Includes, but is not limited to, reconciliation of undiscounted cash flows to operating lease liability recognized in statement of financial position. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityMaturityTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revolving Credit Facility (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Debt Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of Debt |
The amortization of debt issuance costs and interest expense incurred for the years ended March 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Year Ended March 31, | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | Amortization of debt issuance costs | $ | 115 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 34 | | | Interest expense | 253 | | | 253 | | | 75 | | | Total charges | $ | 368 | | | $ | 368 | | | $ | 109 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of information pertaining to short-term and long-debt instruments or arrangements, including but not limited to identification of terms, features, collateral requirements and other information necessary to a fair presentation.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDebtTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Advertising expenses |
$ 8,514
|
$ 8,663
|
$ 9,572
|
| Net foreign currency transaction losses |
$ 2,388
|
$ 1,163
|
$ 0
|
| Stock options, restricted stock units, and shares under the employee stock purchase plan (in shares) |
271
|
3,939
|
505
|
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ 173
|
$ 197
|
|
| Equity securities |
7,318
|
|
|
| Unfunded commitments |
$ 2,645
|
|
|
| Software updates and customer support costs amortization period (in years) |
5 years
|
|
|
| Developed technology |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Acquired finite-lived intangible assets, useful life (in years) |
3 years
|
|
|
| Minimum | Computers, servers and other equipment |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Property and equipment, depreciation period (in years) |
18 months
|
|
|
| Minimum | Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Property and equipment, depreciation period (in years) |
3 years
|
|
|
| Maximum | Computers, servers and other equipment |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Property and equipment, depreciation period (in years) |
3 years
|
|
|
| Maximum | Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Property and equipment, depreciation period (in years) |
12 years
|
|
|
| Customer concentration risk | Arrow | Revenue |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Concentration percentage |
36.00%
|
37.00%
|
37.00%
|
| Customer concentration risk | Arrow | Accounts receivable |
|
|
|
| Summary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Concentration percentage |
29.00%
|
34.00%
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionSummary Of Significant Accounting Policies [Line Items]
| Name: |
cvlt_SummaryOfSignificantAccountingPoliciesLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average amortization period of finite-lived intangible assets acquired either individually or as part of a group of assets, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AcquiredFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsWeightedAverageUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount charged to advertising expense for the period, which are expenses incurred with the objective of increasing revenue for a specified brand, product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 720
-SubTopic 35
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483406/720-35-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdvertisingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479344/326-20-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllowanceForDoubtfulAccountsReceivableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSecurities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) or earnings per unit (EPU) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS or EPU because to do so would increase EPS or EPU amounts or decrease loss per share or unit amounts for the period presented. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmortization period of cost capitalized in obtaining or fulfilling contract with customer, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 40
-Topic 340
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479483/340-40-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CapitalizedContractCostAmortizationPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor an entity that discloses a concentration risk in relation to quantitative amount, which serves as the "benchmark" (or denominator) in the equation, this concept represents the concentration percentage derived from the division. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-21
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-20
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-18
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskPercentage1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of investment in equity security measured at fair value with change in fair value recognized in net income (FV-NI). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(1)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482736/825-10-45-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquitySecuritiesFvNiCurrentAndNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of unfunded commitments for which the entity is obligated, to those certain investments for which net asset value per share is calculated (including by unit, membership interest, or other equity (ownership interest) unit measure) (alternative investments). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-6A
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueInvestmentsEntitiesThatCalculateNetAssetValuePerShareUnfundedCommittments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before tax, of realized and unrealized gain (loss) from foreign currency transaction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482014/830-20-35-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481956/830-20-45-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481926/830-20-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481839/830-10-45-17
| Name: |
us-gaap_ForeignCurrencyTransactionGainLossBeforeTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of long lived, physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Examples include, but not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, furniture and fixtures, and computer equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ComputerEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByTypeAxis=us-gaap_CustomerConcentrationRiskMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_MajorCustomersAxis=cvlt_ArrowMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_SalesRevenueNetMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskByBenchmarkAxis=us-gaap_AccountsReceivableMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Computation of Basic and Diluted Net Income (loss) Per Common Share (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Net income (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
| Net income (loss) |
$ 168,906
|
$ (35,774)
|
$ 33,624
|
| Basic net income (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding (in shares) |
43,885
|
44,664
|
45,443
|
| Basic net income (loss) per common share (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.85
|
$ (0.80)
|
$ 0.74
|
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding (in shares) |
43,885
|
44,664
|
45,443
|
| Dilutive effect of stock options and restricted stock units (in shares) |
1,215
|
0
|
1,777
|
| Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding (in shares) |
45,100
|
44,664
|
47,220
|
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share (in dollars per share) |
$ 3.75
|
$ (0.80)
|
$ 0.71
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasicAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDilutedAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAdditional shares included in the calculation of diluted EPS as a result of the potentially dilutive effect of share based payment arrangements using the treasury stock method. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480454/718-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-22
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 23
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-23
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-28A
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncrementalCommonSharesAttributableToShareBasedPaymentArrangements |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies - Summary of Fair Value of Financial Assets (Details) - USD ($)
|
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
| Financial assets at fair value |
|
$ 0
|
| Fair Value, Recurring |
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
| Cash equivalents |
$ 24,902,000
|
|
| Level 1 | Fair Value, Recurring |
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
| Cash equivalents |
24,902,000
|
|
| Level 2 | Fair Value, Recurring |
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
| Cash equivalents |
0
|
|
| Level 3 | Fair Value, Recurring |
|
|
| Fair Value, Assets and Liabilities Measured on Recurring and Nonrecurring Basis [Line Items] |
|
|
| Cash equivalents |
$ 0
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value portion of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates.
