As filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
on October 31, 2019.
Registration No. 333-234299
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM S-1/A
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
American Cannabis Company, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
8742
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number)
90-1116625
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number)
5690 Logan Street, Unit A
Denver CO. 80216
Telephone: (303) 974-4770
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number,
including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Terry L. Buffalo
American Cannabis Company, Inc.
5690 Logan Street, Unit A
Denver CO. 80216
Telephone: (303) 974-4770
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
Mailander Law Office, Inc.
Tad Mailander
945 4th Avenue, Ste. 311
San Diego, CA 92101
(619) 239-9034
From time to time after the effective date of this
registration statement.
(Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public)
If any of
the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the
Securities Act of 1933 check the following box: ☒
If this Form
is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the
following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the
same offering. ☐
If this Form
is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities
Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form
is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities
Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large
accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large
accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange
Act.
|
Large accelerated filer
|
☐
|
Accelerated filer
|
☐
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
☐
|
Smaller reporting company
|
☒
|
|
(Do not check if a smaller reporting
company)
|
Emerging growth company
|
☒
|
Calculation of Registration Fee
Title
of Each Class
of Securities to be
Registered
|
|
Amount
to be
Registered(1)
|
|
|
Proposed
Maximum
Offering Price
Per Share
|
|
|
Proposed
Maximum
Aggregate Offering
Price
|
|
|
Amount
of
Registration Fee
|
|
|
Common
stock to be offered for resale by selling stockholders
|
|
|
34,090,909
|
|
|
$
|
0.22
|
(2)
|
|
$
|
$7,499,999,98
|
|
|
$
|
973.50
|
(3)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Consists of up to
34,090,909 shares of common stock to be sold to White Lion Capital, LLC under the investment agreement dated October 11,
2019.
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
|
Estimated solely
for the purpose of calculating the amount of the registration fee in accordance with Rule 457(c) under the Securities Act
of 1933.
|
|
|
|
|
(3)
|
Based on the closing
price per share of $0.22 for American Cannabis Company, Inc.’s common stock on October 22, 2019 as reported by the OTC
Markets Group.
|
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement
on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which
specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the
Securities Act of 1933 or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange
Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
|
The
information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. The selling stockholder may not sell these securities until
the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer
to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is
not permitted.
|
Subject to Completion, Dated October 31, 2019
Preliminary Prospectus
American Cannabis Company, Inc.
34,090,909 Shares of Common Stock
This prospectus relates to the resale of 34,090,909 shares
of our common stock, par value $0.00001 per share, (the “Common Shares”), shares issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC
(defined below).
This prospectus relates to the resale of up to 34,090,909
shares of the Common Shares, issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC (“White Lion”), a selling stockholder pursuant to
a “Purchase Notice right” under an investment agreement (the “Investment Agreement”), dated October 11,
2019, that we entered into with White Lion. The Investment Agreement permits us to issue Purchase Notices to White Lion for
up to seven million, five hundred thousand dollars ($7,500,000) in shares of our common stock over a period of up to thirty-six
(36) months or until $7,500,000 of such shares have been subject of a Purchase Notice.
The selling stockholders may sell all or a portion of
the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices, at prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying
prices or at negotiated prices.
White Lion Capital, LLC is an underwriter within the meaning
of the Securities Act of 1933, and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters”
within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such
broker-dealers or agents, and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them, may be deemed to be underwriting commissions
or discounts under the Securities Act of 1933.
Our common stock is quoted by the OTC Markets Group OTCQB
tier under the symbol “AMMJ”. On October 22, 2019, the closing price of our common stock was $0.22 per share.
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares
of our common stock by the selling stockholder. However, we will receive proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock
pursuant to our exercise of the Purchase Notice right offered by White Lion Capital, LLC. We will pay for expenses of this offering,
except that the selling stockholder will pay any broker discounts or commissions or equivalent expenses and expenses of its legal
counsel applicable to the sale of its shares.
INVESTING
IN OUR SECURITIES INVOLVES RISKS. YOU SHOULD REVIEW CAREFULLY THE RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES DESCRIBED UNDER THE HEADING “RISK
FACTORS” CONTAINED ON PAGE 5 HEREIN
AND IN OUR ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2018, AS WELL AS OUR SUBSEQUENTLY FILED PERIODIC AND
CURRENT REPORTS, WHICH WE FILE WITH THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION AND ARE INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE INTO THIS PROSPECTUS.
YOU SHOULD READ THE ENTIRE PROSPECTUS CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU MAKE YOUR INVESTMENT DECISION.
NEITHER THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION NOR
ANY STATE SECURITIES COMMISSION HAS APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED OF THESE SECURITIES OR PASSED UPON THE ADEQUACY OR ACCURACY OF THIS
PROSPECTUS. ANY REPRESENTATION TO THE CONTRARY IS A CRIMINAL OFFENSE.
,
The date of this prospectus is October 31, 2019
Table of
Contents
|
|
|
Page
Number
|
|
About This
Prospectus
|
|
1
|
|
Prospectus Summary
|
|
1
|
|
Risk Factors
|
|
5
|
|
Risks
Related to Our Business
|
|
5
|
|
Risks
Related to Our Company
|
|
5
|
|
Risks
Related to Our Common Stock
|
|
12
|
|
Forward-Looking Statements
|
|
15
|
|
Use of Proceeds
|
|
16
|
|
Dilution
|
|
16
|
|
The Offering
|
|
17
|
|
Selling Stockholders
|
|
18
|
|
Plan of Distribution
|
|
20
|
|
Description of Securities
|
|
22
|
|
Experts and Counsel
|
|
22
|
|
Interest of Named Experts and
Counsel
|
|
23
|
|
Information With Respect to
Our Company
|
|
23
|
|
Description of Business
|
|
23
|
|
Description of Property
|
|
28
|
|
Legal Proceedings
|
|
29
|
|
Market Price of and Dividends
on Our Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters
|
|
29
|
|
Financial Statements
|
|
32
|
|
Management’s Discussion
and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
|
|
67
|
|
Changes in and Disagreements
with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
|
|
74
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers
|
|
74
|
|
Executive Compensation
|
|
78
|
|
Security Ownership of Certain
Beneficial Owners and Management
|
|
80
|
|
Transactions with Related Persons,
Promoters and Certain Control Persons and Corporate Governance
|
|
82
|
|
Where You Can Find More Information
|
|
82
|
ABOUT THIS PROSPECTUS
You should rely only on the information that we have provided
in this prospectus and any applicable prospectus supplement. We have not authorized anyone to provide you with different information.
No dealer, salesperson or other person is authorized to give any information or to represent anything not contained in this prospectus
and any applicable prospectus supplement. You must not rely on any unauthorized information or representation. This prospectus
is an offer to sell only the securities offered hereby, but only under circumstances and in jurisdictions where it is lawful to
do so. You should assume that the information in this prospectus, and any applicable prospectus supplement, is accurate only as
of the date on the front of the document, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus, any applicable prospectus supplement,
or any sale of a security. Our business, financial conditions, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that
date.
References to “Management” in this Prospectus
mean the senior officers of the Company; See “Directors and Executive Officers.” Any statements in this Prospectus
made by or on behalf of Management are made in such persons’ capacities as officers of the Company, and not in their personal
capacities.
As used in this prospectus, the terms “we”,
“us”, the “Company”, “American Cannabis”, and our subsidiary “Hollister & Blacksmith,
Inc.” mean American Cannabis Company, Inc., unless otherwise indicated. All dollar amounts refer to U.S. dollars unless
otherwise indicated.
CAUTIONARY NOTE TO INVESTORS
This Prospectus qualifies the distribution of securities
of an entity that derives substantially all of its revenues from the cannabis industry in certain of the states in the United
States. Cannabis is classified as an illegal Schedule 1 drug and illegal under the Controlled Substances Act, 21 U.S.C. §
811 (hereafter referred to as the “CSA”). On December 20, 2018, President Donald J. Trump signed into law the Agriculture
Improvement Act of 2018, otherwise known as the “Farm Bill.” Prior to its passage, hemp, a member of the cannabis
family, was classified as a Schedule 1 controlled substance, and also illegal under the CSA.
With the passage of the Farm Bill, hemp cultivation is
broadly permitted. The Farm Bill explicitly allows the transfer of hemp-derived products across state lines for commercial or
other purposes. It also puts no restrictions on the sale, transport, or possession of hemp-derived products, so long as those
items are produced in a manner consistent with the law. Despite the passage of the Farm Bill, certain aspects of the cannabis
industry, particularly those not defined as hemp within the Farm Bill, remain illegal under U.S. federal Law. At this time, we
are not engaged in businesses that fall outside of what is permissible under the Farm Bill.
In the future, we could become involved in business activities
that would fall outside of the Farm Bill, such as the research and development, growth, cultivation and/or processing of cannabis
that are not covered under the Farm Bill. Currently, 33 states plus the District of Columbia and Guam, have laws and/or regulations
that recognize, in one form or another, legitimate medical and adult uses for cannabis and consumer use of cannabis in connection
with medical treatment or for recreational use. Many other states are considering similar legislation. Conversely, under the CSA,
the policies and regulations of the federal government and its agencies are that cannabis has no medical benefit and a range of
activities including cultivation and the personal use of cannabis is prohibited. Unless and until Congress amends the CSA with
respect to cannabis, as to the timing or scope of any such potential amendments there can be no assurance, there is a risk that
federal authorities may enforce current federal law, and we may be deemed to be producing, cultivating, dispensing and/or aiding
or abetting the possession and distribution of cannabis in violation of federal law. Active enforcement of the current CSA on
cannabis may thus directly and adversely affect our revenues and profits. The risk of strict enforcement of the CSA in light of
Congressional activity, judicial holdings, and stated federal policy remains uncertain; See sections entitled “Risk Factors”
and “Government Regulation of Cannabis.”
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
The following summary highlights material information
contained in this Prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information you should consider before investing in the
securities. Before making an investment decision, you should read the entire Prospectus carefully, including the risk factors
section, the financial statements and the notes to the financial statements. You should also review the other available information
referred to in the section entitled “Where You Can Find More Information” in this Prospectus and any amendment or
supplement hereto.
The Offering
This prospectus relates to the resale of 34,090,909
shares of our common stock, par value $0.00001 per share, issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC (defined below).
This prospectus relates to the resale of up to 34,090,909
shares of the Common Shares, issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC (“White Lion”), a selling stockholder pursuant to
a Purchase Notice right under an investment agreement (the “Investment Agreement”), dated October 11, 2019, that
we entered into with White Lion. The Investment Agreement permits us to elect to issue Purchase Notices to White Lion for the
sale of up to seven million, five hundred thousand dollars ($7,500,000) in shares of our common stock over a period of up to thirty-six
(36) months or until $7,500,000 of such shares have been sold.
Our Business
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and subsidiary company,
Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc., doing business as American Cannabis Consulting (“American Cannabis Consulting”),
(collectively “the “Company”, “we”, “us”, or “our”) are based in Denver,
Colorado and operate a fully-integrated business model that features end-to-end solutions for businesses operating in the regulated
cannabis industry in states and countries where cannabis is regulated and/or has been de-criminalized for medical use and/or legalized
for recreational use. We provide advisory and consulting services specific to this industry, design industry-specific products
and facilities, manage a strategic group partnership that offers both exclusive and non-exclusive customer products commonly used
in the industry. We do not directly sell, cultivate, manufacture, or transact cannabis. However,
we may choose to take advantage of Colorado Bill HB-19-1090, which was recently passed into Colorado law, effective November 1,
2019. This law allows publicly traded corporations to apply for and qualify for the ownership of Colorado cannabis licenses.
We recently began a new business consulting division called
“American Hemp Services,” which offers hemp producers with consulting and professional services including business
plan creation, greenhouse and farm design, license acquisition, seed sales, hemp processing, operational deployment, and crop
improvement. Furthermore, the Company seeks to partner with accredited universities nationwide to further the advancement of hemp
related research.
We are a publicly listed company quoted on the OTCQB under
the symbol “AMMJ”.
We were incorporated in the State of Delaware on September
24, 2001 under the name Naturewell, Inc. to develop and market clinical diagnostic products using immunology and molecular biologic
technologies.
On March 13, 2013, Naturewell, Inc. completed a merger
transaction whereby it acquired 100% of the issued and outstanding share capital of Brazil Interactive Media, Inc. (“BIMI”),
which operated as a Brazilian interactive television company and television production company through its wholly owned Brazilian
subsidiary company, EsoTV Brasil Promoção Publicidade Licenciamento e Comércio Ltda. (“EsoTV”).
Naturewell’s Certificate of Incorporation were amended to reflect a new name: Brazil Interactive Media, Inc.
On May 15, 2014, BIMI entered into a merger agreement
(“the Merger Agreement”) to acquire 100% of the issued and outstanding American Cannabis Consulting while simultaneously
disposing of 100% of the issued share capital EsoTV (“the Separation Agreement”). Both the merger with American Cannabis
Consulting and disposal of EsoTV were completed on September 29, 2014. BIMI subsequently amended its Certificate of Incorporation
to change its name to American Cannabis Company, Inc. On October 10, 2014, American Cannabis Company, Inc. changed its stock symbol
from BIMI to AMMJ.
Immediately following the completion of the Merger Agreement,
former shareholders of American Cannabis Consulting owned 31,710,628 shares of American Cannabis Company, Inc.’s common
stock, representing 78.4% of American Cannabis Company, Inc.’s issued and outstanding share capital. Accordingly, American
Cannabis Consulting was deemed to have been the accounting acquirer in a Reverse Merger which resulted in a recapitalization of
the Company. Consequently, the Company’s consolidated financial statements reflect the results of American Cannabis
Consulting since Inception (March 5, 2013) and of American Cannabis Company, Inc. (formerly BIMI) since September 29, 2014.
Government Regulation of Cannabis
The United States federal government regulates drugs through
the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. § 811), which places controlled substances, including cannabis, in a schedule. Cannabis
is classified as a Schedule I drug, which is viewed as highly addictive and having no medical value. The United States Federal
Drug Administration has not approved the sale of cannabis for any medical application.
Doctors may not prescribe cannabis for medical use under federal law; however, they can recommend its use under the First Amendment.
In 2010, the United States Veterans Affairs Department clarified that veterans using medicinal cannabis will not be denied services
or other medications that are denied to those using illegal drugs.
As of October 31, 2019, 33 states, the District
of Columbia and Guam have laws legalized cannabis in some form for either medicinal or recreational use governed by state specific
laws and regulations.
These state laws are in conflict with the federal Controlled
Substances Act, which makes cannabis use and possession illegal on a national level. However, on August 29, 2013, the U.S. Department
of Justice issued a memorandum providing that where states and local governments enact laws authorizing cannabis-related use,
and implement strong and effective regulatory and enforcement systems, the federal government will rely upon states and local
enforcement agencies to address cannabis activity through the enforcement of their own state and local narcotics laws. The memorandum
further stated that the U.S Justice Department’s limited investigative and prosecutorial resources will be focused on eight
priorities to prevent unintended consequences of the state laws, including distribution of cannabis to minors, preventing the
distribution of cannabis from states where it is legal to states where it is not, and preventing money laundering, violence and
drugged driving.
On December 11, 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice issued
another memorandum with regard to its position and enforcement protocol with regard to Indian Country, stating that the eight
priorities in the previous federal memo would guide the United States Attorneys' cannabis enforcement efforts in Indian Country.
On December 16, 2014, as a component of the federal spending bill, the Obama administration enacted regulations that prohibits
the Department of Justice from using funds to prosecute state-based legal medical cannabis programs.
On January 4, 2018, Attorney General Jeff Sessions issued
a memorandum for all United States Attorneys concerning cannabis enforcement. Mr. Sessions rescinded all previous prosecutorial
guidance issued by the Department of Justice regarding cannabis , including the August 29, 2013 memorandum. Mr. Sessions stated
that U.S. Attorneys must decide whether or not to pursue prosecution of cannabis activity based upon factors including: the seriousness
of the crime, the deterrent effect of criminal prosecution, and the cumulative impact of particular crimes on the community. Mr.
Sessions reiterated that the cultivation, distribution and possession of cannabis continues to be a crime under the U.S. Controlled
Substances Act.
Government Regulation of Hemp
On December 20, 2018, President Donald J. Trump signed
into law the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018, otherwise known as the “Farm Bill”. Prior to its passage, hemp,
a member of the cannabis family, was classified as a Schedule 1 controlled substance, and so illegal under the Controlled Substances
Act.
With the passage of the Farm Bill, hemp cultivation is
broadly permitted. The Farm Bill explicitly allows the transfer of hemp-derived products across state lines for commercial or
other purposes. It also puts no restrictions on the sale, transport, or possession of hemp-derived products, so long as those
items are produced in a manner consistent with the law.
Additionally, there will be significant, shared state-federal
regulatory power over hemp cultivation and production. Under Section 10113 of the Farm Bill, state departments of agriculture
must consult with the state’s governor and chief law enforcement officer to devise a plan that must be submitted to the
United States Department of Agriculture (“USDA”). A state’s plan to license and regulate hemp can only commence
once the USDA approves that state’s plan. In states opting not to devise a hemp regulatory program, USDA will construct
a regulatory program under which hemp cultivators in those states must apply for licenses and comply with a federally-run program.
This system of shared regulatory programming is similar to options states had in other policy areas such as health insurance marketplaces
under Affordable Care Act, or workplace safety plans under Occupational Health and Safety Act—both of which had federally-run
systems for states opting not to set up their own systems.
The Farm Bill outlines actions that are considered violations
of federal hemp law (including such activities as cultivating without a license or producing hemp with more than 0.3 percent THC,
the psychoactive agent in cannabis).
The 2018 Farm Bill extends the protections for hemp research
and the conditions under which such research can and should be conducted. Further, Section 7501 of the Farm Bill extends hemp
research by including hemp under the Critical Agricultural Materials Act. This provision recognizes the importance, diversity,
and opportunity of the plant and the products that can be derived from it, but also recognizes that there is a still a lot to
learn about hemp and its products from commercial and market perspectives.
Where You Can Find Us
The principal offices of our company are located at 5690 Logan St., Unit A,
Denver, CO 80216. Our telephone number is (303) 974-4770.
The Offering
|
Common Stock Offered by
the Selling Security Holders
|
|
34,090,909
shares of common stock that may be subject of a Purchase Notice to White Lion.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock Outstanding Before the Offering
|
|
52,978,605 shares
of common stock as of October 31, 2019.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock Outstanding After the Offering
|
|
87,069,514 shares
of common stock. (1)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terms of the Offering
|
|
The selling security
holder will determine when and how they will sell the common stock offered in this prospectus.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Termination of the Offering
|
|
The offering will
conclude upon such time as all of the common stock has been sold pursuant to the registration statement.
|
|
Use of Proceeds
|
|
We are
not selling any shares of common stock in this offering and, as a result, will not receive any proceeds from this offering. See
“Use of Proceeds.”
|
|
|
|
|
|
Risk Factors
|
|
The common stock
offered hereby involves a high degree of risk and should not be purchased by investors who cannot afford the loss of their entire
investment. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
OTCQB Symbol
|
|
AMMJ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
This total shows
how many shares of common stock will be outstanding assuming 34,090,909 shares of common stock are sold to White Lion.
|
Summary of Financial Data
The
following information represents selected audited financial information for our company for the years ended December 31, 2018
and 2017 and selected unaudited financial information for our company for the six month period ended June 30, 2019. The
summarized financial information presented below is derived from and should be read in conjunction with our audited and
unaudited financial statements, as applicable, including the notes to those financial statements which are included elsewhere
in this prospectus along with the section entitled Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and
Results of Operations beginning on page 67 of
this prospectus.
|
Statements
of Operations Data
|
|
Six
Month Period Ended June 30, 2019
|
|
|
Six
Month Period Ended June 30, 2018
|
|
|
Year
Ended December 31, 2018
|
|
|
Year
Ended December 31, 2017
|
|
|
Revenue
|
|
$
|
1,141,281
|
|
|
$
|
454,205
|
|
|
$
|
982,349
|
|
|
$
|
2,443,055
|
|
|
Cost of Revenue
|
|
$
|
456,414
|
|
|
$
|
222,611
|
|
|
$
|
523,847
|
|
|
$
|
805,820
|
|
|
Net Operating Expenses
|
|
$
|
636,130
|
|
|
$
|
569,532
|
|
|
$
|
1,183,109
|
|
|
$
|
1,358,388
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss)
|
|
$
|
(21,264)
|
|
|
$
|
(375,942)
|
|
|
$
|
(950,691)
|
|
|
$
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Basic and Diluted Net Income (Loss) per Share
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.01)
|
|
|
$
|
(0.02)
|
|
|
$
|
(0.03
|
)
|
|
Balance
Sheets Data
|
|
As
of June 30, 2019
|
|
|
As
of June 30, 2018
|
|
|
As
of December 31, 2018
|
|
|
Cash and Cash Equivalents
|
|
$
|
918,127
|
|
|
$
|
1,299,452
|
|
|
$
|
1,086,565
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
$
|
1,261,280
|
|
|
$
|
1,522,015
|
|
|
$
|
1,267,331
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
$
|
242,925
|
|
|
$
|
195,400
|
|
|
$
|
270,048
|
|
|
Working Capital (deficit)
|
|
$
|
1,018,355
|
|
|
$
|
1,326,615
|
|
|
$
|
997,283
|
|
|
Total Stockholders’ Equity
|
|
$
|
1,027,801
|
|
|
$
|
1,326,615
|
|
|
$
|
1,005,321
|
|
|
Accumulated Deficit
|
|
$
|
(7,195,377
|
)
|
|
$
|
(6,599,364
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,174,113
|
)
|
RICK FACTORS
An investment in our common stock involves a number of
very significant risks. You should carefully consider the following risks and uncertainties in addition to other information in
this prospectus in evaluating our company and our business before purchasing our securities. Our business, operating results and
financial condition could be seriously harmed as a result of the occurrence of any of the following risks. You could lose all
or part of your investment due to any of these risks. You should invest in our common stock only if you can afford to lose your
entire investment.
There could be unidentified risks involved with
an investment in our securities.
The following risk factors are not a complete list or
explanation of the risks involved with an investment in the securities. Additional risks will likely be experienced that are not
presently foreseen by the Company. Prospective investors must not construe the information provided herein as constituting investment,
legal, tax or other professional advice. Before making any decision to invest in our securities, you should read this entire prospectus
and consult with your own investment, legal, tax and other professional advisors. An investment in our securities is suitable
only for investors who can assume the financial risks of an investment in the Company for an indefinite period of time and who
can afford to lose their entire investment. The Company makes no representations or warranties of any kind with respect to the
likelihood our business will succeed, or regarding the value of our securities, any financial returns that may be generated or
any tax benefits or consequences that may result from an investment in the Company.
Risks Related to Our Business
Cannabis remains illegal under federal law.
Cannabis is a Schedule I controlled
substance and is illegal under the CSA. Even in states that have legalized the use of cannabis, its sale and use remain violations
of federal law. The illegality of cannabis under federal law preempts state laws that legalize its use. Therefore, strict enforcement
of federal law regarding cannabis would likely result in our inability to proceed with our business plan.
Our business is dependent on laws pertaining to
the cannabis industry.
The United States federal government regulates drugs through
the CSA, which places controlled substances, including cannabis, in a schedule. Cannabis is classified as an illegal Schedule
I drug, which is viewed as highly addictive and having no medical value. The United States Federal Drug Administration has not
approved the sale of cannabis for any medical application. Doctors may not prescribe cannabis for medical use under federal law;
however, doctors can recommend its use under the First Amendment. In 2010,
the United States Veterans Affairs Department clarified that veterans using medicinal cannabis will not be denied services or
other medications that are denied to those using illegal drugs.
As of October 31, 2019, 33 states, the District
of Columbia and Guam allow their citizens to use cannabis for medicinal and/or recreational purposes through de-criminalization.
These noted state laws conflict with the CSA, which makes
cannabis use and possession illegal on a national level. However, on August 29, 2013, the U.S. Department of Justice issued a
memorandum providing that where states and local governments enact laws authorizing cannabis-related use, and implement strong
and effective regulatory and enforcement systems, the federal government will rely upon states and local enforcement agencies
to address cannabis activity through the enforcement of their own state and local narcotics laws. The memorandum further stated
that the U.S Justice Department’s limited investigative and prosecutorial resources will be focused on eight priorities
to prevent unintended consequences of the state laws, including distribution of cannabis to minors, preventing the distribution
of cannabis from states where it is legal to states where it is not, and preventing money laundering, violence and drugged driving.
On December 11, 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice issued
another memorandum with regard to its position and enforcement protocol with regard to Indian Country, stating that the eight
priorities in the August 29, 2013 federal memo would guide the United States Attorneys' cannabis enforcement efforts in Indian
Country. On December 16, 2014, as a component of the federal spending bill, the Obama administration enacted regulations that
prohibit the Department of Justice from using funds to prosecute state-based legal medical cannabis programs.
On January 4, 2018, Attorney General Jeff Sessions issued
a memorandum for all United States Attorneys concerning cannabis enforcement. Mr. Sessions rescinded all previous prosecutorial
guidance issued by the Department of Justice regarding cannabis , including the August 29, 2013 memorandum. Mr. Sessions stated
that U.S. Attorneys must decide whether or not to pursue prosecution of cannabis activity based upon factors including: the seriousness
of the crime, the deterrent effect of criminal prosecution, and the cumulative impact of particular crimes on the community. Mr.
Sessions reiterated that the cultivation, distribution and possession of cannabis continues to be a crime under the U.S. Controlled
Substances Act.
The Farm Bill recently passed, and undeveloped shared
state-federal regulations over hemp cultivation and production may impact our business.
The Farm Bill was signed into law on December 20, 2018.
Under Section 10113 of the Farm Bill, state departments of agriculture must consult with the state’s governor and chief
law enforcement officer to devise a plan that must be submitted to the United States Department of Agriculture (“USDA”).
A state’s plan to license and regulate hemp can only commence once the USDA approves that state’s plan. In states
opting not to devise a hemp regulatory program, USDA will construct a regulatory program under which hemp cultivators in those
states must apply for licenses in order to comply with the USDA-run program. The details and scopes of each state’s plans
are not known at this time and may contain varying regulations that may impact our business. Even if a state creates a plan in
conjunction with its governor and chief law enforcement officer, the USDA must approve it. There can be no guarantee that any
state plan will be approved. Review times may be extensive. There may be amendments and the ultimate plans, if approved by states
and the USDA, may materially limit our business depending upon the scope of the regulations.
Laws and regulations affecting our industry to be
developed under the Farm Bill are in development.
As a result of the Farm Bill’s recent passage, there
will be a constant evolution of laws and regulations affecting the hemp industry could detrimentally affect our operations. Local,
state and federal hemp laws and regulations may be broad in scope and subject to changing interpretations. These changes may require
us to incur substantial costs associated with legal and compliance fees and ultimately require us to alter our business plan.
Furthermore, violations of these laws, or alleged violations, could disrupt our business and result in a material adverse effect
on our operations. In addition, we cannot predict the nature of any future laws, regulations, interpretations or applications,
and it is possible that regulations may be enacted in the future that will be directly applicable to our business.
Laws and regulations affecting our industry
are constantly changing.
The constant evolution of laws
and regulations affecting the cannabis and hemp industries could detrimentally affect our operations. Local, state and federal
cannabis and hemp laws and regulations are respectively broad in scope and subject to changing interpretations. These changes
may require us to incur substantial costs associated with legal and compliance fees and ultimately require us to alter our business
plan. Furthermore, violations of these laws, or alleged violations, could disrupt our business and result in a material adverse
effect on our operations. In addition, we cannot predict the nature of any future laws, regulations, interpretations or applications,
and it is possible that regulations may be enacted in the future that will be directly applicable to our business.