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsFairValueDisclosure |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 820
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482106/820-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueAssetsAndLiabilitiesMeasuredOnRecurringAndNonrecurringBasisLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueByMeasurementFrequencyAxis=us-gaap_FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue - Additional Information (Details)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024
USD ($)
|
|---|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Subscription arrangement term |
3 years
|
| Revenue expected to be recognized from remaining performance obligations (inclusive of deferred revenues) |
$ 618,907
|
| Revenue recognized in period, included in opening deferred revenue balance |
$ 313,766
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction, Start Date [Axis]: 2024-04-01 |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Revenue, remaining performance obligation, percentage |
68.00%
|
| Revenue, remaining performance obligation, expected timing of satisfaction, period |
12 months
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction, Start Date [Axis]: 2025-04-01 |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Revenue, remaining performance obligation, percentage |
32.00%
|
| Revenue, remaining performance obligation, expected timing of satisfaction, period |
|
| Minimum |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Subscription arrangement term |
1 year
|
| Maximum |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Subscription arrangement term |
5 years
|
| X |
- DefinitionSubscription Arrangement Term
| Name: |
cvlt_SubscriptionArrangementTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized that was previously included in balance of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration from customer has been received or is due. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityRevenueRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of transaction price allocated to performance obligation that has not been recognized as revenue. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod in which remaining performance obligation is expected to be recognized as revenue, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage of remaining performance obligation to total remaining performance obligation not recognized as revenue. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionStartDateAxis=2024-04-01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionStartDateAxis=2025-04-01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MinimumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue - Performance Obligations (Details)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
|---|
| Term-based software licenses |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Performance obligation, expected payment terms |
90 days
|
| Perpetual software licenses |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Performance obligation, expected payment terms |
90 days
|
| Other professional services (except for education services) |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Performance obligation, expected payment terms |
90 days
|
| Education services |
|
| Revenue, Remaining Performance Obligation, Expected Timing of Satisfaction [Line Items] |
|
| Performance obligation, expected payment terms |
90 days
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRemainingPerformanceObligationExpectedTimingOfSatisfactionLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_TermBasedSoftwareLicensesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_PerpetualSoftwareLicensesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_ProfessionalServicesOtherMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=cvlt_ProfessionalServicesEducationServicesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue - Disaggregation of Revenue (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 839,247
|
$ 784,590
|
$ 769,591
|
| Americas |
|
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
498,545
|
469,244
|
457,895
|
| International |
|
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 340,702
|
$ 315,346
|
$ 311,696
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, excluding tax collected from customer, of revenue from satisfaction of performance obligation by transferring promised good or service to customer. Tax collected from customer is tax assessed by governmental authority that is both imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue-producing transaction, including, but not limited to, sales, use, value added and excise. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 924
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.L)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479941/924-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerExcludingAssessedTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=srt_AmericasMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=cvlt_InternationalMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Revenue - Opening and Closing Balances of Accounts Receivables, Unbilled Receivables, and Deferred Revenues (Details) (Details)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024
USD ($)
|
|---|
| Deferred Revenue (current) |
|
| Opening balance |
$ 307,562
|
| Ending balance |
362,450
|
| Deferred Revenue (long-term) |
|
| Opening balance |
174,393
|
| Ending balance |
168,472
|
| Unbilled Receivable (current) |
|
| Accounts Receivable |
|
| Opening balance |
188,736
|
| Increase/(decrease), net |
8,215
|
| Ending balance |
196,951
|
| Unbilled Receivable (current) |
|
| Opening balance |
21,705
|
| Increase/(decrease), net |
4,027
|
| Ending balance |
25,732
|
| Unbilled Receivable (long-term) |
|
| Unbilled Receivable (long-term) |
|
| Opening balance |
9,867
|
| Increase/(decrease), net |
4,604
|
| Ending balance |
14,471
|
| Deferred Revenue (current) |
|
| Deferred Revenue (current) |
|
| Opening balance |
307,562
|
| Increase/(decrease), net |
54,888
|
| Ending balance |
362,450
|
| Deferred Revenue (long-term) |
|
| Deferred Revenue (long-term) |
|
| Opening balance |
174,393
|
| Increase/(decrease), net |
(5,921)
|
| Ending balance |
$ 168,472
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccounts Receivable [Roll Forward]
| Name: |
cvlt_AccountsReceivableRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Asset, Net, Current, Increase (Decrease)
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetCurrentIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Asset, Net, Current [Roll Forward]
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetCurrentRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Asset, Net, Noncurrent, Increase (Decrease)
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetNoncurrentIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Asset, Net, Noncurrent [Roll Forward]
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetNoncurrentRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Liability, Current, Increase (Decrease)
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrentIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract with Customer, Liability, Current [Roll Forward]
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrentRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Liability, Noncurrent, Increase (Decrease)
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityNoncurrentIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionContract With Customer, Liability, Noncurrent [Roll Forward]
| Name: |
cvlt_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityNoncurrentRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration from customer for product sold and service rendered in normal course of business. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480833/946-310-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(5)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 310
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481058/954-310-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsReceivableNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration in exchange for good or service transferred to customer when right is conditioned on something other than passage of time, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allowance for credit loss, of right to consideration in exchange for good or service transferred to customer when right is conditioned on something other than passage of time, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerAssetNetNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of obligation to transfer good or service to customer for which consideration has been received or is receivable, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479837/606-10-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractWithCustomerLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in amount due within one year (or one business cycle) from customers for the credit sale of goods and services. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=us-gaap_TradeAccountsReceivableMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=us-gaap_OtherAssetsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=cvlt_DeferredRevenueCurrentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=cvlt_DeferredRevenueNoncurrentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Goodwill expected tax deductible amount |
$ 0
|
|
|
| Goodwill impairment |
0
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| Amortization expenses |
$ 1,250,000
|
$ 1,250,000
|
$ 208,000
|
| Developed technology |
|
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Acquired finite-lived intangible assets, useful life (in years) |
3 years
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average amortization period of finite-lived intangible assets acquired either individually or as part of a group of assets, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AcquiredFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsWeightedAverageUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense charged against earnings to allocate the cost of intangible assets (nonphysical assets not used in production) in a systematic and rational manner to the periods expected to benefit from such assets. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of goodwill arising from a business combination that is expected to be deductible for tax purposes. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 805
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479581/805-30-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessAcquisitionPurchasePriceAllocationGoodwillExpectedTaxDeductibleAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of loss from the write-down of an asset representing the future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillImpairmentLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated impairment loss of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482548/350-20-55-24
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482598/350-20-45-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(10)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Goodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) of an asset representing future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482573/350-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillPeriodIncreaseDecrease |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Goodwill and Intangible Assets, Net - Intangible Assets, Net (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Net Carrying Value |
$ 1,042
|
|
| Developed technology |
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Gross Carrying Amount |
3,750
|
$ 3,750
|
| Accumulated Amortization |
(2,708)
|
(1,458)
|
| Net Carrying Value |
$ 1,042
|
$ 2,292
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccumulated amount of amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 928
-SubTopic 340
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483147/928-340-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_DevelopedTechnologyRightsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Assets Held for Sale (Details) - Disposal Group, Held-for-sale, Not Discontinued Operations - Corporate Headquarters in Tinton Falls, NJ
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024
USD ($)
|
|---|
| Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Additional Disclosures by Disposal Groups, Including Discontinued Operations [Line Items] |
|
| Cash consideration from sale of properties |
$ 40
|
| Property's previous carrying amount |
92,161
|
| Amount written down to estimated fair value, less estimated costs to sell |
38,680
|
| Impairment charge of properties to be disposed of |
53,481
|
| Non-refundable escrow amount |
$ 1,670
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisposal Group, Not Discontinued Operation, Non-Refundable Escrow
| Name: |
cvlt_DisposalGroupNotDiscontinuedOperationNonRefundableEscrow |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of consideration received or receivable for the disposal of assets and liabilities, including discontinued operation.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisposalGroupIncludingDiscontinuedOperationConsideration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount classified as property, plant and equipment attributable to disposal group held for sale or disposed of. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-SubTopic 20
-Topic 205
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483475/205-20-45-10
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5B
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-5B
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483475/205-20-45-11
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisposalGroupIncludingDiscontinuedOperationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before tax, of (gain) loss recognized for the (reversal of write-down) write-down to fair value, less cost to sell, of a disposal group. Excludes discontinued operations. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisposalGroupNotDiscontinuedOperationLossGainOnWriteDown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of write-downs for impairments recognized during the period for long-lived assets held for abandonment, exchange or sale. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482130/360-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfLongLivedAssetsToBeDisposedOf |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementBalanceSheetAndAdditionalDisclosuresByDisposalGroupsIncludingDiscontinuedOperationsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisposalGroupClassificationAxis=us-gaap_DisposalGroupHeldforsaleNotDiscontinuedOperationsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementBalanceSheetAndAdditionalDisclosuresByDisposalGroupsIncludingDiscontinuedOperationsAxis=cvlt_CorporateHeadquartersInTintonFallsNJMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Property and Equipment - Schedule of Property and Equipment (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 59,540
|
$ 56,805
|
| Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(51,579)
|
(48,518)
|
| Property and equipment, net |
7,961
|
8,287
|
| Computers, servers and other equipment |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
45,620
|
43,135
|
| Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
2,965
|
3,264
|
| Leasehold improvements |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
8,180
|
8,433
|
| Purchased software |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
2,586
|
1,862
|
| Construction in process |
|
|
| Property, Plant and Equipment [Line Items] |
|
|
| Property and equipment, gross |
$ 189
|
$ 111
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization for physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedDepreciationDepletionAndAmortizationPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(13))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization of physical assets used in the normal conduct of business to produce goods and services and not intended for resale. Examples include, but are not limited to, land, buildings, machinery and equipment, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 360
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480842/942-360-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ComputerEquipmentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_FurnitureAndFixturesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_LeaseholdImprovementsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentByTypeAxis=us-gaap_ConstructionInProgressMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for allocation of cost of tangible and intangible assets over their useful lives directly used in production of good and rendering of service. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfGoodsAndServicesSoldDepreciationAndAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of expense recognized in the current period that reflects the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over the assets' useful lives. Includes production and non-production related depreciation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482099/360-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Depreciation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable, pertaining to costs that are statutory in nature, are incurred on contractual obligations, or accumulate over time and for which invoices have not yet been received or will not be rendered. Examples include taxes, interest, rent and utilities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.15(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedLiabilitiesCurrentAndNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses incurred but not yet paid classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.15(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAccruedLiabilitiesCurrentAndNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PayablesAndAccrualsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Commitments and Contingencies (Details) - USD ($)
|
1 Months Ended |
12 Months Ended |
Jun. 30, 2022 |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
|
| Non-cancellable purchase commitments, 2025 |
|
$ 42,011,000
|
|
|
| Non-cancellable purchase commitments, 2026 |
|
9,652,000
|
|
|
| Non-cancellable purchase commitments, 2027 |
|
1,532,000
|
|
|
| Non-cancellable purchase commitments, 2028 and beyond |
|
111,527,000
|
|
|
| Non-cancellable purchase commitments, Total for all periods through fiscal 2024 |
|
164,722,000
|
|
|
| Purchase commitment |
$ 200,000,000
|
|
|
|
| Remaining obligation under purchase commitment |
|
111,500,000
|
|
|
| Royalty expense |
|
$ 9,717,000
|
$ 9,339,000
|
$ 11,188,000
|
| Maximum software warranty period (in days) |
|
90 days
|
|
|
| Product warranty accrual |
|
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
0
|
| Gain related to settlement |
|
|
|
$ 7,900,000
|
| X |
- DefinitionMaximum software warranty period.
| Name: |
cvlt_MaximumSoftwareWarrantyPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRecorded Unconditional Purchase Obligation, To Be Paid, Year Four And Thereafter
| Name: |
cvlt_RecordedUnconditionalPurchaseObligationToBePaidYearFourAndThereafter |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe minimum amount the entity agreed to spend under the long-term purchase commitment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LongTermPurchaseCommitmentAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred through that date and payable for estimated claims under standard and extended warranty protection rights granted to customers. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (c)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (c)(5)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-8
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.15(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProductWarrantyAccrual |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMinimum amount of purchase arrangement in which the entity has agreed to expend funds to procure goods or services from a supplier.