Risk of government action.
While we will use our best efforts to comply with all
laws, including federal, state and local laws and regulations, there is a possibility that governmental action to enforce any
alleged violations may result in legal fees and damage awards that would adversely affect us.
Because our business is dependent upon continued
market acceptance by consumers, any negative trends will adversely affect our business operations.
We are substantially dependent on continued market acceptance
and proliferation of consumers of cannabis used for medicinal and recreational uses. We believe that as cannabis becomes more
accepted the stigma associated with cannabis use will diminish and as a result consumer demand will continue to grow. While we
believe that the market and opportunity in the cannabis space continues to grow, we cannot predict the future growth rate and
size of the market. Any negative outlook on the cannabis industry will adversely affect our business operations.
In addition, it is believed by many that large well-funded
businesses may have a strong economic opposition to the cannabis industry. We believe that the pharmaceutical industry clearly
does not want to cede control of any product that could generate significant revenue. For example, medical cannabis will likely
adversely impact the existing market for the current “marijuana pill” Marinol, sold by the mainstream pharmaceutical
industry, should cannabis displace other drugs or encroach upon the pharmaceutical industry's products. The pharmaceutical industry
is well funded with a strong and experienced lobby that eclipses the funding of the medical cannabis movement. Any inroads the
pharmaceutical could make in halting the impending cannabis industry could have a detrimental impact on our business.
FDA Regulation of cannabis and the possible registration
of facilities where medical cannabis is grown could negatively affect the cannabis industry which would directly affect our financial
condition.
Should the federal government legalize cannabis for medical
use, it is possible that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ("FDA") would seek to regulate it under the Food, Drug
and Cosmetics Act of 1938. Additionally, the FDA may issue rules and regulations including cGMPs (certified good manufacturing
practices) related to the growth, cultivation, harvesting and processing of medical cannabis. Clinical trials may be needed to
verify efficacy and safety. It is also possible that the FDA would require that facilities where medical cannabis is grown be
registered with the FDA and comply with certain federally prescribed regulations. In the event that some or all of these regulations
are imposed, we do not know what the impact would be on the cannabis industry and what costs, requirements and possible prohibitions
may be enforced. If we are unable to comply with the regulations and/or registration as prescribed by the FDA, we may be unable
to continue to operate our business.
Our clients may have difficulty accessing the service
of banks.
On February 14, 2014, the U.S. government issued rules
allowing banks to legally provide financial services to state-licensed cannabis businesses. A memorandum issued by the Justice
Department to federal prosecutors re-iterated guidance previously given, this time to the financial industry that banks can do
business with legal cannabis businesses and "may not" be prosecuted. The Treasury Department's Financial Crimes Enforcement
Network (FinCEN) issued guidelines to banks that "it is possible to provide financial services"" to state-licensed
cannabis businesses and still be in compliance with federal anti-money laundering laws. The guidance falls short of the explicit
legal authorization that banking industry officials had pushed the government to provide and to date, it is not clear if any banks
have relied on the guidance and taken on legal cannabis companies as clients. The aforementioned policy may be administration dependent, and a change in presidential
administrations may cause a policy reversal and retraction of current policies, wherein legal cannabis businesses may not have
access to the banking industry. Also, the inability of potential clients in our target markets to open accounts and otherwise
use the service of banks may make it difficult for them to contract with us.
Due to our involvement in the cannabis industry,
we may have a difficult time obtaining the various insurances that are desired to operate our business, which may expose us to
additional risk and financial liability.
Insurance that is otherwise readily available, such as
general liability, and directors and officer’s insurance, is more difficult for us to find, and more expensive, because
we are service providers to companies in the cannabis industry. There are no guarantees that we will be able to find such insurances
in the future, or that the cost will be affordable to us. If we are forced to go without such insurances, it may prevent us from
entering into certain business sectors, may inhibit our growth, and may expose us to additional risk and financial liabilities.
The Company’s industry is highly competitive
and we have less capital and resources than many of our competitors which may give them and advantage in developing and marketing
products similar to ours or make our products obsolete.
We are involved in a highly competitive
industry where we may compete with numerous other companies who offer alternative methods or approaches, who may have far greater
resources, more experience, and personnel perhaps more qualified than we do. Such resources may give our competitors an advantage
in developing and marketing products similar to ours or products that make our products obsolete. There can be no assurance that
we will be able to successfully compete against these other entities.
There could be unidentified
risks involved with an investment in our securities.
The foregoing risk factors are not a complete list or
explanation of the risks involved with an investment in our securities. Additional risks will likely be experienced that are not
presently foreseen by the Company. Prospective investors must not construe this the information provided herein as constituting
investment, legal, tax or other professional advice. Before making any decision to invest in our securities, you should read this
entire prospectus and consult with your own investment, legal, tax and other professional advisors. An investment in our securities
is suitable only for investors who can assume the financial risks of an investment in the Company for an indefinite period of
time and who can afford to lose their entire investment. The Company makes no representations or warranties of any kind with respect
to the likelihood of the success or the business of the Company, the value of our securities, any financial returns that may be
generated or any tax benefits or consequences that may result from an investment in the Company.
The Company may be unable to respond to the rapid
technological change in its industry and such change may increase costs and competition that may adversely affect its business.
Rapidly changing technologies, frequent
new product and service introductions and evolving industry standards characterize
the Company’s market. The continued
growth of the Internet and intense competition in the Company’s
industry exacerbate these market characteristics. The Company’s future
success will depend on its ability to adapt to rapidly changing technologies
by continually improving the performance features and reliability of its products
and services. The Company may experience difficulties that could delay or prevent
the successful development, introduction or marketing of its products and
services. In addition, any new enhancements must meet the requirements of
its current and prospective users and must
achieve significant market acceptance. The Company could
also incur substantial costs if it needs
to modify its products and services
or infrastructures to adapt to these
changes.
The Company also expects that new competitors may introduce
products, systems or services that are
directly or indirectly competitive with the Company.
These competitors may succeed in developing, products, systems
and services that have greater
functionality or are less costly than the Company’s products, systems and services,
and may be more successful in marketing
such products, systems and services. Technological changes
have lowered the cost of operating communications and computer systems
and purchasing software. These changes reduce the Company’s
cost of providing services but also facilitate
increased competition by reducing competitors’ costs in providing similar
services. This competition could increase
price competition and reduce anticipated
profit margins.
The Company’s industry
is highly competitive and we have less capital and resources than many of our competitors, which may give them an advantage in
developing and marketing products similar to ours or make our products obsolete.
We are involved in a highly competitive
industry where we may compete with numerous other companies who offer alternative methods or approaches, who may have far greater
resources, more experience, and personnel perhaps more qualified than we do. Such resources may give our competitors an advantage
in developing and marketing products similar to ours or products that make our products obsolete. There can be no assurance that
we will be able to successfully compete against these other entities.
The Company’s services
are new and its industry is evolving.
You should
consider the Company’s prospects in light of the risks, uncertainties and
difficulties frequently encountered by companies in
their early stage of
development, particularly companies in the rapidly evolving legal cannabis
industry. To be successful
in this industry, the Company
must, among other things:
|
|
●
|
develop
and introduce functional and attractive
service offerings;
|
|
|
●
|
attract
and maintain a large base of clients;
|
|
|
●
|
increase
awareness of the Company brand and
develop consumer loyalty;
|
|
|
●
|
establish
and maintain strategic relationships with
distribution partners and service providers;
|
|
|
●
|
respond
to competitive
and technological developments;
|
|
|
●
|
build
an operations structure
to support the Company business;
and
|
|
|
●
|
attract,
retain and motivate qualified personnel.
|
The Company cannot guarantee that
it will succeed in achieving these goals,
and its failure to do so would have
a material adverse effect on its business,
prospects, financial condition and
operating results.
Some of the Company’s
products and services are new and are only in early stages
of commercialization, such as its hemp consulting services division. The Company is
not certain that its products and
services will function as anticipated
or be desirable to its intended market. Also, some of
the Company’s products and services may have
limited functionalities, which may limit
their appeal to consumers and put the
Company at a competitive disadvantage. If the Company’s
current or future products and
services fail to function properly or if the Company does not
achieve or sustain market acceptance, it could
lose customers or could be subject to claims which could have a material
adverse effect on the Company business,
financial condition and operating results.
As is typical in
a new and rapidly evolving industry,
demand and market acceptance for
recently introduced products and services
are subject to a high level of uncertainty
and risk. Because the market for the
Company is new and evolving, it is
difficult to predict with any certainty the
size of this market and its growth
rate, if any. The Company cannot guarantee
that a market for the Company will
develop or that demand for Company services will
emerge or be sustainable. If the market
fails to develop, develops more slowly than expected or becomes
saturated with competitors, the Company’s business, financial condition
and operating results would be materially
adversely affected.
Our Business Can be Affected by Unusual Weather
Patterns
Hemp cultivation can be impacted by weather patterns and
these unpredictable weather patterns may impact our ability to consult, and our client’s corresponding ability to grow,
cultivate and harvest hemp. In addition, severe weather, including drought and hail, can destroy a hemp crop, which would have
a material impact on our hemp consulting division.
Our business and financial performance may be adversely
affected by downturns in the target markets that we serve or reduced demand for the types of products we sell.
Demand for the products we sell is often affected by general
economic conditions as well as product-use trends in our target markets. These changes may result in decreased demand for our
products. The occurrence of these conditions is beyond our ability to control and, when they occur, they may have a significant
impact on our sales and results of operations. The inability or unwillingness of our customers to pay a premium for our products
due to general economic conditions or a downturn in the economy may have a significant adverse impact on our sales and results
of operations.
The Company’s failure to continue to attract,
train, or retain highly qualified personnel could harm the Company’s business.
The Company’s
success also depends on the Company’s ability to attract, train, and
retain qualified personnel, specifically those with management and product development
skills. In particular, the Company must
hire additional skilled personnel to further
the Company’s research and development efforts. Competition for
such personnel is intense. If the Company does not
succeed in attracting new personnel or retaining and motivating the Company’s
current personnel, the Company’s
business could be harmed.
Risks Related to the Company
Uncertainty of profitability.
Our business strategy may result in increased volatility
of revenues and earnings. As we will only develop a limited number of products and services at a time, our overall success will
depend on a limited number of products and services, which may cause variability and unsteady profits and losses depending on
the products and services offered.
Our revenues and our profitability may be adversely affected
by economic conditions and changes in the market for medical and recreational marijuana. Our business is also subject to general
economic risks that could adversely impact the results of operations and financial condition.
Because of the anticipated nature of the products and
services that we will attempt to develop, it is difficult to accurately forecast revenues and operating results and these items
could fluctuate in the future due to a number of factors. These factors may include, among other things, the following:
|
|
|
|
·
|
Our ability to raise
sufficient capital to take advantage of opportunities and generate sufficient revenues to cover expenses.
|
|
·
|
Our ability to source
strong opportunities with sufficient risk adjusted returns.
|
|
·
|
Our ability to manage
our capital and liquidity requirements based on changing market conditions generally and changes in the developing legal medical
cannabis and recreational cannabis industries.
|
|
·
|
The acceptance of
the terms and conditions of our licenses and/or the acceptance of our royalties and fees.
|
|
·
|
The amount and timing
of operating and other costs and expenses.
|
|
·
|
The nature and extent
of competition from other companies that may reduce market share and create pressure on pricing and investment return expectations.
|
|
·
|
Adverse changes
in the national and regional economies in which we will participate, including, but not limited to, changes in our performance,
capital availability, and market demand.
|
|
·
|
Adverse changes
in the projects in which we plan to invest which result from factors beyond our control, including, but not limited to, a
change in circumstances, capacity and economic impacts.
|
|
·
|
Adverse developments
in the efforts to legalize cannabis or increased federal enforcement.
|
|
·
|
Changes in laws,
regulations, accounting, taxation, and other requirements affecting our operations and business.
|
|
·
|
Our operating results
may fluctuate from year to year due to the factors listed above and others not listed. At times, these fluctuations may be
significant.
|
Management of growth will be necessary for us to
be competitive.
Successful expansion of our business will depend on our
ability to effectively attract and manage staff, strategic business relationships, and shareholders. Specifically, we will need
to hire skilled management and technical personnel as well as manage partnerships to navigate shifts in the general economic environment.
Expansion has the potential to place significant strains on financial, management, and operational resources, yet failure to expand
will inhibit our profitability goals.
We are entering a potentially highly competitive
market.
The markets for ancillary businesses in the medical cannabis
and recreational cannabis industries are competitive and evolving. In particular, we face strong competition from larger companies
that may be in the process of offering similar products and services to ours. Many of our current and potential competitors have
longer operating histories, significantly greater financial, marketing and other resources and larger client bases than we have
(or may be expected to have).
Given the rapid changes affecting the global, national,
and regional economies generally and the medical cannabis and recreational cannabis industries, in particular, we may not be able
to create and maintain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Our success will depend on our ability to keep pace with any
changes in its markets, especially with legal and regulatory changes. Our success will depend on our ability to respond to, among
other things, changes in the economy, market conditions, and competitive pressures. Any failure by us to anticipate or respond
adequately to such changes could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, operating results, liquidity, cash
flow and our operational performance.
If we
fail to protect our intellectual property, our business could be adversely affected.
Our viability will depend, in
part, on our ability to develop and maintain the proprietary aspects of our technology and brands to distinguish our products
and services from our competitors' products and services. We rely on patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, and confidentiality
provisions to establish and protect our intellectual property.
Any infringement or misappropriation
of our intellectual property could damage its value and limit our ability to compete. We may have to engage in litigation to protect
the rights to our intellectual property, which could result in significant litigation costs and require a significant amount of
our time. In addition, our ability to enforce and protect our intellectual property rights may be limited in certain countries
outside the U.S., which could make it easier for competitors to capture market position in such countries by utilizing technologies
that are similar to those developed or licensed by us.
Competitors may also harm our
sales by designing products that mirror the capabilities of our products or technology without infringing on our intellectual
property rights. If we do not obtain sufficient protection for our intellectual property, or if we are unable to effectively enforce
our intellectual property rights, our competitiveness could be impaired, which would limit our growth and future revenue.
We may also find it necessary
to bring infringement or other actions against third parties to seek to protect our intellectual property rights. Litigation of
this nature, even if successful, is often expensive and time-consuming to prosecute and there can be no assurance that we will
have the financial or other resources to enforce our rights or be able to enforce our rights or prevent other parties from developing
similar technology or designing around our intellectual property.
Our trade secrets may be
difficult to protect.
Our success depends upon
the skills, knowledge and experience of our scientific and technical personnel, our consultants and advisors, as well as our
licensors and contractors. Because we operate in a highly competitive industry, we rely in part on trade secrets to protect
our proprietary technology and processes. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. We enter into confidentiality or
non-disclosure agreements with our corporate partners, employees, consultants, outside scientific collaborators, developers
and other advisors. These agreements generally require that the receiving party keep confidential and not disclose to third
parties confidential information developed by the receiving party or made known to the receiving party by us during the
course of the receiving party's relationship with us. These agreements also generally provide that inventions
conceived by the receiving party in the course of rendering services to us will be our exclusive property, and we enter into assignment
agreements to perfect our rights.
These confidentiality, inventions
and assignment agreements may be breached and may not effectively assign intellectual property rights to us. Our trade secrets
also could be independently discovered by competitors, in which case we would not be able to prevent the use of such trade secrets
by our competitors. The enforcement of a claim alleging that a party illegally obtained and was using our trade secrets could
be difficult, expensive and time consuming and the outcome would be unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the U.S. may be
less willing to protect trade secrets. The failure to obtain or maintain meaningful trade secret protection could adversely affect
our competitive position.
Our lack of patent and/or copyright protection and
any unauthorized use of our proprietary information and technology may affect our business.
We currently rely on a combination of protections by contracts,
including confidentiality and nondisclosure agreements, and common law rights, such as trade secrets, to protect our intellectual
property. However, we cannot assure you that we will be able to adequately protect our technology or other intellectual property
from misappropriation in the U.S. and abroad. This risk may be increased due to the lack of any patent and/or copyright protection.
Any patent issued to us could be challenged, invalidated or circumvented or rights granted thereunder may not provide a competitive
advantage to us. Furthermore, patent applications that we file may not result in issuance of a patent, or, if a patent is issued,
the patent may not be issued in a form that is advantageous to us. Despite our efforts to protect our intellectual property rights,
others may independently develop similar products, duplicate our products or design around our patents and other rights. In addition,
it is difficult to monitor compliance with, and enforce, our intellectual property rights on a worldwide basis in a cost-effective
manner. In jurisdictions where foreign laws provide less intellectual property protection than afforded in the U.S., our technology
or other intellectual property may be compromised, and our business could be materially adversely affected. If any of our proprietary
rights are misappropriated or we are forced to defend our intellectual property rights, we will have to incur substantial costs.
Such litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of our resources, including diverting the time and effort of our
senior management, and could disrupt our business, as well as have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, financial
condition and results of operations. We can provide no assurance that we will have the financial resources to oppose any actual
or threatened infringement by any third party. Furthermore, any patent or copyrights that we may be granted may be held by a court
to infringe on the intellectual property rights of others and subject us to the payment of damage awards.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
Because we will likely issue additional shares of
our common stock, investment in our company could be subject to substantial dilution.
Investors’ interests in our Company will be diluted
and investors may suffer dilution in their net book value per share when we issue additional shares. We are authorized to issue
100,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.00001 par value per share. As of October 31, 2019, there were 52,978,605 shares of
our common stock issued and outstanding. We anticipate that all or at least some of our future funding, if any, will be in the
form of equity financing from the sale of our common stock. If we do sell more common stock, investors’ investment in our
company will likely be diluted. Dilution is the difference between what you pay for your stock and the net tangible book value
per share immediately after the additional shares are sold by us. If dilution occurs, any investment in our company’s common
stock could seriously decline in value.
The sale of our stock could encourage short sales
by third parties, which could contribute to the future decline of our stock price.
In many circumstances, the provision of financing based
on the distribution of equity for companies that are traded on the OTCQB has the potential to cause a significant downward pressure
on the price of common stock. This is especially the case if the shares being placed into the market exceed the market’s
ability to take up the increased stock or if we have not performed in such a manner to show that the equity funds raised will
be used to grow our business. Such an event could place further downward pressure on the price of our common stock. Regardless
of our activities, the opportunity exists for short sellers and others to
contribute to the future decline of our stock price. If there are significant short sales of our common stock, the price decline
that would result from this activity will cause the share price to decline more, which may cause other stockholders of the stock
to sell their shares, thereby contributing to sales of common stock in the market. If there are many more shares of our common
stock on the market for sale than the market will absorb, the price of our common shares will likely decline.
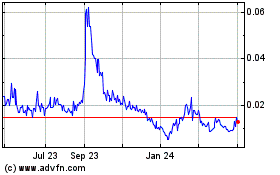
Trading in our common stock on the OTCQB has been
subject to wide fluctuations.
Our common stock is currently quoted for public trading
on the OTCQB. The trading price of our common stock has been subject to wide fluctuations. Trading prices of our common stock
may fluctuate in response to a number of factors, many of which will be beyond our control. The stock market has generally experienced
extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of companies
with no current business operation. There can be no assurance that trading prices and price earnings ratios previously experienced
by our common stock will be matched or maintained. These broad market and industry factors may adversely affect the market price
of our common stock, regardless of our operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price
of a company’s securities, securities class-action litigation has often been instituted. Such litigation, if instituted,
could result in substantial costs for us and a diversion of management’s attention and resources.
Our Certificate of Incorporation and by-laws provides
for indemnification of officers and directors at our expense and limit their liability which may result in a major cost to us
and hurt the interests of our shareholders because corporate resources may be expended for the benefit of officers and/or directors.
Our Certificate of Incorporation and By-Laws include provisions
that eliminate the personal liability of our directors for monetary damages to the fullest extent possible under the laws of the
State of Delaware or other applicable law. These provisions eliminate the liability of our directors and our shareholders for
monetary damages arising out of any violation of a director of his fiduciary duty of due care. Under Delaware law, however, such
provisions do not eliminate the personal liability of a director for (i) breach of the director's duty of loyalty, (ii) acts or
omissions not in good faith or involving intentional misconduct or knowing violation of law, (iii) payment of dividends or repurchases
of stock other than from lawfully available funds, or (iv) any transaction from which the director derived an improper benefit.
These provisions do not affect a director's liabilities under the federal securities laws or the recovery of damages by third
parties.
We do not intend to pay dividends on any investment
in the shares of stock of our Company and any gain on an investment in our Company will need to come through an increase in our
stock’s price, which may never happen.
We have never paid any cash dividends and currently do
not intend to pay any dividends for the foreseeable future. To the extent that we require additional funding currently not provided
for in our financing plan, our funding sources may prohibit the payment of a dividend. Because we do not intend to declare dividends,
any gain on an investment in our company will need to come through an increase in the stock’s price. This may never happen
and investors may lose all of their investment in our company.
Because our securities are subject to penny stock
rules, you may have difficulty reselling your shares.
Our shares of Common Stock are deemed to be "penny
stock" as that term is defined in Regulation Section 240.3a51-1 of the Securities and Exchange Commission. Penny stocks are
stocks: (a) with a price of less than $5.00 per share; (b) that are not traded on a "recognized" national exchange;
(c) whose prices are not quoted on the NASDAQ automated quotation system (NASDAQ - where listed stocks must still meet requirement
(a) above); or (d) in issuers with net tangible assets of less than $2,000,000 (if the issuer has been in continuous operation
for at least three years) or $5,000,000 (if in continuous operation for less than three years), or with average revenues of less
than $6,000,000 for the last three years.
Section 15(g) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and
Regulation 240.15g(c)2 of the Securities and Exchange Commission require broker dealers dealing in penny stocks to provide potential
investors with a document disclosing the risks of penny stocks and to obtain a manually signed and dated written receipt of the
document before effecting any transaction in a penny stock for the investor's account. Potential investors in our shares of Common
Stock are urged to obtain and read such disclosure carefully before
purchasing any shares of Common Stock that are deemed to be "penny stock".
Moreover, Regulation 240.15g-9 of the SEC requires broker
dealers in penny stocks to approve the account of any investor for transactions in such stocks before selling any penny stock
to that investor. This procedure requires the broker dealer to: (a) obtain from the investor information concerning his or her
financial situation, investment experience and investment objectives; (b) reasonably determine, based on that information, that
transactions in penny stocks are suitable for the investor and that the investor has sufficient knowledge and experience as to
be reasonably capable of evaluating the risks of penny stock transactions; (c) provide the investor with a written statement setting
forth the basis on which the broker dealer made the determination in (ii) above; and (d) receive a signed and dated copy of such
statement from the investor confirming that it accurately reflects the investor's financial situation, investment experience and
investment objectives. Compliance with these requirements may make it more difficult for investors in our shares of Common Stock
to resell their shares to third parties or to otherwise dispose of them. Holders should be aware that, according to SEC Release
No. 34-29093, dated April 17, 1991, the market for penny stocks suffers from patterns of fraud and abuse.
Our Management is aware of the abuses that have occurred
historically in the penny stock market. Although we do not expect to be in a position to dictate the behavior of the market or
of broker-dealers who participate in the market, Management will strive within the confines of practical limitations to prevent
the described patterns from being established with respect to our securities.
FINRA sales practice requirements may also limit
a stockholder’s ability to buy and sell our stock.
In addition to the “penny stock” rules described
above, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (known as “FINRA”) has adopted rules that require that in recommending
an investment to a customer, a broker-dealer must have reasonable grounds for believing that the investment is suitable for that
customer. Prior to recommending speculative low priced securities to their non-institutional customers, broker-dealers must make
reasonable efforts to obtain information about the customer’s financial status, tax status, investment objectives and other
information. Under interpretations of these rules, FINRA believes that there is a high probability that speculative low priced
securities will not be suitable for at least some customers. FINRA requirements make it more difficult for broker-dealers to recommend
that their customers buy our common shares, which may limit your ability to buy and sell our stock and have an adverse effect
on the market for our shares.
Since our shares of Common Stock are thinly traded
it is more susceptible to extreme rises or declines in price, and you may not be able to sell your shares at or above the price
paid.
Since our shares of Common Stock are thinly traded its
trading price is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to extreme fluctuations in response to various factors, many
of which are beyond our control, including (but not necessarily limited to): the trading volume of our shares, the number of analysts,
market-makers and brokers following our shares of Common Stock, new products or services introduced or announced by us or our
competitors, actual or anticipated variations in quarterly operating results, conditions or trends in our business industries,
additions or departures of key personnel, sales of our shares of Common Stock and general stock market price and volume fluctuations
of publicly traded, and particularly microcap, companies.
Investors may have difficulty reselling shares of our
Common Stock, either at or above the price they paid for our stock, or even at fair market value. The stock markets often experience
significant price and volume changes that are not related to the operating performance of individual companies, and because our
shares of Common Stock are thinly traded it is particularly susceptible to such changes. These broad market changes may cause
the market price of our shares of Common Stock to decline regardless of how well we perform as a company. In addition, there is
a history of securities class action litigation following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities.
Although there is no such litigation currently pending or threatened against us, such a suit against us could result in the incursion
of substantial legal fees, potential liabilities and the diversion of management’s attention and resources from our business.
Moreover, and as noted below, our shares are currently traded on the OTCQB and are subject to the penny stock regulations. Price
fluctuations in such shares are particularly volatile and subject to potential manipulation by market-makers, short-sellers and
option traders.
White Lion will pay less than the then-prevailing
market price for our common stock.
Our common stock to be issued to White Lion pursuant to
the Investment Agreement dated October 11, 2019 will be purchased at 97% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock the five
Business Day prior to the Closing Date. White Lion has a financial incentive to sell our common stock immediately upon receiving
the shares to realize the profit equal to the difference between the discounted price and the market price. If White Lion sells
the shares, the price of our common stock could decrease. If our stock price decreases, White Lion may have a further incentive
to sell the shares of our common stock that it holds. These sales may have a further impact on our stock price.
Your ownership interest may be diluted and the
value of our common stock may decline by our exercising the Purchase Notice right pursuant to the investment agreement
with White Lion.
Pursuant to the investment agreement with White Lion,
when we deem it necessary, we may raise capital through the private sale of our common stock to White Lion at a discounted
price. Because the Purchase Notice price is lower than the prevailing market price of our common stock, to the extent that
the Purchase Notice right is exercised, your ownership interest may be diluted.
We may not have access to the full amount available
under the investment agreement with White Lion.
Our ability to draw down funds and sell shares under the
investment agreement with White Lion requires that the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part to be declared
effective and continue to be effective. The registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part registers the resale
of 34,090,909 shares issuable under the investment agreement with White Lion, and our ability to sell any remaining shares issuable
under the investment with White Lion is subject to our ability to prepare and file one or more additional registration statements
registering the resale of these shares. These registration statements may be subject to review and comment by the staff of the
Securities and Exchange Commission, and will require the consent of our independent registered public accounting firm. Therefore,
the timing of effectiveness of these registration statements cannot be assured. The effectiveness of these registration statements
is a condition precedent to our ability to sell all of the shares of our common stock to White Lion under the investment agreement.
Even if we are successful in causing one or more registration statements registering the resale of some or all of the shares issuable
under the investment agreement with White Lion to be declared effective by the Securities and Exchange Commission in a timely
manner, we may not be able to sell the shares unless certain other conditions are met. For example, we might have to increase
the number of our authorized shares in order to issue the shares to White Lion. Increasing the number of our authorized shares
will require board and stockholder approval. Accordingly, because our ability to draw down any amounts under the investment agreement
with White Lion is subject to a number of conditions, there is no guarantee that we will be able to draw down any portion or all
of the proceeds of $7,500,000 under the investment with White Lion.