| Name: |
us-gaap_PurchaseObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of the recorded obligation to transfer funds in the future for fixed or minimum amounts or quantities of goods or services at fixed or minimum prices (for example, as in take-or-pay contracts or throughput contracts). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_RecordedUnconditionalPurchaseObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of recorded unconditional purchase obligation to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_RecordedUnconditionalPurchaseObligationDueInSecondYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of recorded unconditional purchase obligation to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_RecordedUnconditionalPurchaseObligationDueInThirdYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of recorded unconditional purchase obligation to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_RecordedUnconditionalPurchaseObligationDueWithinOneYear |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense related to royalty payments under a contractual arrangement such as payment for mineral and drilling rights and use of technology or intellectual property. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_RoyaltyExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Capitalization (Details) - USD ($)
$ / shares in Units, shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
Apr. 18, 2024 |
Apr. 30, 2023 |
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding (in shares) |
43,548
|
44,140
|
|
|
|
| Common stock, par value (in dollars per share) |
$ 0.01
|
$ 0.01
|
|
|
|
| Share repurchase program, authorized amount available |
|
|
|
|
$ 250,000
|
| Repurchase of common stock |
$ 184,021
|
$ 150,921
|
$ 305,239
|
|
|
| Number of shares repurchased (in shares) |
2,479
|
|
|
|
|
| Share repurchase program, remaining available amount |
$ 71,944
|
|
|
|
|
| Capital shares reserved for future issuance (in shares) |
6,149
|
|
|
|
|
| Subsequent Event |
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
| Share repurchase program, remaining available amount |
|
|
|
$ 250,000
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483014/272-10-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482987/272-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfStockLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate number of common shares reserved for future issuance. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.29)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockCapitalSharesReservedForFutureIssuance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow to reacquire common stock during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRepurchaseOfCommonStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of stock repurchase plan authorized.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchaseProgramAuthorizedAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount remaining of a stock repurchase plan authorized.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchaseProgramRemainingAuthorizedRepurchaseAmount1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares that have been repurchased during the period and have not been retired and are not held in treasury. Some state laws may govern the circumstances under which an entity may acquire its own stock and prescribe the accounting treatment therefore. This element is used when state law does not recognize treasury stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockRepurchasedDuringPeriodShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventTypeAxis=us-gaap_SubsequentEventMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
|
12 Months Ended |
Aug. 29, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Awards vesting period |
|
3 years
|
|
|
| Unrecognized stock-based compensation expense |
|
$ 125,213
|
|
|
| Awards expected to be recognized over a weighted average period (in years) |
|
1 year 9 months 3 days
|
|
|
| Total intrinsic value of options exercised |
|
$ 1,378
|
$ 1,176
|
$ 12,704
|
| Restricted stock units |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Total fair value of awards vested |
|
$ 118,047
|
$ 114,422
|
$ 122,259
|
| 2016 Incentive Plan |
|
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
| Maximum number of shares of common stock that may be delivered under plan (in shares) |
14,250,000
|
|
|
|
| Addition shares authorized (in shares) |
3,200,000
|
|
|
|
| Options available for future grant (in shares) |
|
3,754,000
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost not yet recognized for nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted-average period over which cost not yet recognized is expected to be recognized for award under share-based payment arrangement, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognizedPeriodForRecognition1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod over which grantee's right to exercise award under share-based payment arrangement is no longer contingent on satisfaction of service or performance condition, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, combination of market, performance or service condition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFair value of share-based awards for which the grantee gained the right by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodTotalFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of additional shares authorized for issuance under share-based payment arrangement.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfAdditionalSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares authorized for issuance under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe difference between the maximum number of shares (or other type of equity) authorized for issuance under the plan (including the effects of amendments and adjustments), and the sum of: 1) the number of shares (or other type of equity) already issued upon exercise of options or other equity-based awards under the plan; and 2) shares (or other type of equity) reserved for issuance on granting of outstanding awards, net of cancellations and forfeitures, if applicable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfSharesAvailableForGrant |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated difference between fair value of underlying shares on dates of exercise and exercise price on options exercised (or share units converted) into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodTotalIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_PlanNameAxis=cvlt_A2016IncentivePlanMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans - Stock-Based Compensation Expense (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
$ 94,551
|
$ 105,746
|
$ 105,163
|
| Cost of revenues |
|
|
|
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
6,832
|
4,787
|
4,474
|
| Sales and marketing |
|
|
|
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
36,630
|
43,081
|
37,431
|
| Research and development |
|
|
|
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
21,585
|
28,540
|
33,870
|
| General and administrative |
|
|
|
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
27,987
|
26,731
|
27,679
|
| Restructuring |
|
|
|
| Employee Service Share-based Compensation, Allocation of Recognized Period Costs [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Stock-based compensation expense |
$ 1,517
|
$ 2,607
|
$ 1,709
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationAllocationOfRecognizedPeriodCostsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_CostOfSalesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementLocationAxis=us-gaap_RestructuringChargesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans - Stock Option Activity (Details)
$ / shares in Units, shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024
USD ($)
$ / shares
shares
|
|---|
| Number of Options |
|
| Outstanding beginning balance (in shares) | shares |
553
|
| Options granted (in shares) | shares |
0
|
| Options exercised (in shares) | shares |
(58)
|
| Options forfeited (in shares) | shares |
0
|
| Options expired (in shares) | shares |
(371)
|
| Outstanding ending balance (in shares) | shares |
124
|
| Exercisable at current period end (in shares) | shares |
124
|
| Weighted- Average Exercise Price |
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Outstanding beginning balance (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
$ 73.58
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Options granted (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
0
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Options exercised (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
48.88
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Options forfeited (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
0
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Options expired (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
86.95
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Outstanding ending balance (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
45.25
|
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price, Exercisable at current period-end (in dollars per share) | $ / shares |
$ 45.25
|
| Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) |
|
| Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Term, Outstanding at current period-end |
7 months 17 days
|
| Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Term, Exercisable at current period-end |
7 months 17 days
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Outstanding at current period-end | $ |
$ 6,969
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value, Exercisable at current period-end | $ |
$ 6,969
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Options, Aggregate Intrinsic Value [Abstract]
| Name: |
cvlt_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsAggregateIntrinsicValueAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare based Compensation Arrangement by Share based Payment Award, Other than Options, Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term [Abstract]
| Name: |