Certain restrictions on the extent of puts and the
delivery of advance notices may have little, if any, effect on the adverse impact of our issuance of shares in connection with
the investment agreement with White Lion, and as such, White Lion may sell a large number of shares, resulting in substantial
dilution to the value of shares held by existing stockholders.
White Lion has agreed, subject to certain exceptions listed
in the investment agreement, to refrain from holding an amount of shares which would result in White Lion or its affiliates owning
more than 4.99% of the then-outstanding shares of our common stock at any one time. These restrictions, however, do not prevent
White Lion from selling shares of our common stock received in connection with a Purchase Notice, and then receiving additional
shares of our common stock in connection with a subsequent Purchase Notice. In this way, White Lion could sell more than 4.99%
of the outstanding common stock in a relatively short time frame while never holding more than 4.99% at one time.
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Prospectus may contain certain “forward-looking”
statements as such term is defined by the SEC in its rules, regulations and releases, which represent the registrant’s expectations
or beliefs, including but not limited to, statements concerning the registrant’s operations, economic performance, financial
condition, growth and acquisition strategies, investments, and future operational plans. For this purpose, any statements contained
herein that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Without limiting the generality
of the foregoing, words such as “may,” “will,”
“expect,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “intent,” “could,” “estimate,”
“might,” “plan,” “predict” or “continue” or the negative or other variations thereof
or comparable terminology are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements by their nature involve substantial
risks and uncertainties, certain of which are beyond the registrant’s control, and actual results may differ materially
depending on a variety of important factors, including uncertainty related to acquisitions, governmental regulation, managing
and maintaining growth, the operations of the Company and its subsidiary, volatility of stock price, federal enforcement and state
enforcement, and any other factors discussed in this and other registrant filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
The risks and uncertainties and other factors include
but are not limited to those set forth under “Risk Factors” of this Prospectus. Given these risks and uncertainties,
readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. All subsequent written and oral forward-looking
statements attributable to us or to persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by these cautionary
statements. Except as otherwise required by applicable law, we undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking
statements or the risk factors described in this Prospectus or in the documents we incorporate by reference, whether as a result
of new information, future events, changed circumstances or any other reason after the date of this Prospectus.
Actual events or results may differ materially from those
discussed in forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including, without limitation, the risks outlined under
“Risk Factors” and matters described in Prospectus generally. In light of these risks and uncertainties, there can
be no assurance that the forward-looking statements contained in this Prospectus will in fact occur. We caution you not to place
undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. In addition to the information expressly required to be included in this Prospectus,
we will provide such further material information, if any, as may be necessary to make the required statements, in light of the
circumstances under which they are made, not misleading.
Except as required by federal securities laws, we do not
intend to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
USE OF PROCEEDS
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares
of our common stock by the selling stockholders. However, we will receive proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock
pursuant to our exercise of the Purchase Notice offered by White Lion Capital, LLC. We will use these proceeds for general corporate
and working capital purposes and acquisitions or assets, businesses or operations or for other purposes that our board of directors,
in its good faith, deems to be in the best interest of the Company. We may choose to take
advantage of Colorado Bill HB-19-1090, which was recently passed into Colorado law, effective November 1, 2019. This law allows
publicly traded corporations to apply for and qualify for the ownership of Colorado cannabis licenses.
We will pay for expenses of this offering, except that
the selling stockholder will pay any broker discounts or commissions or equivalent expenses and expenses of its legal counsel
applicable to the sale of its shares.
DILUTION
The sale of our common stock to White Lion Capital, LLC
in accordance with the Investment Agreement dated October 11, 2019 will have a dilutive impact on our stockholders. As a result,
our net loss per share could increase in future periods and the market price of our common stock could decline. In addition, the
lower our stock price is at the time we exercise our Purchase Notice, the more shares of our common stock we will have to issue
to White Lion in order to drawdown pursuant to the investment agreement. If our stock price decreases during the pricing period,
then our existing stockholders would experience greater dilution.
THE OFFERING
Investment Agreement with White Lion Capital, LLC
On October 11, 2019, we entered into an investment agreement
with White Lion Capital, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“White Lion”). Pursuant to the terms of the investment
agreement, White Lion committed to purchase up to $7,500,000 of our common stock over a period of up to 36 months. From time to
time during the 36 month period commencing from the effectiveness of the registration statement, we may deliver a Purchase Notice
to White Lion which states the dollar amount that we intend to sell to White Lion on a date specified in the Purchase Notice.
The maximum investment amount per notice must be no more than 250% of the average daily trading dollar volume of our common stock
for the five (5) consecutive trading days immediately prior to date of the applicable Purchase Notice. The purchase price per
share to be paid by White Lion will be the 97% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock the five Business Day prior to the
Closing Date.
In connection with the investment agreement with White
Lion, we also entered into a registration rights agreement with White Lion, pursuant to which we agreed to use our best efforts
to, within 60 business days of October 11, 2019, file with the Securities and Exchange Commission a registration statement, covering
the resale of 34,090,909 shares of our common stock underlying the investment agreement with White Lion.
The 34,090,909 shares being offered pursuant to the investment
agreement with White Lion represents 64.34% of the shares issued and outstanding, assuming that the selling stockholders will
sell all of the shares offered for sale. The 34,090,909 shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus represent 117.04% of
the shares issued and outstanding held by non-affiliates of our company. The investment agreement with White Lion is not transferable
and any benefits attached thereto may not be assigned.
At an assumed purchase price under the Investment Agreement
of $0.21 (equal to 97% of the closing price of our common stock of $0.22 on October 22, 2019, we will be able to receive up to
$7,159,090 in gross proceeds, assuming the sale of the entire 34,090,909 Purchase Notice Shares being registered hereunder pursuant
to the Investment Agreement. At an assumed purchase price of $0.21 under the Investment Agreement, we would be required to register
1,623,376 additional shares to obtain the balance of $340,909 under the Investment Agreement. Due to the floating offering price,
we are not able to determine the exact number of shares that we will issue under the Investment Agreement.
There are substantial risks to investors as a result of
the issuance of shares of our common stock under the investment agreement with White Lion. These risks include dilution of stockholders’
percentage ownership, significant decline in our stock price and our inability to draw sufficient funds when needed.
We intend to sell White Lion periodically our common stock
under the investment agreement and White Lion will, in turn, sell such shares to investors in the market at the market price.
This may cause our stock price to decline, which will require us to issue increasing numbers of common shares to White Lion to
raise the same amount of funds, as our stock price declines.
The aggregate investment amount of $7,500,000 was determined
based on numerous factors, including the following: The proceeds received from any Purchase Notices tendered to White Lion under
the investment agreement will be used for general corporate and working capital purposes and acquisitions or assets, businesses
or operations or for other purposes that our board of directors, in its good faith deem to be in the best interest of the Company.
We may choose to take advantage of Colorado Bill HB-19-1090, which was recently passed into
Colorado law, effective November 1, 2019. This law allows publicly traded corporations to apply for and qualify for the ownership
of Colorado cannabis licenses.
We may have to increase the number of our authorized shares
in order to issue the shares to White Lion if we reach our current amount of authorized shares of common stock. Increasing the
number of our authorized shares will require board and stockholder approval. Accordingly, because our ability to draw down any
amounts under the investment agreement with White Lion is subject to a number of conditions, there is no guarantee that we will
be able to draw down any portion or all of the proceeds of $7,500,000 under the investment agreement with White Lion.
SELLING STOCKHOLDERS
This prospectus relates to the resale of 34,090,909 shares
of our common stock, par value $0.00001 per share, issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC (“White Lion”).
This prospectus relates to the resale of up to 34,090,909
shares of the Common Shares, issuable to White Lion, a selling stockholder pursuant to a Purchase Notice under an investment agreement
dated October 11, 2019, that we entered into with White Lion. The Investment Agreement permits us to Purchase Notices for
up to seven million, five hundred thousand dollars ($7,500,000) in shares of our common stock to White Lion over a period of up
to thirty-six (36) months or until $7,500,000 of such shares have been subject to Purchase Notices.
The selling stockholder may offer and sell, from time
to time, any or all of shares of our common stock to be sold to White Lion under the Investment Agreement dated October 11, 2019.
The following table sets forth certain information regarding
the beneficial ownership of shares of common stock by the selling stockholder as of October 11, 2019 and the number of shares
of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus. We believe that the selling stockholder has sole voting and investment
powers over its shares.
Because the selling stockholder may offer and sell all
or only some portion of the 34,090,909 shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus, the numbers in the
table below representing the amount and percentage of these shares of our common stock that will be held by the selling stockholder
upon termination of the offering are only estimates based on the assumption that the selling stockholder will sell all of its
shares of our common stock being offered in the offering.
The selling stockholder has not had any position or office,
or other material relationship with us or any of our affiliates over the past three years.
To our knowledge, the selling stockholder is not a broker-dealer
or an affiliate of a broker-dealer. We may require the selling stockholder to suspend the sales of the shares of our common stock
being offered pursuant to this prospectus upon the occurrence of any event that makes any statement in this prospectus or the
related registration statement untrue in any material respect or that requires the changing of statements in those documents in
order to make statements in those documents not misleading.
|
Name
of Selling Stockholder
|
|
Shares Owned by the
Selling Stockholder before the Offering(1)
|
|
|
Total
Shares Offered in the Offering
|
|
|
Number
of Shares to Be Owned by Selling Stockholder After the Offering and Percent of Total Issued and Outstanding Shares(1)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#
of
Shares(2)
|
|
%
of
Class(2),(3)
|
|
White Lion Capital, LLC(4)
|
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
34,090,909
|
|
|
34,090,909
|
|
64.34%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes
|
|
|
*
|
Less than 1%.
|
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance
with Securities and Exchange Commission rules and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to shares of
common stock. Shares of common stock subject to options and warrants currently exercisable, or exercisable within 60 days,
are counted as outstanding for computing the percentage of the person holding such options or warrants but are not counted
as outstanding for computing the percentage of any other person.
|
|
|
|
|
(2)
|
We have assumed that the selling stockholder
will sell all of the shares being offered in this offering.
|
|
|
|
|
(3)
|
Based on 52,978,605 shares of our common
stock issued and outstanding as of October 31, 2019. Shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus
by a selling stockholder are counted as outstanding for computing the percentage of the selling stockholder.
|
|
|
|
|
(4)
|
Dmitriy Slobodskiy has the
voting and dispositive power over the shares owned by White Lion Capital, LLC.
|
|
|
|
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
This prospectus relates to the resale of 34,090,909
shares of our common stock, par value $0.00001 per share, issuable to White Lion Capital, LLC (“White
Lion”).
This prospectus relates to the resale of up to
34,090,909 shares of the Common Shares, issuable to White Lion, a selling stockholder pursuant to a Purchase Notice under an
investment agreement dated October 11, 2019, that we entered into with White Lion. The Investment Agreement permits us
to issue, from time to time, Purchase Notices for up to seven million, five hundred thousand dollars ($7,500,000) in shares
of our common stock to White Lion over a period of up to thirty-six (36) months or until $7,500,000 of such shares have been
subject to a Purchase Notice.
The Investment Agreement with White Lion is not transferable.
At an assumed purchase price under the Investment
Agreement of $0.21 (equal to 97% of the closing price of our common stock of $0.22 on October 22, 2019, we will be able to
receive up to $7,159,090 in gross proceeds, assuming the sale of the entire 34,090,909 Purchase Notice Shares being
registered hereunder pursuant to the Investment Agreement. At an assumed purchase price of $0.21 under the Investment
Agreement, we would be required to register 1,623,376 additional shares to obtain the balance of $340,909 under the
Investment Agreement. Due to the floating offering price, we are not able to determine the exact number of shares that we
will issue under the Investment Agreement.
The selling stockholder may, from time to time, sell any
or all of shares of our common stock covered hereby on the OTCQB, or any other stock exchange, market or trading facility on which
the shares are traded or in private transactions. A selling stockholder may sell all or a portion of the shares being offered
pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices, at prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices or at negotiated
prices. A selling stockholder may use any one or more of the following methods when selling securities:
|
|
●
|
ordinary
brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
block trades in
which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the shares as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal
to facilitate the transaction;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
purchases by a broker-dealer
as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
an exchange distribution
in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
privately negotiated
transactions;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
in transactions
through broker-dealers that agree with the selling stockholder to sell a specified number of such securities at a stipulated
price per security;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
through the writing
or settlement of options or other hedging transactions, whether through an options exchange or otherwise;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
a combination of
any such methods of sale; or
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
●
|
any other method
permitted pursuant to applicable law.
|
The selling stockholder may also sell securities under
Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, if available, rather than under this prospectus.
Broker-dealers engaged by the selling stockholder may
arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the selling
stockholder (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of securities, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated,
but, except as set forth in a supplement to this prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary
brokerage commission in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction a markup or markdown in compliance
with FINRA IM-2440.
In connection with the sale of the securities or interests
therein, the selling stockholder may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions, which
may in turn engage in short sales of the securities in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The selling stockholder
may also sell securities short and deliver these securities to close out its short positions, or loan or pledge the securities
to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The selling stockholder may also enter into option or other transactions
with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or create one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to
such broker-dealer or other financial institution of securities offered by this prospectus, which securities such broker-dealer
or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
White Lion Capital, LLC is an underwriter within the meaning
of the Securities Act of 1933 and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters”
within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such
broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions
or discounts under the Securities Act of 1933. We are required to pay certain fees and expenses incurred by us incident to the
registration of the securities.
The selling stockholder will be subject to the prospectus
delivery requirements of the Securities Act of 1933 including Rule 172 thereunder.
The resale securities will be sold only through registered
or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the resale
securities covered hereby may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an
exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations under the Securities
Exchange Act of 1934, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale securities may not simultaneously engage in market
making activities with respect to the common stock for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M, prior to
the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the selling stockholder will be subject to applicable provisions of the Securities
Exchange Act of 1934 and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing of purchases
and sales of securities of the common stock by the selling stockholder or any other person. We will make copies of this prospectus
available to the selling stockholder and will inform it of the need to deliver a copy of this prospectus to each purchaser at
or prior to the time of the sale (including by compliance with Rule 172 under the Securities Act of 1933).
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES
Capital Stock
|
We are authorized to issue 5,000,000 shares
of Preferred stock, $0.01 par value, and 100,000,000 shares of Common stock, $0.00001 par value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Stock
As of October 31, 2019, we had 0 shares of preferred stock issued and outstanding.
Common Stock
As of October 31, 2019, 52,978,605, shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
The holders of our common stock have equal ratable rights
to dividends from funds legally available if and when declared by our board of directors and are entitled to share ratably in
all of our assets available for distribution to holders of common stock upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up of our affairs.
Our common stock does not provide the right to a preemptive, subscription or conversion rights and there are no redemption or
sinking fund provisions or rights. Our common stock holders are entitled to one non-cumulative vote per share on all matters on
which stockholders may vote.
All shares of common stock now outstanding are fully paid
for and non-assessable. We refer you to our certificate of incorporation, bylaws and the applicable statutes of the state of Delaware
for a more complete description of the rights and liabilities of holders of our securities. All material terms of our common stock
have been addressed in this section.
Holders of shares of our common stock do not have cumulative
voting rights, which means that the holders of more than 50% of the outstanding shares, voting for the election of directors,
can elect all of the directors to be elected, if they so choose, and, in that event, the holders of the remaining shares will
not be able to elect any of our directors.
Dividends
We have not declared or paid dividends on our common stock
since our formation, and we do not anticipate paying dividends in the foreseeable future. Declaration or payment of dividends,
if any, in the future, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on our then current financial condition,
results of operations, capital requirements and other factors deemed relevant by the Board of Directors. There are no contractual
restrictions on our ability to declare or pay dividends. Consequently, you will only realize an economic gain on your investment
in our common stock if the price appreciates. You should not purchase our common stock expecting to receive cash dividends. Since
we do not anticipate paying dividends, and if we are not successful in establishing an orderly public trading market for our shares,
then you may not have any manner to liquidate or receive any payment on your investment. Therefore, our failure to pay dividends
may cause you to not see any return on your investment even if we are successful in our business operations. In addition, because
we may not pay dividends in the foreseeable future, we may have trouble raising additional funds which could affect our ability
to expand our business operations.
Warrants
In connection with his appointment
to the Company’s board of directors on November 19, 2014, the Company granted its independent board member, Vincent “Tripp”
Keber, warrants to purchase up to two hundred and fifty thousand (250,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three
cents ($0.63) per share, exercisable within five (5) years of the date of issuance on November 19, 2014. Concurrently, the Company
agreed to award Mr. Keber an option to purchase three hundred thousand (300,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of
sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants and options expire on November 19, 2019.
On August 31, 2017, the Company
issued Anthony Baroud warrants to purchase up to fifty thousand (50,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.93
in a cashless transaction. The warrants expired on March 1, 2018.
On December 31, 2018, pursuant
to the Company’s Equity Incentive Plan, the Company issued an aggregate of 895,000 warrants to the following persons to
purchase common stock in cashless transactions, with an aggregate value of $204,995.
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Michael Schwanbeck warrants to purchase twenty-five thousand (25,000)
shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Mitchell Day warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common
stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Tad Mailander warrants to purchase one hundred thousand (100,000) shares
of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Tyler A. Schloesser warrants to purchase one hundred and fifty thousand
(150,000) shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued April Robertson warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common
stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust four hundred thousand (400,000)
shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Ellis Smith one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Jon Workman one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
|
As of December 31, 2018, and
the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, the Company had the following warrant activity:
|
|
|
Common
Stock Warrants
|
|
Weighted
Average Grant Date Fair Value
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2015
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2016
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2017
|
|
|
300,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
1,685,000
|
|
|
|
0.58
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired
or forfeited
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Outstanding
at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
|
Vested
at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
Options
In addition to the warrants as described above, on November
19, 2014, the Company granted its Vincent “Tripp” Keber, its former independent board member, an option to purchase
three hundred thousand (300,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants
and options expire on November 19, 2019. None have been exercised.
EXPERTS
AND COUNSEL
The financial statements of our company included in this
prospectus, for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, were audited by L&L CPAs to the extent and for the period
set forth in their report appearing elsewhere in the prospectus, and are included in reliance upon such report given upon the
authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
Mailander Law Office, Inc. will render a legal opinion
as to the validity of the shares of the common stock to be registered hereby.
INTEREST OF NAMED EXPERTS AND COUNSEL
No expert named in the registration statement of which
this prospectus forms a part as having prepared or certified any part thereof (or is named as having prepared or certified a report
or valuation for use in connection with such registration statement) or counsel named in this prospectus as having given an opinion
upon the validity of the securities being offered pursuant to this prospectus, or upon other legal matters in connection with
the registration or offering such securities was employed for such purpose on a contingency basis. Also at the time of such preparation,
certification or opinion or at any time thereafter, through the date of effectiveness of such registration statement or that part
of such registration statement to which such preparation, certification or opinion relates, no such person had, or is to receive,
in connection with the offering, a substantial interest, as defined in Item 509 of Regulation SK, in our company or any of its
parents or subsidiaries. Nor was any such person connected with our company or any of its parents or subsidiaries as a promoter,
managing or principal underwriter or voting trustee.
INFORMATION WITH RESPECT TO OUR COMPANY
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and subsidiary is a publicly
listed company quoted on the OTCQB under the symbol “AMMJ”. We are based in Denver, Colorado and operate a fully-integrated
business model that features end-to-end solutions for businesses operating in regulated cannabis industry in states and countries
where cannabis is regulated and/or has been de-criminalized for medical use and/or legalized for recreational use. We provide
advisory and consulting services specific to this industry, design industry-specific products and facilities, and manage a strategic
group partnership that offers both exclusive and non-exclusive customer products commonly used in the industry.
We are a Delaware corporation formed on September 24,
2001 with the name Naturewell, Inc., which became Brazil Interactive Media, Inc. (“BIMI”) on March 13, 2013 pursuant
to a merger transaction that resulted in the Company becoming the owner of a Brazilian interactive television technology and television
production company, BIMI, Inc. We became American Cannabis Company, Inc. on September 29, 2014, pursuant to an Agreement and Plan
of Merger dated May 15, 2014 (the “Merger Agreement”) between the Company, Cannamerica Corp. (“Merger Sub”),
a wholly-owned subsidiary of BIMI, and Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. d/b/a American Cannabis Consulting (“American Cannabis
Consulting”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, which was consummated and became effective on September 29, 2014, Merger
Sub was merged with and into American Cannabis Consulting through a reverse triangular merger transaction (the “Reverse
Merger”), we changed our name to “American Cannabis Company, Inc.”, and our officers and directors in office
prior to the Merger Agreement resigned and American Cannabis Consulting appointed new officers and directors to serve our Company.
In concert with the Merger Agreement, we consummated a complete divestiture of BIMI, Inc. pursuant to a Separation and Exchange
Agreement dated May 16, 2014 (the “Separation Agreement”) between the Company, BIMI, Inc., a Delaware corporation
and wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, and Brazil Investment Holding, LLC (“Holdings”), a Delaware limited liability
company. On October 10, 2014, we changed our stock symbol from BIMI to AMMJ.
Industry and Regulatory Overview
As of October 31, 2019, 33 states, the District of Columbia
and Guam have laws legalized cannabis in some form for either medicinal or recreational use governed by state specific laws and
regulations.
These state laws are in conflict with the federal Controlled
Substances Act, which makes cannabis use and possession illegal on a national level. However, on August 29, 2013, the U.S. Department
of Justice issued a memorandum providing that where states and local governments enact laws authorizing cannabis-related use,
and implement strong and effective regulatory and enforcement systems, the federal government will rely upon states and local
enforcement agencies to address cannabis activity through the enforcement of their own state and local narcotics laws. The memorandum
further stated that the U.S Justice Department’s limited investigative and prosecutorial resources will be focused on eight
priorities to prevent unintended consequences of the state laws, including distribution of cannabis to minors, preventing the
distribution of cannabis from states where it is legal to states where it is not, and preventing money laundering, violence and
drugged driving.
On December 11, 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice issued
another memorandum with regard to its position and enforcement protocol with regard to Indian Country, stating that the eight
priorities in the previous federal memo would guide the United States Attorneys' cannabis enforcement
efforts in Indian Country. On December 16, 2014, as a component of the federal spending bill, the Obama administration enacted
regulations that prohibit the Department of Justice from using funds to prosecute state-based legal medical cannabis programs.
As of June 28, 2016, in addition to the 25 states, the District of Columbia and Guam, which had already passed legislation allowing
citizens to use cannabis in some form.
On December 11, 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice issued
another memorandum with regard to its position and enforcement protocol with regard to Indian Country, stating that the eight
priorities in the August 29, 2013 federal memo would guide the United States Attorneys' cannabis enforcement efforts in Indian
Country. On December 16, 2014, as a component of the federal spending bill, the Obama administration enacted regulations that
prohibit the Department of Justice from using funds to prosecute state-based legal medical cannabis programs.
On January 4, 2018, Attorney General Jeff Sessions issued
a memorandum for all United States Attorneys concerning cannabis enforcement. Mr. Sessions rescinded all previous prosecutorial
guidance issued by the Department of Justice regarding cannabis , including the August 29, 2013 memorandum. Mr. Sessions stated
that U.S. Attorneys must decide whether or not to pursue prosecution of cannabis activity based upon factors including: the seriousness
of the crime, the deterrent effect of criminal prosecution, and the cumulative impact of particular crimes on the community. Mr.
Sessions reiterated that the cultivation, distribution and possession of cannabis continues to be a crime under the U.S. Controlled
Substances Act.
Investment Agreement with White Lion Capital, LLC
On October 11, 2019, we entered into an investment agreement
with White Lion Capital, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“White Lion”). Pursuant to the terms of the investment
agreement, White Lion committed to purchase up to $7,500,000 of our common stock over a period of up to 36 months. From time to
time during the 36 month period commencing from the effectiveness of the registration statement, we may deliver a Purchase Notice
to White Lion which states the dollar amount that we intend to sell to White Lion on a date specified in the Purchase Notice.
The maximum investment amount per notice must be no more than 250% of the average daily trading dollar volume of our common stock
for the five (5) consecutive trading days immediately prior to date of the applicable Purchase Notice. The purchase price per
share to be paid by White Lion will be the 97% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock the five Business Day prior to the
Closing Date.
In connection with the investment agreement with White
Lion, we also entered into a registration rights agreement with White Lion, pursuant to which we agreed to use our best efforts
to, within 60 business days of October 11, 2019, file with the Securities and Exchange Commission a registration statement, covering
the resale of 34,090,909 shares of our common stock underlying the investment agreement with White Lion.
The 34,090,909 shares being offered pursuant to the investment
agreement with White Lion represents 64.34% of the shares issued and outstanding, assuming that the selling stockholders will
sell all of the shares offered for sale. The 34,090,909 shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus represent 117.04% of
the shares issued and outstanding held by non-affiliates of our company. The investment agreement with White Lion is not transferable
and any benefits attached thereto may not be assigned.
At an assumed purchase price under the Investment Agreement
of $0.21 (equal to 97% of the closing price of our common stock of $0.22 on October 22, 2019, we will be able to receive up to
$7,159,090 in gross proceeds, assuming the sale of the entire 34,090,909 Purchase Notice Shares being registered hereunder pursuant
to the Investment Agreement. At an assumed purchase price of $0.21 under the Investment Agreement, we would be required to register
1,623,376 additional shares to obtain the balance of $340,909 under the Investment Agreement. Due to the floating offering price,
we are not able to determine the exact number of shares that we will issue under the Investment Agreement.
There are substantial risks to investors as a result of
the issuance of shares of our common stock under the investment agreement with White Lion. These risks include dilution of stockholders’
percentage ownership, significant decline in our stock price and our inability to draw sufficient funds when needed.
We intend to sell White Lion periodically our common stock
under the investment agreement and White Lion will, in turn, sell such shares to investors in the market at the market price.
This may cause our stock price to decline, which will require us to issue increasing numbers of common shares to White Lion to
raise the same amount of funds, as our stock price declines.
The aggregate investment amount of $7,500,000 was determined
based on numerous factors, including the following: The proceeds received from any Purchase Notices tendered to White Lion under
the investment agreement will be used for general corporate and working capital purposes and acquisitions or assets, businesses
or operations or for other purposes that our board of directors, in its good faith deem to be in the best interest of the Company.
We may have to increase the number of our authorized shares
in order to issue the shares to White Lion if we reach our current amount of authorized shares of common stock. Increasing the
number of our authorized shares will require board and stockholder approval. Accordingly, because our ability to draw down any
amounts under the investment agreement with White Lion is subject to a number of conditions, there is no guarantee that we will
be able to draw down any portion or all of the proceeds of $7,500,000 under the investment agreement with White Lion.
There are substantial risks to investors as a result of
the issuance of shares of our common stock under the investment agreement with White Lion. These risks include dilution of stockholders’
percentage ownership, significant decline in our stock price and our inability to draw sufficient funds when needed.
There are no broker fees or commissions with respect to
the Investment Agreement and Registration Rights Agreement payable for any Purchase Notice. Other than as discussed below, we
have not entered into any prior transactions with White Lion or its affiliates.
Business Overview
We primarily operate within two
divisions within the regulated cannabis industry: (i) consulting and professional services; and, (ii) the sale of products and
equipment commonly utilized in the cultivation, processing, transportation or retail sale of cannabis. We do not hold any ownership
interests, direct or indirect, in businesses which hold a license to produce and/or sell cannabis. We do not sell, cultivate,
manufacture, or transact cannabis. However, we may choose to take advantage of Colorado Bill HB-19-1090, which was recently passed
into Colorado law, effective November 1, 2019. This law allows publicly traded corporations to apply for and qualify for the ownership
of Colorado cannabis licenses.
Consulting Services
We offer consulting services
for companies associated with the cannabis industry in all stages of development. Our service offerings include the following:
|
•
|
|
Cannabis
Business Planning. Our commercial cannabis business planning services are structured to help those pursuing state based
operational licensing to create and implement effective, long-range business plans. We work with our clients to generate a
comprehensive strategy based on market need and growth opportunities, and be a partner through site selection, site design,
the development of best operating practices, the facility build-out process, and the deployment of products. We understand
the challenges and complexities of the regulated commercial cannabis market and we have the expertise to help client businesses
thrive.
|
|
•
|
|
Cannabis
Business License Applications. Our team has the experience necessary to help clients obtain approval for their state license
and ensure their company remains compliant as it grows. We have crafted successful, merit-based medical cannabis business
license applications in multiple states and we understand the community outreach and coordination of services necessary to
win approval. As part of the process for crafting applications, we collaborate with clients to develop business protocols,
safety standards, a security plan, and a staff training program. Depending on the nature of our clients’ businesses
and needs, we can work with our clients to draft detailed cultivation plans, create educational materials for patients, or
design and develop products that comply with legal state guidelines
|
|
•
|
|
Cultivation
Build-out Oversight Services. We offer cultivation build-out consulting as part of our Cannabis Business Planning service
offerings. We help clients ensure their project timeline is being met, facilities are being designed with compliance and the
regulated cannabis industry in mind, and that facilities are built to the highest of quality standards for cannabis production
and/or distribution. This enables a seamless transition from construction to cultivation, ensuring that client success is
optimized and unencumbered by mismanaged construction projects.
|
|
•
|
|
Cannabis
Regulatory Compliance. Based on our thorough understanding of regulated commercial cannabis laws nationwide, we can help
client cultivation operations, retail dispensaries and/or infused-product kitchen businesses to meet and maintain regulatory
compliance for both medical and recreational markets. We partner with our clients to establish standard operating procedures
in accordance with their state’s regulation and help them implement effective staff hiring and training practices to
ensure that employees adhere to relevant guidelines.
|
|
•
|
|
Compliance
Audit Services. Our regulatory compliance service offerings include compliance auditing. The regulated cannabis industry
is developing rapidly with evolving laws and regulations, and navigating through current and new regulations and systems can
be tedious and daunting. To assist our clients in addressing these challenges, we offer compliance audits performed by
our experienced and knowledgeable staff; our team members maintain comprehensive oversight of the cannabis industry while
staying up-to-date on current and new laws and regulations. Our compliance audits assess various regulatory topics, including:
(1) licensing requirements; (2) visitor intake procedures; (3) seed-to-sale inventory tracking; (4) proper waste disposal
procedures; (5) recordkeeping and documentation requirements; (6) cannabis transportation procedures; (7) packaging and labeling
requirements; (8) security requirements; (9) product storage; (10) mandatory signage; and (11) preparedness for state and
local inspections.
|
|
•
|
|
Cannabis
Business Growth Strategies. Our team shares its collective knowledge and resources with our clients to create competitive,
forward-looking cannabis business growth strategies formulated to minimize risk and maximize potential. We customize individual
plans for the unique nature of our client businesses, their market and big-picture goals, supported with a detailed analysis
and a thorough command of workflow best practices, product strategies, sustainability opportunities governed by a core understanding
or regulatory barriers and/or opportunities.
|
|
•
|
|
Cannabis
Business Monitoring. The regulated commercial cannabis industry is constantly growing and shifting, and the ongoing monitoring
of a cannabis business allows it to remain responsive to evolving consumer demands and state regulations as well as potential
operations problems. We offer fully-integrated business analysis solutions. Our monitoring services include sales tracking,
market assessment, loss prevention strategies, review of operational efficiency and workflow recommendations. Additionally,
our services include Strength, Weakness, Opportunity and Threat (“SWOT”) analysis, where we analyze client operations
to pinpoint strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Our SWOT analyses allow clients to focus their efforts and resources
on the most critical areas along these dimensions.
|
|
•
|
|
Hemp
Business Consulting. We recently began
a new business consulting division called “American Hemp Services,” which offers hemp producers with consulting
and professional services including business plan creation, greenhouse and farm design, license acquisition, seed sales, hemp
processing, operational deployment, and crop improvement. Furthermore, the Company seeks to partner with accredited universities
nationwide to further the advancement of hemp related research.
|
Equipment and Supplies
In addition to professional consulting
services, we operate an equipment and supplies division for customers in the cannabis industry, including through American Cultivator
Co., our Group Purchasing Organization that enables customers to procure commonly used cultivation supplies at low prices associated
with high volume purchases. Our major product offerings include the following:
|
•
|
|
The
Satchel™. The Satchel was invented in response to regulatory changes in Colorado and elsewhere that require child-proof
exit containers. The Satchel is a pouch-like case designed as a high-quality, child-proof exit package solution for the regulated
cannabis industry. The Satchel meets child-safety requirements of the Consumer Products Safety Commission (“CPSC”),
making it compliant in all states, and the Satchel’s drawstring and toggle lock fulfills the requirements of the Poison
Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 (16 CFR part 1700). There are few products meeting regulatory standards, and even fewer that
offer distinctive quality. The Satchel will meet all current exit packaging regulations, featuring a child-proof closure that
completely conceals the contents inside. On March 29, 2016, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office issued us Patent No.
9,296,524 B2 for the Satchel.
|
|
•
|
|
SoHum
Living Soil™. The right grow methodology is critical to the success of any cannabis cultivation operation, and SoHum
Living Soil™ is our solution to ensure that our customers can implement an optimal methodology that will maximize quality
and yields while simplifying the cultivation process and reducing risk of operator error and test failure. The SoHum medium
is a fully amended Just-add-water soil that contains none of the synthetic components found in other potting mixes and requires
no chemical additives to spur growth. Compared with comparable methodologies, SoHum Living Soil™ offers a number of
key advantages, including: (1) consistent Pyto-pharmaceutical-grade product quality; (2) improved plant resistance to disease;
and (3) reduced operator error.
|
|
•
|
|
High
Density Cultivation System (HDCS™). A key metric in the success of a cultivation operation is the maximization
of available space to grow. Our High Density Cultivation System is a solution designed to ensure that space is used in the
most efficient manner possible. The system takes advantage of the existence of vertical space, with racks installed vertically
and placed on horizontal tracking to eliminate multiple isles and create multiple levels of space with which to grow plants.
The High Density Cultivation System allows customers to increase production capacity without the need to add additional square
footage to the operation.
|
|
•
|
|
The
Cultivation Cube™. The Cultivation Cube™ is a self-contained, scalable cultivation system that is compliant
with regulatory guidelines. The Cultivation Cube™ allows commercial cannabis cultivation operations to maximize space,
yield and profit through an innovative design that provides a fully integrated growing solution. The Cultivation Cube utilizes
more lights per square foot than traditional grow systems, which translates to profit increases per square foot. The Cultivation
Cube™ is also stackable, which allows customers to achieve vertical gains and effectively doubles productive square-footage.
It is an ideal solution for commercial-scale cultivation within limited space, with numerous advantages over other traditional
grow systems, including: (1) flexibility to fit customer build-out sites; (2) efficient speed-to-market with fast delivery
and set-up; (3) increased security with limited access units; (4) risk mitigation through precision environmental controls;
and, (5) is compatible with lean manufacturing principles and operations.
|
|
•
|
|
Other
Products. We offer our clients a diverse array of commonly utilized product offerings from across all areas of the regulated
cannabis industry, including cultivation operations, medicinal and recreational cannabis dispensary operations, and infused-products.
Examples of products available through American Cultivator Co. include HID Ballasts, reflectors, MH and HPS bulbs, T5 fixtures,
mediums, nutrients and fertilizers, growing containers, flood tables, reservoirs, and various other supplies, including cleaning
products and office supplies. We also offer a Group Purchasing Organization (“GPO”) focused on disposables
to creates purchasing power by leveraging groups of businesses to obtain discounts from vendors based on the collective
buying power of the GPO.
|
Sales and Marketing
We sell our services and products
throughout the United States in states that have implemented regulated cannabis programs as well as Canada. We intend to expand
our offerings as more new countries, states and jurisdictions as they adopt state-regulated or Federal programs.
Research and Development
As a component of our equipment
and supplies offerings, from time-to-time we design and develop our own proprietary products to meet demand in markets where current
offerings are insufficient. These products include, but are not limited to: the Satchel™, Cultivation Cube™, So-Hum
Living Soils™ and the HDCS™. Costs associated with the development of new products are expensed as occurred as research
and development operating expenses. During the year ended December 31, 2018, our research and development costs were $590, as
compared to $2,403 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
Significant Customers
For the year ended December 31, 2018, three customers
accounted for 47.50% or more, respectively of the Company’s total product sales revenues, and four customers accounted for
70.65% or more respectively of the Company’s total service based revenue. For the year ended December 31, 2017, three customers
accounted 48.95% or more, respectively of the Company’s total product sales revenues, and four customers accounted for 40.18%
or more respectively of the Company’s total service based revenue.
Intellectual Property
On March 29, 2016, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
issued us Patent No. 9,296,524 B2 for the Satchel.
We may file for additional patent
protection as we deem appropriate to protect new products. We also had trademark applications pending to protect our branding
and logos. These pending applications included trademarks for the Cultivation Cube™ (stylized and/or with design logo),
our slogan, and two word marks and the logo associated with SoHum Living Soil™.
Competition
Our competitors include professional
services firms dedicated to the regulated cannabis industry as well as suppliers of equipment and supplies commonly utilized in
the cultivation, processing, or retail sale of cannabis. We compete in markets where cannabis has been legalized and regulated,
which includes various states within the United States, it’s territories and Indian Country therein and Canada. We expect
that the quantity and composition of our competitive environment will continue to evolve as the industry matures. Additionally,
increased competition is possible to the extent that new states and geographies enter the marketplace as a result of continued
enactment of regulatory and legislative changes that de-criminalize and regulate cannabis products. We believe that by being well
established in the industry, our experience and success to date, and continued expansion of service and product offerings in new
and existing locations are factors that mitigate the risk associated with operating in a developing competitive environment. Additionally,
the contemporaneous growth of the industry as a whole will result in new customers entering the marketplace, thereby further mitigating
the impact of competition on our operations and results.
Employees
As of December 31, 2018, we have 8 full-time employees, all of whom are U.S
based, primarily in Colorado at our Denver headquarters. None of our U.S employees are represented by a labor union.
DESCRIPTION OF PROPERTY
Our Offices
Our headquarters are located
at 5690 Logan Street, Unit A, Denver CO. 80216, where
we lease office space under a contract effective July 28, 2015, expiring on July 31, 2020. Under the terms of the lease,
payments are $4,500 per month for the first 36 months of the lease, and escalate thereafter.
We believe that our existing office facilities are adequate for our needs.
Should we require additional space at that time, or prior thereto, we believe that such space can be secured on commercially reasonable
terms.
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
None.
MARKET PRICE OF AND DIVIDENDS ON OUR COMMON EQUITY AND
RELATED STOCHOLDER MATTERS
Market information
Our common stock trades on the OTCQB. As
of October 31, 2019, there were 487 holders of record of our common stock.
The following table sets forth the quarterly high and
low sale prices for our common shares for the last two completed fiscal years and the subsequent interim periods. The prices set
forth below represent interdealer quotations, without retail markup, markdown or commission and may not be reflective of actual
transactions. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low closing sales prices of our common stock:
|
2019
|
|
High
|
|
Low
|
|
|
Quarter
Ended June 30
|
|
|
$
|
0.45
|
|
|
$
|
0.26
|
|
|
|
Quarter Ended March
31
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
|
$
|
0.33
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
High
|
|
|
|
Low
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended December
31
|
|
|
$
|
0.65
|
|
|
$
|
0.22
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended September
30
|
|
|
$
|
0.78
|
|
|
$
|
0.39
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended June
30
|
|
|
$
|
1.28
|
|
|
$
|
0.60
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended March
31
|
|
|
$
|
1.05
|
|
|
$
|
0.81
|
|
|
2017
|
|
High
|
|
Low
|
|
|
Quarter
ended December 31
|
|
|
$
|
1.36
|
|
|
$
|
0.51
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended September
30
|
|
|
$
|
1.26
|
|
|
$
|
0.45
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended June
30
|
|
|
$
|
0.76
|
|
|
$
|
0.35
|
|
|
|
Quarter ended March
31
|
|
|
$
|
1.53
|
|
|
$
|
0.62
|
|
On October 22, 2019, the closing price of our common stock
as reported by the OTC Markets Group was $0.22 per share.
Transfer Agent
Pacific Stock Transfer Company, located at 6725 Via Austi
Pkwy., #300, Las Vegas NV 89119 and telephone number of (702) 361-3033 is the registrar and transfer agent for our common stock.
Approximate Number of Equity Security Holders
As of October 31, 2019, there were approximately 487 holders
of record of our common stock. Because shares of the Company’s common stock are held by depositaries, brokers and other
nominees, the number of beneficial holders of the Company’s shares is substantially larger than the number of stockholders
of record.
Dividends
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our
common stock. We currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to increase our working capital and do not anticipate paying
any cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
|
Plan Category
|
Number of securities to be issued upon
exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights(1)
|
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding
options, warrants and rights(2)
|
Number
of securities remaining available for issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column
(a))(3)
|
|
Equity
compensation plans approved by security holders
|
−
|
−
|
−
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity
compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
250,000
|
$0.63
|
−
|
|
Options
Issued to Vincent “Tripp” Keber
|
300,000
|
$0.63
|
−
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
$0.59
|
|
|
Total
|
2,485,000
|
$0.61
|
−
|
|
(1)
|
|
Historically,
the Company has granted restricted shares that are subject to forfeiture. Pursuant to SEC guidance, these RSUs are not reportable
in the table above.
|
|
(2)
|
|
Historically,
the Company has granted restricted shares that are subject to forfeiture. Pursuant to SEC guidance, these RSUs are not reportable
in the table above. Restricted shares subject to forfeiture have a weighted average exercise price of $0.00.
|
|
(3)
|
|
The Company equity compensation grants to
date have been approved on a grant-by-grant basis, as opposed to under an umbrella equity compensation plan establishing
a total number of grants available.
|
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
Financial Statements
for the Years Ended December 31, 2018 and 2017
|
|
|
|
American Cannabis Company, Inc.
|
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered
Public Accounting firm
|
|
31
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
32
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
33
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’
Equity (Deficit)
|
|
34
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
35
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
36
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financial Statements
for the Three Month and Six Month Periods Ended June 30, 2019 and 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
51
|
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
52
|
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
53
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
54
|

|
19270
Jetton Road, 3rd Floor
Cornelius, NC 28031
Tel: 704-897-8336
Fax:704-919-5089
|
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING
FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and Subsidiary
Opinion on the Financial
Statements
We have audited the accompanying
consolidated balance sheets of American Cannabis Company Inc. and Subsidiary (“the Company”) as of December 31, 2018
and December 31, 2017 and the related consolidated statements of operations, statements of cash flows, stockholders’ deficit
and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”) for the years ended December 31, 2018
and December 31, 2017. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility
is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements
referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2018 and
December 31, 2017, and the results of its operations, changes in stockholders’ deficit and cash flows for the years then
ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the
responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated
financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal
securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards
of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial
statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we
engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain
an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness
of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing
procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing
procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and
disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates
made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide
a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ L&L CPAS, PA
L&L CPAS, PA
Certified Public Accountants
Cornelius, NC
The United States of America
April 15, 2019
We have served as the Company's auditor since August 2018.
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(AUDITED)
|
|
|
December 31,
2018
|
|
December 31,
2017
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and equivalents
|
|
$
|
1,086,565
|
|
|
$
|
1,648,087
|
|
|
Accounts receivable, net: (see note 3)
|
|
|
58,884
|
|
|
|
146,804
|
|
|
Deposits
|
|
|
4,500
|
|
|
|
4,500
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
61,005
|
|
|
|
35,757
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
56,376
|
|
|
|
11,326
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
1,267,331
|
|
|
|
1,846,474
|
|
|
Property and equipment - net:
|
|
|
8,037
|
|
|
|
11,782
|
|
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
|
$
|
1,275,369
|
|
|
$
|
1,858,256
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDER'S EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
$
|
32,931
|
|
|
$
|
28,002
|
|
|
Advances from clients
|
|
|
147,349
|
|
|
|
100,587
|
|
|
Warrant liability
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
895,860
|
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities
|
|
|
89,768
|
|
|
|
52,352
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
270,048
|
|
|
|
1,076,801
|
|
|
Shareholder's Equity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized; 0 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.00001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 51,513,064 and 51,434,050 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively
|
|
|
515
|
|
|
|
514
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
8,178,919
|
|
|
|
7,004,363
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(7,174,113
|
)
|
|
|
(6,223,422
|
)
|
|
Total Shareholder's Equity
|
|
|
1,005,321
|
|
|
|
781,455
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDER'S EQUITY
|
|
$
|
1,275,369
|
|
|
$
|
1,858,256
|
|
The accompanying notes are
an integral part of these audited consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(AUDITED)
|
|
|
For the year ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2018
|
|
2017
|
|
Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consulting services
|
|
$
|
395,840
|
|
|
$
|
2,054,484
|
|
|
Product and equipment
|
|
|
548,878
|
|
|
|
388,570
|
|
|
Shipping services
|
|
|
37,630
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total Revenues
|
|
|
982,349
|
|
|
|
2,443,054
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of consulting services
|
|
|
121,641
|
|
|
|
463,298
|
|
|
Cost of products and equipment
|
|
|
402,206
|
|
|
|
342,522
|
|
|
Total Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
523,847
|
|
|
|
805,820
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
|
458,502
|
|
|
|
1,637,234
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
868,294
|
|
|
|
1,042,889
|
|
|
Investor relations
|
|
|
20,983
|
|
|
|
34,554
|
|
|
Selling and marketing
|
|
|
293,241
|
|
|
|
278,542
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
590
|
|
|
|
2,403
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
|
|
1,183,109
|
|
|
|
1,358,388
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) from Operations
|
|
|
(724,607
|
)
|
|
|
278,846
|
|
|
Other Income (Expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest (expense)
|
|
|
(52
|
)
|
|
|
9,288
|
|
|
Stock based compensation (expense)
|
|
|
(73,742
|
)
|
|
|
(893,857
|
)
|
|
Bad debt recovery (expense)
|
|
|
(2,815
|
)
|
|
|
89,715
|
|
|
Settlement (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(118,450
|
)
|
|
Warrant (expense)
|
|
|
(204,955
|
)
|
|
|
(895,860
|
)
|
|
Other income
|
|
|
55,481
|
|
|
|
41,844
|
|
|
Total Other Income (Expense)
|
|
|
(226,084
|
)
|
|
|
(1,767,320
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Before Taxes
|
|
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Income tax expense (benefit)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCOME (LOSS)
|
|
$
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per common share
|
|
$
|
(0.02
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.03
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding
|
|
|
51,465,188
|
|
|
|
51,336,522
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these
audited consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES
IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
2018 AND 2017
(AUDITED)
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Additional
Paid-In
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
Total Stockholder's
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
Amount
|
|
Capital
|
|
Deficit
|
|
Equity
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2016
|
|
|
49,847,593
|
|
|
$
|
498
|
|
|
$
|
5,389,384
|
|
|
$
|
(4,734,948
|
)
|
|
$
|
654,934
|
|
|
APIC cashless warrants
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
228,250
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
228,250
|
|
|
Shares issued for PY conversion of debt and interest
|
|
|
237,885
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
(2
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash
|
|
|
909,390
|
|
|
|
9
|
|
|
|
602,684
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
602,693
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
430,227
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
391,698
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
391,702
|
|
|
Shares issued for legal settlement
|
|
|
8,955
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
5,999
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
6,000
|
|
|
Shares return to treasury on settlement
|
|
|
(100,000
|
)
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Shares issued on settlement
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
112,449
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
112450
|
|
|
Options issued on settlement
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
273,900
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
273,900
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2017
|
|
|
51,434,050
|
|
|
|
514
|
|
|
|
7,004,363
|
|
|
|
(6,223,422
|
)
|
|
|
781,455
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
29,014
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
APIC cashless warrants
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
204,955
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
204,955
|
|
|
Warrants to employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
895,859
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
895,860
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation granted to employees
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
48,500
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
48,500
|
|
|
Shares issued for cash
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Shares issued for settlements
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Options issued for settlements
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2018
|
|
|
51,513,064
|
|
|
$
|
515
|
|
|
$
|
8,178,919
|
|
|
$
|
(7,174,113
|
)
|
|
$
|
1,005,321
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these audited consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASHFLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
2018 AND 2017
(AUDITED)
|
|
|
2018
|
|
2017
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss ) to net cash (used in )
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bad debt expense (recovery)
|
|
|
2,815
|
|
|
|
(89,715
|
)
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
3,745
|
|
|
|
4,487
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation to employees
|
|
|
48,500
|
|
|
|
893,857
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation to service providers
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Warrant expense
|
|
|
204,955
|
|
|
|
895,860
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
85,104
|
|
|
|
107,362
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
(25,248
|
)
|
|
|
6,743
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
(45,050
|
)
|
|
|
(1,502
|
)
|
|
Advances from clients
|
|
|
46,762
|
|
|
|
(121,601
|
)
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities
|
|
|
37,416
|
|
|
|
15,628
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
4,929
|
|
|
|
(27,780
|
)
|
|
Accounts payable, related party
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(14,325
|
)
|
|
Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities
|
|
|
(561,522
|
)
|
|
|
180,540
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(4,629
|
)
|
|
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(4,629
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common shares
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
721,138
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
721,138
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCREASE IN CASH
|
|
|
(561,522
|
)
|
|
|
897,049
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
|
|
1,648,087
|
|
|
|
751,038
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT END OF YEAR
|
|
$
|
1,086,565
|
|
|
$
|
1,648,087
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid during the period for interest
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Cash paid during the period for income taxes, net
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Common Stock issued for debt converted in prior year
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
The
accompanying notes are an integral part of these audited consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN
CANNABIS COMPANY, INC. AND SUBISIDIARY
NOTES
TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2018 and 2017
Note 1.
Principles of Consolidation.
The
consolidated financial statements include the accounts of American Cannabis Company, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Hollister
& Blacksmith, Inc., doing business as American Cannabis Company, Inc. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Note 2. Description
of Business.
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and its wholly owned
subsidiary Company, Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc., doing business as American Cannabis Consulting (“American Cannabis
Consulting”), (collectively “the “Company”) are based in Denver, Colorado and operate a fully-integrated
business model that features end-to-end solutions for businesses operating in the regulated cannabis industry in states and countries
where cannabis is regulated and/or has been de-criminalized for medical use and/or legalized for recreational use. We provide
advisory and consulting services specific to this industry, design industry-specific products and facilities, and sell both exclusive
and non-exclusive customer products commonly used in the industry.
Note 3. Summary of Significant Accounting
Policies
Basis of Accounting
The financial statements are prepared in accordance
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP"). The Company has elected
a fiscal year ending on December 31.
Use of Estimates in Financial Reporting
The preparation of financial statements in conformity
with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures
of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenues and expenses
during the periods presented. Actual results could differ from these estimates. Estimates and assumptions are reviewed periodically
and the effects of revisions are reflected in the financial statements
in the period they are deemed to be necessary. Significant estimates made in the accompanying financial statements include but
are not limited to following: those related to revenue recognition, allowance for doubtful accounts and unbilled services, lives
and recoverability of equipment and other long-lived assets, contingencies and litigation. The Company is subject to uncertainties,
such as the impact of future events, economic, environmental and political factors, and changes in the business climate; therefore,
actual results may differ from those estimates. When no estimate in a given range is deemed to be better than any other when estimating
contingent liabilities, the low end of the range is accrued. Accordingly, the accounting estimates used in the preparation of
the Company's financial statements will change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information
is obtained and as the Company's operating environment changes. Changes in estimates are made when circumstances warrant. Such
changes and refinements in estimation methodologies are reflected in reported results of operations; if material, the effects
of changes in estimates are disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Cash
and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments
with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are held in operating accounts
at a major financial institution. Cash balances may exceed federally insured limits. Management believes the financial risk associated
with these balances is minimal and has not experienced any losses to date. As of December 31, 2018, and 2017, the Company had
cash balances in excess of FDIC insured limits of $836,565 and $1,398,087, respectively.
Inventory
Inventory is comprised of products and equipment
owned by the Company to be sold to end-customers. Inventory is valued at cost, using the first-in first-out and specific identification
methods, unless and until the market value for the inventory is lower than cost, in which case an allowance is established to
reduce the valuation to market value. As of December 31, 2018, market values of all of the Company’s inventory were greater
than cost, and accordingly, no such valuation allowances was recognized.
Research and Development
As a component of our equipment
and supplies offerings, from time-to-time we design and develop our own proprietary products to meet demand in markets where current
offerings are insufficient. These products include, but are not limited to: The Satchel™, Cultivation Cube™, So-Hum
Living Soils™ and the HDCS™. Costs associated with the development of new products are expensed as occurred as research
and development operating expenses. During the year ended December 31, 2018, our research and development costs were $590 as compared
to $2,403 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
Deposits
Deposits is comprised of advance payments made to
third parties, primarily for inventory for which the Company has not yet taken title. When the Company takes title to inventory
for which deposits are made, the related amount is classified as inventory, then recognized as a cost of revenues upon sale (see
“Costs of Revenues” below).
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets is primarily
comprised of advance payments made to third parties for independent contractors’ services or other general expenses. Prepaid
services and general expenses are amortized over the applicable periods which approximate the life of the contract or service
period.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are recorded at the net value
of face amount less an allowance for doubtful accounts. On a periodic basis, the Company evaluates its accounts receivable and,
based on a method of specific identification of any accounts receivable for which it deems the net realizable
value to be less than the gross amount of accounts receivable recorded, establishes an allowance for doubtful accounts for those
balances. In determining its need for an allowance for doubtful accounts, the Company considers historical experience, analysis
of past due amounts, client creditworthiness and any other relevant available information. However, the Company’s actual
experience may vary from its estimates. If the financial condition of its clients were to deteriorate, resulting in their inability
or unwillingness to pay the Company’s fees, it may need to record additional allowances or write-offs in future periods.
This risk is mitigated to the extent that the Company receives retainers from its clients prior to performing significant services.
The allowance for doubtful accounts, if any, is
recorded as a reduction in revenue to the extent the provision relates to fee adjustments and other discretionary pricing adjustments.
To the extent the provision relates to a client's inability to make required payments on accounts receivables, the provision is
recorded in operating expenses. As of December 31, 2018, and December 31, 2017 our allowance for doubtful accounts and was $2,635
and $21,581, respectively. For December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, we recorded bad debt expense of $2,815 and recovery of
bad debt of ($89,715), respectively, which is reflected as a component of general and administrative expenses on the consolidated
statement of operations.
Significant Customers
For the year ended December
31, 2018, three customers accounted for 47.5% or more, respectively of the Company’s total product sales revenues, and four
customers accounted for 70.65% or more respectively of the Company’s total service based revenue. For the year ended December
31, 2017, three customers accounted 48.95% or more, respectively of the Company’s total product sales revenues, and four
customers accounted for 40.18% or more respectively of the Company’s total service based revenue.
Property and Equipment,
net
Property and Equipment is stated at net book value,
cost less depreciation. Maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred. Depreciation of owned equipment is provided using the
straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from two to seven years. Depreciation of capitalized
construction in progress costs, a component of property and equipment, net, begins once the underlying asset is placed into service.
Property and equipment is reviewed for impairment as discussed below under “Accounting for the Impairment of Long-Lived
Assets.” The Company had not capitalized any interest as of December 31, 2018 and 2017.