cvlt_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOtherThanOptionsWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTermAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares into which fully or partially vested stock options outstanding as of the balance sheet date can be currently converted under the option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted-average price as of the balance sheet date at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance on vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options or other stock instruments for which the right to exercise has lapsed under the terms of the plan agreements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExpirationsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares under options that were cancelled during the reporting period as a result of occurrence of a terminating event specified in contractual agreements pertaining to the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNet number of share options (or share units) granted during the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount by which the current fair value of the underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of options outstanding. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingIntrinsicValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of options outstanding, including both vested and non-vested options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees can acquire the shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageExercisePriceRollforward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which option holders acquired shares when converting their stock options into shares. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisesInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options of the plan that expired. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsExpirationsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average price at which grantees could have acquired the underlying shares with respect to stock options that were terminated. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsForfeituresInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average per share amount at which grantees can acquire shares of common stock by exercise of options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementsByShareBasedPaymentAwardOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageExercisePrice |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of difference between fair value of the underlying shares reserved for issuance and exercise price of vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableIntrinsicValue1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for vested portions of options outstanding and currently exercisable or convertible, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsExercisableWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining contractual term for option awards outstanding, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardOptionsOutstandingWeightedAverageRemainingContractualTerm2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of share options (or share units) exercised during the current period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesStockOptionsExercised |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that were forfeited during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeitedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average fair value as of the grant date of equity-based award plans other than stock (unit) option plans that were not exercised or put into effect as a result of the occurrence of a terminating event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsForfeituresWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value at grant date for nonvested equity-based awards issued during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of non-vested equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that validly exist and are outstanding as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPer share or unit weighted-average fair value of nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes share and unit options. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsNonvestedWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValueRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of equity-based payment instruments, excluding stock (or unit) options, that vested during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value as of grant date pertaining to an equity-based award plan other than a stock (or unit) option plan for which the grantee gained the right during the reporting period, by satisfying service and performance requirements, to receive or retain shares or units, other instruments, or cash in accordance with the terms of the arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsVestedInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod over which grantee's right to exercise award under share-based payment arrangement is no longer contingent on satisfaction of service or performance condition, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, combination of market, performance or service condition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage of vesting of award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingRightsPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionShare-based Compensation Arrangement By Share-based Payment Award, Equity Instruments Other Than Options, Potential To Vest, Percent
| Name: |
cvlt_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsPotentialToVestPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types1:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-Based Compensation Arrangement By Share-Based Payment Award, Equity Instruments Other than Options, Potential To Vest, Shares
| Name: |
cvlt_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsPotentialToVestShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-Based Compensation Arrangement By Share-Based Payment Award, Number Of Annual Vesting Tranches
| Name: |
cvlt_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardNumberOfAnnualVestingTranches |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod over which grantee's right to exercise award under share-based payment arrangement is no longer contingent on satisfaction of service or performance condition, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Includes, but is not limited to, combination of market, performance or service condition. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardAwardVestingPeriod1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of grants made during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe weighted average fair value at grant date for nonvested equity-based awards issued during the period on other than stock (or unit) option plans (for example, phantom stock or unit plan, stock or unit appreciation rights plan, performance target plan). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardEquityInstrumentsOtherThanOptionsGrantsInPeriodWeightedAverageGrantDateFairValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_RangeAxis=srt_MaximumMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Stock Plans - Employee Stock Purchase Plan (Details) - USD ($)
shares in Thousands, $ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Compensation expense |
$ 94,551
|
$ 105,746
|
$ 105,163
|
| Unrecognized stock-based compensation expense |
$ 125,213
|
|
|
| ESPP |
|
|
|
| Share-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Purchase price as a percentage of fair market value |
85.00%
|
|
|
| Length of offering period (in months) |
6 months
|
|
|
| Maximum employee payroll percent deduction of salary |
10.00%
|
|
|
| Maximum amount of stock purchasable by employees within a calendar year |
$ 25
|
|
|
| Number of shares purchased by employees (in shares) |
188
|
213
|
|
| Proceeds received |
$ 10,578
|
$ 10,873
|
|
| Compensation expense |
3,146
|
$ 3,740
|
$ 3,341
|
| Unrecognized stock-based compensation expense |
$ 1,177
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Maximum Annual Purchases Per Employee, Amount
| Name: |
cvlt_SharebasedCompensationArrangementbySharebasedPaymentAwardMaximumAnnualPurchasesPerEmployeeAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionShare-based Compensation Arrangement by Share-based Payment Award, Offering Period
| Name: |
cvlt_SharebasedCompensationArrangementbySharebasedPaymentAwardOfferingPeriod |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense for award under share-based payment arrangement. Excludes amount capitalized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 14.F)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479830/718-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllocatedShareBasedCompensationExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cost not yet recognized for nonvested award under share-based payment arrangement. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EmployeeServiceShareBasedCompensationNonvestedAwardsTotalCompensationCostNotYetRecognized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow associated with the amount received from the stock plan during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromStockPlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 1D
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-1D
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480483/718-10-35-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(1)(iv)(04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(02)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)(2)(iii)(03)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(iv)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (f)(2)(v)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe highest percentage of annual salary that an employee is permitted to utilize with respect to the plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 718