Accounting for the
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company evaluates long-lived assets for impairment
whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Upon such an
occurrence, recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of an asset to forecasted
undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its estimated future
cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value
of the asset. For long-lived assets held for sale, assets are written down to fair value, less cost to sell. Fair value is determined
based on discounted cash flows, appraised values or management's estimates, depending upon the nature of the assets. The Company
did not record any impairment charges related to long-lived assets during the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017.
Beneficial Conversion Feature
If the conversion features of conventional convertible
debt provide for a rate of conversion that is below market value at issuance, this feature is characterized as a beneficial conversion
feature (“BCF”). A BCF is recorded by the Company as a debt discount pursuant to Financial Accounting Standards
Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ACF”) Topic 470-20 Debt with Conversion and
Other Options. In those circumstances, the convertible debt is recorded net of the discount related to the BCF, and the Company
amortizes the discount to interest expense over the life of the debt using the effective interest method.
Embedded Conversion Features
The Company evaluates embedded conversion features
within convertible debt under ASC 815 “Derivatives and Hedging” to determine whether the embedded conversion feature(s)
should be bifurcated from the host instrument and accounted for as a derivative at fair value with changes in fair value recorded
in earnings. If the conversion feature does not require derivative treatment under ASC 815, the instrument is evaluated under
ASC 470-20 “Debt with Conversion and Other Options” for consideration of any beneficial conversion features.
Derivative Financial Instruments
Fair value accounting requires bifurcation of embedded
derivative instruments such as conversion features in convertible debt or equity instruments, and measurement of their fair value
for accounting purposes. In determining the appropriate fair value, the Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. In
assessing the convertible debt instruments, management determines if the convertible debt host instrument is conventional convertible
debt and further if there is a beneficial conversion feature requiring measurement. If the instrument is not considered conventional
convertible debt, the Company will continue its evaluation process of these instruments as derivative financial instruments.
Once determined, derivative liabilities are adjusted
to reflect fair value at each reporting period end, with any increase or decrease in the fair value being recorded in results
of operations as an adjustment to fair value of derivatives. In addition, the fair value of freestanding derivative instruments
such as warrants, are also valued using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model.
Revenue Recognition
For annual reporting periods
after December 15, 2017, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) made effective ASU 2014-09 “Revenue
from Contracts with Customers” to supersede previous revenue recognition guidance under current U.S. GAAP. As a smaller
reporting company, the Company elected to not adopt FASB ASC Topic 606, Revenue Recognition as of December 31, 2017. Currently,
revenue is now recognized in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 606. The guidance presents a single five-step model for comprehensive
revenue recognition that requires an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers
in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
Two options are available for implementation of the standard which is either the retrospective approach or cumulative effect adjustment
approach. The guidance becomes effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods
within that reporting period, with early adoption permitted. We determined to implement the cumulative effect adjustment approach
to our implementation of FASB ASC Topic 606, with no restatement of the comparative periods presented. We intend to apply this
method to any incomplete contracts we determine are subject to FASB ASC Topic 606 prospectively. As is more fully discussed below,
we are of the opinion that none of our contracts for services or products contain significant financing components that require
revenue adjustment under FASB ASC Topic 606.
In accordance with FASB
ASC Topic 606, Revenue Recognition, we will recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of a significant financing component exists
in our consulting and product sales contracts. We examine and evaluate when our customers become liable to pay for goods and services;
how much consideration is paid as compared to the cash selling price of the goods or services; and, the length of time between
our performance and the receipt of payment.
Product Sales
Revenue from product and equipment sales, including
delivery fees, is recognized when an order has been obtained from the customer, the price is fixed and determinable when the order
is placed, the product is shipped, title has transferred and collectability is reasonably assured. Generally, our suppliers’
drop-ship orders to our clients with shipping-point or destination terms. For any shipments with destination terms, the Company
realizes revenue upon shipment to the customer. Given the facts that (1) our customers exercise discretion in determining the
timing of when they place their product order; and, (2) the price negotiated in our product sales contracts is fixed and determinable
at the time the customer places the order, we are not of the opinion that our product sales indicate or involve any significant
financing that would materially change the amount of revenue recognized under the contract, or would otherwise contain a significant financing component
for us or the customer under FASB ASC Topic 606. During the year ended December 31, 2018, sales returns were $210 comprised of
product returns and replacement.
Consulting Services
We also generate revenues
from professional services consulting agreements. These arrangements are generally entered into: (1) on an hourly basis for a
fixed-fee; or, (2) on a contingent fee basis. Generally, we require a complete or partial prepayment or retainer prior to performing
services.
For hourly based fixed
fee service contracts, we utilize and rely upon the proportional performance method, which recognizes revenue as services are
performed. Under this method, in order to determine the amount of revenue to be recognized, we calculate the amount of completed
work in comparison to the total services to be provided under the arrangement or deliverable. We segregate upon entry into a contract
any advances or retainers received from clients for fixed fee hourly services into a separate “Advances from Clients”
account, and only recognize revenues as we incur and charge billable hours, and then deposit the funds earned into our operating
account. Because our hourly fees for services are fixed and determinable and are only earned and recognized as revenue upon actual
performance, we are of the opinion that such arrangements are not an indicator of a vendor or customer based significant financing,
that would materially change the amount of revenue we recognize under the contract or would otherwise contain a significant financing
component under FASB ASC Topic 606.
Occasionally, our fixed-fee
hourly engagements are recognized under the completed performance method. Some fixed fee arrangements are for completion of a
final deliverable or act which is significant to the arrangement as a whole. These engagements do not generally exceed a one-year
term. If the performance is for a final deliverable or act, we recognize revenue under the completed performance method, in which
revenue is recognized once the final act or deliverable is performed or delivered for a fixed fee. Revenue recognition is affected
by a number of factors that change the estimated amount of work required to complete the deliverable, such as changes in scope,
timing, awaiting notification of license award from local government, and the level of client involvement. Losses, if any, on
fixed-fee engagements are recognized in the period in which the loss first becomes probable and reasonably estimable. FASB ASC
Topic 606 provides a practical expedient to disregard the effects of a financing component if the period between payment and performance
is one year or less. As, our fixed fee hourly engagements do not exceed one year, no significant customer-based financing is implicated
under FASB ASC Topic 606. During the year ended December 31, 2018, and December 31, 2017, we have incurred no losses from fixed
fee engagements that terminate prior to completion. We believe if an engagement terminates prior to completion, we can recover
the costs incurred related to the services provided.
We occasionally enter into
arrangements for which fixed and determinable revenues are contingent and agreed upon achieving a pre-determined deliverable or
future outcome. Any contingent revenue for these arrangements is not recognized until the contingency is resolved and collectability
is reasonably assured.
Our arrangements with clients
may include terms to deliver multiple services or deliverables. These contracts specifically identify the services to be provided
with the corresponding deliverable. The value for each deliverable is determined based on the prices charged when each element
is sold separately or by other vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) or estimates of stand-alone selling prices.
Revenues are recognized in accordance with our accounting policies for the elements as described above (see Product Sales). The
elements qualify for separation when the deliverables have value on a stand-alone basis and the value of the separate elements
can be established by VSOE or an estimated selling price.
While assigning values
and identifying separate elements requires judgment, selling prices of the separate elements are generally readily identifiable
as fixed and determinable as we also sell those elements individually outside of a multiple services engagement. Contracts with
multiple elements typically incorporate a fixed-fee or hourly pricing structure. Arrangements are typically terminable by either
party upon sufficient notice and do not include provisions for refunds relating to services provided.
Reimbursable expenses,
including those relating to travel, other out-of-pocket expenses and any third-party costs, are included as a component of revenues.
Typically, an equivalent amount of reimbursable expenses is included in total direct client service costs. Reimbursable expenses
related to time and materials and fixed-fee engagements are recognized as revenue in the period in which the expense is incurred
and collectability is reasonably assured. Taxes collected from customers and remitted to governmental authorities are presented
in the statement of operations on a net basis.
Costs of Revenues
The Company’s policy is to recognize costs
of revenue in the same manner in conjunction with revenue recognition. Cost of revenue includes the costs directly attributable
to revenue recognition and includes compensation and fees for services, travel and other expenses for services and costs of products
and equipment. Selling, general and administrative expenses are charged to expense as incurred.
Advertising and Promotion
Costs
Advertising and promotion costs are included as
a component of selling and marketing expense and are expensed as incurred. During the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, these
costs were $293,241 and $278,542, respectively.
Shipping and Handling Costs
For product and equipment sales, shipping and handling
costs are included as a component of cost of revenues.
Stock-Based Compensation
Restricted shares are awarded to employees and entitle
the grantee to receive shares of common stock at the end of the established vesting period. The fair value of the grant is based
on the stock price on the date of grant. We recognize related compensation costs on a straight-line basis over the requisite vesting
period of the award, which to date has been one year from the grant date. During the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, stock-based
compensation expense for restricted shares for Company employees and service providers was $73,742 and $893,857, respectively.
Compensation expense for warrants and options is based on the fair value of the instruments on the grant date, which is determined
using the Black-Scholes valuation model, and are expensed over the expected term of the awards.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities
for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns in accordance
with applicable accounting guidance for accounting for income taxes, using currently enacted tax rates in effect for the year
in which the differences are expected to reverse. We record a valuation allowance when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets
to the amount expected to be realized. For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, we recorded a valuation allowance
against our deferred tax asset that reduced our income tax benefit for the period to zero. As of December 31, 2018, and 2017,
we had no liabilities related to federal or state income taxes and the carrying value of our deferred tax asset was zero.
Net Income (Loss) Per Common Share
The Company reports net income (loss) per common
share in accordance with FASB ASC 260, “Earnings per Share”. This statement requires dual presentation of basic and
diluted earnings with a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator of the earnings per share computations. Basic net income
(loss) per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares
of common stock outstanding during the period and excludes the effects of any potentially dilutive securities. Diluted earnings
per share is equal to basic earnings per share because there are no potential dilutable instruments that would have an anti-dilutive
effect on earnings. Diluted net income (loss) per share gives effect to any dilutive potential common stock outstanding during
the period. The computation does not assume conversion, exercise or contingent exercise of securities since that would have an
anti-dilutive effect on earnings.
Related
Party Transactions
The
Company follows FASB ASC subtopic 850-10, Related Party Disclosures, for the identification of related parties and
disclosure of related party transactions. Related parties include: a) affiliates of the Company; b) entities for which investments
in their equity securities would be required, absent the election of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection
of Section 825–10–15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing entity; c) trusts for the benefit
of employees, such as pension and profit-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship of management; d) principal
owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one party controls or
can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting parties
might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) other parties that can significantly influence the management
or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can
significantly influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing
its own separate interests.
Material related party transactions are required
to be disclosed in the consolidated financial statements, other than compensation arrangements, expense allowances, and other
similar items in the ordinary course of business. However, disclosure of transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of
consolidated or combined financial statements is not required in those statements. The disclosures shall include: a) the nature
of the relationship(s) involved; b) a description of the transactions, including transactions to which no amounts or nominal amounts
were ascribed, for each of the periods for which statements of operation are presented, and such other information deemed necessary
to an understanding of the effects of the transactions on the financial statements; c) the dollar amounts of transactions for
each of the periods for which statements of operations are presented and the effects of any change in the method of establishing
the terms from that used in the preceding period; and d) amounts due from or to related parties as of the date of each balance
sheet presented and, if not otherwise apparent, the terms and manner of settlement.
Reclassifications
Certain
balance sheet reclassifications have been made to prior period balances to reflect the current period’s presentation format;
such reclassifications had no impact on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations or consolidated statements of
cash flows and had no material impact on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
Recent
Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the FASB
issued its new lease accounting guidance in Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). Under the new guidance,
the following will be required to be recognized for all leases (with the exception of short-term leases) as of the commencement
date:
|
|
•
|
A
lease liability, which is a lessee‘s obligation to make lease payments arising from a lease, measured on a discounted
basis; and
|
|
|
•
|
A
right-of-use asset, which is an asset that represents the lessee’s right to use, or control the use of, a specified
asset for the lease term.
|
|
|
•
|
Under
the new guidance, lessor accounting is largely unchanged. Certain targeted improvements were made to align, where necessary,
lessor accounting with the lessee accounting model and Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers.
|
|
|
•
|
The
new lease guidance simplified the accounting for sale and leaseback transactions primarily because lessees must recognize
lease assets and lease liabilities. Lessees will no longer be provided with a source of off-balance sheet financing.
|
Public business entities should apply the amendments
in ASU 2016-02 for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years (i.e.,
January 1, 2019, for a calendar year entity). The Company is currently evaluating the effects, if any, that the application of
ASU 2016-02 will have on disclosures associated with its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB
issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-09, Compensation —Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based
Payment Accounting. The amendments are intended to improve the accounting for employee share-based payments and affect all organizations
that issue share-based payment awards to their employees. Several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment award transactions
are simplified, including: (a) income tax consequences; (b) classification of awards as either equity or liabilities; and (c)
classification on the statement of cash flows. For public companies, the amendments are effective for annual periods beginning
after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. For private companies, the amendments are effective
for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018.
Early adoption is permitted for any organization in any interim or annual period.
In April 2016, the FASB
issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-10, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations
and Licensing. The amendments clarify the following two aspects of Topic 606: (a) identifying performance obligations; and (b)
the licensing implementation guidance. The amendments do not change the core principle of the guidance in Topic 606. This guidance
became effective for annual reporting and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company adopted the modified
standard on January 1, 2018, and has concluded that the adoption of this standard did not have a material impact or cause the
Company to make any adjustments to the Company’s consolidated financial statements and results of operations.
In
January 2017, FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition
of a Business. The amendments in ASU 2017-01 became effective for public entities for annual and interim periods after December
15, 2017. The Company adopted the modified standard on January 1, 2018 and has concluded that the adoption of this standard did
not have a material impact or cause the Company to make any adjustments to the Company’s consolidated financial statements
and results of operations.
In June 2018, FASB issued
Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2018-7, Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvement to Non-Employee
Share Based Payment Accounting. The amendments in ASU 2018-7 became effective for public entities after December 15, 2018. The
Company is currently evaluating the effects, if any, that the application of ASU 2018-7 will have on disclosures associated with
fair value measurement.
In August 2018, FASB issued
Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure of Fair Value Measurement. The amendments
in ASU 2018-13 becomes effective for public entities December 15, 2019. The Company is currently evaluating the effects, if any,
that the application of ASU 2018-13 will have on disclosures associated with fair value measurement.
Note 3.
Accounts Receivable, net
Accounts
receivable, net, was comprised of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Gross accounts receivable
|
|
$
|
61,519
|
|
|
$
|
168,385
|
|
|
Less: allowance for doubtful accounts
|
|
|
(2,635
|
)
|
|
|
(21,581
|
)
|
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
|
$
|
58,884
|
|
|
$
|
146,804
|
|
For
the years ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, the Company had bad debt expense of $2,815 and bad debt recovery of ($89,715),
respectively.
Note 4
Inventory
Inventory as of December
31, 2018 and 2017 consisted of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Raw materials
|
|
$
|
1,646
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Demo
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Finished goods
|
|
|
59,359
|
|
|
|
35,757
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
61,005
|
|
|
$
|
35,757
|
|
Note 5. Property and Equipment, net
Property
and equipment, net, was comprised of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Office equipment
|
|
$
|
8,482
|
|
|
$
|
8,482
|
|
|
Furniture and fixtures
|
|
|
7,240
|
|
|
|
7,240
|
|
|
Machinery and equipment
|
|
|
7,336
|
|
|
|
7,336
|
|
|
Property and equipment, gross
|
|
|
23,058
|
|
|
|
23,058
|
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation
|
|
|
(15,020
|
)
|
|
|
(11,276
|
)
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
$
|
8,037
|
|
|
$
|
11,782
|
|
For the year ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, the Company recorded depreciation expense of $3,745 and $4,487, respectively.
Note 6. Accrued
and Other Current Liabilities
Accrued
and other current liabilities consisted of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Accrued legal fees
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Accrued payroll liabilities
|
|
|
10,924
|
|
|
|
8,323
|
|
|
Other Accrued Expenses & Payables
|
|
|
78,844
|
|
|
|
44,029
|
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities
|
|
$
|
89,768
|
|
|
$
|
52,352
|
|
Note 8. Related Party
Transactions
During the year ended December 31, 2018, and 2017,
the Company incurred $15,000 and $66,000 of expenses respectively to Prince & Tuohey CPA, LTD, an accounting firm in which,
the Company’s former Chief Financial Officer, was a partner. As of December 31, 2018, the Company had $0 due to this related
party.
Note 9. Commitments
and Contingencies
On July 28, 2015, the Company
entered into a 5-year lease for 6,500 square feet of office space to house its corporate offices. Under the terms of the lease,
payments are $4,500 per month for the first 36 months of the lease and escalate thereafter.
Rent expense was $54,000 and $54,000 for the years
ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
The following table summarizes
the Company’s future lease obligations:
|
Year
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
$
|
54,000
|
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
|
31,500
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
$
|
85,550
|
|
Note 10. Stock-based
Compensation
During the year ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, the Company issued stock-based compensation for employees and service providers pursuant to its
2015 Equity Incentive Plan. As of December 31, 2017, the Company determined to issue employees and services providers warrants
instead of common stock. During the year ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, the Company’s expense for restricted
shares to Company employees and service providers was $73,742 and $893,857, which was the result of the following activity:
Restricted Shares
From time to time, the
Company grants certain employees restricted shares of its common stock to provide further compensation in-lieu of wages and to
align the employee’s interests with the interests of its stockholders. Because vesting is based on continued employment,
these equity-based incentives are also intended to attract, retain and motivate personnel upon whose judgment, initiative and
effort the Company’s success is largely dependent.
The following table summarizes
the Company’s restricted share award activity during the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017:
|
|
Restricted
Shares
|
|
Weighted
Average
|
|
|
Common
Stock
|
|
Grant
Date Fair Value
|
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2016
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
430,227
|
|
|
|
0.92
|
|
|
|
Vested
restricted shares
|
|
|
430,227
|
|
|
|
0.92
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2017
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
79,014
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
|
Vested
restricted shares
|
|
|
79,014
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
Outstanding
unvested at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
During the year ended December
31, 2018, the Company granted 79,014 restricted shares to Company employees and service providers and recognized $73,742 in associated
stock-based compensation expense. During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company granted 430,227 restricted shares and recognized
$893,857 in associated employee stock-based compensation expense. The fair value of restricted stock units is determined based
on the quoted closing price of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant.
Warrants
In connection with his
appointment to the Company’s board of directors on November 19, 2014, the Company granted its independent board member,
Vincent “Tripp” Keber, warrants to purchase up to two hundred and fifty thousand (250,000) shares of common stock
at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share, exercisable within five (5) years of the date of issuance on November
19, 2014. Concurrently, the Company agreed to award Mr. Keber an option to purchase three hundred thousand (300,000) shares of
common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants and options expire on November 19, 2019.
On August 31, 2017, the
Company issued Anthony Baroud warrants to purchase up to fifty thousand (50,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of
$0.93 in a cashless transaction. The warrants expired on March 1, 2018.
On December 31, 2018, pursuant
to the Company’s Equity Incentive Plan, the Company issued an aggregate of 895,000 warrants to the following persons to
purchase common stock in cashless transactions, with an aggregate value of $204,995.
The Company issued Michael
Schwanbeck warrants to purchase twenty-five thousand (25,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Mitchell
Day warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Tad
Mailander warrants to purchase one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Tyler
A. Schloesser warrants to purchase one hundred and fifty thousand (150,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued April
Robertson warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Terry
L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust four hundred thousand (400,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Ellis
Smith one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
The Company issued Jon
Workman one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
The Company used the Black-Scholes
valuation model to determine the fair value of warrants as of the grant date. Assumptions used in this calculation for the warrant
award to purchase 250,000 shares of common stock include expected volatility of 144.2%, based on an average of historical data
of the Company’s stock price and the stock prices of three comparable companies that are also included in the marijuana
index, a risk-free rate of 1.23%, based on U.S. Treasury yields as published by the Federal Reserve, a dividend yield of
0.0%, as the Company has not historically paid dividends nor does it have any plans to do so in the foreseeable future, and an
expected term of five years. The grant date fair value of the warrants, as calculated based on these assumptions, was $0.91 per
share.
During 2018 the Company
had the following warrant activity. During 2017 the Company had no warrant activity:
|
|
|
Common Stock Warrants
|
|
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2015
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2016
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2017
|
|
|
300,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
1,685,000
|
|
|
|
0.58
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
|
Vested at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
Note 11.
Income Taxes
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
(the Tax Legislation) in the United States enacted on December 22, 2017 significantly revised the United States corporate income
tax by, among other things, lowering the corporate income tax rate to 21% effective January 1, 2018, implementing a modified territorial
tax system and imposing a one-time repatriation tax on deemed repatriated earnings and profits of U.S.-owned foreign subsidiaries
(the Toll Charge). As a fiscal-year taxpayer, certain provisions of the Tax Legislation impacted us in fiscal 2018, including
the change in the corporate income tax rate, while other provisions will be effective starting at the beginning of fiscal 2019.
Accordingly, our federal statutory income tax rate for fiscal 2018 reflected a blended rate of approximately 21%.
The following table displays a reconciliation from
the U.S. statutory rate to the effective tax rate and the provision for (benefit from) income taxes for the years ended December
31, 2018 and 2017, respectively:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Tax benefit at the US statutory rate of 21% and 34% for 2018 and 2017, respectively
|
|
$
|
199,645
|
|
|
$
|
506,081
|
|
|
State income tax benefit
|
|
|
44,017
|
|
|
|
68,916
|
|
|
Non-deductible expenses including non-deductible pre-merger losses
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Change in valuation allowance
|
|
|
(243,662
|
)
|
|
|
(574,997
|
)
|
|
Total income tax benefit
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) consisted of the
following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
Net operating loss carryforwards
|
|
$
|
2,305,640
|
|
|
$
|
1,354,949
|
|
|
Beneficial conversion feature accumulated amortization
|
|
|
13,791
|
|
|
|
13,791
|
|
|
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
|
|
|
2,635
|
|
|
|
7,855
|
|
|
Valuation allowance
|
|
|
(2,322,066
|
)
|
|
|
(1,376,595
|
)
|
|
Total deferred tax assets
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
The Company determined that it is not more likely
than not that its deferred tax asset would be realizable. Accordingly, the Company recorded a valuation allowance for the full
amount of its deferred tax asset, resulting in a zero carrying value of the Company’s deferred tax asset and no benefit
from or provision for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2017. Federal and state operating loss carry forwards
are $2,305,640 and $1,354,949 as of December 31, 2018 and 2017, respectively, begin expiring on 2034. The years 2010 to 2015 remain
subject to examination by the Company’s major tax jurisdictions.
Utilization of the net operating loss carry forwards
and credits may be subject to a substantial annual limitation due to ownership change limitations provided by Section 382 of the
Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and similar state provisions.
Note 12. Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred Stock
The American Cannabis Company, Inc. is authorized
to issue 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock at $0.01 par value.
No shares of preferred stock were issued and outstanding
during the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2017.
Common Stock
On January 22, 2018, pursuant
to a written agreement with Vincent “Tripp” Keber, the Company issued Mr. Keber an option to purchase 300,000 shares
of common stock for a price of $0.63 per share. The option expires on November 19, 2019.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 6,060 common shares to Av Singh for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 2,500 common shares to Randy Fleming for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 17,954 common shares to Gayle Barr for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 2,500 common shares to Pamela Staley for services rendered.
On September 27, 2018,
the Company issued 50,000 common shares to R. Leslie Hymers, III, based on contract.
Note 13. Subsequent Events
On January 16, 2019, the
Company issued 39,708 common shares to Gayle Barr for services rendered.
On January 16, 2019, the
Company issued 400,000 shares of common stock to the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust for conversion of a cashless warrant.
On January 29, 2019, the
Registrant appointed Tyler A. Schloesser, age 28, as its Chief Operations Officer.
On January 29, 2019, the
Registrant appointed Jon Workman, age 55 as Vice-President for Hemp Business Development.
On February 12, 2019, the
Company announced its creation of a Hemp Business Development Division, and appointed Jon Workman as Vice President responsible
for Hemp Business Development.
Financial Statements for the Three Month and Six
Month Periods Ended June 30, 2019 and 2018
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
(Unaudited)
|
|
2018
(Audited)
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and Equivalents
|
|
$
|
918,127
|
|
|
$
|
1,086,565
|
|
|
Accounts Receivable, Net
|
|
|
236,825
|
|
|
|
58,884
|
|
|
Deposits
|
|
|
4,500
|
|
|
|
4,500
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
40,396
|
|
|
|
61,005
|
|
|
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
|
|
|
61,432
|
|
|
|
56,376
|
|
|
Total Current Assets
|
|
|
1,261,280
|
|
|
|
1,267,331
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and Equipment - Net
|
|
|
9,446
|
|
|
|
8,037
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
|
$
|
1,270,726
|
|
|
$
|
1,275,369
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDER'S EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Payable
|
|
|
23,888
|
|
|
|
32,931
|
|
|
Advances from Clients
|
|
|
146,422
|
|
|
|
147,349
|
|
|
Accrued and Other Current Liabilities
|
|
|
72,614
|
|
|
|
89,768
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
|
|
242,925
|
|
|
|
270,048
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shareholder's Equity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Stock, $0.01 par value, 5,000,000 shares authorized; 0 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.00001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 52,137,772 and 51,513,064 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively
|
|
|
521
|
|
|
|
515
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
8,222,657
|
|
|
|
8,178,919
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(7,195,377
|
)
|
|
|
(7,174,113
|
)
|
|
Total Shareholder's Equity
|
|
|
1,027,801
|
|
|
|
1,005,321
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDER'S EQUITY
|
|
$
|
1,270,726
|
|
|
$
|
1,275,369
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these condensed consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Three Months
|
|
Three Months
|
|
Six Months
|
|
Six Months
|
|
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consulting Services
|
|
|
492,184
|
|
|
|
97,090
|
|
|
|
653,838
|
|
|
|
182,692
|
|
|
Shipping Services
|
|
|
13,127
|
|
|
|
3,461
|
|
|
|
23,122
|
|
|
|
30,383
|
|
|
Product & Equipment
|
|
|
225,657
|
|
|
|
77,705
|
|
|
|
464,321
|
|
|
|
241,130
|
|
|
Total Revenues
|
|
|
730,968
|
|
|
|
178,256
|
|
|
$
|
1,141,281
|
|
|
$
|
454,205
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Consulting Services
|
|
|
79,324
|
|
|
|
24,711
|
|
|
|
113,251
|
|
|
|
81,772
|
|
|
Cost of Products and Equipment
|
|
|
150,741
|
|
|
|
53,829
|
|
|
|
343,163
|
|
|
|
140,839
|
|
|
Total Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
230,064
|
|
|
|
78,540
|
|
|
$
|
456,414
|
|
|
$
|
222,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
|
500,903
|
|
|
|
99,716
|
|
|
$
|
684,867
|
|
|
$
|
235,055
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and Administrative
|
|
|
207,182
|
|
|
|
199,794
|
|
|
|
450,265
|
|
|
|
431,039
|
|
|
Investor Relations
|
|
|
14,085
|
|
|
|
4,895
|
|
|
|
31,932
|
|
|
|
10,824
|
|
|
Selling and Marketing
|
|
|
78,399
|
|
|
|
71,711
|
|
|
|
153,738
|
|
|
|
127,079
|
|
|
Research and Development
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
196
|
|
|
|
590
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
|
|
299,667
|
|
|
|
276,400
|
|
|
$
|
636,130
|
|
|
$
|
569,532
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) from Operations
|
|
|
201,236
|
|
|
|
(176,684
|
)
|
|
$
|
48,737
|
|
|
$
|
(334,477
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income (expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest (expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
121
|
|
|
Stock Based Compensation
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(25,242
|
)
|
|
|
(43,744
|
)
|
|
|
(25,242
|
)
|
|
Bad Debt (expense)
|
|
|
(41,481
|
)
|
|
|
(3,553
|
)
|
|
|
(43,774
|
)
|
|
|
(19,985
|
)
|
|
Settlement (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Warrant (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other Income
|
|
|
13,267
|
|
|
|
635
|
|
|
|
17,517
|
|
|
|
3,641
|
|
|
Total other income (expense)
|
|
|
(28,214
|
)
|
|
|
(28,074
|
)
|
|
$
|
(70,001
|
)
|
|
$
|
(41,465
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) before taxes
|
|
|
173,023
|
|
|
|
(204,758
|
)
|
|
$
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
$
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
Income Tax Expense (benefit)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCOME (LOSS)
|
|
$
|
173,023
|
|
|
$
|
(204,758
|
)
|
|
$
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
$
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per common share
|
|
$
|
0.00
|
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)*
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.01
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding
|
|
|
51,611,448
|
|
|
|
51,452,174
|
|
|
|
52,074,072
|
|
|
|
51,452,174
|
|
|
*Denotes a loss of less than ($0.01)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these condensed consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
FOR THE SIX MONTHS PERIODS ENDING JUNE 30, 2019 AND 2018
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Paid-In
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
Stockholder's
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
Amount
|
|
Capital
|
|
Deficit
|
|
Equity
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2017
|
|
|
51,434,050
|
|
|
$
|
514
|
|
|
$
|
7,004,363
|
|
|
$
|
(6,223,422
|
)
|
|
$
|
781,455
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
29,014
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
Warrants to employees
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
895,859
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
895,860
|
|
|
Net (Loss)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
|
(375,942
|
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2018
|
|
|
51,463,064
|
|
|
$
|
515
|
|
|
$
|
7,925,464
|
|
|
$
|
(6,599,364
|
)
|
|
$
|
1,326,615
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2018
|
|
|
51,513,064
|
|
|
$
|
515
|
|
|
$
|
8,178,919
|
|
|
$
|
(7,174,113
|
)
|
|
$
|
1,005,321
|
|
|
Shares issued for services
|
|
|
89,708
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
43,743
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43,744
|
|
|
Warrants to employees
|
|
|
535,000
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
(5
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
----
|
|
|
Net (Loss)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
Balance, June 30, 2019
|
|
|
52,137,772
|
|
|
$
|
521
|
|
|
$
|
8,222,657
|
|
|
$
|
(7,195,377
|
)
|
|
$
|
1,027,801
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral
part of these condensed consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR SIX MONTHS PERIODS ENDED JUNE 30, 2019 AND 2018
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Six Months Ended June 30
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
$
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) to net cash (used in) operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bad Debt Expense
|
|
|
43,774
|
|
|
|
19,985
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
1,893
|
|
|
|
1,998
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation to service providers
|
|
|
43,743
|
|
|
|
25,542
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
(221,714
|
)
|
|
|
22,826
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
20,609
|
|
|
|
(58,531
|
)
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
|
|
(5,056
|
)
|
|
|
1,327
|
|
|
Advances from Clients
|
|
|
(926
|
)
|
|
|
26,575
|
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities
|
|
|
(17,153
|
)
|
|
|
(5,943
|
)
|
|
Accounts Payable
|
|
|
(9,043
|
)
|
|
|
(6,173
|
)
|
|
Net Cash provided by (used in) Operating Activities
|
|
|
(165,136
|
)
|
|
|
(348,635
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of property and equipment
|
|
|
(3,302
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net cash used in Investing Activities
|
|
|
(3,302
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common shares
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Net cash Provided by Financing Activities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET (DECCREASE) IN CASH
|
|
|
(168,438
|
)
|
|
|
(348,635
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
|
|
1,086,565
|
|
|
|
1,648,087
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AT END OF PERIOD
|
|
$
|
918,127
|
|
|
$
|
1,299,452
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid during the period for interest
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Cash paid during the period for income taxes, net
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Common stock issued for debt converted in prior year
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are
an integral part of these condensed consolidated financial statements
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
NOTES TO THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
(Unaudited)
Note 1. Description of the Business
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and its subsidiary
Company, Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc., doing business as American Cannabis Consulting (“American Cannabis Consulting”),
(collectively “the “Company”) are based in Denver, Colorado and operate a fully integrated business model that
features end-to-end solutions for businesses operating in the regulated cannabis industry in states and countries where cannabis
is regulated and/or has been decriminalized for medical use and/or legalized for recreational use. The Company provides advisory
and consulting services specific to this industry, designs industry specific products and facilities, and manages a strategic
group partnership that offers both exclusive and nonexclusive customer products commonly used in the industry. American Cannabis
Company, Inc. is a publicly listed company quoted on the OTC Pink Tier under the symbol “AMMJ”
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Accounting
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial
statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States
of America, pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. Certain information and footnote
disclosures have been omitted pursuant to such rules and regulations. In the opinion of management, the accompanying consolidated
financial statements include normal recurring adjustments that are necessary for a fair presentation of the results for the interim
periods presented. These financial statements should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements
and notes thereto for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018 included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K. The results of operations
for the three and six months ended June 30, 2018 are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for the full fiscal
year or any other periods.
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements
in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make a number of estimates and judgments
that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, expenses, and related disclosures. Actual results may differ from these
estimates.
Certain balance sheet reclassifications have been
made to prior period balances to reflect the current period’s presentation format; such reclassifications had no impact
on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations or consolidated statements of cash flows and had no material impact
on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
Use of Estimates in Financial Reporting
The preparation of financial statements in conformity
with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amount of assets and liabilities, and disclosures
of contingent assets and liabilities, as of the date of the financial statements during the periods presented. Actual results
could differ from these estimates. Estimates and assumptions are reviewed periodically, and the effects of revisions are reflected
in the financial statements in the period in which they are deemed to be necessary. Significant estimates made in the accompanying
financial statements include but are not limited to following: those related to revenue recognition, allowance for doubtful accounts
and unbilled services, lives and recoverability of equipment and other long-lived assets, contingencies and litigation. The Company
is subject to uncertainties, such as the impact of future events, economic, environmental and political factors, and changes in
the business climate; therefore, actual results may differ from those estimates. When no estimate in a given range is deemed
to be better than any other when estimating contingent liabilities, the low end of the range is accrued. Accordingly, the accounting
estimates used in the preparation of the Company's financial statements will change as new events occur, as more experience is
acquired, as additional information is obtained and as the Company's operating environment changes. Changes in estimates are made
when circumstances warrant. Such changes and refinements
in estimation methodologies are reflected in reported results of operations; if material, the effects of changes in estimates
are disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Unaudited Interim Financial Statements
The accompanying unaudited financial statements
have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP for interim financial information and with the instructions to Form 10-Q and Regulation
SX. Accordingly, the financial statements do not include all of the information and footnotes required by generally accepted accounting
principles for complete financial statements. In the opinion of management, all adjustments consisting of normal recurring entries
necessary for a fair statement of the periods presented for: (a) the financial position; (b) the result of operations;
and (c) cash flows, have been made in order to make the financial statements presented not misleading. The results of operations
for such interim periods are not necessarily indicative of operations for a full year.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original
maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are held in operating accounts at a major
financial institution.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are recorded at the net
value of face amount less an allowance for doubtful accounts. The Company evaluates its accounts receivable periodically based
on specific identification of any accounts receivable for which the Company deems the net realizable value to be less than the
gross amount of accounts receivable recorded; in these cases, an allowance for doubtful accounts is established for those
balances. In determining its need for an allowance for doubtful accounts, the Company considers historical experience, analysis
of past due amounts, client creditworthiness and any other relevant available information. However, the Company’s actual
experience may vary from its estimates. If the financial condition of its clients were to deteriorate, resulting in their inability
or unwillingness to pay the Company’s fees, it may need to record additional allowances or write-offs in future periods.
This risk is mitigated to the extent that the Company receives retainers from its clients prior to performing significant services.
The allowance for doubtful accounts, if any,
is recorded as a reduction in revenue to the extent the provision relates to fee adjustments and other discretionary pricing adjustments.
To the extent the provision relates to a client's inability to make required payments on accounts receivables, the provision is
recorded in operating expenses. As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, the Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts
was $43,116 and $2,635, respectively. The Company recorded bad debt expense during the six months ended June 30, 2019 of $43,774
and $19,985 during the six months ended June 30, 2018.
Deposits
Deposits is comprised of advance payments made to third parties, primarily
for inventory for which the Company has not yet taken title. When the Company takes title to inventory for which deposits are
made, the related amount is classified as inventory, then recognized as a cost of revenues upon sale.
Inventory
Inventory is comprised of products and equipment
owned by the Company to be sold to end customers. Inventory is valued at cost, based on the specific identification method, unless
and until the market value for the inventory is lower than cost, in which case an allowance is established to reduce the valuation
to market value. As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, market values of all of the Company’s inventory were greater
than cost, and accordingly, no such valuation allowances were recognized.
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets is primarily
comprised of advance payments made to third parties for independent contractors’ services or other general expenses. Prepaid
services and general expenses are amortized over the applicable periods which approximate the life of the contract or service
period.
Significant Clients and Customers
For the three months ended June 30, 2019, three
customers individually accounted for $222,125 of the Company’s total revenues equaling approximately 30.4% of the Company’s
total revenues for the period.
Property and Equipment, net
Property and Equipment is stated at net book value,
cost less depreciation. Maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred. Depreciation of owned equipment is provided using the
straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from two to seven years. Costs associated with in
progress construction are capitalized as incurred and depreciation is consummated once the underlying asset is placed into service.
Property and equipment is reviewed for impairment as discussed below under “Accounting for the Impairment of Long-Lived
Assets.” The Company did not capitalize any interest as of June 30, 2019.
Accounting for the Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The Company evaluates long-lived assets for impairment
whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Upon such an
occurrence, recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of an asset to forecasted
undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its estimated future
cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value
of the asset. For long-lived assets held for sale, assets are written down to fair value, less cost to sell. Fair value is determined
based on discounted cash flows, appraised values or management's estimates, depending upon the nature of the assets. The Company
had not recorded any impairment charges related to long-lived assets as of June 30, 2019 or December 31, 2018
Beneficial Conversion Feature
If the conversion features of conventional convertible
debt provides for a rate of conversion that is below market value at issuance, this feature is characterized as a beneficial conversion
feature (“BCF”). A BCF is recorded by the Company as a debt discount pursuant to Financial Accounting Standards Board
(“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ACF”) Topic 470-20 Debt with Conversion and Other Options.
In those circumstances, the convertible debt is recorded net of the discount related to the BCF, and the Company amortizes the
discount to interest expense, over the life of the debt using the effective interest method.
Revenue Recognition
For annual reporting periods after December 15,
2017, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) made effective ASU 2014-09 “Revenue from Contracts with
Customers” to supersede previous revenue recognition guidance under current U.S. GAAP. Revenue is now recognized in accordance
with FASB ASC Topic 606, Revenue Recognition. The guidance presents a single five-step model for comprehensive revenue recognition
that requires an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that
reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Two options are
available for implementation of the standard which is either the retrospective approach or cumulative effect adjustment approach.
The guidance becomes effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within
that reporting period, with early adoption permitted. We determined to implement the cumulative effect adjustment approach to
our implementation of FASB ASC Topic 606, with no restatement of the comparative periods presented for reporting periods after
January 1, 2018. We applied this method to any incomplete contracts we determine are subject to FASB ASC Topic 606 prospectively.
As is more fully discussed below, we are of the opinion that none of our contracts for services or products contain significant
financing components that require revenue adjustment under FASB ASC Topic 606.
In accordance with FASB ASC Topic 606, Revenue Recognition,
we will recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of a significant financing component exists in our consulting and product sales
contracts. We examine and evaluate when our customers become liable to pay for goods and services; how much consideration is paid
as compared to the cash selling price of the goods or services; and, the length of time between our performance and the receipt
of payment.
Product Sales
Revenue from product and equipment sales, including
delivery fees, is recognized when an order has been obtained from the customer, the price is fixed and determinable when the order
is placed, the product is shipped, title has transferred and collectability is reasonably assured. Generally, our suppliers’
drop-ship orders to our clients with shipping-point or destination terms. For any shipments with destination terms, the Company
defers revenue until delivery to the customer. Given the facts that (1) our customers exercise discretion in determining the timing
of when they place their product order; and, (2) the price negotiated in our product sales contracts is fixed and determinable
at the time the customer places the order, we are not of the opinion that our product sales indicate or involve any significant
financing that would materially change the amount of revenue recognized under the contract, or would otherwise contain a significant
financing component for us or the customer under FASB ASC Topic 606. During the six months ended June 30, 2019, sales returns
were $15,528 comprised of product returns and replacement.
Consulting Services
We also generate revenues from professional services
consulting agreements. These arrangements are generally entered into: (1) on an hourly basis for a fixed-fee; or, (2) on a contingent
fee basis. Generally, we require a complete or partial prepayment or retainer prior to performing services
For hourly based fixed fee service contracts, we
utilize and rely upon the proportional performance method, which recognizes revenue as services are performed. Under this method,
in order to determine the amount of revenue to be recognized, we calculate the amount of completed work in comparison to the total
services to be provided under the arrangement or deliverable. We segregate upon entry into a contract any advances or retainers
received from clients for fixed fee hourly services into a separate “Advances from Clients” account, and only recognize
revenues as we incur and charge billable hours, and then deposit the funds earned into our operating account. Because our hourly
fees for services are fixed and determinable and are only earned and recognized as revenue upon actual performance, we are of
the opinion that such arrangements are not an indicator of a vendor or customer based significant financing, that would materially
change the amount of revenue we recognize under the contract or would otherwise contain a significant financing component under
FASB ASC Topic 606.
Occasionally, our fixed-fee hourly engagements are
recognized under the completed performance method. Some fixed fee arrangements are for completion of a final deliverable or act
which is significant to the arrangement as a whole. These engagements do not generally exceed a one-year term. If the performance
is for a final deliverable or act, we recognize revenue under the completed performance method, in which revenue is recognized
once the final act or deliverable is performed or delivered for a fixed fee. Revenue recognition is affected by a number of factors
that change the estimated amount of work required to complete the deliverable, such as changes in scope, timing, awaiting notification
of license award from local government, and the level of client involvement. Losses, if any, on fixed-fee engagements are recognized
in the period in which the loss first becomes probable and reasonably estimable. FASB ASC Topic 606 provides a practical expedient
to disregard the effects of a financing component if the period between payment and performance is one year or less. As, our fixed
fee hourly engagements do not exceed one year, no significant customer-based financing is implicated under FASB ASC Topic 606.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019 and the year ended December 31, 2018, we have incurred no losses from fixed fee engagements
that terminate prior to completion. We believe if an engagement terminates prior to completion, we can recover the costs incurred
related to the services provided.
We occasionally enter into arrangements for which
fixed and determinable revenues are contingent and agreed upon achieving a pre-determined deliverable or future outcome. Any contingent
revenue for these arrangements is not recognized until the contingency is resolved and collectability is reasonably assured.
Our arrangements with clients may include terms
to deliver multiple services or deliverables. These contracts specifically identify the services to be provided with the corresponding
deliverable. The value for each deliverable is determined based on the prices charged when each element is sold separately or
by other vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) or estimates of stand-alone selling prices. Revenues are recognized
in accordance with our accounting policies for the elements as described above (see Product Sales). The elements qualify for separation
when the deliverables have value on a stand-alone basis and the value of the separate elements can be established by VSOE or an
estimated selling price.
While assigning values and identifying separate
elements requires judgment, selling prices of the separate elements are generally readily identifiable as fixed and determinable
as we also sell those elements individually outside of a multiple services engagement. Contracts with multiple elements typically
incorporate a fixed-fee or hourly pricing structure. Arrangements are typically terminable by either party upon sufficient notice
and do not include provisions for refunds relating to services provided.
Reimbursable expenses, including those relating
to travel, other out-of-pocket expenses and any third-party costs, are included as a component of revenues. Typically, an equivalent
amount of reimbursable expenses is included in total direct client service costs. Reimbursable expenses related to time and materials
and fixed-fee engagements are recognized as revenue in the period in which the expense is incurred and collectability is reasonably
assured. Taxes collected from customers and remitted to governmental authorities are presented in the statement of operations
on a net basis.
Costs of Revenues
The Company’s policy is to recognize costs of revenue in
the same manner in conjunction with revenue recognition. Cost of revenue includes the costs directly attributable to revenue recognition
and includes compensation and fees for services, travel and other expenses for services and costs of products and equipment. Selling,
general and administrative expenses are charged to expense as incurred.
Advertising and Promotion Costs
Selling and Marketing costs are included as a component of selling
and marketing expense and are expensed as incurred. During the three months ended June 30, 2019 and June 30, 2018, these costs
were $78,399 and $71,711, respectively.
Shipping and Handling Costs
For product and equipment sales, shipping and handling costs are
included as a component of cost of revenues.
Stock-Based Compensation
Restricted shares are awarded to employees and entitle the grantee to
receive shares of common stock at the end of the established vesting period. The fair value of the grant is based on the stock
price on the date of grant. The Company recognizes related compensation costs on a straight-line basis over the requisite vesting
period of the award. During the three months ended June 30, 2019 and June 30, 2018, the Company had stock based compensation expense
of $0 and $25,242, respectively. During six months ended June 30, 2019 and June 30, 2018, there was $43,744 and $25,242 in stock
based compensation expense respectively.
Income Taxes
The Company’s corporate status changed from
an SCorporation, which it had been since inception, to a CCorporation during the year ended December 31, 2014. As provided in
Section 1361 of the Internal Revenue Code, for income tax purposes, SCorporations are not subject to corporate income taxes;
instead, the owners are taxed on their proportionate share of the SCorporation’s taxable income. Accordingly, we were not
subject to income taxes for the three months ended June 30, 2019. We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected
future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns in accordance with applicable
accounting guidance for accounting for income taxes, using currently enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences
are expected to reverse. We record a valuation allowance when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to
be realized. For the three months ended June 30, 2019, due to cumulative losses since our corporate status changed, we recorded
a valuation allowance against our deferred tax asset that reduced our income tax benefit for the period to zero. As of June 30,
2019, and December 31, 2018, we had no liabilities related to federal or state income taxes and the carrying value of our deferred
tax asset was zero.
Related Party Transactions
The Company follows FASB ASC subtopic 850-10, Related Party Disclosures,
for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to ASC 850-10-20, related parties include:
a) affiliates of the Company; b) entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the
election of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of Section 825–10– 15, to be accounted for
by the equity method by the investing entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and profit sharing
trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management
of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one party controls or can significantly influence the
management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing
its own separate interests; and g) other parties that can significantly influence the management or operating policies of
the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can significantly influence the
other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests.
Net Income (Loss) Per Common Share
The Company reports net income (loss) per common
share in accordance with FASB ASC 260, “Earnings per Share”. This statement requires dual presentation of basic and
diluted earnings with a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator of the earnings per share computations. Basic net income
(loss) per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares
of common stock outstanding during the period and excludes the effects of any potentially dilutive securities. Diluted net income
(loss) per share gives effect to any dilutive potential common stock outstanding during the period. The computation does not assume
conversion, exercise or contingent exercise of securities that would have an antidilutive effect on earnings.
Due to the Company’s net losses for the
three months ended June 30, 2019, any potentially dilutive shares outstanding for these periods, respectively, were not presented
in the EPS computations, as their effect would have been antidilutive.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases
(Topic 842). This ASU requires lessees to recognize a lease liability, on a discounted basis, and a right-of-use asset for substantially
all leases, as well as additional disclosures regarding leasing arrangements. In July 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-11, Leases
(Topic 842), which provides an optional transition method of applying the new lease standard. Topic 842 can be applied using either
a modified retrospective approach at the beginning of the earliest period presented, or as permitted by ASU 2018-11, at the beginning
of the period in which it is adopted.
We adopted this standard using a modified retrospective
approach on January 1, 2019. The modified retrospective approach includes a number of optional practical expedients relating to
the identification and classification of leases that commenced before the adoption date; initial direct costs for leases that
commenced before the adoption date; and, the ability to use hindsight in evaluating lessee options to extend or terminate a lease
or to purchase the underlying asset.
The Company elected the package of practical expedients
permitted under ASC 842 allowing it to account for its existing operating lease that commenced before the adoption date as an
operating lease under the new guidance without reassessing (i) whether the contract contains a
lease; (ii) the classification of the lease; or, (iii) the accounting for indirect costs as defined in ASC 842.
In considering its qualitative disclosure obligations
under ASC 842-20-50-3, the Company examined its one lease for office space that has a fixed monthly rent with no variable lease
payments and no options to extend. The lease is for an office space with no right of use assets. The lease does not provide for
terms and conditions granting residual value guarantees by the Company, or any restrictions or covenants imposed by the lease
for dividends or incurring additional financial obligations by the Company. The Company also elected a short-term lease exception
policy and an accounting policy to not separate non-lease components from lease components for our facility lease, as we determined
our right of use asset to be zero.
Consistent with ASC 842-20-50-4, for the Company's
June 30, 2019, quarterly financial statements, the Company calculated its total lease cost based solely on its monthly rent obligation.
The Company had no cash flows arising from its lease, no finance lease cost, short term lease cost, or variable lease costs. Our
office lease does not produce any sublease income, or any net gain or loss recognized from sale and leaseback transactions. As
a result, the Company did not need to segregate amounts between finance and operating leases for cash paid for amounts included
in the measurement of lease liabilities, segregated between operating and financing cash flows; supplemental non-cash information
on lease liabilities arising from obtaining right-of-use assets; weighted-average calculations for the remaining lease term; or
the weighted-average discount rate.
The adoption of this guidance resulted in no significant impact to our
results of operations or cash flows.
Reclassification
Prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year
presentation.
Note 3. Accounts Receivable, net
Accounts receivable, net, was comprised of the following as of June 30,
2019 and December 31, 2018:
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Gross accounts receivable
|
|
$
|
279,941
|
|
|
$
|
61,519
|
|
|
Less: allowance for doubtful accounts
|
|
|
(43,116
|
)
|
|
|
(2,635
|
)
|
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
|
$
|
236,825
|
|
|
$
|
58,884
|
|
The Company had bad debt expense during the three months ended June 30,
2019 of $41,481, whereas bad debt expense during the three months ended June 30, 2018 was $3,553.
Note 4. Inventory
Inventory as of June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018 consisted of the
following:
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Raw materials
|
|
$
|
800
|
|
|
$
|
1,646
|
|
|
Demo
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Finished goods
|
|
|
39,595
|
|
|
|
59,359
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
40,396
|
|
|
$
|
61,005
|
|
Note 5. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net, was comprised of the following as of June
30, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Office equipment
|
|
$
|
11,324
|
|
|
$
|
8,482
|
|
|
Furniture and fixtures
|
|
|
7,240
|
|
|
|
7,240
|
|
|
Machinery and equipment
|
|
|
7,795
|
|
|
|
7,336
|
|
|
Property and equipment, gross
|
|
|
26,360
|
|
|
|
23,058
|
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation
|
|
|
(16,914
|
)
|
|
|
(15,020
|
)
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
$
|
9,446
|
|
|
$
|
8,037
|
|
Note 6. Deposits
Deposits were comprised of the following as of June 30, 2019 and December
31, 2018:
|
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
|
Deposits
|
|
|
|
$
|
4,500
|
|
|
$4,500
|
|
|
Deposits
|
|
|
|
$
|
4,500
|
|
|
$4,500
|
Deposits as of June 30, 2019
and December 31, 2018 reflect down payments made to vendors and service providers.
Note 7. Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets were comprised of the following
as of June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Prepaid Expenses
|
|
$
|
61,432
|
|
|
$
|
56,376
|
|
|
Other Current Assets
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
61,432
|
|
|
$
|
56,376
|
|
Note 8. Accrued and Other Current Liabilities
Accrued and other current liabilities was comprised of the following
at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018
|
|
|
June 30,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Accrued payroll liabilities
|
|
|
10,821
|
|
|
|
10,924
|
|
|
Other accruals
|
|
|
61,793
|
|
|
|
78,884
|
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities
|
|
$
|
72,614
|
|
|
$
|
89,768
|
|
Note 9. Related Party Transactions
During the six months ended June 30, 2019, the
Company incurred no related party expenses.
Note 10. Stock based Compensation
Restricted Shares
From time to time, the Company grants certain employees
restricted shares of its common stock to provide further compensation in lieu of wages and to align the employee’s interests
with the interests of its stockholders. Because vesting is based on continued employment, these equity based incentives are also
intended to attract, retain and motivate personnel upon whose judgment, initiative and effort the Company’s success is largely
dependent.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018,
the Company granted 89,708 and 29,014 restricted shares, and incurred total stock based compensation expense of $43,744 and $25,242
respectively.
Warrants
As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, the
Company issued fully vested warrants to the Company’s independent board member to purchase up to two hundred and fifty thousand
(250,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share were outstanding, exercisable within
five (5) years of the date of issuance on November 19, 2014. The grant date fair value of the warrants, as calculated based on
the BlackScholes valuation model, was $0.59 per share. There were no outstanding unvested warrants or new issuances of warrants
during the three months ended June 30, 2019; consequently, no stock based compensation expense associated with warrants was
recorded during the three months ended June 30, 2019.
As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, as the
exercise price per share exceeded the price per share of our common shares, there was no aggregate intrinsic value of outstanding
warrants. As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, the warrants had 1.4 years and 1.9 years remaining until expiration respectively.
No warrants were issued or outstanding during or preceding the three months ended June 30, 2019.
As of December 31, 2018, the Company issued cashless
warrants to employees to purchase an aggregate of 895,000 shares. The warrants exercisable within three (3) years of the date
of issuance, expiring February 23, 2021. The grant date fair value of the warrants, as calculated based on the BlackScholes valuation
model, was $0.23 per share. As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, as the exercise price per share exceeded the price per
share of our common shares, there was no aggregate intrinsic value of outstanding warrants.
Stock Options
In addition to the warrants as described above, on November 19, 2014,
the Company granted its independent board member, Vincent “Tripp” Keber an option to purchase three hundred thousand
(300,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants and options expire
on November 19, 2019. None have been exercised.
Stock Issuable in Compensation for Professional Services
From time to time, the Company enters into agreements
whereby a professional service provider will be compensated for services rendered to the Company by shares of common stock in
lieu of cash. During the three months ended June 30, 2019, no common stock was issued.
Note 11. Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred Stock
American Cannabis Company, Inc. is authorized
to issue 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock at $0.01 par value. No shares of preferred stock were issued and outstanding during
the three months ended June 30, 2019, and 2017 respectively.
Common Stock
American Cannabis Company, Inc. is authorized to issue 100,000,000 common
shares at $0.00001 par value per share.
For the three months ended June 30, 2019, the Company did not issue any
stock based compensation.
For the six months ended June 30, 2019, the Company issued 50,000
common shares to Tyler A. Schloesser as a signing bonus valued at $22,500 and 39,708 common shares to Gayle Barr for services
rendered valued at $21,244.
Note 12. Commitments and Contingencies
The Company rents space for its corporate offices paying a monthly rent
of $4,500. The monthly rent is fixed and is for office space only. Our lease provides for no other right of use assets. There
is no residual value guarantee associated with the lease. There are no restrictions or covenants providing for dividends, or imposing
additional financial obligations by the Company. We elected to apply a short-term lease exception and accounting policy to not
separate lease and non-lease components from our office lease, as we determined our right of use asset to be zero.
Note 13. Subsequent Events
On July 9, 2019, the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable
Living Trust delivered elections to exercise two cashless warrants: one for 400,000 shares and one for 100,000 shares. The Company
issued a total of 500,000 common shares to the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust.