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480429/718-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShareBasedCompensationArrangementByShareBasedPaymentAwardMaximumEmployeeSubscriptionRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPurchase price of common stock expressed as a percentage of its fair value.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharebasedCompensationArrangementBySharebasedPaymentAwardPurchasePriceOfCommonStockPercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued during the period as a result of an employee stock purchase plan. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesEmployeeStockPurchasePlans |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AwardTypeAxis=us-gaap_EmployeeStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes - Components of Income Before Income Taxes (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Domestic |
$ 62,082
|
$ (35,288)
|
$ 25,905
|
| Foreign |
21,531
|
19,926
|
17,509
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
$ 83,613
|
$ (15,362)
|
$ 43,414
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes - Components of Income Tax Expense (Benefit) (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Current: |
|
|
|
| Federal |
$ 7,845
|
$ 6,986
|
$ 284
|
| State |
4,242
|
3,375
|
361
|
| Foreign |
12,220
|
10,725
|
9,096
|
| Deferred: |
|
|
|
| Federal |
(82,773)
|
(607)
|
28
|
| State |
(19,740)
|
0
|
0
|
| Foreign |
(7,087)
|
(67)
|
21
|
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
$ (85,293)
|
$ 20,412
|
$ 9,790
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current foreign income tax expense (benefit) pertaining to income (loss) from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentForeignTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current state and local tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current regional, territorial, and provincial tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes - Components of Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
| Net operating losses |
$ 6,533
|
$ 9,106
|
| Equity investment/Capital losses |
952
|
889
|
| Stock-based compensation |
5,338
|
11,912
|
| Deferred revenue |
29,748
|
24,025
|
| Tax credits |
28,020
|
42,986
|
| Accrued expenses |
1,775
|
1,816
|
| Allowance for doubtful accounts and other reserves |
928
|
572
|
| R&D Capitalization under IRC § 174 |
58,867
|
32,091
|
| Depreciation and amortization |
9,305
|
9,449
|
| Other, DTA |
2,228
|
98
|
| Less: valuation allowance |
(18,140)
|
(122,921)
|
| Total deferred tax assets |
125,554
|
10,023
|
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
| Withholding taxes |
(1,091)
|
(393)
|
| Deferred commissions |
(12,573)
|
(9,764)
|
| Other, DTL |
(2,426)
|
0
|
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
(16,090)
|
(10,157)
|
| Deferred tax asset |
$ 109,464
|
|
| Deferred tax liability |
|
$ (134)
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Assets, R&D Capitalization
| Name: |
cvlt_DeferredTaxAssetsRDCapitalization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Liabilities, Deferred Commissions
| Name: |
cvlt_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesDeferredCommissions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDeferred Tax Liabilities, Withholding Taxes
| Name: |
cvlt_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesWithholdingTaxes |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from deferred income. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsDeferredIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from equity method investments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsEquityMethodInvestments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after allocation of valuation allowances and deferred tax liability, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible differences and carryforwards, without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsLiabilitiesNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsNetAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of valuation allowance, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences, classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from property, plant, and equipment.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsPropertyPlantAndEquipment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of a valuation allowances, of deferred tax assets attributable to deductible tax credit carryforwards including, but not limited to, research, foreign, general business, alternative minimum tax, and other deductible tax credit carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxCreditCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from share-based compensation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseCompensationAndBenefitsShareBasedCompensationCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences from accrued liabilities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseReservesAndAccrualsAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, before allocation of valuation allowance, of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary difference from allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsTaxDeferredExpenseReservesAndAccrualsAllowanceForDoubtfulAccounts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deferred tax asset, of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable differences without jurisdictional netting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax liability attributable to taxable temporary differences classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxLiabilitiesOther |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes - Additional Information (Details) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
|
| Valuation allowance |
$ 18,140,000
|
$ 122,921,000
|
| Increase in deferred tax benefit |
104,781,000
|
|
| Unrecognized Tax Benefits |
|
|
| Remaining unrecognized tax benefits |
0
|
|
| Capital loss carryforwards |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
3,988,000
|
|
| Federal |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| NOL carryforwards |
5,981,000
|
|
| Federal | Research tax credit carryforward |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
5,177,000
|
|
| Federal | Foreign tax credits |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
3,999,000
|
|
| State and local |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| NOL carryforwards |
1,013,000
|
|
| State and local | Research tax credit carryforward |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
26,467,000
|
|
| State and local | Research tax credit carryforward | NEW JERSEY |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
16,857,000
|
|
| State and local | Research tax credit carryforward | CALIFORNIA |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
9,610,000
|
|
| Foreign |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| NOL carryforwards, subject to expiration |
3,064,000
|
|
| NOL carryforwards, not subject to expiration |
34,035,000
|
|
| Foreign | Capital loss carryforwards |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
310,000
|
|
| Foreign | Foreign tax credits |
|
|
| Tax Credit Carryforward [Line Items] |
|
|
| Tax credit carryforwards amount |
$ 215,000
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards that are not subject to expiration dates.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsNotSubjectToExpiration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards that are subject to expiration dates.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwardsSubjectToExpiration |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of the unrecognized tax benefit of a position taken for which it is reasonably possible that the total amount thereof will significantly increase or decrease within twelve months of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantChangeInUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIsReasonablyPossibleAmountOfUnrecordedBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of the tax credit carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in the valuation allowance for a specified deferred tax asset. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ValuationAllowanceDeferredTaxAssetChangeInAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAxis=us-gaap_CapitalLossCarryforwardMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAxis=us-gaap_ResearchMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxCreditCarryforwardAxis=cvlt_ForeignTaxCreditsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=stpr_NJ |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=stpr_CA |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Income Taxes - Reconciliation of Amounts of Unrecognized Tax Benefits (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Reconciliation of Unrecognized Tax Benefits, Excluding Amounts Pertaining to Examined Tax Returns [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Beginning balance |
$ 9,388
|
$ 9,224
|
$ 2,211
|
| Additions for tax positions related to current fiscal period |
502
|
394
|
2,808
|
| Reductions for tax positions related to prior years |
|
(90)
|
|
| Additions for tax positions related to prior years |
3
|
|
90
|
| Settlements and effective settlements with tax authorities and related remeasurements |
0
|
0
|
0
|
| Reductions related to the expiration of statutes of limitations |
(220)
|
(140)
|
(117)
|
| Additions for tax positions related to purchase accounting |
0
|
0
|
4,232
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
0
|
0
|
0
|
| Ending balance |
$ 9,673
|
$ 9,388
|
$ 9,224
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ReconciliationOfUnrecognizedTaxBenefitsExcludingAmountsPertainingToExaminedTaxReturnsRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrecognized tax benefits. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10B
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-10B
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefits |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from foreign currency translation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsDecreasesResultingFromForeignCurrencyTranslation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions taken in prior period tax returns. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsDecreasesResultingFromPriorPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from settlements with taxing authorities. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsDecreasesResultingFromSettlementsWithTaxingAuthorities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from acquisitions.