On July 10, 2019, Tyler A. Schloesser delivered
elections to exercise two cashless warrants: one for 100,000 shares and one for 102,500 shares. On July 13, 2019 the Company issued
a total of 202,500 shares to Tyler A. Schloesser.
On July 13, 2019, Jon Workman delivered an election
to exercise a cashless warrant for 100,000 shares. The Company issued 100,000 shares to Jon Workman on July 13, 2019.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial
condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements and supplementary
data referred to in this Form S-1. The statements contained in this report that are not statements of historical fact, including
without limitation, statements containing the words “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates” and
similar words, constitute forward-looking statements that are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties. From time to time
we may make other forward-looking statements. Investors are cautioned that such forward-looking statements are subject to an inherent
risk that actual results may materially differ as a result of many factors, including the risks discussed from time to time in
this report, including the risks described under “Risk Factors” in any filings we have made with the SEC.
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition
and results of operations are based upon our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments
that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. On an on-going basis, we evaluate these estimates,
including those related to useful lives of real estate assets, cost reimbursement income, bad debts, impairment, net lease intangibles,
contingencies and litigation. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed
to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of
assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. There can be no assurance that actual results will not
differ from those estimates.
Background
American Cannabis Company, Inc. and subsidiary is
a publicly listed company quoted on the OTCQB under the symbol “AMMJ”. We are based in Denver, Colorado and operate
a fully-integrated business model that features end-to-end solutions for businesses operating in the regulated cannabis industry
in states and countries where cannabis is regulated and/or has been de-criminalized for medical use and/or legalized for recreational
use. We provide advisory and consulting services specific to this industry, design industry-specific products and facilities,
and sell both exclusive and non-exclusive customer products commonly used in the industry.
The Company was incorporated in the State of Delaware
on September 24, 2001 under the name “Naturewell, Inc.” On March 13, 2013, the Company completed a merger transaction
whereby it acquired Brazil Interactive Media, Inc. (“BIMI”), a Brazilian interactive television company and television
production company. The Company’s Certificate of Incorporation were amended to reflect a new name: Brazil Interactive Media,
Inc. On May 15, 2014 the Company entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger with Cannamerica Corp. (the “Merger Sub”),
a wholly-owned subsidiary of BIMI, and Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. doing business as American Cannabis Consulting (“American
Cannabis Consulting”). The merger was completed on September 29, 2014, resulting in American Cannabis Consulting being merged
with and into the Merger Sub (the “Reverse Merger”). The Company subsequently amended its Certificate of Incorporation
to change its name to “American Cannabis Company, Inc.” Upon the closing of the Reverse Merger, all of the Company’s
officers and directors appointed designee officers and directors from American Cannabis Consulting and resigned. Consistent with
the Merger Agreement, the Company consummated a complete divestiture of BIMI, Inc., a Delaware corporation and wholly-owned subsidiary
of the Company, pursuant to a Separation and Exchange Agreement dated May 16, 2014 (the “Separation Agreement”) between
the Company, BIMI, Inc., and Brazil Investment Holding, LLC (“Holdings”), a Delaware limited liability company.
On October 10, 2014, the Company changed its stock
symbol from BIMI to AMMJ.
Results of Operations
Year ended December 31, 2018 compared to year ended December 31, 2017
The following table presents our operating results for the year ended
December 31, 2018 compared to December 31, 2017:
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(AUDITED)
|
|
|
For the year ended
December 31,
|
|
|
|
2018
|
|
2017
|
|
Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consulting services
|
|
$
|
395,840
|
|
|
$
|
2,054,484
|
|
|
Product and equipment
|
|
|
548,878
|
|
|
|
388,571
|
|
|
Shipping services
|
|
|
37,630
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total Revenues
|
|
|
982,349
|
|
|
|
2,443,055
|
|
|
Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of consulting services
|
|
|
121,641
|
|
|
|
463,298
|
|
|
Cost of products and equipment
|
|
|
402,206
|
|
|
|
342,522
|
|
|
Total Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
523,847
|
|
|
|
805,820
|
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
|
458,502
|
|
|
|
1,637,235
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
868,294
|
|
|
|
1,042,889
|
|
|
Investor relations
|
|
|
20,983
|
|
|
|
34,554
|
|
|
Selling and marketing
|
|
|
293,241
|
|
|
|
278,542
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
590
|
|
|
|
2,403
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
|
|
1,183,109
|
|
|
|
1,358,388
|
|
|
Income (Loss) from Operations
|
|
|
(724,607
|
)
|
|
|
278,847
|
|
|
Other Income (Expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense)
|
|
|
(52
|
)
|
|
|
9,288
|
|
|
Stock based compensation (expense)
|
|
|
(73,742
|
)
|
|
|
(893,857
|
)
|
|
Bad debt (expense)
|
|
|
(2,815
|
)
|
|
|
89,715
|
|
|
Settlement (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(118,450
|
)
|
|
Warrant (expense)
|
|
|
(204,955
|
)
|
|
|
(895,860
|
)
|
|
Other income
|
|
|
55,481
|
|
|
|
41,884
|
|
|
Total Other Income (Expense)
|
|
|
(226,084
|
)
|
|
|
(1,767,320
|
)
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Before Taxes
|
|
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Income tax expense (benefit)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
NET INCOME (LOSS)
|
|
$
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,488,474
|
)
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per common share
|
|
$
|
(0.02
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.03
|
)
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding
|
|
|
51,465,188
|
|
|
|
51,336,522
|
|
Revenues
Total revenues for the year ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, were $982,349 and $2,443,054 respectively, a decrease of $1,460,705. This decrease was primarily
due to a decrease in the demand for consulting services in 2018 as the result of fewer states enacting legislation legalizing cannabis
for medical and/or recreational use, and also due to some of our consulting clients being in various early stages of their projects,
which results in periodic fluctuations of cyclical consulting revenues. For the year ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017,
consulting services revenue was $395,840 and $2,054,484, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017,
products and equipment revenues were $548,878 and $388,571 respectively. The increase attributable to our product and services
revenues was due to our clients ordering products and equipment to support their businesses. We also realized revenue of $37,630
from shipping services that are charged to customers for our product and equipment sales. We expect to see growth in the future
as more states legalize the medical and recreational use and sale of cannabis, and we continue to establish our products and equipment
offerings as our business and the industry matures.
Costs of Revenues
Costs
of revenues primarily consist of labor, travel, marketing and other costs directly attributable to providing services or offering
products. For the year ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, our total costs of revenues were $523,847 and $805,820,
respectively. The decrease was primarily due to lower operating expenses related to providing consulting services. For the year
ended December 31, 2018, consulting related costs were $121,641 or 12.4% of total revenues, and costs associated with products
and equipment were $402,206 or 40.9% of total revenues. For the year ended December 31, 2017, consulting related costs were $463,298
or 18.8% of total revenues, and costs associated with products and equipment were $342,522 or 14.02% of total revenues.
Gross Profit
For the year ended December 31, 2018 and December
31, 2017, gross profit was $458,502 and $1,637,234, respectively. This decrease of $1,178,732 was primarily due to a reduction
in our client base and volume of operations for consulting services. As a percentage of total revenues, gross profit was 46.7%
and 67.02% for the years ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, respectively. This decrease was primarily due to the year
ended December 31, 2017 having a higher proportion of total revenues from consulting services as compared to product and equipment
sales, as consulting services have a higher profit margin as compared to product and equipment sales.
Operating Expenses
Total operating expenses for the years ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017 was $1,183,109 and $1,358,388, respectively. This decrease of $175,279 was due to a reduction in
operating expenses caused by a decline of consulting services provided.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income (expense) for the years ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017 included an expense of ($226,084), and ($1,767,320), respectively. This decrease of ($1,541,236)
was due to the Company’s reducing its 2018 stock based compensation by ($820,115) and its warrant expenses by ($690,905).
Income Tax Expense (Benefit)
We did not have any income tax expense or benefit
for the years ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, respectively. Although our tax status changed from a non-taxable
pass-through entity (S-Corporation) to a taxable entity (C-Corporation) during the year ended December 31, 2014, due to cumulative
losses since we became a C-Corporation, we recorded a valuation allowance against our related deferred tax asset which netted
our deferred tax asset and benefit for income taxes to zero. We were an S-Corporation throughout the period from Inception (March
5, 2013) through December 31, 2013, and accordingly, no provision or benefit for income taxes was applicable. The years 2010 to
2018 remain subject to examination by the Company’s major tax jurisdictions.
Net Income (Loss)
As a result of the factors discussed above, net
income for the year ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017 was a profit of ($954,441) and ($1,488,474), respectively. For
December 31, 2018 our net loss was 96.8% of total revenues. For December 31, 2017, our net losses represented a 60.9% of total
revenues for the respective periods.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2018, and December 31, 2017,
our primary internal sources of liquidity were cash and cash equivalents of $1,086,565 and $1,648,087, respectively. We also have
the ability to raise additional capital as needed through an external equity financing transactions. For the years ended December
31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, the Company had a source (use) of cash from operations of ($561,522) and $180,540, respectively.
For December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, we generated non-cash expenses of $278,697 and $1,789,717 respectively. The decrease
of $1,511,020 related to stock-based compensation and warrant expenses. Due to this factor and considering that our fixed overhead
costs are relatively low, we have the ability to issue stock and stock equivalents to compensate employees and management, and
the level of future revenue we expect to generate from executed client contracts, we believe our liquidity and capital resources
to be adequate to fund our operational and general and administrative expenses for the next 12 months.
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
for the year ended December 31, 2018 was ($561,522). Net cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31,
2017 was $180,540. The net cash used in operations increased by ($742,062). This was due to a net loss
of ($950,691) and an increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets of $45,050.
Investing Activities
For the years ended December 31, 2018 and December
31, 2017, net cash used in investing activities was $0 and $4,629, respectively.
Financing Activities
For the years ended December 31, 2018 and December
31, 2017, financing activities were a source of cash of $0 and $721,138, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2018 and
2017, the Company received $0 and $721,138 from the sale of registered common stock to Tangiers Global, LLC under an amended and
restated Investment Agreement and Registration Rights Agreement dated August 4, 2016.
For the years ended December 31, 2018 and December
31, 2017 we had cash and cash equivalents of $1,086,565 and $1,648,087, respectively. We believe our liquidity and capital resources
to be adequate to fund our operational and general and administrative expenses for the next 12 months.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2018, and December 31, 2017, we
did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial
condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital
resources.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
We use Adjusted EBITA,
a non-GAAP metric, to monitor our overall business performance. We define Adjusted EBITA as net income (loss) before interest
expense, net, provision for (benefit from) income taxes, stock-based compensation and certain non-recurring expenses, which for
the year ended December 31, 2014 were limited to costs associated with the Reverse Merger. We believe that such adjustments to
arrive at Adjusted EBITA provides us with a more comparable measure for managing our business. We also believe that it is a useful
measure for securities analysts, investors, and other interested parties in the evaluation of our Company.
A reconciliation of net income to Adjusted EBITA
is provided below.
|
Adjusted EBITA Reconciliation
|
|
For the Year Ended
December 31, 2018
|
|
For the Year Ended
December 31, 2017
|
|
Net Gain (Loss)
|
|
$
|
(950,691
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1,488,473
|
)
|
|
Interest Expense, Net
|
|
$
|
52
|
|
|
$
|
(9,288
|
)
|
|
Tax Expense (benefit)
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Stock Based Compensation expense
|
|
$
|
73,742
|
|
|
$
|
893,857
|
|
|
Adjusted EBITA
|
|
$
|
(876,897
|
)
|
|
$
|
(603,904
|
)
|
The statements contained in this report that are
not statements of historical fact, including without limitation, statements containing the words “believes,” “expects,”
“anticipates” and similar words, constitute forward-looking statements that are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties.
From time to time we may make other forward-looking statements. Investors are cautioned that
such forward-looking statements are subject to an inherent risk that actual results may materially differ as a result of many
factors, including the risks discussed from time to time in this report, including the risks described under “Risk Factors”
in any filings we have made with the SEC.
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition
and results of operations are based upon our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments
that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. On an on-going basis, we evaluate these estimates,
including those related to useful lives of real estate assets, cost reimbursement income, bad debts, impairment, net lease intangibles,
contingencies and litigation. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed
to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of
assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. There can be no assurance that actual results will not
differ from those estimates.
Results of Operations
For the three months and six months ended June 30, 2019 compared to
three and six months ended June 30, 2018.
AMERICAN CANNABIS COMPANY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Three Months
|
|
Three Months
|
|
Six Months
|
|
Six Months
|
|
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
Ended
June 30,
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
2019
|
|
2018
|
|
Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consulting Services
|
|
|
492,184
|
|
|
|
97,090
|
|
|
|
653,838
|
|
|
|
182,692
|
|
|
Shipping Services
|
|
|
13,127
|
|
|
|
3,461
|
|
|
|
23,122
|
|
|
|
30,383
|
|
|
Product & Equipment
|
|
|
225,657
|
|
|
|
77,705
|
|
|
|
464,321
|
|
|
|
241,130
|
|
|
Total Revenues
|
|
|
730,968
|
|
|
|
178,256
|
|
|
$
|
1,141,281
|
|
|
$
|
454,205
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Consulting Services
|
|
|
79,324
|
|
|
|
24,711
|
|
|
|
113,251
|
|
|
|
81,772
|
|
|
Cost of Products and Equipment
|
|
|
150,741
|
|
|
|
53,829
|
|
|
|
343,163
|
|
|
|
140,839
|
|
|
Total Cost of Revenues
|
|
|
230,064
|
|
|
|
78,540
|
|
|
$
|
456,414
|
|
|
$
|
222,611
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
|
500,903
|
|
|
|
99,716
|
|
|
$
|
684,867
|
|
|
$
|
235,055
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and Administrative
|
|
|
207,182
|
|
|
|
199,794
|
|
|
|
450,265
|
|
|
|
431,039
|
|
|
Investor Relations
|
|
|
14,085
|
|
|
|
4,895
|
|
|
|
31,932
|
|
|
|
10,824
|
|
|
Selling and Marketing
|
|
|
78,399
|
|
|
|
71,711
|
|
|
|
153,738
|
|
|
|
127,079
|
|
|
Research and Development
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
196
|
|
|
|
590
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
|
|
299,667
|
|
|
|
276,400
|
|
|
$
|
636,130
|
|
|
$
|
569,532
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) from Operations
|
|
|
201,236
|
|
|
|
(176,684
|
)
|
|
$
|
48,737
|
|
|
$
|
(334,477
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Income (expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest (expense)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
121
|
|
|
Stock Based Compensation
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(25,242
|
)
|
|
|
(43,744
|
)
|
|
|
(25,242
|
)
|
|
Bad Debt (expense)
|
|
|
(41,481
|
)
|
|
|
(3,553
|
)
|
|
|
(43,774
|
)
|
|
|
(19,985
|
)
|
|
Settlement (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Warrant (expense)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other Income
|
|
|
13,267
|
|
|
|
635
|
|
|
|
17,517
|
|
|
|
3,641
|
|
|
Total other income (expense)
|
|
|
(28,214
|
)
|
|
|
(28,074
|
)
|
|
$
|
(70,001
|
)
|
|
$
|
(41,465
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) before taxes
|
|
|
173,023
|
|
|
|
(204,758
|
)
|
|
$
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
$
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
Income Tax Expense (benefit)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET INCOME (LOSS)
|
|
$
|
173,023
|
|
|
$
|
(204,758
|
)
|
|
$
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
$
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per common share
|
|
$
|
0.00
|
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)*
|
|
$
|
(0.00
|
)
|
|
$
|
(0.01
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding
|
|
|
51,611,448
|
|
|
|
51,452,174
|
|
|
|
52,074,072
|
|
|
|
51,452,174
|
|
|
*Denotes a loss of less than ($0.01)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
Total revenues were $730,968 for the three months
ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $178,256 for the three months ended June 30, 2018, an increase of $552,712. Total revenues
for the six months ended June 30, 2019 were $1,141,281 as compared to $454,205 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. Consulting
service revenues were $492,184 or 67.3% of total revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2019, versus $97,090 or 54.5% of
total revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2018. Consulting service revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2019 were
$653,838 or 57.3% of total revenues, as comparted to $182,692 or 40.2% of total revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2018.
Our product and equipment revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2019 were $225,657 or 30.9% of total revenues, versus $77,705
or 43.6% of total revenues for three months ended June 30, 2018. For the six months ended June 30, 2019, our product and equipment
revenues were $464,321 or 40.7% of total revenues, as compared to $241,130, 53.1% of total revenues for the six months ended June
30, 2018. The increase in equipment revenue was attributed to increased client orders with the company experiencing spikes in
product revenues during facility design and buildouts. The company increased its focus towards selling soil and equipment for
the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, while two facility buildouts were in progress during the three and six months ended
June 30, 2018. The increase in our consulting service revenues for the three and six months ended June 30 2019, reflects more
states enacting legislation legalizing cannabis during the period.
Costs of Revenues
Costs of revenues primarily consist of labor, travel,
cost of equipment and soil sold, and other costs directly attributable to providing services or products. During the three months
ended June 30, 2019, our total costs of revenues were $230,064, or 31.5% of total revenues. This compares to total costs of revenues
for the three months ended June 30, 2018 of $78,540 or 44.1% of total revenues. For the six months ended June 30, 2019, total
cost of revenues were $456,414 or 40.0% of total revenues, as comparted to $222,611 or 49% of total revenues for the six months
ended June 30, 2018. For the three months ended June 30, 2019, consulting related costs were $79,324, or 10.9% of total revenue,
as compared to costs of $24,711, or 13.9% of revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2018. For the six months ended June 30,
2019, consulting related costs were $113,251 or 9.9% of total revenues, as compared to $81,772 or 18% of total revenues for the
six months ended June 30, 2018. Costs associated with products and equipment were $150,741, or 20.6% of total revenue for the
three months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $53,829, or 30.2% of total revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2018. Costs
associated with products and services were $343,163 or 30.1% of total revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2019 as compared
to $140,839 or 31% of total revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2018. As a percentage of revenues, the increase in costs
associated with product sales during the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, was attributed to spikes in product revenues
resulting from completed design and facility buildouts during the three and six months ended June 30, 2018.
Gross Profit
Total gross profit was $500,903 for the three months
ended June 30, 2019, comprised of consulting services gross profit of $412,860 and products and equipment gross profit of $88,043.
This compares to total gross profit of $99,716 for the three months ended June 30, 2018, comprised of consulting services gross
profit of $72,379 and products and equipment gross profit of $27,337. For the six months ended June 30, 2019, gross profits were
$684,867, comprised gross profits for consulting services of $540,587 and product and equipment $144,280, as compared to gross
profits for the six months ended June 30, 2018 of $235,055, comprised gross profits for consulting services of $100,920 and product
and equipment $134,135. Total gross profits of the six months ended June 30, 2019 as comparted to 2018 reflect an increase of
$449,812. The increase in our consulting services gross profits reflects more states enacting legislation during the period legalizing
cannabis, and so there is a corresponding increase in the demand for our consulting services. The increase in gross profits
for products and equipment was due to the Company expanding its product sales to existing clients during the period. As a percentage
of total revenues, gross profit was 68.5% and 60.0% for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to 55.9% and
51.8% for the three and six months ended June 30, 2018.
Operating Expenses
Total operating expenses were $299,667, or 41.0%
of total revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2019, and $636,130 or 55.74% for the six months ended June 30, 2019, as
compared to $276,400, or 155.1% of total revenues for the three months ended June 30, 2018, and $569,532 or 125.4% for the six
months ended June 30, 2018. This increase was primarily due to an increase in employees whose wages were allocated to general
and administrative expenses for the relevant time periods.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income (expense) for the three months ended
June 30, 2019 was expense of $28,214 as compared with expense of $28,074 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. For the six
months ended June 30, 2019, other income (expense) was expense of $70,001 as compared with expense of $41,465 for the six months
ended June 30, 2018. The increase in our other expense was due to an increase of bad debt expense of $23,789.
Net Income (Loss)
As a result of the factors discussed above, net
income for the three months ended June 30, 2019 was $173,023 or 23.7% of total revenues for the period, as compared to a net (loss)
for the three months ended June 30, 2018 of $(204,758) or (114.9%) of total revenues for the period. For the six months ended
June 30, 2019, the net (loss) was ($21,264) or (1.9%) of total revenues for the period, as compared to the net (loss) was ($375,942)
or (82.8%) of total revenues for the period.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of June 30, 2019, our primary internal sources
of liquidity were our working capital, which included cash and cash equivalents of $918,127 and accounts receivable of $236,825.
Additionally, considering that our fixed overhead costs are low, we have the ability to issue stock to compensate employees and
management, and the level of future revenue we expect to generate from executed client contracts, we believe our liquidity and
capital resources to be adequate to fund our operational and general and administrative expenses for at least the next 12 months
without needing to raise additional debt or equity funding. There is no guarantee we will have the ability to raise additional
capital as needed through external equity financing transactions if required.
Operating Activities
Net cash used by operating activities for the six
months ended June 30, 2019 was a use of $(165,136), consisting of increases in accounts receivable costs of ($221,714), compared
to net cash used by operating activities of $(348,635), consisting of increases in inventory costs of ($58,531) for the six months
ended June 30, 2018.
Investing Activities
For the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, investing activities
were a use of cash of $3,302 and $0 respectively.
Financing Activities
For the three months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, the net cash from
financing activities was $0 and $0 respectively.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of June 30, 2019, and December 31, 2018, we did
not have any off balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial
condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital
resources.
NonGAAP Financial Measures
We use Adjusted EBITA, a non-GAAP metric, to monitor
our overall business performance. We define Adjusted EBITA as net income (loss) before interest expense, net, provision for (benefit
from) income taxes, stock based compensation and certain nonrecurring expenses, which to date have been limited to costs associated
with the Reverse Merger. We believe that such adjustments to arrive at Adjusted EBITA provides us with a more comparable measure
for managing our business. We also believe that it is a useful measure for securities analysts, investors, and other interested
parties in the evaluation of our Company. A reconciliation of net income to Adjusted EBITA
is provided below.
|
|
|
Six Months
Ended
|
|
Six Months Ended
|
|
|
|
June 30,
2019
|
|
June 30,
2018
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
(Unaudited)
|
|
Adjusted EBITA reconciliation:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss)
|
|
|
(21,264
|
)
|
|
|
(375,942
|
)
|
|
Stock-based compensation to employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation to service providers
|
|
|
43,744
|
|
|
|
25,242
|
|
|
Depreciation Expense
|
|
|
1,893
|
|
|
|
1,998
|
|
|
Interest expense, net
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjusted EBITA
|
|
|
24,373
|
|
|
$
|
(348,702
|
)
|
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING
AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
Directors and Executive Officers
Our Board of Directors
The following table sets forth information regarding our
current directors and each director nominee, as of June 30, 2019.
|
Name
|
|
Principal
Occupation
|
|
Age
|
|
Director
Since
|
|
Ellis Smith
|
|
Chief Development Officer
& Chairman of the Board, American Cannabis Company, Inc.
|
|
|
42
|
|
|
|
2014
|
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
|
Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial
Officer American Cannabis Company, Inc.
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
Tad Mailander
|
|
Independent Director
|
|
|
63
|
|
|
|
2018
|
|
Ellis Smith from
June 2014 to the present, Ellis Smith has served as our Chief Development Officer and as a director since September 2014. In March
2013, Mr. Smith co-founded ACC, and from March 2013 to May 2014, Mr. Smith served as a Managing Director of ACC. From September
2010 to July 2013, Mr. Smith co-owned Colorado Kind Care LLC d/b/a The Village Green Society, a Colorado-based Medical Marijuana
Center, where he was responsible for managing the operations and protocols supporting the growth and production of medical marijuana.
From 2008 to 2010, Mr. Smith founded and operated The Happy Camper Organics Inc., a medical cannabis company focused on the growth
of wholesale cannabis for sale to medical cannabis businesses. From 2005 to 2010, Mr. Smith founded and operated Bluebird Productions,
a video production company. Mr. Smith has been published and recognized for his horticultural experience and organic gardening
in the cannabis industry, and he is known for assisting in identifying the Hemp Russet Mite and working with SKUNK magazine to
educate the industry. Our Board believes Mr. Smith’s qualifications to serve as an executive of the Company and as a member
of our Board include his past success in founding and operating businesses, his unique experience in horticultural and organic
gardening, and his recognized qualifications in the emerging medical cannabis markets.
Terry Buffalo from
June 1, 2017 to present; Mr. Buffalo is an executive in the financial services industry, with extensive experience including managing
a hybrid FINRA broker-dealer and Registered Investment Advisor firm. Mr. Buffalo is regarded as an expert in these fields with
publications in Financial Advisor Magazine and NAIFA’s Advisor Today, as well as being a featured interview in Boomer Market
Advisor. Prior to founding Buffalo Financial Solutions, Mr. Buffalo was the Chief Executive Officer of a regional broker dealer
for over 10 years, where he took an underperforming firm and revamped the business model from a corporate to an independent structure,
with an emphasis on attracting brokers with established clienteles. While there, the firm consistently produced net profits of
7%, compared to industry average among peers that ranged between negative to 1.5%, while expanding the firm’s overall assets
from $400 million to over $2 billion.
Tad Mailander from
March 13, 2018 to present; Mr. Mailander is an attorney licensed to practice before all of the Courts in the State of California.
Mr. Mailander has been in practice since 1991 and is a member of the State Bar of California, the bars of the United States District
Court for the Southern District of California, and the United States Court of Appeal for the Ninth Circuit.
Our Executive Officers
We designate persons serving
in the following positions as our named executive officers: our chief executive officer, chief financial officer, chief development
officer, chief operating officer and chief technology officer. The following table sets forth information regarding our executive
officers as of June 30, 2019.
|
Name
|
|
Principal
Occupation
|
|
Age
|
|
Officer
Since
|
|
Terry
Buffalo
|
|
Principal
Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
Ellis
Smith
|
|
Chief
Development Officer
|
|
|
42
|
|
|
|
2014
|
|
|
Tyler
A. Schloesser
|
|
Chief
Operations Officer
|
|
|
29
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
Jon
Workman
|
|
Vice
President, Hemp Division
|
|
|
56
|
|
|
|
2019
|
|
Ellis Smith’s biographical
summary is included under “Our Board of Directors.”
Terry Buffalo’s biographical
summary is included under “Our Board of Directors.”
Tyler A. Schloesser, Mr. Schloesser
attended the University of Colorado at Boulder receiving a double major degree in Psychology and Philosophy. After graduation,
Mr. Schloesser worked in the banking industry with Wells Fargo, U.S. Bank and Credit Union of Colorado. Mr. Schloesser’s
functions with the Registrant. include developing and maintaining policies, procedures, processes and risk mitigation best practices
as well as manage and perform day-to-day internal operational tasks required by the Registrant.
Jon Workman,
Mr. Workman graduated from the University of Arkansas at Little Rock in 1989 and was awarded a Bachelor of Business Administration
and Marketing. Mr. Workman is a member of the Arkansas Cannabis Industry Association and a Charter Member of the Arkansas Hemp
Association. In 2017, the Arkansas Economic Development Commission certified Mr. Workman in its Lean Manufacturing program. Mr.
Workman received his HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) & SQF Food Safety Certifications in 2016.
Employment Agreements
We entered into an Executive Employment Agreement with
Terry Buffalo, our Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer, with an effective date of January 1, 2019. Under
the terms of this agreement, he is serving as an executive of our company. We agreed to pay him a base salary of $80,000 annually.
Such annual salary is payable consistent with the payroll practices as established by the Company. Payments will be subject to
income tax withholding and other payroll tax deductions required by applicable state and federal law. Additionally, the Company
agreed to issue Mr. Buffalo fifty thousand (50,000) shares of the Company’s common stock as compensation for services rendered
for 2019. The shares will be deemed earned and vested on December 31, 2019. In the event this Agreement is terminated before the
December 31, 2019, the shares shall be issued to Executive pro rata to the date of termination. He is also entitled to participate
in all benefit programs made available to our executive and/or salaried employees, paid vacation and reimbursement for business
related expenses. The term of the agreement is one year. The agreement may be terminated by either party giving written notice
of such party’s intention to terminate the agreement and the employment of the Executive at least thirty (30) days prior
to the end of the term. We may also terminate Mr. Buffalo’s employment without notice and without any further compensation
obligations, (except his accrued benefits and any benefit continuation or conversion rights he may have under the terms of the
benefit plan or applicable law) if the termination is based on a material violation of the agreement, fraud, embezzlement, securities
law violation, other gross misconduct which causes material economic damage to the Company or material damage to the business
reputation of the Company.
We also entered into an Executive Employment Agreement
with Ellis Smith, our Chief Development Officer, with an effective date of January 1, 2019. Under the terms of this agreement,
he is serving as our Chief Development Officer. We agreed to pay him a base salary of $87,000 annually. He is also entitled to
participate in all benefit programs made available to our executive and/or salaried employees,
paid vacation and reimbursement for business related expenses. Payments will be subject to income tax withholding and other payroll
tax deductions required by applicable state and federal law. Additionally, the Company agreed to issue Mr. Smith fifty thousand
(50,000) shares of the Company’s common stock as compensation for services rendered for 2019. The shares will be deemed
earned and vested on December 31, 2019. In the event this Agreement is terminated before the December 31, 2019, the shares shall
be issued to Executive pro rata to the date of termination. He is also entitled to participate in all benefit programs made available
to our executive and/or salaried employees, paid vacation and reimbursement for business related expenses. The term of the agreement
is one year. The agreement may be terminated by either party giving written notice of such party’s intention to terminate
the agreement and the employment of the Executive at least thirty (30) days prior to the end of the term. We may also terminate
Mr. Smith’s employment without notice and without any further compensation obligations, (except his accrued benefits and
any benefit continuation or conversion rights he may have under the terms of the benefit plan or applicable law) if the termination
is based on a material violation of the agreement, fraud, embezzlement, securities law violation, other gross misconduct which
causes material economic damage to the Company or material damage to the business reputation of the Company.
We also entered into an Executive Employment Agreement
with Tyler A. Schloesser, our Chief Operations Officer, effective as of January 29, 2019. Under the terms of this agreement, he
agreed to serve as our Chief Operations Officer and we agreed to pay him an annual salary of $72,000, and a one-time signing bonus
of fifty thousand (50,000) shares of the Company’s common stock, Additionally, the Company agreed to issue Mr. Schloesser
fifty thousand (50,000) shares of the Company’s common stock as compensation for services rendered for 2019. The shares
will be deemed earned and vested on December 31, 2019. In the event this Agreement is terminated before the December 31, 2019,
the shares shall be issued to Mr. Schloesser pro rata to the date of termination. He is also entitled to participate in all benefit
programs made available to our executive and/or salaried employees, paid vacation and reimbursement for business related expenses.
The term of the agreement is one year. The agreement may be terminated by either party giving written notice of such party’s
intention to terminate the agreement and the employment of the Executive at least thirty (30) days prior to the end of the term.
We may also terminate Mr. Schloesser’s employment without notice and without any further compensation obligations, (except
his accrued benefits and any benefit continuation or conversion rights he may have under the terms of the benefit plan or applicable
law) if the termination is based on a material violation of the agreement, fraud, embezzlement, securities law violation, other
gross misconduct which causes material economic damage to the Company or material damage to the business reputation of the Company.
We also entered into an Executive Employment Agreement
with Jon Workman, effective as of January 29, 2019. Under the terms of the agreement, he agreed to serve as our Vice President
focusing on the development of the Company’s American Hemp Consulting division. Mr. Workman will be compensated with an
annual salary of seventy-two thousand dollars ($72,000.00). Such annual salary shall be payable consistent with the payroll practices
as established by the Company. Payments will be subject to income tax withholding and other payroll tax deductions required by
applicable state and federal law. Additionally, the Company agreed to issue Mr. Workman fifty thousand (50,000) shares of the
Company’s common stock as compensation for services rendered for 2019. The shares will be deemed earned and vested on December
31, 2019. In the event this Agreement is terminated before the December 31, 2019, the shares shall be issued to Mr. Workman pro
rata to the date of termination. He is also entitled to participate in all benefit programs made available to our executive and/or
salaried employees, paid vacation and reimbursement for business related expenses. The term of the agreement is one year. The
agreement may be terminated by either party giving written notice of such party’s intention to terminate the agreement and
the employment of the Executive at least thirty (30) days prior to the end of the term. We may also terminate Mr. Workman’s
employment without notice and without any further compensation obligations, (except his accrued benefits and any benefit continuation
or conversion rights he may have under the terms of the benefit plan or applicable law) if the termination is based on a material
violation of the agreement, fraud, embezzlement, securities law violation, other gross misconduct which causes material economic
damage to the Company or material damage to the business reputation of the Company.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships between any director or executive officer.
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
None of our directors and executive officers has been involved in any of the
following events during the past ten years:
|
|
(a)
|
any petition under
the federal bankruptcy laws or any state insolvency laws filed by or against, or an appointment of a receiver, fiscal agent
or similar officer by a court for the business or property of such person, or any partnership in which such person was a general
partner at or within two years before the time of such filing, or any corporation or business association of which such person
was an executive officer at or within two years before the time of such filing;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b)
|
any conviction in
a criminal proceeding or being subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offences);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c)
|
being subject to
any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently
or temporarily enjoining such person from, or otherwise limiting, the following activities: (i) acting as a futures commission
merchant, introducing broker, commodity trading advisor, commodity pool operator, floor broker, leverage transaction merchant,
any other person regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or an associated person of any of the foregoing, or
as an investment adviser, underwriter, broker or dealer in securities, or as an affiliated person, director or employee of
any investment company, bank, savings and loan association or insurance company, or engaging in or continuing any conduct
or practice in connection with such activity; engaging in any type of business practice; or (iii) engaging in any activity
in connection with the purchase or sale of any security or commodity or in connection with any violation of federal or state
securities laws or federal commodities laws;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d)
|
being the subject
of any order, judgment or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any federal or state authority barring,
suspending or otherwise limiting for more than 60 days the right of such person to engage in any activity described in paragraph
(c)(i) above, or to be associated with persons engaged in any such activity;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(e)
|
being found by a
court of competent jurisdiction (in a civil action), the Securities and Exchange Commission to have violated a federal or
state securities or commodities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Securities and Exchange Commission
has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(f)
|
Being found by a
court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated any federal
commodities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission has not been
subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(g)
|
being the subject
of, or a party to, any federal or state judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree, or finding, not subsequently reversed,
suspended or vacated, relating to an alleged violation of: (i) any federal or state securities or commodities law or regulation;
or (ii) any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary
or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease- and-desist
order, or removal or prohibition order; or (iii) any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection
with any business entity; or
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(h)
|
being the subject
of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization
(as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934), any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29)
of the Commodity Exchange Act), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority
over its members or persons associated with a member.
|
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Summary Compensation Table
The particulars of compensation paid to the following persons:
|
|
(a)
|
all individuals serving as our principal executive
officer during the year ended December 31, 2018;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b)
|
each of our two
most highly compensated executive officers who were serving as executive officers at the end of the year ended December 31,
2018; and
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c)
|
up to two additional
individuals for whom disclosure would have been provided under (b) but for the fact that the individual was not serving as
our executive officer at December 31, 2018,
|
The following table sets forth information concerning
the compensation of our principal executive officer, our principal financial officer and each of our other executive officers
during 2018.
|
Name and Principal Position
|
|
Year
|
|
($)
|
|
($)
|
|
($)
|
|
($)
|
|
($)
|
|
($)
|
|
J. Michael Tuohey, Chief Financial
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
Officer1
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
66,000
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
66,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
34,250
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
34,250
|
|
|
Ellis Smith, Chief Development
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
86,950
|
|
|
|
―-
|
|
|
|
22,900
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
109,850
|
|
|
Officer
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
85,000
|
|
|
|
23,732
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
12,030
|
|
|
|
120,762
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
86,949
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
86,949
|
|
|
Terry Buffalo, Principal Executive
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
81,950
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
91,600
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
173,550
|
|
|
Officer, Principal Financial Officer
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
80,000
|
|
|
|
7,522
|
|
|
|
―-
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
87,552
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
62,152
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
3,330
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
65,452
|
|
|
R. Leslie Hymers, Chief Financial
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
39,240
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
48,500
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
87,740
|
|
|
Officer2
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
-―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
Michael Schwanbeck, Chief Financial
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
41,308
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
5,725
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
47,033
|
|
|
Officer3
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
-―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
Tyler A. Schloesser, Chief Operations
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
63,296
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
34,350
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
97,646
|
|
|
Officer
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
-―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
Jon Worknam, Vice President
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
|
41,538
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
22,900
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
64,438
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Mr.
Tuohey was terminated on April 24, 2018.
|
|
|
(2)
(3)
|
Mr. Hymers was appointed Chief Financial
Officer on April 24, 2018 and resigned on June 18, 2018.
Mr. Schwanbeck was appointed Chief Financial
Office on June 18, 2018 and resigned on August 26, 2019; On August 26, 2019, Mr. Buffalo was
appointed Principal Financial Officer.
|
Retirement Benefits
We do not currently provide our named executive officers
with supplemental or other retirement benefits.
Outstanding Equity Awards at December 31, 2018
Warrants
In connection with his appointment
to the Company’s board of directors on November 19, 2014, the Company granted its independent board member, Vincent “Tripp”
Keber, warrants to purchase up to two hundred and fifty thousand (250,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three
cents ($0.63) per share, exercisable within five (5) years of the date of issuance on November 19, 2014. Concurrently, the Company
agreed to award Mr. Keber an option to purchase three hundred thousand (300,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of
sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants and options expire on November 19, 2019.
On August 31, 2017, the Company
issued Anthony Baroud warrants to purchase up to fifty thousand (50,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.93
in a cashless transaction. The warrants expired on March 1, 2018.
On December 31, 2018, pursuant
to the Company’s Equity Incentive Plan, the Company issued an aggregate of 895,000 warrants to the following persons to
purchase common stock in cashless transactions, with an aggregate value of $204,995.
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Michael Schwanbeck warrants to purchase twenty-five thousand (25,000)
shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Mitchell Day warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common
stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Tad Mailander warrants to purchase one hundred thousand (100,000) shares
of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Tyler A. Schloesser warrants to purchase one hundred and fifty thousand
(150,000) shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued April Robertson warrants to purchase ten thousand (10,000) shares of common
stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust four hundred thousand (400,000)
shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Ellis Smith one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
|
|
|
·
|
The
Company issued Jon Workman one hundred thousand (100,000) shares of common stock.
|
As of December 31, 2018, and
the six months ended June 30, 2019, the Company had the following warrant activity:
|
|
|
Common Stock Warrants
|
|
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2015
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2016
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Outstanding unvested at December 31, 2017
|
|
|
300,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.91
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
1,685,000
|
|
|
|
0.58
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Expired or forfeited
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.93
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
|
Vested at December 31, 2018
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
Options
In addition to the warrants as described above, on November
19, 2014, the Company granted its Vincent “Tripp” Keber, its former independent board member, an option to purchase
three hundred thousand (300,000) shares of common stock at an exercise price of sixty-three cents ($0.63) per share. The warrants
and options expire on November 19, 2019. None have been exercised.
Compensation of Directors
The Board of Directors determined to issue no compensation for directors for
fiscal year ended December 31, 2018.
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND
MANAGEMENT
The following table sets forth information known
to us regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of December 31, 2018 by (1) each stockholder who is known
by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our common stock, (2) each of our directors, (3) each of our executive officers
named in the Summary Compensation Table above, and (4) all of our directors and executive officers as a group.
|
|
|
Number of
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beneficially
|
|
|
|
Beneficial Owner(1)
|
|
Owned(2)
|
|
Percent(3)
|
|
Named Executive Officers and Directors:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Corey Hollister
|
|
|
11,255,466
|
|
|
|
21.66
|
%
|
|
Ellis Smith
|
|
|
11,702,441
|
|
|
|
22.52
|
%
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
|
|
600,000
|
|
|
|
1.15
|
%
|
|
J. Michael Tuohey
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
|
―
|
|
|
Tad Mailander
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
0.20
|
%
|
|
Tyler A. Schloesser
|
|
|
140,000
|
|
|
|
0.27
|
%
|
|
Michael Schwanbeck
|
|
|
4,630
|
|
|
|
0.01
|
%
|
|
R. Leslie Hymers, III
|
|
|
50,000
|
|
|
|
0.10
|
%
|
|
All executive officers and directors as a group
|
|
|
23,852,537
|
|
|
|
45.91
|
%
|
|
(1)
|
Except as otherwise indicated, the
persons named in this table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock shown as
beneficially owned by them, subject to community property laws where applicable and to the information contained in the
footnotes to this table.
|
|
(2)
|
Under SEC rules, a person is deemed
to be the beneficial owner of shares that can be acquired by such person within 60 days upon the exercise of options
or the settlement of other equity awards.
|
|
(3)
|
Calculated
on the basis of 51,513,064 shares of common stock outstanding as of December
31, 2018, plus any additional shares of common stock that a stockholder has the right to acquire within 60 days after
December 31, 2018.
|
Equity Compensation Plan Information
|
Plan Category
|
|
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights(1)
|
|
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights(2)
|
|
Number of securities remaining available for issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a))(3)
|
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.63
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Options awarded to Vincent “Tripp” Keber
|
|
|
300,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.63
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,935,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.59
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
2,485,000
|
|
|
$
|
0.61
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(1)
|
Historically, the
Company has granted restricted shares that are subject to forfeiture. Pursuant to SEC guidance, these RSUs are not reportable
in the table above.
|
|
|
(2)
|
Historically,
the Company has granted restricted shares that are subject to forfeiture. Pursuant to SEC guidance, these RSUs are not reportable
in the table above. Restricted shares subject to forfeiture have a weighted average exercise price of $0.00.
|
|
|
(3)
|
The
Company equity compensation grants to date have been approved on a grant-by-grant basis, as opposed to under an umbrella equity
compensation plan establishing a total number of grants available.
|
Long-Term Incentive Plans
There are no arrangements or plans in which we provide
pension, retirement or similar benefits for directors or executive officers, except that our directors and executive officers
receive stock options at the discretion of our Board. We do not have any material bonus or profit sharing plans pursuant to which
cash or non-cash compensation is or may be paid to our directors or executive officers, except that stock options may be granted
at the discretion of our Board.
We have no plans or arrangements in respect of remuneration
received or that may be received by our executive officers to compensate such officers in the event of termination of employment
(as a result of resignation, retirement, change of control) or a change of responsibilities following a change of control, where
the value of such compensation exceeds $60,000 per executive officer.
Changes in Control
We are unaware of any contract or other arrangement the operation of which
may at a subsequent date result in a change in control of our company.
TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PERSONS, PROMOTERS AND CERTAIN
CONTROL PERSONS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
There has not been, and there is not currently
proposed, any transaction or series of similar transactions to which we were or will be a party in which the amount involved exceeded
or will exceed $120,000 and in which any of our directors, executive officers, holders of more than 5% of any class of our voting
securities or any member of the immediate family of the foregoing persons had or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
|
(a)
|
Any director or executive officer of our company;
|
|
|
|
|
(b)
|
Any person who beneficially owns, directly or
indirectly, more than 5% of any class of our voting securities; and
|
|
|
|
|
(c)
|
Any member of the immediate family (including
spouse, parents, children, siblings and in- laws) of any of the foregoing persons.
|
Director Independence
We currently act with three directors consisting of Terry
Buffalo, Ellis Smith and Tad Mailander. Our common stock is quoted on the OTCQB, which does not impose any director independence
requirements. Under NASDAQ Rule 5605(a)(2), a director is not independent if he or she is also an executive officer or employee
of the corporation or was, at any time during the past three years, employed by the corporation. Using this definition of independent
director, we have one independent director, Tad Mailander.
Where You Can Find More Information
We are not required to deliver an annual report to our
stockholders unless our directors are elected at a meeting of our stockholders or by written consents of our stockholders. If
our directors are not elected in such manner, we are not required to deliver an annual report to our stockholders and will not
voluntarily send an annual report.
We file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements
and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Such filings are available to the public over the Internet
at the Securities and Exchange Commission’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
We have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission
a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act of 1933 with respect to the securities offered under this prospectus.
This prospectus, which forms a part of that registration statement, does not contain all information included in the registration
statement. Certain information is omitted and you should refer to the registration statement and its exhibits.
You may review a copy of the registration statement at
the Securities and Exchange Commission’s public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E. Washington, D.C. 20549 on official
business days during the hours of 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. You may obtain information on the operation of the public reference room by
calling the Securities and Exchange Commission at 1-800-SEC-0330. You may also read and copy any materials we file with the Securities
and Exchange Commission at the Securities and Exchange Commission’s public reference room. Our filings and the registration
statement can also be reviewed by accessing the Securities and Exchange Commission’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
|
The
information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. The selling stockholder may not sell these securities until
the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer
to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is
not permitted.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
American Cannabis
Company, Inc.
|
|
|
|
34,090,909 Shares
of Common Stock
|
|
|
|
Prospectus
|
|
|
|
October 31, 2019
|
|
|
Part II
Information Not Required in Prospectus
Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following table sets forth the costs and expenses
payable by us in connection with the issuance and distribution of the securities being registered hereunder. The selling stockholder
will bear no expenses associated with this offering except for any broker discounts and commissions or equivalent expenses and
expenses of the selling stockholder’s legal counsel applicable to the sale of its shares. All of the amounts shown are estimates,
except for the Securities and Exchange Commission registration fees.
|
Securities and Exchange Commission registration fees
|
|
$
|
973.50
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounting fees and expenses
|
|
$
|
4,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legal fees and expenses
|
|
$
|
5,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Miscellaneous fees and expenses
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
9,973.50
|
|
Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 102(b)(7) of the Delaware General
Corporation Law, or DGCL, allows a corporation to provide in its certificate of incorporation that a director of the corporation
will not be personally liable to the corporation or its stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director,
except where the director breached the duty of loyalty, failed to act in good faith, engaged in intentional misconduct or knowingly
violated a law, authorized the payment of a dividend or approved a stock repurchase in violation of Delaware corporate law or
obtained an improper personal benefit. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will provide for this limitation
of liability.
Section 145 of the DGCL, or Section 145,
provides, among other things, that a Delaware corporation may indemnify any person who was, is or is threatened to be made, party
to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other
than an action by or in the right of such corporation), by reason of the fact that such person is or was an officer, director,
employee or agent of such corporation or is or was serving at the request of such corporation as a director, officer, employee
or agent of another corporation or enterprise. The indemnity may include expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments,
fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by such person in connection with such action, suit or proceeding,
provided such person acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the corporation’s
best interests and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe that his or her conduct
was illegal. A Delaware corporation may indemnify any persons who were or are a party to any threatened, pending or completed
action or suit by or in the right of the corporation by reason of the fact that such person is or was a director, officer, employee
or agent of another corporation or enterprise. The indemnity may include expenses (including attorneys’ fees) actually and
reasonably incurred by such person in connection with the defense or settlement of such action or suit, provided such person acted
in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the corporation’s best interests,
provided further that no indemnification is permitted without judicial approval if the officer, director, employee or agent is
adjudged to be liable to the corporation. Where an officer or director is successful on the merits or otherwise in the defense
of any action referred to above, the corporation must indemnify him against the expenses which such officer or director has actually
and reasonably incurred.
Section 145 further authorizes a corporation to purchase
and maintain insurance on behalf of any person who is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation or is or
was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation or enterprise,
against any liability asserted against him and incurred by him in any such capacity, or arising out of his or her status as such,
whether or not the corporation would otherwise have the power to indemnify him or her under Section 145.
Our bylaws provide that we must indemnify our directors
and officers to the fullest extent authorized by the DGCL and must also pay expenses incurred in defending any such proceeding
in advance of its final disposition upon delivery of an undertaking, by or on behalf of an indemnified person, to repay all amounts
so advanced if it should be determined ultimately that such person is not entitled to be indemnified under this section or otherwise.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, we shall not be obligated to indemnify a director or officer in respect of a proceeding (or part
thereof) instituted by such director or officer, unless such proceeding (or part thereof) has been authorized by the Board of
Directors pursuant to the applicable procedure outlined in the bylaws.
Section 174 of the DGCL provides, among other
things, that a director, who willfully or negligently approves of an unlawful payment of dividends or an unlawful stock purchase
or redemption, may be held jointly and severally liable for such actions. A director who was either absent when the unlawful actions
were approved or dissented at the time may avoid liability by causing his or her dissent to such actions to be entered in the
books containing the minutes of the meetings of the board of directors at the time such action occurred or immediately after such
absent director receives notice of the unlawful acts.
The indemnification rights set forth above shall
not be exclusive of any other right which an indemnified person may have or hereafter acquire under any statute, provision of
our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our bylaws, agreement, vote of stockholders or disinterested directors
or otherwise.
We maintain standard policies of insurance that
provide coverage (1) to our directors and officers against losses arising from claims made by reason of breach of duty or
other wrongful act and (2) to us with respect to indemnification payments that we may make to such directors and officers.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 6,060 common shares to Av Singh for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 2,500 common shares to Randy Fleming for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 17,954 common shares to Gayle Barr for services rendered.
On May 17, 2018, the Company
issued 2,500 common shares to Pamela Staley for services rendered.
On September 27, 2018, the Company
issued 50,000 common shares to R. Leslie Hymers, III, based on contract.
On January 16, 2019, the Company
issued 39,708 common shares to Gayle Barr for services rendered.
On January 16, 2019, the Company
issued 400,000 shares of common stock to the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust for conversion of a cashless warrant.
On April 4, 2019, the Company
issued 100,000 shares of common stock to Tad Mailander for the conversion of a cashless warrant.
On April 4, 2019, the Company
issued 25,000 shares of common stock to Michael Schwanbeck for the conversion of a cashless warrant.
On July 9, 2019, the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living
Trust delivered elections to exercise two cashless warrants: one for 400,000 shares and one for 100,000 shares. The Company issued
a total of 500,000 common shares to the Terry L. Buffalo Revocable Living Trust.
On July 10, 2019, Tyler A. Schloesser delivered elections
to exercise two cashless warrants: one for 100,000 shares and one for 102,500 shares. On July 13, 2019 the Company issued a total
of 202,500 shares to Tyler A. Schloesser.
On July 13, 2019, Jon Workman delivered an election to
exercise a cashless warrant for 100,000 shares. The Company issued 100,000 shares to Jon Workman on July 13, 2019.
Exhibit
Number
|
|
|
Description
|
|
(2)
|
|
|
Plan
of Acquisition, Reorganization, Arrangement, Liquidation, or Succession
|
|
2.1
|
|
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger between Naturewell, Incorporated, BIMI Acquisition Corp., and Brazil Interactive Media, Inc., dated March 13, 2013 (incorporated by reference from our Current Report Form 8-K filed on March 21, 2013)
|
|
2.1(a)
|
|
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 15, 2014, by and among the Company, Cannamerica, Inc., and Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. (incorporated by reference from our Current Report Form 8-K filed on October 3, 2014)
|
|
2.1(b)
|
|
|
Separation and Exchange Agreement, dated as of May 16, 2014, by and among the Company, BIMI, Inc., and Brazil Investment Holding, LLC. (incorporated by reference from our Current Report Form 8-K filed on October 3, 2014)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3)
|
|
|
Certificate
of Incorporation and Bylaws
|
|
3.i
|
|
|
Certificate
of Incorporation (incorporated by reference from our Registration Statement on Form SB-2, filed on October 12, 1995
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.i(a)
|
|
|
Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference from our Form 14C filed on April 16, 2013
|
|
3.i(b)
|
|
|
Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to our Form 14 filed on September 9, 2014)
|
|
3.1(c)
|
|
|
Amendment
to our Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to our Form 8-K filed on September 9, 2014)
|
|
3.1(d)
|
|
|
Certificate of Amendment of the Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Brazil Interactive Media, Inc., effective as of September 29, 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5)
|
|
|
Opinion
regarding Legality
|
|
5.1*
|
|
|
Opinion of Mailander Law Office, Inc. regarding the legality of the securities being registered
|
|
(10)
|
|
|
Material
Contracts
|
|
10.1*
|
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement between Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. and Terry Buffalo dated January 1, 2019.
|
|
10.2*
|
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement between Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. and Ellis Smith, dated January 1, 2019.
|
|
10.3*
|
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement between Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. and Tyler Schloesser, dated January 29, 2019.
|
|
10.4*
|
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement between Hollister & Blacksmith, Inc. and Jon Workman, dated January 29, 2019.
|
|
10.5*
|
|
|
Investment Agreement dated October 11, 2019 with White Lion Capital, LLC (incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on October 15, 2019)
|
|
10.6*
|
|
|
Registration Rights Agreement dated October 11, 2019 with White Lion Capital, LLC (incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on October 15, 2019)
|
|
23.1*
|
|
|
Consent of Independent Auditing Firm
|
* Filed herewith.
Undertakings
(A) The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To file, during any period in which offers or
sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement:
i. To include
any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
ii. To reflect
in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective
amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the
registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total
dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the
estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b)
if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price
set forth in the "Calculation of Registration Fee" table in the effective registration statement.
iii. To include any material
information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change
to such information in the registration statement;
(2) That, for the purpose of determining any liability
under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating
to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide
offering thereof.
(3) To remove from registration by means of a post-effective
amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
(4) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising
under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to
the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission
such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim
for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director,
officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such
director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the
opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the
question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final
adjudication of such issue.
(5) Each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part
of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses
filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is
first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that
is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration
statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior
to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of
the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
(6) The undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary
offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method
used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following
communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities
to such purchaser:
(i) Any preliminary prospectus or
prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424 (§ 230.424 of
this chapter);
(ii) Any free writing prospectus relating
to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
(iii) The portion of any other free writing
prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided
by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and
(iv) Any other communication that
is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser.
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements
of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement
to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
AMERICAN
CANNABIS COMPANY, INC
|
|
Date: October
31, 2019
|
|
|
|
|
By:
|
/s/Terry
Buffalo
|
|
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer
|
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS,
that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Terry Buffalo, with full power of substitution and re-substitution
and full power to act without the other, as his true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent to act in his or her name, place and
stead and to execute in the name and on behalf of each person, individually and in each capacity stated below, and to file, any
and all documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and
agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing, ratifying and confirming all
that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them or their and his or her substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause
to be done by virtue thereof.
Pursuant to the requirements
of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this registration statement has been signed below by the following persons
on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Terry
Buffalo
|
Chief Executive Officer and Director
|
October 31, 2019
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Terry
Buffalo
|
Chief Financial Officer
|
October 31, 2019
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
(Principal Financial Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Terry
Buffalo
|
Chief Accounting Officer
|
October 31, 2019
|
|
Terry Buffalo
|
(Principal Accounting Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Ellis
Smith
|
|
October 31, 2019
|
|
Ellis Smith
|
Chief Development Officer and Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Tad
Mailander
|
|
|
|
Tad Mailander
|
Director
|
October 23, 2019
|
American Cannabis (CE) (USOTC:AMMJ)
Historical Stock Chart
From Oct 2024 to Nov 2024
American Cannabis (CE) (USOTC:AMMJ)
Historical Stock Chart
From Nov 2023 to Nov 2024