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromAcquisition |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions that have been or will be taken in current period tax return. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromCurrentPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from tax positions taken in prior period tax returns. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsIncreasesResultingFromPriorPeriodTaxPositions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of decrease in unrecognized tax benefits resulting from lapses of applicable statutes of limitations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15A
-Subparagraph (a)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-15A
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnrecognizedTaxBenefitsReductionsResultingFromLapseOfApplicableStatuteOfLimitations |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationAndRetirementDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of contribution received by defined benefit plan from employer which increases plan assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 17
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480482/715-20-55-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480482/715-20-55-18
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 715
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)(iv)(01)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480506/715-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DefinedBenefitPlanContributionsByEmployer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of operating segments. An operating segment is a component of an enterprise: (a) that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses (including revenues and expenses relating to transactions with other components of the same enterprise), (b) whose operating results are regularly reviewed by the enterprise's chief operating decision maker to make decisions about resources to be allocated to the segment and assess its performance, and (c) for which discrete financial information is available. An operating segment may engage in business activities for which it has yet to earn revenues, for example, start-up operations may be operating segments before earning revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_NumberOfOperatingSegments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:integerItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Segment Information - Schedule of Revenue by Geographic Area (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 839,247
|
$ 784,590
|
$ 769,591
|
| United States |
|
|
|
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
437,560
|
416,347
|
398,632
|
| Other |
|
|
|
| Revenues from External Customers and Long-Lived Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Total revenues |
$ 401,687
|
$ 368,243
|
$ 370,959
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenuesFromExternalCustomersAndLongLivedAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_US |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=us-gaap_NonUsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionLong-lived assets other than financial instruments, long-term customer relationships of a financial institution, mortgage and other servicing rights, deferred policy acquisition costs, and deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoncurrentAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenuesFromExternalCustomersAndLongLivedAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_US |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=us-gaap_NonUsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Restructuring - Restructuring Charges (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Restructuring and Related Activities [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Employee severance and related costs |
$ 2,811
|
$ 12,845
|
$ 4,483
|
| Lease exit costs |
220
|
0
|
0
|
| Stock-based compensation |
1,517
|
2,607
|
1,709
|
| Total restructuring charges |
$ 4,548
|
$ 15,452
|
$ 6,192
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Includes, but is not limited to, one-time termination benefits, termination of an operating lease or other contract, consolidating or closing facilities, and relocating employees, and termination benefits associated with an ongoing benefit arrangement. Excludes expenses associated with special or contractual termination benefits, a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessExitCosts1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of other expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses associated with a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherRestructuringCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses associated with exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482047/420-10-45-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses for special or contractual termination benefits provided to current employees involuntarily terminated under a benefit arrangement associated exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to one-time termination benefits, a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_SeveranceCosts1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Restructuring - Activity in Restructuring Accruals (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Restructuring Reserve [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Beginning balance |
$ 3,211
|
$ 2,261
|
|
| Employee severance and related costs |
2,811
|
12,845
|
$ 4,483
|
| Payments |
(3,276)
|
(11,895)
|
|
| Ending balance |
2,746
|
3,211
|
$ 2,261
|
| Restructuring Cost and Reserve [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Payments |
3,276
|
$ 11,895
|
|
| 2022 Restructuring Program |
|
|
|
| Restructuring Reserve [Roll Forward] |
|
|
|
| Payments |
(3,149)
|
|
|
| Restructuring Cost and Reserve [Line Items] |
|
|
|
| Payments |
$ 3,149
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash payments made as the result of exit or disposal activities. Excludes payments associated with a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsForRestructuring |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(b)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.P.4(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringCostAndReserveLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying amount (including both current and noncurrent portions of the accrual) as of the balance sheet date pertaining to a specified type of cost associated with exit from or disposal of business activities or restructuring pursuant to a duly authorized plan. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482017/420-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 420
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 5.P.4(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479823/420-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringReserve |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA roll forward is a reconciliation of a concept from the beginning of a period to the end of a period.
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringReserveRollForward |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expenses for special or contractual termination benefits provided to current employees involuntarily terminated under a benefit arrangement associated exit or disposal activities pursuant to an authorized plan. Excludes expenses related to one-time termination benefits, a discontinued operation or an asset retirement obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_SeveranceCosts1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RestructuringPlanAxis=cvlt_A2022RestructuringProgramMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Leases - Net Lease Costs Recognized (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
12 Months Ended |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 31, 2022 |
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Operating lease cost |
$ 5,770
|
$ 5,449
|
$ 7,129
|
| Short-term lease cost |
272
|
631
|
123
|
| Variable lease cost |
1,333
|
1,360
|
1,608
|
| Net lease cost |
$ 7,375
|
$ 7,440
|
$ 8,860
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lease cost recognized by lessee for lease contract. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of single lease cost, calculated by allocation of remaining cost of lease over remaining lease term. Includes, but is not limited to, single lease cost, after impairment of right-of-use asset, calculated by amortization of remaining right-of-use asset and accretion of lease liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of short-term lease cost, excluding expense for lease with term of one month or less. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShortTermLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of variable lease cost, excluded from lease liability, recognized when obligation for payment is incurred for finance and operating leases. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableLeaseCost |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionIncrease (Decrease) in Operating Lease, Right Of Use Asset
| Name: |
cvlt_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingLeaseRightOfUseAsset |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash outflow from operating lease, excluding payments to bring another asset to condition and location necessary for its intended use. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeasePayments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
Leases - Maturities of Lease Liabilities (Details) - USD ($)
$ in Thousands |
Mar. 31, 2024 |
Mar. 31, 2023 |
| Leases [Abstract] |
|
|
| 2025 |
$ 4,624
|
|
| 2026 |
2,973
|
|
| 2027 |
1,740
|
|
| 2028 |
1,601
|
|
| 2029 |
932
|
|
| Thereafter |
683
|
|
| Total minimum lease payments |
12,553
|
|
| Less: Imputed interest |
463
|
|
| Present value of operating lease liabilities |
12,090
|
|
| Less: Current portion of operating lease liabilities |
4,935
|
$ 4,518
|
| Long-term operating lease liabilities |
$ 7,155
|
$ 8,260
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease due after fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in next fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueNextTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fifth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in fourth fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in third fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payment for operating lease to be paid in second fiscal year following current fiscal year. Excludes interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported from current statement of financial position date (rolling approach). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityPaymentsDueYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of lessee's undiscounted obligation for lease payments in excess of discounted obligation for lease payments for operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_LesseeOperatingLeaseLiabilityUndiscountedExcessAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiability |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPresent value of lessee's discounted obligation for lease payments from operating lease, classified as noncurrent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479041/842-20-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseLiabilityNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average discount rate for operating lease calculated at point in time. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageDiscountRatePercent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionWeighted average remaining lease term for operating lease, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 53
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479589/842-20-55-53
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 842
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (g)(3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147478964/842-20-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLeaseWeightedAverageRemainingLeaseTerm1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionLessee, Operating Lease, Lease Not yet Commenced, Minimum Commitment
| Name: |
cvlt_LesseeOperatingLeaseLeaseNotYetCommencedMinimumCommitment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
cvlt_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LeasesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionPercentage points added to the reference rate to compute the variable rate on the debt instrument.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentBasisSpreadOnVariableRate1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPeriod of time between issuance and maturity of debt instrument, in PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentTerm |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe carrying value as of the balance sheet date of the current and noncurrent portions of long-term obligations drawn from a line of credit, which is a bank's commitment to make loans up to a specific amount. Examples of items that might be included in the application of this element may consist of letters of credit, standby letters of credit, and revolving credit arrangements, under which borrowings can be made up to a maximum amount as of any point in time conditional on satisfaction of specified terms before, as of and after the date of drawdowns on the line. Includes short-term obligations that would normally be classified as current liabilities but for which (a) postbalance sheet date issuance of a long term obligation to refinance the short term obligation on a long term basis, or (b) the enterprise has entered into a financing agreement that clearly permits the enterprise to refinance the short-term obligation on a long term basis and the following conditions are met (1) the agreement does not expire within 1 year and is not cancelable by the lender except for violation of an objectively determinable provision, (2) no violation exists at the BS date, and (3) the lender has entered into the financing agreement is expected to be financially capable of honoring the agreement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(22))
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 210
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(16)(a)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCredit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionMaximum borrowing capacity under the credit facility without consideration of any current restrictions on the amount that could be borrowed or the amounts currently outstanding under the facility. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19(b),22(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityMaximumBorrowingCapacity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe fee, expressed as a percentage of the line of credit facility, for available but unused credit capacity under the credit facility.
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityUnusedCapacityCommitmentFeePercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe remaining balance of debt issuance expenses that were capitalized and are being amortized against income over the lives of the respective bond issues. This does not include the amounts capitalized as part of the cost of the utility plant or asset.
| Name: |
us-gaap_UnamortizedDebtIssuanceExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=cvlt_SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CreditFacilityAxis=us-gaap_RevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_VariableRateAxis=cvlt_SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense attributable to debt issuance costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482925/835-30-45-3
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfFinancingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal interest costs incurred during the period and either capitalized or charged against earnings. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 835
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483013/835-20-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestCostsIncurred |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the portion of interest incurred in the period on debt arrangements that was charged against earnings, excluding amortization of debt discount (premium) and financing costs. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69E
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69E
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 69F
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481568/470-20-55-69F
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1F
-Subparagraph (b)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481139/470-20-50-1F
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestExpenseDebtExcludingAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(f))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LineOfCreditFacilityLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CreditFacilityAxis=us-gaap_RevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DebtInstrumentAxis=cvlt_SeniorSecuredRevolvingCreditFacilityMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.1.u2
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of consideration transferred, consisting of acquisition-date fair value of assets transferred by the acquirer, liabilities incurred by the acquirer, and equity interest issued by the acquirer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 30
-Paragraph 8
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 805
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479637/805-30-30-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 805
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479581/805-30-50-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 30
-Paragraph 7
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 805
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479637/805-30-30-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessCombinationConsiderationTransferred1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDetail information of subsequent event by type. User is expected to use existing line items from elsewhere in the taxonomy as the primary line items for this disclosure, which is further associated with dimension and member elements pertaining to a subsequent event. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483399/855-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessAcquisitionAxis=cvlt_AppranixIncMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventTypeAxis=us-gaap_SubsequentEventMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
CommVault Systems (NASDAQ:CVLT)
Historical Stock Chart
From Apr 2024 to May 2024
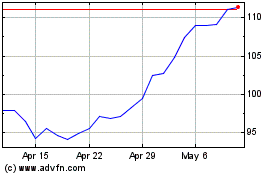
CommVault Systems (NASDAQ:CVLT)
Historical Stock Chart
From May 2023 to May 2024